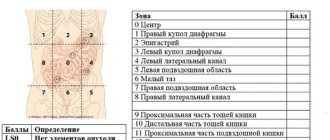
Symptoms
The large intestine performs a number of functions in the body. Unhealthy diet, bad habits, and lack of physical activity lead to slagging of the organ. The large intestine works intermittently and is attacked by harmful substances. Hyperplastic colon polyps occur in overweight people over forty-five years of age.
What gives impetus to the appearance of growths on the inner layer of the epithelium is not known with certainty. The seals protrude into the intestinal cavity. Without surgical intervention, the lesions continue to grow. The area of thickening with folds is localized in the large intestine on the left. The diameter is one to five millimeters. In addition to hyperplastic polyps, there is a danger of the formation of adenomatous malignant growths.
Factors of occurrence
The disease often does not manifest itself in any way. Polyposis is discovered unexpectedly in a person who is undergoing a routine medical examination or a standard examination of the abdominal cavity. Symptoms that are not characteristic of the disease, but are of secondary importance:
- Bloody discharge during bowel movements. The darker the blood, the higher the source of intestinal damage is located. Scarlet color indicates the presence of seals in the lower intestine.
- Rectal pain. Burning and itching sensations are dulled after taking enzyme agents. A warm heating pad can temporarily soothe the pain.
- The stool is often disturbed. Constipation or diarrhea occurs.
- Abdominal pain on the side or in the anus. The sore attacks subside for a while after defecation.
- Iron-deficiency anemia.
The listed signs may be symptoms of colitis, ulcers, hemorrhoids. A series of tests and a detailed examination of the person will help determine the cause of bleeding and pain.
Symptoms of ileitis
The acute process is characterized by rapid manifestation of symptoms, and in the future - rapid recovery, sometimes spontaneous (without treatment). It is characterized by pain in the right iliac region, rumbling and bloating, loose stools up to 20 times a day. The patient is worried about nausea and vomiting, fever up to 39°C, headaches and weakness. Severe dyspepsia can lead to severe dehydration, and untimely assistance for exicosis can lead to the development of hypovolemic shock, convulsions, and blood coagulation disorders.
Chronic ileitis is characterized by a gradual onset of the disease and moderate severity of symptoms. Patients complain of moderate pain in the right iliac region and around the navel, rumbling and bloating, and the appearance of watery yellowish stool mixed with undigested food immediately after eating. The act of defecation does not bring relief, but can provoke increased pain and collapse. Due to impaired absorption of nutrients, vitamins and minerals, gradual weight loss, hypovitaminosis, and osteoporosis are observed.
Causes of the disease
The etiology of the occurrence is that the mucous layer of the intestine thickens. A pink compaction grows near the lumen of the crypt. The crypt is an epithelial depression in the mucous layer. The growth does not show signs of dysplasia, there are no branches. The formation is more often found in the distal colon and is miliary in nature. It is not defined as a separate disease, having more than one focus of inflammation.
Classification of formations in the colon
Formations in the intestines are benign or malignant. Both types are divided into:
- Adenomatous polyp. They are determined by their size and density, and are attached to the mucosa with a wide stalk. The color matches the shade of the mucous layer. Prone to ulcers and bleeding.
- Adenomas. The villous type resembles the appearance of raspberries.
- Cyst. Cavity pathology with contents and walls in the tissue where the cyst is located.
Hyperplasiogenic polyps - neoplasms similar to cauliflower stalks - are not found in the intestines. The weak ability of the gastric mucosa to recover provokes the formation of hyperplasiogenic growths. Do not lead to cancer.
Tracking the prevalence of colon disease is not easy. People sometimes do not discover polyps in their lifetime. Medical research indicates that the disease may be more common in men.
Prerequisites for the formation of hyperplastic polyps
The appearance of polyps on the walls of the colon and rectum remains poorly studied. Scientists are inclined to the following reasons for the occurrence of abnormal proliferation of epithelial cells:
- Genetic predisposition. Often children whose relatives have a history of diagnosis associated with colon disease are prone to developing pathologies. Heredity is an inexorable thing. Parents are advised to monitor deviations in the digestion of food and pain during bowel movements in the child.
