Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder (cholestasis) leads to inflammation and causes the formation of concretions in this organ, popularly called simply stones.
They are based on the so-called biliary sludge, which is precipitated and crystallized components of bile (cholesterol and bilirubin). This is due not only to improper diet and regimen, but also to an insufficiently active lifestyle. Exercises for stones in the gall bladder are designed to prevent stagnation in this organ, and are a good prevention of stone formation and cholecystitis (inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder). And in cases where the patient already has diseases of this organ, physical therapy can improve bile flow and increase the overall tone of the diseased body.
Diet No. 5 - the basis of a healthy lifestyle
Exercises for the liver and gallbladder are simple and do not take much time, but the benefits from them are undeniable. It is also recommended to take forty-minute walks, swim in the pool and dance. This also helps improve the motility of the digestive system and prevents bile stagnation. But yoga is recommended only during the stone-free stage of gallstone disease. If stones have already formed in the gall bladder, it is better to refuse it.
Experts consider the morning hours to be the best time to practice therapeutic exercises. This allows you to activate the functions of this organ, which is very important at the beginning of the day, since at night it is practically inactive.
The presence of stones and inflammation in this bile reservoir requires constant medical supervision, since these pathologies are fraught with very serious complications.
Recommended physical activity for gallstones is usually combined with diet No. 5 and drug therapy, which together gives the best effect.
The benefits of exercise for the digestive system
Any sport that requires energy expenditure increases internal metabolism. How does this happen? The body, giving away part of its energy reserves, requires replenishment of what was expended. Violent chemical reactions begin inside the cells to break down compounds to release energy. This is how part of the reserves of subcutaneous fat stored for a rainy day, the own fatty membrane of the internal organs, is consumed. This is very good. Old fatty compounds are poorly broken down, it takes a lot of effort to remove them, they impair the functioning of internal organs and lead to obesity. Constant, active lipid metabolism, stimulated by physical activity, produces light fats that are quickly broken down, providing more energy.
Active lipid metabolism improves the characteristics and properties of bile. Liver secretion, produced by liver cells, receives the necessary composition and consistency for the breakdown of fats, animal proteins and vitamins in the intestines.
Sports activities improve mood, relieve severe psycho-emotional stress, nervous system tension, and treat poor sleep and anxiety. Most diseases of the gastrointestinal tract begin with a disorder of the nervous system.
Digestion suffers from an imbalance between its central and peripheral parts. Various functional disorders occur, such as biliary dyskinesia, decreased tone of the gallbladder, bile stagnation, and intestinal weakness. Any physical activity is beneficial. The World Health Organization has divided people into groups according to their degree of mobility and activity. The first group includes people who prefer watching TV on the sofa to all types of recreation and their sedentary work does not involve physical activity. The last group includes those whose work involves physical activity and they prefer an active form of recreation. The intermediate two include people with average levels of physical activity and exercise intensity. The closer a person is to the first group, the greater the opportunity to acquire diseases and functional disorders, the shorter the life expectancy. This factor is always taken into account when collecting anamnesis and choosing a treatment method, especially if it concerns diseases of the gallbladder and excretory canals.
HOW
WHY AND WHO MOST OFTEN HAVE OMISSION
Prolapse of internal organs is a lower than normal location of one or more internal organs (stomach, liver, intestines, kidneys, etc.). As a result of hypotonia of the muscles surrounding the abdominal cavity and pelvic floor, their supporting function is disrupted: the stomach, intestines and pelvic organs are displaced downward, and the ligaments that hold them are stretched. The disease primarily affects narrow-shouldered and thin-boned asthenics with overly extensible connective tissue. Their insides can sink due to constant physical strain and chronic fatigue, when neuromuscular tone decreases. Prolapse of the stomach, kidneys, transverse colon, and pelvic organs is most often observed. Depending on which organ is omitted, certain features of the clinical picture of the disease are revealed. But any form of prolapse is characterized by complaints of constipation, decreased appetite, decreased performance, and sleep disturbances. The pain appears over time, gradually and intensifies towards the end of the working day, while at the same time it is weaker in a horizontal position. As muscle strength decreases, the ligamentous apparatus weakens, the balance created by the pressure of the internal organs on each other is disturbed, and the lower abdomen protrudes. Abdominal adipose tissue plays a certain role in maintaining the normal position of organs. With significant weight loss, the layer of adipose tissue decreases and the entire burden of the internal organs falls on the muscles. Intermittent aching and nagging pain in the abdomen may indicate prolapse of the stomach and intestines. Unpleasant sensations usually occur in an upright position and subside when you lie down. When the kidneys prolapse, pain in the lumbar region bothers you. If it is accompanied by a nagging pain in the lower abdomen and sacrum, episodes of urinary incontinence appear when coughing, sneezing, laughing, or physical exertion; prolapse of the uterus and vagina is possible, which sometimes ends with their loss.
