Causes of fibrosis
The process of tissue scarring does not occur as a separate disease. For the development of the disease, factors are necessary that will trigger the mechanism of formation of connective tissue. The root causes of the disease are divided into the following groups:
- Congenital diseases:
- galactosemia;
- hemochromatosis;
- Wilson-Konovalov disease;
- congenital fibrosis.
- Acquired diseases:
- hepatitis;
- poisoning;
- biliary cirrhosis;
- hepatosis;
- accompanying pathologies.
What is fibrosis?
The hepatitis C virus, affecting liver cells, leads to their death, either due to direct effects or through the activation of imperfect protective mechanisms of the patient’s own immune system. In response to this, the body launches an active process of regeneration (restoration) with the formation of new liver cells - hepatocytes, which for the time being stabilizes the situation. However, at a certain stage, the liver’s resources are depleted and, instead of the appearance of new hepatitis, the formation of fibrous tissue is activated, which does not perform any useful functions and over time even begins to interfere with the liver’s ability to perform its function.
Symptoms of liver fibrosis
The process of replacing liver tissue with connective tissue develops very slowly and a person with minor fibrosis does not feel any discomfort. The first symptoms most often occur in the later stages of the disease. The absence of specific complaints is the main danger of the disease. Doctors recommend that if the following signs appear, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination to clarify the diagnosis:
- headache;
- yellowness of the skin, sclera;
- periodic pain in the right hypochondrium;
- nosebleeds and other bleeding;
- weakness, general malaise;
- bloating;
- itchy skin;
- lack of appetite, nausea, vomiting;
- increase in body temperature.
The combination of the above symptoms may indicate the accumulation of harmful substances, which resulted from liver or gallbladder disease.
This is interesting: Periportal liver fibrosis: causes, symptoms and treatment
Liver fibrosis stage 3 - how long do people live with this pathology?
If stage 3 fibrosis is not treated, cirrhosis begins. When this disease develops, the mortality rate is approximately 50% over 10 years. From the moment of infection with fibrosis, and up to stage 4 (severe) it takes about 30 years. However, there is a risk of developing cirrhosis in a shorter period of time.
The life expectancy of patients with stage 3 fibrosis is different. A specialist can give a prognosis. The course of the disease and how it progresses is influenced by many factors. Therefore, such a forecast cannot be called objective. In patients at the same stage, the disease can progress differently.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make a final diagnosis, additional laboratory and instrumental research methods are prescribed:
- Clinical blood test. Decrease in level: leukocytes, platelets, hemoglobin. The ESR indicator increases. Sometimes the level of white blood cells increases.
- General urine analysis. The following appears in the urine: protein, bilirubin, casts.
- Blood chemistry. Electrolyte imbalance and changes in levels of: cholesterol, protein, bilirubin, urea, prothrombin, fibrinogen and other blood components.
- Immunological studies. Necessary for studying immunity and identifying the primary disease that can be caused by: viruses, bacteria or parasites.
- Fibrotest, fibromax. Allows you to assess the degree of scar changes in the organ.
- Biopsy. Refers to the gold standard in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis. Only the results of a biopsy can make an accurate diagnosis.
- Elastography. It is a modern type of ultrasound. On a special device, pathological changes in hepatocytes are highlighted in blue.
- CT, MRI, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. These instrumental methods are designed for a detailed study of the structure of the affected organ. The data obtained is not enough to make a final diagnosis.
What is the Metavir scale?
The state of liver health in medical practice is assessed using the METAVIR (Metavir) scale. It is most useful and helps to interpret biopsy data, which is considered the most reliable way in diagnosing many diseases. By evaluating a sample of liver tissue under a microscope, this system assigns two standard numbers: one to represent the degree of general inflammation, the second to determine the stage of fibrosis, which is scored on a scale from 0 to 4. The intensity of necro-inflammatory lesions is determined on a 4-point scale.
