Liver biopsy
The main goal of a biopsy is to identify the causes of liver disease, the stage of development of the pathology, and the level of damage to the organ. Let's consider what is a liver biopsy?
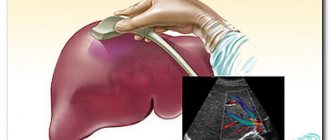
Removing a small piece of liver tissue for necessary research is called a biopsy. This is an important analysis to confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis.
Liver puncture is a puncture of an organ to remove a small piece of tissue for further analysis. A small wound remains at the puncture site; the organ itself is not opened.
When is a liver biopsy necessary?
Main indications for liver biopsy:
- Splenomegaly and inflammation of the spleen are the first to indicate liver dysfunction.
- Liver function test results are difficult to interpret.
- Determination of the form of alcoholic cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis without obvious symptoms. In this case, a biopsy is prescribed to assess the dynamics.
- The need to confirm intrahepatic cholestasis (bile stagnation).
- Suspicion of cancer. The biopsy result may be positive even if the scan results are negative.
- Granulomatous infiltration. Most often, the disease is asymptomatic.
What a liver biopsy is, the hepatologist has to explain to patients whose blood test results raise suspicions of pathological changes in the parenchyma of the organ.
Carrying out the procedure
Liver biopsy is performed in several ways: histological (tissue), cytological (cellular) and bacteriological.
How is a liver biopsy done? The answer depends on how the procedure is performed. There are only three of them, let's look at them.
Percutaneous biopsy
The patient does not experience any particular inconvenience from the procedure, since it is done within just a few seconds and under local anesthesia. The result of the procedure is high – 98%. This is done in two ways:
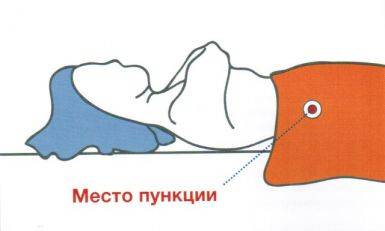
- Using ultrasound analysis, the site for the biopsy is selected - a “blind” method.
- The puncture is performed under ultrasound control.
Liver biopsy
For a reliable analysis, a piece of liver 1-3 cm long and 1.2-2 mm in diameter is required.
We recommend reading:
TSH norm
You should always take into account the fact that only a small part of the diseased organ is taken for analysis, so the analysis result may not always be reliable.
This type of biopsy is prescribed for the following indications:
- jaundice of unknown origin;
- diagnosis of liver cirrhosis;
- to monitor the treatment of viral hepatitis;
- diagnosis of tumor conditions in the body;
- diagnosis of hepatitis of all types.
The procedure cannot be performed if tests show low blood clotting, it is impossible to determine the puncture site, with vascular tumors, with allergic reactions to medications, with obesity.
The biopsy needle is most often taken from Menghini or Trucut. A stylet is used for puncture, which penetrates to a depth of 2-4 mm. After this, a needle is inserted into the liver parenchyma through a stylet, which is connected to a syringe filled with isotonic sodium chloride solution. The plunger of the syringe bites off a piece of organ tissue, which is transferred for examination.
Ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy
Ultrasound-guided liver biopsy
The puncture site is numbed under local anesthesia. The procedure is performed for focal liver lesions, as well as for suspected cancer. It is practically safe for cancer patients and is possible for echinococcal and vascular lesions.
In an ultrasound-guided liver biopsy, the doctor makes a small incision in the neck and then inserts a plastic tube into the jugular vein. Once the hepatic vein is reached, a special substance is injected into the tube to take pictures. A sample of liver tissue is taken through this tube and carefully removed. A bandage is applied to the neck.
Laparoscopic biopsy
The procedure is performed on the operating table using general anesthesia. Through a small incision in the abdomen, special equipment and a small video camera are inserted into the patient. With its help, the doctor can view the weight of the organ on the monitor screen and select the necessary parts for analysis. After the procedure is completed, all instruments are removed and the incisions are sutured.
