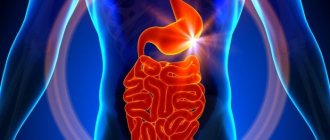
Duodenal ulcer is a chronic disease that is characterized by the presence of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the intestinal wall, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region after eating, and seasonal exacerbations (in spring and autumn). Has a tendency to relapse.
According to medical statistics, the pathology most often occurs in men aged 20–50 years.
Kinds
There are several classifications based on different characteristics. Pathology is classified according to a combination of the following signs:
- acute with bleeding;
- acute with perforation;
- acute with perforation and bleeding;
- acute without bleeding or perforation;
- chronic or unspecified form with bleeding;
- unspecified or chronic with perforation;
- unspecified or chronic with bleeding and perforation;
- unspecified or chronic without perforation and bleeding;
- unspecified, as acute, or chronic without bleeding and perforation.
By frequency of exacerbations:
- with rare exacerbations - acute symptoms occur no more than once a year;
- with frequent exacerbations - more than once a year.
By educational status:
- scarring;
- remission;
- active exacerbation.
Due to the occurrence:
- shock – occur as a result of burns, injuries;
- hormonal – appear after long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- stressful – develop due to depression and strong negative experiences.
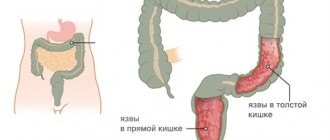
According to the number of formations, multiple and single ulcers are distinguished, and according to the depth of the lesion - deep and superficial.
By localization, ulcers are determined in the post-bulb and bulbous (expanded part of the intestine) sections.
Causes
Causes of duodenal ulcer development:
- Helicobacter Pylori infection.
- Increased acidity of gastric juice. Acid disrupts the integrity of the duodenal mucosa.
- Regular intake of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and hormones.
In addition to direct causes, there are factors that significantly increase the risk of pathology. These include:
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- violation of diet and consumption of large amounts of unhealthy foods;
- binge eating;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic duodenitis;
- heart and vascular diseases;
- congestion in the portal vein;
- contusion;
- abdominal injuries;
- extensive burns and frostbite;
- lesions of the spinal cord and brain;
- anemia, chlorosis and other blood diseases;
- frequent chemical or thermal strokes;
- disorders of the immune system;
- chronic intoxication;
- psycho-emotional instability;
- syphilis;
- disruption of hormone production (enterogastron, gastrin, secretin);
- consequences of surgical operations (appendectomy, amputation of limbs);
- working the night shift (increases the likelihood of developing the disease by 50%).
Disorders leading to increased secretion of pepsins, hydrochloric acid, decreased production of mucous substances, and impaired motility of the gastroduodenal zone occur for various reasons. These include changes in the autonomic and central nervous systems - they can provoke the formation of ulcers on the surface of the walls, since as a result of their occurrence, the balance between aggressive factors and the body’s defenses is disrupted.
Drug treatment of ulcers. Cost of drugs for treating ulcers
Medicines for intestinal ulcers are taken during periods of exacerbation. The main drugs include:
- antibiotics to reduce the colony of Helicobacter pylori and other pathogens;
- antacids to reduce acidity levels;
- antisecretory agents - drugs to reduce the production of gastric juice.
During an exacerbation, the patient is in most cases in a hospital setting. If he complains of stomach cramps and pain, he may ask for antispasmodic medications; for constipation, laxatives or a cleansing enema. The ulcer should be treated for at least 2-5 weeks.
Medicines that reduce the production of gastric juice
The leading positions in this group are held by proton pump blockers, which slow down the secretion of hydrochloric acid:
- Products based on omeprazole - omez, gastrozole, bioprazole, demeprazole, lomac, zerocid, krismel, zolser, omegast, losek, omezol, omitox, omepar, zhelkizol, pepticum, omipix, promez, pepticum, ricek, orthanol, romsec, sopral, ultop , chelicide, cisagast, chelol.