- Poor nutrition. Unhealthy dietary habits of people cause the accumulation of toxins and waste in the large intestine. Foods that consist primarily of simple carbohydrates and saturated fats displace balanced foods. Food additives lead to atrophy and a distorted perception of the taste of food. As a result, a person abuses junk food, neglecting fiber, lactic acid products and vegetables.
- Physical inactivity. Neoplasms develop more often in obese and sedentary people than in those who lead an active lifestyle. Age plays an important role. Polyposis occurs against the background of aging of the body.
- Violation of the integrity of the mucous layer. The proliferation of epithelial cells in the crypts after a hormonal imbalance or an inflammatory process.
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The structure of a healthy mucosa is not susceptible to the development of hyperplastic polyps. Provocation is caused by current gastrointestinal diseases. Aging of the mucous membrane is caused by alcohol, smoking, and rich food. Long-term use of laxatives affects the body of people suffering from constipation. The epithelium of the inner layer of the intestine wears out and tries to regenerate.
Diagnosis
The epithelial type of benign polyps is a common diagnosis option. This species develops on the inner surface of the large intestine. Capable of developing into a malignant neoplasm.
Histological examination divides the epithelial type of polyposis into:
- hyperplastic;
- villous;
- glandular;
- glandular-villous.
The size of the formations influences the degeneration of a benign polyp into a malignant tumor. The greater the number of growths, the higher the potential for malignancy. Doctors identify diffuse polyposis of the large intestine. With this disease, growths develop not only on the mucous membrane of the colon. Single seals pose less risk to the wearer. Multiple – more often degenerate into cancer.
Diagnostic actions
If a person suspects signs of colon polyposis in the body, then he should contact a proctologist or gastroenterologist. A doctor of specialized practice will examine the medical history and send the patient for examination. Making an accurate diagnosis when the whole picture of the patient’s condition is before your eyes is not easy. Too many diseases have similar causes.
The doctor performs palpation and prescribes laboratory tests (donating blood for hemoglobin, testing stool for occult blood). Morphological symptoms will be clear after instrumental methods of studying the body:
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- gastroscopy;
- ultrasonography;
- colonoscopy;
- irrigoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy.
Using the above methods, the concomitant cause of the development of formations in the large intestine is established. The doctor will also detect the location of the growths and their size.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of hyperplastic polyps comes down to surgical removal of the formations. The risk of degeneration of benign growths into cancer is high. Histological examination of a large specimen will help determine the presence of cancer cells. A small polyp is not suitable for histology. Polyposis is an unpleasant disease that interferes with the smooth functioning of the body, relief during bowel movements and other painful manifestations.
Growths in the lower intestine are neutralized through sigmoidoscopy. Smaller polyps are removed during a colonoscopy. After the transformation of benign growths into malignant ones, the patient is prescribed chemotherapy, radiation and immunostimulating procedures. The patient's large intestine is removed when the lining becomes cancerous.
The danger of a hyperplastic polyp of the colon is that the course of the disease is not expressed by specific symptoms. The person realizes it too late. An annual examination of the body and standard tests will help determine the disease. And a healthy lifestyle preserves the quality of human life.
The human gastrointestinal tract is susceptible to a large number of diseases and disorders. Lymphoid hyperplasia is a pathological proliferation of cells of different layers.
Forecast and some recommendations
The most favorable prognosis occurs when the disease is detected in a timely manner and urgent measures are taken to prevent further growth of the gastric mucosa.
No less important is the type of disease and the degree of its intensity.
If you strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, it is usually possible to bring the pathological process under control.
In addition, the following instructions from specialists in diseases of the digestive system must be observed:
- Diagnose any disorders in the gastrointestinal tract in a timely manner.
- Get tested regularly for H. Pylori.
- Monitor prescribed therapy.
- Stabilize the pH level of gastric juice.
- Follow the diet strictly.
- Give up bad habits forever.
- Chew food thoroughly.
- Watch the chair.
- Normalize the activity of the nervous system.
