If a person has been examined and is sure that his liver hurts, then the doctor prescribes a course of treatment. It is impossible to get rid of this symptom quickly. The pain will decrease as the activity of the process decreases.
Different liver diseases require different approaches to therapy. At home, they usually continue the started inpatient treatment, but in smaller dosages. Acute hepatitis is treated for up to two years to prevent it from becoming chronic.
Recommendations on what to do at home can be obtained from specialists in infectious diseases in the treatment of viral hepatitis, or from a gastroenterologist. Hepatologists have appeared in large medical centers.
When is treatment prescribed?
True pain in the liver is rarely intense. Localized in the right hypochondrium. Feels like dullness, aching or constant heaviness. They can radiate to the right side, back, and epigastric region.
Additionally, signs of impaired digestion appear: bloating, diarrhea or constipation, weakness. With a long course of chronic diseases, the main symptoms are disorders of all types of metabolism: bleeding gums, loss of appetite and weight loss, itching of the skin, decreased mental abilities (severe memory impairment).
With hepatitis, some time after the onset of pain, jaundice, darkening of urine and discoloration of feces should be expected. Men gradually develop impotence, and women are often treated for infertility.
The diagnosis takes into account localization, irradiation, and the nature of pain.
Pain becomes intense with a growing malignant tumor, cyst suppuration and abscess formation, and fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity (ascites). Heart defects with circulatory failure are accompanied by an increase in congestive liver and throbbing pain in time with heart contractions.
Patients should know that the liver cannot suffer from sudden attacks. Cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, and pancreatitis are of a similar nature. This pathology can occur in parallel with liver disease, maintain its activity, and cause additional digestive disorders.
A gradual increase in pain with movement to the iliac region on the right is typical for acute appendicitis. If there is severe pain in the hypochondrium and in the back, one should think about diseases of the right kidney.
There are quite a few pathological conditions that simulate pain in the liver. Only an experienced attending physician can correctly differentiate their origin. He will figure out what causes the pain and tell you how best to get rid of it. Timely seeking medical help helps to avoid a severe neglected condition.
Diet for the liver
Since the liver is the filtration apparatus of the entire body, our task is to ensure that as little harmful and polluting elements as possible enter this filter. And for this we need to carefully (if possible) monitor what we eat, drink, and what we breathe. And, if you cannot stop the production of metallurgy or chemicals in your city, then you can and should control what goes into your mouth. Let's start with food, or rather, with diet. The diet prescribed for liver diseases has one specific goal - to ease the work of an already “tired” liver. Therefore, we draw up a precise diet and follow it strictly.
Must be present: • Milk in any form and products associated with it, naturally, not fatty. • Lean meat (chicken, veal, beef), cooked in any way you can, except frying. • Lean fish, also cooked, in any way other than frying. • Vegetables in the form of soup, side dish, or both. A special highlight is sauerkraut - a very powerful absorbent for heavy metals. • Cereals, pasta. • For sweets: honey and what you can make at home (marmalade). If you buy it in a store, read the ingredients.
Undesirable, but allowed in the diet: • Butter no more than 30-50 grams for children and adults, respectively. • Cheeses, sausages, home preserves • Chicken eggs no more than twice a week, ideally replaced with quail eggs.

If you have liver disease, it is especially important to adhere to the principles of a healthy diet.
Absolutely exclude: • Alcohol, especially low-alcohol cocktails. • Everything that is fried, smoked, pickled. • Fatty meat, regardless of the cooking method (pork, lamb, goose). • By-products (liver, heart, lungs). • Beans and those foods that specifically cause flatulence in you. • Anything that contains cocoa beans. • Store-bought sweets that are high in fat. It is recommended to replace it with homemade cakes, where you can replace, for example, buttercream with custard. • Hot spices and seasonings, especially if vinegar is present. It should be remembered that this list is general and your attending physician may introduce individual restrictions and/or relaxations in the diet.
Treatment regimen for liver diseases
It is impossible to quickly relieve pain without general liver therapy. Almost any organ pathology requires the restoration of dying hepatocytes, the fight against inflammation and swelling. Treatment will require following a diet, giving up alcohol and smoking, and stopping heavy physical activity.
