Cause
.
90% of cases of severe
hyperthyroidism are caused by the presence of activating anti-antibodies to TSH receptors.
In this case, the disease is called von Basedow's disease
(in Russian and European literature),
Graves'
(in American literature).
Clinical picture
. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism are difficulty falling asleep, emotional lability and nervousness (tearfulness), heat intolerance, hair loss, dry nails, weight stability due to increased appetite, tachycardia, muscle weakness, sweating, wet palms.
With a more pronounced form, low-grade fever (up to 37.5°C) is noted, especially in the evening, nervous agitation, exophthalmos, tremor, diarrhea, weight loss, infertility and scanty menstruation in women.
Table of Contents
Liver hepatosis - what is it?
Hepatosis is a group of non-inflammatory liver diseases. A characteristic common feature is a violation of hepatocyte trophism. Damage to the structure of cells and intercellular space (against the background of metabolic disorders), as well as disruption of material metabolism in liver cells, are the main “companions” of hepatosis. There are acute and chronic forms.
Healthy human liver
Symptoms include:
- liver failure;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence);
- jaundice.
The most common type is fatty lesion (excessive accumulation of lipids in the liver).
Causes of the disease
The acute form of hepatosis is usually caused by various intoxications. Provoking factors may include:
- intoxication with toxic chemicals (arsenic);
- poisoning with large amounts of ethyl alcohol;
- intoxication with poisonous mushrooms;
- taking hepatotoxic drugs (tetracyclines, cytotoxic drugs, some hormonal drugs);
- viral hepatitis can cause acute gapatosis.
The chronic form of the disease is a common consequence of alcoholism.
The development of the non-alcoholic form can be triggered by a number of reasons, including:
- protein deficiency;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- poisoning by poisons (organic phosphorus compounds);
- hypercortisolism syndrome - an excessive amount of adrenal hormones in the body;
- diabetes;
- lesions of the thyroid gland;
- pregnancy (with severe cholestasis);
- overweight;
- unbalanced diets (excessive consumption of fatty foods, prolonged fasting, etc.);
- surgical manipulations at the gastrointestinal tract level (gastric resection, cholecystectomy);
- liver injury (can lead to cystic formations in the organ);
- parasites – can cause stagnation of bile, formation of cysts, inflammation of the gland (echinococci, roundworms).
The hereditary type is caused by genetic disorders. The reasons in this case may be:
- Gilbert's syndrome - increased levels of free bilirubin, which has a toxic effect on hepatocytes;
- enzymopathic jaundice - a defect in which the normal release of conjugated bilirubin from liver cells does not occur;
- Rotor syndrome is a disturbance in the excretion of bilirubin, direct hyperbilirubinemia is observed, but the activity of liver enzymes remains normal.
Classification of adrenal hyperfunction
The cortex of these paired glands consists of the medulla, retina, zona glomerulosa and zona fasciculata. Each cortical part of the adrenal glands produces hormones. The following disorders can lead to disruption of their functioning:
excess mineralocorticoids, which control the number of electrolytes in the blood; adrenal hyperandrogenism; excess catecholamines, which are formed from a malignant tumor or during stress; excess glucocorticoids, responsible for maintaining normal blood pressure, immunity and metabolism.

Types of liver hepatosis
Depending on the moment of occurrence, 2 types of hepatosis can be distinguished:
- Acquired.
- Hereditary.
This is interesting: Menu for a week for liver steatosis: the right diet
Acquired types that arise throughout life can be divided into:
- toxic - the result of toxic effects on the liver of toxic substances;
- fatty hepatosis (steatosis) – excessive deposition of fat in the liver, accompanied by lipid degeneration of hepatocytes.
The cause of hereditary hepatic lesions is genetic disorders:
- Gilbert's syndrome;
- Rotor disease;
- Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
There are also types of fatty hepatosis depending on the area of organ damage:
- Disseminated focal - small volumes of lipids are concentrated in various areas of the liver. It is asymptomatic.
- Pronounced disseminated type - voluminous accumulations of fat in different parts of the gland. Symptoms appear.
- Zonal - lipid damage to various parts of the gland lobules.
- Diffuse type - lipids accumulate evenly over the entire area of the liver lobule.
Depending on the microscopic picture of steatohepatosis, the following are distinguished:
- Small-droplet type – there is no damage to the structure of hepatocytes.
- Large-droplet type - the structure of the liver cells is disrupted, necrosis is observed.
