Gallbladder bend diet
Following a diet when treating any pathology of the biliary system of our body (liver + gallbladder) is a prerequisite for effective treatment. This diet is called “Healing Table No. 5”. Its main principles:
- fragmentation of nutrition (eating 5-6 times a day in small portions at equal time intervals);
- exclusion of fatty, fried and spicy foods;
- giving up alcohol and tobacco;
- The following methods of cooking are allowed: boiling, baking and steaming;
- drink plenty of fluids (1.5 – 2 liters per day);
- food should be warm, since hot and cold negatively affect digestion.
In addition, the following should be excluded from the menu:
- fatty meat (lamb, pork, goose and duck);
- fatty fish;
- broths based on the first two prohibitions;
- canned food and semi-finished products;
- salo;
- smoked products;
- sausage;
- baked goods;
- confectionery;
- fast food;
- legumes (beans, peas, lentils);
- all types of mushrooms;
- fish caviar;
- sauces (mayonnaise, ketchup, etc.);
- seasonings and spices;
- butter and other animal fats;
- sweets (including chocolate);
- strong tea;
- black coffee;
- sour berries and fruits.
Carbonated drinks (especially sweet ones) are also prohibited. You should limit your salt intake.
Recommended for use:
- dietary meat and poultry (veal, rabbit, turkey and white chicken meat);
- low-fat types of fish and seafood;
- vegetable broth soups;
- vegetables (both fresh and in the form of salads, and boiled or baked);
- sweet ripe berries and fruits (including watermelons and melons);
- porridge from buckwheat, oatmeal, pearl barley, rice, millet and semolina;
- durum wheat pasta;
- cottage cheese and fermented milk products with a low fat content;
- for sweets – honey and dried fruits.
As you can see, a menu of such products can be not only tasty, but also quite varied. If you follow all medical recommendations, the prognosis for recovery is very favorable.
Never ignore negative symptoms or self-medicate, as the consequences of such behavior are dangerous and unpredictable! Prescribing effective therapy is within the exclusive competence of the attending physician, who, after making an accurate diagnosis, is based on instrumental and laboratory diagnostic data.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of inflection
Pollen contains a lot of vitamins and nutrients
As already indicated in the article, the use of traditional medicine is possible in the treatment of this pathology, but you must first consult with your doctor.
Let's look at the most common recipes:
- Flower pollen. You need to take one teaspoon of pollen, then add 150 g of water to it and stir thoroughly. The resulting liquid should be drunk half an hour after meals, but not more than three times a day.
- Rose hip tea. Rosehip decoction not only has a choleretic effect and restores the immune system, but is also an excellent and tasty alternative to ordinary tea.
- Corn silk. A decoction of corn silk is the most effective choleretic agent from the natural reserves of traditional medicine.
Traditional methods of treatment
For better health and normal gallbladder function, medicinal herbs are used. Pharmacies have a choleretic collection intended for this purpose. It is sold in the form of tea bags. One package should be filled with 200 ml of boiled water, then left for 5 minutes and drunk warm, 1/3 cup 3 times a day. The course should last from 7 days to 3 months.
It is recommended to drink a choleretic preparation, which can be purchased at a pharmacy.
Let's consider other treatment methods:
Treatment methods for gallbladder constriction
When drawing up a treatment plan, the gastroenterologist pursues the following goals: reduce pain, stabilize the flow of bile, eliminate inflammation. Treatment for children is somewhat different from treatment for adults. First of all, in the acute stage of the disease, bed rest, therapeutic nutrition, and intake of vitamins C, group B, A and E are prescribed. The use of medications includes painkillers, choleretic agents, probiotics and antispasmodics. Additionally, a number of physical procedures and detoxification therapy may be recommended, because stagnation of bile in the deformed area leads to bile entering the general bloodstream, and therefore to general intoxication of the body.
It is mandatory to prescribe a diet, which in case of congenital pathology should become permanent. It involves avoiding sweets (jam, sugar, honey, confectionery), hot, sour, spicy, bitter and highly salty foods. It is recommended to boil, bake or steam dishes. The temperature of the dishes should not exceed 37 - 40 degrees; Food should not be cold either. Products that stimulate the flow of bile are welcome: corn silk, corn oil, pumpkin (boiled, raw, in the form of juice).
Although this pathology will remain with the child for life, proper nutrition and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations give a good prognosis for life.