IF THE OPERATION COULD NOT BE AVOIDED...
Today, the usual solution is surgery, however, as practice shows, there is a possibility of relapse, depending on many reasons, and it is impossible to take into account and prevent all factors. If, unfortunately, you had to undergo surgery, then after some time it will still be necessary to perform exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, because the body is even more weakened by surgical intervention, which means it requires constant attention and systematic strengthening so that there is no need for repeated operations. Don't rely on a bandage - it will only make the problem worse. After a temporary improvement, which can last 1–2 years, the symptoms of the disease begin to bother you with triple strength: pain increases, constipation and nausea that cannot be treated appear. General weakness, increased fatigue and irritability occur, and sleep is disturbed. It is already very difficult to help: the muscles, accustomed to inactivity under the bandage, have completely atrophied and are not able to provide the slightest support to the sagging organs. Where to start treatment? Prolapse of internal organs is very often associated with problems of the spine - so first of all start with it. It is necessary to check the condition of the spine. What should you do from gymnastics? Pump up the abdominal muscles, back muscles, oblique abdominal muscles, intercostal muscles. The exercises for this are very different: twisting and bending back and forth from different positions and at different angles, the total number of movements performed per day should be about 1000.
SPECIAL EXERCISES WILL HELP
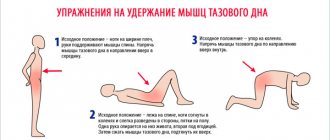
Countless people have successfully avoided pelvic organ prolapse surgery by undergoing several sessions of abdominal muscle therapy. In general, the task is to, against the background of general strengthening of the body and its psycho-emotional state, increase the tone of the muscles of the pelvic floor, abdominal wall, lumbar region, and improve the functional state of the digestive organs. To strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor, abdominals, lumbar region and diaphragm, increase the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, tone the ligamentous apparatus of internal organs, and activate redox processes in the body, special exercises are performed. — Lying on your back, on a couch with your head raised by 10-12 cm, perform static breathing exercises (diaphragmatic, full breathing). Perform the movements rhythmically, at an average pace, full amplitude, rhythmic breathing. — Lying on your back, diaphragmatic breathing. Exercises for the lower extremities - free and with tension. - Lying on your right side. Diaphragmatic breathing, limb movements. The same on the left side. - Knee-wrist, knee-elbow position. Exercises for the muscles of the limbs and torso. - Lying on your stomach. Exercises to strengthen the back muscles (movements of the lower limbs and lower torso). — Lying on your back, diaphragmatic breathing. Exercises for all muscles of the lower extremities and torso (without increasing pressure in the upper third of the abdominal cavity, the transition from a supine position to a sitting position is excluded). The duration of all exercises is 15 - 20 minutes. Exercises can be performed with each leg separately. The range of motion is full. At the final stage, exercises are performed for small and medium-sized muscles of the limbs and breathing exercises. Lying on your back. Static (diaphragmatic, full) and dynamic breathing exercises involving arms and legs. Exercises for the muscles of the trunk and lower extremities with an emphasis on the muscles of the pelvic floor, abdominal wall, lower back, and diaphragm. Standing on the shoulders (“birch tree”). Exercises for the lower extremities. Sitting on a chair. Exercises for the muscles of the limbs and torso. When walking with arm movements, perform breathing exercises. The exercises should be simple; when performing them, the abdominal organs should shift towards the diaphragm - these are movements of the lower limbs and torso with lifting of its lower end. Physical exercises must be performed on an inclined plane with the foot end raised by 10-12 cm, unless there are contraindications. The first 6-8 weeks - lying on your back, on your side, on your stomach, standing on all fours. Starting from the 6-8th week, after achieving a lasting positive result (improved subjective state, appetite, sleep, performance, normalization of stool), exercises are introduced into the complex to develop posture in the initial standing position, excluding bending the torso forward. During the course of treatment, it is advisable to use no more than three individualized sets of exercises, changing them no earlier than after 1-2 months of training. The duration of classes during the 1st week is 15-20 minutes once a day; 2-3 weeks - 20-30 minutes twice a day; for 4-8 weeks and beyond - 30-40 minutes twice a day. When the position of the lowered organ approaches normal, classes are carried out once a day. I recommend lifting things from the floor after sitting down; When getting out of bed, you must first turn on your side, then simultaneously lower your legs and raise your torso. For one year, I do not recommend bending the body forward, jumping, skipping, or running. To activate the motor function of the gastrointestinal tract, massage of the lumbosacral region, colon massage, and self-massage of the abdomen are indicated.