Stages of hepatosis
There are 3 stages of fatty liver hepatosis:
| Stage | Characteristic |
| Stage 1 | Accumulation of a small amount of lipids in an organ. The structure of the organ cells is not disturbed. |
| Stage 2 | Fatty infiltration of moderate severity. The structure of hepatocytes is disrupted, necrotic changes occur. Cystic formations appear. |
| Stage 3 | Large areas of fatty lesions. A condition of the gland bordering on cirrhosis. |
Staging is necessary to characterize the degree and prevalence of liver damage in the disease.
Symptoms of liver hepatosis
Signs of hepatosis may often not appear for a sufficiently long period of time. At this time, the patient's condition may worsen. The disorder is often detected by chance, during preventive checks or when diagnosing other pathologies. It is important that stage 1 is asymptomatic.
Symptoms of liver hepatosis at stages 2 and 3 include:
- heaviness in the area of the right hypochondrium, a feeling of compression in the abdominal cavity, pain when pressing in the projection of the liver;
- chronic fatigue;
- feeling of nausea (excessive salivation, sensitivity to the smell of food);
- flatulence and dyspepsia;
- partial or complete lack of appetite;
- yellowish color of the mucous membranes and skin is a consequence of hyperbilirubinemia;
- skin itching;
- skin manifestations - small spots of hemorrhages;
- xanthomas are neoplasms on the skin containing fatty inclusions (a consequence of lipid metabolism disorders).
Hepatosis includes symptoms associated with organic changes in the liver: an increase in the size of the organ (during palpation) and pronounced echogenicity (during ultrasound diagnosis). It must be said that the symptoms and treatment of the disorder are interconnected: the more pronounced the symptoms, the more severe the stage and the more difficult the treatment.
This is interesting: Dosage regimen and course of treatment with ursosan for fatty liver hepatosis
Clinical features
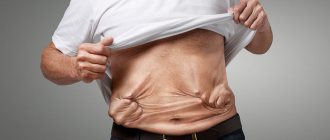
Patients with a long course of the described disease have a rather characteristic appearance. Due to the selective effect of cortisol on fat metabolism, coupled with the sensitizing effect of adrenaline, a special type of obesity occurs, called Cushingoid. The limbs become thin, the layer of fatty tissue quickly thins out. The face takes on a Cushingoid appearance - it looks like a moon, a saucer. In women, cervical lordosis becomes pronounced.
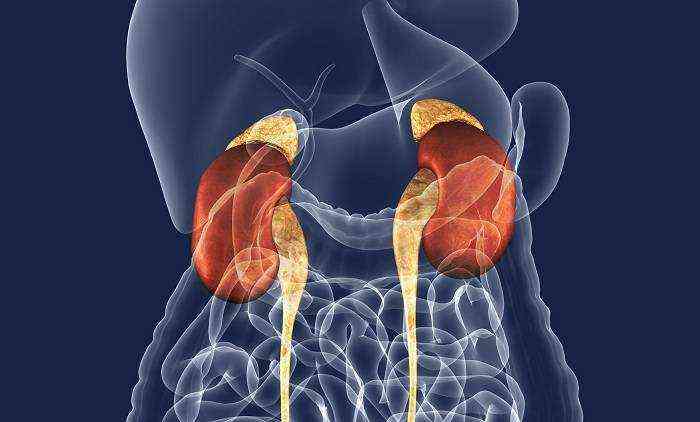
As adrenal function increases, changes also affect the skin and muscular system. Patients complain of weakness in the limbs. Moreover, this applies specifically to the proximal parts of the arm or leg. The skin takes on a grey, sallow or brown hue. The thing is that there is a compensatory increase in the precursor of melanin - proopiomelanocortin.
Against this background, the skin has maculopapular rashes, sometimes with purulent contents. For this reason, the described dermatological picture resembles acne. In 80% of cases, purple stripes appear - these are the so-called stretch marks. They appear less frequently in women than in men.
Damage to the cardiovascular system is nonspecific. If hypercortisolemia occurs, various rhythm and conduction disturbances are recorded. Hyperfunction of the adrenal medulla is most often caused by pheochromocytoma, a tumor of chromaffin cells responsible for the synthesis of adrenaline. This condition manifests itself as a tendency to high blood pressure. The systolic level can reach 300 mm. rt. Art. Diastolic blood pressure also increases, but at a slower rate.