How to determine the disease
It should be understood that it is almost impossible to determine the disease without examining a specialist. The conclusion should be made by professionals who conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the body. It is these studies that provide a clear picture of the shape and size of the gallbladder.
It is impossible to determine the presence of a problem based only on the clinical picture. In order to identify pathology, an ultrasound is usually prescribed. Tomography is often performed in the area of the gallbladder.
Constrictions of this organ can be observed in a variety of areas. Most often they occur in the area of the bottom and neck of the gallbladder. With an ultrasound examination, a specialist can determine the area of increased echogenicity. It looks like the lumen of the gallbladder.
If the gallbladder is located in the patient’s body more or less accessible, the doctor has the opportunity to study the problem in detail and accurately determine whether the patient is suffering from a constriction or an inflection. These phenomena are similar to each other, but their treatment must differ.
Consequences and complications
Stagnation of bile in a deformed organ provokes digestive problems. The breakdown of fats is disrupted, and the patient quickly gains weight.
In this case, incomplete absorption of fat-soluble vitamins occurs. Because of this, vision decreases, cardiovascular problems appear, and skin quality deteriorates.
Bile helps remove excess bilirubin from the body in feces. Congestion causes its accumulation and the development of jaundice.
The formation of stones due to organ constriction provokes severe complications:
- Blocking of the excretory duct with a stone.
- Formation of a crack or rupture of the gallbladder due to blockage of the duct.
- The development of peritonitis after perforation of the walls of an organ as a result of necrotization of its walls. May be fatal.
In all cases, urgent surgical intervention is necessary, possibly with removal of the gallbladder. There is a threat not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient. Cholecystectomy is performed using surgery or a special laparoscopy method.
What is laparoscopic bladder removal? This is an operation using a device with a built-in camera and two controlled surgical instruments that are inserted into the abdominal cavity through 3 punctures.
The image on the screen reproduces the surgical field. It enables the doctor to perform the correct actions.
Surgery
If an existing constriction causes frequent and severe exacerbations of chronic gallbladder diseases in a patient, it makes sense to think about surgical intervention, which is the only radical method of eliminating this pathology.
Surgical treatment is aimed at resection of the gallbladder - cholecystectomy. This operation is performed under anesthesia in two ways:
- open intervention, when an incision is made in the anterior abdominal wall to access the gallbladder;
- laparoscopic intervention, when the gallbladder is removed with special instruments through small punctures in the abdominal wall.
Often, gallbladder constriction is asymptomatic and does not cause significant problems for the patient. If such an anomaly is accompanied by symptoms of bile stasis, following a diet and conservative therapy is quite sufficient. Provided proper nutrition and following doctor's orders, this pathology does not pose a serious threat to life.
Reasons for the formation of a kink in the gallbladder
The appearance of constriction may be due to the following reasons:
- The gallbladder became inflamed and the inflammatory process spread to the serous layer. Inflammation of the superficial membrane causes adhesions, after which the gallbladder bends.
- Gallstone disease – the formation of stones in the organ causes constriction.
- Liver injury.
- Lifting heavy weights.
- Prolapse of the gallbladder due to weight loss.
- Increased liver size due to hepatitis of any form, hepatosis or liver destruction.
- Passive lifestyle, lack of movement and physical activity, irregular and irrational nutrition, especially if the patient does not consume food all day.
With congenital constriction, the patient may not be bothered when the gallbladder is deformed; most often, parents and the baby complain about something else, and the gastroenterologist prescribes an ultrasound examination. Strong changes in the structure of the organ cause pronounced symptoms - a nausea reflex and even vomiting - if the mother transfers the child from milk feeding to solid foods. The type of constriction can be determined by undergoing a tomography or at least an ultrasound.
Prevention
The following preventive measures can prevent the occurrence of acquired constrictions:
- compliance with a healthy lifestyle with moderate physical activity;
- proper and rational nutrition;
- lack of physical overload;
- maintaining normal weight;
- performing gymnastic exercises and exercise therapy;
- frequent exposure to fresh air.
If symptoms similar to those characteristic of gallbladder constriction appear, it is worth undergoing a medical examination and clarifying the diagnosis.
Correct diagnosis made using high-quality equipment and competent interpretation will allow you to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
How to eat properly if you have a deformed gallbladder
Deformation of the gallbladder is detected by ultrasound examination in almost every person. Previously, it was believed that it was this anatomical feature of the organ that leads to the symptoms that are currently associated with biliary dyskinesia. However, in most people, gallbladder deformation, even severe, is asymptomatic.
