Megacolon is an abnormal increase in the length or diameter of the colon. This condition can be congenital or acquired, but megacolon in children is most often a congenital developmental anomaly. Among the clinical signs of the disease, the leading one is chronic constipation. Both conservative and surgical options for solving the problem can be used in treatment.
Megacolon in adults: causes of development
Thickening of the colon is associated with hypoganglionosis (underdevelopment) or complete aganglionosis (absence) of ganglion cells of the intermuscular submucosal Meissner and Auerbach plexuses.
And the hypoganglionic zones have a local location in some part of the large intestine and completely affect the entire intestine, spreading to the ileum. Based on all this, anatomically, rectosigmoid, subtotal, segmental, total and rectal forms of megacolon are distinguished. In 90% of patients, areas of aganglionosis are located in the rectosigmoid region.
A segment of the colon deprived of intramural nerve plexuses does not peristalt, but spasms due to the predominance of the influence of sympathetic innervation. Prolonged stagnation of feces in the intestines leads to intoxication of the body, as well as ulcers of the intestinal mucosa.
What is megacolon
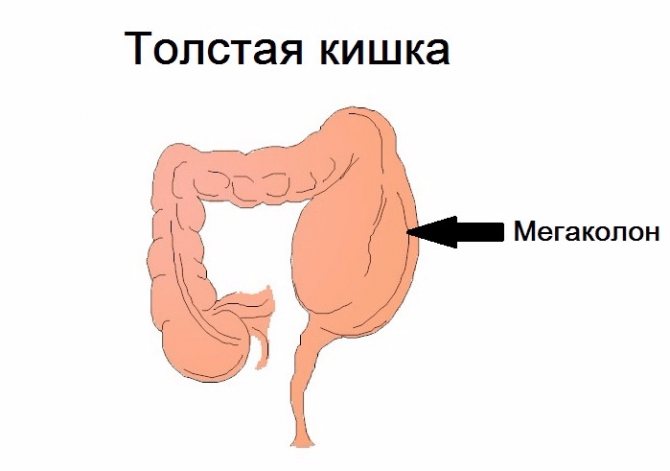
Megacolon is a malformation of the large intestine, characterized by gigantism throughout its entire length or only in certain areas.
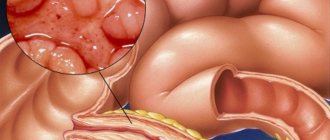
The cornerstone of the disease is either congenital or acquired anomalies of the colon
Normally, the intestine has different diameters along its length. Therefore, we can talk about pathological increase only when these indicators are overcome.
The intestine is considered enlarged if the cecum is more than 12 cm, the ascending colon and transverse colon is > 8 cm, the rectosigmoid region is > 6.5 cm.
The pathology occurs in both adults and children.
Megacolon in adults: types
Megacolon can be congenital or acquired. Congenital megacolon (Hirschsprung's disease) is characterized by aganglionosis - the absence of nerve plexuses inside the walls of the rectosigmoid colon. The deinnervated section of the intestine is narrowed, lacks peristalsis and is an organic obstacle to the passage of feces.
Congenital megacolon occurs due to:
- anomalies in the development of Favalli-Hirschsprung disease (development of the intramural system of the colon);
- fistulous forms of atresia, stenosis of the rectum and anus (anorectal defects).
The formation of acquired megacolon may be associated with secondary changes in the colon as a result of:
- scars in the colon after injury and inflammation (adhesions, strictures);
- blockage by a tumor;
- endocrine disorders (gigantism, hypothyroidism);
- damage to the central nervous system;
- occurrence of atonic constipation (intestinal atony);
- medicinal action.
Idiopathic megacolon, which is characterized by the absence of any changes in the ganglia of the intermuscular plexuses:
- inert rectum (megarectum);
- megadolichosigma, megadolichocolon;
- dolichomegasigma, dolichomegacolon.
Causes and symptoms of toxic megacolon
Megacolon is a disease that can develop for several reasons. Among these reasons are the following:
- Intestinal damage of mechanical type;
- Cancerous or benign neoplasm in the intestine, which is located near the nerve plexuses;
- Systemic connective tissue diseases;
- Neurological diseases;
- Intestinal fistulas;
- Dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- Scar processes that remain after surgery;
- Fistulas in the intestines, adhesive disease.
