Basics of the disease
If urgent measures are not taken in the acute form of appendicitis, the pathology can be life-threatening, as it leads to perforation of the appendix and purulent diffuse peritonitis.
The main symptom of acute appendicitis is the sudden onset of abdominal pain. The pain syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Initially, sensations are aggravated in the epigastric region;
- after 6-8 hours the pain moves to the right iliac region;
- later it takes on a diffuse character;
- the pain manifests itself constantly, with periodic intensification and weakening, but there are no painless moments;
- with any movement, pain increases, so a person with acute appendicitis moves with his hand on the right side of his abdomen, which is one of the characteristic symptoms of this disease;
- acute pain indicates purulent inflammation;
- a decrease in pain in the acute form of the disease indicates the onset of the gangrenous process and the death of nerve endings.
Main symptoms of appendicitis by authors
Doctors know more than 70 ways to palpate the abdomen to determine pathology. Among them are 40 symptoms characteristic of acute appendicitis and complications of inflammation of the appendix.
What is appendicitis
The appendix is an extension of the cecum, which, when inflamed, is burdened with life-threatening complications.
Acute appendicitis occurs due to:
- blockage of an area of the intestine;
- development of harmful microflora;
- spasm of the walls of the appendix;
- blood stagnation;
- infections;
- overeating;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
In pregnant women, appendicitis becomes inflamed due to the fact that the enlarged uterus damages the appendix.
The functions of the appendix are varied. Among them are the digestion of food and the effect on intestinal motility. It is believed that the appendix is a vestigial organ and some patients try to inflame appendicitis on their own at home.
Do not do this under any circumstances. According to statistics, people who have had their appendix removed have an increased risk of developing stomach and intestinal cancer. In addition, it is more difficult for people without an appendix to restore intestinal microflora after infections.
Signs of appendicitis in adult men
If appendicitis is suspected, symptoms in adults are as follows:
- Deterioration in health.
- Abdominal pain.
- Weakness.
- Abnormal stool.
- Rapid pulse.
- Nausea and single vomiting.
Scar after appendectomy in a man
The first signs of appendicitis in women
Women more often than men suffer from inflammation of the appendix. In women, appendicitis occurs in the evening or at night. From the first minutes, abdominal pain appears, which shifts to the right iliac region.
With an anatomical anomaly in the location of the appendix, patients complain of pain in:
- lower back;
- groin;
- right hypochondrium.
If the pain suddenly goes away during acute appendicitis, this is a reason for urgent surgery. Dulling of pain is associated with the development of peritonitis, a complication after appendix. With peritonitis, the contents of the stomach enter the peritoneum, and the nerve endings die.
In women, inflammation of the peritoneum is disguised as a gynecological disease
Before surgery to remove the appendix in women, the doctor excludes the possibility of ectopic pregnancy and inflammation of the ovaries, since the symptoms of the diseases are similar.
In pregnant women
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendix in pregnant women are less pronounced than in men and children. Some palpation symptoms do not appear due to stretching of the anterior peritoneal wall by the fetus.
To confirm suspicion of appendicitis in pregnant women, patients are prescribed an ultrasound of the abdomen.
Inflammation in the peritoneum - risk to the fetus
Appendicitis during pregnancy creates a risk of:
- placental abruption.
- infection of amniotic fluid.
- miscarriage.
Symptoms of appendicitis in pregnant women:
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Pain in the lower right corner of the abdomen.
- Heat.
Symptoms of appendicitis in children
Children and adolescents have bodies that are not as strong as adults. Children are a particular risk area: fragile health and the inability to speak complicate the disease. But in infants under 1 year of age, inflammation of appendicitis is rare.
Inflammation develops faster in children than in adults
Most often, appendicitis becomes inflamed in children and adolescents aged 10 to 18 years.
What causes appendicitis in children:
- hypothermia.
- helminthic infestation.
- poor nutrition.
The main symptoms of acute appendicitis in children:
- wandering pain in the abdomen.
- My right side hurts and I feel nauseous.
- the temperature rises.
- weakness, shortness of breath, rapid pulse.
How it hurts
In the first minutes, inflammation of the appendix is accompanied by heaviness near the navel or in the right side in the iliac region. The person cannot straighten up and walking is difficult. The pain is dulled only when lying down - all these are signs of inflammation.
Abdominal pain preventing you from walking? Call a doctor at home
Acute appendicitis
Pain during appendicitis provokes spasm and swelling of the walls of the appendix. Without the help of doctors, after the stage with acute pain, tissue necrosis occurs - necrosis. The walls of the appendix perforate, and gangrenous-perforated appendicitis develops.
In the catarrhal (first) stage, the pain is sharp and intense. The nature of the pain is aching. Accompanied by heaviness in the abdomen and cutting pain in the right side.
