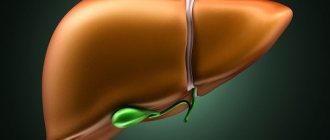
The gallbladder plays the role of a reservoir of bile - a secretion of liver cells, which is necessary for the digestion of fats, normal intestinal motility, suppression of putrefactive microflora of the colon and the synthesis of a number of biologically active substances.
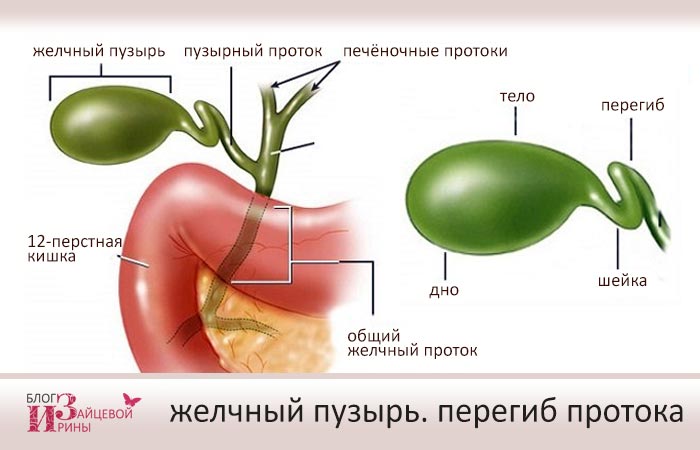
This is a hollow pear-shaped pouch, consisting of three sections - the bottom, body and neck. Sometimes a pathological deformation called a kink occurs at different levels. As a result, bile cannot be released into the cavity of the duodenum in the same way as normally, and stagnation occurs. This causes metabolic disorders and a wide variety of diseases.
Causes of the disease
Bend of the gallbladder: clearly
The reasons that can cause organ deformation are varied. Depending on the cause of the disease, symptoms of a bent gallbladder appear, and appropriate therapy is prescribed. Deformation of the bladder can be caused by various diseases of the organ, in particular, cholecystitis in acute or chronic form, cholelithiasis, etc. The inflammation accompanying the disease covers the outer wall of the organ and leads to the appearance of adhesions, which deform the organ.
Often, a kinked bladder is a congenital disease. In this case, they are not talking about pathology, but about the unusual shape of the organ. As a rule, congenital inflection of the bladder does not lead to disruption of its functions and digestion in general and is diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound or x-ray examination of the abdominal organs for some other reason.
Often sudden movements or heavy lifting lead to a short twisting or bending of the bubble along its axis. In the vast majority of cases, such painful conditions are asymptomatic. Most often, they are diagnosed in older people who have severe prolapse of internal organs, an enlarged gallbladder, and the presence of stones in it. It is extremely rare that, as a result of strong physical exertion or heavy lifting, the bladder twists around its axis several times. This leads to impaired blood circulation in the organ, the appearance of cracks in its walls and the outpouring of bile into the abdominal cavity. This condition, accompanied by acute pain and a sharp deterioration in health, requires emergency medical attention.
In children, as well as elderly people, the bending of the gallbladder is caused by poor nutrition and excess body weight. Excess fat is deposited on the walls of internal organs, including the walls of the gallbladder, which can lead to deformation of the organ.
Causes of bending
With congenital bending of the cervix or isthmus, in addition to heredity, the main cause of the development of the disease is the mother’s poor lifestyle during pregnancy. This includes smoking and drinking alcohol. In addition, the use of medications not approved by a doctor can also become a risk factor.
Bends in the cervical body area acquired during life can result from the following factors:
- past infectious diseases,
- being overweight,
- unhealthy diet
- presence of liver diseases,
- limited physical activity,
- surgical operations,
- impaired metabolism,
- taking a large number of medications.
One or more of the above reasons may well lead to pathology. A sharp increase or decrease in body weight can also lead to deformation of the organ.
The gallbladder (GB) has the shape of an elongated pear and consists of a fundus, body and neck. Bile accumulates in it and is released when necessary, for example, during the process of eating and digesting it. This organ can be bent and pulled in the neck or body, and sometimes in several places, which happens less frequently.