Treatment of the disease
At the moment, there is no single drug with antifibrosis effect in the world. Treatment of the disease begins with diet. Therapy is based on eliminating the cause of the disease, reducing the intensity of inflammatory processes and suppressing the activity of stellate cells in the parenchymal organ.
Etiotropic therapy must begin with proper nutrition, normalization of body weight, and cessation of the use of hepatotoxic substances. Table No. 5 according to Pevzner is assigned. After the examination, they will find out about the cause of the development. Depending on the underlying factors, the following are prescribed: antibiotics, thrombolytics, detoxifying, immunomodulating, anthelmintic, antiprotozoal drugs.
Further replacement of normal tissue by fibrous tissue can be prevented with the help of drugs that reduce inflammatory processes in the liver: cytostatics, antioxidants, immunosuppressants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hepatoprotectors.
The main producer of fibrous cells in the liver are stellate cells. Conclusion: the more stellate cells are activated, the more fibrous cells appear. The activity of producers of pathological cells can be suppressed using drugs from the group: interferons, ACE inhibitors, antiproliferative agents, microcirculation correctors and endothelin receptor antagonists.
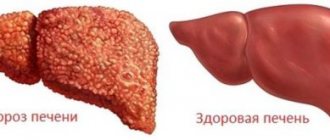
Typically, liver fibrosis is a reversible process. If drug treatment is ineffective, surgery is performed. If treatment is not started in a timely manner or is chosen incorrectly, cirrhosis may develop.
Treatment of stage 3 fibrosis
With the correct selection of treatment, the development of the disease can be stopped even at stage 3. The patient needs a comprehensive approach to treatment.
Etiotropic therapy
This type of treatment eliminates the causes of stage 3 fibrosis. Etiotropic therapy includes:
- eliminating alcoholic beverages and combating alcohol addiction;
- the use of antiviral agents for the viral nature of the pathology;
- avoiding contact with medications or toxic substances that could trigger the development of the disease;
Pathogenetic therapy
Aimed at slowing down the pathogenic processes that occur in the body during the course of the disease. This treatment consists of:
- immunosuppressive therapy;
- eliminating excess copper that accumulates in tissues;
- normalizing the activity of the gallbladder, by eliminating stagnation of bile and suppressing inflammatory processes in it.
Symptomatic therapy
This therapy is aimed at combating the symptoms of the disease. It is aimed at:
- removing excess fluid from the abdominal cavity through the use of diuretics;
- special diet, antibacterial therapy.
This is interesting: Signs, degrees and treatment of liver fibrosis in hepatitis C
Antifibrotic therapy
Helps suppress the development of fibrinogenic cells. For this purpose, special drugs are prescribed.
General restorative therapy
This therapy involves the administration of vitamin complexes to improve the immune system, as well as diet therapy.
Drug treatment for fibrosis is individual. If drugs that strengthen and stimulate the immune system are used for the majority of patients, then the use of choleretic drugs is not prescribed to everyone. For correct selection, a thorough study of the nature of the disease and its causes is necessary. The patient is prescribed suitable medications.
Such drugs include hepatoprotectors (protecting liver cells and preserving their activity), hormone-containing drugs (if fibrosis is caused by autoimmune disorders), cytostatics (reducing the amount of scar tissue), anti-inflammatory drugs (to reduce the severity of inflammation in the liver).
Surgery
Surgical treatment is used only when all measures have failed. Various methods of surgical intervention are used:
- splenectomy - complete or partial removal of the spleen;
- endoscopic sclerosis of dilated veins or gastrotomy with suturing of these veins in order to stop bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus and stomach.
Stages of disease development
The stages of the disease are different and depend on the degree of liver damage. There are 4 stages in total:
- The first stage - at this stage of the disease only the spleen is affected.
If you take a blood test, you can even see with the naked eye an increase in the number of red blood cells, platelets and white blood cells. At this stage there is still little fabric. Stages of destruction - The second stage is characterized by changes in the liver, the tissue begins to grow.
