Abdominal carcinomatosis is a serious disease of the human body, which is characterized by a pathological condition of the entire peritoneum and tissues of internal organs.
This disease is a complication of an existing cancer tumor, the metastases of which have spread beyond its main location. Migration of malignant cells into the abdominal cavity occurs along with the flow of the bloodstream, as well as lymphatic fluid.
In medical practice, this disease is also found under the term “peritoneal carcinomatosis.” Treatment of this disease involves the use of chemotherapy drugs, as well as the effective fight against malignant neoplasms.
Stages and degrees
Carcinomatosis of the abdominal cavity is characterized by gradual and staged development. In this regard, treatment of this disease should begin at the earliest possible stages, when severe complications and disturbances in the functional activity of internal organs have not yet occurred.
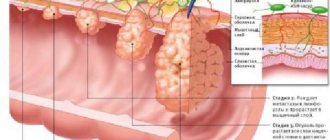
Carcinomatosis is a secondary pathology, the progression of which directly depends on the dynamics of the tumor process. In this regard, several stages of this disease are distinguished.
initial stage
At the first stage of development of carcinomatosis, migration of tumor cells occurs from the focus of the malignant neoplasm to the tissues of the abdominal cavity. The spread of metastases occurs due to the oncological process reaching stages 3-4 of its development, damage to the blood vessels of the tumor as a result of surgical intervention.
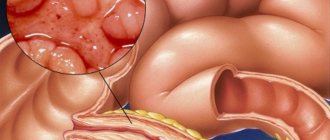
Degenerated cells trapped inside the abdominal cavity form multiple areas with signs of an altered structure of epithelial tissue.
In fact, the process of spreading a large number of small tumor bodies, which can be localized in any part of the peritoneum, begins. At the initial stage, metastases most often affect the greater omentum, pouches of Douglas and the cecum.
Active growth stage
The next stage in the development of carcinomatosis is the active interaction of degenerated cells with the abdominal mesothelium. Metastases are fixed in tissues of this type, and also continue to spread over the entire surface of the peritoneum.
Invasive penetration of cancerous tumors with their active germination into the connective tissue of the peritoneum, as well as the basement membrane, is observed. At this stage of development of abdominal carcinomatosis, there is still a chance for the success of the therapeutic process, but subject to simultaneous treatment of the primary oncology.
Stage of complete damage to the abdominal cavity
This stage of carcinomatosis is characterized by the formation of a large number of secondary malignant neoplasms that affect certain areas of the abdominal cavity. This stage of the development of the disease is characterized by severe symptoms and an increasing inflammatory process, covering the pleural lobes of the peritoneum.
At this stage of carcinomatosis, the prognosis for patient survival is unfavorable. Most patients with signs of complete damage to the abdominal cavity are in a supine state, move with difficulty and with the help of strangers, and also require regular painkillers.
Forecast
Typically, involvement of the peritoneum characterizes a stage 3-4 cancer. The prognosis for patients diagnosed with peritoneal carcinomatosis is not the most favorable. It is impossible to say exactly how long a patient with this diagnosis will live, since much depends on the size of the affected area and the prevalence of metastases. In cases where a small area of the peritoneum is affected, it can be removed, which will increase the patient's life expectancy by several years.
If carcinomatosis affects a large part of the peritoneum, the lifespan is only a few months. Such patients are prescribed palliative therapy, which involves maintaining the patient’s vital functions during this period.
Symptoms and signs
Abdominal carcinomatosis (treatment of this pathology occurs simultaneously with cancer therapy) has various forms of manifestation. The clinical picture of this disease depends on the dynamics of the development of the tumor process.
In most patients with metastasis of cancer cells in the peritoneum, the following symptoms of carcinomatosis are observed:
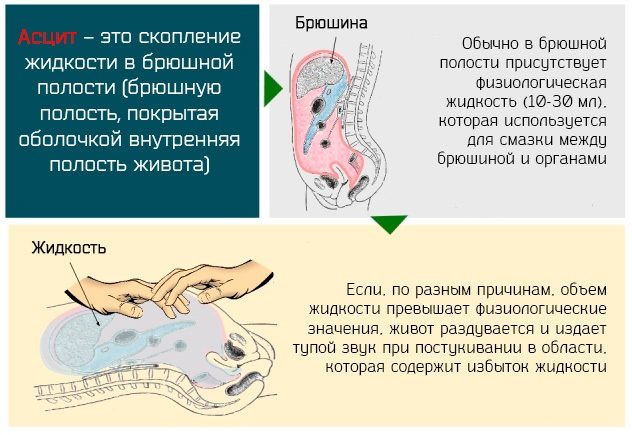
- active formation of effusion inside the abdominal cavity, which leads to ascites (this sign of carcinomatosis is characterized by the presence of a spherical abdomen, the appearance of which is associated with the accumulation of serous fluid);
- inflammation of the pleural layers;
- attacks of acute or spasmodic pain inside the abdomen, which can only be eliminated with the help of potent painkillers (in the later stages of carcinomatosis, narcotic drugs are used to improve the quality of life of patients);
- rapid weight loss;
- severe physical weakness;
- rapid fatigue, which appears even after minor exertion;
- nausea and vomiting;
- complete lack of appetite;
- dizziness and loss of coordination of movements;
- disruption of the bowel movement, which may result in diarrhea or prolonged constipation;
- fainting state;
- bitterness in the mouth and a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, if cancer metastases have spread not only into the abdominal cavity, but also affected the liver tissue;
- increased body temperature, which reaches 39-40 degrees Celsius;
- Strong headache;
- fever, chills.