Factors that predispose to the development of chronic megacolon are the following conditions:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Intoxication with medications or other toxins;
- Emotional overload, neuroses;
- Metabolic disorders throughout the digestive tract.
All of the above reasons for the appearance of chronic megacolon narrow the intestinal lumen in different places, which as a result makes it difficult to remove feces from it. Excessive amounts of feces provoke elongation and expansion of the organ. This phenomenon is called megadolichocolon. Overload of the entire digestive tract leads to atrophy of smooth muscles and its nerve receptors. As a result of a large accumulation of feces in part of the pathology, general intoxication of the human body occurs. The severity of symptoms and features of the clinical picture of megacolon depend on the general condition of the patient’s body and the extent of the pathological process.
The main signs by which diseases in adults are determined are the following symptoms:
- Flatulence. Excessive gas formation begins in the intestines, which leads to enlargement and asymmetry of the anterior abdominal wall.
- Chronic constipation. Characterized by the absence of stool, which can last up to 7 days. After defecation, the stool has a rotten smell, and there are also particles of undigested food, blood and mucus.
- Signs of intoxication. They are expressed by such manifestations as fatigue, weakness, increased body temperature, which directly depends on how long constipation lasts. These symptoms occur as a result of the penetration of toxins from stool through the wall of blood vessels and into the bloodstream. Intoxication signs of the disease are enhanced by toxic megacolon.
- Changes in other organs occur as a result of an increase in intestinal volume and provoke an elevation of the diaphragm. After this, the organs that are located in the mediastinum are displaced. This process leads to increased heart rate, shortness of breath, and cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle.
- Pain syndrome with megacolon develops as a result of stretching of the rectum by an excessive amount of compressed feces. The intensity of the pain depends on how long the constipation continues.
In children, megacolon generally has the same clinical picture as in adults. But the symptoms of the disease are characterized by certain features:
- The child has a significant increase in the abdominal wall, which experts call a “frog” belly;
- Characterized by a complete absence of stool discharge. Only with the help of an enema can bowel movements be achieved;
- Lack of appetite, as a result of which children practically do not gain weight;
- Pale skin is a sign of anemia. Usually the child is bothered by nausea and vomiting with bile particles, which does not bring relief.

Megacolon in adults: symptoms
The severity of the course and clinical features of the disease are directly related to the extent of the affected area and the compensatory capabilities of the body. In adults with megacolon, flatulence develops, abdominal circumference increases, and chronic fecal intoxication increases. Vomiting with bile occurs periodically. Bowel movement occurs only after performing a cleansing or siphon enema. Feces are characterized by a putrid odor, mucus, blood, and particles of undigested food. Patients with megacolon experience exhaustion, retarded physical development, and anemia.
Progressive chronic constipation and intestinal bloating with megacolon lead to thinning and sagging of the abdominal wall, the formation of the so-called “frog belly”. Through the anterior abdominal wall, peristalsis can be observed in the distended intestinal loops. Expansion and swelling of the colon with megacolon is accompanied by a high position of the dome of the diaphragm, a decrease in the respiratory excursion of the lungs, displacement of the mediastinal organs, and a change in the size and shape of the chest (barrel chest). Against this background, cyanosis, shortness of breath, and tachycardia develop, changes are recorded on the electrocardiogram, and conditions are created for recurrent pneumonia and bronchitis.
Frequent complications of megacolon are dysbiosis and the development of acute intestinal obstruction. With dysbacteriosis, secondary inflammation develops in the intestines, ulceration of the mucous membrane occurs, which is manifested by “paradoxical” diarrhea. The development of the intestines is accompanied by uncontrollable vomiting and abdominal pain. In severe cases - perforation of the colon and fecal peritonitis. When intestinal volvulus or nodulation occurs, strangulation intestinal obstruction may occur. Depending on the severity of megacolon symptoms, there are three main stages:
- megacolon compensation;
- subcompensation of megacolon;
- megacolon decompensation.
Treatment
Treatment tactics depend on the extent of the lesion, the general condition of the patient, and the cause of the disease. For uncomplicated idiopathic dilatation of the intestine, conservative therapy is carried out. Main goals: reducing abdominal discomfort and selecting the optimal bowel movement. The size of the intestine does not change during treatment. In case of secondary megacolon, treatment of the underlying disease is prescribed.
