Causes
Causes of appendicitis include:
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system, which increase the risk of the spread of infections in the body, including in the appendix;
- the presence of obstacles in the lumen of the appendix (dense stool, for example);
- diseases associated with parasites and worms (ascariasis, enterobiasis, opisthorchiasis, giardiasis);
- tumor formations of the intestines and bladder;
- foreign objects getting inside.
These factors lead to blockage, that is, the appearance of a plug in the lumen of the appendix, as a result of which pathogenic microbes actively multiply in this area. As the appendix stretches, it is not sufficiently supplied with blood, and an inflammatory process develops. It causes significant pain as it irritates nerve cells. Lack of timely diagnosis of the disease leads to the transition of appendicitis to the purulent stage.
Some infectious diseases can contribute to the development of appendicitis:
The cause of this disease can be vasculitis - inflammation of the walls of blood vessels.
Complications after surgery
Significant complications of the surgery for a woman’s health include discomfort from scarring of a surgical wound (when the suture hurts from appendicitis during pregnancy), and an increase in peritonitis (if proper antibiotic therapy is not carried out). The consequence of surgical treatment in the first trimester is fetal death, the risk of which can also occur in the event of rupture of the inflamed appendage of the cecum.
If inflammation of the appendix is suspected in pregnant women, prophylactic treatment with antibiotics is necessary in all cases of laparotomy.
Appendicitis is rare during pregnancy but can have serious consequences, especially for the fetus. Unfavorable outcomes include even his death. A thorough medical history and physical examination of the patient will help avoid death and save the child.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease in nursing mothers depend on its stage. Signs of acute appendicitis include:
- pain - as a rule, they are localized in the area above the navel or near it, but there are situations when it is difficult to identify the location of the pain. As the disease progresses, the discomfort shifts to the right side of the abdomen. In this case, the pain can be described as dull, continuous, but tolerable, which progresses with movement and even coughing. More serious stages of the disease can occur without pain, which is associated with the death of the nerve endings of the appendix. This situation is extremely dangerous, since it is assessed by the nursing mother as an improvement, although, in fact, significant complications in the form of peritonitis and intestinal obstruction may appear in the near future;
- disturbances in the normal functioning of the stomach, resulting in nausea, rare episodes of vomiting, a feeling of dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth, decreased appetite, one-time bowel disorders;
- increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- disruptions in the processes of breathing and heartbeat (rhythm instability).
The chronic stage of appendicitis does not have clear symptoms. A girl who is breastfeeding may regularly experience pain in the abdominal area, which becomes more noticeable with intense physical activity and changes in position. As a rule, this form of the disease is not accompanied by other symptoms and does not manifest itself in any way.
Diagnosis of the disease is based on a preliminary history taking, analysis of complaints and examination of the patient. The doctor also takes into account family history and life history, that is, he will be interested in the following questions:
- what diseases were present in childhood;
- whether there were infections with infectious diseases;
- whether surgical interventions were performed;
- Do close blood relatives suffer from gastrointestinal problems?
A mandatory examination of the patient is carried out, including:
- palpation of the abdomen;
- measuring body temperature;
- assessment of the condition of mucous membranes and skin.
An experienced specialist may be able to diagnose some specific symptoms of appendicitis, such as:
- flow of pain from the area around the navel to the right lower abdomen;
- the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the right iliac zone upon percussion of the anterior abdominal wall;
- severe pain when raising the arm lying on the right iliac region;
- progression of pain when trying to roll over onto the left side of the body.
The list of mandatory laboratory tests when diagnosing appendicitis includes:
- blood, stool, urine tests;
- tests for the presence of parasites and worms (ascaris, pinworms, opisthorchiasis, lamblia);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- Ultrasound of the appendix;
- ECG (additional examination, which excludes the possibility of pain due to impaired blood flow in the heart).
Signs of appendicitis in women: 9 main symptoms
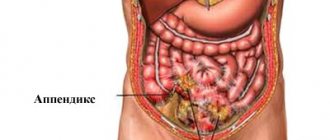
The appendix (vermiform appendix) is a rudimentary organ of the digestive tract into which the lumen of the cecum opens.
Its functions and tasks in the body have not been fully studied, but a connection with the immune and lymph circulation systems has been noted. Features of the anatomical structure and physiology of the appendix are the reasons for the high risk of inflammation. Acute appendicitis is one of the most common surgical diseases in the world. It can develop in any person, regardless of age, gender, or nationality.
What are the first symptoms of appendicitis in women, and what features does the pathology have in the fair sex? The basics of clinical diagnosis of inflammation of the appendix are in our article.