As the ascitic syndrome progresses, general intoxication of the body develops. In 35% of cases of abdominal carcinomatosis, the accumulation of serous exudate inside the abdomen is the only symptom of this pathology. Only after this do other signs of a painful condition of the peritoneum begin to appear.
Classification
In modern medicine, there are three main groups of neoplasms:
- Benign tumor (occurs in the form of angioma, neurofibroma, fibroma, lipoma, lymphangioma). The reasons for the formation have not yet been determined. It occurs in an asymptomatic form during the first 2-3 years. In the presence of large nodes, a sharp increase in abdominal volume is observed. Diagnosed using laparoscopy.
- Primary malignant tumor (peritoneal mesothelioma). Typical for men over 50 years of age. The main symptoms include: severe pain and a feeling of compression of neighboring organs, weight loss. The presence of a tumor can be diagnosed by palpation.
- Secondary malignant tumor (formed during the spread of malignant tumors from neighboring organs).
There are also mucus-forming tumors (pseudomyxomas). Some experts classify them as primary tumors, others as secondary tumors.
Often, secondary malignant tumors are formed due to the spread of cancer cells from organs located intraperitoneally, mesoperitoneally and extraperitoneally.
A tumor formed due to implantation metastasis is detected in the presence of cancer of the stomach, intestines (large and small), liver, pancreas, kidneys, gallbladder, uterine cervix, ovaries, etc.
The presence of lymphogenous spread of metastases of a chest tumor is periodically diagnosed. It is caused by the retrograde nature of the movement of lymph along the lymphatic pathways.
Causes
Carcinomatosis of the abdominal cavity (treatment of this disease is effective only in the early stages of its manifestation) is a secondary pathology that occurs only in the presence of progressive cancer.
The main reason for the development of this disease is the presence of a malignant tumor in the tissues of the following organs:
- pancreas;
- ovaries in women;
- stomach walls;
- uterus;
- small intestine;
- pancreas;
- fallopian tubes.
Much less often, carcinomatosis appears due to a primary tumor inside the peritoneum. In this case, the tumor process is primary in nature.
The following are the main causative factors that contribute to the development of carcinomatosis:
- alcohol abuse, smoking, taking drugs;
- unbalanced diet;
- consumption of industrially processed meat products (sausages, canned food, semi-finished products);
- work in production workshops with hazardous working conditions, when a person is in daily contact with chemicals of toxic etiology;
- being under the influence of radioactive or any other ionizing radiation;
- previous injuries or surgery on abdominal tissues;
- genetic predisposition to the development of malignant neoplasms, inherited from blood relatives who have previously encountered this disease.
Carcinomatosis of the abdominal cavity (treatment of the disease is a long process) is a little-studied disease, the development of which is quite difficult to predict. Determining the causative factors that influenced the occurrence of a malignant neoplasm allows us to organize a better therapeutic process, as well as eliminate the source of negative influence.
What is this
Abdominal cancer begins its formation process in the peritoneum, the membrane that covers the stomach, intestines and liver. The main purpose of this shell is organ protection. It also produces a lubricant that protects organs from damage due to friction during human movements. Often the tumor forms in the lower abdominal cavity.
The peritoneum contains epithelial cells that cover the ovaries. And despite the fact that the percentage of tissue in the ovaries is very small, the inflammatory process begins precisely from these organs.
At the next stage, ovarian cancer affects the surface of the peritoneum. This is the main reason that abdominal cancer most often develops in females who have previously had ovarian cancer.
A form of peritoneal cancer is also known as peritoneal mesothelioma. The source of the disease is considered to be injury to the tissue lining the abdominal cavity.
