Total information
Multislice computed tomography of the kidneys is not just a modern method of instrumental research - this method of radiation diagnostics in its information content is ahead of other methods of instrumental research (x-ray, ultrasound and others).
note
The main advantages of MSCT of the kidneys are the ability to obtain more information than with other research methods. In addition, this information is more accurate, thanks to which an accurate diagnosis is made and adequate treatment is prescribed.
Advantages of the method
CT is a common diagnostic method for a number of reasons:
- Computed tomography of organs is painless and non-invasive.
- The method allows you to detect changes in organs that are not noticeable during other examinations.
- The tomography results will be processed and given to the patient within two hours.
- Due to the weak radiation exposure, doing a CT scan of the abdominal cavity is not as harmful as a regular x-ray.
- CT makes it possible to study an organ in different planes.
- Tomography clearly differentiates bone and soft tissues, blood vessels and lymph nodes.
- It is possible to conduct an examination if there are implants and other devices in the body.
Benefits of MSCT of the kidneys
This method is an improved version of computed tomography. The main advantages are:
higher level of image quality;- faster scanning;
- thanks to faster scanning – reduction of patient examination time;
- improved contrast resolution;
- reduction of noise compared to the signal;
- wider survey area;
- reducing the radiation exposure to the patient, which means reducing the risk of any consequences.
note
Even more information about the condition of the kidneys is obtained by performing MSCT with contrast. In particular, thanks to the contrast study, changes will be identified that may not have been recorded during non-contrast MSCT.
Often, multislice computed tomography of the kidneys is preceded by other examination methods.
What is better, MSCT, CT or MRI, how do they differ?
MRI is ideal for scanning soft tissues and hollow organs, while multispiral diagnostics is more suitable for diagnosing hard tissues (for example, bone).
CT differs from the multi-slice type of study. The latter is considered more advanced and relatively safe. Multislice CT, compared to conventional CT, makes it possible to obtain volumetric images of organs with a layer thickness of less than 1 mm and significantly expand the area of anatomical examination.
The new technique is better and compares favorably with simple CT in the following respects:
- less harmful radiation;
- better contrast resolution;
- effective use of the X-ray tube;
- scanning is done faster;
- temporal and spatial resolution has been improved.
Contraindications
There are no critical contraindications to performing this research method. Some exceptions are when examining such categories of patients as:
- pregnant women;
- breastfeeding;
- Small children.
The decision whether to perform MSCT of the kidneys in such categories or not using alternative research methods is decided on a case-by-case basis.
There are some limitations to the described method - this means that if factors interfering with the research are eliminated, the procedure can be carried out. The most important limitations are the presence of a contrast agent in the gastrointestinal tract, the patient’s psychological unpreparedness for this examination method, obesity, fear of being in a closed space, a plaster cast or a metal structure in the study area (usually in the area of the lumbar spine or hip joint).
Preparation for MSCT of the kidneys
The rules for preparing for MSCT of the kidneys are the same as the rules for preparing for this examination of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (the kidneys are located in the retroperitoneal space). The basic rule is to stop eating solid foods and carbonated drinks 4-6 hours before the test.
note
Before performing MSCT of the kidneys, the medical worker briefly tells the patient how the study will proceed.
After the examination, the diagnostician evaluates the results and makes a conclusion.
What is multislice CT?
A distinctive feature of this study is short-term exposure of the abdominal organs with low doses of X-rays. This produces clear layer-by-layer sections less than 1 mm thick, which are subsequently transformed into a three-dimensional model of the abdominal organs. The method shows the actual location, structure and condition of the organs being studied.
Moreover, MSCT of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space makes it possible to detect pathologies of small abdominal organs in the early stages of development. Most abdominal organs are hollow, that is, limited by a wall with space inside (for example, the pancreas), so sometimes a contrast agent is used to improve visualization.
How is MSCT of the kidneys done?
Multislice computed tomography is performed using special equipment, which is located in an isolated room. There is no tomograph for exclusively MSCT of the kidneys; it is universal for conducting the same examination of other organs and tissues.