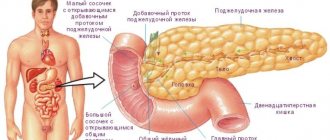
Barrier function of the liver
Antibacterial drugs are used when bacterial abscess formation is detected; echinococcosis is treated with special antiparasitic agents.
The treatment of viral hepatitis requires expensive antiviral drugs and immunomodulators. For autoimmune processes, high doses of corticosteroids and cytostatics are used.
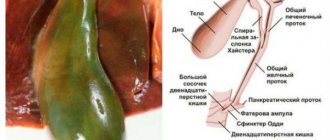
In order to support cell regeneration, drugs from the hepatoprotector group and vitamins are prescribed. To improve the processes of bile formation and outflow, choleretic drugs of different effects (choleretics and cholekinetics) are used.
With concomitant cholecystitis and spastic duct dyskinesia, antispasmodics are used to relieve pain. How to treat pain in a particular patient becomes clear after the examination.
The effect of alcohol on the liver
One of the worst catalysts that causes organ disease is alcoholic drinks. Despite the fact that their harm is known to everyone, many people continue to drink alcohol every day.

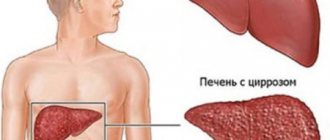
Each body reacts to intoxication in its own way. Essentially, alcohol destroys liver cells. Thanks to the high regenerative functions of this organ, they are restored. But with constant drinking of alcohol, the cells do not have time to regenerate. Gradual destruction occurs. In addition, connective tissue begins to grow. And this leads to an increase in the volume of the gland.
The above processes lead to diseases such as fibrosis and cirrhosis. Already at the initial stages of alcoholism, steatosis begins to develop. This is a disease that causes heaviness in the liver area. It causes many unpleasant sensations. In addition to the liver, alcohol affects the gallbladder and stimulates the occurrence of cholecystitis. These ailments should be dealt with promptly. Below we will discuss how to cure the liver with folk remedies.
The occurrence of chronic alcoholism is expressed in aching pain. From a medical point of view, not only the liver will become thickened and enlarged. The spleen will also be affected.
What to do if the pain is not associated with pathology?
Pain in the liver can occur in a practically healthy person if they try to run or exercise after drinking alcohol. Without constant support for the body's fitness, when playing sports, the liver capsule becomes overstrained due to filling with blood.
Failure or improper breathing disrupts the movements of the diaphragm. This causes pain.
You shouldn't give up training. You need to review your preparation and:
- reduce the load;
- add time for rest;
- learn to control your breathing;
- Do not allow physical activity immediately after lunch, you can eat food no later than 2 hours before training, while trying to avoid fatty foods, heavy fried and spicy foods.

The main advice is not to get drunk to the point of toxicity, then you won’t need to look for medications
If pain bothers you the morning after a party with alcoholic drinks, then it is necessary to “unload” the liver while it processes alcohol. Alkaline mineral water without gas, liquid oatmeal, herbal tea, and low-fat cottage cheese are suitable for this. You can start taking hepatoprotectors, although you cannot expect a quick effect from these drugs.
Sometimes pain appears while taking antibiotics prescribed by a doctor to treat some process. You should remember about the possibility of negative effects on the liver and individual sensitivity to the drug. It is necessary to inform the doctor and change the medicine.
What drugs are there?
Medicines for liver diseases are prescribed only after the causes of the disease have been determined. Depending on the provoking factors, medications from several pharmacological groups are used in therapy. Among them:
- antiviral;
- anti-inflammatory;
- choleretic;
- cholelitholytics (used for “crushing” stones in the treatment of the liver and gallbladder);
- antispasmodics;
- correctors of insulin resistance (for example, Metformin);
- anti-obesity drugs (Orlistat);
- vitamins;
- amino acids;
- adsorbents;
- hepatoprotectors.