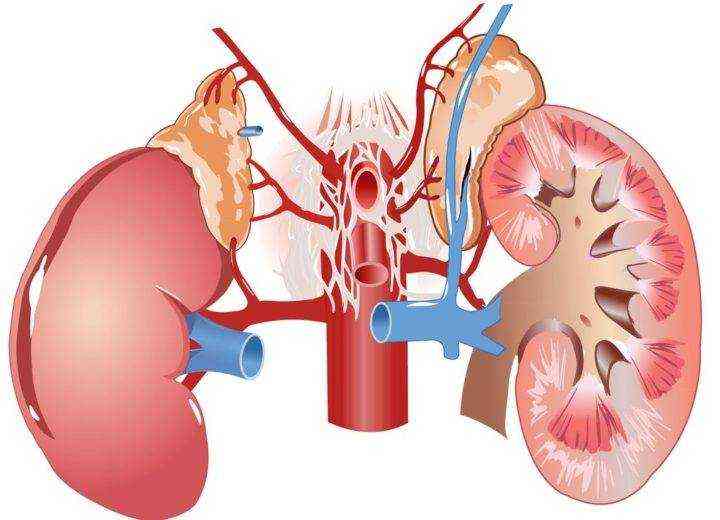
Arterial hypertension, refractory to antihypertensive drugs, develops. It has a crisis course, and crises are provoked even by palpation of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space. Women have a more vivid picture of crises than men. Increases in blood pressure are accompanied by pronounced vegetative and emotional manifestations.
The tendency to bradycardia is typical of hyperaldosteronism - a situation when the level of aldosterone in the blood serum increases in isolation. This entails increased excretion of potassium, which is manifested by various disorders of electrolyte metabolism.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of liver hepatosis can be made by a hepatologist and a gastroenterologist. A person with impaired liver function should constantly consult these specialists.
Determining the form, stage and type of hepatic disorder involves a number of diagnostic methods:
- anamnesis (questioning) of the patient - information about the patient’s complaints, symptoms, diet, and concomitant diseases is clarified;
- examination of the patient - includes examination of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as palpation of the affected area;
- laboratory tests - general and biochemical blood tests, liver tests;
- instrumental diagnostics - ultrasound, MRI, computed tomography, liver biopsy and elastographic diagnostics.
For accurate diagnosis and correct diagnosis, it is necessary to use several diagnostic methods.
How does adrenal hyperfunction manifest in the weaker sex?
Symptoms in women with excess hormone production are as follows:
acne; skin pigmentation; depression.
If a pregnant woman has been diagnosed with hyperandrogenism, in other words, increased production of male hormones, then she should be constantly monitored by a gynecologist to avoid miscarriage. Most often, for the treatment of such a disease, artificial cortisol analogues are prescribed, which suppress the production of androgens. To normalize the activity of this paired organ, vitamins B and C, as well as microelements, can be prescribed.
In addition, if the activity of the paired glands is disrupted, women may have problems conceiving and bearing a child. Hyperfunction of the adrenal glands in women is often manifested by clitoral enlargement, chest pain, menstrual irregularities, and even a decrease in the size of the uterus.

A woman taking contraceptives will need to stop taking them in order to normalize the functioning of the paired glands. In general, if a woman is diagnosed with adrenal hyperfunction, she will have to change her lifestyle, avoid stressful situations and, of course, get proper rest. With such a disorder, it is imperative to eat properly. In addition, it is necessary to find out what other stress the adrenal glands may experience with this disease. Symptoms of the disease, diagnosis and timely treatment of hyperfunction of paired glands allows you to quickly restore health.
Treatment of liver hepatosis
Liver hepatosis: treatment of the toxic type involves hospitalization. In case of toxic damage, it is necessary to urgently eliminate the cause of intoxication and prevent the toxin from entering the body. Treatment areas include: antihemorrhagic therapy, treatment of general intoxication and hypokalemia.
You might be interested in:
Treatment of fatty hepatosis with folk remedies.
Liver hepatosis, its symptoms and treatment require compliance with the doctor’s instructions:
- Avoid drinking alcohol.
- Following a diet (high in protein and low in fat).
- Observation at the dispensary.
- Treatment of concomitant gastrointestinal diseases.
Liver hepatosis must also be treated with pharmacotherapy.
Drug treatment is aimed at protecting hepatocytes, reducing lipidemia, antioxidant protection of cells, and combating hypoxia.
How to treat hepatic disorders and associated dysfunctions? Drugs for the treatment of hepatosis include:
- Hepatoprotectors – protect and restore the structure of hepatocytes.
- Essential phospholipids - are part of the membranes of hepatocytes and counteract the replacement of the liver parenchyma with connective tissue (Essentiale, Phosphogliv, Rezalut).
- Herbal medicines are complexes of medicinal plants with various effects: antioxidant, choleretic, hepatoprotective (Allohol, Silymarin, LIV-52).