- The third stage of the disease, during which the tissue becomes scarred and begins to enlarge. This stage is quite serious and only a doctor can make any predictions about the possibility of getting rid of the disease.
- Stage four is the final stage in which complete decomposition of the liver occurs. Here the prognosis is already disappointing and not a single doctor can give you a prognosis for life.
Please note that there is no way to tell how quickly one stage can progress to another. This question is individual and depends on a number of factors: immunity, compliance with the recommendations given by the doctor, the gender of the patient (fibrosis develops faster in men than in women).
Prevention of fibrosis
Understanding and having studied all the possible causes of the disease, we can conclude that, to a large extent, the person himself is to blame for the fact that he began to get sick. Therefore, to avoid illness, the minimum you need to do is take a responsible approach to your health.
Hepatitis A incubation period - how long does it last?
As a preventative measure, you should act as follows:
Proper nutrition
- Everyone probably knows that excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages is harmful to human health. When we drink alcohol, we know that they only cause harm, but at the same time we continue to drink them. Therefore, to avoid liver disease, it is necessary to give up alcohol.
- By eating healthy food, you help your body. Therefore, the products must be fresh, it is better if they are steamed rather than in sunflower oil. Your diet should include fruits and vegetables every day (in any form - raw, stewed, baked).
- Medicines also lead to illness, so it is better to take all medications as prescribed by a doctor. There is no need to take painkillers unless absolutely necessary, as the drugs destroy the liver.
- If the disease is still detected, physical and emotional stress must be reduced to nothing.
- Drink only clean water.
In a word, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and love, first of all, your body, and not your desires.
Treatment with folk remedies
The most common folk remedies are:
- infusion of white cinquefoil, which slows down the process of fibrotic degeneration;
- seeds, as well as milk thistle tincture. Improves the overall outflow of bile and normalizes the functioning of the hepato-bisiological system;
- decoction of young corn leaves. Has a choleretic effect, partially helps dissolve small stones in the biliary tract;
- a mixture of honey and olive oil in equal proportions. Clears the choleretic tract, slows down the formation of scars.
All traditional methods can only be used as additional measures of influence, and not as primary ones. Fibrosis can be treated with such means only in the initial stages or during remission for a longer duration.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that liver fibrosis is a serious disease. It is impossible to stop the process once it has started, since the process is irreversible. With the help of treatment, it is possible to slow down the process of degeneration of hepatocytes, delaying the onset of some consequences. Early diagnosis is of great importance for successful treatment. If you suspect a pathology of the liver, you should immediately consult a doctor to undergo a specialized examination.
Differences between the fourth stage and others
In its development, liver fibrosis during hepatitis goes through several stages.
Highlight:
- Liver fibrosis stage 1. Minor changes are observed in the tissues of the organ. There is an increase in the portal tracts and the formation of septa, that is, walls dividing the cavities into parts. Patients complain of increased fatigue, decreased performance, irritability, and pain in the spleen area. On examination, a slight enlargement of the liver may be observed. When the diagnosis is made at the first stage of fibrosis and treatment is started, the prognosis is favorable.
- Liver fibrosis of the 2nd degree in hepatitis is characterized by a further increase in the portal tracts and the formation of portoportal septa. Patients may experience nausea and pain in the upper abdomen. The second degree is reversible with timely diagnosis and treatment of both fibrosis and hepatitis.
- Liver fibrosis stage 3. Portocentral septa are formed. At least 50% of the liver tissue underwent fibrotic changes. Signs of the third stage of liver fibrosis in hepatitis: a sharp decrease in the body's defenses, susceptibility to frequent colds. Blood test results worsen with a significant increase in leukocyte levels. The therapy is aimed at slowing down the process of sclerosis. The prognosis is favorable only if the body responds well to treatment and the patient complies with the doctor’s instructions.