- Medicines based on pantoprazole - controloc, sanpraz, nolpaza, peptazole.
- Lansoprazole preparations - helicol, lanzap, lansofed, lanzotope, epicure, lancid.
- Based on rabeprazole - zulbex, zolispan, pariet, ontime, hairabezol, rabeloc.
- Esomeprazole - Nexium.
H2-histamine receptor blockers have practically ceased to be used to treat peptic ulcers, as they cause withdrawal syndrome (with abrupt cessation of use, the symptoms of the disease return).
- These are ranitidine (Gistac, Rannisan), famotidine (quamatel, ulfamid, gastrsidine), cimetidine (Belomet).
Selective blockers of M-cholinergic receptors (gastrocepin, pirencipin) reduce the production of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. Used as auxiliary medications for severe pain. May cause palpitations and dry mouth.
Agents that increase the protective properties of the mucous membrane
- Sucralfate (Venter) forms a protective coating at the bottom of the ulcer.
- Sodium carbenoxolone (Ventroxol, Biogastron, Kaved-s) accelerates the restoration of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
- Colloidal bismuth subcitrate (de-nol) forms a film on the ulcer.
- Synthetic prostaglandins (enprostil) stimulate mucus production and cell restoration.
Talcid
Talcid is a powerful antacid drug
A powerful antacid drug that is taken one hour after meals. Typically, adults are prescribed two tablets of the drug, and the number of daily doses is four. It is recommended to chew the pills thoroughly and then wash them down with a small amount of any liquid other than coffee and alcohol. In childhood, you can take 0.5-1 tablet per dose three times a day. The duration of therapy is approximately one month.
Relzer
Drug Relzer
You can take the medication in the form of a suspension or tablets. It is recommended to drink Relzer an hour after meals, as well as before going to bed, to prevent the occurrence of night hunger pains. Adult patients and children over 15 years of age should take 1-2 scoops of the drug four times a day. In tablet form, after 15 years, the drug is taken in two doses, also four times a day. The recommended duration of therapy is approximately two weeks; treatment should not be terminated earlier, even if symptoms disappear.
No-Shpa
No-Shpa tablets for duodenal ulcers
It is taken for severe pain for three to five days. The patient can take up to four tablets per day. There is no need to chew or divide them; wash them down with clean water only. You can take the recommended dose of the antispasmodic at any time, without taking into account food intake. If within three days the pain does not decrease, a mandatory additional examination is required to exclude bleeding and perforation of the ulcer.
Omez
Omez quickly relieves pain and inflammation
Belongs to a class of antibiotics that contain the active substance omeprazole. Quickly relieves pain, inflammation and severe pain associated with duodenal ulcers. If there is an ulcerative lesion, the patient is recommended to take 20 mg of the active substance twice a day for three weeks. If the ulcer has already caused serious health complications, Omez is taken by intravenous infusion of 40 mg per day. The duration of such therapy is strictly individual.
Famotidine
The use of Famotidine helps prevent damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum
A medication whose action is aimed at reducing the acidity of gastric juice, which helps prevent damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. Take 20 mg twice a day for four to eight weeks. If necessary, the patient may be advised to take 40 mg of the active substance once a day just before going to bed. The duration of therapy in this case is also 1-2 months.
Attention! Antacids are strictly prohibited from being mixed with other medications. If it is necessary to take several medications at once, antacids are taken two hours earlier or later.
Symptoms
The signs of an ulcer are similar to many of the symptoms that occur with other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of duodenal ulcer:
- bloating and flatulence;
- belching;
- nausea;
- feeling hungry several hours after eating;
- sharp, piercing pain below the sternum, in the upper abdomen, which can radiate to the heart and back;
- disappearance of pain immediately after eating;
- sleep disturbance due to pain at night;
- weight loss regardless of food intake and calorie content;
- chronic vomiting of blood, which can be fatal.
Cases of asymptomatic disease have been recorded. This form of ulcer most often develops in elderly patients.