Features of lymphoid hyperplasia
Causes of pathological disorder
Doctors associate the occurrence of hyperplasia with various processes affecting the tissue. Thus, there is a systematic increase in the number of cells. Stopping the pathogenic process can be very problematic. Various health problems (obesity, liver pathology, hyperglycemia) can become a prerequisite for the onset of this disease. Particularly worth highlighting is a group of factors such as heredity.
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia occurs for the following reasons:
- dysfunctional processes of internal secretion of the gastric mucosa;
- deviations in hormonal ratios;
- disorder in the nervous regulation of the digestive tract;
- negative effects of carcinogens that activate pathological cell division;
- activity of elements that are formed after tissue decay;
- blastomogenic factors;
- the influence of digestive system disorders of a chronic, autoimmune, atrophic nature;
- biological functioning of bacteria such as Helicobacter pylori;
- systematic nervous disorders + stress;
- herpes virus infection;
- disturbance of the motility process of the stomach and duodenum;
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system (including pathological ones).
Pathogenic symptoms

The localization of the pathological segment in most cases affects the course of the disease. Medicine identifies the following criteria: rising temperature, general weakness, a significant increase in lymphocytes and a decrease in albumin levels. Lymphofollicular hyperplasia does not have symptoms when the system is benign. Negative symptoms (severe cases) are associated with hyperplastic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. Patients complain of abdominal pain + dyspeptic disorders.
Hyperplasia and its stages of development directly correlate with the size and distribution of follicles:
- Zero stage. Complete absence of follicles or their weak form. The position of these structures is chaotic;
- First stage. Growth of small-sized formations (bubble) into diffuse and single structures;
- Second phase. Dense formations without the formation of complex conglomerates;
- Third stage. The follicles unite into large colonies, and the mucous membrane becomes completely hyperemic;
- Fourth stage. The presence of erosive areas, which are expressed by hyperemia of the mucous membrane with the presence of fibrin-type plaque. The mucous membrane has a matte color + vascular pattern.
Practical medicine today has concentrated a large knowledge base regarding the features of the formation and course of pathology.
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the gastrointestinal tract manifests clinical indicators only at the 4th stage in the form of intestinal bleeding. Pain syndrome of varying intensity develops (abdominal area). Also, the definition of diseases can be a simple event. This is due to the fact that there are simply no specific symptoms.
Intestinal hyperplasia

The lower section of the small intestine is called the ileum. From anatomy lessons we can recall that this area of the suction organ is lined with a mucous membrane with a large number of villi. The surface of the digestive organ is filled with lymphatic vessels and capillaries, which take an active part in the consumption of beneficial nutrients. The lymphatic sinus effectively absorbs fatty elements, and sugar and amino acid structures are absorbed by blood vessels. The mucous and submucosal layers (section of the small intestine) are distinguished by circulation folds in their structure. In the process of absorption of necessary substances, special enzymes are formed that take part in the digestion of food.
Lymphoid hyperplasia is a consequence of human immunodeficiency. Proliferative processes of the intestinal walls also have a significant impact. Disorders are diagnosed by specialists in the event of an extraordinary reaction to an external source of irritation of the lymphoid tissue. The clinical manifestations of the pathological disorder are as follows:
- Presence of loose stools (frequent urge 7 times in 24 hours);
- Feces contain impurities in the form of mucus and blood;
- Spasmodic pain is abdominal in nature;
- A sharp and significant decrease in body weight;
- Increased gas production + bloating (rumbling) in the stomach;
- The patient experiences apathy to action. The body is characterized by weakness.
Fiber endoscopy and qualitative tests (blood, urine, feces) are quite effective and reliable ways to diagnose the disease. Lymphoid hyperplasia is studied in segments of the ileum and does not require the use of a therapeutic technique. A set of therapeutic and preventive measures includes strict adherence to an optimized nutritional plan (diet). In case of serious inflammation (cancer, Crohn's disease), attention is paid to taking medications. An alternative may be surgery.