Diet and lifestyle
The fight against constipation begins with diet correction and lifestyle changes.
Basic principles
- Individuality - the set of products and the way they are processed depends on the underlying disease.
- The basis of the diet consists of products with a laxative effect; if tolerated well, a high-slag diet is recommended.
- Products with a fixing effect and increasing bloating are prohibited.
- Adequate drinking regimen – at least 2 liters of liquid per day, including first courses, fruits and vegetables.
- Moderate physical activity activates the intestines: morning exercises, walking, swimming.
List of foods for idiopathic megacolon
| Recommended (laxative effect) | Prohibited (reinforcing action) |
|
|
Medicines and dietary supplements
- Prebiotics - contain ballast substances that are not digested in the intestines, increase the volume of contents, soften feces. They use products based on seaweed, wheat bran, and microcrystalline cellulose.
- Laxatives. Treatment begins with polyethylene glycol (Macrogol) and lactulose (Duphalac). If ineffective, stimulant medications are prescribed (Bisacodyl, Regulax Picosulfate, Guttalax).
- Choleretic agents (Hofitol, Allochol) are used in the complex treatment of constipation, since bile has a laxative effect.
- Preparations based on simethicone are used to combat flatulence (Espumizan, Bobotik).
- Antispasmodics - reduce smooth muscle tone, reduce abdominal pain (No-spa, Dicetel, Papaverine).
- Probiotics. For constipation, use products containing beneficial intestinal bacteria (Linex, Bifiform).
- Antibiotics are prescribed for megacolon against the background of an infectious intestinal lesion (Metronidazole, Amoxiclav, Vancomycin, Ceftriaxone).
- Sulfasalazine is a drug with an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect, indicated for intestinal ulcers.
Cleansing enemas
In patients with damage to the rectum and distal sigmoid, laxatives are combined with regular cleansing enemas. The regimen is selected individually: from 1 time a month to 2-3 times a week.
Read more: Cleansing enema using a syringe and an Esmarch mug
Physiotherapy
To stimulate intestinal function, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures:
- rectal and cutaneous electrical myostimulation of the intestine;
- laser therapy;
- acupuncture.
Surgery
Indications for surgical treatment: complications of megacolon, their high risk, ineffectiveness of conservative therapy. The operation is performed in coloproctology departments.
Techniques:
- Resection (excision) of the affected area with maximum preservation of intact intestine, anastomosis.
- Colectomy – removal of the entire colon, removal of a section of the intestine to the abdominal wall (formation of a colostomy), anastomosis after 6-12 months.
- Vertical reduction rectoplasty is a reduction in the size of the rectum by vertical suturing.
The surgical technique depends on the extent of the lesion.
Megacolon in adults: diagnosis
When diagnosing megacolon, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital take into account data from clinical symptoms, objective examination, results of X-ray and endoscopic diagnostics, laboratory tests (stool for dysbacteriosis, coprograms, histology).
During an examination by a proctologist, an enlarged, asymmetrical abdomen is revealed. On palpation, intestinal loops filled with feces have a doughy consistency, and in the case of fecal stones, a dense consistency. With megacolon, a symptom of “clay” is noted - pressing with fingers on the anterior abdominal wall leaves marks of indentation on it.
Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity with megacolon reveals swollen and dilated intestinal loops of the colon, a high-lying dome of the diaphragm. X-ray contrast irrigoscopy allows you to determine the aganglionic zone - the area of narrowing of the colon with expansion of its overlying sections, the smoothness of their contours, the absence of folding and haustra. In this case, expansion of the rectum (megarectum), sigmoid (megasigma) or the entire colon (megacolon) may predominate. Using sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy, the large intestine is examined and a transanal endoscopic biopsy is performed. The absence of nerve cells of the Auerbach plexus in the biopsy specimen of the muscular lining of the rectum confirms the diagnosis.
Differential diagnosis for megacolon is carried out with:
- colon tumors;
- chronic colitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- diverticular disease;
- habitual constipation caused by anal fissures.

General diagnostic rules

The necessary initial examination and mandatory set of studies will be prescribed by a pediatrician or family doctor. In the future, consultation with specialized specialists may be required: pediatric surgeon, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist.