With timely diagnosis, relief of exacerbations, and adherence to diet, the prognosis is favorable. It is possible to achieve long-term remission and scarring of the ulcer.
The discomfort that the patient complains about is the reason for conducting a detailed examination and comparing the data obtained with the described symptoms of duodenal ulcer.
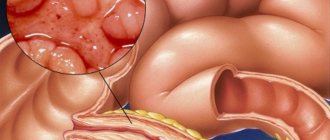
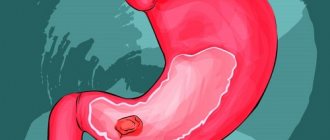
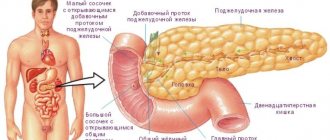
What is a duodenal ulcer
The duodenum (DU) is the initial section of the small intestine in which the absorption of nutritional components occurs.
This part of the organ connects the stomach, the rest of the intestines and the bile ducts. Therefore, the duodenum is most at risk of developing inflammatory diseases. The area remains unprotected from the negative effects of stomach hydrochloric acid, semi-digested food and caustic bile. Peptic ulcer disease progresses over a long period of time due to the alternation of remission with periods of exacerbation. Unlike erosive diseases, which are concentrated on the surface of the mucous membranes, intestinal ulcers penetrate into the submucosal layers. Disease of the duodenum affects the choroid plexuses and smooth muscles of the organ.
The breakdown of the food coma occurs in the duodenum. In the walls of the organ there are glands that actively produce mucous secretions. In response to fatty and acidic stimuli, the release of cholecystokinin begins. With the development of pathological processes, a protective shell of mucus is not formed and the walls of the organ are subjected to aggressive damage from bile and digestive enzymes.
Diagnostics
For diagnosis, a complex of laboratory and instrumental studies is used, which make it possible to determine the pathology, its form and degree of development, and accurately determine the location.
The following methods are used to identify ulcers:
- Endoscopy is the most informative method. Allows you to obtain extensive information about the condition of the mucous membranes, including sampling of tissues and stomach contents for laboratory analysis.
- Test for the presence of Helicobacter Pylori. It is carried out on the basis of material taken from the patient during endoscopy, or feces, vomit, and blood are examined. Breath test.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity.
- Palpation.
- Antroduodenal manometry.
- Fecal blood test (Gregersen test), general blood and urine test, biochemical blood test, gastric juice analysis to determine the level of acidity, histological analysis of the material to determine the malignant nature of the formation.
- X-ray examination using barium suspension.
- Electrogastroenterography.
Differential diagnosis:
- granulomatous enteritis (Crohn's disease);
- stomach ulcer;
- cholelithiasis;
- symptomatic ulcers;
- non-ulcer dyspepsia;
- gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome).
Associated pathologies:
- chronic renal failure;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- reactive pancreatitis;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- Wermer's syndrome.
Diagnostic measures
To make a diagnosis, the doctor needs to interview the patient, identify complaints that bother the patient, the circumstances under which they arose, and the duration of the symptoms. In addition, a number of instrumental and laboratory studies will be required:
- X-ray and fibrogastroscopy to assess the condition of the tissues of the stomach and intestines and detect lesions. Determination of their location and size;
- Blood test for hemoglobin level to detect internal bleeding;
- Examination of stool to determine the presence of a bleeding ulcer;
- Study of gastric juice for hydrochloric acid content to determine the possible cause of the development of the ulcerative process.
History taking and examination
At the first stage, the doctor clarifies the nature of the pain, its duration, conditions of occurrence, and asks about other complaints. During the conversation, he finds out the possible causes of the disease.
The next stage is a general inspection. The doctor assesses the condition and color of the skin and mucous membranes, identifies swelling, measures height, weight, and blood pressure. Then he listens to the heart and lungs. With peptic ulcers, patients often experience disruptions in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system:
- cold damp palms;
- “marbling” of the skin;
- rare pulse;
- low blood pressure.