Symptoms of chronic appendicitis
From acute to chronic appendicitis develops after appendectomy if the stump of the appendix continues to periodically become inflamed. Doctors diagnose a relapse of the disease.
Symptoms that accompany chronic appendicitis in adults:
- right side hurts after eating;
- sometimes the pain radiates to the leg or lower back;
- nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- pain during bowel movements;
- painful sexual intercourse.
Unlike acute inflammation, patients do not complain of weakness and malaise. Chronic appendicitis in women is often confused with gynecological diseases.
Diagnostics
During the initial examination, doctors palpate the patient’s abdomen to identify surgical pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. By observing the body's reaction to palpation, the doctor diagnoses a suspected disease.
Ultrasound is a popular method for diagnosing abdominal diseases.
After the examination, the patient is sent for examinations to confirm or refute the diagnosis. Or to the operating table, if delay is life-threatening.
Kocher-Wolkovich sign
Symptom of wandering pain. It consists of observing the movement of pain from the epigastric region to the lower right side.
Diagram showing how pain moves
It is considered the main symptom of acute appendicitis.
Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom
Diagnosed with inflammatory processes in the peritoneum. Most often accompanied by peritonitis and acute appendicitis.
Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom
The patient lies down on a flat surface. The doctor identifies a painful area in the peritoneum and presses on it, holding it for 2-3 seconds. After this, he quickly removes his hand and observes the patient’s reaction. Increasing pain means a positive Shchetkin-Blumberg sign.
Voskresensky's symptom
The patient is examined in clothes - a shirt or T-shirt.
Voskresensky's sign (shirt sign)
The patient lies down on the couch. The doctor sits down next to you and grabs the edge of the patient’s clothing with his left hand, pulling it towards himself. The patient takes a deep breath, and the doctor runs his right hand along the abdomen from the navel to the right iliac region.
If the pain intensifies, the symptom is considered positive.
Sitkovsky's symptom
The patient lies on his left side and describes the sensations. If the dull pain in the right side intensifies, then Sitkovsky’s symptom is positive.
Increased pain with Sitkovsky's symptom
Increased pain is explained by the displacement of intestinal loops, which put pressure on the appendix, increasing pain during inflammation.
Rovsing's symptom
The patient lies down. The doctor presses on the right side, making pushes along the peritoneum.
Palpation for Rovsing's symptom
There is a shift of gases in the intestines into the appendix. An inflamed appendix responds with pain to the doctor’s manipulations.
Obraztsov's symptom
The symptom is determined by the retrocecal position of the appendix - behind the cecum. The patient lies down and raises his straightened right leg.
Positive Obraztsov's sign
The muscles of the peritoneum tense, acting on the receptors of the appendix. With inflammation, the patient will complain of nagging pain in the right side of the lower abdomen.
Other symptoms - table
SymptomExecutionReaction
| Barthomier | The patient lies on his left side. The doctor palpates the right side | Pain increases with inflammation |
| Razdolsky | The patient lies on his back. The doctor taps his fingers lightly on the right iliac region | The severity of the pain determines the area of pathology |
| Zattler | The patient sits down and raises his straightened right leg | When the appendix is inflamed, the entire right side hurts |
| Aaron | The doctor palpates the patient's right iliac fossa | There is muscle tension and pain around the navel |
| Krymova | Palpation of the inguinal canal | Right lower abdomen hurts |
| Laroca | In acute appendicitis in men, the muscle that lifts the testicles contracts | Both testicles are raised |
| Cope | Used to diagnose the pelvic appendix. Lying on his back, the patient bends his right leg at the knee | Pain in the right iliac fossa |
| Ikramova | The doctor presses on the femoral artery | Pain on the right side of the body gets worse |
| Mikhelson | Suitable for pregnant women. Woman lies on her right side | The pain intensifies due to the fact that the uterus puts pressure on the inflamed organ |
| Krasnobaeva | The anterior abdominal wall is palpated | Muscle tension is noted |
| Kushnirenko | The patient is coughing | Identifies pain point when coughing |
| Moscow | With inflammation, the pupil of the right eye is dilated |
Summarize
It is impossible to create a complete clinical picture of the disease with symptoms alone. Do not self-medicate or try to diagnose appendicitis at home. The sooner you see a doctor, the more time you will give specialists to thoroughly analyze your health.