A FEW MORE USEFUL EXERCISES
Sitting on the mat, keep your back straight, bend your arms at the elbows, as if running. In this case, you need to exhale and draw in your stomach and small pelvis (pelvic floor muscles). Exhale - “ha-a-a-a-a-a.” And, moving only with straight legs, begin to move on your buttocks. First forward, then back. The next exercise is related to anti-gravity action. Lie on your back, put your hands behind your head, bend your knees and rest your feet (legs slightly apart). On the count of “one,” lift your pelvis up, pull in your stomach “ha-a-a-a,” and touch your knees. So: inhale - spread your knees, exhale - bring your knees together. Perform such inhalation and exhalation at least three times. Now lower yourself to the starting position. Rest and repeat again. Another exercise taken from yoga. Imagine that you are standing (or sitting on a chair), leaning forward, resting your hands on your knees. Take a deep breath, then exhale with your head tilted, after exhaling, hold your breath. Try to make several breathing movements deeply, but without air, while holding your breath, while relaxing your abdominal muscles. There should be an active retraction of the abdominal organs into the chest, the stomach seems to stick to the spine. As the chest expands, negative pressure should pull the abdominal organs inward. During one breath-hold (after exhalation), you need to make several of these supposed breathing movements. Each time the abdominal organs will rise and fall (5 – 10 times). If something hurts you, do not do this exercise, wait until it goes away, you need to do it on an empty stomach, best in the morning on an empty stomach or 3-4 hours after eating. In total, such “retractions” need to be done 30-40 times over several breath holds, but reach this number gradually, waiting for all the pain in the stomach to go away.
WE TIGHTEN THE PELVIC ORGANS
When you pulled in your stomach, you probably noticed that your lower abdomen didn’t pull in and didn’t participate in the gymnastics. But it would be nice to get rid of ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, prostatitis, prostate adenomas, prolapses and prolapses, incontinence, hemorrhoids and other problems. A significant addition needs to be made to the previous exercise - pulling up the upper pelvic organs so that they fall into the zone of action of the negative pressure created by the chest. This is done with a strong contraction of the pelvic muscles. We repeat several times. From now on and forever we do both of these exercises together. You can have a specific effect on the pelvic organs with the following exercise: inhale deeply with your head tilted forward, exhale and hold your breath, use your chest to pull in your stomach and leave it in that position, strongly contract and relax only the pelvic muscles several times, lifting and lowering the organs. Repeat a couple of times. It is important to monitor your breathing and your abdominal muscles. This helps restore and elevate the pelvic organs. Special breathing exercises are useful. They should be performed before going to bed in a lying position. Take a deep breath and then exhale as much air as possible. Repeat one more time. This exercise “puts” the organs in place, and also strengthens the abdominal muscles and makes the waist slimmer. As a result, the use of such methods of traditional medicine allows you to normalize the balance of the muscular corset that holds the internal organ, and normalize the location of the organ, as well as straighten your posture, get rid of pelvic pain, excess weight, back pain, and feel healthier, stronger, and younger.