Causes
The attack usually begins suddenly. Immediately before it starts, the person feels great. Typically, the first signs of the disease appear in the evening or at night.
Here are the main causes of appendicitis that make up the clinical picture:
- Individual features of the structure of the appendix;
- Infection from the intestines or through the blood;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Inflammation begins due to disturbances in the circulatory system of the appendix;
- There are cases when inflammation of the appendix spreads from the genital organs.
- Obstruction or mechanical blockage of the process. Due to the fact that the lumen is blocked due to a foreign body or fecal stone, the contents stagnate in the appendix, an infection occurs and a rapid inflammatory process begins. Blockage occurs due to enlarged lymph nodes, due to parasites, due to the appearance of some tumors or neoplasms.
In this regard, among the preventive measures for appendicitis in women are:
- Fight allergic conditions, which also contribute to decreased immunity;
- Try to prevent the development of dysbacteriosis;
- It is advisable to minimize the number of stressful situations;
- Proper nutrition to help eliminate the problem of constipation, diarrhea and indigestion. This means that you need to have a sufficient amount of fiber, and you also need to eat less fatty and hard-to-digest foods;
- Maintain immunity (frequent inflammatory diseases can lead to infection in the appendix) Chronic diseases of the stomach, pancreas, intestines, genitourinary system organs and persistent inflammation of the tonsils are especially dangerous.
On which side is appendicitis located in women?
In most people, appendicitis is located on the right side, between the ilium and the navel - the most painful sensations appear in this place. Pain is the main typical symptom of appendicitis, but it is not always possible to diagnose it correctly.
An attack in women usually begins with moderate painful sensations concentrated in the epigastric region. This is the epigastric space area located in the upper abdomen. In some women, pain may be localized in the center of the umbilical ring or in the periumbilical space.
Within 10-12 hours, the pain usually maintains its intensity and begins to intensify 1-2 days after the onset of the attack. Most patients describe the nature of the sensations as intermittent, cramping pain with short periods of subsidence.
The intensity of pain during the first day remains within moderate levels.
A typical symptom of inflammation of the appendix is the displacement of pain to the right iliac zone.
In approximately 13% of patients, unpleasant sensations immediately appear in this projection, but this clinical picture is not considered typical for classic cases of catarrhal appendicitis.
Women with a low pain threshold may describe the pain syndrome as diffuse or girdling pain, without indicating a clear localization or identifying the point of maximum pain.
Unpleasant sensations with appendicitis intensify with any physical stress, for example, changing body position or walking, so the woman tries to take a lying position (on the right side), in which the pain weakens slightly.
An attack of appendicitis can also be recognized by a characteristic position when a woman tries to relieve the abdominal muscles by bringing her knees to her stomach.
This position is called the “fetal position” and is considered one of the main signs of acute inflammation.
The first signs of appendicitis
In addition to pain, acute appendicitis in women has other symptoms. Usually the disease manifests itself suddenly, often in the evening and at night. Its first signs include:
- loss of appetite;
- an increase in body temperature to 37.5-38 °C (in adult women over 40 years of age, this symptom may be absent; on the contrary, the temperature may decrease);
- chills, increased heart rate - general symptoms of inflammation and intoxication;
- dry mouth;
- yellow coating on the tongue;
- bloating;
- upset stomach, loose stools;
- frequent urge to urinate.
In some cases, symptoms of appendicitis in women can mimic food poisoning, an attack of cholecystitis and other diseases of the digestive tract. In addition, the manifestations of this surgical pathology are similar to the clinical picture of ectopic pregnancy, rupture of an ovarian cyst, and inflammation of the appendages.
Pregnant women represent a special category of patients with appendicitis. Compression of the abdominal organs by the growing uterus creates the preconditions for the development of inflammatory processes in the intestines. Often expectant mothers associate discomfort and pain with their special situation, which in the case of appendicitis can be very dangerous.
In pregnant women, the disease proceeds according to the standard scenario. In most cases, pain develops in the epigastrium, and only after a few hours it “descends” to the right iliac region (Kocher’s symptom).
Most patients characterize it as acute, of moderate intensity. At the first signs of pathology, it is important to consult a doctor, who will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Appendectomy (an operation to remove an inflamed appendix) is well tolerated by pregnant women and does not harm the unborn child.
Symptoms in pregnant women
Pregnancy complicates the diagnosis. The longer the period, the more difficult it is to determine the true cause of the pain and perform surgery. Some symptoms of appendicitis in pregnant women are normal signs of fetal development.