The range of studies prescribed in such cases most often includes:
- general clinical detailed analysis of peripheral blood and urine;
- biochemical tests reflecting the condition and functional integrity of the liver and kidneys;
- coprogram, culture of feces for dysbacteriosis and pathogenic flora;
- colonoscopy and irrigoscopy;
- survey contrast radiography (with a contrast barium mixture) to assess the location and extent of the altered area of the colon;
- tomography (positron emission or magnetic resonance imaging) to assess the condition of other abdominal organs;
- genetic and histochemical tests to exclude or confirm hereditary diseases and syndromes.
Megacolon in adults: treatment
If specialists at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose a patient with “megacolon”, then treatment is carried out using surgical intervention. The purpose of the operation is to remove the aganglionic zone along with the dilated segment of the colon, as well as to restore patency. The diameter of the colon in this disease can reach, for example, 30-70 centimeters. The transition zone from the healthy area directly to the affected area is gradual, narrowing like a funnel.
In the Yusupov Hospital for megacolon, the most common operations are Duhamel-Bairov, Soave-Lenyushkin, and Swenson-Hiatt-Isakov. The last operation includes two main stages:
In patients with severe megacolon, 2- and 3-stage surgical intervention is used: during the first stage, a colostomy is applied to the area of the colon that is functioning, and after a few months, resection of the altered parts of the intestine is performed. Then the intestinal continuity is restored, after which the colostomy is closed.
Conservative treatment includes the following:
- diet (mushrooms, vegetables, berries, fruits - up to 50% of the daily diet);
- intestinal massage, therapeutic physical education (PT), the use of enemas, electroacopuncture stimulation, siphon enemas;
- parenteral nutrition (protein hydrolysates, protein, amino acids, albumin);
- restorative (vitamin) therapy.
Yusupov Hospital is a multidisciplinary hospital that provides a full range of services for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of various surgical and therapeutic diseases. The doors of the clinic are always open to everyone.
Yusupov Hospital is an innovative hospital. The diagnostic departments of the hospital operate at a modern technological and professional level: specialized laboratories - clinical diagnostic, immunological, bacteriological, express biochemical. Progressive techniques are actively used - magnetic resonance imaging, endoscopy, X-ray and ultrasound diagnostics. The hospital has a powerful rehabilitation and physiotherapeutic complex.
The inpatient unit of the Yusupov Hospital has comfortable wards and beds, where every patient will feel at home - in a cozy and familiar environment. To make an appointment with a proctologist at the Yusupov Hospital, call the phone number listed on the official website. You can also leave your application online. The Yusupov Hospital operates around the clock, without breaks and weekends.
Author
Igor Valerievich Zakharov
Doctor for X-ray endovascular diagnostics and treatment, Ph.D.
Treatment of toxic intestinal megacolon
Activities carried out by specialists at the Yusupov Hospital to identify megacolon include clinical and additional diagnostic methods. The clinical examination is carried out by the attending physician. The proctologist carries out the following activities:
- Anamnesis collection. During these activities, all possible causes are clarified, as well as predisposing factors of the pathology;
- A general examination of the patient is carried out, which determines the violation of symmetry and enlargement of the abdomen;
- Troubling symptoms of the disease are determined by collecting patient complaints;
- palpation of the abdomen - enlarged intestinal loops and possible fecal stones are diagnosed.
After conducting the basic examination methods, the doctor refers the patient to a set of instrumental studies:
- Invasive methods for diagnosing the organ include visual examination of the intestinal mucosa and taking a biopsy for histological examination;
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity - a raised diaphragm and enlarged intestinal loops are diagnosed;
- Irrigoscopy is an X-ray diagnosis with contrast, which reveals changes in the walls of the organ, their expansion and smoothness;
- Laboratory tests, such as clinical analysis of urine and blood, feces for dysbacteriosis, coprogram. They are carried out to assess the general condition of the patient’s body and identify possible concomitant pathologies.
The Yusupov Hospital successfully uses a method of non-drug treatment of megacolon, which involves the following methods:
- Nutrition adjustments. In this case, the diet is aimed at softening the stool to facilitate bowel movements. The diet includes many foods that are rich in plant fiber, such as fruits, unground cereals, and vegetables. It is allowed to eat prunes, fermented milk products, beets, figs, and greens.
- Physiotherapy. Its main goal is to strengthen the muscles of the abdominal wall. Experts recommend performing abdominal swings, scissors exercises, and swings with a bent leg.
