Types of diffuse changes and their manifestations
The following types of violations are distinguished:
- A slight change is observed in the initial stages of bacterial, viral inflammation or under the influence of external unfavorable factors.
- Moderate diffuse changes in the liver parenchyma appear with long-term use of hepatotoxic drugs, alcohol abuse and fatty foods.
- Pronounced - in hepatitis, cirrhosis, tumors, when in addition to diffuse changes throughout the organ, local destruction and swelling of the liver tissue is detected.
Treatment
Treatment begins with identifying the causes of hepatomegaly, diffuse changes in the liver and pancreas. In order to stop the process, it is necessary to detect the source of the disease. After this, complex treatment is prescribed, including:
- diet;
- suppression of symptoms;
- taking hepatoprotectors (drugs that protect the liver).
In severe stages of the disease, surgical treatment of the disease is possible.
Drug treatment
The prescription of drugs depends on the stage and causes of hepatomegaly.
This is interesting: Causes, symptoms, treatment and diet for hepatomegaly with enlarged pancreas
If the changes are not pronounced, then restoration of liver cells is necessary. For this, the patient is prescribed drugs such as Essentiale and Gepabene.
For moderate hepatomegaly, vitamins, antibacterial and antihistamines are prescribed.
If the disease is viral in nature, then the use of antiviral drugs is required. In severe stages, hormonal medications are prescribed.
In case of helminthic infestation, antiparasitic medications, vitamins and hepatoprotectors should be taken.
Drug treatment of diffuse changes in the pancreas consists of alleviating the symptoms of the disease. Drugs are prescribed to facilitate the functioning of the organ - painkillers and enzymes.
Diet
In case of hepatomegaly, the following should be excluded from the diet: spicy foods, smoked foods, sweets, flour products, fried foods and fatty foods. Alcohol consumption is prohibited. All types of sausages, eggs, pork, and fatty cheeses are prohibited.
Preference should be given to stewed and boiled foods. Increasing fiber intake is recommended. Meals should be frequent, it is better to eat in small portions.
Folk remedies
Treatment with home remedies must be coordinated with your doctor. There are several famous recipes:
- Mix a spoonful of honey in warm water. Add a spoonful of lemon. Take 2 times a day, morning and evening.
- Grate half the beets and mix with olive oil. Eat the resulting mass for breakfast.
- Take 3 cups of oats, 3 tablespoons of birch buds and lingonberry leaves. Grind everything thoroughly and add 3 liters of cold water. Let stand for 24 hours, then put on fire. Stir occasionally, after boiling, remove and cool. You should take half a glass of decoction daily before meals.
- Between meals, eat at least 14 juniper berries every day. Start with 2 berries.
- Brew corn hairs in a thermos. Insist for a day. It is recommended to use this decoction in the morning and evening; it can be used instead of tea. For 3 liters of water you need 300 grams of hairs.
- Olive oil effectively helps in cleansing the liver of toxins. You should start with a teaspoon per day. Within 2 weeks, you need to increase your oil intake to a tablespoon. It is recommended to limit the course to 30 days.
This is interesting: What to do with an enlarged liver and how to treat it?
Surgery
Radical measures are used in the most severe cases. They are prescribed when:
- portal hypertension - increased pressure in the portal vein;
- with metastases;
- if a cyst or tumor is detected.
Causes
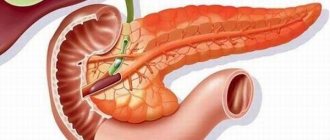
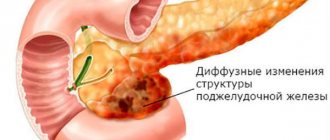
A diffuse change in the liver parenchyma is a transformation of the liver tissue in which not a separate area of the organ is affected, but the entire liver as a whole: hepatocytes increase in size, their density changes, and the homogeneity of the structure is lost. Depending on the causative factor, either the processes of dystrophy predominate - infiltration of liver cells with fatty deposits - steatosis, or connective tissue is formed in the form of scars and fibrous nodes in place of dead hepatocytes.
Diseases in which the structure of the organ changes:
- endocrine pathologies: metabolic syndrome with obesity, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus;
- chronic hepatitis;
- fatty degeneration - steatohepatosis;
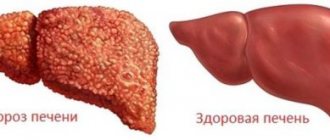
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- tumors: benign, malignant;
- viral infections;
- parasitic infestation.
Factors leading to changes in the structure of the liver
Poor nutrition. Abuse of products containing animal fats or hydrogenated oil (mayonnaise, chips, baked goods, fast food, processed foods) leads to increased load on the liver, which can no longer cope with the utilization of fats, but begins to deposit them in its parenchyma.
Chronic alcoholism. An intermediate product of ethanol metabolism, acetaldehyde, has a detrimental effect on liver cells. Hepatocytes begin to break down and fatty inclusions take their place.