Next, the doctor begins to palpate (feel) the abdomen. The following symptoms are characteristic of a duodenal ulcer:
- soreness and tension in the abdominal muscles under the xiphoid process on the right;
- pain in this area when tapping with bent fingers.
Laboratory research
- Clinical blood test - no changes in uncomplicated ulcers; decrease in hemoglobin and red blood cells during bleeding.
- Fecal occult blood analysis is the simplest method for diagnosing occult intestinal bleeding;
- Urinalysis, blood biochemistry - without pathology;
- Examination for Helicobacter pylori - blood test (detection of specific antibodies), stool analysis, urease breath test, histology and cytology of the material obtained from the biopsy.
- Daily monitoring of intragastric pH – assesses the secretion of hydrochloric acid. With peptic ulcer disease it increases.
Instrumental methods
- FGDS is the main method for diagnosing the disease. During an endoscopic examination, an ulcer is found, its shape and size are assessed, the stage of the pathology is determined, and a biopsy is taken. In case of exacerbation, the edges of the defect are swollen, bright red, the bottom is covered with a coating of fibrin. With treatment, these signs gradually decrease and the ulcer heals. In the remission phase, scars are visible at the site of the defect.
- X-ray examination with a contrast agent - after taking barium porridge, several pictures are taken. The ulcer looks like a niche of various shapes; the duodenum can be deformed due to scars.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - used if another pathology is suspected. The condition of the liver and pancreas is assessed, cysts, tumors, and infiltrates in the abdominal cavity are identified.
Treatment
Dietary nutrition is important. The patient must always comply with the restrictions, but doctors also allow a zigzag regime, when a strict diet is needed only during the months of exacerbation - in spring and autumn. The rest of the time, it is allowed to eat foods not from the dietary list.
Taking medications is necessary during periods of exacerbation.
For the treatment of duodenal ulcer, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Antibiotics – to eliminate pathogenic bacteria.
- Antacids - to reduce the acidity of gastric juice.
- Antisecretory drugs - to reduce the level of gastric juice produced.
- Antispasmodics – to relieve pain.
Exacerbation of ulcers is treated in a hospital setting. The course takes on average from 2 to 5 weeks, depending on the pathology’s response to therapy.
Surgery is usually required only if there is associated bleeding or a perforated ulcer. In other cases, drug treatment during periods of exacerbation and dietary nutrition are sufficient.
Prescribed treatment
Successful treatment of pathology is getting rid of Helicobacter pylori, which causes inflammation of the walls and lining of the duodenum. In order to heal an ulcer, patients are recommended to take medications that can reduce the secretion of gastric juice and neutralize it. In addition, antibiotics are used. Treatment includes diet and complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages and tobacco products, as well as caffeine.
It is important that the patient is not stressed, as this can aggravate the course of the disease. If there is no proper effect from the therapy and there is a threat of severe bleeding, surgery is prescribed to remove the inflamed area.
The list of mandatory medications that are included in the treatment of ulcers is as follows:
- methandrostenolone and pentoxyl;
- vitamins of groups B, A, and U (methionine);
- methyluracil and retabolil;
- biogenic stimulants, the action of which is aimed at the process of separation and metabolism.
In some cases, treatment of peptic ulcer disease includes physical therapy: paraffin bath, mud therapy, diathermy, and many others. etc. if the patient has a stable stage of remission, then the doctor recommends sanitary-spa treatment.

As mentioned above, the causes of ulcers are the influence of special bacteria that corrode the walls of the organ. Treatment should be comprehensive, consisting of taking medications that can relieve pain. Plus, diet is one of the most effective ways to get rid of the disease. The patient's daily diet must be thought out to the smallest detail.
Hospital treatment and surgery
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, treatment should be carried out in a hospital setting. The first two weeks should include bed rest, the rest of the time - ward rest. The diet should be complete based on fractional meals, the number of meals should be at least 5. The menu must be balanced and mechanically gentle - table No. 1A and 1B, and then No. 1.