- Abdominal massage. The massage should be performed clockwise using light movements. These manipulations stimulate intestinal motility, and as a result, the movement of feces through it.
- Physiotherapy. Electrical stimulation of the intestines is the main physiotherapeutic method. The effect of low-frequency current on the intestines helps accelerate motility.
- Enemas. Depending on the severity and form of the disease, enemas can be siphon, cleansing or hypertonic. In addition to the above methods, taking vegetable oil has a good laxative effect. Experts recommend consuming 15 ml three times a day.
Conservative treatment of megacolon is used in the Yusupov Hospital using the following medications:
- Antibacterial - these drugs are used to prevent the possible development of infectious inflammation. Usually the doctor prescribes drugs that have a wide spectrum of action, such as Cefazolin, Gentamicin, Flurithromycin, Ofloxacin.
- Probiotics are taken if there are disturbances in the intestinal microflora. Doctors successfully use drugs such as Linex, Bificol, Acipol, Enterol.
- Agents that enhance intestinal motility, such as Cerucal, Motilak, Motilium, Metoclopramide.
- Enzymatic preparations - are used to improve the digestion of food consumed in the gastrointestinal tract. (Pancreatin, Panzinorm, Creon).
Surgical intervention for chronic megacolon is used for the following conditions:
- Hirschsprung's disease;
- Ineffectiveness of conservative methods;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Intestinal bleeding;
- Intestinal perforation;
- Peritonitis.
Surgery for toxic megacolon is radical in nature, because the entire part of the intestine that was affected is removed. With the obstructive type of megacolon, the obstacle that contributed to the development of the disease - adhesions, stenotic areas, scars - is eliminated. After the operation, the ends of the intestines are sutured together. Sometimes such an operation is carried out in several stages, so a temporary colostomy is applied to evacuate feces from the organ. For the postoperative period, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and immunomodulating agents. For rehabilitation, treatment continues with all of the above non-drug methods - exercise therapy, diet, physiotherapy.
The doctor decides how to treat chronic megacolon after making a diagnosis. You can make an appointment with a proctologist at the Yusupov Hospital 24 hours a day by calling the hotline.
Author
Prevention and prognosis
There are no specifically designed preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of megacolon in a child or adult. However, clinicians highlight a number of general recommendations to reduce the likelihood of developing such a disease:
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- lifelong renunciation of addictions;
- taking medications prescribed by a clinician must strictly adhere to the daily dosage and duration of use;
- compliance with individual safety rules when contacting poisons, toxins or chemicals;
- timely and complete elimination of pathologies that can provoke the development of this disease;
- regular visits to a gastroenterologist and other specialists to undergo a full preventive examination.
The outcome of megacolon is often favorable, especially with early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment of the disease. However, it is worth noting that in cases of complications, there is a possibility of death.
Megacolon - why is this disease dangerous?
This type of megacolon develops as a result of a mental health disorder or harmful habits of sloppiness. Many psychiatrist patients suffer from coprostasis and constipation, which rarely debuts in childhood. Most often, such megacolon in adults begins in middle age. With depression, neuroses, and schizophrenia, patients ignore intestinal urges.
Over time, they subside, coprostasis continues to progress, and bowel movements appear within days. Megacolon is detected with the development of severe intestinal obstruction. Sometimes patients begin to get carried away with taking laxatives, and constipation gives way to diarrhea. Occurs in organic pathologies of the nervous system.
Often, such patients have a history of meningoencephalitis. Pathogenesis is associated with dysregulation of the motor and evacuation functions of the gastrointestinal tract from the brain. Constipation is pronounced and persistent. In diseases affecting the lower spinal cord, syphilis, oncology, the large intestine expands sharply due to chronic coprostasis.
There may be no stool for a week. Pathologies of the endocrine glands of the endocrine organs are often accompanied by constipation. Coprostasis is one of the very first signs of cretinism and myxedema hypothyroidism. Later, with insufficiency of the thyroid gland, other symptoms appear: a rough voice, swelling of the face and limbs, bradycardia, etc. During pregnancy, chronic constipation can also develop, including enlargement of the colon.
This is due to hyperproduction of progesterone, compression of the intestines by the uterus, and physical inactivity. Diabetes mellitus, which occurs as a complication in the form of neuropathy, is often accompanied by persistent constipation.
