Causes Symptoms of cholecystitis Diagnosis Treatment Treatment of cholecystitis with herbs Treatment with folk remedies Regimen and diet Complications and prevention
Cholecystitis is an inflammatory disease of the gallbladder. It is the most common disease of the abdominal organs. Currently, 10-20% of the adult population suffers from cholecystitis, and this disease tends to further increase. This is due to a sedentary lifestyle, diet (excessive consumption of foods rich in animal fats - fatty meat, eggs, butter), and an increase in endocrine disorders (obesity, diabetes). Women get sick 4 times more often than men, this is due to taking oral contraceptives and pregnancy.
Among the numerous diseases of the biliary tract, functional disorders (dyskinesia), inflammatory (cholecystitis), and metabolic disorders (cholelithiasis) are distinguished. These conditions are phases of one pathological process: first, a disturbance in the motility of the gallbladder occurs - dyskinesia, then an inflammatory process joins - acalculous cholecystitis is formed, which over time transforms into cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis).
Causes of cholecystitis: main and additional.
The main reasons include the infectious factor. The infection enters the gallbladder through the blood, lymph and ascending from the intestines.
Primary sources of infection may be:
- acute or chronic inflammatory processes of the gastrointestinal tract (infectious enterocolitis - inflammatory bowel disease, pancreatitis, appendicitis, intestinal dysbiosis), - respiratory tract (sinusitis, tonsillitis), oral cavity (periodontal disease), - inflammatory diseases of the urinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis ), — reproductive system (adnexitis in women, prostatitis in men), — viral liver damage, — parasitic invasion of the biliary tract (giardiasis, ascariasis).
Additional factors:
1. Biliary dyskinesia. These are functional disorders of the tone and motility of the biliary system (gallbladder and bile ducts). Occurs in any case of chronic cholecystitis, leading to impaired outflow and stagnation of bile. 2. Congenital anomalies of the gallbladder. 3. Pancreatic reflux. Rejection of duodenal contents into the bile ducts. Pancreatic juice with active enzymes causes enzymatic damage to the walls of the gallbladder. Occurs in diseases of the pancreas and duodenum. 4. Impaired blood supply to the gallbladder. They occur against the background of atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and lead to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels. 5. Violation of the normal composition of bile (dyscholia). A change in the composition of gallbladder bile and the ratio of its components leads to damage to the wall of the gallbladder. This is facilitated by eating monotonous, fat-rich foods. 6. Allergic and immunological reactions cause inflammatory changes in the wall of the gallbladder. 7. Hereditary factor. 8. Endocrine changes (pregnancy, taking oral contraceptives, obesity, menstrual irregularities).
Additional factors create conditions for the development of inflammation and prepare favorable soil for the introduction of microbial flora.
What is a disease
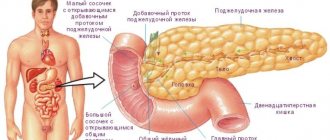
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped internal organ that stores bile. The gallbladder is located at the bottom of the right side of the liver. Organ diseases can be divided into three stages:
Inflammation of the gallbladder
- Functional disorders
- Inflammatory process
- Exchange disorders
Cholecystitis belongs to the second group and it develops as a result of an infection from the intestine entering the gallbladder. When the disease occurs, the amount of bile released into the intestines decreases, so the digestion and absorption of fats becomes more difficult.
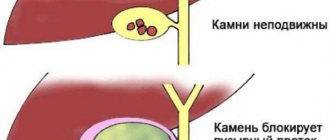
Acute cholecystitis is rare and usually occurs with cholelithiasis, when a stone blocks the duct. Chronic cholecystitis can develop after acute cholecystitis; it manifests itself gradually.
Calculous cholecystitis is one of the manifestations of cholelithiasis; in gastroenterology it is called cholelithiasis. This is chronic cholecystitis, which is characterized by the presence of stones, that is, gallstones, in the gallbladder or bile duct. Thus, in addition to signs of inflammation, stones are detected in the lumen. The disease is most often diagnosed after the age of forty, but its occurrence is possible even in children. Calculous cholecystitis more often affects women than men.
Symptoms of cholecystitis.
Cholecystitis can be acute or chronic.
Acute cholecystitis
Acute acalculous cholecystitis is rare, usually proceeds without complications and ends with recovery, sometimes it can become chronic. The disease most often develops in the presence of stones in the gall bladder and is a complication of cholelithiasis. At the beginning of the disease, intense paroxysmal pain appears in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, and body temperature rises to 38-39 degrees. Chills, yellowness of the sclera and skin, and retention of stool and gas may appear.