Preparing for the study
Usually the biopsy is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. Three days before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude high-fiber raw vegetables and fruits from the menu, as they cause gas formation. It is forbidden to eat food that is difficult to digest (nuts, rye bread, margarine, mayonnaise and other products). The day before the procedure, you should not have a heavy dinner. Buckwheat porridge, a slice of stale wheat bread, a cutlet made from dietary meat (steamed) will do.
Seven days before the procedure, the patient must stop taking the following medications:
- sedatives (calming);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- enzyme digestive;
- anticoagulant (reduce blood clotting).

On the eve of the biopsy, physical and psycho-emotional stress should be avoided. Also, the day before the diagnostic procedure, you should not take a hot bath, sunbathe in the sun, or overheat. Before going to bed at night, an enema is given to cleanse the intestines.
Before taking a sample, the puncture site is disinfected with chlorhexidine solution or other antiseptic. An anesthetic injection is given in the area of the right hypochondrium. Before the procedure, the person must be asked about the presence of allergic reactions to medications.
How to do a liver biopsy
Typically, a liver puncture is performed under ultrasound guidance, when the doctor checks his actions with the readings on the monitor. Before the procedure, the person must sign an informed consent form. After this, blood donation is scheduled for a detailed clinical analysis. Then they are sent for an ultrasound examination to assess the current state of the organ parenchyma. Before the puncture begins, pulse and blood pressure are measured.
Percutaneous puncture
This type of biopsy is indicated under the following conditions:
- obstruction of the common bile duct;
- inflammation of the spleen and liver of unknown origin;
- preparation for liver transplantation or rehabilitation after it;
- tumor, destruction of hepatocytes.
A percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver is performed with a special needle in a few seconds. The syringe is filled with saline solution, which, when the needle is inserted, penetrates into the tissue and thereby prevents foreign biological fluid from entering it. Principle:
- The patient lies on his back with his right arm under his head.
- The puncture area is treated with an antiseptic solution. An anesthetic is administered.
- In the area between the 9th and 10th ribs, a small puncture is made with a puncture needle (depth up to 40 mm). The patient inhales deeply and holds the exhalation while the surgeon performs the manipulation to collect the biomaterial.
- The surgical site is disinfected and bandaged.
Fine needle aspiration
This type of biopsy is prescribed for people with vascular diseases and parasitic infestations. The procedure is also indicated in the presence of tumor nodes and other formations in the parenchyma of the organ, to clarify their origin. The operation is performed using ultrasound or SCT:
- The person lies on his back or left side.
- The puncture site is disinfected and anesthetized.
- Under the control of spiral computed tomography or ultrasound, the puncture point is outlined, and a thin needle is penetrated into the organ.
- As soon as the needle reaches the area where the biopsy is taken, an aspirator with saline solution is attached to it. Through translational movements, pathological tissue is collected.
- After removing the needle, the surgical site is treated with an antiseptic and bandaged.
Biopsy material is taken from cancer patients at an advanced stage of the tumor process. An aspirate biopsy excludes the spread of cancer cells to other organs.
Trephine biopsy
The operation is indicated for dense neoplasms in the liver parenchyma (cysts). With its help, it is possible to determine the type of tumor and determine the presence of metastases. A biopsy involves the extraction of biomaterial with a thick threaded needle, thereby increasing the information content of the method. Using a special gun, the needle is screwed into the gland and then sharply removed. The biomaterial remains on the cutting edge. The procedure is painful, so it is performed under anesthesia.
Transvenous
Transjugular liver biopsy is prescribed for patients with bleeding disorders, as well as for those undergoing a blood purification course. Transvenous puncture is performed using a catheter. It is injected through the inguinal or jugular vein into the right hepatic artery. A pathological sample is then collected. The manipulation is carried out under ultrasound control. Lasts about an hour.
Laparoscopic and incisional techniques
Such procedures for collecting biomaterial are carried out only during planned surgical intervention (removal of tumors, necrotic areas).
With the laparoscopic method, the sample is taken with biopsy forceps, which are inserted through laparoscopic incisions. All manipulations are visible on the monitor screen.
The incisional method involves taking a fragment of a pathological area of the liver for analysis using a scalpel or surgical coagulator.
How does the procedure work?