The expectant mother does not always associate nausea and low fever with illness. Therefore, it is important to know how to recognize incipient inflammation. If there is an acute pain in the abdomen that becomes aching, intestinal upset, or other symptoms of acute appendicitis, consult a doctor immediately.
Appendicitis: how to identify symptoms in women at home
If there are suspicions that nagging pain in the lower abdomen is a consequence of appendicitis, then the pathology can be diagnosed at home using the palpation method.
We lay the woman on a flat surface and carefully bend her legs at the knees. Next, gently press with your fingers on the right side of the abdomen. You need to apply gentle pressure with your fingers on the abdomen, as strong pressure may damage the inflamed appendix and cause it to burst.
If the pain increases during palpation, this indicates that the appendix is inflamed and the patient urgently needs medical attention. When palpating, you need to use your index finger. Using the pad of a bent finger, lightly tap on the right pelvic area.
With light pressure in the event of an attack of appendicitis, the pain is always localized there.
To compare sensations, you can gently press on the left area. With appendicitis, these movements will not cause discomfort. The main thing is that movements be careful, since a ruptured appendix can provoke peritonitis.
To diagnose appendicitis, you can resort to a simple method - cough loudly. If the pain intensifies in the area of the right ilium, then this confirms the diagnosis.
In addition, you can press with your palm in the area of the abdomen where the greatest pain is observed. You need to hold your hand for about 10 seconds, at which point the pain subsides. Then we remove our hand and if the pain intensifies, then most likely it is acute appendicitis.
Only doctors can help in this case, so do not hesitate and urgently call a medical team.
So, you can recognize inflammation of this appendix at home by the following signs:
- the pain intensifies and then goes away;
- when coughing, laughing, hiccups and any other movements, the pain in the side increases;
- if you turn over from one side to the other, the discomfort increases;
- after vomiting there is no relief;
- Most often, attacks of appendicitis occur in the evening or at night;
- When palpating the abdomen, the patient feels severe pain.
If you suspect you have appendicitis, do not take painkillers under any circumstances.
Features of the clinic of inflammation of the appendix with an atypical location
With a retrocecal location, the pain may be of low intensity. The process is usually limited. Irradiation to the lumbar region is noted. An increase in pain while lying down is detected when trying to raise the right leg.
When the process is localized retroperitoneally, the characteristic signs from the abdomen are erased. The pain is localized in the lumbar region and intensifies with beating. Signs of urinary dysfunction appear.
Body temperature rises to more than 39 °C.
When the appendix is in the pelvis, there is slight pain above the pubis. There is loose stool, the urge to defecate, and difficulty urinating. With a midline position, the pain is localized around the navel.
There is a high fever and flatulence. There is tension in the abdominal muscles in the umbilical region. If the appendix located in the subhepatic space is damaged, the clinical picture is identical to acute cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder).
There is a dull pain in the right hypochondrium.
With left-sided appendicitis, pain is localized on the left. Determination of the heartbeat on the right side indicates the reverse arrangement of the organs.
Diagnostics
For any symptoms, it is recommended to call an emergency team. This will save lives if the disease is confirmed. Early stages of an attack of appendicitis are more operable, the development of pathologies is minimized.
At the medical facility, blood is initially drawn. If the level of leukocytes is elevated, the patient is sent for a general examination and research procedures (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, radiography).
A urine test is also checked to rule out diseases of the genitourinary system.
If for some reason the diagnosis is not established, laparoscopy is performed (modern technologies make it possible to carry out the procedure with minimal damage to the skin, the scar will be invisible).
During the examination, you need to fully describe the pain symptoms and indicate the nature of the manifestation. If possible, remember the exact time the pain began.
Complications
Appendicitis is dangerous due to the development of severe consequences. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, the following complications may occur:
- Peritonitis. It is characterized by an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity, in which the blood becomes infected. Most often, this pathology leads to death.
- Abscess. This formation forms on the intestinal walls and omentum.
- Adhesive process. In the future, it usually provokes intestinal obstruction, pain syndromes in organs that enter the pelvis, and infertility.
- Inflammatory process in the portal vein, which is located in the liver. Various infections from the appendix enter it hematogenously. Survival in such a situation is reduced to zero.
Thus, to avoid the development of dangerous complications, women need to pay attention to symptoms such as acute abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. But these symptoms may indicate other diseases. Therefore, it is important to seek medical help to confirm or refute a diagnosis such as appendicitis and begin treatment.
How is appendicitis removed?
Surgery to remove the appendix is the main method of treating the pathological condition.