Most often, this pathology is congenital and forms in the embryonic stage, at the 5th week of pregnancy, when the gallbladder is formed. If this process is disrupted, then with further growth the organ develops with structural defects, the most common of which is a bend of the neck.
- Congenital anomaly;
- Acquired anomaly: Stone deposits; Chronic inflammatory processes.
Symptoms
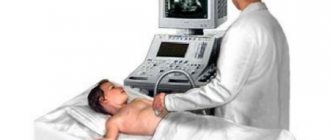
Ultrasound of the gallbladder
Depending on the reasons that caused the deformation of the bladder, as well as on the location of the bend, the clinical picture of the pathology can vary significantly. As a rule, when the bladder is bent, a sharp pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium, which can radiate to the right shoulder blade, subclavian region and even to the spine. Sometimes the pain takes on the character of intestinal colic. This is due to disturbances in digestion and the passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract.
The bending of the bladder may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite or complete refusal to eat, increased gas production, constant and severe belching, constipation, and diarrhea. Due to a violation of the outflow of bile, bitterness may appear in the mouth. A patient with a bent gallbladder may complain of rapid breathing, palpitations, watery eyes and drooling.
Symptoms of the disease
A kinked gallbladder is characterized as an abnormal phenomenon in the body, in some cases it is congenital, in others it is acquired. In a child, pathology sometimes manifests itself during the first months of life, when parents cannot immediately determine why he is crying, what his needs are at one time or another.
Parents notice the following symptoms:
- the baby often spits up;
- gas formation is observed;
- there is a feeling of bloating;
- periodically the child experiences the urge to vomit and nausea.
These conditions become especially aggravated if, in addition to breastfeeding, complementary foods are introduced into the diet. Sometimes these manifestations occur as a result of the baby eating solid foods.
When a child is older, identifying symptoms becomes much easier, these include:
- in the morning before breakfast and after each meal there is a feeling of nausea;
- in the mouth - an unpleasant taste with a feeling of bitterness, observed during meals and in the period between them;
- the parent may see a yellow coating on the tongue;
- bouts of vomiting are felt;
- unpleasant sensations appear in the middle part of the abdomen after eating fatty and fried foods;
- pain and discomfort are felt in the right hypochondrium.
An irregularly shaped organ in adults is in most cases considered an acquired deformity; it entails the following symptoms:
- in the right hypochondrium there is severe pain, localized in other areas of the body that border the bladder (sternum, right shoulder blade or collarbone);
- a state of weakness with the appearance of nausea and vomiting is observed;
- heart rate increases;
- temperature rises;
- The patient's complexion changes, it becomes yellowish.
Symptoms appear if the gallbladder is pulled between its parts (neck and body). Severe pain does not stop, the temperature rises sharply.
If these signs appear, urgent medical care, timely diagnosis is advisable, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, strict adherence to the therapeutic treatment regimen chosen by the doctor.
Diagnosis of bending of the gallbladder
Diagnosing a bent gallbladder is not difficult. The most informative method for diagnosing pathology is ultrasound. It allows not only to identify pathology, but also to determine the functional state of the organ, the exact location of the bend, and also to evaluate the anatomical features of the walls, neck, and body.
Determining the cause of the pathology is more difficult. To differentiate a congenital disease from an acquired one, an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder is performed twice: on an empty stomach and after eating egg yolks, which cause increased secretion of bile. When the inflection of the bladder is a congenital pathology, the deformation of the organ remains unchanged.
Diagnostics
The disease can only be detected using special equipment. At the first stages of diagnosis, gastroenterologists interview the patient to clarify the clinical symptoms, severity of the lesion, and identify the strength of the symptoms. The doctor must review the medical history and clarify the patient’s heredity.
After the described primary diagnosis, a physical examination is carried out by palpation of the anterior wall of the abdominal region, the place under the ribs on the right, the skin and sclera are examined.