WHAT CAUSES GASTROPTOSIS
Now I will focus more specifically on the problems of prolapse of the stomach and intestines - gastroptosis. The main cause of acquired gastroptosis is a sharp weakening of the muscle tone of the abdominal wall. This can occur due to rapid weight loss, after removal of a large tumor or pumping of fluid from the abdominal cavity, and in women also after a long or rapid labor. In addition, women are at risk of developing gastric prolapse when lifting heavy bags, and men are at risk of weightlifting and jumping from heights. Lifting weights leads to stretching of the ligaments that fix the stomach and weakening the tone of the muscle wall of the stomach. As a result, the stomach moves below its normal position. There are three degrees of gastroptosis: initial, moderate and severe - with a pronounced downward displacement of the stomach. Changing the correct position of the stomach complicates its digestive function, impairs peristalsis and the movement of food into the intestines. At the same time, the condition of the valves that separate the stomach cavity from the esophagus and the duodenum is disrupted. Due to incomplete closure of the valves, air enters the stomach through the esophagus, which causes belching, and bile is released from the duodenum. Bile causes heartburn, and also corrodes the gastric mucosa and causes the development of erosive gastritis and stomach ulcers. A number of symptoms may indicate a prolapsed stomach. First of all, it is belching, heartburn, heaviness in the stomach. Impaired gastric motility causes bloating and rumbling in the abdomen, leading to a feeling of fullness even when eating a small amount of food. Due to slow digestion of food, bad breath appears, stool disturbances occur - either prolonged constipation or loose stools in the form of diarrhea. Gastroptosis can be accompanied by changes in appetite - an aversion to food appears or, conversely, a “ravenous appetite” develops against the background of weight loss and unhealthy thinness. Urination becomes more frequent. When symptoms worsen, severe pain appears in the abdomen, and the temperature may rise. Sometimes gastroptosis occurs after severe weight loss, removal of large tumors in the abdominal cavity, or after childbirth, especially in women who have given birth many times. Long-term protein starvation and vitamin deficiency can lead to prolapse of the stomach. Mild disease is usually asymptomatic. But after eating, especially a large meal, there is a feeling of heaviness, bloating, and a feeling of fullness in the epigastric region. It's about fat. The slag masses between the abdominal organs disappear very quickly, and as a result, prolapse of the stomach may actually appear. During this period, you need to eat more salads from tomatoes, cucumbers, red cabbage, bananas, peanuts, honey, blueberries, cherries.
HOW TO RAISE YOUR STOMACH
I recommend starting treatment with exercises to elevate the stomach. Classes are carried out while lying on a couch with the leg end raised. In this position, the stomach returns to its “rightful” place. Perform the exercises at a calm pace, without jerks or sudden movements. Do not start therapeutic exercises: in the later stages and with some concomitant diseases, it is strictly contraindicated. Starting position: lying on your back, arms along your body. 1. Raise your straight legs one at a time without holding your breath (4-5 times each). 2. Bend your knees. Raise your pelvis, resting on your feet, elbows, and the back of your head, forming a “half-bridge” (4-5 times). 3. Inhale, bend your knee and, as you exhale, pull your hands towards your stomach (4-5 times each). 4. As you inhale, raise both legs, and as you exhale, lower them (4-5 times). 5. Imitation of cycling (4-5 times). 6. Raise and lower your arms (6-8 times). Breathing is voluntary. 7. Inhale, as you exhale, turn your legs bent at the knees towards you and to the right, return to i. p. Then repeat the same thing, but with a turn to the left (4-5 times in each direction). 8. Inhale, and as you exhale, pull both legs toward your stomach with your hands (4-8 times). Finish your sessions with a light self-massage of the abdomen. Do it while lying on your back, bending your knees, and moving your arms clockwise. After exercise, try to ensure that the abdominal organs are in a normal position for 15-20 minutes. To do this, simply lie down on the couch with your feet elevated. The duration of training in the first three weeks is 10-15 minutes once a day, and later - 15 minutes 2-3 times a day.