Every day the patient must take antacids, astringents, and enveloping agents. In addition, ganglion blockers and antispasmodics, for example, No-Shpa or Papaverine Hydrochloride, may be prescribed. In order to relieve tension and relieve stress and depression, sedatives, bromine-based medications, and tranquilizers are used.
Surgical treatment is mandatory in cases of ulcer perforation, pyloric valve obstruction, or severe bleeding. The surgeon's intervention is an emergency measure, since quite often after surgery dangerous complications can arise - metabolic disorders, frequent bleeding, inflammation.
Features of therapeutic nutrition
A diet for duodenal disease involves not only the correct selection of food products, but also the time of consumption, as well as the method of preparation and portion size. Nutrition for medicinal purposes involves eating meals in fractions. Only by following all the recommendations of specialists and taking prescribed medications can you get rid of the main cause of the ulcer and its painful symptoms. Diet and medications will speed up recovery and improve well-being.

Every patient must remember that they need to eat food at least 5 times a day, the portions are small. It is strictly forbidden to fry foods in oil; the ideal option is steaming with a minimum amount of salt, spices and all kinds of seasonings. You cannot eat food that is too cold or too hot; you must chew each piece slowly and thoroughly. Dinner should be no later than 3 hours before bedtime. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day. The number of calories daily should not be less than 3,000 units.
Permitted and prohibited products
A diet for peptic ulcers must include boiled foods: lean fish, poultry. It is very healthy to drink milk, but not its derivatives - kefir, fermented baked milk, etc. In addition, the following foods and drinks are allowed:
- compotes, juices, still mineral water;
- a variety of vegetables;
- chicken and quail eggs;
- cereals;
- soups based on milk, vegetables and chicken;
- pasta.
Drinks containing alcohol and caffeine are excluded, including coffee and strong black tea. You will also have to avoid eating pickled foods, as well as spicy and salty foods. You cannot eat rye bread, lard and baked goods. The same goes for foods that can damage the mucous membrane: peas, dried fruits, radishes, hard-skinned fruits and beans. In some cases, the basis of treatment is not a mechanically gentle diet, but food intake, characterized by regularity and fractionation. It has been proven that foods containing a large amount of dietary fiber reduce high acidity several times more than refined foods. These include: polished rice, premium flour, and semolina.
The main thing that a patient suffering from painful manifestations of a duodenal ulcer should remember is the correct approach to treatment prescribed by a specialist. You cannot make your own decisions about what to eat and what medications to take. Any medical recommendations about following a diet and taking medications must be fully followed.
Complications
- Perforation of an ulcer is a rupture of the intestinal wall at the location of the wound. Occurs after physical activity or overeating. Accompanied by very sharp stabbing pains, vomiting, nausea, abdominal muscle tension, cold sweat and rapid heartbeat.
- Chronic duodenitis.
- Ulcer malignancy.
- Narrowing of the intestine due to scar tissue.
- Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneum due to perforation of an ulcer.
- Bleeding. Manifested by vomiting like coffee grounds, dark feces.
In the absence of treatment for duodenal ulcer, the pathology becomes a dangerous disease that can lead to death as a result of peritonitis, bleeding or the development of an oncological tumor.
What to do during an attack of peptic ulcer?
If an attack of a peptic ulcer occurs to you suddenly and you do not have the opportunity to call a doctor, then you should follow some rules:
- Provide yourself with peace, take time off from work and lie down. In case of nervous chills, you can take valerian tablets.
- Drink any antispasmodic that is in your home medicine cabinet - no-shpu, papaverine, buscopan or duspatalin. It must be remembered that the first drugs are not selective, therefore, together with smooth muscles, they also dilate blood vessels. This is fraught with a decrease in pressure, so slight dizziness may develop.
- Taking liquid antacids that coat the walls of the stomach and duodenum helps a lot. As a last resort, you can use baking soda, which should be taken literally on the tip of a knife. However, you should not overuse soda, as after a certain time it will cause a new round of hydrochloric acid synthesis and the condition may worsen.