Biliary dyskinesia is manifested by a combination of stabbing or aching pain in the right hypochondrium with nausea some time after eating. The reasons for the occurrence of this symptom complex are not fully understood by either doctors or scientists; only one thing is clear: in this case, ultrasound does not reveal changes in the gallbladder that could explain this disease. The most reliable hypothesis for the occurrence of biliary dyskinesia today is considered to be a spasm of the muscles that make up the wall of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
It follows from this that if, according to the results of an ultrasound, a deformation of the gallbladder is detected in a person, then in the absence of other problems with the gastrointestinal tract and in the absence of complaints, one should adhere to the general principles of a healthy diet.
If there is pain in the right hypochondrium, and doctors have not identified other changes in the organs located in this area (except for deformation of the gallbladder), then the cause of the pain is not the deformation itself. It is most likely that biliary dyskinesia occurs, that is, episodes of spasm or impaired contractions of the biliary system. The psychological state of a person plays an important role. In people with biliary dyskinesia, hidden depression and anxiety are often detected.
For diseases of the gallbladder, a diet was previously recommended: table No. 5. However, now the list of products included in the specified table has been recognized as suboptimal and has been cancelled. Many patients eating according to diet No. 5 do not notice any improvement in their well-being.
Unfortunately, it is not yet clear what the ideal diet for biliary dyskinesia is.
- Scientists agree that to prevent bile stagnation, caused, among other things, by a violation of its motor activity due to dyskinesia, it is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits and foods containing fiber.
- It is recommended to limit animal fats in the diet.
- There are also studies confirming the positive effect of coffee on the gallbladder: the substances contained in this drink improve bladder emptying and normalize its tone.
Thus, deformation of the gallbladder itself does not require a diet. Observing dietary restrictions will not “straighten” the gallbladder, but the human body may not receive enough important substances. If there is not just a deformity, but pain in the right hypochondrium is bothering you, then the issue of nutrition must be resolved after the diagnosis has been made by a doctor.
Treatment of congenital pathology
In cases where the congenital anomaly does not cause discomfort to the patient, no treatment is required. If such a pathology causes concern, then the same therapy is necessary that is prescribed for acquired constriction.
How to cure a child from gallbladder constriction
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky believes that therapy for such pathologies should be carried out individually. In this case, it is necessary to influence not the pathology itself, but those factors that contribute to its appearance.
Since in most cases this pathology appears due to errors in nutrition and poor lifestyle, parents should obtain information from their pediatrician about their child’s diet, daily routine and other points.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends adhering to the following recommendations:
- You should not allow your child to overeat; the best option is portion feeding;
- the child should eat only when he has an appetite;
- You should not allow your child to eat a lot of fatty foods and sweets;
- Do not give your child spicy or salty foods;
- In order for the baby to have a good appetite, he must actively walk and play;
- He must drink the required amount of clean water per day.
Komarovsky claims that bending, constriction of the gallbladder and dyskinesia do not pose a danger to the child, which means that drug therapy is not required. The child will grow, and the shape of his gallbladder will also change. Therefore, the problem may resolve itself.
Drug therapy may be prescribed for a child with hypomotor dyskinesia to stimulate motor skills and thus get rid of uncomfortable symptoms. Most often, choleretic drugs made from plants are prescribed, for example, “Hofitol”, “Flamin”, “Allohol”, “Holosas”.
Choleretic herbal remedies
For hypermotor dyskinesia, antispasmodics are required to help relax the gallbladder and relieve pain.
For complex treatment, medications to improve liver function and vitamins may be prescribed.
If the disease was caused by bacteria or helminths, antibiotics and antiparasitic drugs are prescribed.
If we talk about homeopathic remedies that are recommended for diseases of the gallbladder, Dr. Komarovsky calls them ineffective, but at the same time emphasizes that they will not cause harm.
Of the auxiliary methods of treating dyskinesia, Komarovsky prescribes physical therapy and physiotherapy. All this increases blood supply to the biliary tract, increases the activity of muscle tissue in the liver area, promotes the outflow of bile, which helps restore the functioning of the gallbladder.
What is a gallbladder bend?
The full functioning of the organ depends on how regularly the outflow of bile occurs.
