Pancreatitis is a common disease. Every year, approximately 50 thousand people in Russia turn to gastroenterologists with symptoms of acute inflammation of the pancreas. The main causes of the development of pathology remain alcoholism and cholelithiasis. Diagnosis of the disease includes examination of the patient, instrumental and laboratory techniques. During the examination of the patient, the doctor can use existing proprietary methods for diagnosing the disease, recording the symptoms that appear in the patient. In this article we will talk about the Mayo Robson symptom, which indicates the development of pancreatitis and can help the doctor make the correct diagnosis.
Mayo Robson's symptom: the essence of the technique
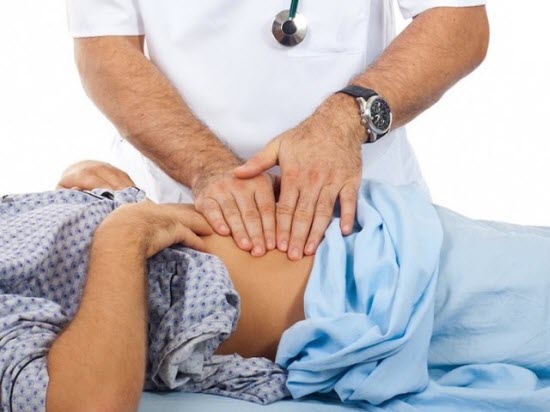
Before the advent of diagnostic equipment, the main method for determining inflammation of the pancreas was palpation (palpation of the organ). The palpation technique has been used since the mid-twentieth century to this day, increasing the accuracy of the doctor’s diagnosis. One of its varieties is the Mayo Robson method. The method was named in honor of its creator, the English surgeon Arthur William Mayo-Robson, who studied diseases of internal organs, including the pancreas.
It is impossible to palpate a healthy pancreas. When an organ becomes inflamed, pain appears when pressure is applied to certain areas, such as the point of Mayo Robson, Desjardins, Katch, etc. By changing the nature of the pain, the doctor can understand what form the disease is taking and what stage of development it is at.
The principle of palpation for pancreatitis
This method has been used since the mid-20th century, when it was not possible to use special equipment for diagnostics; doctors trusted their fingers during examination. And now palpation and percussion are included in the research complex for making a diagnosis.
In a healthy person, the pancreas cannot be palpated. The only thing that will help is excellent knowledge of the anatomical structure of the human body. You can feel the pulsation of the aorta on the anterior abdominal wall during examination, a large vascular trunk lying on the spine. When palpating and percussing the pancreas, it is necessary to observe changes in the nature of the patient's pain.
How does the Mayo Robson sign manifest itself?
Pain when pressing on the Mayo Robson point appears with the development of acute pancreatitis. It is worth noting that the method only works in 45% of cases.
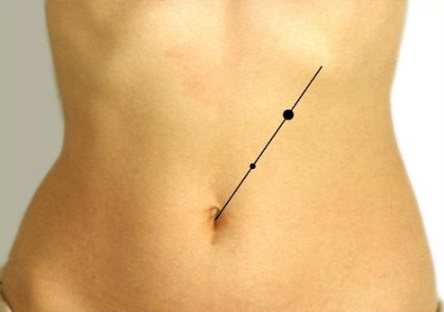
How to find the right point?
When pressing on the Mayo Robson point, a patient with pancreatitis feels a sharp, severe pain. The diagnostic method is based on this. But to use it, the doctor must correctly determine the location of the point:
- first you need to determine point A, it is located in the middle of the lowest left edge;
- point B is located in the navel area;
- an imaginary line connects points A and B;
- the line is mentally divided into 3 parts;
- the point located on the border between parts 2 and 3 is the desired one.
If the tail of the gland is affected, the pain will radiate to the back or abdominal wall. For other organ lesions, the method will not be informative.
Characteristic signs of pathology
Pancreatic damage to the pancreas is expressed in the development of an inflammatory process in the cavity of this organ. The mechanism of formation of this pathology has several main reasons and may include:
- in hereditary predisposition,
- in excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages,
- in the development of pathological disorders in other organs of the digestive tract and abdominal cavity, especially with damage to the gallbladder and bile ducts, provoking the development of cholecystitis or cholelithiasis,
- and pancreatitis can occur with the progression of peritonitis.
We should not forget about the negative impact on the condition of the pancreas from dietary violations, poor diet and abuse of fatty foods.