WILL HELP THE INTESTINES... A BALL OF WOOL THREAD
More specifically about colonoprosis - prolapse of the large intestine. As a rule, other underlying organs are also involved in the pathological process when the stomach prolapses. A sinking stomach puts pressure on the small and large intestines. Patients with colon prolapse are bothered by pain in the lower abdomen, bloating, and prolonged persistent constipation. To treat and restore the correct position of organs, in addition to herbal medicine, I recommend acupressure and acupuncture. It is imperative to follow the diet. The food should be light, but satisfying; after each meal you need to lie down for a while. Small meals are recommended – 5-6 times a day in small portions. Physical activity should be limited during treatment. When intestinal prolapse occurs, there is an old method. Take a ball of woolen thread, 20 centimeters in diameter. Lie on your stomach, place a ball in the navel area and roll it under your weight around the navel for 5-10 minutes. Gradually the intestines fall into place. There is also a method of abdominal massage, when the internal organs are lifted with your hands and pulled out with large cans. Another old method. The stomach should be smeared with vegetable oil, 2 potatoes cut in half should be placed around the navel, and matches should be stuck in them, 5-6 in each, and these matches should be set on fire. Next, take a liter jar with a wide neck and place it so that the matches are inside. The matches will burn out the oxygen and most of the belly will be pulled into the jar. You can move this jar clockwise; it moves easily through the oil. And thus, not only the stomach, intestines, but also the genitals come into place.
A FEW TIPS FOR PREVENTING PROPRESSION OF INTERNAL ORGANS
Learn not to be nervous, learn to relax; lead a lifestyle taking into account your natural constitution; eat according to your natural constitution: either maintain the digestive “fire” of the stomach, or, conversely, pacify it; periodically eliminate stagnation of energy and blood in the body with the help of simple physical exercises, massage, acupuncture, cupping and other procedures, avoid lifting heavy objects. Do not forget that if the internal organs are prolapsed, it is prohibited to carry heavy objects in your hands or backpacks, or to perform household and housework associated with great physical effort. I also recommend to everyone the technique developed by Professor S.M. Bubnovsky. To ensure that the impact was directed, he developed a system of special simulators that make it possible to create an “anti-gravity” mode, that is, allowing the patient to take the starting position in which the pelvis is above the level of the lumbar region. These are the most common simulators. And the technique is unique, tested by me personally. At the first stage, it requires the mandatory assistance of an instructor; in the future, it is quite possible for a person to study independently. Also remember that movement is life, you just need to learn how to use it correctly!
lecheniebolezni.com
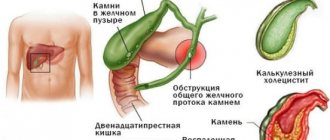
What to do if a stone is found in the gall bladder
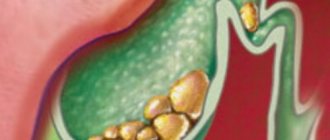
If the process of formation of stones in the gall bladder occurs without the manifestation of any symptoms, it can only be detected by chance, for example, during an ultrasound of the abdominal organs during a medical examination, during examinations of other internal organs, during an operation to remove appendicitis, excess fat deposits, figure correction. Small rudiments of stones in the form of a suspension are treated with the help of choleretic agents of both chemical and plant origin, hepatoprotectors, and antispasmodics. The formation of bile clots is called sludge syndrome or dirt in the gallbladder. Against the background of normal contractile and motor activity of the bladder and bile ducts, this syndrome is not dangerous and can be easily treated with folk remedies. The causes are varied: from poor nutrition to severe emotional stress.
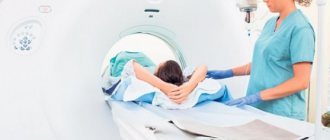
Ultrasound diagnostics
If an ultrasound reveals a full-fledged calculus over 3 mm, then the doctor will insist on surgery. The stone can leave the gallbladder at any time and enter the common excretory duct. Small stones up to 5–6 mm are not capable of blocking the channel that removes bile in its initial and central part. The danger is that with the flow of bile it can enter the distal section of the duct, where the internal diameter narrows by about half, and block the outlet of the fluid into the duodenum. The consequences of this depend on how quickly a person gets to the hospital, how quickly the presence of a stone in the bile duct is determined, what size it is, and where exactly it is located. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend that if an asymptomatic gallstone is detected, do not take risks, go for a planned operation, and remove the gallbladder.
