Atony of the stomach and intestines is a stable relaxation of the muscles of these organs, a complete or partial loss of tone in their walls. The pathological process in the stomach is expressed in the inability of the organ to perform basic functions, resulting in stagnation of food. Because of this, inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract can develop, for example, gastritis, as well as impaired blood supply in the walls of the stomach.
How does portal (congestive) gastropathy develop?
This is a disease in which inflammation of the gastric mucosa does not occur, but the epithelial cells of its walls are still damaged. In addition, the development of congestive gastropathy is facilitated by a lack of some enzymes. Stagnation in the stomach leads to disruption of the microcirculation of the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in the so-called collateral circulation, which damages the walls of the stomach. Complications of congestive gastropathy are hidden bleeding and severe anemia - a life-threatening condition.
Causes
The causes of impaired muscle contractile function are problems with the nervous system. Often, gastric atony is considered as a psychosomatic pathology against the background of neurasthenia or depression.
Somatic causes of this condition:
- infectious lesions: enteroviruses, atony and paralysis due to botulism,
- peritonitis or acute inflammation of the peritoneum,
- consequence of myocardial infarction due to disruption of nerve fibers,
- sharp weight loss with asthenia of the patient and often prolapse of the stomach,
- injuries to the abdominal wall,
- severe types of pneumonia,
- stressful situations, get out of them, somatized depression,
- complication of surgery.
Most often, gastric atony develops against the background of weakness of the abdominal wall and abdominal muscles, as well as due to slower intestinal motility. Attacks of gastric atony can develop in women during pregnancy and after childbirth.
The pathological process is facilitated by obesity and physical inactivity, that is, a sedentary lifestyle. Sometimes diabetic atony of the stomach occurs against the background of diabetes mellitus.
Acute gastric atony can develop against the background of pyloric stenosis or thrombus in the gastric choroid plexus. Relief of the emergency condition is required, and the atonic process in the stomach will soon end on its own with the help of diet and symptomatic therapy.
Risk factors for congestive gastropathy
The etiology of this disease has not been fully explained, but liver cirrhosis to be a causative factor in its development. Organ damage leads to portal vein occlusion and hemorrhage. The risk of getting sick increases with age. A cause-and-effect factor for congestive gastropathy is also an unhealthy lifestyle, for example, a person’s addiction to alcohol and smoking. In addition, certain medications can cause portal infections. Long-term use of analgesics, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs damages the mucous membrane of the stomach and liver, which is unable to get rid of excess toxins. People with stomach ulcers, reflux disease, and chronic bacterial infections, especially Helicobacter pylori, are also vulnerable to gastric congestion.
Atony therapy
Nutrition plays a significant role in the treatment of the disease. In this case, a mechanically gentle, high-calorie, fortified diet is recommended. It is also necessary to strengthen the immune system and nervous system.
Treatment usually includes the following drugs:
- Medicines that improve gastric motility and have an antiemetic effect based on domperidone: Motilium, Passazhix, Motilak. You can also use similar products with itopride as the main active ingredient: Itomed, Ganaton, or with trimebutine: Trimedat.
- Potassium and calcium preparations.
- Cell regeneration stimulators.
- Immunity boosters, including vitamins.
In some cases, treatment with insulin is prescribed. The injection should be given 30 minutes before meals. The dose ranges from 5 to 20 units. Treatment of stomach atony with mineral water gives good results; it is recommended if visiting special sanatoriums or resorts is possible.
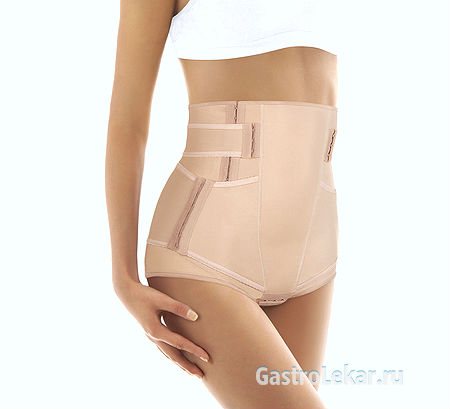
Since gastric hypotension occurs due to weakening of muscles, a complex of physical therapy is usually recommended to the patient. Also, in severe cases of the disease, the patient should wear a support bandage. It is especially necessary for a large sagging belly. It must be put on in a supine position. Constantly wearing a bandage often quickly improves the patient's condition and eliminates discomfort associated with sprains and atony.
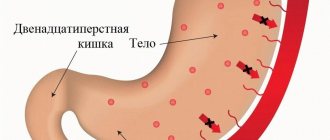
Types of portal gastropathy
Depending on the course of the disease, portal cholestasis is divided into two types:
- Mild degree - on the endoscopic image of the stomach, a mosaic of the mucous membrane is noticeable, but it is not yet very pronounced. The probability of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract is 3-30%.
- Severe degree - membranous mosaic of submucosal hemorrhage of the stomach is very noticeable. The risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract is 40-60%.
The diagnosis of congestive gastropathy is complicated by the fact that at first the disease does not manifest itself with any characteristic symptomatic signs.