The last of these groups includes drugs with various active ingredients that are intended to protect and restore the cellular structure of the liver. Despite the common goal, hepatoprotectors differ in their mechanisms of action, contraindications, and degree of effectiveness in certain cases. The form of release of the drugs is also of great importance.
Taking any medications without a doctor's prescription poses a threat to human life!
Pills
This dosage form is achieved by pressing active and additional substances. Effective tableted hepatoprotectors are:
- Silymarin;
- Cyclalon;
- Liv 52.
Taking these drugs increases the synthesis and growth of hepatocytes. Tablets are convenient to use independently, but in some cases their use is impossible or ineffective. In such situations, the doctor will recommend a product in a different form of release.
Medicines in another form
Often hepatoprotectors are produced in the form of capsules. The advantage of this category of drugs is the presence of a gelatin shell that is resistant to the action of gastric juice. Drugs that dissolve in the intestines include:
- Gepabene;
- Hepatosan;
- Rezalut Pro.
The components inside the capsules can be in liquid or powder form. The coating makes it possible to hide the unpleasant taste or smell of the medicine.
Injection is indicated for severe forms of disease, when the liver needs to be treated quickly and effectively.
Hepatoprotectors in ampoules include:
- Heptral;
- Essentiale N;
- Remaxol;
- Phosphogliv;
- Cryomert MN.
The drugs can be injected into a vein or muscle. The active ingredients in the ampoules reach their goal much faster, without having a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
The liquid form of release in the form of drops is released by a high concentration of active substances. For internal use, these can be tinctures, extracts or aqueous solutions. Drops used for the liver:
- Galstena;
- Ovesol;
- Hofitol.
Their advantage is that they can be used to treat small children or people with impaired swallowing reflex.
The doctor must choose the form of release of the drug. In addition, the following precautions must be observed:
- Do not chew tablets or open capsules before taking them;
- the joint use of different drugs for the same pathology is permissible, but only for medical purposes;
- dilution of products in ampoules should be done only with the solution specified in the instructions;
- drugs of various pharmacological groups should be taken at two-hour intervals.
Injectable medications for the liver should not be mixed with other drugs - this can cause a severe allergic reaction.
In addition to the release form, hepatoprotectors differ from each other in their active ingredients.
Hepatoprotectors
The active substances of hepatoprotectors act at the cellular level, restoring hepatocytes (the main cells of the liver), enhancing their functionality.
In addition, the drugs:
- relieve inflammation;
- stop oxidation reactions;
- stop the synthesis of keloid tissues in the organ.
Different substances have certain effects that are advantageous, so they are used to treat various liver pathologies.
Hepatoprotectors are divided into drugs:
- plant etiology, which are produced on the basis of milk thistle, licorice, artichoke and some other plants (Gepabene, Hofitol, Galstena, Tykveol);
- animal origin, often from pork liver (Sirepar, Gepadif);
- based on essential phospholipids (Essentiale Forte, Phosphogliv, Antraliv);
- predominantly detoxifying action (Hepa-merz, Glutargin);
- with bile (ursodeoxycholic) acid - Ursofalk, Ursosan, Livodex;
- different groups (containing thioctic acid) - Octolipen, Berlition.
All of the drugs listed have their pros and cons, as well as individual contraindications. They must be taken strictly following the dosage and instructions for use. It is not possible to quickly cure the liver; the average course of taking hepatoprotectors is from three to six months.
If you can't see a doctor
Every person can face a situation where the pain is not severe, but interferes with work and business. To reduce intensity it is recommended:
- go on a diet diet for at least 2 weeks;
- take an antispasmodic tablet (No-shpa, Spazmalgon, Papaverine), the pain will decrease if it is associated with a violation of the outflow of bile;
- drink slightly warmed alkaline mineral water (Borjomi, Essentuki 4) and lie on your right side;
- Brew herbal tea with corn silk, immortelle, chamomile and drink it throughout the day;
- start a course of treatment with hepatoprotectors, which can be purchased at a pharmacy without a prescription (Essentiale, Karsil, Gepabene, Darsil, Methionine);
- if you feel nausea and bitterness in your mouth, you should choose one of the choleretic drugs (Allohol, Hofitol, Cholemax).