Detailed video about palpation
Source: https://drevmassiv46.ru/simptomy-appendicita-po-avtoram-osnovnye/
Diagnostic nuances
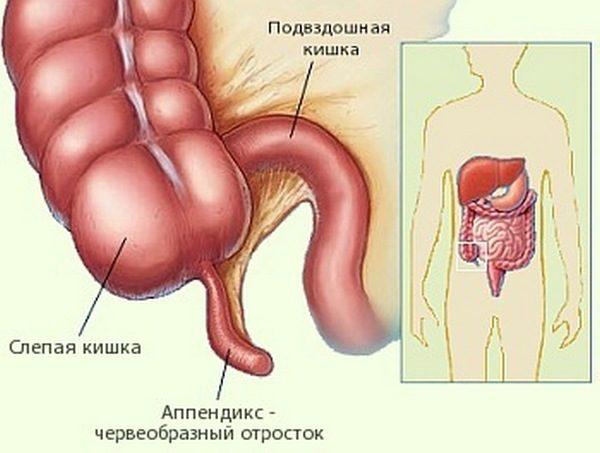
Usually the disease does not cause difficulties in diagnosis. Appendicitis is determined based on its characteristic signs, which include positive symptoms of Rovsing, Sitkovsky, etc.
So, when determining the latter, pain on the right in the iliac region intensifies when the patient lies on his left side. According to Sitkovsky's observations, the increase in pain is due to the fact that the cecum is stretched and its deformation causes pain. The pain is aggravated by the tension of the mesentery of this process.
And Rovsing’s symptom in appendicitis is characterized by the appearance of pain in the right iliac region if the doctor performs jerky palpation in the projection of the lateral canal, in the left part of the abdomen (from left to right).
The following signs are also among the most significant:
- Barthomier-Mikhelson's symptom is the appearance of pain on palpation of the cecum if the patient lies on his left side.
- Obraztsov's symptom is an increase in pain when applying pressure to the cecum, with a simultaneous attempt to raise the straightened right leg.
Appendiceal symptoms by author
Appendicitis is a rather dangerous disease with its consequences. That’s why the main task of a specialist is to diagnose it as quickly and accurately as possible. A number of signs, named after the researchers who first identified them, help to recognize the disease - symptoms of Rovsing, Sitkovsky, Bartomier-Mikhelson, Voskresensky, etc. Let's take a closer look at them.
Causes of appendicitis
There are several causes of appendicitis:
- Blockage of the entrance to the vermiform end of the rectum is the most common. This can happen due to the ingress of foreign bodies or feces. Blockage can also occur from compression of the upper part of the appendix by the formation of adhesive processes during enteritis and cholecystitis.
- Stagnation of the contents of the appendage. This leads to a weakening of its protective functions, which is why pathogenic bacteria - staphylococci, E. coli, streptococci - begin to actively multiply in the appendix. They cause inflammation.
- Spasm of the vessels that supply blood to the appendix.
- Trauma to the peritoneum, which may result in displacement or damage to the appendix.
- Pregnancy. The process may become displaced due to the growth of the uterus.
- Tendency to constipation.
- Poor intestinal motility.
- Binge eating.
- Lack of plant fibers, microelements, vitamins in the diet.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Hereditary factors.
- Infectious diseases.
- Presence of parasites.
- Bad habits.
- Stress.
About the diagnosis of appendicitis in Russia
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix of the rectum. For its initial diagnosis, confirmation or refutation of the diagnosis, doctors in Russia use certain symptoms of peritoneal irritation that have been proven over the years. There are few of them, but they are the reliable “old-timers” in clinical practice. Named after the surname of their author:
- Sitkovsky's symptom.
- Kocher's sign.
- Voskresensky's symptom.
- Obraztsov's symptom.
- Rovsing's sign.
- Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom.
The manifestation of each of them depends on a number of factors: the location of the appendix, the cause of inflammation, the advanced stage of the disease, etc. Let's analyze Sitkovsky's symptom and others in more detail.
Kocher's sign
The surest sign by which acute appendicitis can be identified is Kocher syndrome. There is even an expression among doctors: “Kocher doesn’t lie.” Half of the patients suffering from appendicitis have this particular symptom.
It manifests itself as follows: pain from the epigastric region gradually migrates to the right iliac region. It is determined by collecting an anamnesis, interviewing the patient - clarifying the location of the pain syndrome and its nature.
Rovsing's symptom
It is quite rarely used in practice, which does not negate its validity, which is why the symptoms of Rovsing and Sitkovsky are constantly mentioned in the literature. It is determined when pain occurs due to the accumulation of gases in the rectum.
Source: https://kishechnik-zhivot.ru/simptomy/appendikulyarnye-simptomy-po-avtoram
Detailed consideration of Rovsing's symptom
Rovsing's symptom consists of an increase in the painful condition on the right when pressure is applied to the sigmoid colon (it is located in the left iliac region) and in the manifestation of convulsive spasms above it. When examining the abdominal wall in the left part of the iliac region, press with the fingers of the left hand, brought together, and without taking them away, with the right hand make a short push on the overlying area of the colon. Rovsing's symptom is designed to move gases during a push.
However, in some cases, when examining a patient, it is difficult to make a correct diagnosis, since Rovsing’s symptom may be absent. It is especially difficult to distinguish from the manifestations of the described disease the symptoms of a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, with the spread of blood in the right iliac zone.
