The number of people who suffer from diseases of the digestive tract is growing every year around the world. Focal atrophy of the gastric mucosa is a pathology that leads to the death of the glands that are responsible for the production of gastric juice. With this type of atrophy, disorders that occur in the mucous membrane are pathologically progressive. The insidiousness of this disease lies in the ability of cells in the affected areas to degenerate into malignant ones. Therefore, experts classify focal atrophy as a precancerous condition.
Below we consider the symptoms and treatment of atrophic gastritis.
Main reasons
The gastric mucosa can be damaged under the influence of internal and external factors.

The following can be noted as the reasons for the development of pathological changes:
- long-term use of medications, especially those included in the group of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and hormones;
- inflammatory processes develop on the mucous membrane during gastritis and ulcerative pathology of any form;
- due to drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking, taking drugs;
- penetration of pathogenic microflora into the stomach, in particular the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter, helminthic infestations, etc.;
- incorrect and irregular nutrition;
- nervous shocks, worries, stress, prolonged depression;
- lack of vitamin B by the body;
- thermal damage associated with the consumption of hot food and drinks;
- chemical damage;
- chronic gastrointestinal pathologies;
- acute inflammatory processes developing against the background of exacerbation of diseases such as cholecystitis, pancreatitis, colitis, etc.
After pathological changes begin to occur in the gastric mucosa, a person may experience the following symptoms:
- heartburn;
- belching;
- nausea;
- disturbances in intestinal function;
- vomiting reflex;
- burning in the stomach (begins to intensify after eating)4
- pain syndrome, etc.
Symptoms
The symptoms of focal atrophic lesions are blurred and rather weakly expressed, so in the early stages of the disease patients are not aware of its existence.
Classic symptoms of focal atrophy of the gastric mucosa differ in the degree of intensity and severity:
- Nausea occurs. If this phenomenon occurs frequently and without objective reasons, it may indicate inflammatory processes.
- Changing the stool. Diarrhea or constipation are a sign of a violation of the full process of digestion of food, malfunctions of the intestines.
- Unpleasant sensations in the stomach. After eating, patients complain of a feeling of heaviness, fullness, and pressure in the epigastric region. For this reason, patients suffering from focal atrophy eat poorly and quickly lose weight.
- Flatulence. With mucosal atrophy, food is poorly digested, its remains decompose, which leads to increased gas formation.
- Belching, which is a sign of insufficient production of gastric juice to break down food. There is belching with an unpleasant odor and bitterness. Some patients complain of dry mouth and an unpleasant taste.
- Pain syndrome. Pain in focal atrophic lesions is dull, intermittent, and occurs after eating. In advanced cases, the pain is permanent.
- The appearance of a white coating on the tongue, which is most typical during exacerbations of the disease.
- Weight loss, which occurs due to a weakened general condition of the body and insufficient absorption of food.
The periodic occurrence of 2-3 of the above symptoms should be cause for concern and contact a gastroenterologist.
How to restore the gastric mucosa?
After a person discovers alarming symptoms, he needs to go to a medical facility and get advice. You should make an appointment with a gastroenterologist who diagnoses and treats various gastrointestinal diseases. This highly specialized specialist will first examine the patient and prescribe a set of laboratory and instrumental procedures that will identify the cause of damage to the mucosa, as well as assess the extent of its damage.
To reduce acidity in the stomach, the gastroenterologist will prescribe drugs such as Maalox or Almagel to the patient. They contain antacids, which, after penetrating the organ, begin to create a protective film on its walls, minimizing the harmful effects of aggressive acids.

To speed up the recovery of the mucous membrane, a specialist may prescribe the following drugs:
- Cytotec, reduces the effect of acid (hydrochloric acid) on the walls of the stomach;
- Pepto-Bismol;
- Venter, etc.
Treatment
A gastroenterologist deals with the treatment of chronic gastritis with atrophy of the mucous membrane. If the process worsens, the doctor may prescribe:
- antibiotics to remove Helicobacter pylori;
- drugs that relieve inflammation;
- means that normalize the acidity of gastric juice and improve digestion.
In case of insufficient digestive function, the following are indicated:
- enzymes;
- vitamins;
- minerals;
- symptomatic remedies that normalize stool and eliminate symptoms of flatulence and intestinal dysbiosis.
During the period of remission of the disease it is indicated:
- treatment with mineral waters;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Chronic atrophic gastritis autoimmune . During the progression of the disease, short courses of glucocorticosteroid hormones (Prednisolone in medium therapeutic doses or its analogues).
In the presence of digestive insufficiency and reduced acidity of gastric juice:
- drugs that improve gastric motility - Motilium, Motilak;
- gastric juice;
- diet – table No. 2;
- pancreatic enzymes - Pancreatin, Panzinorm, Creon.
If B12-deficiency anemia has developed, then vitamin B12 injection is also indicated.
Chronic atrophic gastritis with low acidity . If H. pylori is present, a course of antibiotic therapy is required. Depending on the duration of the disease, drug tolerance and the sensitivity of the bacterium itself to antibiotics, the following drugs may be included in the regimen:
- Amoxicillin;
- Bismuth;
- Metronidazole, etc.
What medications can you take to restore the gastric mucosa?
Damage to the gastric mucosa often occurs against the background of the development and progression of the following gastrointestinal pathologies:
- gastritis;
- ulcerative lesions;
- helminthic infestations;
- previous radiation or chemotherapy, etc.
For patients who have been diagnosed with such diseases, gastroenterologists prescribe drugs that restore the mucous membrane. For each patient, medications are selected individually that will accelerate regeneration processes and help improve blood supply to the affected areas of the organ.
Specialists can prescribe the following drugs to accelerate the regeneration of the gastric mucosa:
- Cytotech;
- Misoprostol;
- Lansoprazole;
- Omeprazole;
- Lactobacterin;
- Bifiform, etc.
Patients may be prescribed the following medications to restore the mucous membrane:
- Cymed . This medication is prescribed to patients who have undergone complex therapy for pathologies such as gastritis, ulcers, helminthic infestations, etc. etc.
- Regesol . This drug is able to restore the mucous membrane of the stomach, oral cavity, intestines, and esophagus.