If there is no effect and the pain increases, you will have to find an opportunity and consult a doctor.
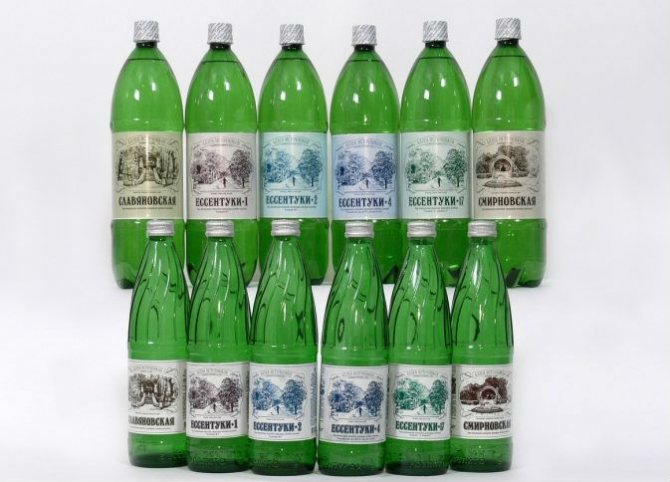

When choosing mineral water, you should be guided by low salt concentration and alkaline reaction, this corresponds to “Essentuki 4”
Dietary requirements for liver pain
At home, it is necessary to provide a person with liver pain with proper dietary nutrition. It must correspond to the task of maximum unloading of the organ with a sufficient supply of necessary nutritional components.
Nutrition rules include:
- mandatory avoidance of animal fats, preservatives, alcohol, carbonated water, hot seasonings, coffee, chocolate, and fried foods;
- ensuring protein composition through products with easily digestible forms (rabbit meat, poultry, veal);
- maximum replacement of butter with vegetable oil, it is better to use purified, refined types (sunflower, flaxseed, olive);
- reduce the amount of carbohydrates by avoiding culinary products, cookies, and sweets;
- cook food by steaming, boiling, baking, stewing;
- feedings should be frequent (every 2–3 hours), but in small portions;
- To cleanse the intestines, provide a sufficient amount of fiber through bran and diet bread, salads with fresh vegetables.
The diet can be formed from the following set of products:
- dried bread made from rye flour or with bran;
- soups with vegetables, lean meat, sea fish;
- boiled and steamed meat cutlets, meatballs, meatballs made from chicken, lean beef, veal;
- steamed or boiled fish (hake, flounder, cod, horse mackerel);
- butter up to 30 g per day, and vegetable oil - up to 50 ml;
- vegetable casseroles from pumpkin, cabbage, carrots, zucchini;
- porridge with water;
- fresh fruit juices, jellies, whole fruits only sweet;
- dairy products, cottage cheese, low-fat cheese;
- green tea with honey, rosehip infusion.

For dietary nutrition, you need to monitor not only the concentration of fat, but also the period of its production, and patients with liver diseases need to take kefir and yogurt not exceeding a two-day date
Treatment at home: pros and cons
Treatment of liver inflammation should be comprehensive. The doctor may prescribe medications containing phospholipids and amino acids, medications of plant or animal origin, a special diet and therapeutic exercises. The use of traditional medicine at home effectively affects the restoration of the liver.

But such drugs are more effective in the early stages of the disease and require long-term use, so they should be used only as a complement to drug treatment.
Home medicine methods: recipes
- Chicory. Leave two tablespoons of chopped chicory in two glasses of boiling water for half an hour. Add lemon juice and two tablespoons of honey. Drink a glass three times a day.
- Radish. Drink half a glass of a mixture of equal parts radish juice and beet juice every day.
- For cirrhosis, it is good to drink two tablespoons of radish juice twice a day before meals.
- Corn silks, collected from ripened cobs, are brewed as tea and drunk for at least six months.
- Strawberries. Brew strawberry leaves with roots dried in the shade as tea and drink, adding sugar and milk.