Diagnostic process
The pathological condition of the mucous membrane is quite problematic to identify. Asymptomaticity is the main enemy of identifying the disease (in the early stages) even for qualified specialists. In some cases, lymphoid follicles are discovered randomly (for example, during colonoscopy). Unfortunately, a decent number of patients go to the doctor with intestinal bleeding (or acute abdominal pain). These signs indicate the last stage of the disease.
The growth of the layer in the stomach and intestines is examined using endoscopic technology. Colonoscopy, FGDS, sigmoidoscopy are those methods that have proven themselves effectively and reliably in medicine. The list can also include radiography + contrast agents. The mechanism allows you to qualitatively assess the level of development of newly formed cells. The endoscopic technique makes it possible to obtain biological material for histological studies. The diagnosis of hyperplasia (including follicles) informs the patient that there is a risk of transformation of abnormal areas into malignant formations. The prejudice of illness is a banal, but quite effective mechanism for maintaining health for many years.
Differentiation of the disease
Differentiation of the disease occurs on the basis of laboratory tests of stool, urine, blood and the results of fibrin fiber endoscopy. Most often, lymphofollicular dysplasia can be diagnosed when it affects the terminal zone of the ileum. This suggests that the pathological process is secondary in nature and therapeutic action on it is not required. As a preventive and therapeutic measure, a strict diet may be recommended, in which a number of foods are prohibited. In cases where the inflammation is serious and there is a suspicion of Crohn's disease or cancer, surgical intervention or drug therapy is indicated.
How to treat lymphofollicular hyperplasia
About the disease
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia can affect the organs of the endocrine system and intestines, but the most common is hyperplasia of the stomach and intestines. This is probably due to a large number of risk factors for all parts of the gastrointestinal tract:
- long-term inflammatory processes in the stomach, for example, chronic gastritis; - consumption of carcinogens, that is, products containing dangerous additives with the letter code E; — damage to the mucous membrane by Helicobacter pylori bacteria; - prolonged stress.
When the endocrine system is damaged, the trigger is often an existing endocrine or systemic disease. Thus, there is lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the thymus, which develops against the background of an existing lesion of the pituitary gland.
Symptoms
Depending on the location of the pathological process, symptoms can be very diverse. Common symptoms include fever, weakness, changes in the blood picture: increased levels of lymphocytes and decreased albumin. Most often, lymphofollicular hyperplasia is benign and therefore asymptomatic.
In severe cases of hyperplasia in the gastrointestinal tract, the patient begins to experience abdominal pain and dyspeptic symptoms.
Diagnostics
Since the disease is characterized by the proliferation of the mucous layer, its localization in the stomach and intestines can be detected using endoscopic methods (FGDS, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy), as well as during X-ray examination with contrast. During X-ray diagnostics, using contrast distribution, you can determine the degree of proliferation of newly formed tissues. And with endoscopic methods, it is possible to obtain altered tissue for histological examination.
Damage to the endocrine system is characterized by changes in the blood picture with high lymphocytosis. A significant increase in lymphocytes should always alert the doctor.
Diagnostics
It is possible to establish a diagnosis and exclude other pathologies when the epithelial layer grows only after histology, therefore it is necessary to perform a biopsy of the mucous membrane with further microscopic examination of the obtained material.
To obtain samples for research, gastroscopy is prescribed. This is a manipulation during which a flexible probe equipped with a video camera and lighting is inserted into the stomach.
During this examination, the specialist is able to visually examine the condition of the mucous membrane (the image is displayed on the screen). In the presence of hyperplasia, thickening of the mucosa will be noticeable, as well as the presence of deep folds on its surface. During the gastroscopy, a biopsy is also performed.
