Last updated January 30, 2020 at 4:14 pm
Reading time: 5 min
Infection of a person with bacteria and viruses quickly manifests itself in various symptoms. But there are “silent” enemies, which are difficult to detect, and they cause enormous harm. These are the simplest organisms - parasites. There are many known species of such creatures; they can live in different human organs.
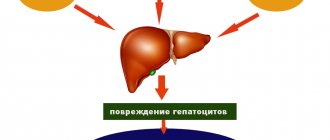
Giardia in the liver is especially dangerous. This organ gets a lot of workload, and infection with protozoa can lead to significant damage to the entire body.
Danger of disease
Giardia infection is called giardiasis. This is a very dangerous disease. Protozoa, settling in the human body, feed along with it, so the internal organs receive less useful substances.
Parasites release toxic substances during their life processes, which are absorbed into the blood. Toxins negatively affect the nervous system, especially in children. The entire digestive system is also greatly affected.
Giardiasis of the liver is also dangerous because it is very difficult to diagnose. A person can undergo treatment for many years for other diseases with varying success, but everything will continue until liver parasites are identified.
Giardia constantly multiplies at an incredible speed, so not only one person becomes infected, but his environment, his home. It is difficult to treat the disease; it is easier to prevent infection; to do this, you need to know the routes of transmission of parasites.
How to treat lamblia in the liver?
To completely get rid of lamblia in the liver, you will need to take comprehensive measures. Treatment is carried out in several stages.
Preparatory stage
How to treat lamblia in the liver? To successfully treat Giardia in the liver, you will have to be patient - this process is not quick and requires not only long-term medication, but also a special diet. So, at the first stage it is necessary to prepare the body for further interventions.
At this time, they drink enzyme-containing drugs that normalize the functioning of the digestive system, drugs to improve immunity, and enterosorbents that relieve intoxication from a high content of toxins.
In terms of nutrition at this time, special emphasis is placed on foods containing proteins. Food containing carbohydrates, especially simple ones, should be kept to a minimum at this time. As a result, the consumption of sugar, sweets, bread, and pastries is completely excluded from the diet.
Priority is given to lean meat and fish, fermented milk products. Fatty foods should also be completely avoided.
Second phase
At this stage you should also adhere to a diet, the rules are the same. But antiparasitic drugs are added to the drugs. Depending on the age and degree of the disease, the doctor makes a choice in favor of one or another drug. Thus, adult patients are often prescribed Trichopolum or Furazolidone. For children, you should choose “easier” drugs, for example, Macmiror.
Trichopolum
Furazolidone
McMirror
Taking enterosorbents at this stage should also be continued. Since severe intoxication occurs after the death of Giardia, in order to reduce its negative effect, it is recommended to take laxatives that accelerate the elimination of waste products.
At this stage, the parasites should be completely eliminated from the body, both from the intestines and the liver.
Third stage
At this time, the main efforts are devoted to eliminating defects caused by giardiasis and increasing immunity. Since hepatic giardiasis affects not only the small intestine, but also the liver, it takes a lot of time to eliminate all losses, restoring not only the functionality of the intestines, but also eliminating the resulting liver disorders.
At this stage, vitamin complexes are especially important; traditional medicine methods should not be neglected. Special diet in nutrition is still important. Protein, which helps regenerate the intestinal mucosa, more porridge with water without oil and sugar, eating in small portions, but at least 4-5 times a day. Only in this case the chances of a complete cure remain quite high.
Throughout therapy, the doctor prescribes tests. This is necessary in order to track the dynamics of treatment. If tests reveal the ineffectiveness of therapy, the doctor should review the list of medications, and also pay attention to how accurately the patient follows nutritional rules.