Symptoms of hypotension development
memory impairment,
absent-mindedness and instability of attention.
The performance of patients with signs of hypotension is significantly reduced. They may experience a feeling of lack of air at rest, and shortness of breath appears even with slight physical exertion. In some cases, by the evening the legs of such patients swell. Hypotension almost always leads to a decrease in libido, potency is disrupted in men, and the menstrual cycle is disrupted in women. Often the disease is accompanied by a general deterioration in mood. Irritable weakness and tearfulness may occur.
Headache as a symptom of incipient hypotension
Sometimes the only sign of hypotension is a habitual headache that occurs after sleep (often during the day) or due to fatigue disproportionate to the work done (physical or mental). Fatigue takes on the characteristics of exhaustion. Most often, the headache covers the frontotemporal or frontoparietal region; it can be dull, pressing, tightening, bursting or pulsating and last from several hours to two days. Headache due to hypertension in some cases is similar to migraine and is accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Headache with hypotension goes away from exposure to cold, after a walk in the fresh air or exercise. It may stop on its own. Some patients experience headaches several times a day.
In addition to headaches, the patient may be bothered by dizziness and increased sensitivity to bright light, noise, loud speech, and skin sensations. Dizziness leads to the fact that a person staggers when walking, and therefore it is difficult for him to endure being at a height, and sometimes it is not easy to even cross a bridge or street.
Painful symptoms of hypotension can cause a short-term loss of consciousness - fainting, which is considered a hypotensive crisis. Most often, fainting occurs in stuffy and hot rooms, when driving in city transport, especially when the car brakes sharply. Tall, thin men sometimes lose consciousness as a result of prolonged standing motionless in an upright position.
Types of hypotension and their signs
Blood pressure in adults under 25 years of age is below 100/60 mmHg. Art. and for the age group 25-40 years - below 105/65 mmHg. considered a symptom of the disease. However, blood pressure may decrease in some cases in healthy people. This is called physiological hypotension. No painful manifestations of the disease are observed.
Physiological hypotension often occurs in athletes due to dilation of blood vessels supplying blood to the muscles. With this form of the disease, according to the Japanese, people live longer. In this case, there is no need to strive to increase pressure. Experts call this condition high-training hypotension.
Another type of disease is the so-called acclimatization hypotension. Residents of the Far North, tropics and subtropics, and highlands are susceptible to it. Such hypotension is also not a sign of any disease and occurs due to the adaptation of the entire body and, in particular, blood circulation to special stress.
Secondary hypotension may be a sign of some infectious disease, for example
To get rid of hypotension in this case, it is necessary first of all to treat not the hypotension, but the underlying disease of which it is a symptom.
The disease also occurs as a result of significant blood loss. Low blood pressure occurs with insufficient adrenal function and in some other conditions. Hypotension almost always accompanies acute conditions of the human body - crises: acute cardiovascular failure, anaphylactic shock (allergic crisis), etc.
The disease, which is not caused by organic disorders, relates entirely to the psycho-emotional sphere; it occurs as a result of a primary dysfunction of the central nervous system, which regulates vascular tone and blood pressure. It is called chronic arterial hypotension or hypotension.
There is so-called positional hypotension. It manifests itself in a sudden decrease in pressure after a sharp transition from a horizontal to a vertical position, which can result in fainting. Blood pressure and pulse during hypotension are very flexible, they are influenced by body position, time of day, and the patient’s mood.
The large number and variety of signs of the disease, the lack of patterns in the course of the disease and specific symptoms do not allow hypotension to be identified as an independent disease. Most often it is an external reflection of mental disorders. If neurosis is not observed, then the matter is in some unrecognized damage to the internal organs.
Symptoms of portal (congestive) gastropathy
The onset of the disease is completely asymptomatic. Only over time does a number of signs of dyspeptic disorders appear, for example:
- progressive general weakness,
- abdominal pain of varying intensity,
- nausea, sometimes vomiting,
- lack of appetite,
- feeling full after eating, regardless of the amount of food eaten,
- burning in the stomach and esophagus, belching,
- dark color of the stool if bleeding occurs from the gastrointestinal tract.
Portal gastropathy may present with anemia, which is visible on laboratory tests.
Nutrition for atony
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of the disease. You need to eat in small portions: often and in small portions, so the food is better absorbed and overeating does not occur. You should also limit the amount of liquid.
For atony of the stomach and intestines, the diet should include:
- carrot;
- bran bread;
- kefir and yogurt;
- beets;
- oranges;
- buckwheat porridge;
- fruit and vegetable juices;
- lean poultry and fish.
The diet involves complete abstinence from foods:
- whole milk;
- fried and smoked;
- cakes and pastries;
- chocolate and coffee;
- canned food
In addition, astringent fruits, mushrooms, garlic, legumes and radishes should be consumed in minimal quantities.
How to recognize portal (congestive) gastropathy?
When diagnosing congestive gastropathy, an effective test is endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, patients are recommended to undergo gastroscopy and colonoscopy of the intestines . The examination is not very pleasant, so in many cases it is performed under general anesthesia or sedation. Preparation for diagnostic procedures is of no small importance. The patient needs to follow dietary recommendations and undergo additional examination - abdominal ultrasound, blood test, and so on.