- Venter . It is usually prescribed to patients diagnosed with ulcerative pathology, gastritis accompanied by an increased level of acidity, and reflux.
Rehabilitation after taking antibiotics
If the patient was treated with antibiotics for a long time, then pathological changes occurred in his gastric mucosa.
To restore it, gastroenterologists make the following appointments:
- prostaglandins are prescribed;
- reparants are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at healing injured areas of the mucosa;
- diagnostics are carried out to identify pathogenic microflora, in particular the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter.
Recovery for gastritis
With a pathology such as gastritis, a person’s gastric mucosa is damaged, as inflammatory processes develop in it, which can lead to the appearance of erosions and ulcers.
The task of the gastroenterologist is to select the most effective medication regimen for the patient, which will include targeted drugs:
- creation of protective mucus;
- enveloping the walls of the stomach;
- acceleration of regeneration processes;
- restoration of mucosal epithelial cells;
- decreased production of hydrochloric acid, etc.
Restoration of beneficial microflora

For people who have gastrointestinal pathologies, which are accompanied by both increased and decreased levels of acidity, gastroenterologists prescribe drugs that can restore beneficial microflora.
The following appointments are made for this category of patients:
- normalization of diet;
- diet;
- taking medications whose action is aimed at suppressing or activating the process of hydrochloric acid production;
- taking prostaglandins and reparants;
- taking proton pump blockers, etc.
Classification
This disease has a specific classification:
- Focal atrophy of the gastric mucosa is characterized by the appearance of pathological foci in the connective tissue in place of the dead glands of the inner lining. The lesions have different sizes and shapes; their morphological structure and appearance resemble an atrophic scar on the skin of the face - a pink, flabby area with noticeable borders. Focal atrophy is dangerous because there are often no symptoms during its development.
- Focal atrophy of the mucous membrane of the antrum of the stomach is a type of pathological process that is characterized by damage to the distal part of the stomach and the death of the glands responsible for the production of hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As a result, the walls of the stomach begin to become inflamed. With an old course, bacterial damage and the development of ulcers may occur.
- Moderate atrophy, which can be mild, severe and moderate. A weak one is characterized by a slight change in the main glands. For moderate, negative measurements are more significant, in addition, the formation of pathological areas is observed. Severe atrophy is characterized by extensive necrotic lesions.
How should you eat?
When treating various gastrointestinal pathologies, patients must follow a diet. In this case, they will be able to quickly stop all inflammatory processes and accelerate the regeneration of epithelial cells of the mucosa.
It is extremely important to follow the following recommendations from specialists during drug therapy:
- It is necessary to give up all addictions, smoking, and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- All harmful foods are excluded from the diet.
- Patients should avoid fried, spicy, salty, smoked, fatty and peppery foods.
- It is strictly forbidden to snack on the go, consume fast food, sweet soda, instant foods or those with a long shelf life.
- Patients' diets should include boiled and grated vegetables.
- You can eat meat and fish dishes cooked in a double boiler.
- It is useful to introduce low-fat dairy products into your diet.
- It is recommended to drink jelly, herbal infusions, and mineral water (medicinal) daily.
- Without fail, the patient’s menu must contain a sufficient amount of fruit (it is recommended to be subjected to heat treatment), from which the body will receive the necessary vitamins.
Nutritional Features
Diet plays a very important role in the treatment of focal atrophic gastritis. The basic principle is gentle, fractional nutrition. It is preferable to steam food. You should not eat food that is too hot or cold, which will injure the walls of the organ. The basis of the diet should be:
Fatty foods, canned food, foods with vinegar and spices, carbonated drinks, and artificial juices are prohibited.
Restoring the mucous membrane with folk remedies
To restore the gastric mucosa at home, people should use the most effective folk recipes:
- Plantain leaves are collected , after which they are thoroughly washed and dried with a rag or paper towel. The juice is squeezed out of this herb and should be drunk 1 tbsp. 20-25 minutes before meals 3 times a day. It is recommended to dilute a single dose of juice in boiled water (50 ml) before taking it.
- You can restore damaged mucous membranes using special herbal tea . You can make a healing collection yourself. To do this, you should purchase the following types of herbs (dried and crushed) at any pharmacy: marshmallow rhizome, St. John's wort leaves, chamomile inflorescences. 10g of each type of herb is placed in an enamel or glass container, then poured with boiling water (1 tbsp). The container is moved to a water bath, where the healing mixture should simmer for 20-25 minutes. Once the time has expired, the dishes are removed and left on the kitchen table until the mixture cools. The contents of the container are filtered, the herb is squeezed out, and the resulting liquid is diluted with boiled water to a volume of 200 ml. Patients should drink this decoction half a glass 3-4 times a day.
- Healing jelly made from flaxseed . To prepare this healthy drink, you need to proceed as follows. A tablespoon of flaxseeds is poured into a deep glass bowl, after which they are filled with hot water (1 tbsp). The contents of the container should be beaten with a mixer for at least 5-7 minutes. A pinch of chicory (ground) is added to the mixture, after which it is beaten for another 1-2 minutes. The patient should drink the finished drink immediately after preparation, after which he should have a meal. If he is not allergic to beekeeping products, then a small amount of natural honey can be added to flaxseed jelly, which will significantly improve its taste and benefit the regenerating mucous membrane.
- From home agave, whose age ranges from 3-5 years, several lower leaves are cut off. They should be washed from dust, wiped with a towel and wrapped in film (food film). After this, the bundle is placed in the refrigerator for 14 days. After 2 weeks, the leaves are removed from the film and the juice is squeezed out of them. This healing drink should be drunk 1 tsp. before meals, 3 times a day. It is allowed to mix the juice with a small amount of bee honey.
How to choose a medicine
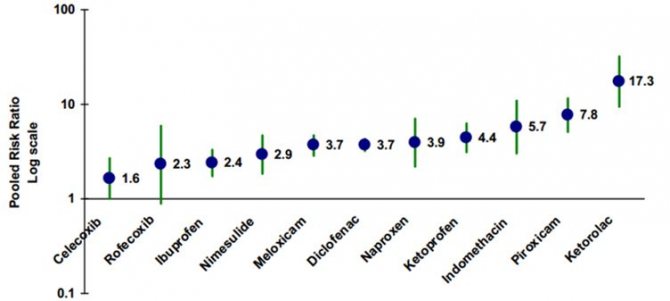
In fact, the most important point is which medications we take. In the figure you can see the scale of aggressiveness of various drugs from the NSAID group in relation to the stomach.
