2924
0
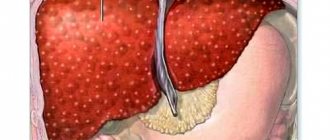
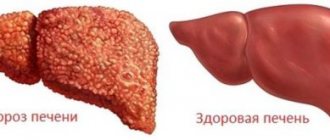
According to statistics, liver cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. It affects women and men equally, has no age restrictions and, as a rule, has a high level of aggressiveness. Its characteristic feature is the frequent formation of a secondary tumor in the organ itself. That is, the appearance of metastases from the primary cancer site. This type rarely has pronounced symptoms of liver cancer, which significantly impairs diagnosis and further treatment. Therefore, cancer is often detected in late stages and one of the first pressing questions becomes how long people with this diagnosis live.
Causes of the disease
To this day, all the causes of cancer have not been identified. But risk factors have been identified that affect the likelihood of developing cancer. Some of them can be changed (smoking), others (the patient's age or heredity) cannot be changed. However, even if several factors are present, it is impossible to say with 100% certainty that you will get hepatoma. The reasons influencing the development of pathology have been established:
- hepatitis (viral, in chronic form) – mutations in gland cells at the genetic level lead to hepatoma, due to viral inflammatory processes;
- Liver cirrhosis is a change in the structure of the gland, as a result of which normal cells are replaced by scar tissue. This leads to the fact that the organ begins to perform its functions poorly. Alcohol, taking certain medications, viral pathology are the most common causes of this disease;
- aflatoxin B1 – if corn, soybeans, nuts, and low-grade rice are stored improperly, the mold fungus aflatoxin B1 develops. This fungus increases the risk of developing hepatoma;
- penetration of parasitic worms into the gland;
- bad habits (drugs, smoking, alcoholism) – abuse of these habits leads to overload and disruption of the filtering organ, since one of its functions is the destruction and removal of toxic substances from the body. This will ultimately lead to hepatoma. There is also a high risk of developing secondary gland cancer from metastases of cancer of the lung, esophagus or stomach, which are also formed due to the abuse of nicotine, drugs and alcohol;
- Excess iron in the body (hemochromatosis) – the body absorbs too much iron, which leads to damage to organs, including the liver. The consequence of this hereditary disease can be cirrhosis, and then cancer;
- Cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis) - the risk of developing pathology increases, since stones injure tissues and interfere with the normal outflow of bile;
- taking steroids (hormonal drugs) - leads to an increase in the load on the filtering organ, as a result of which the likelihood of developing a formation increases, it can be benign and malignant;
- prolonged contact with carcinogens, potent chemicals and radiation lead to the development of angiosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma.
This is interesting: Stage 4 intestinal cancer with liver metastases: prognosis, symptoms and treatment
The development of pathology is influenced by gender: hepatocellular carcinoma is much more common in men than in women. Fibrolamellar carcinoma is more common in women.
The causes of secondary formation are very different from the causes of primary formation. This is because secondary liver cancer means that the lesion formed in one organ and then metastasized to others.
Causes and mechanism of formation
The causes of carcinoma in the liver can be different. Most often, the development of pathological processes in the organ is observed when:
- long-term course of hepatitis B and C;
- alcohol abuse;
- poisoning by chemical, toxic substances;
- use of hormonal drugs.
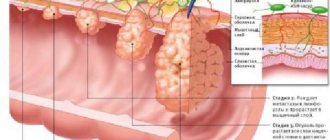
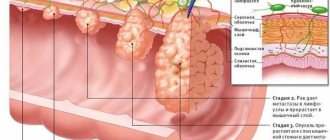
Liver carcinoma develops in stages. Depending on the severity of symptoms and the nature of changes in tissues, 4 degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- At the first stage, the tumor is small. It does not affect blood vessels and does not spread to healthy tissue. It is impossible to determine it by palpation.
If the tumor has reached a size of 50 mm, the disease is at the second stage of development. The vascular system is involved in pathological processes, but the lymph nodes are not affected.- At the third stage, the carcinoma increases even more. Multiple foci of pathological cells are detected. The vessels are severely affected, there are metastases in other organs (gallbladder, pancreas).
- At the fourth stage of tumor development, the lymphatic system is affected. Due to the large size of the carcinoma, the patient’s well-being deteriorates significantly. Internal bleeding and mental disturbances are possible due to the spread of metastases to the brain.
The longer pathological processes in the liver take place, the less likely it is for successful treatment. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the first signs of carcinoma and immediately consult a doctor.
Factors that contribute to the degeneration of hepatocytes into cancer cells include:
- regular consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking: nicotine and alcohol cause the death of hepatocytes;
- untimely treatment of hepatitis;
- constant contact with toxic substances.
Liver carcinoma can occur in anyone. But the likelihood of its occurrence is higher in people who have:
- cirrhosis;
- fatty hepatosis;
- heart failure;
- parasitic diseases: amoebiasis, opisthorchiasis;
- cholelithiasis;
- hemochromatosis;
- hereditary predisposition to tumors;
- diabetes.