Gastric atony: causes of the disease, main symptoms, treatment and prevention
Doctor of the highest category. Participant of many Russian and international conferences, congresses, seminars on gastroenterology and internal diseases. He has scientific publications on therapy and gastroenterology in domestic and foreign publications. He is a member of the Russian Gastroenterological Association. Specialization: diseases of the liver and biliary tract, parasitic diseases, viral hepatitis, toxic hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, alcoholic liver damage, etc. On our project. More diseases. Ordering medications. First aid.
How are they related?
Treatment of congestive (portal) gastropathy
Portal infiltration is treated carefully. The therapeutic goal of clinicians is to suppress the development of the underlying disease. If the disease is caused by alcohol abuse or cirrhosis of the liver, then the patient is recommended to completely abstain from alcoholic beverages. In cases where Helicobacter pylori is responsible for the disease, antibiotic therapy should be used. If portal gastropathy occurs during long-term therapy with analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs, then drugs are used that suppress the secretion of gastric acid. The patient should be under constant supervision of a gastroenterologist. Regular endoscopic examinations should also be performed to eliminate the risk of bleeding. In severe conditions, surgery is recommended. Take care of yourself and always be healthy!
Treatment methods for gastrostasis
There is no single treatment regimen for gastrostasis. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the cause of the pathology. An important role in this is played by diagnostics and determination of the causes of impaired evacuation of food from the stomach. Treatment methods common to all patients include following the diet prescribed by the doctor.
Of the medications prescribed to most patients, it is worth highlighting antiemetics. They relieve nausea and make eating possible. Antiemetic drugs are prescribed in the form of rectal suppositories and injection solutions.

Among medications for delayed gastric emptying, prokinetic drugs are prescribed. Most often, intravenous injections of Erythromycin and Cisapride solution are prescribed. Metoclopramide may be prescribed in tablet form. It also has antiemetic properties. The drug Domperidone and its analogues: Motillium, Passazhix, Motilak are considered effective.
If eating naturally becomes impossible, nutrition is delivered to the patient through a small intestinal tube. In difficult cases, when conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment of the pathology is resorted to.
We recommend finding out which foods cause heartburn.
Read: What does the level of pancreatic elastase indicate?
Find out how gastric adenoma is treated.
Diet for gastrostasis
Due to the fact that liquid food leaves the stomach cavity more easily than solid food, with gastrostasis it should prevail in the patient’s menu. To do this, broths, liquid porridges, and liquefied foods are introduced into the diet. You can take protein supplements diluted in milk.
Multivitamin complexes in liquid form can be a source of vitamins and minerals. For gastrostasis, a diet with a reduced amount of fat and plant fiber is recommended. Fatty foods stay longer in the stomach, which slows down the emptying process, and fiber is not digested in the body.

Gastrostasis is a condition that prevents a person from eating normally. If it is impossible to eat food, the body loses strength, there is a lack of energy and nutrients. This leads to many other health problems. Pathology requires qualified medical care.
Diagnosis of pathology
Stagnation of food in the stomach is accompanied by a symptom complex similar to many other gastrointestinal diseases, so you should consult a gastroenterologist if digestive dysfunction occurs. A violation can be suspected by the nature of the vomit and its smell. After the examination, the doctor will write a referral for examination. The following instrumental diagnostic procedures will be informative:
Pathology can be diagnosed using x-rays.
- Fibrogastroscopy. Inserting a probe into the stomach to identify the cause of the blockage and examine the walls of the organ. During the study, if indicated, it is possible to perform a tissue biopsy.
- X-ray with barium contrast. Determines the shape of the stomach and the size of the stenosis.
Return to contents
What to do if your stomach stops working
- If there are signs of food stagnation in the stomach after overeating, you should try to forcefully induce vomiting and not eat at all for the first day.
- Then eat small portions every two hours, following a strict diet, gradually making the diet more varied, and increasing the amount of food per meal.
The situation is unpleasant, so in order to get your stomach moving and not harm yourself, you need the following sequence of actions:
- Diagnostics.
- Drug treatment.
- Treatment with folk remedies.
- Diet therapy.
Diagnostics
The above symptoms can accompany not only the irrational consumption of certain “harmful” foods and a violation of the diet, but also be signs of dangerous diseases - gastritis, peptic ulcers or tumor processes.
Therefore, if your stomach is upset, and you cannot quickly cope with this condition on your own, you should contact a specialist for a thorough examination and prescribe timely therapy.
Basic diagnostic methods:
- Conversation, examination, palpation and listening to the patient’s painful area.
- Laboratory examination - tests of blood, urine, feces, gastric contents.
- Internal examination of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, with a special probe with a built-in miniature video camera.
- X-ray with contrast agent.
- Instrumental examination without the use of a gastric tube - ultrasound, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), CT (computed tomography), gastropanel, capsule gastroscopy (videopill).
Of the listed methods, the doctor prescribes only those that he considers necessary in a particular situation. Then, after comparing the results, he determines the diagnosis and prescribes individual treatment.