In addition, the absence of deformation, constrictions, and bends is important. A kinked gallbladder is a pathology associated with a change in the shape of the organ, which causes discomfort and numerous health problems.
All important digestive processes change in a person, complex chemical compounds begin to break down incorrectly.
After making a diagnosis such as a bend, twisting or curvature of the gallbladder, patients are concerned about the issue of treatment. If you do not start a therapeutic course in time, stones may form in the diseased organ, bile stagnation or erosion. If the disease has been advanced, drugs and traditional methods of treatment may not produce results, so surgical intervention is required.
Symptoms
The human gallbladder consists of a fundus, body, neck and has an oval-pear-shaped shape. A congenital defect is diagnosed by performing an ultrasound scan on the patient. If the pathology in a child is not clearly expressed, then it can be detected at school age if bloating, bitterness in the mouth, and nausea in the morning appear. With severe deformation of the organ, already in infancy, signs such as regurgitation, bloating, and nausea appear (when new foods are introduced into the diet).
Different types of pathology are accompanied by different symptoms:
- A twisted gallbladder in the area between the fundus and the body causes the patient to experience nausea, unhealthy weight loss, changes in complexion, severe pain in the ribs or scapular area, and increased sweating.
- A bend in the neck of the bile organ (fixed or labile) is characterized by an acute course. Main signs: increased body temperature, nausea, pain in the left side, bloating.
- Functional bending (temporary) makes itself felt when lifting heavy objects with acute pain in the side.
- A gallbladder with multiple kinks is a deformation in several places that is less common. At the same time, different parts of the organ increase in volume, adhesions form, stones form, and normal blood circulation is disrupted. This type of disease is severe, accompanied by frequent nausea and acute pain.
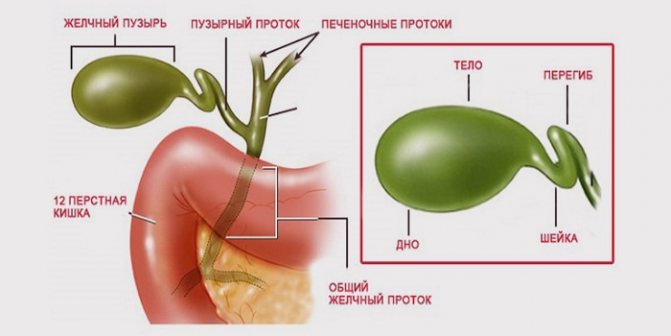
Causes
To the question of why such a disorder may appear in a newborn baby, doctors have not yet given an exact answer. It is possible that torsions or kinks are inherited by children, for example, when the mother or father had such an abnormal shape. In adult patients, there may be different reasons for the appearance of pathology.
What could be the cause of the disease:
- liver injury;
- cholelithiasis;
- complicated cholecystitis;
- peritoneal adhesions;
- heavy loads on the body;
- a consequence of liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis, hepatosis);
- sudden prolapse of internal organs after rapid weight loss;
- physical inactivity.
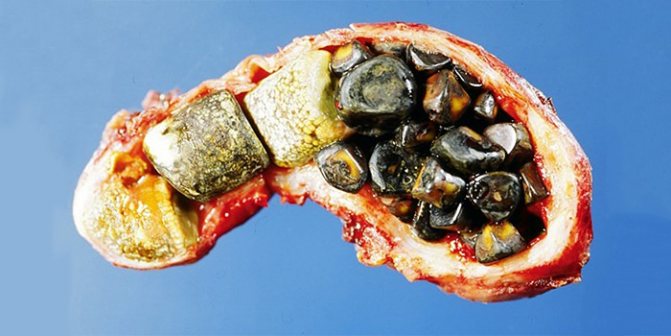
Consequences
The disease is not a life-threatening disease for a person if it is treated in a timely manner. The consequences of the pathology take years to form and make themselves felt only when the disease is neglected, there is no therapy, or the doctor’s recommendations are not followed. As a result, cracks (or even ruptures) form on the walls of the bladder, through which bile can spill into the peritoneum. If this happens, the patient will undergo surgery to remove the organ.
Traditionally, this disorder leads to cholelithiasis. Some patients develop constipation, dysbiosis, chronic cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia and other diseases. To prevent this from happening, you need to control your diet, regularly take courses of choleretic tablets, use infusions of beneficial herbs, and undergo a full examination annually.