The patient is required to undergo the following laboratory tests:
- blood;
- urine;
- feces
Ultrasound diagnostics must be organized to determine the strength of the deformations. Sometimes a computed tomography scan is additionally prescribed - it helps to get a complete picture of the disease. The treatment tactics are selected in accordance with the diagnostic results - the form and severity of the disease.
Treatment
People with congenital bending of the gallbladder can live with it all their lives and discover the pathology by chance during an ultrasound of the abdominal organs. In such cases, the pathology does not require treatment. Treatment for a bent bladder that appears as a result of any disease takes quite a long time. The patient is prescribed medication, physiotherapy and mandatory adherence to a gentle diet.
Drug treatment involves taking choleretic drugs, which must be taken in courses. The duration of each course is 10-14 days, but you need to complete at least four courses. Most often, for the treatment of pathology, gastroenterologists prescribe the drug Flamin, the active ingredients of which are flavonoids and glycosides of immortelle sandy, Odeston, which accelerates the evacuation of bile into the intestinal lumen and relieves spasm of the bile ducts, Aritohol, Chophytol, Tsikvalog, etc.
Physiotherapy is effective in treating a bent gallbladder. To relieve symptoms of pathology, electrophoresis with novocaine and ultrasound are prescribed. After symptoms are relieved, it is advisable to attend physical therapy groups.
Folk remedies are a good addition to traditional methods of treatment. The use of certain medications can alleviate the patient's condition and speed up recovery. As a rule, to normalize the function of the gallbladder and improve the outflow of bile, decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs that have a choleretic effect are used. Such herbs include corn silk, calendula, peppermint, chamomile, etc.
Basic treatment
Treatment of a kink in the gallbladder directly depends on the cause of the deformation and the severity of the symptoms. The treatment regimen includes therapy for the underlying disease (cholecystitis, cholelithiasis).
However, even after effective treatment, the bend requires additional therapy aimed at improving the outflow of bile and preventing its stagnation.
If for any reason a person has a congenital or acquired bend of the gallbladder, it is no longer possible to restore its original anatomical shape.
In the absence of life-threatening symptoms, surgical treatment is not prescribed. This pathology may not manifest itself at all and may not reduce the patient’s quality of life.
Typically, therapy for gallbladder abnormalities is aimed primarily at restoring its normal, full functioning. Treatment should pay attention to the main painful symptoms and eliminate them. First of all, it is necessary to establish the process of bile outflow so that its stagnation does not lead to dystrophic changes and inflammation.
Treatment includes medications, following a special gentle diet, consuming herbal remedies and performing gymnastic exercises.
Symptoms associated with bile stagnation can be relieved with choleretic drugs. Medicines help liquefy and dissolve stones, relieve inflammation and activate peristalsis.
The most common choleretic drugs are: Gepabene, Flamin, Odeston, Ursofalk, etc. They have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. These medications can not only eliminate the main symptoms of gallbladder deformation, but also protect it from aggressive influences and infections.
Do you need a diet?
A bent gallbladder is a fairly common problem.
Dietary nutrition is designed to alleviate the main symptoms of the pathology and help restore impaired gallbladder function. The diet involves adherence to the principles of fractional nutrition, which will ensure normal outflow of bile and prevent stagnation. The patient is recommended to eat small portions of 250-300 grams at least five times a day.
The therapeutic diet involves the inclusion of protein products of plant origin, a small amount of vegetable fats and butter in the diet. The consumption of animal fats, products containing essential oils, for example, garlic, onions, radishes, radishes, etc., hot sauces and marinades, vegetable pickles, smoked meats and fish, fatty soups and broths, whole milk, easily digestible carbohydrates, etc. As for the heat treatment of dishes, it is important to give preference to boiled and baked dishes, fried foods irritate the gallbladder and liver and significantly increase the symptoms of the pathology.
It is important to ensure that the patient drinks plenty of fluids. The approximate daily fluid intake is 1.5-2 liters.
Forecast
Pathology should not be underestimated. The bend entails disruption of the function of the bladder and ducts that remove bile into the duodenum. If this liquid does not enter the gastrointestinal tract, normal digestion will be disrupted, which can lead to various diseases of the digestive tract and liver.