- Stage 4 liver fibrosis is otherwise called cirrhosis. The organ is completely replaced by scar tissue, and false lobules are formed. Clinically, the stage is manifested by liver failure. The skin and sclera acquire a yellow tint, swelling increases, internal bleeding is observed, and consciousness is impaired.
The rate of progression of liver fibrosis in hepatitis is determined by many factors. You can speed up the process:
- substance abuse (alcohol and drugs),
- non-compliance with dietary nutrition,
- concomitant infection with viral hepatitis B,
- existing HIV (human immunodeficiency virus).
Typically, each stage of fibrosis lasts 5-6 years.
Correct determination of the stage of the disease allows you to choose the most appropriate treatment. The prognosis for recovery largely depends on it.
Patient reviews of different treatment methods for hepatitis C
Symptoms
The peculiarity of fibrosis is its initial course without pronounced symptoms. For a long time (from several months to several years) the patient does not have any subjective complaints from the hepato-biliary system. Minor manifestations of asthenic syndrome may appear. However, more often such symptoms are minimal or absent.
Morphologically, stage 1 liver fibrosis is manifested by destruction of the portal tracts. Replacement of normal tissue at the cellular level with connective cords is observed. However, the formation of septa is absent.
There are a number of nonspecific symptoms that characterize early changes in the liver during fibrosis. These signs include:
- emotional lability, sleep disturbances, increased irritability, absent-mindedness, partial apathy;
- increased fatigue in the absence of objective reasons, decreased ability to work;
- a large number of hematomas, bleeding, which is due to the lack of normal hemoglobin metabolism;
- anemia in blood test;
- low level of cellular immunity, increased susceptibility to viral infections.
Symptoms of periportal fibrosis
Regardless of what type of fibrosis the patient has, the symptoms are all the same, only if it is the first stage of the disease, then they are not as noticeable as they are noticeable at the fourth. The fourth is the last stage, when all the signs are already obvious. The most common symptoms of periportal syndrome are the following and, moreover, some of them may be noticed by the patient himself:
- there are complaints of tiredness and tiredness
- changes in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract
- decreased immunity, a person begins to get sick more
- iron levels in the blood drop to unacceptable levels
- the appearance of spider veins on the skin, as well as bruises
- During the examination, the doctor may see an increase in the size of the liver. In addition, the spleen also enlarges
Types of fibrosis
Despite the fact that the disease is associated with the liver, it has many varieties, forms and stages. Therefore, we will consider each separately.
Periportal form
In total, 5 forms of the disease have been identified in medicine according to the volume of growing tissue:
- When the central part of the liver is affected, venicular fibrosis is distinguished
- If scar tissue begins to surround the hepatocides, then this form is usually called the pericellular form
- A large number of areas where the tissue has died and many areas where there is fibrous formation is called the septile form
- Formations and decompositions occur around the bile ducts, called periductal form
Please note: in some cases there are also mixed forms, which are listed above.
How to cleanse the liver of alcohol: we consider the best ways
Diagnostics
The liver does not have nerve endings, so pain syndrome appears only when the surrounding tissue (for example, the membranes or ligaments of the liver) is involved in the pathological process. For this reason, early diagnosis of fibrosis is very difficult. The tendency to bleeding and hematomas due to chronic fatigue may prompt thoughts about the degeneration of hepatocytes. When collecting anamnesis, it is worth paying attention to the presence of risk factors that could cause the progression of fibrosis.
In laboratory blood tests, nonspecific manifestations may occur. This is, for example, an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (20 mm/hour or more). Progressive anemia is also a nonspecific symptom. A decrease in total hemoglobin occurs against the background of a decrease in the number of red blood cells.
Among instrumental studies, ultrasound and liver biopsy are indicative. Diagnostics using ultrasound helps to determine changes in the contours or echogenicity of the organ. A biopsy involves taking a piece of the diseased liver. With a study of this kind, it is possible to determine the nature of the lesion, as well as its location.