How to detect a bend in this organ
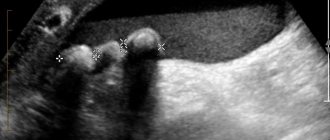
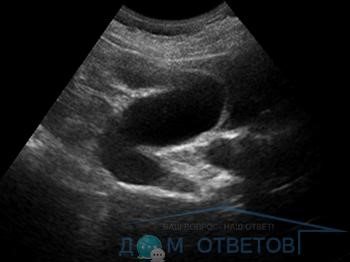
The most common and effective method for diagnosing this anomaly is ultrasound.
Gallbladder on ultrasound
This study visualizes the anomaly well and makes it possible to assess the degree of functionality of the organ. In addition, ultrasound results provide doctors with information about the location of the deformation and the general condition of the muscular walls of the gallbladder.
In order to determine the type of deformity and its nature (acquired or congenital), such a study is performed twice: the first time on an empty stomach, and the second time after taking a choleretic breakfast. With congenital pathology, the shape of the deformity does not change.
Constriction of the gallbladder in a child
Why do constrictions of the gallbladder occur, what are the symptoms of such a pathology, what medications and folk remedies help cure the anomaly?
Factors of pathology and symptoms
A bend in the gallbladder occurs due to a congenital pathology or such a disease occurs after birth (acquired form of the disease).
In old age or adulthood, constrictions are no longer so harmless and their appearance does not bring anything good to the human body. Excesses can trigger the formation of stones (cholelithiasis) or cause a diagnosis called pericholecystitis. This is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the peritoneal wall covering the posterior and lateral surfaces of the bladder, as well as in the connective tissue located above and separating the anterior surface from the liver.
Among other things, bending of the organ can be caused by numerous adhesions, which mainly form on the wall of the bladder inside. Lifting weights or long-term abstinence from food, as well as overeating, often leads to consequences such as bends.
What are the dangers of gallbladder constriction?
Bile cannot move unhindered through the bile ducts; as a result, stagnation of bile acids can occur, and this, in turn, leads first to the formation of suspensions in the gallbladder, and over time to the formation of sand and stones.
The disease in which constriction of the gallbladder is diagnosed has characteristic symptoms:
It should be noted that symptoms may vary depending on in which areas the constrictions occur.
Treatment
To eliminate discomfort and pain, patients are prescribed antispasmodics. Mainly “No-shpu”, “Atropine”, “Baralgin” and others. Doctors recommend intramuscular administration for a more pronounced effect, but these drugs are also allowed to be used orally (by mouth).
Medicines containing natural ingredients are prescribed as choleretic agents. For example, “Gepabene”, “Flamin” or “Odeston”.
It is advisable to take “Bifiform” along with antibiotics, because this drug normalizes the intestinal microflora and eliminates the harmful effects of antibacterial agents on the body.
Treatment of children is carried out in slightly different ways. If the disease has not yet reached an advanced stage, then, first of all, the doctor will recommend bed rest, diet, and will also prescribe vitamins B, A, C and E.
A very useful product for constrictions of the bladder neck or other parts is pumpkin. It can be consumed raw, boiled, and also in the form of juice. Half a liter of pumpkin juice per day for adults, and one glass for children. The pumpkin diet is recommended for patients to make the gallbladder work normally.
Food pectins (apple, beet, pumpkin) have the same effect on the body.
Method for preparing the decoction:
- One large spoon of herbal mixture is poured with 500 ml of boiling water.
- Wrap the decoction and leave for 12 hours.
- Filter and take warmed before meals.
It is not recommended to drink a cold decoction, because it can provoke an attack of pain. Actually, any cold food and liquid has the same effect if there are constrictions of the bladder.
During the period of remission of the disease (in the stage of remission), it is recommended to perform therapeutic exercises. All types associated with abdominal tension should be excluded from the set of exercises. Lifting heavy weights or barbells should also not be performed.
Diet rules and regulations
The special diet should not contain the following:
- confectionery baked goods;
- honey and jam;
- salty food;
- fatty foods;
- sour foods;
- spicy snacks and spices;
- dishes prepared by frying;
- carbonated drinks;
- concentrates.
Indeed, we usually treat the consequences, not the cause. And often our problem is our laziness. After all, in any program about health, doctors shout about the need to be examined by doctors at least once a year.
Very useful information. If there are symptoms such as bitterness in the mouth, especially in the morning, then it is necessary, on the recommendation of a gastroenterologist, to do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and take a biochemical blood test.