How is a puncture percutaneous biopsy performed in modern clinics? We will describe the procedure step by step, from preparation for liver biopsy to recovery after taking the material.
Preparation
Already a week before the procedure, you should begin preparing. How to prepare for a biopsy? Firstly, you should avoid taking blood thinning medications (such as aspirin, etc.) for 7 days before the intervention. This is to avoid bleeding during and after the tissue sample is taken.
The procedure should be carried out on an empty stomach. Usually it is done in the morning; You should not have breakfast on this day. Dinner the day before should be light; you should avoid brown bread, dairy products, raw vegetables and fruits (these foods stimulate gas formation, which can lead to bloating). The attending physician may advise you to perform a cleansing enema in the evening or in the morning before the intervention.
If you are taking medications, be sure to check with your doctor to see if you can take them on the day of your biopsy.
Material collection procedure
On the day of the operation, the patient undergoes a follow-up examination, including blood pressure measurement, a blood clotting test, a complete clinical blood test and an ultrasound of the liver. If there are no violations, proceed to the procedure.
First, the patient is asked to change into sterile surgical clothing and lie on his back on the examination table. Doctors often offer the patient a sedative so that he does not experience severe nervous tension during the intervention.
The skin on the patient's abdomen is disinfected, and the area in the projection of the liver is numbed with local anesthetics. The patient may experience some pain during the injection, but will feel quite fine after the biopsy. In other words, the pain of this procedure can be called moderate.
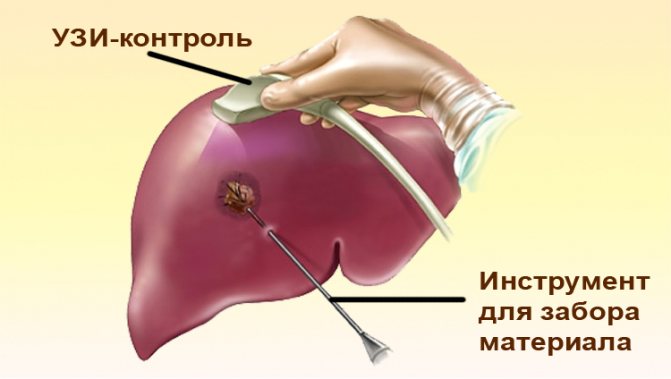
It takes a few minutes for the anesthesia to take effect. At this time, the patient is told how to breathe correctly during the collection of biomaterial. After this, the doctor inserts a special needle into the patient's right side, removing a small amount of liver tissue. The material is usually collected under ultrasound guidance. Ultrasound-guided liver biopsy allows you to accurately select the point for needle insertion. Thanks to this, the cut is more informative and eliminates the possibility of puncturing large blood vessels, the colon, etc.
A percutaneous needle biopsy takes only a few seconds and is performed under local anesthesia.
After taking the material
After the liver biomaterial is taken, it is sent to the laboratory for testing. The patient remains in a supine position for another 4 hours, during which it is forbidden to get out of bed, go to the toilet, eat, etc. All this time the patient is under medical supervision, since complications of the biopsy usually appear in the first 2-3 hours after the procedure.
Gradually, the effect of anesthesia wears off, so the patient may experience pain in the right side, shoulders, etc. If the pain is severe, the doctor will give an additional injection of pain medication.
Post-procedure care
After a puncture biopsy, the patient is positioned so that his body is slightly turned to the right side. He should remain in this position for about two hours. During this period, the doctor periodically examines the puncture area. Medical staff measures blood pressure and monitors the patient’s general well-being.

It is considered that the liver puncture was successful if during the first 5-6 hours after the diagnostic procedure the patient does not develop a high fever, severe pain or bleeding.
In the first week after a liver biopsy (puncture), it is important to follow diet No. 5, avoid physical activity and not take a hot shower or bath.
Modern alternative diagnostic methods
Elastography is a type of ultrasound diagnostics, a modern alternative to biopsy. Its use makes it possible to assess the severity of fibrosis in chronic liver pathologies. Using a special ultrasound probe, the specialist palpates the organ. The results of the condition of the liver tissue displayed on the monitor are compared with the reference value.