The most aggressive drugs are Aspirin, Ketorolac, Piroxicam, Indomethacin. If possible, it is recommended to use selective drugs that have minimal gastrointestinal risks. Their use is always more desirable, these include Celecoxib and Rofecoxib. But despite their relative safety, they should be prescribed strictly according to indications by the attending doctor, do not forget about this.
Main reasons
It is very often observed that if food lingers in the stomach for a long time, the most likely reason for this may be frequent overeating, snacking during work hours or on the go, unhealthy food or fast food, inclusion of poorly combined foods in the diet, chronic diseases of the esophagus. It is clear that stress, depression and daily hassles also have a significant impact on health.
A predisposing factor to the development of morning dyspepsia is a late dinner or a high-calorie meal before bedtime. The stomach, like, in fact, the entire body, must rest. Those elements of food that have not been digested remain in the stomach until the morning.
As a result, after a person wakes up, he is in an unhealthy state, feels heaviness, has a headache, and is generally depressed.
Why do people's hemoglobin levels drop? Why are pharmaceutical drugs not always helpful, and sometimes even harmful, and how to avoid this? How to easily increase hemoglobin at home? You will learn all this in this article.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin
How can a person determine a decrease in hemoglobin? First of all, this is the presence of asthenic symptoms: the patient feels general weakness, quickly gets tired, drowsiness, dizziness, and headaches are possible. disturbances in heartbeat and blood pressure (reduced). In severe cases, patients may experience fainting.
When a decrease in hemoglobin is a consequence of a lack of iron in the body, degenerative symptoms are noted: the skin is dry, cracks form in the corners of the mouth, nails and hair become brittle, fall out, and grow back slowly. Smell and taste disturbances may occur.
chronic iron deficiency anemia;
blood loss;
thinning of the gastric mucosa (chronic atrophic gastritis);
long-term infectious diseases (hepatitis, gastroenetrocolitis, tuberculosis, pneumonia, kidney inflammation, etc.);
malignant blood pathologies;
malignant tumor lesions, especially of the gastrointestinal tract.
Hemoglobin determination
Hemoglobin is a complex compound of iron and protein. It is found in erythrocytes - red blood cells.
Hemoglobin performs the most important function for the body - the transfer of oxygen molecules to all organs and tissues. It captures oxygen in the lungs and carries out further oxidation, transferring it to all necessary structures.
Oxygen is necessary for the body to ensure vital functions, obtain and exchange energy and carry out recovery reactions.
Let's try to figure out why the stomach hurts after drinking alcohol and what needs to be done to prevent it from hurting. Let us remember the formula of ethyl alcohol: C2H5OH. Any alcoholic drink includes ethyl alcohol (ETHANOL), it is a potent drug that causes excitement. Agree, few people think about the fact that when we buy our favorite red wine or light beer, we are buying drugs.
Ethanol is a serious toxin that destroys the body at the cellular and molecular level. Ethanol molecules damage organ molecules in the body.
Damaged cells die. Some people love white wine, some red, some prefer cognac, some like to mix red with white and something else, but in the end we deliberately poison our body.
It doesn’t matter whether it’s red or white, champagne or martini, vodka or beer, any alcoholic drink is poison.
Once in the stomach, ethanol damages the protective mucous layer. A specific burn forms on the walls of the esophagus and stomach. At the same time, hydrochloric acid, which is released in the stomach to digest food, destroys the walls of the stomach. In places where a burn has formed, the stomach, along with food, digests itself. Hence the pain.
Most people cannot find time to sit quietly and eat. Frequent snacking on the run leads to various gastrointestinal diseases.
Heaviness in the stomach after eating: causes and treatment. This symptom significantly worsens a person’s quality of life and indicates systemic failures within the body.
Most common reasons
Every person has experienced heaviness in the stomach in their life. In this regard, the reasons for the appearance can be very diverse.
The gastric mucosa can be damaged under the influence of internal and external factors.
The most effective drugs for the treatment of reflux esophagitis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) has become a massive epidemic in the 21st century. Every third resident of developed countries has had the misfortune of experiencing symptoms of inflammation of the esophagus. Doctors believe that the development of new effective drugs for the treatment of reflux esophagitis is a priority task of modern pharmacology.
Goals and methods of conservative treatment
Drug treatment of reflux inflammation of the esophagus is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, reducing the severity of external manifestations, and recovery of the patient.
To successfully treat GERD with medications, you must:
- increase the obturator ability of the cardiac sphincter;
- eliminate motor disorders of the esophagus and stomach;
- normalize the acidity of gastric juice;
- restore the balance between protective mechanisms and aggressive factors of the esophageal mucosa.
Treatment of reflux with medications takes place against the background of changing eating habits, quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages, and observing a work-rest regime.
Medicines for GERD are divided into several main groups:
- enveloping agents;
- antacid drugs;
- proton pump inhibitors (pumps) or PPIs for short;
- histamine receptor blockers;
- prokinetics;
- antibiotics;
- enzymes;
- healing agents.
Combinations of drugs are selected in accordance with the underlying disease that caused gastroesophageal reflux.
Enveloping agents
The esophageal mucosa experiences constant irritation and inflammation. The depth of damage to the walls of the esophageal canal depends on the degree of aggressiveness of gastric and intestinal enzymes. Alginates and antacids can protect the esophageal mucosa. Alginates contain a gel-like substance that creates a barrier to the penetration of hydrochloric acid into the esophagus.
Biogel Laminal is made from processed seaweed and contains alginic acid, iodine, selenium, zinc. Removes toxins, accelerates the healing of mucous membranes, relieves pain, and enriches the diet with minerals. Used for GERD for children from 6 years of age, a tablespoon 2 times a day 30 minutes before meals. Adults are recommended two tablespoons. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
Antacids
Antiacid drugs for esophagitis neutralize hydrochloric acid in the stomach by reacting with it. Gels, suspensions, and chewable tablets contain aluminum, magnesium, and calcium salts. New generation products precipitate HCI to insoluble salts, which are excreted unchanged from the body. The most effective preparations combine aluminum and magnesium.