Treatment in children
The vast majority of cases of gastric constriction in children are congenital in origin and do not cause any symptoms, so treatment is not necessary. If symptoms of bile stagnation nevertheless appear, therapy begins with a diet that excludes the consumption of fatty, fried, smoked and spicy foods, and normalization of weight. If these measures are ineffective, choleretic agents are used in age-specific doses.
Cholecystectomy in childhood is performed very rarely. This operation is performed in the presence of stones in the gallbladder, acute or severe chronic pancreatitis.
For traditional treatment of acquired constrictions in adult patients, medication is required:
- painkillers (“Nurofen”, “Ibuprofen”) and antispasmodics (“Drotaverine”, “No-shpa”);
- choleretic drugs (“Flamin”, “Gepabene”, “Hofitol”), but provided that there are no stones in the organ;
- if there are stones in the lumen of the gallbladder, hepatoprotectors (Ursosan, Ursohol) are prescribed that can protect the liver, dissolve stones, and normalize the excretion of bile.
- To relieve inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed (Cefolasporin, Ampiox), and after them probiotics (Bifiform, Linex).
Therapy with the prescription of medications is supplemented with physiotherapy. If the patient suffers from colic or spasms, they are relieved using ultrasound or electrophoresis.
Removal of stagnant bile from the bladder and ducts is done using a mineral water tube. This procedure, like exercise therapy, promotes the proper functioning of the organ.
For complex therapy, traditional medicine methods are recommended - for example, drinking decoctions of plants that have a choleretic effect (dandelion inflorescences, corn silk, immortelle, yellow gentian).
Raw pumpkin seeds and its juice, and pollen can help relieve congestion in the gallbladder.
To eliminate inflammation, use anti-inflammatory herbal decoctions based on chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort and nettle. Some of these herbs help the flow of bile.
Diet is an integral part of treatment. Experts advise eating small portions. The dishes must be warm.
Salted, smoked, fatty and fried foods, marinated foods, as well as bone broths and semi-finished products are prohibited. It is prohibited to consume chocolate, sweets, high-fat dairy products, sour apples, and coffee. Fatty meats and fish, beans and mushrooms can cause harm.
In some situations, children may show signs of congenital constriction. They need to be put on a diet. On the advice of specialists, you can give your child various remedies.
If necessary, use painkillers and choleretic agents, as well as antispasmodics in small doses, if they have no contraindications for children.
Constriction changes the shape of an organ without consequences or pathology
This type of deformity is diagnosed in adults and children, regardless of gender. In this case, constrictions are determined in any part of the organ or in several places at once. They can change their location.
In children, congenital deformation of the organ is most often detected. This is an intrauterine anomaly in the development of the gallbladder under the influence of negative causes on the body of a pregnant woman.
It may disappear with age without treatment. A significant congenital narrowing of the organ lumen by constriction manifests itself in a child during the period of first feeding. These are intestinal symptoms.
Acquired deformity appears from the action of many etiological factors. Its symptoms are similar to other gallbladder pathologies. Therefore, only instrumental research methods confirm the presumptive diagnosis.
Constrictions cause stagnation of bile in the organ, which provokes inflammation and disruption of the digestive process. It becomes more concentrated and thickens. A fine suspension appears in it (calcium salts, potassium salts, protein particles), which precipitates, combines and forms calculi (stones). It may have a different composition.
Etiology of occurrence and development
Acquired constrictions are formed during life. Their appearance is provoked by the following reasons:
- adhesions on the walls of the organ as a result of inflammation;
- prolapse, abnormal arrangement of internal organs that put pressure on the gallbladder;
- liver injuries;
- gallstones;
- increase in liver volume due to diseases;
- constant physical overload with heavy lifting;
- prolonged abstinence from food followed by overeating;
- sudden weight gain;
- frequent stress accompanied by eating large amounts of food.
In some cases, the causes of constrictions in a patient are associated with existing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pregnant women are at risk due to possible compression and displacement of the gallbladder and liver. Also people whose professional activities involve constant sitting.