Rovsing's symptoms are not used very often, but, by the way, they are considered one of the most reliable for the correct diagnosis of appendicitis.
The importance of a correct diagnosis
In modern medicine, for mild forms of appendicitis, laparoscopic operations are performed, which do not require the creation of an abdominal incision. In this case, an endoscopic instrument is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small incision in the tissue. This method allows you to avoid surgical intervention, as well as significantly shorten the rehabilitation period. The risk of postoperative complications after laparoscopic appendectomy is minimal.
But, unfortunately, the symptoms of appendicitis are periodically confused with manifestations of other pathologies:
- pancreatitis;
- renal colic;
- acute cholecystitis;
- stomach ulcer;
- acute inflammation of the bladder and female organs.
Positive Rovsing symptoms and other signs play an important role in diagnosing this pathology, but in cases of abnormal position of the process, the clinical picture may be blurred. Therefore, it is very important to promptly pay attention to the characteristics of the pain that has arisen.
In order to avoid serious consequences, you should seek specialized medical help, otherwise it could end tragically. It is important to understand that self-diagnosis in such cases is extremely dangerous.
Proper nutrition after appendectomy
Often a disease such as appendicitis cannot be treated without surgery. Upon successful completion of surgery, it is important to speed up the healing process. At the same time, proper nutrition is of great importance.
Experts recommend this diet for the first three days of the postoperative period:
- First. After the patient has regained consciousness, he can be given a glass of still water. Moreover, you need to drink it in small sips and slowly. Water will help the body recover, which has already lost a large amount of fluid during the operation. After several hours, the patient can be offered a little low-fat kefir. Doctors also advise patients on the first postoperative day to eat a small amount of chicken broth without seasonings, potatoes and meat. Just before going to bed, you can offer the patient a little warm low-fat milk, which will help him sleep soundly.
- Second. During this period, it is extremely important to eat food that will help the patient restore the intestinal microflora, for example, kefir and cottage cheese. Under no circumstances should you eat hard, fatty or heavy foods. It’s great if the patient eats a little semolina or oatmeal porridge on the second day, washing it down with warm milk.
- Third. As a rule, on the third day the patient can already get out of bed, and this will require considerable effort. Therefore, doctors recommend offering him nutritious, but not heavy food: yogurt, kefir, milk porridge, etc.
To speed up the recovery process of the body after appendicitis surgery, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Adhere to dietary nutrition from the first postoperative day.
- Until the patient recovers completely from anesthesia, it is strictly forbidden to give him, even water, you can only gently moisten his lips with water and lemon.
- It is not recommended to use newfangled recipes, but it is better to use the old recipe for simple chicken broth without meat and potatoes.
- It is forbidden to eat fatty and sweet foods, as they are difficult to tolerate and digested by the intestines.
- Under no circumstances should you eat chips, foods rich in fiber, or drink mineral water.
The first week after surgery is the early postoperative period. At this time, special attention should be paid to older people who may have problems with their heart or respiratory system.
Since they have a difficult time undergoing surgery and move little, the speed of the recovery process in such people is much lower than in other patients.
Breathing exercises after surgery
In order to help them with this, it is recommended to do special breathing exercises with them every hour: several inhalations and exhalations, as deep as possible.
On the second day, you need to help them roll over from one side to the other.
It will be a little difficult to do such rollovers without outside help the first few times, but you should try not to leave the patients and help them.
On the third day, you can already try to sit up in bed or stand up a little.
In this case, doctors believe that the more a patient who has undergone appendicitis surgery moves, even when the pain prevails, the faster he will recover and the functioning of his respiratory and cardiac systems will improve.
Unfortunately, it is not uncommon for patients to develop bloating during the postoperative period. Voskresensky's symptom in acute appendicitis will help specialists quickly determine the development of this condition in the patient.
The reason for this lies in the surgical procedure itself, in which the doctor has to touch the patient’s intestines.
This condition is dangerous for the patient, as it provokes a disruption in the process of removing toxic gases from the body, which have a fairly large impact on the functioning of all internal human organs.
To avoid this and other unpleasant situations, it is necessary to follow the correct diet in the postoperative period, and also try to lead a correct lifestyle, without overloading with physical activity, but also not to neglect it.
How to eat properly after appendicitis is presented in the video:
♦ Category: Diseases.
Read for Health one hundred percent:
- What does pain in the lower abdomen indicate?
- How does the stomach hurt with appendicitis: necessary information
- What is tachycardia and why is it dangerous during pregnancy, treatment and prevention of the disease
- Still's syndrome in adults: features of development, course and treatment of the disease
- The main signs of the development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
- Discharge from the anus: main causes and therapy
- Duodenal ulcer: symptoms and diagnosis
- How does Kocher's sign manifest itself in inflammation of the appendix?