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible. We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in brackets are [1], [2], etc. Gigantism of the entire colon, or part of it, acquired or congenital, is designated by the term megacolon.
Sometimes it becomes one of the leading symptoms of diabetes. A connection has been established between chronic coprostasis and the systematic use of certain medications.
For example, antihypertensives, antidepressants, diuretics, sedatives, hypnotics, laxatives. Toxic megacolon can develop from lead poisoning. With frequent exacerbations of chronic infection, destruction of ganglia in the large intestine and the development of acquired aganglionosis are possible.
The main signs that can be used for differential diagnosis from other diseases:. During the course of the disease, three stages are distinguished: complete, incomplete compensation and decompensation. Unfortunately, adults usually go to the doctor at stages 2 or 3, when laxatives and cleansing enemas no longer help.
After an external examination, a patient with complaints of persistent constipation undergoes a digital rectal diagnosis. The rectum in Hirschsprung's pathology remains free, but in the idiopathic version it is filled with feces.
Additional research methods are:. Differentiation is carried out with diseases that are also accompanied by constipation. First of all, with IBS, irritable bowel syndrome, chronic colitis, diverticula pockets in the wall of the colon, oncology, dolichosigma, elongated sigmoid region.
It is usually possible to establish an end to the diagnosis using irrigoscopy. Resection of part of the affected intestine, removal of mechanical obstacles and other types of interventions are performed. For idiopathic and other types of megacolon, conservative methods can lead to a decrease in intestinal diameter.
Clinical recommendations are as follows:. All prescriptions are made by a doctor depending on the type, stage of the disease and the characteristics of the patient’s body. Patient complaints of persistent constipation should always raise red flags regarding megacolon. Prolonged retention of feces can lead to the formation of stones, which can lead to the development of bedsores, ulcers, perforation of the intestinal wall and peritonitis.
Therefore, if home methods for treating constipation are not effective, you should consult a doctor to find out the cause and eliminate it. Many intestinal pathologies in children are classified as acute surgical diseases. For such ailments, surgery is often necessary.
After all, when the blood supply to the small or large intestine is disrupted, tissue death develops, as well as widespread inflammation in the abdominal cavity - peritonitis. Also, stool obstruction may occur. All these complications are dangerous not only in childhood, but also in adulthood.
One of the pathological conditions of the large intestine is megacolon. This disease must be diagnosed as quickly as possible before severe consequences develop. If megacolon is detected in a timely manner, treatment begins with conservative methods. In some cases, surgery is not necessary. However, if the risk of complications is high, surgery should be performed immediately. Marked enlargement of part of the large intestine or the entire organ is called megacolon.
Often, this disease is observed in early childhood. In some cases, it appears already in the first days or months of life. In this case, intestinal hypertrophy is classified as a congenital malformation of the digestive system. Less commonly, pathological enlargement of the organ is observed in adulthood.
In such cases, the disease is considered secondary, that is, developing against the background of some other ailment. Intestinal hypertrophy occurs due to its lengthening, thickening of the walls and expansion of the lumen.
Often, changes affect the distal sections. To diagnose megacolon, instrumental examinations of the digestive tract are used. The treatment tactics for the disease in most cases depend on the cause of intestinal hypertrophy. The main indication for surgery is complications or risk or development.
If the disease is diagnosed during the neonatal period or in the first year of life, then this condition is regarded as congenital. The cause of colon defects is considered to be teratogenic factors. These include:. The cause of congenital megacolon is a violation of the migration of nerve cells in the embryo. As a result, receptor insufficiency occurs, leading to a slowdown or absence of impulse conduction along the nerve fibers of the digestive tract. Acquired megacolon can develop at any age.
It is more often diagnosed among the pediatric population. One of the underlying diseases for the occurrence of megacolon is considered to be Hirschsprung's disease. This pathological condition is characterized by a lack of innervation of a section of the intestine.
Similar changes in the functioning of the digestive system develop in other diseases. Among them:. In some cases, it is impossible to determine the cause of organ hypertrophy. In this case, a diagnosis is made: idiopathic megacolon. Due to disruption of the innervation of the colon, its functions suffer.
The affected part of the organ relaxes. As a result, the formed feces move through the intestines more slowly, or even stagnate in its lumen.