Possibilities of infection
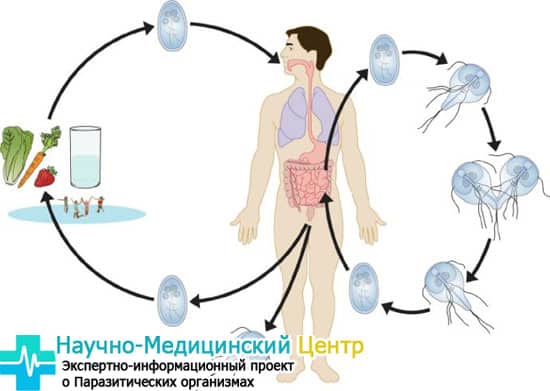
Giardia exists in two forms, which differ significantly from each other:
- vegetative;
- cyst.
These shapes represent the life cycle of parasites. Vegetative lamblia lives in the intestines and liver, actively feeding on the juices of the internal organ and reproducing. When Giardia enters the large intestine, it passes into the cyst stage, that is, it becomes covered with a protective membrane. Then everything is excreted from the body with feces.
In the natural environment, only cysts survive; they can exist outside the host’s body for several months. With food and water, the cyst again enters the living organism. The protective shell reliably protects it from the action of gastric juice and pancreatic bile. The parasite safely reaches the intestines, where it enters the active vegetative stage - everything repeats all over again.
You can become infected in numerous ways. Through the mouth - drinking water with cysts, choking while swimming in an unclean body of water. You can eat unwashed fruits and berries. Upon contact with the carrier. Cysts survive well on objects, so you can become infected in transport, when using other people's hygiene products, clothes, toys.
Many animals suffer from giardiasis. Children are more likely to become infected through contact with them. They love to kiss animals on the face and allow themselves to be licked, which is a direct way of insemination with cysts.
Giardia infection as a disease
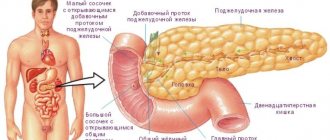
Giardia are the simplest single-celled microorganisms that can parasitize the intestines, gallbladder and duodenum. The main localization in the human body is the lumens of the small intestine (about 85% of cases). Cases of damage to liver tissue by microorganisms are quite rare due to the lack of a favorable nutrient environment, but with a long course of the disease, Giardia creates the necessary conditions for pathogenic life activity. The hepatobiliary form of giardiasis is a serious disease, as it is combined with damage to the bile ducts. Giardia in the liver can provoke gastritis, gastroduodenitis, pancreatitis, cholestasis and biliary dyskinesia. There are two forms of existence of Giardia:
Vegetative. Giardia in this form is capable of parasitizing inside the host’s body. Cysts. They are spore forms when active life activity stops. Existence in the form of cysts is necessary to maintain viability outside the host body.
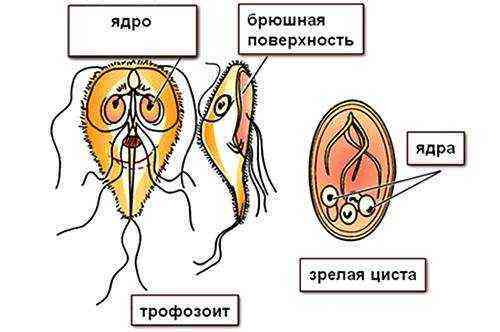
The vegetative form is transformed into cysts after microorganisms enter the carrier’s large intestine, from where they are excreted with feces into the external environment. Cysts can exist outside the human or mammal body for many months before entering a new body. Giardiasis of the liver is the subject of research among gastroenterologists, parasitologists and pediatricians (in pediatric practice).
Manifestation of the disease

Infection with parasites is difficult to recognize; it is necessary to seek a diagnosis from specialists who will identify the disease and determine how to treat it.
Adults experience constant headaches, insomnia, and increased irritability. You may be concerned about a decrease in blood pressure, and sometimes loss of consciousness occurs. There is pain in the navel and lower abdomen.
Symptoms of Giardia in the liver:
- yellowish coating on the tongue;
- flatulence, rumbling in the stomach;
- an increase in the size of the liver and its hardening.
Without proper and timely treatment, the disease enters the chronic stage. Then the digestive system will experience constant disturbances - constipation, diarrhea, nausea, belching. The skin will also react to the intoxication of the body. The patient will suffer from rashes, blisters, and itching. The color of the skin, especially the palms and soles, will change and become reddish-brown.
