Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern, safe, non-invasive method for studying organs and tissues. It allows you to obtain maximum information about the area of the body being studied. Medicine today offers MRI studies of any organs, joints, and bone tissue. The procedure is carried out using a magnetic field and radio frequency pulses. MRI data is used both for diagnosis and to monitor the results of treatment.
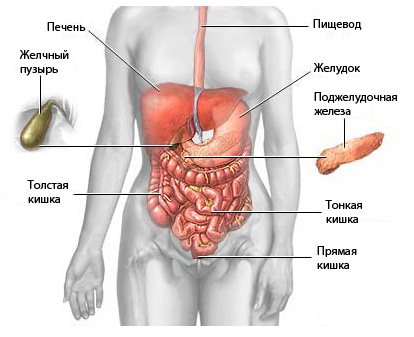
In this article you will learn about the indications, contraindications, and methods of performing magnetic resonance imaging. You will find out what an MRI of the abdominal organs shows. These are the liver, gall bladder, spleen, stomach, intestines, kidneys and bladder, as well as lymph nodes.
Types of abdominal MRI
Modern medicine classifies tomography methods according to the method of obtaining information:
- survey magnetic resonance imaging;
- with and without the introduction of a contrast agent into the organ under study;
- tomography of venous sinuses and lymph nodes;
- magnetic resonance angiography.
Today, the survey method is most often used. It has proven itself excellent both for diagnosing diseases of the joints and organs. The method of introducing a contrast agent into the organ under study is used relatively rarely today.
What does an abdominal MRI show?
Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the most comprehensive and informative studies in medical practice. What organs are checked on an abdominal MRI? This procedure allows you to get an accurate picture of the condition of the following tissues and organs:
- liver and bile ducts;
- pancreas;
- veins and arteries of the abdominal cavity;
- stomach and spleen;
- intestines;
- lymph nodes;
- kidneys, adrenal glands and organs of the urinary system.
The undeniable advantage of magnetic resonance imaging is that it allows one to assess the impact of one pathology on the condition of neighboring organs.
What does an abdominal MRI show? Scanning allows you to detect the presence and progression of the following pathological conditions:
- abnormal size or growth of an organ;
- deviations in the structure of organs and blood vessels of the abdominal cavity;
- inflammatory, cystic, obstructive manifestations in tissues;
- neoplasms of various etiologies;
- aneurysms, thrombosis, ruptures, deformations - degenerative changes in blood vessels;
- pathologies in the nerve trunks;
- stones, sand and flakes in the kidneys, bladder, biliary and urinary tracts;
- metastases.
Now you know what an MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space shows.
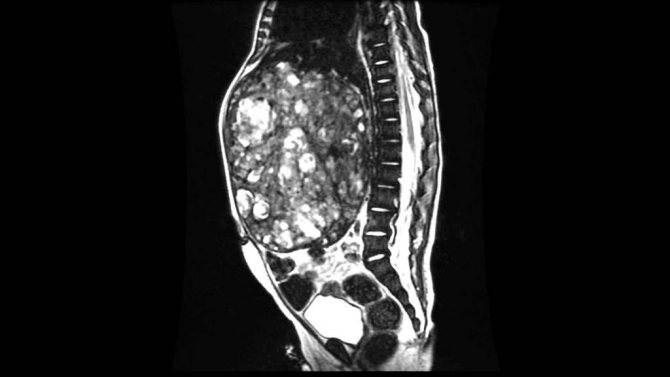
Diseases of the retroperitoneum
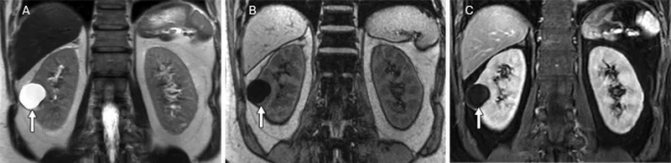
In this anatomical region, magnetic scanning can identify many pathologies. What does MRI of the retroperitoneum show:
- Tumors and cysts. Neoplasms are divided into those originating from organs (kidneys, ureters, duodenum, etc.) and free tissues (fatty tissue, muscles, fascia, nerve and lymph nodes, blood vessels). Tumors can be benign or malignant, single or multiple. For a long time, the neoplastic process is asymptomatic, complaints appear when compression is applied to a nearby organ. A large volumetric formation compresses the vascular and lymphatic collectors, which leads to stagnation of blood in the lower extremities, ascites (accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity), and dilation of the subcutaneous veins of the abdomen. A benign tumor does not cause cancer intoxication, but can be complicated by dysfunction of neighboring organs. MRI of the retroperitoneal space shows the localization of the formation, suggests the origin (including metastatic), and differentiates it from an abscess, hematoma, or aneurysm of the abdominal aorta. Definitive diagnosis is impossible without a biopsy followed by morphological examination. Among organ tumors, the first place is occupied by neoplasms of the kidneys, the second - by the adrenal glands.