- Ursodeoxycholic acid is a natural component of bile. The active substance improves bile levels, prevents the formation of gallstones, has a hypolipidemic and immunostimulating effect. Preparations: Ursosan, Ursofalk and others.
- Amino acid derivatives – Heptral, Hepa-merz, Lecithin.
- Hypoglycemic drugs. The therapeutic effects of these drugs include: normalizing body weight, reducing the level of “bad” cholesterol, improving the metabolism of insulin and glucose (Metformin).
- Lipid-lowering drugs - lower the level of cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins (prevent the deposition of cholesterol on the intima of blood vessels). Drugs in this group include: statins (Atorvastatin, Simvastatin) and fibrates (Clofibrate, Fenofibrate).
- Antioxidants. How to get rid of the damaging effects of oxidizing agents on hepatocytes? It is necessary to take antioxidant drugs: Mexidol, vitamins A, E and C. These substances help improve microcirculation, reduce cholesterol levels and strengthen vascular walls (preventing hemorrhagic hepatic manifestations).
- Drugs against hypoxia - Carnitine, Trimetazidine, Actovegin. Improves redox processes in cells and glucose metabolism.
This is interesting: What is steatosis of the liver and pancreas?
To achieve the desired therapeutic effect, it is necessary to combine different drugs.
Recommended:
To find out whether fatty liver disease can be completely cured, read the article: Is it possible to cure fatty liver hepatosis completely?
Classification of pathology of hormone production
Hypofunction of the adrenal glands
Pathology in the release of hormones can provoke a decrease or increase in their quantity. Hypo and hyperfunction of the glands equally have a negative effect on the body, so the patient needs emergency medical care. Hypofunction of the glands occurs in 2 forms: primary and secondary. The primary stage of the disease is characterized by a decrease in the amount of hormones due to irreversible damage to the adrenal cortex. At the next stage of the disease, the hypothalamic-pituitary system is affected, that is, the pathological process spreads from the adrenal glands to the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. As a result, the pathology reduces the endocrine function of the glands and affects the nervous system. Atypical skin pigmentation will indicate the presence of adrenal insufficiency. The spots cover the neck, arms and face. The longer the disease remains untreated, the darker the pigmentation on the skin.
Return to contents
Adrenal hyperfunction
Damage to the adrenal cortex provokes the appearance of dark pigment spots on the skin.
The adrenal cortex consists of the medulla, retina, glomerular and fascicular regions. Each of the components is responsible for the production of a specific hormone. There are several types of glandular hyperfunction. The specific type of disease depends on which cortical hormones are secreted in excess:
Excess of corticosteroid hormones, which are responsible for the number of electrolytes in the blood. Adrenal hyperandrogenism - increased secretion of sex steroids. Increased secretion of glucocorticoids, the functions of which include normalizing blood pressure, supporting the immune system and metabolism (Cushing's syndrome). Excess of catecholamines, the cause which is considered to be pheochromocytoma or prolonged exposure to a stressful environment. Return to contents
Diet for hepatosis
Treatment and prevention of the disease requires diet. Controlling the level of incoming protein, fats and carbohydrates helps to avoid obesity and increased cholesterol levels. It is recommended to stick to table No. 5.
Basic principles of diet for hepatic hepatosis:
- minimal consumption of fatty foods and fried foods;
- mandatory presence in the diet of vegetables that promote the removal of bile (zucchini, carrots, pumpkin);
- increasing the amount of protein consumed. The best sources are lean meat and fish, steamed, boiled or stewed;
- consumption of clean water (at least 2 liters per day);
- consume low-fat dairy products: kefir, fermented baked milk, yoghurts;
- reduce glucose consumption (especially with diabetes);
- completely exclude from the diet: alcohol, mayonnaise, sweets, sparkling water, baked goods, white bread and sausages.
Read more about the diet for fatty hepatosis here.
Prevention
If you want to avoid the occurrence of this disease, it is very important to follow preventive measures. What will be relevant in this case?
- Proper nutrition.
- Maintaining normal weight.
- You need to lead an active lifestyle. Walking in the fresh air is very important, as well as moderate physical activity on the body.
- You need to drink at least two liters of water per day.
- You also need to give up bad habits. Especially from drinking alcohol.
- It is important to monitor your blood sugar levels.
Fatty liver disease is a reversible liver disease. This pathology can be successfully treated in the early stages. There is no specific treatment. It all comes down to changing your lifestyle, reviewing your diet, and eliminating etiological (causal) factors.