Diagnostics
A surgeon with a sufficient level of qualifications and practical experience who examines a patient with signs of abdominal carcinomatosis can determine the presence of this disease only on the basis of existing symptoms. The main symptom of this disease in the form of increasing ascitic syndrome indicates a progressive pathology.
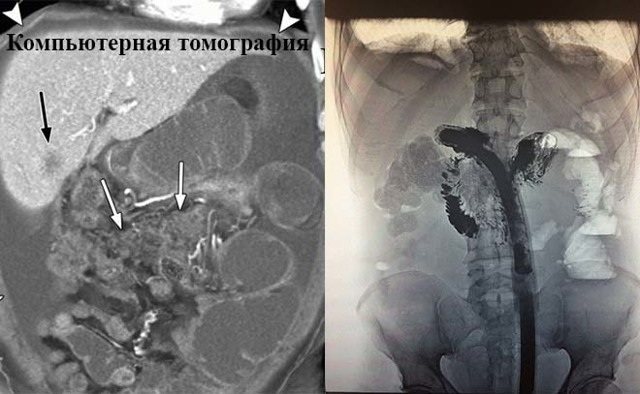
To confirm or refute peritoneal carcinomatosis, laboratory and instrumental examination of a potential focus of localization of malignant cells is carried out. The table below presents the main methods of diagnostic examination of patients with symptoms of this disease.
| Type of study | Diagnostic characteristics, price |
| Ultrasound | Patients with signs of ascites, as well as those with concomitant symptoms of peritoneal lesions, undergo an ultrasound examination of the internal organs. Particular attention is paid to the diagnosis of the stomach, large intestine, cecum, pancreas, liver tissue and gall bladder. Women undergo ultrasound diagnostics of the pelvic organs, since in most cases the primary cause of peritoneal carcinomatosis is tumor processes in the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Based on the results of this examination, an appropriate medical report is drawn up. The average cost of ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal organs is 670 rubles. |
| Cytological analysis of ascitic fluid | A patient with ascitic syndrome is hospitalized in an inpatient surgical department, where he is prescribed drainage of the abdominal cavity with forced drainage of accumulated fluid. In the process of outflow of serous exudate present in the abdominal cavity, it is selected for cytology. This type of laboratory analysis shows the cellular composition of biological material. In case of damage to the abdominal cavity by malignant cells of oncological origin, a cytological examination will confirm the fact of metastasis. The average cost of this type of diagnosis varies from 1350 to 1600 rubles. |
| Laparoscopy | This type of examination is considered one of the most informative, as it allows the attending physician to examine the internal contents of the patient’s abdominal cavity, as well as assess the condition of the tissues. To carry out this type of diagnosis, an incision is made in the lateral part of the peritoneum and a special laparoscopic probe is inserted into its cavity, which transmits a video image in real time to the computer monitor screen. If signs of an inflammatory process or foci of pathological tissue changes are detected, fragments of biological material are collected. Selected tissues are transferred to a biochemical laboratory for further research. The average cost of laparoscopy is 4,000 rubles. This examination procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and its duration is from 20 to 45 minutes. depending on the severity of the clinical case. |
| Histological analysis | Histology is a diagnostic research method that confirms or refutes the oncological process occurring inside the abdominal cavity. The tissue fragments that are removed during laparoscopy are subject to examination. Histological analysis allows us to identify cancer cells that can cause damage to the abdominal cavity. Based on the results of this diagnosis, a laboratory conclusion is drawn up about the nature of the origin of ascitic syndrome. The average cost of this type of examination is 1850 rubles. |
| Biochemical study of venous blood | Laboratory testing of venous blood makes it possible to obtain general information about the patient’s health status, indicators of the level of functional activity of his internal organs and the body’s life support systems. In the case of extensive metastasis of cancer cells into the abdominal cavity, degenerated cells will be found in the venous blood. Such laboratory test results indicate the last stage of oncology, and the prognosis for the patient’s recovery is unfavorable. In this case, multiple cancerous tumors can be localized not only in the tissues of the peritoneum, but also in any other part of the body. The average cost of this type of diagnostics is 1100 rubles. |
| MRI | MRI examination of the abdominal cavity is one of the most informative methods that displays structural changes in the tissues of the abdominal cavity. In the presence of extensive metastasis of malignant cells inside the peritoneum, local foci of the pathological process of tumor germination into the basal layer will be detected. An MRI examination should always be accompanied by tissue histology, as well as cytological analysis of ascitic fluid. The average cost of magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity is at least 3,500 rubles. |
Depending on the clinical picture of the development of the disease, the attending physician who examines a patient with signs of abdominal carcinomatosis may prescribe diagnostics of other types. Based on the results of the above studies, a decision is made on which therapeutic methods should be used in a particular clinical case.