Causes
The causes of gallbladder constriction can be grouped into two main categories:
- congenital - there is incomplete development of the gallbladder in the fetus. During the transition of a child from breastfeeding to solid food, this organ lengthens and takes on an irregular shape. As a rule, constriction of the gallbladder in a child, formed in this way, does not affect the functioning of the digestive tract and does not require correction;
- acquired - the constriction is formed during life against the background of infectious and inflammatory processes of the biliary tract, cholelithiasis, subject to incorrect treatment of such diseases or the absence of any therapy at all. Improper diet, obesity, and bad habits are also risk factors for the development of this anomaly. The presence of a constriction can provoke an exacerbation of symptoms of chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
Diagnostic tests
With the help of the patient's complaints, examination and anamnesis, the doctor can only make a presumptive diagnosis. When palpating, he notes pain under the right hypochondrium and in the epigastric region (the area where the stomach is located).
To confirm the diagnosis, general laboratory tests of stool, blood and urine are prescribed. Based on their results, the presence of inflammatory processes and complications is determined.
In the blood, the level of cholesterol, bilirubin, protein, and changes in liver enzymes are important for biochemistry.
The most reliable methods for detecting deformities of the gallbladder are instrumental, primarily ultrasound.
Additionally, other diagnostics are prescribed:
- Layer-by-layer scanning using CT to clarify deformations and changes identified in the organ using ultrasound.
- Cholangiography is an X-ray examination of the bile ducts after injection of a contrast agent into them. Establishes their passability, condition and functionality.
An ultrasound scan examines the size and shape of the organ, the presence of constrictions, the number and location. The inflammatory process in it, thickening of the walls, and adhesions are determined. Assess level of functioning.
In a healthy organ, the bile secretion is homogeneous - echo-negative. During deformation and stagnation, its structure is disrupted. An echogenic suspension appears in the gallbladder. It reflects ultrasonic waves during ultrasound.
The study determines the presence of precipitate and its quantity. This compacted secretion is the first sign of the development of cholelithiasis.
During an ultrasound scan of the organ, flakes are visualized - this is a suspension. Even the smallest particles are detected. Its composition may vary. To determine it, duodenal intubation is prescribed, bile is collected and the echo suspension in it is examined.
Timely detection and treatment of pathology at this stage prevents serious consequences and complications. The reasons for the formation of suspensions during organ deformation have not been fully studied; the provoking factor is considered to be stagnation and disruption of the outflow of bile from it.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor determines what to do next, that is, what treatment methods to use. Patients with congenital anomalies of organ development without functional impairment are observed. Treatment is carried out only during the period of exacerbation of the disease.
The acquired pathology is examined, and conservative therapy is most often prescribed. It can last up to 3 months and is aimed at eliminating inflammation, relieving pain, and normalizing the functioning of the gallbladder.
Surgery is performed only in case of severe development of the disease.
Diagnostics
In most cases, gallbladder constriction is diagnosed accidentally when an examination is performed for another pathology or surgery is performed.
Examination methods:
- Ultrasound is the most commonly used technique for examining organs, helping to correctly determine their shape, location, and condition.
- Cholangiography is a technique for studying the bile ducts. It can be performed with or without the introduction of a contrast agent.
- Physical examination usually performed for cholecystitis.
After examining the ultrasound findings of patients, the doctor may find that the walls of the bladder become denser. Hardening of the walls indicates a chronic inflammatory process in the gallbladder.
But to make sure of this, a physical examination is necessary. The characteristic symptoms of cholecystitis include the following symptoms:
- Ker's symptom – pain on palpation at the point of projection of the gallbladder;
- the appearance of discomfort during palpation while inhaling;
- Murphy's symptom is increasing pain on palpation in the area of projection of the organ.
All these symptoms are characteristic of both chronic and acute cholecystitis. Therefore, an ultrasound is necessary to check the walls of the bladder for density.
Bend of the gallbladder in a child, treatment
Once your child is diagnosed with a kinked gallbladder, the doctor will prescribe treatment. As a rule, it is conservative and its purpose is to improve the flow of bile. Treatment includes the following methods:
- a diet that excludes the consumption of fried, fatty, spicy, sour foods;
- for the period of exacerbation - a special diet, taking choleretic drugs, antispasmodics and painkillers;
- in case of inflammation, antibiotics are prescribed;
- phytotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
The information in the articles is for general informational purposes only and should not be used for self-diagnosis of health problems or for therapeutic purposes. See your doctor first. All copyrights to materials belong to their respective owners
Bend gallbladder in a child symptoms
You can suspect problems with the gallbladder and bile flow based on the following signs:
- the child complains of abdominal pain (in the right hypochondrium);
- he feels sick, maybe vomiting;
- bitterness appears in the mouth, bloating;
- temperature may rise, etc.