In medical terminology, it is called an appendectomy. To do this, an incision is made in the abdominal cavity, after which the organ is removed. This operation lasts from 30 minutes to two hours.
In addition, laparoscopic surgery is increasingly being performed. A laparoscope is used to make a hole through which the appendix is removed.
This method has an advantage over the first: the number and visibility of scars is minimized. The duration of this operation is up to 40 minutes.
Surgery can be emergency or planned. Emergency surgery is prescribed at the last stages of the pathology. This type of intervention is also indicated when there is a risk of developing peritonitis and sepsis, which lead to death.
Planned operations are performed if inflammation of the appendix occurs at the initial stage.
Postoperative period
After the operation, the doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy. Medicines and their regimen are selected on an individual basis. If there is a predisposition to thromboembolism, anticoagulants are prescribed.
A scar measuring up to 10 cm is formed at the site of the operation. It heals for about six months. Immediately after the operation, it has a burgundy tint, and over time it turns white. To resolve it, specialized ointments and creams are prescribed. Following your doctor's recommendations ensures a quick recovery. With proper care, the likelihood of wound suppuration is significantly reduced.
Diagnosis is simplified by specific symptoms of appendicitis in women; how to determine the disease at home becomes clear after studying physiology. The main difference is the location and nature of the pain. But only a specialist can make a final diagnosis.
Source: https://doc-doc.net/appenditsit-u-zhenshhin-simptomy/
Treatment
Treatment of appendicitis is carried out exclusively by surgery, so self-therapy can cause significant harm to the health of a nursing mother and cause serious complications. If alarming symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately call a doctor.
Before the operation, the doctor conducts an examination and special preparation of the patient. During surgery, the appendix can be removed from the body in two ways: through an incision (laparotomy) or a small hole (laparoscopy) in the abdominal wall. The latter option is becoming increasingly popular and has the least consequences for the health and appearance of a nursing girl.
The postoperative period requires a reduction in physical activity for about 1-2 months, bed rest in the first days, observation by a surgeon and therapist, as well as timely treatment of the wound.
In the future, the patient should adhere to a certain diet, excluding baked goods, fatty, sour, fried, spicy foods, coffee, alcohol and processed foods. Meals should be small and frequent. Additional vitamins may be required.
Effective treatment
Surgery is the only treatment for appendicitis during pregnancy.
Surgery is the only way to promptly and quickly solve this problem. You should not take painkillers and hope that it will go away on its own, wasting valuable time for successful treatment.
Surgical procedures are performed only under anesthesia, but the postoperative period is considered the most critical for the expectant mother, since the risk of complications is increased.
That is why drug therapy is very important, which includes taking medications that relax the muscles of the uterus and antibiotics - in order to avoid extremely unwanted infection. Also, upon completion of the operation, a weight or ice is placed on the woman’s abdomen, which casts doubt on the pregnancy after appendicitis.
After discharge, doctors continue to monitor the condition of the woman and fetus, since complications can arise even after a month after surgery.
If labor occurs
If childbirth occurs in the early period after appendectomy, it is carried out under special attention. To avoid divergence of surgical sutures, the mother's abdomen is tightly bandaged. Pain relief is carried out with broad-spectrum antispasmodics.
One of the conditions for successful delivery after surgical removal of the inflamed appendix is the prevention of lack of oxygen supply to the fetus. This condition is called intrauterine hypoxia.
The perineum is dissected to shorten the expulsion period, since pushing increases pressure on the abdominal wall, and this can cause disruption of the postoperative sutures.
The mother's blood clotting status is monitored and risks are assessed - the possibility of bleeding in the postpartum period, weakness of pushing.
Prevention
There are no special measures to prevent appendicitis. A girl who feeds her child with breast milk must adhere to a proper, balanced diet and treat infectious, parasitic and chronic diseases in a timely manner. These measures will help reduce the risk of appendicitis.
Hi all! I have a sudden problem and there is no way to look for information, I rely on you. My daughter is 1.11, and I think I have appendicitis. Now I’m home alone with the child, dad is on a business trip until Wednesday. I’m waiting for my grandmother to get home from work (at 10 pm) and call an ambulance, because the pain is still bearable, but it’s getting worse and is localized in the “right” place. Or I’m screwing myself up (but I don’t have the right to die from peritonitis in an empty apartment next to a child). In any case, I'm feverishly trying to prepare for a possible operation. The biggest question is breastfeeding. My daughter is very attached to the breast, she suffered an intestinal infection just recently, drank only solid milk and now breastfeeds a hundred times a day. I don't limit it. Falling asleep all with the breast, sleeping together with the breast in the mouth, the whole set in short