Treatment methods
Carcinomatosis of the abdominal cavity (treatment of this disease must be comprehensive) is difficult to treat.
Medicines and surgical intervention will not bring a positive effect in case of further progression of the main cancerous tumor, which caused the metastasis of degenerated cells into the peritoneal cavity.
Chemotherapy
The use of chemotherapy drugs is one of the basic methods of drug treatment for abdominal carcinomatosis. This method of therapy allows you to simultaneously combat the main tumor tumor, which is localized in the tissues of internal organs, and also suppresses the further growth of cancer tumors inside the peritoneum.

Chemical drugs are introduced into the patient's body intravenously in the form of drip solutions. This treatment method is carried out in short courses over a long period of time. The type of chemotherapeutic agents is selected individually depending on the type of malignant neoplasm and its sensitivity to the constituent substances of the drug.
Abdominal drainage
Patients with abdominal carcinomatosis, which is accompanied by progressive ascitic syndrome, undergo surgical treatment that involves installing a drainage system. The patient is transported to the sterile conditions of the operating room.
The surgeon makes incisions in the side walls of the abdominal cavity, and then inserts the hoses of the drainage system inside. At this stage, the tubes are fixed to force the ascitic fluid to be drained into a special container.
This therapeutic procedure is carried out with the aim of suppressing the inflammatory process inside the peritoneum, as well as preventing the development of pathological complications. During the operation, the patient is under general anesthesia.
Cytoreductive surgery
This method of treating peritoneal carcinomatosis involves performing a complex surgical operation. The attending surgeon performs a simultaneous peritonectomy of the affected tissues, and also removes the primary tumor of a malignant nature, which initially provoked carcinomatosis.
This method of surgical intervention carries a large number of risks associated with a high probability of developing postoperative complications.
Upon completion of the surgical operation, the patient is required to undergo a course of chemotherapy drugs designed to suppress the pathogenic activity of malignant tumors remaining in other tissues of the internal organs.
Therapy with cytotoxic drugs
Medicines from the pharmacological group of cytostatics are prescribed in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs, or are used as an independent means of treating carcinomatosis. The advantage of using these drugs is that their constituent components exclusively affect the cells of malignant neoplasms.
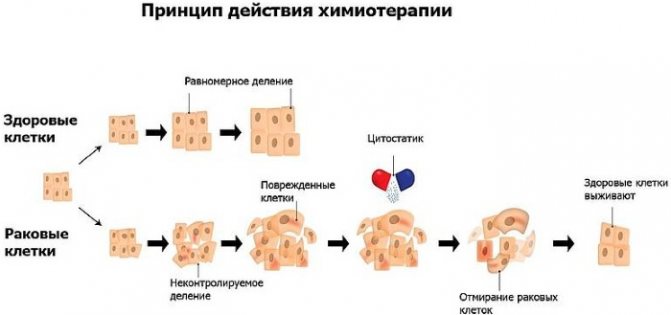
In this case, there is no damage to healthy cells of internal organs. The use of cytostatics allows minimizing the manifestation of side effects of the therapeutic process. These drugs are administered intravenously using droppers. The main disadvantage of medications of this pharmacological group is their high cost.
Possible consequences and complications
Carcinomatosis of the abdominal cavity is a severe pathology that entails the development of total tissue damage to internal organs. A similar outcome can occur even in the presence of an intensive therapeutic process.
Lack of treatment for this disease is fraught with the following complications and negative consequences:
- the addition of a bacterial infection with extensive insemination of abdominal tissue;
- accumulation of a large amount of ascitic fluid;
- the beginning of a purulent-inflammatory process inside the peritoneum;
- a significant decrease or complete cessation of the functional activity of internal organs that are located in close proximity to the source of pathology;
- blood poisoning, which develops against the background of extensive inflammation of the peritoneum, as well as the addition of a bacterial infection;
- metastasis of malignant cells to the tissues of the liver, lungs, heart and other vital organs;
- prolonged attacks of excruciatingly acute pain that cover the entire abdominal cavity, and their removal requires the use of strong painkillers or narcotics;
- the onset of death.
In the absence of a properly organized therapeutic process aimed at sanitizing the focus of pathology inside the abdominal cavity, the onset of biological death of the patient is an inevitable process.
A diagnosis of abdominal carcinomatosis does not provide a favorable prognosis for full recovery. The life expectancy of 80% of patients with this pathology does not exceed 3 months.
About 20% of patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis and a primary tumor of the stomach or colon who receive quality treatment continue to live for an additional 2 years on average. After the specified time, death inevitably occurs, which occurs against the background of progressive metastasis of malignant cells.