These include:
- Maalox;
- Gaviscon;
- Almagel;
- Rutacid;
- Gastal;
- Rennie.
In addition to the antacid effect, aluminum salts create a protective film, absorb bile enzymes, and increase the tone of the cardiac sphincter. Magnesium salts increase the secretion of protective mucus.
Take symptomatically for heartburn attacks, without exceeding the indicated dosage. The effect of the drugs occurs within 5-10 minutes and lasts up to 3 hours.
Proton pump inhibitors
Treatment of esophagitis is impossible to imagine without proton pump inhibitors. Antacids from this group of drugs disrupt the synthesis of hydrochloric acid at the ionic level, thereby reducing the acidity of the stomach. All proton acidity blockers are benzimedazole derivatives.
The main active ingredients are:
- Omeprazole - drugs Omez, Promez, Losek.
- Pantoprozol – trade names Pantap, Nolpaza, Ulsepan.
- Lansoprazole is commercially available under the name Lantarol.
- Rabeprazole - found in the drugs Beret, Razo, Pariet, Rabeprazole.
- Esomeprazole - considered the most effective PPI, is available in the pharmacy chain as Emanera, Nexium, Ezokar, Neo-Zext.
In-demand inhibitor drugs for the treatment of reflux esophagitis in adults act for 24 hours. Take once a day before breakfast or after meals. Therapy is continued for up to 2 months. Together with antibiotics, they can cure gastritis and stomach ulcers - the original causes of reflux.
Long-term uncontrolled PPI therapy is fraught with complications - nausea, headache, stomach polyps, insomnia, kidney failure.
Histamine receptor blockers
H-2 histamine blockers inhibit the action of histamine. Secretion of HCI occurs in the parietal cells of the gastric mucosa. Secretory cells are located mainly in the fundus.
Histamine is a mediator in the reaction of synthesis and release of hydrochloric acid. The substances in histamine blockers are similar in structure to histamine.
They bind to histamine-sensitive receptors, turning them off temporarily.
Medicines from the group of histamine blockers:
- Lafutidine;
- Cimetidine - analogues Belomet, Simesan, Gistodil, Primamet;
- Roxatidine – marketed as Roxane;
- Ranitidine - found in the drugs Acyloc, Gistak, Zantac, Ranisan;
- Famotidine - can be found under the names Gasterogen, Kvamatel, Ulfamid, Famotel.
The production of drugs for esophagitis has been launched in injection solutions and tablets. Ranitidine is included in the list of vital drugs that relieve allergic manifestations on the lining of the esophagus and promote the healing of shallow damage to the mucosa.
Prokinetics
Prokinetic drugs and acid blockers play an important role in the treatment of esophagitis. The action of prokinetics is aimed at stimulating peristalsis of the antrum.
The process of evacuation of stomach contents into the intestines is accelerated, congestion is eliminated, and the tone of the esophageal sphincters increases. The cardiac sphincter is located at the junction of the esophagus and the stomach.
The intensity and frequency of heartburn depends on the tone of its muscles.
Indications for taking prokinetic medications include nausea after eating, heaviness in the stomach, flatulence, belching, and heartburn. All known trade names of prokinetics are based on the substance domperidone.
Pharmacy chains offer medications:
- Domet;
- Motilium;
- Domstal;
- Domridon;
- Motinorm;
- Passengers.
Use in children over 5 years of age, pregnant and lactating women with caution. Possible side effects are dry mouth, thirst, stool disorders, and menstrual cycle disorders in women.
Since the late 80s of the last century, antibiotics have taken a leading position in the treatment of gastritis, ulcers and their consequences in the form of erosive reflux esophagitis. They fight the cause of erosive lesions of the mucous membrane - Helicobacter pylori.
Elimination of bacterial infection is carried out by the combined effects of penicillins and macrolides. Acid-fast antibiotics for inflammation of the stomach and esophagus - amoxicillin and clarithromycin. Apply 2 times a day.
The dosage is calculated individually, taking into account age, weight, and concomitant diseases. It is preferable to treat reflux with the simultaneous use of PPIs and antibiotics.
Reducing stomach acidity accelerates the healing of ulcers and erosions at any stage of tissue damage.
Candidal fungal infection of the esophagus is treated with Nystatin, Ketoconazole, Fluconazole, Clotrimazole, Miconazole. Candidiasis occurs in weakened, elderly people suffering from autoimmune diseases.
Taking antimicrobial agents can lead to antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Abnormal stool occurs from the death of beneficial microflora in the intestine and its colonization by pathogenic microbes - clostridia.
Prevent imbalance of the symbiotic flora by prophylactic use of probiotics. The most common probiotics are Linex, Eubicor, Acipol, Enterol, Bifiform.
Pharmaceutical drugs are replaced by products with probiotics - acidophilus, bifilux, kefir, fermented baked milk, sauerkraut.
Enzyme preparations
A decrease in the enzyme activity of gastric juice leads to a deterioration in the digestive function of the stomach. In this case, congestion, heartburn, and belching with an unpleasant odor are observed. To digest food, enzyme medications containing pepsin, pancreatin, lipase, amylase, and chymotrypsin are prescribed.
Taking enzymes improves the digestibility of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Preparations are obtained from the pancreas of animals. Prescribe Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal, Creon, Penzital after meals, 2 tablets.
Healing agents
Non-atrophic superficial gastritis has a chronic course, inflammation affects the upper layer of the mucosa. You can relieve swelling and redness of the mucous membrane during exacerbation of the disease with folk remedies. Decoctions of medicinal herbs will gently but effectively restore the integrity of the mucous membrane.
They will accelerate tissue regeneration, healing erosions and ulcers. The best herbal remedies in the treatment of reflux esophagitis are chamomile, sage, calendula, oak bark, and flaxseed. A tablespoon of dry raw material is brewed with 300 ml of boiling water in a thermos and left for 30 minutes. Warm, strained decoction is taken 100 ml three times a day 20 minutes before meals.