Inactivation of drugs occurs in the liver, many of which (antibiotics, steroid hormones, cardiac glycosides, cytostatics) have a hepatotoxic effect. Destructive processes under the influence of medications lead to damage to liver tissue in the form of drug-induced hepatitis and a decrease in the functional activity of the liver.
Unfavorable environmental conditions. People living near large industrial production and busy highways have an increased risk of liver damage. With prolonged intake of harmful substances into the body, metabolic processes in hepatocytes slow down, toxins accumulate, which causes the development of various diseases.
Psycho-emotional overload. During stress, the hormone adrenaline is released from the adrenal glands into the blood. In high concentrations, it negatively affects the function of hepatocytes.
Carrying out pathology therapy
If you suspect the presence of a disease, you should contact a therapist. The doctor will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe therapeutic measures.
Treatment of lipomatosis should be carried out comprehensively. To treat the pathology, surgical methods, dietary nutrition and medication are used.
With the help of surgery, tumors are removed, and the use of diet and medications prevents the formation of new lipomas and maintains a stable condition of the body
When carrying out drug treatment, a whole range of medications is used:
- Hepatoprotectors - Essentiale, Essliver, Berlition, Hepaforte, Phosphogliv, Essel Forte, Maksar, FanDetox, Liv 52, Heptral, Heptor, Karsil, Ovesol, Ursofalk, Hofitol, Gepabene, Galstena, Rezalut Pro.
- Antioxidants – Retinol, Tocopherol.
- Vitamin complexes containing B vitamins.
- Medicines containing selenium.
According to most doctors, if pathology is detected at an early stage, it is enough to correct the diet by excluding foods and dishes containing large amounts of fats and carbohydrates for recovery.
Most patient reviews indicate that identifying pathology at an early stage and the combined use of medication and dietary interventions can stabilize the body’s condition and prevent further deterioration of health.
The pancreas is responsible for processing consumed food and distributing nutrients into the blood. The organ is quite sensitive to external and internal negative factors that can cause severe pathologies. Pancreatic lipomatosis is an irreversible process accompanied by the replacement of adipose epithelium. This pathology is also called fatty degeneration. The disease requires urgent treatment. Lack of medical care can lead to serious complications.
Symptoms of changes in the liver parenchyma
If changes in the liver occur as fatty hepatosis, a compensatory enlargement of the organ develops - hepatomegaly.
- pain in the right hypochondrium is dull aching in nature;
- bitter or metallic taste in the mouth;
- dyspeptic syndrome: nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea;
- dense brown-yellow coating on the surface of the tongue;
- deterioration of skin condition: change in color (gray, yellowish), swelling, dryness, peeling, itching, rashes;
- with cholestasis - jaundice of varying severity, dark urine, discolored feces;
- decreased immunity, increased susceptibility to colds;
- increased sweating. Sweat acquires an unpleasant, pungent odor;
- asthenic syndrome: general weakness, severe fatigue, headaches;
- increased psycho-emotional excitability, sudden mood swings, poor sleep;
- due to disturbances in the metabolism of hormones in the liver, women develop problems with the reproductive system: menstruation disorders, problems conceiving a child;
- the appearance of bruises, spider veins, and petechiae on the skin. Due to the increased fragility of blood vessels, various bleedings are possible: nasal, uterine;
- elevated body temperature not associated with a cold.
In childhood, along with the reasons that cause disturbances in the structure of the liver in adults, genetically determined pathology often comes first:
- enzyme defects, protein metabolism disorders.
- congenital fibrosis, multicystic disease, liver cirrhosis.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis for life expectancy depends on the degree of damage to the body and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. Following a diet and quitting alcohol and smoking increases the chances of recovery and restoration of organ function. If simple rules are followed, healthy tissues will continue to produce the necessary hormones with enzymes for food digestion and metabolism.
Refusal of the doctor's recommendations can cause severe damage to the tissues of the stomach, liver and intestines. Repeated intoxication of the body with serious consequences is possible.
Pathology of the pancreas is incurable and develops slowly. It will not be possible to completely cure the patient, but it is possible to block further growth of atypical cells and normalize the functioning of the organ. This requires taking prescribed medications and eating right.
Lipoma is a type of neoplasm that has a “good” character, which does not become malignant, but tends to grow and develop, which entails certain damage to the health and functioning of organs. Such formations on the liver are characterized in medicine as liver lipomatosis. Typically, lipomas consist primarily of fatty tissue, but some varieties include muscle tissue.
Preventive measures
To avoid the occurrence of diseases and deterioration of the liver, it is better for older people to avoid fatty and fried foods. It is worth eating vegetables and fruits containing fiber. Sudden weight loss has a negative impact on liver function; it is better to lose weight gradually and without harming your health. It is advisable to reduce alcohol intake, because the liver is directly involved in its elimination. It is problematic for older people to reduce the number of pills they take, so it is better to consult a doctor and choose medications that are less harmful to the organ. Compliance with these rules and a moderately active lifestyle will help avoid diseases.