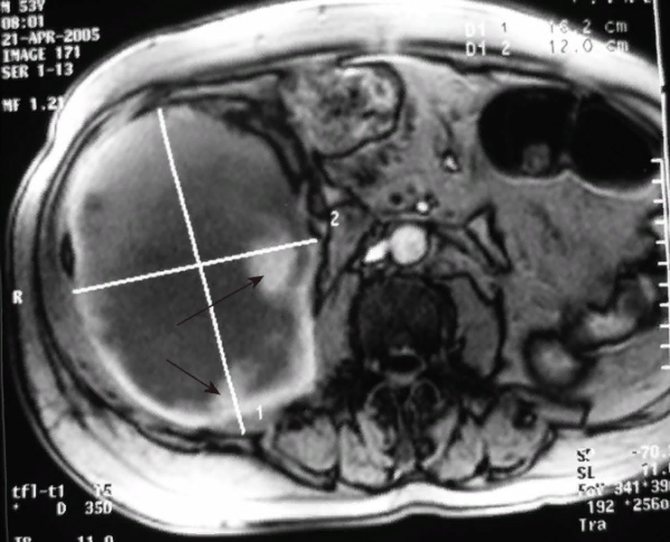
Giant hematoma while taking heparin-like drugs on an MR scan (secondary hemorrhages are indicated by black arrows)
- Injuries. A retroperitoneal hematoma is formed by a direct blow to the lumbar or abdominal area, a traffic accident, or a fall from a height. Often combined with bone fractures and other injuries. In emergency situations with severe clinical manifestations, computed tomography remains the priority test due to the speed of obtaining results. CT scans are better at assessing bleeding and fractures. MRI can show hidden damage to bones, ligaments, etc.
- Vascular changes. If contrast is applied, magnetic resonance imaging shows an aneurysm, stenosis, atherosclerotic lesions, thrombus formation, developmental anomalies, etc.
- Inflammatory processes. For uncomplicated cases, ultrasound is sufficient. Abscesses and phlegmon are considered as a complication of inflammation of organs with retroperitoneal localization. Using magnetic resonance scanning, paracolitis, paranephritis, peritonitis, and the formation of a fistula are diagnosed. The study is informative for differentiating chronic and acute pancreatitis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrotic transformation, kidney carbuncle, etc.
MRI of the retroperitoneal space helps to establish the cause of pathological changes, for example, external compression of the ureters by a tumor and, as a consequence, expansion of the collecting system. When performing contrast, the doctor is able to judge the excretory function of the kidneys. Nephrolithiasis and areas of calcification are best assessed with CT. Chronic inflammation of the retroperitoneal organs can lead to the development of Ormond's disease, characterized by excessive production of scar tissue, as shown by magnetic resonance imaging. Sometimes the fibrotic process is idiopathic (without identifying the cause).
Indications for the magnetic resonance imaging procedure
The study is one of the most expensive in modern medicine. Therefore, for prevention and because the patient is prone to hypochondria, it is not performed free of charge. Most often, MRI is performed when there is doubt about establishing a final diagnosis or when the disease is severe.