Among the main characteristic symptomatic signs of pancreatic disease are:
- yellowness of the skin and mucous sclera of the eyes,
- pale face, which over time changes its shade to an earthy color,
- sunken eyes,
- the appearance of red spots in the groin area and abdomen,
- plaque formation on the surface of the tongue,
- the appearance of a constant feeling of nausea, as well as uncontrollable vomiting, which does not bring any sense of relief after its cessation,
- the appearance of the smell of acetone from the oral cavity,
- formation of shortness of breath,
- increase in heart rate,
- the appearance of pain in the epigastric area, which can radiate to the lumbar region, sternum to the side and to the lower part of the jaw joint, and when walking and bending, increase its intensity of manifestation,
- disorder of the dyspeptic organ system.
We recommend reading: Diarrhea with foam: causes of occurrence in adults and children
Other techniques
In addition to the Mayo Robson symptom, in pancreatitis, other manifestations are used to diagnose the disease. Let's take a closer look at them.
Mondor syndrome: bruises of varying sizes and locations appear on the body of a patient with an acute disease. Bruises can even occur on the skin of the face. Their appearance is explained by the fact that when the pancreas becomes inflamed, toxins are released into the blood and then into the dermal layers. In this case, the person feels severe pain in the abdomen.
Kach's symptom: allows you to determine the presence of chronic pancreatitis. When you press on the Kacha point, which is located in the area of the 8th thoracic vertebra, painful sensations appear. The pain may be so severe that the patient does not allow the doctor to carry out further examination.
Razdolsky syndrome: manifestations are observed in the severe stage of the disease, when inflammation of the peritoneum occurs. If the pathological process is mild, the method may not be informative. It manifests itself as sharp pain in the abdomen when tapping the skin in the area of the inflamed gland with your fingertips.
Find out what salads you can prepare for pancreatitis.
Read: what features does Diet 5 have for pancreatitis?
Kerthe syndrome: the patient feels severe pain when palpating the abdomen in an area located 5 centimeters above the navel. The symptom is observed in approximately 6 out of 10 patients with acute pancreatitis.
All of the above signs can be used by a gastroenterologist as auxiliary tools in diagnosing the disease. Their use does not require the presence and use of special equipment and reagents, and is available to any doctor in any medical institution.

Mechanism of disease development
Pancreatitis is a malfunction of the pancreatic juice produced by the pancreas.
The juice contains enzymes necessary to break down complex elements (fat, protein, carbohydrates). If the food that enters the intestines is not processed properly, indigestion, stool disorders, and exhaustion of the body due to nutritional deficiency occur. A lack of supply of pancreatic enzymes most often occurs due to obstruction of the duct. This can happen as a result of damage to the organ or the presence of stones blocking the flow of juice.
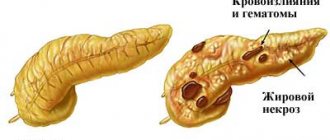
Pancreatic juice trapped inside the pancreas corrodes the tissue of the pancreas itself. The organ becomes inflamed, and the outflow of pancreatic juice becomes even more difficult. In addition, necrosis (death of damaged cells) causes the appearance of pseudocysts, tumor formations, and replacement of parenchyma cells with fat or connective tissue.
The mechanism described above develops against the background of the underlying causes:
- the presence of cholelithiasis, diabetes or other chronic ailments;
- infection by infections, fungi, viruses;
- hormonal disorders;
- receiving physical injuries in the abdominal area.
The most common scenario for the development of pancreatitis occurs due to an unhealthy lifestyle: fatty foods, alcohol, lack of exercise, permanent stress, lack of sleep, overwork.
Signs of pancreatitis by author
The characteristic signs reveal how advanced the disease is and determine the form of its course. Let's take a closer look briefly.
- Mondor's sign. The sign is characteristic of acute pancreatitis. It appears in the form of dark blue spots on the skin, and the spots are located throughout the human body, even on the face. Bruises are accompanied by severe abdominal pain. This happens due to the release of toxins by the gland, initially into the blood, then into the thickness of the skin. Dark spots on the face indicate the appearance of intoxication and the severity of the disease, when surgical intervention is required.
- Razdolsky's symptom. The sign reveals acute pancreatitis with obvious inflammation of the peritoneum. When you tap your fingers on the skin in the area where the gland is projected, the patient will feel a sharp pain. The symptom is explained by the irritating effect of fingers on the inflamed peritoneum. At a mild stage of the disease, the syndrome may not appear.