Acute calculous cholecystitis is characterized by a severe course with the spread of the inflammatory process to surrounding organs and tissues.
Cholecystitis is complicated by liver abscess, local or diffuse peritonitis, cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts), pancreatitis. In this condition, you should immediately consult a doctor - surgeon, therapist to resolve the issue of hospitalization in a surgical hospital.
Chronic cholecystitis
The disease begins gradually, often in adolescence. Complaints arise under the influence of poor diet and psycho-emotional stress.
The main manifestation of the disease is pain in the right hypochondrium. It can be displaced to the left hypochondrium, the upper half of the abdomen. Non-calculous cholecystitis is accompanied by one or another form of secondary dyskinesia, this often determines the nature of the pain. With concomitant hypomotor dyskinesia, the pain is constant, aching, and not intense. Often the equivalent of pain is a feeling of heaviness or burning in the right hypochondrium. In cases of hyperkinetic dyskinesia, the pain is intense, short-term, and has a paroxysmal nature. The pain radiates to the supraclavicular fossa, to the lumbar region, to the subscapular region, to the region of the heart.
Cholecystocardial syndrome - includes pain in the heart, palpitations, cardiac arrhythmias, this is associated with an infectious-toxic effect on the heart muscle.
With a long course of the disease, the solar plexus may be involved in the pathological process, and solar syndrome occurs. Its main symptom is burning, intense pain in the navel area, radiating to the back.
The occurrence and intensification of pain is associated with errors in diet, physical activity, vibration, hypothermia, emotional overload, and alcohol consumption.
Nausea and vomiting occur in 30-50% of cases; it is of a reflex nature and is associated with impaired tone of the gallbladder or is caused by concomitant gastroduodenitis or pancreatitis. An admixture of bile is detected in the vomit. Vomiting, like pain, is provoked by alcohol intake and dietary errors.
A feeling of bitterness in the mouth, “bitter” belching - these complaints are most common with inflammation of the gallbladder.
Skin itching, its appearance is associated with impaired bile secretion and is the result of irritation of skin receptors by bile acids accumulated in the blood. Violation of the outflow of bile leads to the short-term appearance of jaundice.
Chills and increased temperature are observed with exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the gallbladder.
Patients often suffer from severe vegetative-vascular dystonia. Their painful attacks are accompanied by neurotic syndromes, such as weakness, sweating, palpitations, headache, emotional lability (mood instability), sleep disturbance.
For patients suffering from allergies, exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis can cause allergic reactions (urticaria, Quincke's edema).
Women may develop premenstrual tension syndrome. 2-10 days before menstruation, headaches, pastiness of the face, hands, legs, and mood instability appear. During the same period, symptoms of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis are also observed.
Video about the causes, symptoms and treatment of chronic cholecystitis:
The manifestations of chronic cholecystitis are diverse, they consist of various signs; a general practitioner or gastroenterologist can establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the necessary set of examinations.
Causes causing exacerbation
The causes of pancreatitis can cause inflammation of not only the pancreas, but also the gallbladder and ducts. The chronic form of cholecystitis is divided into 2 groups: calculous (stones form inside the organ) and acalculous.
Exacerbation of the non-calculous form is provoked by the following factors:
- Poor nutrition, lack of coarse fiber and plant fibers in the diet.
- Binge eating.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Severe stress.
- Allergic reaction, in particular food.
In order for calculous cholecystitis to worsen, intense shaking in transport, abuse of heavy physical activity, or a sudden change in body position after a heavy lunch is enough. In addition, exacerbation of an inflamed gallbladder can be caused by obesity, dyskinesia of the bile ducts, pregnancy, hypothermia, viral and bacterial infections, and exacerbation of chronic forms of other diseases of the internal organs.
Remember! Exacerbation of attacks of cholecystitis can occur from 4 times a year to 1 time a month. It all depends on the form of the disease and its severity. Nutrition and treatment of the underlying pathology play a significant role.
Diagnosis of cholecystitis
Laboratory research:
1. General blood test. Reveals signs of inflammation. 2. Biochemical blood test: total bilirubin and its fractions, transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, cholesterol. Their moderate increase is observed. 3. Blood sugar. For the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. 4. General urine analysis. For differential diagnosis with kidney diseases. 5. Feces on worm eggs. To identify Giardia, Ascorids. 6. Microscopic and bacteriological examination of bile. 7. Immunoenzymatic blood test for giardiasis. 8. Analysis of feces for elastase 1. To diagnose pancreatitis.