MRI is often prescribed to assess the growth dynamics of tumors, cysts, and fibrosis. Ultrasound in most cases does not allow reliably assessing the size of the tumor and its structure. But for magnetic resonance imaging there is no difficulty in this.
Here are some of the most common reasons for doing it:
- obtaining insufficiently reliable results after ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography;
- acute conditions of the liver and kidneys that require the fastest possible diagnosis;
- enlarged liver for unknown reasons (with relatively normal liver parameters);
- ischemic processes in organs or tissues;
- ascites or other causes of fluid accumulation around internal organs;
- disorders of bile outflow of unknown origin;
- pancreatitis during the period of complications or acute form;
- stones in the kidneys and urinary tract, in the gall bladder;
- cysts, neoplasms, hemangiomas, adenomas and other benign neoplasms;
- suspicion of complications after surgery;
- impossibility of using other diagnostic methods.
Possible contraindications
If the following conditions exist, MRI is strictly prohibited:
- an electronic or ferromagnetic device in the patient's body, this could be a pacemaker or defibrillator, a cochlear implant, a bone support structure;
- the patient has tattoos made with dyes containing certain metals;
- the first and beginning of the second trimesters of pregnancy (the final decision on the advisability of the study is made by the attending physician);
- patients with the third stage of obesity (over 140 kg) can damage the equipment, so this study is not suitable for them.
Modern braces for straightening the bite and new generation dental implants are not a contraindication.
Abdominal MRI using contrast is prohibited for the following symptoms:
- individual intolerance to any component of the contrast composition;
- chronic renal failure and the patient being on hemodialysis;
- liver failure (the final decision on the advisability of the study is made by the attending physician);
- period of pregnancy and lactation.
Indirect contraindications for MRI of the abdominal cavity:
- claustrophobia;
- hyperactivity;
- conditions in which the subject cannot maintain complete immobility.
Modern MRI machines are equipped with an open capsule with a glass top - this makes it easier to conduct examinations in patients with phobias of closed spaces. But, alas, not all hospitals are equipped with such modern equipment.
Indications and contraindications
The most important indications for MRI of the abdominal cavity are:
- various natures of trauma to the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space;
- an increase in the size of one or another abdominal organ (primarily the liver and spleen);
- pancreatitis;
- ascites;
- obstructive jaundice;
- focal inflammation in the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space;
- pathologies of the vessels of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space;
- different nature of the neoplasm.
However, like any hardware examination, abdominal tomography has its contraindications and limitations. What factors exclude the possibility of performing an MRI?
Video:
The list of contraindications includes:
- electrical appliances in the body;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- age from 0 to 6 years;
- allergy;
- kidney disease in advanced stages;
- fear of confined spaces, severe pain;
- weight more than 130 kg.
READ Advantages of an open type MRI machine
The presence in the body of electrical devices such as a pacemaker, stents in veins, and cochlear implants makes MRI impossible.
At the same time, patients with neurostimulators, metal plates and prosthetic limbs can be examined, but before the procedure, the doctor must be informed that there is a particular device in the body.
In the first trimester of pregnancy - the period of the most intensive development of fetal organs - women should not undergo any type of magnetic resonance imaging.
The examination can be carried out starting from the second trimester of pregnancy, but only on the recommendation of the attending physician (if possible, during pregnancy it is better to abstain from MRI or give preference to ultrasound) and without the use of a contrast agent.
It is strictly forbidden to examine a preschool child using a contrast agent.
However, magnetic resonance imaging without contrast can be done even in young children.
MRI of the retroperitoneum and abdominal cavity with contrast should not be performed on patients who have already had an allergic reaction to gadolinium.
In this case, the attending physician may recommend an MRI without contrast or alternative research methods: ultrasound, CT.