We recommend reading:
Medicines for patients with gallstones
Self-massage of the gallbladder
Self-massage of the bile excretion organs also has a positive effect on improving the outflow of bile. To do this, the patient should lie on his back and massage the abdominal organs, starting from the edge of the right costal arch and clockwise. Movements should be gliding, smooth, and not painful.
The self-massage technique should exclude all sudden hand movements. You should do the massage yourself using the third and fourth fingers of the hand, while the stroking method has the best effect for self-massage.
Self-massage should help reduce pain symptoms in gallbladder diseases. If you experience any discomfort or side effects, you should immediately stop self-massage and seek the advice of a specialist.
If a person does not agree to cholecystectomy
An operation to remove a gallbladder with stones, in the case of an asymptomatic course of the disease, is performed only with the consent of the person. If he refuses, then he himself is responsible for his health. Many people expect to remove or split the stone using traditional medicine recipes. Choleretic pharmaceutical preparations, monastery tincture, corn silk tea, decoctions of Rosehip, Milk Thistle, and dill have proven themselves well. Active, mobile people continue to go to gyms, play active sports, and lead their usual fast-paced lifestyle, risking worsening their health and putting their lives at risk. We must not forget that all activities that stimulate the functioning of the biliary apparatus and the body as a whole can lead to increased mobility of gallstones.
What sports are strictly contraindicated for gallstones?

Exercise with weight lifting
All physical exercises that involve jumping, pushing, vibration, lifting weights, grueling long-term training, sudden changes in body position are dangerous for gallstones. It is unknown how they will behave. Perhaps they will remain in the gallbladder, or they may exit into the excretory ducts, block the outflow of bile, cause an attack of hepatic colic, injure the wall of the canal, and provoke peritonitis. It’s like a negative delayed effect; no one knows at what moment it will appear. Therefore, it is better to exclude all exercises that stimulate, activate, or warm up the body from your workouts if you have gallstones.
Possible sports for gallstones
You can indulge in pleasure, strengthen and tighten the muscles of the body even if there are stones in the cavity of the gallbladder. You just need to change the way you achieve your goal. Intense running with acceleration should be replaced by walking with elements of running. Exercises on the treadmill are allowed at low speed and for no more than 10–15 minutes.
Athletics exercises should be replaced with a set of stretching and breathing exercises. They have no less pronounced results in stimulating the muscles of the body. Breathing exercises for the abdominal muscles strengthen the outer and inner walls of the peritoneum and have a positive effect on the functioning of the internal organs. A calm, long inhalation with retraction of the abdomen improves the excretion of bile and acts as a choleretic agent. Short shallow inhalation and exhalation normalize the functioning of the common bile duct.
Abdominal pumping exercises should be completely avoided. They can be replaced with the following set of exercises:
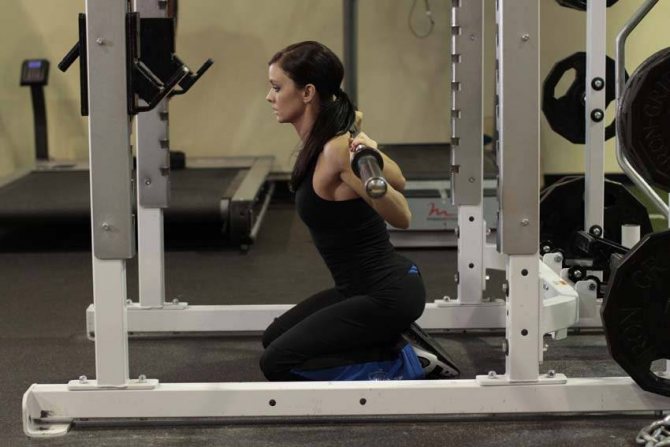

Squat on your knees
- You need to sit on the floor, cross your legs at the knees in front of you, straighten up as much as possible, turn your body to the right and left, without leaning on your hands or helping with them. You need to fix the position of the body at the extreme points for 5–10 seconds. The return to the starting position occurs smoothly without jerking.