The risk group also includes workers in the chemical industry and those who take anabolic steroids and contraceptive drugs. In most cases, liver tumors are diagnosed after 40 years of age. In women, organ pathology is detected less frequently than in men.
Stages of liver cancer
How long a person with liver pathology will live depends on the stage of tumor development at which it was discovered. Thanks to the ability of the filtering organ to regenerate, gland diseases can be successfully treated.
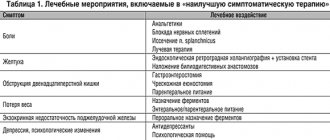
| Stage | Substage | Treatment |
| The first is a single lesion that does not spread to other parts of the body. | The formation is removed by surgery. This is called localized resectable cancer. | |
| The second is that one or more formations spread to nearby blood vessels. | The tumor is completely removed surgically, in the absence of cirrhosis. | |
| Third - has two substages | Stage IIIA – many tumors, at least one of which is larger than five centimeters in size. Or when one tumor has entered large blood vessels near the liver. | Not all formations can be removed surgically, for example, if the formation is larger than 5cm. This is called localized inoperable cancer. |
| Stage IIIB - several neoplasms of any size have migrated to neighboring organs (but not to the gallbladder) or to the capsule in which the gland is located. | ||
| Stage IIIC – cancer cells migrate to neighboring lymph nodes; there may be several tumor nodes of different sizes. | Advanced cancer, for which surgery is an effective treatment in many cases. | |
| The fourth is the metastatic, advanced stage. The abnormal cells migrated to other organs and tissues, such as bones, blood vessels, lungs and lymph nodes. | Surgery is often not an effective treatment at this stage. Patients with this degree of pathology do not have long to live. |
This is interesting: How to cure liver cancer: are malignant neoplasms curable or not?
The first stage is best treated. When less than 25% of the organ is affected, there are no symptoms of hepatoma, which means that detection of the disease at an early stage is rare. Among patients, the survival rate for liver cancer in this case is 75% over a period of five years. But since there are no obvious symptoms, detection of cancer often occurs in the second or third stages. Here the survival rate is 40%.
The human immune system plays an important role in the fight against cancer.
Stages of liver adenocarcinoma
The development of cancer can be divided into certain stages, which are characterized by their own symptoms. Doctors distinguish four stages:
- It is recognized extremely rarely, mainly during annual medical examinations. It is characterized by a tumor up to 2 cm in size, which does not disrupt the functioning of the liver, does not affect the main vessels and does not invade nearby organs. It is because of these features that it is difficult to diagnose.
- Large vessels are involved in feeding the tumor or several neoplasms up to 2 cm have developed. The main reason people go to the doctor is pain in the right hypochondrium.
- A tumor larger than 2 cm is located entirely in one of the lobes of the liver and affects the main vessels. Possible metastasis to lymph nodes. All the characteristic symptoms of the disease appear.
- The tumor progresses in both lobes of the liver and also spreads by metastases to neighboring organs. Stage 4 is characterized by lesions in distant organs. The chance of cure is less than 25%.
There are three forms of disease development:
- Diffuse (12% of cases). In this form, the cells are poorly differentiated and quietly replace healthy ones without enlarging the affected organ.
- Massive. A single node developing in one lobe of the liver. Accounts for 25% of detected tumors.
- Nodal. The most common form. Several nodules separated from healthy organ tissue.
Symptoms
Symptoms of primary and secondary tumors have common features:
- discomfort in the right hypochondrium, as the gland begins to grow and put pressure on neighboring organs;
- abdominal enlargement due to ascites;
- yellow tint of the skin and visible mucous membranes;
- darkening of urine;
- lightening of stool;
- nausea;
- aversion to fatty foods;
- hyperthermia and chills;
- causeless weight loss;
- instant satiation when eating a small amount of food;
- increased fatigue;
- malaise.
With secondary cancer, manifestations of hepatocellular carcinoma are added (with lung pathology, severe cough and shortness of breath will be added).
Diagnostics
How long a person with organ pathology will live depends on the stage of the tumor at which it was discovered. As with other types of cancer, early diagnosis and intervention are key.
It is almost impossible to detect cancer at an early stage with a routine examination. To establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a complete examination:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- tumor markers;
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- MRI.
For successful treatment, a biopsy is necessary; it will determine the histology of the pathological cells.
This is interesting: Stage 4 liver cancer: symptoms during illness and before death, treatment, life expectancy
Diagnosis of liver adenocarcinoma
First, standard blood tests are performed: general analysis and biochemistry. The attending physician determines the approximate location of the tumor by palpation. Ultrasound determines the exact size of the tumor, its structure and the presence of metastases in neighboring organs. After confirmation of the development of adenocarcinoma, nonspecific examinations are performed. These include:
- tumor marker AFP;
- laparoscopy;
- CT scan;
- endoscopy;
- biopsy;
- angiography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- fluoroscopy.
Treatment
The main method of treatment is surgery; it gives hope for complete elimination of the malignant tumor. In this case, surgery is possible if the tumor does not exceed 5 cm in diameter and is located in an area accessible for removal. The 2 most popular surgical methods are used: resection - if the formation is small and lobectomy - performed for liver metastases or when a large part of the organ is affected.