Photo:
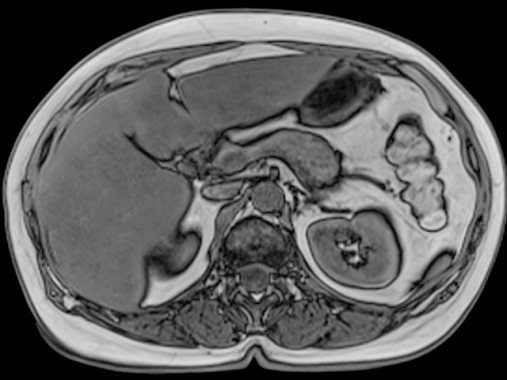
Kidney disease is a contraindication to magnetic resonance imaging with contrast, but MRI of the retroperitoneum and abdominal cavity can be done even in the presence of renal failure.
Since the examination lasts at least half an hour, lying quietly for such a period of time may be impossible for patients with claustrophobia or severe pain.
In this situation, the solution to the problem may be to take sedatives (in the first case) or painkillers (in the second case).
Also, a patient with a fear of closed spaces can independently look for a clinic that has open-type tomographs.
Due to the fact that there are weight restrictions in the operation of tomographs, it is impossible to examine patients whose body weight exceeds 130 kg.
Preparing for tomography
Two days before the study, the patient must take care of the following rules:
- Eliminate foods that cause increased gas formation from your diet.
- If we are talking about MRI of the pancreas or liver, you should adhere to a carbohydrate-free diet, which helps relieve the load on these organs.
- Preparing for an MRI of the abdominal cavity involves completely abstaining from alcoholic beverages.
- In case of flatulence, it is necessary to drink laxatives or carminative medications (the name and dosage will be reported by the doctor).
- If the procedure is carried out with a contrast liquid, you need to make sure that the patient does not have an allergic reaction to the components of the solution.
- Women need to ensure that they are not pregnant before undergoing an abdominal MRI.
- On the day of the procedure, you should not smoke, drink alcoholic or carbonated drinks. In some cases, any food intake is prohibited (this is additionally reported by the attending physician).
Preparing for the study
Diagnosis of the abdominal cavity using MRI requires special preparation of the patient for the procedure. Before carrying out the procedure, the following requirements must be met:
- 3-4 days before the test, start a special diet with the exclusion of foods that cause increased gas formation from the diet;
- take sorbents (for example, activated or white carbon) in the dosage prescribed by your doctor;
- on the day of the procedure, refrain from eating 8 hours before the procedure.
The accumulation of gases in the human intestine, as well as increased intestinal motility, can reduce the quality of the results obtained and reduce the possibility of a quick and correct diagnosis, so these recommendations should not be neglected.
To perform magnetic resonance imaging, the patient should:
- Wear loose clothing (for example, a housecoat or hospital gown provided by the clinic).
- Get rid of metal accessories that distort the picture.
- Take out dentures (if any) and get rid of hearing aids.
Attention! MRI is prohibited for patients with a pacemaker, due to the fact that its operation may be disrupted by the magnetic field created by the tomograph.
How is the procedure itself carried out?
The patient changes into a spacious disposable medical gown. He is told about the procedure. If necessary, blood pressure is measured and a contrast agent is administered intravenously.
Then the patient lies down on a retractable table, and earplugs are inserted into his ears (so as not to disturb sounds in the capsule). Arms and legs are secured with elastic straps. Then the table slides into the capsule and the hole is closed.
The doctor goes into the next room to conduct research using a special computer. The patient should not move during the examination. The duration of an MRI is from twenty minutes to one and a half hours (depending on the area and damage to the organ being examined). An MRI of the abdomen and retroperitoneum usually takes about an hour.
After completion, the patient should not experience any discomfort. The doctor studies the materials received and can draw a conclusion within a couple of hours after the study.
MRI, CT, ultrasound – what to choose?
The answer to the question of which method of visualization of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space - MRI, CT or ultrasound - should be chosen by the patient should be given by his attending physician, based on the purposes of the examination and existing data.
Despite the fact that each of the listed procedures shows internal organs, there is a significant difference between the research methods.
First of all, the method of influencing the patient is different: during an MRI study, the human body is affected by electromagnetic waves, during an ultrasound, respectively, ultrasound waves, and during a CT scan, X-ray radiation.