With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable: it responds well to treatment and does not lead to the development of various complications. The prognosis of the pathology is unfavorable only when a bend in the body of the organ or an s-shaped bend is diagnosed, when the outflow of bile is completely blocked. In this case, accumulation of bile may occur, overflow of the bladder, followed by rupture of its walls and pouring of bile into the abdominal cavity. Treatment of the pathology involves surgical intervention when the gallbladder is removed.
Thematic video material will tell you about diseases of the gallbladder:
Bends, as well as bends of such a structure as the gallbladder, are characterized by a violation of the anatomical structure of the organ with a general decrease in its functional state. The structure of the gallbladder is divided into three components: the neck, the fundus and the body itself. When filled, the properly positioned gallbladder takes on a pear-shaped shape. The bending condition leads to its deformation and partial or complete change in the correct shape of the bubble. This phenomenon is characterized as an inflection or bend of this organ. This pathological condition often occurs in childhood.
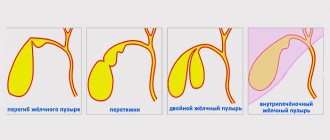
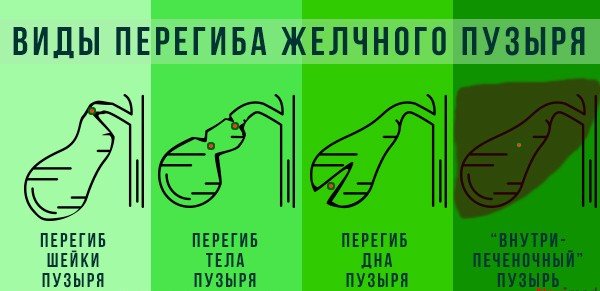
Types of bends
Based on the location of the bend, three types of pathology are distinguished:
- bend between the bottom and body of the bubble;
- bend of the neck;
- double inflection of the gallbladder.
As a result of bending, the organ is capable of forming a wide variety of shapes (hook, figure eight, arc, etc.). So, double deformation has a second name - S-shaped bend of the gallbladder, because at the same time it becomes similar to the corresponding letter.
What is inflection?
Bend of the gallbladder: ultrasound
Excesses in the gallbladder are both congenital and acquired as a result of a number of environmental factors. If it is congenital, the bend can be detected completely in a newborn baby and corrected. Such natural disorders are diagnosed by computer research using an ultrasound procedure. Since children's organs are formed by interacting with each other, a change in the shape of the gallbladder will not interfere with its normal functioning and will not cause any problems. The acquired nature of excesses in the gallbladder must be treated. Most often, treatment is lengthy and labor-intensive.
Twisting resulting from any reason prevents the patient from leading a full life, due to disruption of the outflow of the bile flow and disruption of the digestive tract.
Prevention
There are no special means of preventing cervical bending in medicine yet, but there are several rules that can reduce the risks of development and will also improve the patient’s condition with advanced pathology:
- Completely give up bad habits, especially drinking alcohol.
- Adjust your diet and monitor it constantly.
- Monitor your weight and lose extra pounds if necessary.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle and exercise.
- Don't overeat or starve.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner, especially liver diseases and those that can cause cervical kinks.
- Go through a comprehensive examination with a doctor 2-3 times a year.
When the neck of the gallbladder is bent, the prognosis for each person is individual. If the pathology is congenital, then they are favorable because they rarely cause complications, but you can achieve a positive outcome if you monitor your health.
If the disease is acquired, complications appear more often, and prognoses change significantly, in some cases there may be death.
Why do kinks occur?
As mentioned earlier, this pathology can be congenital or acquired. Birth defects occur under the influence of a person’s genotype and negative factors during intrauterine development. Typically, congenital abnormalities do not cause additional discomfort to a person, and may disappear on their own in childhood. Acquired kinks in the bladder in children can occur for the following reasons:
- prolonged emotional stress in a child;
- excessive physical activity;
- severe obesity;
- violation of proper diet;
- backbreaking physical labor;
- exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis.