Intestinal megacolon: types, causes and treatment
Due to the accumulation of feces, the proximal parts of the organ begin to stretch and increase in size. The walls of the enlarged area become thinner, and the muscle tissue in them is damaged. As a result, it is replaced by connective tissue that normally should not be there.
Even after bowel movement, atony remains. Due to stagnation of feces, intoxication of the body often occurs, and the damaged area of the intestine becomes inflamed. Fibrosis and edema lead to even greater hypertrophy. Megacolon develops much more often in children than in adults.
This applies not only to congenital pathology, but also to acquired intestinal hypertrophy. The high incidence of megacolon among young patients is associated with the absence of complaints, as well as the inability to identify them at an early age. In addition, it is worth considering that children cannot manage their own nutrition.
Depending on the location of the lesion, the origin and cause of the disease, different types of megacolon are distinguished. One of the classifications is the division of the disease into a congenital defect and acquired hypertrophy of the colon. According to the etiological factor, they distinguish:. Depending on which part of the organ is affected, there are: rectal, sigmoid, mixed, segmental, total and subtotal forms of megacolon.
Often, hypertrophy occurs in the rectosigmoid colon. The course of the disease can be acute, subacute, subcompensated and chronic. Megacolon in children: symptoms. Symptoms of a pathological condition in children are most often detected by parents.
At an early age, the first sign of the disease may be: refusal of the mother's breast, crying and sleep disturbances. Later, a specific clinical picture appears. With a congenital defect of the digestive system, the following signs are observed:.
With prolonged constipation, signs of intoxication develop. Body temperature rises, weakness is observed.
The same symptoms bother children with acquired megacolon. Chronic intestinal hypertrophy leads to sagging muscles and skin of the abdominal muscles. On examination, peristaltic movements can be seen. Children experience flatulence, pain in the lower abdomen, and chronic constipation. Diagnostic measures include: assessment of complaints and medical history, often from the parents’ words, physical examination of the gastrointestinal tract, laboratory and instrumental methods.
Diagnosing megacolon
Diagnosing megacolon involves taking into account clinical data, as well as the results of X-ray studies, as well as diagnostics involving the use of endoscopy. Laboratory test data should also be taken into account. The so-called clay effect is characteristic for diagnosing the described condition. In such cases, finger marks are squeezed out on the anterior wall of the peritoneum after palpation.
Areas of bifurcation and expansion of colon loops are identified, which contributes to its deformation. Anorectal biometry is performed if it is necessary to correctly assess the rectal effect, as well as to distinguish between congenital and acquired varieties of a painful condition. Differential diagnosis is performed exclusively in the presence of tumor formations in the large intestine.
Types of disease
Today, there are 7 types of the disease. The division occurs according to the causal factor. This kind of classification is necessary for competent selection of therapy.
- Hirschsprung's disease (congenital megacolon). This is a congenital malformation of the colon, which is clinically manifested by its gigantism. The disease occurs 3–4 times more often in boys than in girls.
In 1887, Danish pediatrician Harold Hirschsprung noticed a strange disease in two boys that he had not seen before. Since the pathology was based on gigantism of the colon, the doctor gave it the name megacolon.
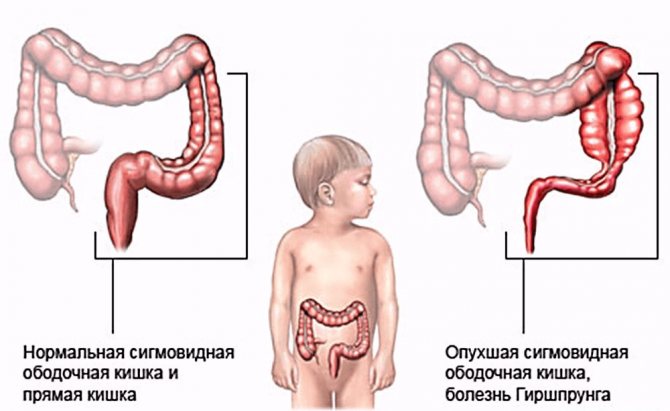
Intestinal changes in Hirschsprung's disease
- Obstructive. Characterized by the presence of some kind of mechanical obstacle to the contents of the gastrointestinal tract. This could be various pathological narrowings of the intestinal passage or a tumor.