- Voskresensky's symptom. Used to identify the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. The point is in the characteristic feature: during examination, pulsation of the abdominal aorta zone at the intersection with the pancreas will not be felt. This point will be located approximately 5 cm above the navel, moving towards the gallbladder by 3-4 cm. It is enough to move it with a light, smooth movement along the stretched tissue from the epigastric area towards the liver. The beat will not be palpable. Occurs due to swelling of the gland that occurs during inflammation. A thickening appears in the peritoneum through which the pulse cannot be felt. The method is not suitable for people with large body weight; the fat layer does not allow proper palpation.
- Kach's symptom. Characteristic of chronic pancreatitis. When palpating the projection of the tail of the organ, obvious painful sensations will appear, making it impossible to continue the examination. The Kacha point is located in the area of the transverse process of the eighth thoracic vertebra. Signs of skin sensitivity may appear in the indicated area.
- Kerte's sign. Characteristic for confirmation of acute pancreatitis. It is explained by the occurrence of tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the appearance of pain when palpating with fingers in the area of the left hypochondrium, 5 cm above the navel. Actions occur due to the protective properties of the body in an attempt to hide the organ under tense tissue in the area of inflammation. This is a fairly common symptom.
- Mayo-Robson sign. Let's consider the method in more detail.
Mayo-Robson sign
A similar symptom appears in acute pancreatitis, during an attack, but is not detected in every patient. The symptom is detected in the form of sharp pain when you press the Mayo-Robson point, its position is detected in a certain way:
- the point is located in the projection of the body and tail of the pancreas;
- visually draw a line from the navel up to the center of the lower rib on the left side;
- the source of pain is localized in the middle third of the drawn line.
If the tail of the pancreas is affected, pain will appear in the front or back of the body; in other cases, the method does not work.
This nominal syndrome was studied in detail and scientifically substantiated by the English surgeon Arthur William Mayo-Robson at the beginning of the 20th century. In addition to the symptom, the doctor studied many topics related to diseases of the internal organs, which became the basis of the treatment method.
The article lists the author's main signs of pancreatitis. Additional symptoms of the disease are also known. As a rule, the detection of at least two symptoms during examination becomes the basis for admitting the patient to the hospital and carrying out appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of pancreatic inflammation by authors
The doctor also determines the symptoms of pancreatitis according to the authors. A thorough examination of the patient in the initial stages helps to avoid invasive (penetrating) tests.
The main symptoms of acute pancreatitis during an objective examination include several techniques. Among them:
- Voskresensky's symptom, also called the “shirt” symptom. The doctor makes a sliding movement from top to bottom towards the projection area of the pancreas as the patient exhales. At the end of the movement, the patient notes increased pain in this area. The sign is positive. The “shirt” symptom is also determined in acute appendicitis, so you cannot rely on this method alone.
- Mayo-Robson sign for pancreatitis. On the left in the costovertebral angle or in the area above the pancreas, the patient notes severe pain. The doctor palpates the Mayo-Robson point, pressing lightly on it. In this case, the person notices increased pain.
- Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom. The doctor slowly presses his hand on the patient's abdominal wall and sharply removes it. The consequence is sharp pain in the affected area caused by irritation of the peritoneum.
- Kerte's sign. Increased pain and muscle tension during superficial palpation in the area above the navel (about 4-5 fingers) along the midline of the abdomen.
- Razdolsky's sign. While tapping over the inflamed gland, the patient notices increased pain. This is due to peritonitis. Razdolsky's sign is positive in acute pancreatitis.
- Sign of Kach. When trying to palpate the area of the tail of the pancreas, the patient experiences severe pain. More often the symptom is positive during an exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
If emergency medical personnel detect one of the above signs and symptoms, the patient should be immediately hospitalized in a hospital to confirm the diagnosis and further treatment.
There are also additional signs of pancreatitis. The most commonly used symptoms in practice are the following:
- Cullen - characterized by the appearance of cyanosis in the patient's navel. This indicates the “impregnation” of nearby tissues with the decay products of the inflamed gland.
- Mondora - is characterized by the fact that the patient, together with abdominal pain, vomiting and signs of irritation of the abdominal wall, has cyanosis of the face, and spots of blue and purple colors appear on the body. This indicates that the breakdown products of the gland enter the bloodstream and, as a result, more distant tissues are affected.