The general condition will worsen as other internal organs become involved in the pathological process.
In adults, the lymph nodes become noticeably enlarged; an elevated body temperature may persist for several days for no reason. A bitter taste appears in the mouth, appetite worsens, and weight loss occurs.
Symptoms of Giardia in the liver in adults
Signs of giardiasis of the liver do not appear immediately after infection. For this to happen, time must pass for the disease to gain momentum. In most cases, in adults, giardiasis in the liver is almost asymptomatic.
The person remains a carrier of parasites, but the disease never occurs. This occurs due to strong immunity or too little Giardia that has entered the intestines.
In the event that a massive infection has occurred and enough Giardia individuals have entered the adult’s body for the rapid development of infection, the following clinical signs are likely:
- Enlarged liver and spleen. This syndrome is called hepatolienal.
- The development of cholecystitis and impaired motility of the biliary tract are clear signs of giardiasis in the liver.
- Giardia in the liver is often accompanied by a symptom such as unstable stool. There are frequent transitions from foamy diarrhea to constipation.
- Gas formation, bloating after eating, and often severe pain in the right side and lower abdomen. At the same time, it is very difficult to determine exactly where the source of pain is. Such a symptom in an adult is a reason to undergo testing for lamblia in the liver.
- Due to blockage of the hepatic ducts and bile ducts, frequent heartburn and belching occur.
- Often during hepatic giardiasis, all kinds of allergic reactions, skin rashes, and redness occur. It is worth paying special attention to the fact of a suddenly appearing allergy, especially since after some time this condition can develop into atopic dermatitis and even bronchial asthma.
- During giardiasis, the skin often dries, peels, and a marbled pattern and a jaundiced tint appear. Cracks often appear in the corners of the mouth. All this is due to a lack of vitamins and nutrients, which lamblia actively absorb for their growth and reproduction.
- Giardiasis is characterized by a depressive state, since the parasites die in the body, leading to the production of toxins in large quantities. This process negatively affects the functioning of the body as a whole and the nervous system in particular.
- Patients often report poor sleep, sudden changes in mood, and overexcitability.
If you do not start treating giardiasis in a timely manner, it passes from the acute stage to the chronic stage:
- As a result of prolonged lack of nutrients and vitamins, a person begins to lose weight (this happens gradually, but steadily,
- For the same reason, a person loses working capacity, becomes more and more irritable and nervous,
- Intestinal disorders at this stage make themselves felt with greater force.
Against the backdrop of a long-term illness, intoxication appears. It is also possible to determine whether this process exists in the body by a number of signs, especially since they, unlike the previous ones, manifest themselves more actively and clearly:
- Often there is an enlargement of the adenoids,
- Lymph nodes also become larger in size,
- Often there is a low-grade fever that does not rise above 37.5 and does not fall below 37.1,
- Infections that occur during this time are very difficult to treat, requiring longer than usual recovery time,
- Against the background of intoxication, the immune system is suppressed, and colds are common as a result.
Signs of giardiasis in children
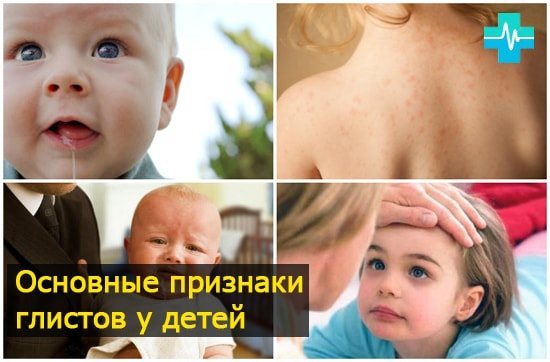
In childhood, they become infected with parasites very quickly. Small children put everything in their mouths and suck their fingers - this makes it much easier for protozoa to enter the body. Manifestations of giardiasis in children are somewhat different. Infection can occur through contact with carriers, as well as with mother's milk.
Symptoms of infection in children:
- persistent colds;
- severe allergy to even a small allergen;
- growth and development delays;
- poor appetite;
- constant nasal congestion;
- grinding teeth at night;
- lethargy, sleep disturbance.