Video:
That is, the first two methods are practically harmless to the human body, and the third - computed tomography - carries a serious radiation load.
Ultrasound is important for diagnosing diseases of the digestive and urinary system, especially the female genital organs, however, for example, it is almost impossible to monitor the condition of the stomach using an ultrasound machine.
But the most important thing is that ultrasound reveals pathological changes in the organs of the listed systems only at the stage when these changes began to have a negative effect on the tissue.
It is difficult to notice pathologies at the initial stages of their development using ultrasound; in this case, it is preferable to perform an MRI.
Ultrasound diagnostics is used to visualize large organs of the abdominal cavity, primarily the stomach, kidneys, to determine the location of bleeding. Ultrasound is also indispensable in obstetrics and gynecology (for example, neither MRI nor CT can be done for pregnant women in the first trimester).
Photo:
It is possible to determine the cause of the patient’s ailments and establish a diagnosis using CT. CT is a quick procedure for examining the abdominal cavity, which, like MRI, allows you to identify neoplasms and diagnose diseases at the initial stages of their development.
READ Detection of pathologies of the genitourinary system on MRI of the pelvis in men
CT allows you to clarify the presumptive diagnosis made according to ultrasound data.
However, as already noted, computed tomography has a large number of contraindications, since it carries a very large radiation load on the body: CT scanning cannot be done often.
MRI of the liver and biliary tract
Today, the study of these organs is most often carried out with a contrasting composition.
MRI of the liver shows:
- condition and size of the gallbladder and bile ducts;
- causes of jaundice and increased liver parameters;
- size and structure of hemangiomas, neoplasms, cysts;
- visualization of stones and polyps;
- strictures of the bile ducts.
The average cost of examining the liver and biliary tract in paid diagnostic centers is from four to twenty thousand rubles (depending on the complexity of the case, the quality of the equipment and the qualifications of the doctor).
MRI of the pancreas
It will help to identify any diseases of the organ - both acute and chronic. If there are neoplasms, the procedure will show what stage of tumor development is and in which specific lobe of the gland it is located.
The presence of insulinoma in the tail of the pancreas can also be seen using MRI. With chronic pancreatitis, you can track its stage and not miss the onset of pancreatic necrosis.
Which abdominal organs are most cost-effective to examine using MRI of the abdominal cavity? This is precisely a study of the pancreas: in paid diagnostic centers, a study of this organ will cost from two to three thousand rubles.
In what cases is MRI uninformative?

The doctor decides whether it is advisable to perform an MRI
If you need to examine the stomach to identify an ulcer or tumor of the glandular layer, to detect stones in the gallbladder or a tumor of the intestinal wall, an MRI of the abdominal cavity in this case is less informative than an ultrasound or radiography with contrast. There will be no harm from such an examination, but there will be no benefit either.
That is why patients are advised to consult a doctor rather than prescribe tests on their own. Based on clinical symptoms, the doctor will be able to determine indications and contraindications and prescribe the optimal diagnostic method that will allow you to see the changes that have occurred.
Not all diseases of the abdominal organs are convenient to diagnose using MRI; there are cases when the use of ultrasound or contrast radiography is preferable.
MRI of the stomach and esophagus
The most common and popular study among patients. Helps to identify the degree of damage to stomach tissue in case of any erosions, gastritis, ulcers. Reliably displays the size and position of cysts, adenomas and neoplasms. It will tell you about the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, the presence of ulcers and erosions on it, and the presence of bleeding in the gastric walls.
The cost of such a study will cost from three to fifteen thousand rubles, depending on the diagnostic center (prices are taken as the average for Moscow and the region).
MRI of the intestines
Magnetic tomography can detect tumors in any part of the intestine, polyps and ulcers.
Before the examination, the proctologist prescribes laxative medications. The procedure can be performed either with or without the injection of contrast fluid.
Carrying out the study without a solution is completely safe; with contrast, accurate visualization of tumors is possible - but the radiation exposure will be more serious.