- You can reduce your waist and strengthen your stomach by doing a kind of squat while sitting on your knees on the floor. Starting position, sitting on the floor on your knees, then move your torso to the right, touch your butt to the floor, take the starting position. The same goes to the left side.
- The oblique plank strengthens the abs well, when the emphasis is on one arm, straightened at the elbow, with the torso turned to the side.
If you have gallstones, you should not perform exercises while lying on your back or stomach, because this stimulates the emptying of the bladder and the release of stones into the ducts.
We recommend reading:
Stones in the gallbladder ducts after bladder removal
Weight lifting can be replaced by swimming. Doctors allow swimming up to an hour a day without the threat of dislodging a gallstone.
It is better to change boxing, wrestling, and gymnastics to Pilates. Smooth movements without jerks, jumps, or dismounts will lead to excellent athletic shape, improve your mood, and strengthen the internal muscles of the body.
Yoga is not recommended for gallstones. Yoga exercises have worked well for sludge syndrome; they successfully remove suspension from the gallbladder, improve the functioning of the common bile duct and the liver as a whole.
Training in lying positions
To conduct classes in a lying position, you need to lay a mat or towel.
After this, you need to lie on your back and point your legs forward. Place your arms parallel to your body. The first exercise is to conduct breathing training. It is worth placing your hands on the abdominal area and exhaling so that the stomach protrudes. Then take a deep breath so that your stomach becomes flat. Repeat the gymnastics five to six times.
The next exercise has the same initial pose. In this case, you need to slide your foot along the floor and bend your knees. Such movements are repeated with each leg alternately 5–7 times.
Then you need to turn on your right side and begin the gymnastics by establishing proper breathing. Lying on your right side, hands are placed on the stomach area. First, exhale with the abdomen protruding forward, and then inhale strongly. The lesson is repeated five to six times. Lying on your right side, bend your knees. One hand is placed under the head, the other hand acts as a support. Inhale as you point your leg back. As you exhale, bend and press against the chest area. The exercise is repeated five times.
Sports diet for gallstones

Protein food
A sports diet involves a lot of protein foods, a minimum of cholesterol and clean water. This will have a positive effect on the functioning of the liver, gall bladder, excretory tract and intestines. Cheese, cottage cheese, egg whites, lean meat, fish, cereals, vegetable and butter - this is all that is included in the treatment table for gallstone disease. The exception is that sports nutrition consists of 40 percent fresh fruits, vegetables and herbs, and in case of gallbladder diseases complicated by stones, these products are prohibited. You will also have to give up pasta, sweets, offal, mayonnaise, and tomato paste-based sauces.
Absolute contraindications to sports
Any stages of exacerbation, a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, indigestion due to pain in the liver, an unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth in the morning are contraindications to engaging in any sport, even physical therapy. If these symptoms are accompanied by nausea, frequent bouts of vomiting, hepatic colic, attacks of acute tearing pain on the right, pain under the right shoulder blade, then you need to urgently go to the hospital, because these symptoms mean blockage of the bile duct with stones.
There is no need to ignore the warning signs of gallstone disease. If you often experience a feeling of bloating, seething, a skin rash of a non-allergic nature, a decrease in appetite against the background of complete health, a decrease in physical activity, or increased fatigue, you can assume the development of gallstones, you need to be examined by a gastroenterologist.

It is necessary to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist
Is it possible to exercise if you have gallstones? It is possible, if they do not bother you, there are no attacks of pain or symptoms characteristic of cholelithiasis, your mood and general well-being are not of concern. It is necessary to change active sports with heavy loads, jumping and pushing to calmer sets of exercises, such as stretching, breathing exercises, swimming. If hepatic colic, pain and nausea appear, all exercises end, you need to take a sitting position, relax, if the pain does not go away within a few minutes, you need to consult a doctor.
A set of physical therapy exercises for cholecystitis
It is now generally accepted that diseases of the biliary system, in particular cholecystitis, are accompanied by functional disorders of biliary excretion. This disorder is based on a decrease in the general motor activity of the patient’s body, which must be taken into account when prescribing exercise therapy for the purpose of rehabilitation of patients of this nosological group.