Instrumental examinations:
1. Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Detects thickening of the walls of the gallbladder (thickening more than 4 mm is the main diagnostic criterion for cholecystitis), stagnation and thickening of bile - “sludge”, the presence of stones in the gallbladder, deformation of the gallbladder. 2. Ultrasound with a choleretic breakfast - to detect dyskinesia of the gallbladder. 3. Multifractional duodenal intubation (carried out only in the absence of cholelithiasis) with microscopy and bile culture. Registration of duodenal contents is carried out every 10 minutes, allows you to establish the type of secretion (hypersecretory, irregular, hyposecretory), the state of the sphincters of the biliary tract, determines the nature of the contractility of the gallbladder, the presence of inflammatory elements and bacterial flora. 4. X-ray examination of the abdominal cavity (to identify radiopaque stones). 5. FEGDS – fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy. 6. ECG. For differential diagnosis with diseases of the cardiovascular system. 7. Computed tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance. Carry out in cases that are difficult to diagnose.
Specialist consultations:
An examination by a therapist and gastroenterologist is required.
According to indications: - surgeon, if complications are suspected (pericholecystitis, cholelithiasis, gallbladder empyema, pancreatitis); — a cardiologist, to exclude pathologies of the cardiovascular system; - a gynecologist, if necessary, correction of hormonal levels in women; - psychotherapist, conducting rational psychotherapy.
Treatment of cholecystitis
If there are clinical symptoms and laboratory signs of inflammation, and positive bile culture results, antibacterial treatment is prescribed. The choice of antibiotic is made by the doctor, assessing its ability to concentrate in bile.
Symptomatic therapy
To normalize the function of the biliary tract and eliminate pain, the following are prescribed: - anticholinergics (riabal 2 ml IM or 1-2 tablets 3 times a day), myotropic antispasmodics (no-spa 2 tablets 3 times a day, papaverine 2 ml 2% solution IM 2-3 times a day, mebeverine 1-2 tablets 3 times a day), anticholinergics (platifillin), analgesics (analgin, baralgin).
If there are signs of hypotension of the gallbladder and in the absence of stones, the following is prescribed:
- choleretic drugs. Allohol (1-2 tablets 3 times a day after meals), cholenzyme (2 tablets 3 times a day after meals), and herbal medicine are used.
Traditional medicine recipes - herbal treatment - are widely used.
Folk remedies for the treatment of cholecystitis
Immortelle - 15g flowers, St. John's wort 10g herbs, pour the mixture into 0.5 liters of water, boil for 5 minutes, filter. Take 0.5 cups 3 times a day 15 minutes before meals. Corn silk - 10 g, pour 200 ml of water, boil for 5 minutes, take ¼ cup 3 times a day before meals. Tansy – 5g of flowers are infused in 250 ml of boiling water for 30 minutes, take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals. A 5g peppermint leaf is poured into 200 ml of boiling water and placed in a water bath for 15 minutes. Take ½ glass 3 times a day before meals. Rose hip. Syrup from condensed aqueous extract of rose hips and sugar - holosas, take 2 teaspoons 3 times a day before meals. Rosehip infusion - 10g of crushed fruits are poured into 400 ml of boiling water and kept in a water bath for 15 minutes, infused. Take ½ glass 3 times a day before meals.
These drugs increase the secretion of bile, reduce its viscosity, and have an anti-inflammatory effect. Prescribed during remission (out of exacerbation) for 2-4 weeks.
Mineral waters have the same effect. Depending on their composition, they can have a stimulating effect on the contractile function of the gallbladder. Mineral waters without gas are taken as prescribed by a doctor 3 times a day, 1 glass 30 minutes - 1.5 hours before meals (depending on the state of stomach secretion) warm or hot (40 - 50 degrees);
- blind probing - tubing, 1 time per week, 3-5 times.
It is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. Slowly (in small sips) you should drink 150-200 ml of warm (40-45 degrees) mineral water with the addition of 20-25 g of sorbitol or xylitol. Lie on your right side, on your back for an hour. A warm heating pad is placed under the right side. After bowel movements, it is recommended to take a shower and rest for 20 minutes. The first meal is 1-1.5 hours after the end of the procedure. This is a glass of tea with honey, cottage cheese.
In the presence of microlites in bile, hypotension of the gallbladder, cholestatic syndrome, bile acid preparations (ursodeoxycholic acid) are used for 1-3 months, under medical supervision. Read more about herbal medicine for cholecystitis >>
In order to normalize the biliary function of the liver, hepatoprotectors with choleretic properties are prescribed. Chophytol is a hepatoprotector of plant origin, containing a dry aqueous extract from the juice of field artichoke leaves. Take 2 tablets 3 times a day 20 minutes before meals for a month. Gepabene is a combined preparation of plant origin, containing extract of fumaria officinalis and dry extract of milk thistle fruits. Take 1 capsule 3 times a day after meals.