As soon as you notice these symptoms, consult your doctor. The bending of the gallbladder can be diagnosed by ultrasound.
A bend in the gallbladder causes normal flow of bile. She stagnates. If stagnation is prolonged, then an inflammatory process occurs.
The disease may not make itself felt for a long time. If it is detected, it can occur in two forms, which differ in symptoms. In the first case, your child may experience abdominal pain after eating fatty or fried foods. Abdominal pain can also occur due to excessive physical activity, fast walking, or running. The second variant of the disease is accompanied by prolonged, aching pain in the area of the right hypochondrium. Your child may complain of a bitter taste in the mouth in the morning and nausea.
If, due to deformation of the bladder, inflammation occurs and an infection occurs, then your baby may develop a fever.
What are the consequences of a bent gallbladder:
- indigestion due to incomplete breakdown and poor absorption of fats;
- the likelihood of obesity and the risk of diabetes;
- deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K);
- the occurrence of chronic cholecystitis;
- risk of gallstone disease.
Gallbladder deformities are a rather dangerous disease. With this pathology, there is a high risk of necrosis of part of the organ, which can cause bile to enter the abdominal cavity and peritonitis.
Symptoms of gallbladder constriction and the dangers of the disease
With such pathologies, the patient may suffer from attacks of nausea, often accompanied by vomiting; abdominal pain due to tissue damage or intestinal obstruction; lack of appetite, bloating, weight loss. The urine becomes brick-red in color and the stool becomes light-colored. In rare cases, jaundice may develop.
When the first signs of pathology appear in a child, it is necessary to consult a doctor, because bending and constriction of the gallbladder pose certain health risks. Thus, the formed adhesions on the outer wall of the gallbladder disrupt its contractile function, which means that problems with digestion may arise. Deformation of the organ prevents the normal outflow of bile. In rare cases, with severe constriction in the cervical area, even necrosis of the walls of the organ is possible. To avoid complications for the child’s health, treatment must begin immediately.
Authorized Products
The diet for a bent gallbladder in children includes:
- Soups with vegetable broths: cereal, vegetable or with pasta. Vegetables for seasoning soups are not fried. You can eat low-fat vegetarian borscht.
- Wheat bread (stale), rye bread, with bran. Limit sweet yeast baked goods and fresh bread - they cause bloating and constipation. You can give your child biscuits and low-fat cookies (biscuits).
- Dishes from beef, rabbit, veal, chicken, boiled and baked, in the form of steamed or baked cutlets, quenelles, meatballs.
- Low-fat sea and river fish (pike perch, navaga, cod, blue whiting, pollock, pike, carp, carp, hake).
- Fish dishes are recommended steamed or boiled. Fish can be stuffed with vegetables and baked, but without a distinct crust.
- Omelettes or soft-boiled eggs.
- Low-fat fermented milk products (kefir, natural yogurt, acidophilus, yogurt), cottage cheese and dishes made from it. Milk as an additive to milk porridges. Low-fat sour cream as a seasoning for various dishes.
- Butter is limited to 10-20 g per day. Vegetable oils are added to salads in their natural form. Corn oil is beneficial, and pumpkin seed oil facilitates the flow of bile. It can be consumed by children from 3 years of age (0.5 teaspoon 2-3 times a day, especially 1 teaspoon three times).
- Any porridge according to the child’s preference can be cooked with water or with the addition of milk; you can make casseroles with cereals and cottage cheese.
- Sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits. Vegetables can be consumed boiled, baked, stewed (mashed potatoes, caviar, stew) and fresh. Radishes, spinach, fresh onions, radishes, mushrooms, and garlic are excluded.
- It is good to introduce salads of boiled vegetables with the addition of peas and vegetable oil, as well as vinaigrettes. You can offer non-acidic sauerkraut.
- To improve the flow of bile, pumpkin is useful, which is given to the child baked as a dessert, adding dried fruits. You can offer him sweet pumpkin porridge with millet or rice and dried apricots.
- Get your child used to pumpkin juice, and add a little orange juice to it to improve the taste. Fruits and berries are better than non-acidic varieties - fresh, as well as compotes, jelly and jellies.
- Limited: marmalade, jam, caramel, honey.
- A sufficient amount of liquid to thin the bile and prevent constipation: still water, herbal tea, rosehip infusion, vegetable and fruit juices.