- Celery. For cirrhosis, drink half a glass of a mixture of part parsley juice, part carrot juice and two parts celery juice twice a day.
- St. John's wort. Infuse a spoonful of crushed St. John's wort for 15 minutes in a glass of boiling water and drink ¼ cup three times a day.
- Mix 2 parts milk thistle seeds and 3 parts each of agrimony and crushed rose hips. In 2 tbsp. Brew 2 tbsp boiling water. l. mixture and leave for 30 minutes. Take 100 ml before meals 3 times a day for 21 days. After a week's break, repeat. Course 6 months.
- Cabbage brine. Drink the mixture three times a day: half a glass of cabbage brine and half a glass of tomato juice. The course of treatment is 6 months, then a two-week break and repeat.
- Grapefruit juice. In the evening, do an enema. Mix ¼ tbsp. grapefruit juice and olive oil. Drink before bed. Repeat the enema in the morning. Next appointment in a week.
- Dandelion. Pour 300 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of crushed dandelion roots. After 20 minutes of infusion, drink 1 tbsp. l. three times a day before meals.
- Horseradish. Add 4 tablespoons of grated horseradish to a glass of milk. Heat without bringing to a boil. Leave for half an hour and drink half a glass before meals for about a month.
- Pumpkin. Mix 0.5 kg of grated raw pumpkin with two tablespoons of honey and eat 2 spoons 4 times a day before meals. You can simply drink half a glass of pumpkin juice.
- Mix royal jelly the size of a match head in two tablespoons of honey and dissolve 0.5 tsp under the tongue. twice a day. For cirrhosis, take for a month, then take a break for two weeks and repeat.
- Warming up. Mash the potatoes boiled in their jackets. Wrap in several layers of fabric and apply hot to the right hypochondrium. Cover yourself with a blanket and hold until it cools down. Potatoes can be replaced with hot sand. You need to do 4–5 procedures.
- Bee pollen is taken 1 tsp. three times a day before meals.
- Kefir and buckwheat. Pour 2 tbsp into a glass of kefir. l. buckwheat powder, leave overnight. Add 1 tbsp. l. honey and tsp. walnuts. Drink in a day.
- Cucumbers. A decoction of overgrown cucumbers relieves pain and improves the flow of bile. Boil the fruits for 10 minutes and drink half a glass every day before meals.
- Onion syrup. Mix a glass of onion pulp with half a glass of sugar and simmer in the oven until the juice releases. Take a spoonful on an empty stomach every day for 30 days.
- Fennel. An infusion of fennel seeds effectively relieves pain.
- Purslane. Boil dried crushed purslane or a teaspoon of its seeds for a couple of minutes in a glass of boiling water. After half an hour of infusion, drink a quarter glass three times a day.
- Agrimony. Two tbsp. l. Brew the herbs in 250 ml of boiling water and add a spoonful of honey. Drink 100 ml 4 times a day. A very effective remedy.
- Honey with vinegar is used for hepatitis and jaundice. Mix a glass of liquid honey with 3 tsp. apple cider vinegar and take 1 tbsp. l. three times a day before meals.
- Mix honey with chopped walnuts in equal parts. Divide 100 g of mixture into 4 portions. This is a daily dose.
- Lemon and olive oil. Mix three tablespoons of oil with two tablespoons of lemon juice and a spoon of honey. Drink according to Art. l. before meals.
- Mix black currants and honey, one kilo at a time, and eat two teaspoons half an hour before meals.
- Volodushka is golden. Three tbsp. l. Brew herbs in 2 glasses of boiling water for half an hour. Drink 0.5 tbsp. three times before meals.

Characteristics of hepatoprotectors
At home, it is recommended to take medications that provide liver protection, cellular regeneration, and prevent bile stagnation. Modern hepatoprotectors have these properties. They will help reduce pain and heaviness. Based on their composition and origin, drugs are divided into several groups. We will look at the most common and used means.
Herbal preparations
The most commonly recommended medications are those based on milk thistle flavonoids (Legalon, Karsil, Silimar, Gepabene), licorice (Phosphogliv), from artichoke leaves (Hofitol), and other plants (Liv 52). They strengthen the membrane of hepatocytes and prevent toxins from penetrating inside.