- You can take soft, enveloping foods, such as rice or semolina porridge. On the first day after an attack, you should not eat vegetables and fruits, even boiled ones, as well as fresh bread and meat products (except for boiled poultry). Thick, rich soups are also not recommended, as they can provoke an attack of reactive pancreatitis.
- As soon as possible, you need to make an appointment with a doctor and undergo a full course of treatment for duodenal ulcers.
Features of duodenal ulcer in children
Duodenal ulcers in children can be detected as early as 5–6 years of age. The causes of the pathology are the action of Helicobacter Pylori, psycho-emotional factors and genetic predisposition.
The symptoms do not differ from the signs of the disease in adults, but diagnosis is complicated by the fact that the child, as a rule, cannot explain his feelings. It is typical that children often try to take a comfortable position to relieve pain - pressing their legs to their stomach while sitting or lying on their side.
The disease is also dangerous when it is latent. The lack of discomfort allows the ulcer to progress without proper treatment. A detailed examination of the child can reveal the following signs:
- moderately severe chronic intoxication;
- hypovitaminosis;
- white coating on the tongue;
- pain when palpating the abdomen in the upper part and right hypochondrium.
For diagnosis in children, the method of gastrofibroduodenoscopy is used, and treatment is based on pain relief in the acute period with the help of antispasmodics, antibiotic therapy and dietary nutrition.
What are the symptoms of a duodenal ulcer?
The symptoms of stomach and duodenal ulcers are very close to each other. These are: pain, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, appetite disorders.
- Pain
With ulcers, the duodenum is called late. They occur an hour and a half after eating. Hunger pains that occur if food has not been received for more than 4 hours are also characteristic. A type of such pain is night or early morning, similar to very acute hunger and sucking in the right hypochondrium. The nature of pain may vary from patient to patient. There are stabbing, aching, cutting, sucking or spasmodic pains of varying intensity and duration. In this case, the pain is located in the right half of the epigastric region (bulb ulcer). They can radiate to the right hypochondrium or to the back. With an ulcer located at the end of the intestine, the pain shifts more to the midline of the epigastrium or to its left half. The basis of the pain is a violation of the integrity of the intestinal wall, inflammation and accumulation of under-oxidized metabolic products.
- Heartburn
Features of duodenal ulcer in pregnant women
The pathology worsens most often in the first and third trimesters of pregnancy. Stopping an exacerbation is an important point in pregnancy management, since the disease can lead to serious consequences - the risk of complications in the expectant mother increases.
Diagnosis and treatment are complicated by the fact that pregnancy limits the number of methods used. X-ray diagnostics are contraindicated, as is the use of many medications.
Treatment of exacerbations in pregnant women:
- bed rest;
- fractional meals (small portions 3–6 times a day);
- diet 1–1b according to Pevzner;
- mineral water;
- enzyme preparations (to eliminate bloating).
Women who have suffered an exacerbation of the disease during pregnancy are given preventive treatment 2-3 weeks before the expected date of delivery.
Features of duodenal ulcer in elderly people
According to studies, treatment of ulcers in elderly patients requires a lower dosage.
Surgery is usually required only if there is associated bleeding or a perforated ulcer. In other cases, drug treatment during periods of exacerbation and dietary nutrition are sufficient.
When developing a treatment regimen for older and elderly patients, this feature must be taken into account in order to minimize the intake of medications and facilitate their removal from the body.
Forecast
With timely diagnosis, relief of exacerbations, and adherence to diet, the prognosis is favorable. It is possible to achieve long-term remission and scarring of the ulcer.
Prognosis for different patient groups:
- Elderly patients: the highest percentage of deaths due to complications occurs - callous ulcers, bleeding.
- Juvenile ulcers: the pathology is prone to frequent relapses. The prognosis for recovery is unfavorable.
- Women of childbearing age: high chances of recovery.
The prognosis largely depends on concomitant diseases, household and professional conditions, the location of the ulcer and the characteristics of the clinical course of the disease.