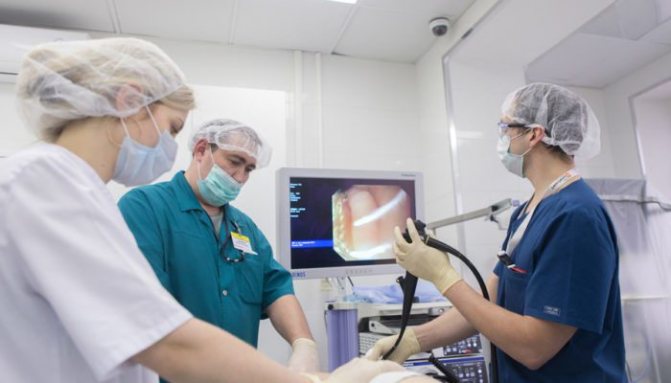
The material obtained as a result of the biopsy is sent for histology. This is the most informative study, which allows not only to 100% confirm the diagnosis of hyperplasia, but also to determine its type. This allows you to prescribe the most effective treatment.
Sometimes during the examination, fluoroscopy using a barium solution is prescribed. In the photographs you can notice thickening of the mucous membrane and the appearance of polyps of significant size. However, in terms of information content, x-rays are much inferior to gastroscopy.
Almost always, if stomach diseases are suspected, they are referred for tests to detect the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Since it is these microorganisms that often provoke the development of inflammatory processes. Tests for infection are as follows:
- blood test for the presence of antibodies to Helicobacter;
- special respiratory analysis: the subject drinks a solution with urea with labeled carbon atoms. In the presence of bacteria, urea will be broken down to form carbon dioxide, which is eliminated through the respiratory system. When analyzing exhaled air, labeled atoms are detected. In the absence of infection, these atoms will not be part of the exhaled air;
- carrying out fecal analysis to detect antibodies to Helicobacter;
- examination of biopsy materials for the presence of infection.
Advice! Additionally, almost all patients are referred for an ultrasound to detect the presence of concomitant diseases of the liver or pancreas. Sometimes a computed tomography scan is prescribed to rule out other diagnoses.
Intestinal diseases treatment
Intestinal diseases. Treatment of intestinal diseases with folk remedies
Intestinal hyperplasia
● Intestinal hyperplasia is a slight thickening of the folds of the intestinal mucosa. Most patients with this intestinal disease have a question: “Is it possible to stop the growth of intestinal epithelium with signs of hyperplasia?” This is possible by following the recommendations below.
● First of all, you need to strengthen your immune system. You will learn how to achieve this by reading the article “Healing herbs to boost immunity .” By increasing the body's defenses and resistance, you gradually get rid of many diseases. Eat more unprocessed fresh vegetables, herbs, berries and fruits every day; in total up to 600 g per day. To rid your body of toxins, drink at least two liters of water, adding to your taste aromatic spices such as mint, cloves, cinnamon, cumin and dill, which enhance the taste. Consume up to 100 g of fermented milk bifidum-bacterin daily.
● And now I bring to your attention two effective traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of intestinal hyperplasia:
#8212; for 12 hours, infuse a teaspoon of mountain arnica herb in a glass of boiling water and drink ⅓ glass of infusion three times a day before meals for five minutes;
#8212; rinse the dandelion roots thoroughly, wilt them until the juice flow stops, then get the powder by grinding them in a coffee grinder; take half a teaspoon of powder three times a day, half an hour before meals, with a small amount of water. Treat with herbs for 4 to 6 weeks, 2-3 times a year.
● Intestinal diseases should also be treated with simple physical exercises: morning 10-minute exercises and dousing with cold water. Depending on your health, practice brisk walking or jogging for thirty minutes three times a week. Swimming once a week and cycling twice a week for one hour will help you.
Spastic colitis complicated by adenoma and hemorrhoids
● This diagnosis was given to one patient who complained of pain in the anus and mucus discharge from the rectum. More precisely, we are dealing here with distal proctitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectal outlet. In such cases, it is advisable to conduct an endoscopic examination of the colon and rectum and bacteriological examination of stool.
● First of all, if you have chronic intestinal colitis and proctitis, you should follow a special non-irritating diet. If you are constipated, eat foods with the addition of wheat bran; if you have loose stools (diarrhea), limit foods rich in fiber. Medicinal microenemas are effective:
#8212; first seven days: in the morning after bowel movement #8212; microenema with rotokan (half a glass of boiled water, a teaspoon of raw materials); at night - with 10 ml of vinylin;
#8212; second seven days: in the morning after bowel movement - microenema with 50 ml of protargol 0.5%; at night - with 10 ml of carotoline.