If a small child’s body contains a large number of parasites, an acute stage of giardiasis may develop. The temperature will begin to rise, especially in the evenings, severe nausea and vomiting will appear, the stool will be greasy with a foul odor.
Only the attending physician can make a diagnosis, taking into account the signs of the disease and examination data.
Symptoms of the disease
Giardia in the liver in adults has certain symptoms and treatment, which is why it is necessary to first identify the first signs of the disease, which will indicate infection of the body with Giardia. Doctors note that the infection does not manifest itself for a long time if giardiasis of the liver occurs in the classical form. The first signs begin to appear a few weeks after infection.
The doctor can prescribe a full course of treatment to the patient, but only if the symptoms are sufficiently severe. The first signs of infection include:
- bowel dysfunction in the form of diarrhea or constipation;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the patient’s mouth;
- enlargement of the liver gland;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- stagnation of bile in the biliary tract;
- gases accumulate in the digestive tract;
- a person loses weight quickly;
- pain appears in the abdominal area;
- there is a loss of appetite;
- intestinal dysbiosis develops;
- the patient becomes more nervous;
- nausea and vomiting occurs.
Fact! Very often, against the background of the development of giardiasis, the patient develops severe lactose intolerance. It is because of this that patients may experience an allergic reaction to any type of dairy product, especially whole milk.
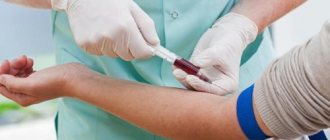
Diagnostic tests
Diagnosis of “giardia in the liver” is made not by symptoms, but by tests. After all, it is very difficult to identify parasites, because this pathology does not have typical symptoms. All manifestations of giardiasis are similar to other diseases.
But if parents have discovered at least some symptoms similar to Giardia in children, it is better to play it safe and go to the doctor. It must be borne in mind that the child cannot always determine the location of the pain; one must focus on other symptoms.
To determine the location of Giardia in the liver, an immunological examination is performed. It detects Giardia antigens in feces and certain antibodies in blood serum.
Special probing helps to detect Giardia, with the help of which the duodenal contents are examined (juices of the duodenum, pancreas with an admixture of digestive juices of the stomach). Feces are also examined for cyst eggs.
Sometimes an additional general blood test is prescribed, the pancreas and liver are examined for Giardia using ultrasound, and computer diagnostics are performed. Changes in the liver can be detected when taking liver tests, on a biochemical hepatogram. There is a possibility that such a broad examination will be able to identify parasites.
How does giardiasis begin in the liver?
The main habitat of Giardia in the body of children and adults is the small intestine, but when the number of individuals reaches a critical level, they can parasitize the bile ducts and liver. There are several ways for Giardia to enter the body:
Giardia can exist in two forms: trophozoite (vegetative stage) and in the form of cysts. Giardia in the vegetative stage has a sucker, with which it attaches to the wall of the small intestine for further reproduction. The danger of Giardia at this stage lies in the ability to reproduce and also infect its host, manifesting itself with corresponding symptoms. However, Giardia in the trophozoite form is very capricious to changes in environmental conditions, so they live in the body for no more than a month, having managed to produce offspring during this time. It is quite difficult to become infected with giardiasis through parasites in this form, since they die when exposed to moisture and temperature.
The most dangerous form, which can persist not only in environmental conditions, but also survive in the acidic gastric environment and not die when exposed to bile, are cysts. It is in this form that they most often penetrate the body and can remain in it for a long time asymptomatically, until under the influence of bile they turn into a trophozoite that actively parasitizes the body. This leads to inflammation of the walls of the small intestine, resulting in disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. Such processes are one of the causes of pathological changes in the liver and pancreas. Therefore, answering the question of what Giardia is in the liver, we can say that this is not necessarily their dislocation in the organ, but also the impact on its work.
Therapeutic measures

Getting rid of parasites is carried out in a complex. Only an experienced specialist can select competent treatment; self-medication can cause harm and prolong the disease. The main therapy is carried out exclusively with medications; at the recovery stage, traditional medicine can be used.