- Endocrine. With various endocrine diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, dysregulation of gastrointestinal motility is possible.
- Toxic. This form develops due to exposure to toxins in various infectious diseases. This condition can also be caused by taking certain medications.
- Psychogenic. This form is characterized by the presence of some kind of mental disorder in the patient. Or the patient, for some reason, suppresses the act of defecation (emptying the bowel), which subsequently leads to an increase in the size of the intestine.
- Neurogenic. With pathologies of the central nervous system, for example, encephalitis or meningitis, dysregulation of the entire body, in particular the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, can occur, which will lead to intestinal akinesia.
- Idiopathic. If it is not possible to determine the specific cause of the disease, then we are talking about the idiopathic form of megacolon.
The acquired form of the disease mainly occurs in adults, while the congenital form (Hirschsprung's disease) predominates in children.
Symptoms of the disease
The main clinical manifestation of this disease is chronic constipation, which subsequently leads to the following symptoms:
- bloating;
- intestinal obstruction;
- intoxication.
Further, lesions of the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems develop against the background of an increase in the size of the intestine.
As the loops of the large intestine swell, they push other organs around them, causing the chest to move upward and take on a barrel shape.
This shows up:
- shortness of breath;
- cyanosis (blue discoloration);
- pain in the heart;
- frequent inflammation of the bronchi and lung tissue.
Adults are characterized by a milder course of the disease or a complete absence of any symptoms.
Signs in children and adults - table
| Symptoms | Peculiarities | |
| in adults | in children | |
| Constipation | It is easier than in children. It is temporary. After some time, constipation is replaced by spontaneous passage of feces. | It can be detected from the first days of life, but is more often observed after a few months. Typically, constipation is constant, and there may be no bowel movements for 2–3 weeks. As a rule, without the use of enemas, the baby cannot go to the toilet on his own. |
| Bloating and pain | Occurs due to constipation. After the passage of stool, pain and bloating may disappear completely, until the next constipation. | Accompanied by an enlarged abdomen. This type of belly is also called a “frog belly.” The manifestations do not subside even after bowel movement. |
| Intestinal obstruction | This symptom begins abruptly - with severe abdominal pain, sweating, weakness, and lack of intestinal peristalsis. | It appears after several months, when parents introduce complementary foods. The baby becomes capricious, constantly cries, and refuses food. Complains of severe abdominal pain. |
| Intoxication | It is mainly detected in patients with severe forms of the disease. Possible:
| Clearly noticeable from the first days. The baby's body weight does not correspond to temporary norms, he refuses to eat. Subsequently, his physical lag behind his peers is possible. |
| Defeat of other systems | These symptoms are observed in advanced forms of the disease. Cardiac signs are more common. | Against the background of gigantism of the large intestine, the organs of the thoracic cavity are pushed upward. It becomes like a barrel. |
Megacolon: treatment
Treatment of megacolon is divided into several main types and is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
Traditional treatment
Traditional methods of treatment involve establishing a diet that includes a high content of plant fiber, as well as installing cleansing enemas to cleanse the intestines, performing abdominal massage, and using bacterial-based drugs. In addition, medications are used that can provide high-quality normalization of intestinal microflora, enzyme agents, as well as modulators of colon motility and stimulation of the rectum using electrical stimulation methods.
Operation
Surgical intervention in the treatment of the disease is possible in the event of the onset of Hirschpung's disease. In such cases, resection of the aganglionic zone is performed, as well as that part of the colon that has undergone the greatest expansion. As a rule, this occurs in children under 3 years of age; in adults, such treatment methods are much less common. When an obstructive form of megacolon occurs, a colostomy is applied and surgical intervention is prepared.
The actual volume of colon removed during surgery is determined by the severity of the disease, as well as the total duration of the affected intestine. In each individual case, the scope of work performed is determined strictly individually.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment involve drinking herbal decoctions that weaken the effects of the disease and have a general calming effect. These include infusions of valerian and mint. It is recommended to drink three times a day, half an hour before meals. If the desired effect does not occur, it is recommended to extend the period of use of herbs for drinking.
An infusion of black currant and horseradish also has a good effect. The proportion in each case is individual and is determined by the total volume of the affected area of the intestine. You should drink in slow sips, without rushing. It is imperative that before prescribing a course of treatment using traditional medicine methods, you should obtain advice from a competent specialist.