For vegetative-vascular dystonia, sedatives (valerian, motherwort), anxiolytics (adaptol 500 mg 3 times a day for 2 months) are recommended.
Emergency help
What will be the first aid to relieve an attack of pain with cholecystitis, what to do if the symptoms of the disease have become unbearable? It is very important to follow everything strictly according to the rules, otherwise you can only worsen the patient’s health:
- Call an ambulance.
- Take a lying position and calm down.
- Place a bottle of cold water or ice on your stomach.
- Drink an antispasmodic: Drotaverine, Papaverine or No-shpu (no more than 2 tablets).
- If you feel nauseous, drink mint tea or still mineral water.
- When vomiting, do not allow the tongue to retract; the head should be on its side in a supine position. After gagging, drink mineral water, but in small sips.
During an attack of cholecystitis, it is prohibited to take alcohol, narcotic and painkillers, medications not prescribed by a doctor, put a warm heating pad on the stomach and do an enema.
( 1 ratings, average: 1.00 out of 5)
Regime and therapeutic nutrition.
During the period of severe exacerbation of cholecystitis, patients are recommended to undergo treatment in a hospital - therapeutic or gastroenterological, adherence to bed rest, and a state of psycho-emotional rest. After the elimination of pronounced signs of exacerbation, the patient’s regimen is expanded to general.
During an exacerbation, in the first two days, only warm liquids are prescribed (weak sweet tea, fruit and vegetable juices diluted with water, still mineral water) in small portions up to 1.5 liters per day and several crackers. As the pain subsides and the general condition improves, the dietary table expands. Recommend:
- pureed soups from vegetables and cereals, - porridge (oatmeal, rice, semolina, buckwheat), - jelly, mousse, jelly, low-fat cottage cheese, - low-fat boiled fish, - pureed and boiled meat, steamed cutlets (veal, chicken, turkey, rabbit) - white crackers.
Food is taken in fractional portions 5-6 times a day.
During the period of exacerbation, it is recommended to carry out fasting days 1 day a week: - cottage cheese - kefir day. 900g kefir for 6 doses, 300g low-fat cottage cheese for 3 doses and 100g sugar; - rice - compote. 1.5 liters of compote prepared from 1.5 kg of fresh or 240 g of dry fruits for 6 servings, rice porridge cooked in water from 50 g of rice - for 3 servings.
After stopping the exacerbation of cholecystitis, a diet is prescribed, table No. 5, which is the main one for this disease.
Patients are recommended: - milk, fruit, vegetable broth soups with cereals, noodles; - boiled meat, steamed cutlets, meatballs (beef, rabbit, chicken, turkey); - low-fat varieties of sea or river fish, boiled or baked, without crust; - eggs, up to 1-2 per day - soft-boiled, in the form of steam omelettes; — dairy products: low-fat milk, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, yogurt, butter (limited); - vegetables boiled, baked, partially raw. Potatoes, beets, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers, pumpkin, sweet peppers, eggplants, cauliflower, zucchini; - fruits and berries. Pears, melons, bananas, peaches, apricots, watermelons, sour apples; - porridge - buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, semolina, with the addition of milk, if tolerated; - sweet dishes - marshmallows, marmalade, honey, jams, preserves, jelly; - flour products - wheat and rye bread, yesterday's bread, white bread crackers, dry unsweetened cookies.
You need to eat food in small portions, slowly 5-6 times a day. Long breaks between meals and fasting are not recommended. Breakfast is required, dinner 2-3 hours before bedtime, not much. The amount of liquid is not limited. A large amount of food, taken once, disrupts the rhythm of bile secretion, causes spasm of the gallbladder and provokes pain.
In case of chronic cholecystitis, it is necessary to increase the consumption of foods that improve the flow of bile and reduce cholesterol levels:
- rich in dietary fiber (bran, vegetables, fruits, berries). The bran is pre-steamed and added to dishes, 1-1.5 tablespoons 3 times a day; - rich in magnesium salts (buckwheat and oatmeal, dried fruits, bran); — containing essential polyunsaturated fatty acids, phospholipids, vitamin E (corn, olive, sunflower and other oils); - containing lactic acid bacteria (fermented milk drinks, cottage cheese).
Products not recommended:
- high in animal fats (fried foods, fatty fish, pork, lamb, duck, sausages, smoked meats, mayonnaise, creams, cakes, pastries); - raw onions, garlic, radishes, sorrel, spinach, mushrooms, bean dishes (peas, beans); - cold and carbonated drinks, concentrated juices, coffee, cocoa, alcoholic drinks.
Rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy and spa treatment is an important component of comprehensive rehabilitation of patients. Inductothermy and a UHF electric field are used as thermal procedures to correct hypertonicity of the gallbladder and have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The course of treatment is 12-15 procedures, daily. In order to stimulate the emptying of the gallbladder, a low-frequency pulsed current is prescribed. To reduce dyskinetic phenomena, electrophoresis of 5% novocaine, 2% papaverine is recommended. To normalize the functional state of the nervous system, a galvanic collar according to Shcherbakov and electrophoresis with bromine are used. For the same purpose, coniferous, oxygen and carbon dioxide baths are prescribed. Sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated no earlier than 2-4 months after an exacerbation of cholecystitis. Patients are sent to balneo-mud resorts: Essentuki, Zheleznovodsk, Truskavets, Morshin.
Prevention of exacerbation of the disease
To prevent exacerbation, it is recommended to follow a diet and follow the doctor’s recommendations. A person who is at risk is advised to control their weight, not to starve or overeat. Spa treatment is recommended. After relieving the symptoms of exacerbation, it is recommended to perform therapeutic exercises.
Herbal infusions for the treatment of pathology can only be used in consultation with the attending physician. Herbal medicine will help reduce the risk of acute attacks. It is useful to use decoctions of immortelle, corn silk, mint, and choleretic tea.
List of references: https://www.nrmed.ru/rus/dlya-vzroslykh/urologiya/hronicheskiy-holecistit/ https://abc-medicina.com/gastrojenterologija/hronicheskiy-holecistit https://www.kp.ru/ putevoditel/zdorove/khronicheskij-kholetsistit/ https://www.smclinic.ru/diseases/kh/kholetsistit/ https://yandex.ru/health/turbo/articles?id=4428 https://medsi.ru/articles /kholetsistit-chto-eto-takoe-prichiny-priznaki-simptomy-lechenie-u-vzroslykh-dieta-i-profilaktika/ https://tsn.ua/ru/blogi/themes/health_sport/nekalkuleznyy-holecistit-snizhaem-riski -i-menyaem-obraz-zhizni-1174455.html https://unionclinic.ru/gastro/holecistit https://www.gosmed.ru/lechebnaya-deyatelnost/spravochnik-zabolevaniy/gastroenterologiya-bolezny/khronicheskiy-kholetsistit/ poliran .ru/lechenie-hronicheskogo-holecistita/ https://www.medkompas.ru/about-health/diseases/holecistit/ https://medportal.ru/enc/gastroenterology/dyskinesia/3/ https://www.lvrach .ru/2006/06/4534015/ www.rcrz.kz/docs/clinic_protocol/Therapy/Gastroenterology/Chronic%20cholecystitis.pdf https://www.obozrevatel.com/health/bolezni/hronicheskij-holetsistit.htm https:/ /www.dobrobut.com/library/c-chto-takoe-holecistit-lechenie-holecistita Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/18/2020
Complications of cholecystitis.
Complications include: pericholecystitis, pancreatitis, cholangitis, reactive hepatitis, duodenitis.
Pericholecystitis occurs when all the walls of the gallbladder and the serous membrane (peritoneum) are involved in the pathological process. In this condition, the pain syndrome is constant and intense, spreads to the right side, and intensifies when turning and bending the torso.
Cholangitis is an inflammatory process in the bile ducts. The main symptom is an increase in temperature to 40 degrees with stunning repeated chills, nausea, vomiting, cramping pain in the right hypochondrium.
With non-calculous cholecystitis, other organs of the digestive system are often involved in the pathological process: if, along with pain in the right hypochondrium, painful sensations of a “girdling” nature appear, loose stools, the pancreas may be involved in the pathological process. If the pain spreads to the entire area of the liver and is accompanied by its enlargement, the addition of reactive hepatitis, the occurrence of late, hungry pain in the upper abdomen indicates the presence of duodenitis.
Complications not only cause loss of ability to work, but also pose a threat to the patient’s life, therefore, when the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor - a therapist or gastroenterologist.
Consultation with a doctor on cholecystitis
Question: Is it possible to relieve an attack of biliary colic during calculous cholecystitis on your own using folk remedies or medications? Answer: No, you need to urgently consult a surgeon. If not treated promptly, life-threatening complications may develop.
Question: What are the contraindications for blind probing? Answer: Blind probing is contraindicated for cholelithiasis, acute infectious diseases, active hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver, and severe diseases of the cardiovascular system. The procedure is not recommended for women during menstruation or pregnancy.
Vostrenkova Irina Nikolaevna, therapist of the highest category