Herbal medicine course – 2 weeks.
Nutrition and lifestyle for reflux esophagitis
Treatment of inflammation of the esophagus with medications takes place against the background of a strict diet. Nutrition rules to follow:
- cooking methods - boiling, stewing in water, baking without oil;
- food temperature from 30 to 50°C;
- consistency of food - mashed potatoes, soufflés, pates, pureed soups, boiled porridges;
- meat – chicken, rabbit, turkey, beef;
- fish - cod, hake, pike perch, greenling, pink salmon;
- cereals – semolina, rice, oatmeal, buckwheat;
- vegetables - potatoes, pumpkin, zucchini, carrots;
- fruits - bananas, apples, pears;
- milk – boiled low-fat, low-fat kefir, cottage cheese;
- bread - without yeast, white, yesterday's bread, dried;
- cookies – dry, unpalatable, without additives;
- drinks - herbal tea, rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote, still mineral table water, jelly.
Diet - even distribution of the daily diet into 5-6 modest meals. It is advisable to eat at the same time. Smoking and drinking alcohol is prohibited. Fried, spicy, fatty, salty, pickled foods, and carbonated drinks are excluded.
The mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach is protected as much as possible from thermal, chemical, and mechanical damage. After eating, you should not bend over or lie down for an hour. You should sleep on a raised headboard.
Reflux esophagitis is treated by reducing acidity, eliminating inflammation, and regulating gastric motility. The drugs are combined to achieve optimal therapeutic effect. The effectiveness of medications is increased by diet and avoidance of harmful addictions. The immune system is strengthened by folk herbal remedies and adherence to work and rest regimes.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
to the doctor We recommend: What is the peculiarity of the operation to remove a hiatal hernia?
Source: https://gastrot.ru/pishhevod/lechenie-reflyuks-ezofagit-preparatami
Signs and treatment of a lazy stomach
Gastroparesis, “lazy” stomach syndrome, is a pathological condition characterized by delayed evacuation of food and impaired motor competence of the organ. The disease can provoke a list of symptoms varying in severity and nature. Usually the disease occurs chronically over a long period of time.
Causal series
A lazy stomach, the symptoms of which can quite significantly disrupt the quality of life, is one of the most common reasons for turning to specialists in gastroenterological diseases. The syndrome is also called functional dyspepsia, since in this case the stomach cannot cope with its functional tasks.
Diagnosis of the disease

During the patient’s lifetime, fibrogastroscopy helps clarify the diagnosis. With its help, you can not only examine the mucous membrane, but also take some tissue for examination. Using the histological method it is possible to determine:
- degree of destruction of epithelial cells;
- severity of thinning;
- violation of folding, etc.
Examining the mucous membrane with a gastroscope, a specialist can make a diagnosis:
- the focal form implies the presence of more normal tissue on the lining of the stomach. Treatment in this case is accompanied by success. Compensation is carried out due to the functioning of healthy cells;
- in the diffuse form, the disease affects almost the entire mucous membrane.
According to severity there are:
- Mild degree of damage, in which only 10% of cells do not perform their function.
- Moderate severity, in which up to 20% of cells are affected.
- Severe degree is accompanied by pathology coverage of more than 20% of cells.
Causes and symptoms of low hemoglobin
Some signs help identify stomach diseases:
- Abdominal pain.
- Belching.
- Heartburn.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Lack of appetite.
- Thirst.
- Constipation.
- Diarrhea.
Diagnosis of stomach diseases is carried out by an experienced specialist in a hospital. The disease cannot be determined visually, so the following methods are used:
- Palpation.
- Gastroscopy.
- X-ray of the stomach.
- CT scan.
- Ultrasound.
- Analysis of gastric juice.
- Blood, stool, urine tests.
Causes
To determine how to restore the stomach and intestines, the doctor needs to determine the cause. Problems usually appear due to:
- Unbalanced diet. This often occurs from eating unhealthy foods that cause an imbalance of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. This also affects the production of enzymes and gastric juice.
- Eating disorders. Having quick snacks instead of a full meal is harmful to the body. Often it is for this reason that problems with the gastrointestinal tract appear.
- Bad ecology. The activity of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted due to low-quality drinking water, harmful additives during the cultivation of vegetables and fruits, and the addition of antibiotics.
- Stress. Psychological stress negatively affects the intestines, which impairs the absorption of beneficial components, disrupts motility and secretory function of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Alcohol and cigarettes. According to statistics, 65% of ulcer exacerbations occur due to active smoking. Cigarettes cause spasms of the smooth muscles of the intestines, leading to a malfunction of the motor-motor system of the gastrointestinal tract. Also, due to oxygen starvation, the required amount of valuable components does not penetrate into the gastrointestinal tract.
- Dysbacteriosis after antibiotics. In the body, there is an increase in the number of intestinal fungi, the proliferation of pathogenic microflora and disruption of digestion.
- Genetic factor.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules when preparing food.
Treatment of helminthic infestations
There are many medicines that can be used at home. They allow you to quickly and effectively cure the stomach.
The best medicines
If you have stomach pain, you should take Rennie. It is made in the form of tablets that must be dissolved in the mouth.
The medicine restores healthy gastric microflora, fights infections and harmful microorganisms. It is allowed to take the drug upon reaching 12 years of age, not earlier.
Optimal dosage: 2-4 tablets per day. The duration of taking the medicine is prescribed by the doctor.
If the patient is bothered by heartburn or feels pain in the stomach, he should take the drug Gastal. It is made in the form of tablets that need to be dissolved in the mouth.
The medicine fights harmful microorganisms that cause stomach diseases. You can take up to six tablets per day.
You are allowed to take one tablet at a time. The best time to take is an hour after eating.
The duration of treatment should not exceed two weeks. The drug should not be used before the age of six.
Soothing for gastritis

The occurrence of gastritis of the stomach is characterized by the appearance of a number of unpleasant symptoms. The patient's condition with gastritis can be extremely serious, so it is important to prevent it. First aid for gastritis is aimed at eliminating pain: the patient is prescribed bed rest, an enema to cleanse the stomach, gastric lavage, administration of antispasmodic drugs, for example, noshpa, plenty of fluids to drink and a gentle diet. Sedatives for gastritis will be described in more detail in the following material.