Often, in parallel with an MRI of the intestine, a colonoscopy or endoscopy is prescribed. These tests are performed using a colonoscope. A portion of the tissue is collected for further analysis.
Kidneys, adrenal glands and urinary organs
MRI of the urinary tract is performed to clarify the diagnosis and study diseases of unknown origin.
Most often, patients turn to this procedure with the following symptoms:
- the appearance of nagging, excruciating pain in the lumbar region;
- disturbances in the outflow of urine - frequent diuresis or, on the contrary, slow diuresis;
- presence of blood, mucus, flakes, sediment in the urine;
- painful urination;
- suspicion of stones, cysts, neoplasms in kidney tissue;
- pathologies of the urinary system - size, integrity of organs.
MRI of the kidneys and urinary tract will show the inflammatory process, the extent of tissue damage due to mechanical damage and injuries of various origins.
How safe is the procedure?
What complications may arise during an abdominal MRI? Are there long-term negative health effects? These are the questions that concern many patients first. The procedure has no cumulative effect and is virtually harmless to health. But small nuances still exist.
Here is a list of possible consequences of an abdominal MRI:
- With a tendency to mental disorders and increased anxiety - attacks of claustrophobia. A person may begin to have a seizure right in the capsule, and a panic attack occurs. after the study, he may be haunted by attacks of claustrophobia in the elevator, toilet, or shops.
- If there are metal parts in the body, under the influence of the tomograph they will begin to attract, tearing the soft tissue. Such points are discussed in advance with the attending physician, and if there are pacemakers or defibrillators, cochlear implants, or bone support structures, MRI will be canceled.
- The effect of the tomograph on the embryo has not been fully studied. When conducting research in the first trimester of pregnancy, disturbances in the development of the fetus may occur. A serious consultation with your doctor is necessary to confirm the need for the procedure during pregnancy.
- When using a contrast agent, allergic reactions are possible. Before conducting the study, it is necessary to do a test for individual intolerance.
Negative impact of abdominal MRI on the condition of human organs and systems
MRI is one of the safest research techniques. Ionizing radiation is completely excluded, that is, the person is not exposed to radiation. The effect of the magnet does not affect the body and internal processes.
The body may react negatively to the contrast agent, but this does not happen often. It is important to inform your doctor about your health status and allergies. The contrast itself is harmless. It does not affect the functioning of organs, is not absorbed into the bloodstream and tissues, and is quickly eliminated from the body. We are talking about individual intolerance to the drug. In this case, it can be replaced.
To avoid adverse reactions and health problems, you need to highlight a list of conditions for which the procedure is contraindicated:
- pregnancy period (the first trimester is considered the most dangerous; examination is possible if absolutely necessary);
- MRI with contrast during breastfeeding (the substance can get into the milk and harm the baby);
- renal and heart failure;
- mental disorders, since patients are given sedatives before the examination;
- implanted metal prostheses, plates, implants, as well as permanent braces;
- an implanted pacemaker or insulin pump (the electronics will immediately malfunction and break, and the tomograph may also be damaged);
- large dimensions and patient weight more than 150 kg.
To ensure that the MRI does not cause harm, and its results are as informative and accurate as possible, it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions. It is important to properly prepare for the procedure and lie still during the scan (up to 1 hour - depending on the type of study).
To obtain reliable data on the state of the digestive organs, MRI of the abdominal cavity is used. This type of examination makes it possible to see sections in several planes. The pictures are clear. This examination is currently the most accurate and informative.
Tomography of the abdominal cavity is done in a number of cases. If a person experiences discomfort in the abdomen, bloating, or pain. The doctor prescribes a wide range of examinations. This list often includes MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum. The doctor may be interested in the result of a CT scan (computed tomography) - this procedure is identical to an x-ray, but a CT scan of the abdominal organs is done with more radiation and the result is processed somewhat differently. MRI is performed using a magnetic field. The impulses that are sent cause hydrogen atoms to move around in the body. Due to this effect, using equipment, the doctor receives a three-dimensional image on the monitor.