The patient lies down on the horizontal surface of the MSCT machine, and the medical worker who conducts the examination sends the patient inside the machine. Clinics make every effort to make the procedure as comfortable as possible for the patient. Thus, in some clinics, the patient is given headphones with pleasant music, which he can listen to during the entire examination, as well as a “pear”, which allows him to signal to the health worker that the patient, for some reason (for example, due to feeling claustrophobia) wants to stop the examination.
Do you need preparation for an abdominal CT scan?
The abdominal cavity contains quite a lot of organs that ensure the normal functioning of the human body: pancreas, liver, stomach, intestines, spleen. Nearby are the pelvic organs responsible for reproductive function, kidneys, and the urinary system.
All organs are located quite close to each other, and even the slightest change in the location of one causes a displacement of the others. The peristalsis of a constantly functioning intestine affects the condition of all abdominal organs - excessive gas formation and accumulation of feces obscure the image, preventing a sufficiently reliable examination result.
If you know how to prepare for a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis, you don’t have to worry that additional examinations will be required, which require time, money, and discomfort.
A special diet before a CT scan of the abdominal organs helps reduce the production of gases, cleanse the intestines of toxins and increase the information content of the scan.
3 days before the examination, gas-forming foods should be excluded from the diet:
- raw fruits and vegetables;
- fermented dishes and pickles;
- legumes;
- sweets, including chocolate and ice cream;
- yeast baked goods and fresh bread, black bread;
- nuts and dried fruits;
- strong tea and coffee.
You may also be prescribed drugs that reduce gas formation: white carbon, activated carbon, enterosorbents - “Polysorb”, “Enterosgel”, “Polyphepan” and the like. These medications must be taken one day before the procedure; they reduce gas formation and help cleanse the intestines of fecal stones and deposits.
The daily menu these days can be compiled based on:
- Dishes made from lean meat, poultry and fish. Cooking technology: boiling, steaming, stewing or baking them in the oven, covered, so that a crispy crust does not form.
- Boiled or steamed vegetables.
- Low-fat fermented milk products and cottage cheese.
- Bakery products - day-old bread and biscuits.
You will only have to fast for 6-8 hours before the examination. If you sign up for a scan in the morning, your eating schedule will be slightly disrupted.
In case of increased peristalsis, before the procedure it is recommended to take antispasmodics - “No-shpu” or “Papaverine”. Sometimes medications are given intravenously.
Can I drink before a CT scan? It is not recommended to drink coffee, tea, carbonated drinks, or juices 6-7 hours before the examination; you will have to stop drinking pure water 2-3 hours before the scan.
Why is Urografin taken orally before an abdominal CT scan?
The contrast agent used during CT helps to obtain clearer images and examine individual anatomical structures in detail for a more accurate description. If you need to study the structure of blood vessels, see neoplasms, evaluate their structure and identify metastases, you cannot do without the use of Urografin or Omnipaque. Currently, most clinics use Urografin; it is less allergenic and cheaper. Both contrasts are based on iodine compounds.
The method of administering the contrast agent depends on the type of examination.
- When scanning the lower - distal - parts of the intestine, contrast is administered immediately before the procedure using an enema. Before rectal administration, the patient must do a cleansing enema at home.
- If a pelvic examination is required, then Urografin is administered orally. Recommendations for use may vary, but usually the day before the examination, you need to purchase 2 ampoules of contrast, dilute one in 1 liter of boiled water and drink, dividing into 2 servings. The second ampoule is diluted in the same way and drunk 1-2 hours before the procedure.
- Separate preparation is required for MSCT with contrast to visualize the vessels of the abdominal cavity. Most often, in this case, the patient is given an intravenous catheter, through which contrast will be injected using a special injector.
When administered intravenously with an injector, the abdominal cavity is first scanned without contrast, and then with contrast. When decoding images, the results are compared. In some cases, the contrast agent is administered in full before the procedure.