What medications should I take after gallbladder removal?
Removing the gallbladder is called cholecystectomy. The operation can eliminate many problems with the biliary system and improve the condition, subject to proper treatment during the rehabilitation period. Therapy is carried out comprehensively: medications, diet, and a course of exercise therapy. Your doctor will tell you what medications to take.
Recovery after bladder surgery is an important and integral part of the patient’s treatment.
Consequences of the operation
After cholecystectomy, the functioning of the digestive system is disrupted, since the main organ that regulates the amount of bile is removed. This is manifested by pain in the upper abdomen and on the right under the ribs.
Common symptoms of this condition are:
- sharp, paroxysmal pain in the abdomen;
- constant nausea;
- flatulence;
- hologenic diarrhea;
- gastric dysfunction;
- hepatic colic;
- obstructive jaundice.
Damage to the gastric mucosa often occurs against the background of the development and progression of the following gastrointestinal pathologies:
- gastritis;
- ulcerative lesions;
- helminthic infestations;
- previous radiation or chemotherapy, etc.
For patients who have been diagnosed with such diseases, gastroenterologists prescribe drugs that restore the mucous membrane. For each patient, medications are selected individually that will accelerate regeneration processes and help improve blood supply to the affected areas of the organ.
Specialists can prescribe the following drugs to accelerate the regeneration of the gastric mucosa:
- Cytotech;
- Misoprostol;
- Lansoprazole;
- Omeprazole;
- Lactobacterin;
- Bifiform, etc.
How to replace foods if you are intolerant
Some people who suffer from gastritis may also be vegetarians or have allergies or food intolerances such as lactose or gluten. In this case, it is necessary to find a replacement for those products whose consumption is recommended for gastritis, for example:
- Milk and yogurt: Those who are lactose intolerant or vegetarians can replace milk and yogurt with similar soy or rice milk-based products.
- Cheese: If you are on a vegetarian diet or are lactose intolerant, you can replace the cheeses with tofu, which is derived from soy.
- Cereals: People with gluten intolerance can replace bread and pasta with similar products made from rice or corn, or commercially available gluten-free products.
- Meat and fish: A vegetarian or vegan diet excludes the consumption of meat and fish. In this case, you can use rice and legume based dishes.
Separate meals: recommendations
If food is retained in the stomach, separate meals will help normalize its condition. It helps reduce the body’s costs for digestion and then it becomes possible to find out which foods or foods provoke the imbalance.
According to the theory of separate nutrition, proteins and carbohydrates cannot be included in one meal, but fats can be combined with proteins and carbohydrates.
This is the main, but not the only rule. There are many nuances in separate nutrition. Also, do not forget about the time it takes to digest one or another food; it is important not to eat food with different digestion times at the same time.
For example, if you eat almonds with oranges, in addition to making it difficult to choose the right enzymes, the incompletely digested fruit will remain in the stomach for several hours along with the nuts. But, for example, if you include oil in a vegetable salad, the food will stay in the stomach longer by about two to three hours.
You need to be careful with liquids. Many people are accustomed to drinking hot tea or coffee immediately after eating, and this has a bad effect on the stomach. This hot liquid washes away gastric juice, which causes food to remain in the stomach for a long time. Therefore, in order not to provoke such a problem as stomach pain, it is important to prepare the drink in advance so that it is consumed approximately 15-20 minutes before meals.
This is explained by the fact that in a warm state it is easier for the stomach to digest food. Therefore, to avoid heaviness in the stomach, you should be careful with both food and liquids.
When treating various gastrointestinal pathologies, patients must follow a diet. In this case, they will be able to quickly stop all inflammatory processes and accelerate the regeneration of epithelial cells of the mucosa.
It is extremely important to follow the following recommendations from specialists during drug therapy:
- It is necessary to give up all addictions, smoking, and drinking alcoholic beverages.
- All harmful foods are excluded from the diet.
- Patients should avoid fried, spicy, salty, smoked, fatty and peppery foods.
- It is strictly forbidden to snack on the go, consume fast food, sweet soda, instant foods or those with a long shelf life.
- Patients' diets should include boiled and grated vegetables.
- You can eat meat and fish dishes cooked in a double boiler.
- It is useful to introduce low-fat dairy products into your diet.
- It is recommended to drink jelly, herbal infusions, and mineral water (medicinal) daily.
- Without fail, the patient’s menu must contain a sufficient amount of fruit (it is recommended to be subjected to heat treatment), from which the body will receive the necessary vitamins.
How is the disease detected?
Previously, it was possible to detect pathology in the stomach only as a result of a post-mortem autopsy. At the moment, diagnosis is also made visually, by fibrogastroscopy. Modern technologies make it possible not only to notice the disease, but also to collect samples of affected tissue for histological examination.
Fluoroscopy is an effective method for detecting gastric atrophy
It is not enough to simply record atrophy; it is also necessary to know the stage of damage, the duration of pathological processes, volumes and localization. In accordance with how large the atrophied territory of the organ is, it is distinguished:
- focal - small areas of diseased tissue alternate with healthy ones, a favorable outcome is more likely;
- diffuse atrophy - the process has affected the entire stomach or some of its parts.
There are also three stages of the disease, depending on the number of transformed cells:
- Severe - more than 25% of the epithelium has turned into scar tissue.
- Medium – no more than 20% of the mucous membrane is affected.
- Mild – 10% of cells function incorrectly.
Table 2. Histological changes in atrophy
| Subatrophy | Moderate | Expressed |
| Glandular cells slightly decrease in number, shorten slightly, additional granulocytes are diagnosed, in which a secretion is formed. Some cells are replaced by mucous, mucocytic cells. | More than half of the glandular cells have been replaced by mucus-forming cells, areas of healthy epithelium are surrounded by infiltrate, and sclerotic foci appear. | There is a minuscule number of healthy glandular cells, the mucous membrane is inflamed, foci of infiltration and sclerotic areas are extensive, metaplasia is possible. |
In addition to gastroscopic examination, other types of diagnostics are prescribed to determine the severity of the disease. In particular, daily pH-metry is carried out, during which the nature of acid formation is revealed and a test for gastrin 17. This is a hormonal substance with the help of which endocrine regulation, restoration of epithelial cells, motility and restoration of stomach tissue take place.