● Next, inject into the rectum for fourteen days in the morning after stool 0.5 cm of methyluracil ointment squeezed out of a tube with a methyluracil suppository; at night - insert a “Tykveol” candle into the anus.
● If you have dysbacteriosis, take one tablespoon in the morning after breakfast - normofolin-L, and before dinner - normofolin-B. Treat for 10 days. Antispasmodics will help you get rid of pain: buscopan or mebeverine - one tablet three times a day for three weeks.
Trophic ulcers near the anus with copious discharge
● Spicy foods with red pepper, horseradish or mustard, as well as alcohol abuse, can provoke excessive mucus secretion. Benign villous tumors of the sigmoid and rectum can also cause mucus formation. X-ray, endoscopic and other examinations (colonoscopy) will help clarify the diagnosis.
● The villous tumor is removed in the hospital using electrocoagulation or excision of the affected area of the intestine. As a rule, the prognosis is favorable. If there are contraindications to surgery, use herbal medicine:
#8212; let a tablespoon of celandine herb brew in 200 ml of boiling water for 15-20 minutes, then before going to bed, inject a cooled ¼ cup of infusion into the rectum for 10 days in a row. Then undergo a control examination of the intestines. As clinical trials have shown, after such treatment the tumor component disappears and its growth is inhibited;
#8212; Immunotherapy described above is an addition to the treatment of the disease.
● Grind the mistletoe herb and fill a 700 ml bottle with it, fill it with vodka and let it steep for three weeks; do not forget to periodically shake the contents of the bottle. Drink 30-40 drops of tincture three times a day before meals for half an hour for a year.
● The homeopathic remedy podophyllum will help you prevent the appearance of new formations in the intestines - 10 drops before meals with water three times a week, then a seven-day break; the course of treatment is six months.
● All patients are recommended to undergo endoscopic examination to clarify the diagnosis. Many patients refuse colonoscopy due to pain during this procedure. But pain is easily relieved by taking analgesics, anesthetics, or, as a last resort #8212; anesthesia. Colonoscopy helps the doctor assess the condition of the disease not by indirect signs, but by the results of accurate observations and promptly prescribe adequate treatment for the disease.
Atony and chronic constipation
● The reason for this may be dolichosigma - an elongated sigmoid colon, which gives kinks and slight inversion of excess loops.
● To normalize the motor-evacuation function of the large intestine and prevent its atony, take proserin thirty minutes before meals, 10-15 mg 2-3 times a day. Or dibazol 20-50 mg before meals two hours or two hours after meals, also 2-3 times a day. Duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks with 2-3 month breaks.
What is hyperplasia
Hearing the unfamiliar word “hyperplasia” in the doctor’s office should not fall into despair. It’s not so scary if you understand the cause of the disease and start treatment on time.
What is it and why did it appear?
Hyperplasia means that in any tissue of the body (not related to a tumor) or organ, the number of cells has increased and this has led to an increase in the volume of the formation or organ.
After such an explanation, it is reasonable to talk about the reason for such changes. But it’s not easy to answer unequivocally, because there are many reasons. The stimulus for cell growth can be tissue growth stimulants, any antigenic stimulus, various oncogenic substances, or previous operations to remove an entire organ or part of it.
If we talk about the symptoms of physiological hyperplasia, then we will talk about the proliferation of the mammary gland epithelium that occurs during pregnancy. There is also such a thing as glandular hyperplasia, which occurs before the onset of menstruation. Only a doctor can understand all the intricacies, and our task is to give general concepts about the disease. Because although it refers to benign formations, there is still a possibility that the process of degeneration into a malignant form may begin.
If we talk about glandular hyperplasia, there are several types of proliferation - cell multiplication, causing tissue growth, which are determined by the degree of disturbance. For example, epithelial separation may have cytologic atypia or may not be found. They observe whether there is invasive growth - penetration of cells into surrounding tissues; with hyperplasia it is not observed.
When the thickness of the endometrium - the inner mucous layer of the uterus - increases, they speak of endometrial hyperplasia.