The use of therapeutic physical culture in rehabilitation for cholecystitis is aimed at restoring the contractility of the gallbladder and bile ducts. From this point of view, the use of means and methods of exercise therapy of a general tonic type, which are characterized by high load and intensity and are aimed at increasing the tone of the smooth muscle tissue of the gallbladder and biliary tract and increasing bile excretion, seems justified [13, p. 318].
The use of physical exercises in a comprehensive rehabilitation program is aimed at solving the following problems: normalizing the function of the autonomic nervous system, restoring cortico-visceral connections, improving the emotional state of patients. Great importance is attached to increasing blood circulation in the abdominal cavity and the flow of arterial blood to the liver and biliary tract, reducing the inflammatory process, stimulating metabolism, as well as strengthening the abdominal muscles, normalizing the motor function of the biliary tract, gall bladder, intestines and reducing hepatic cholestasis.
The physical rehabilitation program, along with various types and forms of movement therapy, includes morning and therapeutic exercises, tasks for individual independent performance, health paths, walks, and jogging.
Therapeutic gymnastics classes are based on generally accepted methods. Morning gymnastic exercises are performed after sleep in order to increase the general and emotional tone of the patient’s body, and a more adequate transition from sleep to wakefulness.
The method of practicing therapeutic gymnastics includes three sections: introductory, main and final. Individual (bed and semi-bed rest) and group (semi-bed and free rest) methods of conducting classes are used.
General strengthening and breathing exercises are combined with special ones, the implementation of which helps to normalize the function of the hepatobiliary system. When selecting exercises, special attention is paid to alternating muscle groups involved in physical activity. As the patient gets tired, pauses of passive rest are included, the duration of which depends on the degree of fatigue of the patient. The classes also include gymnastic exercises for the upper, lower extremities, torso, abdominal muscles and pelvic floor, exercises to relax skeletal muscles, breathing, etc. Diaphragmatic breathing is aimed at improving blood circulation in the abdominal organs, enhancing motility of the gallbladder, biliary tract and intestines [9, p. 26].
The alternating increase and decrease in intra-abdominal pressure due to deep diaphragmatic breathing has a massaging effect on the liver and gallbladder and reduces bile stagnation. Therefore, breathing exercises are special for diseases of the hepatobiliary system. Muscle relaxation exercises and relaxation gymnastics are widely used. They help improve bile secretion processes and restore motility of the biliary tract, accumulate energy and increase overall performance. In this regard, when constructing a method of therapeutic gymnastics, dynamic gymnastic exercises alternate with rest phases and relaxation exercises.
A variety of starting positions are used (on your side, lying on your back, sitting on all fours, standing, kneeling). The starting position lying on the right side is prescribed to improve the outflow of bile. For better emptying of the gallbladder and activation of intestinal function, a variety of exercises are selected, with gradually increasing load, for the abdominal muscles, including in the initial position lying on the stomach, standing on all fours and breathing exercises. The latter, especially in combination with slowing down respiratory movements during inhalation and exhalation, are used to reduce or relieve pain and dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, belching, heartburn, etc.) [25, p. 123].
Forward bending and bending of the torso, combined with rotation of the torso, are used to increase abdominal pressure and improve the outflow of bile. They are prescribed with caution, since nausea, belching and dizziness were often observed with these movements. It is recommended to perform exercises with full amplitude, at a slow and medium pace.
Includes various types of walking, including high hip lifts. The patient is taught various techniques for muscle relaxation, since only the correct combination of elements of strengthening and relaxing skeletal muscles ensures the success of the procedure. The exercises are performed at an average pace, sometimes with a transition to a fast pace, especially when performing gymnastic exercises from lightweight starting positions. Before and after classes, patients are recommended to rest passively for several minutes.
The pace of execution is slow, with a transition to a medium pace. Before exercise, patients are recommended to rest passively for 3-7 minutes in a lying position, in combination with abdominal massage, without involving the liver area in the presence of even slight pain in the right hypochondrium [25, p. 124].