A marker of the existence of atrophy is also considered to be a study that reveals the ratio of pepsinogen I and pepsinogen II in the body - these are protein components with the help of which hydrochloric acid is produced. This ratio shows the remnants of intact, functioning immune cells in the stomach. Blood tests for antibodies to Helicobacter and Castle factor are also necessary.
Timely diagnosis allows you to cure atrophy or significantly reduce the danger
Causes of damage to the mucous membrane
The lining of the stomach consists of several layers.
The inner surface of the organ is lined with epithelium (loose tissue). This layer protects the walls of the digestive organ from pepsins (enzymes contained in gastric juice). Enzymes break protein molecules into small fragments (amino acids). Without the inner loose layer, pepsins will begin to destroy the walls of the stomach, just like food.
The layer lying under the inner one is connective tissue. Between the fibers there are glands that open directly into the cavity of the digestive organ. The function of these glands is to produce hydrochloric acid.
The mucous membrane of the main digestive organ also includes glands and connective tissue.
It is clear that the thickness and integrity of the epithelial layer is important for the healthy functioning of the stomach.
When damage, thinning or inflammation of the mucous membrane (gastritis) occurs, the stomach ceases to cope with its functions. This process causes the following symptoms:
- vomiting and nausea;
- heartburn and belching;
- a burning sensation that intensifies after eating.
Alcoholic drinks and some medications (aspirin, etc.) irritate the mucous membrane and can “break through” the epithelial barrier.
In healthy people, the inner layer is most often restored within 24 hours. But if the body is weakened, there are infections or concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastritis, then the situation changes radically. In the latter cases, the epithelial layer is restored very slowly, erosions of the stomach appear, the inner layer becomes thinner over time, and in certain places disappears altogether.
Atrophic changes
If the situation described above occurs, then we are talking about atrophy of the gastric mucosa. Atrophy is a serious disease that can cause an oncological process in the body.
Atrophy can be caused by the following factors:
- nervous breakdowns;
- Helicobacter bacterium;
- lack of vitamin B in the body;
- long-term drug treatment, especially antibiotics;
- eating unhealthy foods and drinking too much alcohol;
- acute inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract and intestines: cholecystitis, gastritis, colitis, etc.
Without eliminating the irritating factor, it will not be possible to restore the gastric mucosa. The digestive organ must “rest” and then recover.
The recovery process starts when taking dietary supplements and medications, but only a gastroenterologist can prescribe a course of treatment.
Erythematous gastropathy with focal atrophy of the gastric mucosa
Erythematous gastropathy refers to redness of the gastric mucosa, which may be accompanied by swelling, bleeding and excessive mucus production. A similar sign is determined when examining the stomach using an endoscope - fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Hyperemia of the mucous layers of the stomach is provoked by some unfavorable factors, for example, spicy, rough and too hot foods. Under the influence of the causative factor, microcirculation is activated in the affected areas of the stomach, which gives it a bright red color.
Not everyone knows what atrophy of the gastric mucosa is.
Diagnostics
A gastroenterologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective drug treatment after a series of diagnostic examinations. The patient is diagnosed based on a blood test (general and biochemistry), ultrasound, as well as gastroscopy, endoscopy, histology, etc.
The most effective method of examination is endoscopy. The doctor examines the mucous membrane, checks the acidity of the stomach and the functioning of other gastrointestinal organs. Using endoscopy, you can determine the degree of development of gastritis. The acidity of mucous secretion is determined by testing.
The gastroenterologist performs a visual examination of the patient and records his complaints. The doctor can clearly determine the type of illness if the patient tells him what exactly is bothering him. After a detailed analysis of complaints and a visual examination, the doctor prescribes treatment and diet that will help relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane and restore the organ after gastritis.
A balanced, properly selected diet helps prevent and cure gastritis. Bad habits can irritate the mucous membrane, so the patient is advised to give up alcoholic beverages and smoking.
It is advisable to exclude junk food from the daily menu. Minimize the consumption of vegetables, cabbage and mushroom dishes, as well as greens.
The list of dishes is determined by the doctor. You need to eat often, but in small portions.
Food should not be too cold or hot. The food should be dominated by fish, lean meats and plant foods.
You should also exclude from the menu food items that have been in the refrigerator for a long time. Eating fast food is strictly prohibited.
You can only eat dishes that are prepared 3-4 hours before the meal, and only from high-quality products.
Diagnostic measures
If you suspect focal atrophic gastritis, you should contact a gastroenterologist. The specialist collects anamnesis, finds out the patient’s complaints, and the intensity of symptoms.
Diagnosis of atrophy of the gastric mucosa should be comprehensive:
- Detailed and general blood tests, urine tests with determination of protein volume, leukocytes.
- A coprogram, which is a stool test showing how much food is digested and how nutrients are absorbed.
- For the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection - breathing tests, morphological techniques.
- Using an endoscope is a reliable technique that allows you to visually assess the severity and type of atrophic lesions.
- Biopsy of stomach tissue, histological studies, which allow us to determine the stage of morphological changes in the mucous membrane.
- Ultrasound of the liver and pancreas, since with atrophic lesions of a focal nature, their activity may be impaired.
How much stool is needed for analysis? This is indicated by the attending physician when writing a referral. In addition, the following studies are being conducted:
How much stool is needed for analysis in a child, infants and adults? The measure will be almost the same. To do this, use a special sterile container, which can be purchased at the pharmacy. It is sealed and the set includes a spoon. There are marks on the container.
The volume of feces for adults will be no more than the size of a walnut. 15 grams of formed stool is enough to collect for a child.
How to treat atrophy of the gastric mucosa?

Preparations for the restoration of gastric epithelium
Medicines for restoring the epithelium of the stomach belong to different pharmacological groups, but have a similar principle of action: in order for the process of restoring the inner layer to start, it is necessary to improve blood circulation in the walls of the stomach.