In childhood, there is no need to lift excessive weight, as this can provoke prolapse of internal organs and affect the appearance of kinks in the gallbladder. Acquired kinks cause discomfort and must be treated.
Gallstone disease that develops in childhood can also lead to twisting of the bladder. In this case, the gallbladder begins to sag under the influence of gravity of the formed stones and, as a result, an inevitable bend of the cervical part of the organ occurs. In case of this pathology, you should immediately seek advice from a medical institution, otherwise a violation of the outflow of bile formed in the body in most cases leads to problems in the functioning of all digestive organs.
Causes
Considering the fact that when the gallbladder is bent in children, the pathology manifests itself even at the embryonic stage of development, its causes are:
- diseases of viral and infectious etiology previously suffered by the mother;
- taking medications by the expectant mother that negatively affect the fetus;
- presence of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, drugs, psychoactive substances);
- chronic diseases of a pregnant woman;
- environmentally unfavorable environment affecting the health of mother and child.
The occurrence of an abnormal condition in an adult is a consequence of the following reasons:
- disorganized nutrition, its irrationality (the presence of dishes based on frying and smoking);
- the use of diets that exhaust the body with their severity;
- the presence of excess weight, which interferes with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- infections due to food poisoning;
- severe physiological overloads;
- the predominance of a lifestyle in which a person moves little;
- there are diseases - cholelithiasis and cholecystitis;
- operations performed in the area of the deformed organ and liver.
A person who constantly monitors his health and leads a healthy lifestyle has less risk of developing this type of pathology.
Signs of kinks
Compliance with a diet for gallstone inflection is the main condition for treatment
If there are kinks in the gallbladder, the child feels pain at the site of the twisting of the organ. Pain appears in the right side, back and shoulder blades. If, during the bend, bile enters the peritoneum, then severe abdominal pain is felt, moving to the left region. Over time, the pain may subside and then reappear. The child experiences bloating in the abdominal cavity, pain, as well as sudden changes in body temperature and abnormal bowel movements. These symptoms indicate a bend in the cervical region of the bladder.
If the deformation of the gallbladder is caused by the onset of an inflammatory process, then changes in skin color occur, causing it to acquire an earthy tint. Symptoms of pain are associated with the location of the bend. Let's consider the main areas where defects occur, as well as their symptomatic signs:
- If the bend occurs in the border area of the body and the bottom of the gallbladder, then the sick child feels pain in the abdominal region, in the collarbone, sternum and under the scapula. Attacks of nausea and vomiting are frequent, usually occurring after meals. A kind of plaque forms on the outer surface of the child’s tongue, and cracks also appear in the outer corners of the oral cavity. This type of pathology most often occurs in childhood.
- If twisting of the gallbladder occurs in its cervical region, then the most common manifestations of pain in the left hypochondrium, accompanied by nausea and increased gas formation, become apparent.
- There are times when the patient even develops a feverish state. A bend in the neck is the most dangerous and life-threatening, since it is possible for the resulting bile to penetrate into the abdominal cavity, accompanied by the formation of peritonitis in the body.
- If a combined type of inflection is observed, which represents numerous deformations of the gallbladder in its different areas, then the patient experiences severe abdominal pain. Sometimes meals are accompanied by nausea and a gag reflex.
How dangerous is bending for a child?
Unlike the congenital form, the acquired nature of torsion can lead to the development of the following negative consequences for the body:
- increase in liver size
- the occurrence of jaundice
- disruption of normal liver function
- the appearance of chronic diseases of the digestive system
- delay in child development.
At the same time, the resulting bile will accumulate and then stagnate in the body. In this case, there will be no complete breakdown of lipid compounds entering the body with food. The amount of fatty acids in the blood will increase and the rate of glucose oxidation will decrease. The development of diabetes mellitus and, as a consequence, obesity may begin. Fats will not be fully absorbed and a lack of fat-soluble vitamins will develop.
A sick child will experience a general deterioration in vision and weakening of muscle tone, as well as a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels. In addition, if there were inflammatory diseases in the body, chronic cholecystitis will begin to develop. Various types of stones may appear in the bladder, contributing to the development of gallstone disease.