Anemia, some of its forms, can cause proliferation of the components of myeloid (blood-forming) tissue. Infectious diseases sometimes cause hyperplastic processes in the lymphoreticular tissue that makes up the lymph nodes and the spleen.
Between us women
Although the name of the disease is the same, common to all, nevertheless, it also has its own characteristics. Therefore, it is better to conduct the conversation in this direction.
The mucous membrane of a woman's uterus is called the endometrium. Hyperplasia and its growth are classified as benign processes. The endometrium enlarges monthly when, under the influence of estrogen, it prepares to receive a fertilized egg. In the absence of conception, excess endometrium is shed, which is expressed by menstrual bleeding. If the process is disrupted, the mucous membrane begins to grow stronger. The type of disease depends on how much the thickness of the endometrium has increased.
With glandular hyperplasia, the lumen between the endometrial glands is disrupted. But the tissue has a homogeneous structure, the thickness of the endometrium is no more than 1.5 cm.
If cysts are found among the tissues, then the diagnosis already sounds like glandular cystic hyperplasia.
The atypical form of the disease is characterized by a structural change in tissue, the mucous membrane grows up to 3 cm; this condition of the uterus is also called adenomatosis.
Focal hyperplasia means that polyps have formed in the endometrium in the form of separate foci. They are also divided into glandular, fibrous and adenomatous. In the focus of hyperplasia, the thickness of the endometrium can be up to 6 cm.
What is the risk of each type of disease? The danger in terms of degeneration into a malignant formation is represented by atypical and focal hyperplasia. As for glandular and cystic endometrial hyperplasia, doctors consider them benign and not prone to degeneration.
The first sign that endometrial hyperplasia may have appeared is a menstrual irregularity. Menstruation becomes painful and most often occurs as heavy bleeding. There is also amenorrhea - their absence for up to six months or more. In general, endometrial hyperplasia primarily indicates hormonal disorders, which can result in a number of other diseases, such as endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, and infertility.
There are several treatment options for hyperplasia, it all depends on its type, how much the tissue has grown and how old the patient is. In reproductive age, treatment is conservative: therapy using hormonal drugs. With the right treatment, the growth of the endometrium stops. But if hyperplasia has reached a significant size or relapses, then you have to turn to surgeons.
This disease is often accompanied by endocrine disorders - diabetes, obesity. Women over 50 years of age, overweight and suffering from hypertension are susceptible to the disease.
And men suffer too
After the age of 50, about 85% of men come to a urologist with benign prostatic hyperplasia (adenoma). The disease indicates that a nodule or several have appeared in the prostate; they grow, compress the urethra and cause problems with urination. The more the cells grow, the more serious the problem becomes.
The cause of the disease is said to be hormonal changes, the so-called male menopause. But there is no exact data on how much sexual activity, sexual orientation, bad habits, and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs affect the appearance of adenoma.
Symptoms of hyperplasia in men primarily manifest themselves in the form of problems with urination - the bladder does not completely empty. Then everything becomes more complicated: sluggish flow, frequent urges at night, and the abdominal muscles have to be very strained. Delaying a visit to the doctor can result in a number of troubles - chronic renal failure, urinary incontinence. And then complications follow in the form of cystitis, hematuria (blood in the urine), urolithiasis and a number of others.
If the process is not stopped and treatment is not started, the outcome can be quite sad: the urethra will be completely compressed. Only suprapubic puncture will help alleviate the patient’s condition.
Treatment of adenoma hyperplasia depends on the extent of the disease. Medicines can help only in the first stages, when the bladder is still completely emptied.
Non-operative methods, in particular the use of a catheter, are used when a man cannot be operated on for health reasons.
The most effective method of treating hyperplasia remains surgery. If the disease is not advanced, transuretal resection is proposed - the adenoma is removed through the urethra. This operation is more gentle than abdominal surgery.
In general, I would like to say that one article cannot cover all the nuances and symptoms of hyperplasia. The goal was to give general information about it, to show that a diagnosis made at an early stage gives every chance of a complete cure.
«>