- Lagerlef - provokes general cyanosis of the face and limbs.
- Tuzhilina - during the initial examination, the presence of angiomas on the face (proliferation of blood vessels under the skin) is noted. The presence of subcutaneous purple spots with a diameter of up to 5 mm is visually determined.
- Güllen - manifests itself in the fact that the patient develops jaundice in the navel area.
- Grotta - characterized by hypotrophic changes in the area of projection of the inflamed gland.
- Georgievsky-Mussi - a person experiences a sharp sharp pain in the right hypochondrium when pressing a finger into the fossa of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. This is due to irradiation along the nerve branches of the diaphragm.
- Desjardins - when pressing on the area located 4-6 cm from the navel towards the armpit (at Desjardins' point), pain is determined. This symptom in 75% of cases is positive for inflammation of the pancreas.
- Gubergritsa-Skulsky - pain on palpation in the projection of the line connecting the tail part with the head of the pancreas.
- Shoffara - increased pain in the projection of the head of the inflamed gland (Shoffara area) when pressed.
If most of the symptoms are confirmed, then additional laboratory and instrumental non-invasive examination is carried out. If necessary, deeper penetration testing is prescribed. In such cases, once the diagnosis is confirmed, surgical treatment is performed. If there was no invasive intervention, then further treatment tactics depend on the severity of the disease.
Voskresensky's symptom in pancreatitis and some other clinical manifestations are the most important signs of this particular disease. Pancreatitis is an inflammatory-dystrophic disease of pancreatic tissue.
The pathology is characterized by a chronic and rapidly progressive course. The absence of the required drug treatment leads to pancreatic dysfunction, that is, the organ stops working.
There are many causes of pathology. These include alcohol abuse for 3-10 years, some diseases of the biliary system (usually in women), poor diet with a low content of proteins and fats, and hereditary predisposition.
Typically, patients complain of pain in various locations. During an exacerbation, the pain syndrome is acute, haunts the patient, is localized in the upper abdomen, and radiates to the back. In the chronic course, the pain is less pronounced.
Common symptoms of pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a disease that results in inflammation of the pancreas. The cause of pancreatic disease may be hereditary predisposition, alcohol abuse, pathologies of the digestive system, chronic diseases, poor diet and other negative factors.
Characteristic symptoms are:
- Yellowing of the skin and sclera.
- Pallor of the complexion, which later gives way to a so-called sallow tone.
- Sunken eyes.
- The appearance of bloody marks in the groin and abdomen.
- Plaque on the tongue.
- Smell of acetone in the mouth.
- Dyspnea.
- Increased heart rate.
- Pain sensations radiating to the left side and lower back.
- Dyspeptic disorders.
source
Symptoms by author
Pancreatitis according to the ICD-10 code can be infectious and acute, with purulent complications, subacute, hemorrhagic. K86.0 means a chronic disease of alcoholic etiology, K86.1 means other types of chronic disease.
There are only three classic symptoms associated with an acute illness: painful
sensations, increased gas formation, vomiting. This is Mondor's triad for pancreatitis.
The Mayo Robson symptom for pancreatitis is determined by painful sensations at the site of the projection of the pancreas. This is the left side of the costovertebral ganglion. This sign is observed in 45% of clinical pictures. The sign is determined by lightly pressing this point. If there is an increase in pain, this indicates inflammation of the internal organ.
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis by author:
- Kerte's sign. The main symptom is pain upon palpation in the area located above the navel five centimeters from the center line. Usually diagnosed in 65% of all morbidity cases. In addition, this author’s sign is positive when muscle tissue tension is detected in the epigastric area.
- Kach's symptom is defined as intense pain when trying to palpate an area in the projection of the tail of the pancreas. The location of the point is the area of the transverse process of the 8th thoracic vertebra. In most cases, the symptom is positive against the background of the chronic form of the disease. In some pictures it is observed in the form of high susceptibility of the skin in this area.
- Razdolsky's sign is detected in the acute form of the disease. It is characterized by sharp pain that develops during percussion of the skin in the area of the projection of the internal organ. Based on inflammatory processes in the peritoneum.
Chukhrienko's symptom is detected in 38% of pictures. Consists in the presence of pain during jerky movements of the abdominal wall with the hand in the direction from bottom to top.