The drug Cymed has proven itself well, which restores the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract during gastritis and ulcers, acute and chronic inflammatory processes, as well as after infection with parasites.
In addition, Cymed has a beneficial effect on muscles and blood vessels. It is recommended to take the drug 2 times a day. The course of treatment is a month.
The drug Regesol consists only of natural ingredients. The medicine restores the mucous membrane of the entire gastrointestinal tract, as well as the oral cavity and duodenum. The drug reduces the inflammatory process in gastritis, relieves pain and has an antimicrobial effect. The treatment regimen is the same as that of Tsimed.
Venter is a medicine prepared on the basis of sucralfate. In the digestive organ it breaks down into sulfur salt and aluminum. Sulfur salt fixes the mucous secretion in those places of the organ where the epithelial layer is severely damaged or completely destroyed due to gastritis. Duration of protection – 6 hours. The course of treatment is 10 days.
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Tsimed | specify | |
| Regesol | specify | |
| Venter | from 352 rub. |
The medicine is used to protect the upper gastrointestinal tract from erosion, as well as for treatment of exacerbation of ulcers.
Recommended products for those suffering from gastritis
People suffering from gastritis are recommended those foods that do not increase inflammation in the stomach, that do not stimulate additional secretion of hydrochloric acid and that cause a decrease in the secretion of gastric juice.
Recommended products include:
- Milk: It is recommended to consume low-lipid (i.e. reduced fat) skim milk. Milk is an alkaline food, it reduces the acidity of gastric juice and relieves symptoms. However, milk should not be consumed too often, once a day is enough.
- Dairy products: Some low-fat cheeses, such as ricotta cheese, are indicated for gastritis as they reduce stomach acidity. Just like yogurt, preferably made with skim milk, helps reduce stomach acid.
- Grains: Bread, pasta, rice, and grain-based products such as biscuits, crackers, cookies, and crispbreads can help you reduce stomach acid and reduce symptoms.
- Vegetables: cooked vegetables promote digestion, as they do not scratch the walls of the stomach and do not aggravate the inflammatory picture; carrots, potatoes, artichokes, beets, zucchini, asparagus, green beans, and dill are recommended.
- Fruits: Preference should be given to low-acid and ripe fruits to avoid increasing stomach acidity, such as bananas, apples, pears, peaches. You can also drink juices, subject to the same conditions.
- Meat: It is preferable that it does not complicate digestion. Therefore, it is best to eat chicken, turkey, rabbit and white meat.
- Sausages: Choose reduced-fat sausages such as ham, turkey breast and beef jerky. However, in any case, they should be consumed in moderation due to the content of preservatives, which can be irritating.
- Fish: lean fish is preferred, which does not burden the digestive processes. Among them we note cod, flounder, sea bream, and trout.
- Legumes: If legumes do not cause bloating problems, then they can also be consumed. However, it is recommended to consume them boiled and without the peel to ease the digestion process.
- Eggs: Consumption of eggs for those suffering from gastritis is not recommended, however, soft-boiled or poached eggs are allowed.
- Drinks: preference for water and red wine. Barley coffee is also allowed.
- Seasoning: It is recommended to use olive oil as the only seasoning.
Treatment of the gastric mucosa using traditional medicine methods
Damaged epithelium can be restored using traditional medicine, including:
- infusions and decoctions based on medicinal herbs (St. John's wort, celandine, chamomile and yarrow);
- decoction of flax seeds;
- potato and cabbage juice;
- infusions of plantain and parsley root - for low stomach acidity.
Jelly made from flax seed with the addition of chicory helps restore the epithelium.
To prepare a medicinal drink you will need a liter of water, 3 tbsp. spoons of flax seeds, coffee spoon of chicory (condensed). Flax seeds should be poured into a mixer and poured with a liter of hot water. Beat for ten minutes and then add the chicory.
You need to drink the drink warm 30 minutes before meals from one to three times a day, you can add honey. By using medications or traditional medicine for restorative purposes, you can not only get rid of the irritating factor, but also start the body’s own recovery processes.
But before starting a course of treatment for gastritis, you should definitely consult a gastroenterologist.
Related video: Symptoms and treatment of atrophic gastritis
Therapeutic measures
Properly prescribed treatment for focal atrophic gastritis can significantly improve the patient’s condition. To cure and restore the mucous layers of the stomach is the main goal of such therapy, the effectiveness of which directly depends on the reasons that provoked the development of this disease.
If the pathology has developed against the background of Helicobacter pylori infection, inhibitors and antibacterial drugs are prescribed. A one-week therapeutic course is usually sufficient to destroy this bacterium.
The main groups of medications used in the treatment of focal atrophic lesions:
In advanced cases of the disease and precancerous conditions, therapy through surgical intervention is indicated.
Secrets of regeneration of the intestinal mucosa
Increase the amount of digestive enzymes
None of us even think about our digestion until problems start and we experience discomfort, gas, inflammation or even irritable bowel symptoms.
We must remember that the process of digestion begins the very moment we select the food that we then put into our mouth. To protect and strengthen our intestinal mucosa, it is necessary, firstly, that a sufficient amount of digestive enzymes be released.
Thanks to them, the digestion process will go much better and we will help the cells of the intestinal wall to select the nutrients we need, which then enter our blood.
Follow Econet on Pinterest!
Look out for foods that may help your body produce more digestive enzymes:
- Raw vegetables: celery, broccoli, parsley
- Papaya, very suitable, for example, for people whose pancreas does not produce enough enzymes
- Pineapple, ideal for reducing inflammation
- Kiwi
- Grape
- Honey
Cleanse the intestinal mucosa
The layer of harmful bacteria that adheres to the intestinal lining and prevents us from absorbing nutrients adequately is called a “biofilm.” How to solve this problem? These tips will help you:
- Drink two liters of water a day
- Start your morning with a glass of warm water with lemon juice
- Eat red fruits, naturally, without added sugar
- Drink parsley and dandelion infusions
- Eat whole grains rich in carbohydrates: brown rice, buckwheat, oats
- Add flaxseed to your food, you can sprinkle it on your food
- Eliminate sugar, dyes, sugary drinks and unhealthy fats
- Do some form of physical activity every day: walk, bike, swim