The mechanism of action is provided by:
- binding free radicals and stopping lipid oxidation;
- stimulation of antioxidants by increasing glutathione levels;
- synthesis of proteins that accelerate the recovery of damaged hepatocytes.
The drugs are indicated for toxic, alcoholic and drug-induced hepatitis, if biochemical tests confirm activity and for prevention. Caution is required in cases of bile stagnation, since there is evidence of its enhancement by drugs containing milk thistle. There is no evidence of effectiveness in the treatment of viral hepatitis.
Preparations of animal origin
Medicines are made from cattle liver extract (Hepatosan, Progepar). They contain: vitamin B12, amino acids, liver growth factors. Prescribed for chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, drug-induced and toxic liver damage.
It is important to remember that the antioxidant and restorative effects of this group have no evidence. Moreover, the drugs can be dangerous for patients with active hepatitis, since they are pronounced allergens.
Before treatment, sensitivity to the drug should be determined; use may be contraindicated.
Essential phospholipids
The most common group of hepatoprotectors in the Russian Federation. Phospholipids: replace the “building material” of the cell membrane of hepatocytes, increase the activity of the enzyme collagenase, which destroys scar tissue, and are antioxidants.
Indicated for any liver damage. Example - Essliver Forte, a drug that, in addition to essential phospholipids, contains a combination of vitamins that enhance effectiveness:
- B1 - antioxidant and immune stimulant;
- B2 - participates in the regulation of brain activity;
- B6 - as a coenzyme regulates protein metabolism;
- B12 - provides the synthesis of the necessary enzyme for the sheath of nerve fibers;
- Nicotinamide - activates tissue respiration, fat and carbohydrate metabolism;
- E is a strong antioxidant.
The drugs of the group (Lipostabil, Essentiale Forte, Rezalut Pro, Fosphonziale) are also recommended in the treatment of diseases of the biliary tract.
Amino acids
Medicines with amino acids are important for ensuring biochemical transformations and the formation of phospholipids, taurine, glutathione, and the construction of cellular structures of hepatocytes and the brain. Example - Adomethionine.
The ability of the drug to resist fibrosis has also been proven. Especially indicated for hepatic encephalopathy. Prescribed for cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis. The best effect is obtained by injection.
Vitamins with antioxidant effects
The group is represented by vitamins E, C and lipoic acid. α-lipoic acid is a coenzyme involved in the process of energy synthesis by liver cells, regulates carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism. Indicated for viral hepatitis A, chronic hepatitis, fatty hepatosis, alcoholic liver disease, cirrhosis.
Drugs of different groups
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is most effective. It is part of normal human bile in a concentration of 4%. When taken additionally, it reduces the effect of toxic bile acids, suppresses the production of immunoglobulins, increases the outflow of bile and the removal of toxic substances from the liver, and has antioxidant activity. Indicated for any hepatitis.

When using hepatoprotectors, one should not hope for a quick cure: their effect occurs gradually; an ideal remedy does not yet exist
Causes
There are many causes of hepatitis, it all depends on the type:
- Hepatitis A. The cause is viruses that are transmitted by the fecal-oral route (through dirty hands, unwashed vegetables and fruits, feces, contaminated water).
- Hepatitis B. The etiology is also a virus, which, when infected, is present in all biological fluids of the patient.

Transmission of the virus occurs through blood, sharing a needle (drug addiction), through sexual intercourse, sexually from mother to child (at birth). - Hepatitis C. The cause is the use of one needle (drug addiction), cosmetic procedures (manicures, using razors), piercings, tattoos in unfavorable conditions.
Also, the etiological factor in the appearance of hepatitis C is blood transfusion, medical procedures, and sexual contact.
- Hepatitis D. Caused by infected blood.
- Hepatitis E. The cause is contaminated water, registration of the disease in countries with a hot climate and poor sanitary standards.
Also, the causes of this disease may be excessive abuse of alcohol, medications that have a toxic effect on hepatocytes, as well as drug use.