Today, it is also practiced to diagnose liver tissue disorders by analyzing blood for the concentration of specific substances:
- Fibrotest - determines the stage of fibrosis.
- Actitest - determines the degree of inflammation and the amount of necrosis.
- Steatotest—detects the level of fatty degeneration of liver cells.
- Ashtest is effective when it is necessary to determine the stage of alcoholic steatohepatitis (inflammation against the background of fatty cell degeneration).
Evaluation of histology results
Different methods are used to interpret the results of liver biopsy:
- Metavir scale - shows the amount of inflammation of organ tissue and the degree of fibrosis. It is used to study a fragment of a liver affected by hepatitis C.
- The Knodel method helps to assess the amount of hepatocyte death, the degree of inflammation and degenerative changes in organ tissue. Allows you to determine the stage of chronic hepatitis.
- Ishak index - used to diagnose cirrhosis and determine the intensity of fibrosis.
Possible complications
After a liver biopsy (puncture), internal bleeding may develop. To prevent such a consequence, the operation is performed in the surgery department. Against the background of a puncture biopsy, the risk increases:
- perforation of the gallbladder or extrahepatic bile ducts;
- purulent complications (phlegmon, abscess);
- intrahepatic hematomas;
- inflammation of the fibrous liver capsule;
- hemobilia (bleeding from the bile ducts into the intestines);
- streptococcal infection, less often - sepsis.

On average, mortality after puncture biopsy is 0.01%. This fact does not apply to people with decompensated cirrhosis and a progressive tumor.
Risks and complications
The use of modern technologies during the procedure under continuous ultrasound control virtually eliminates the occurrence of complications. But you need to be aware of all the risks. After manipulation, inflammation of the wound, bleeding (including internal bleeding), bile peritonitis may develop, there is a possibility of damage to neighboring organs, and trauma to large vessels.
To prevent the occurrence and development of complications, the procedure must be done in a hospital setting with a qualified specialist. It is important to insist on control ultrasound examinations of the intervention area using Doppler examination methods (they are carried out using special new generation ultrasound devices).
Liver biopsy is one of the most effective, informative methods for diagnosing many diseases, assessing the development of tumors, and the effectiveness of treatment. Carrying out the procedure under continuous ultrasound control makes it as safe as possible, significantly reduces the list of contraindications and improves the quality of the sample taken.
We recommend reading: liver transplantation in adults
Contraindications for carrying out
Liver biopsy (puncture) is strictly contraindicated in the following conditions:
- hemorrhagic diathesis is a group of diseases characterized by bleeding;
- the likelihood of infection spreading;
- blood diseases in the form of bleeding disorders;
- dermatosis in the area of the intended puncture;
- portal hypertension (syndrome of high pressure in the portal vein of the liver);
- unconsciousness of the patient;
- neuropsychic disorder.
Contraindications are ignored if the benefits of biopsy are expected to outweigh the risk of complications. These conditions include:
- past infections;
- heart failure;
- acute form of pancreatitis, cholecystitis, duodenal ulcer;
- anemia when hemoglobin is below 110 g/l;
- allergy to local anesthetics.
There are diseases after treatment of which a liver biopsy is permitted. Their list includes pleural pneumonia, inflammation and blockage of the bile ducts.
Biopsy techniques
The results of a liver biopsy largely depend on the specific technique used to take the biopsy. The most informative is an open biopsy obtained during laparoscopic surgery, since the histological structure of the organ is almost completely preserved. On the other hand, the results of percutaneous aspiration biopsy often turn out to be erroneous, since extremely scattered biomaterial, represented by a cluster of cells and blood, is sent for research.
The table presents the main characteristics of individual types of liver biopsy from the point of view of a pathologist:
| Characteristic | puncture | Trepan | Open |
| Preservation of histoarchitecture | Low | Average | High |
| Volume of biomaterial suitable for research | Minor | Average | Big |
| Assessing the degree of fibrosis | Minimum | Possible | Possible |
| Assessment of the activity of the inflammatory process | Possibly with errors | Possible | Possible |
| Probability of an erroneous result | High | Average | Low |