What is being assessed
Multislice computed tomography of the kidneys is a highly accurate modern diagnostic method. But its capabilities should be assessed realistically - the MSCT device does not give ready-made conclusions, but only provides information about the state of organs and tissues that needs to be interpreted. In this case, this is information about the condition of the kidneys, as well as organs and tissues that are located nearby, which means they can affect the condition of the kidney, and therefore also require study.
When performing multislice computed tomography, the following parameters and characteristics are assessed:
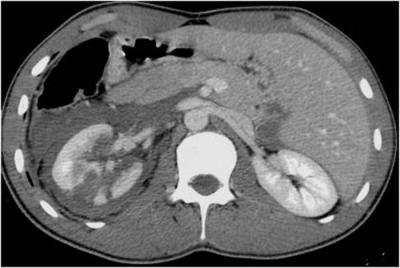
location of the kidneys;- their sizes;
- morphological structure of the kidneys;
- the presence of diffuse changes in the parenchyma (working tissue) of the kidneys;
- the presence of pathological formations and structures in them - in particular, stones, parasites, neoplasms;
- condition of the calyces and pelvis;
- condition of the initial sections of the ureters;
- size, shape, contours, general condition of the lymph nodes;
- the condition of the fatty tissue of the kidney bed - the place in which it is located;
- the condition of neighboring structures - namely the spine of the lumbar spinal column.
Even if the patient complained of any abnormalities in one kidney, a multispiral computed tomography of both kidneys is performed. This will make it possible to compare their characteristics (in particular, to determine the individual characteristics of each individual patient, which can be regarded not as a pathology, but as a variant of the norm).
Indications and contraindications
MSCT is an additional diagnostic method; it is used in cases where the main research methods do not provide a clear medical history of the patient.
Indications for use:
- Diseases of internal organs of an oncological nature, which have many different neoplasms. Multislice tomography helps to identify the most minor formations of internal organs.
- Inflammatory processes . These may be diseases such as pancreatitis, hepatitis, chronic bronchitis, asthma, and heart defects. The method allows you to assess the degree of organ damage, which helps the specialist prescribe correct and effective treatment.
- For chronic injuries of the muscular, bone and joint apparatus. The method is necessary to analyze changes in muscle structure and damaged areas.
- Chronic diseases that are characterized by circulatory failure. During the study, the condition of blood vessels and tissues is diagnosed with a contrast agent.
Diagnostic value
MSCT of the kidneys can detect diseases such as:
- urolithiasis – in this case, the presence of stones in the lumen of the calyces or pelvis;
- Kidney amyloidosis is the deposition in their parenchyma of the protein-polysaccharide complex of amyloid, which is not normally found in the tissues of the human body;
- neoplasms - benign and malignant, and in the latter case - primary and secondary, or metastatic (that is, those formed from tumor cells carried through the blood and/or lymph from malignant neoplasms of other organs and tissues);
- neoplasms of the initial parts of the ureters;
- fatty degeneration of the kidneys – their fatty degeneration;
- hypotrophy and atrophy of the kidneys - malnutrition;
- their hyperplasia - proliferation of renal tissue and increase in organ volume;
- kidney abscess - a limited abscess;
- A kidney cyst is a cavity formation with fluid inside. This could also be a parasitic cyst;
- polycystic kidney disease - the formation of a large number of cysts in them
- consequences of traumatic injury to the kidneys and ureters;
- nephritis - inflammatory damage to the kidney parenchyma;
- glomerulonephritis – inflammation of the kidney glomeruli;
- pyelonephritis – infectious and inflammatory damage to kidney tissue;
- congenital pathologies (anomalies) of the kidneys;
- disorders of the arteries and veins that take part in the blood supply - aneurysm (protrusion of the vascular wall), stenosis (narrowing of the vessel), thrombosis (blockage of the vessel with a blood clot), compression.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
just today
( 57 votes, average: 4.28 out of 5)
Blood test for total calcium: norms and interpretation
Testicular biopsy in men: indications, technique, explanation