Surgery is combined with radiation and chemotherapy.
In case of secondary formation, the main treatment is aimed at combating the primary lesion, and metastases in the gland are treated within the limits of drug treatment.
The main question is how long a patient with such a diagnosis will live depends on a number of reasons.
Methods of diagnosis and therapy
To identify liver pathology and confirm or refute the presence of carcinoma, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. First, the specialist collects the patient’s medical history and complaints. After this, the following laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- general blood test - helps to detect the inflammatory process;
- extended blood test - allows you to determine the level of proteins and bilirubin in the blood;
- test for the presence of antibodies to hepatitis viruses;
- analysis for tumor markers - carried out to identify proteins that are produced by tumor cells;
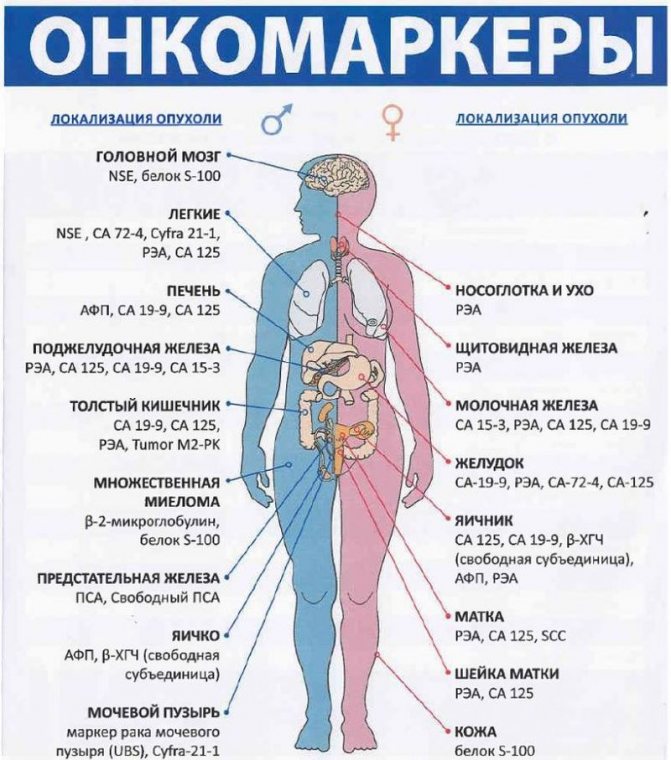
Tumor markers
- coagulogram - prescribed to assess blood clotting;
- ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - allows you to determine the location and structure of the tumor, assess its size and malignancy, and refute the presence of other liver diseases with similar symptoms;
- CT scan. With its help, you can detect small formations that are invisible during ultrasound examination. If necessary, contrast is used during the procedure;
- magnetic resonance imaging – allows you to obtain more complete information about the structure of the liver, the model of the tumor;
- biopsy is a mandatory analysis to make a final diagnosis.
Choosing a method
The doctor decides how to treat liver carcinoma: it all depends on the nature and stage of its development, the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. But, in any case, complex treatment is recommended: surgery, medication, diet and therapy aimed at affecting cancer cells.
Tumor removal is carried out in several ways. Can be assigned:
- Radioembolism is selective radiation therapy. It is indicated in cases where a tumor in the liver cannot be removed surgically.
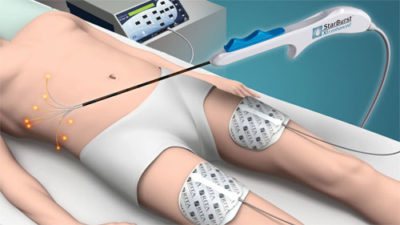
Chemotherapy is the intravenous administration of drugs that destroy pathological cells.- Radiofrequency ablation is the effect of radio waves on the tumor.
- Chemoembolization is the injection of chemicals into the hepatic artery that prevent blood flow to the tumor. This method of treating carcinoma is considered the most effective and does not cause severe side effects.
If the tumor has reached a large size (more than 5 cm), they resort to removing part of the liver or transplantation. Transplantation is performed only if there are no metastases in other organs. Only a completely healthy person can become a donor for a patient. Preferably it should be a relative.
Medical nutrition
In case of cancer, it is necessary to correct the diet. Liver carcinoma is no exception. Patients with this diagnosis are recommended to reduce the load on the organ as much as possible. This can be achieved by eating small meals frequently.
| It is necessary to exclude from the diet | Can be consumed in moderation | Must be present in the diet |
|
|
|
For liver cancer, you need to eat boiled, oven-baked and steamed food. Stewed dishes will also be useful. Sweets can be replaced with honey, jam or marshmallows.
When treating liver carcinoma, you can additionally use folk remedies: take tinctures of propolis or hemlock, carry out therapy with decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs. But their use must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Olga: “For tumors in the liver, an infusion of celandine helps well (you need to drink it three times a day, half an hour before meals, 100-150 ml). Treatment lasts 3 weeks. After 21 days the course can be repeated. You also need to eat beets every day and cottage cheese.”