At the beginning of treatment, conditions are created that prevent the proliferation of Giardia. For this purpose, choleretic drugs, enterosorbents and antihistamines are prescribed - this helps to enhance the production of enzymes and improve immunity. The patient must follow a diet that consists of limiting carbohydrates and increasing protein.
Further treatment is carried out with antiparasitic drugs, which have a detrimental effect on Giardia. She also continues taking antihistamines and entorosorbenots. At the final stage of treatment, it is necessary to increase immunity so that it can prevent the reproduction and spread of parasites. This is done with the help of a diet that should help normalize intestinal motility.
During treatment, severe side effects, vomiting, allergies, abdominal pain, and neurological disorders may occur. This is due to the strong effect of antiparasitic drugs and the toxic content of dead parasites. After about 3 days, these manifestations disappear.
Rules for the treatment of giardiasis in adults
To remove Giardia from the liver, it is necessary to use special drugs that are aimed at combating helminths. The most effective drug is Akrikhin. The doctor prescribes it according to a certain scheme, depending on the stage of the disease and the age of the patient. Usually the course of treatment lasts from three to eight days. If the symptoms indicate that a person is infected with a mixed form of helminths, then the doctor may prescribe the use of furazolidone. Until the age of seventeen, it is customary to use no more than 100 mg of the drug per day. When the form of the disease is advanced, erythromycin is added to the main drug.
During inpatient treatment, the patient is given special medications that fight Giardia, as well as drugs that boost the immune system. The patient is recommended to use choleretic drugs to improve the flow of bile and the digestion process. You can treat with folk remedies to enhance the effect of basic drugs.
Medicinal herbs used for giardiasis:
- clove buds;
- chamomile flowers;
- horseradish root;
- tansy extract or leaves;
- dried yarrow;
- seaweed;
- fresh ginger.
Prevention of infection

It is very difficult to detect and remove protozoa from the body. Giardia in the liver easily adapts to the external environment and tolerates adverse conditions well. But you don’t have to get infected - this is the surest remedy in the fight against protozoan parasites of all types. Preventive measures can protect a person from such infection.
From childhood, the cult of purity must be instilled. After going outside, after interacting with animals, and on every occasion, you should wash your hands or treat them with bactericidal agents. 2 minutes spent on cleanliness can save you from many years of fighting against parasites. It is useful to develop in children a sense of proper disgust, which will not allow them to become infected from animals, but will help them maintain cleanliness of their body and clothes.
Regular wet cleaning of the apartment is not a relic of past times. This way you can reliably get rid of Giardia cysts that come from the street and are carried on clothes. It is imperative to combat cockroaches and flies, which are often carriers of parasitic cysts. If giardiasis is detected, it is necessary to immediately treat and check for the presence of parasites in your immediate environment.
Symptoms of the disease
Giardia can lead to sensations similar to those of poisoning. This includes both general intoxication and pain in various organs:
- headache;
- pain in the abdomen, intestines;
- increased sweating;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- loose stools;
- bloating;
- gastrointestinal disorders.
One of the few specific symptoms of the disease is increased heart rate, which is noticeable in people throughout the entire period of the disease. Thanks to this symptom, specialists often make preliminary assumptions about the patient’s diagnosis. Giardia in the liver also exhibits symptoms of liver disease, which can complicate the differentiation process.
Treatment
Treatment of Giardia in the liver includes taking medicinal antiparasitic drugs, detoxification agents, a special diet and folk recipes. Parasitologists recommend a step-by-step treatment regimen, which includes a preparatory stage, active antiparasitic therapy and a recovery period.
Diet

The preparatory stage begins with the appointment of a diet. By limiting the consumption of certain foods in the human body, unfavorable conditions are created for the life of Giardia in the liver. Patients are advised to limit the consumption of confectionery, flour products, simple sugars, and chocolate.
The patient should enrich the diet with cereals, bran, fruits and vegetables. Also, once a week it is necessary to arrange fasting days that improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Drug treatment of lamblia in the liver
After starting the diet, the patient is prescribed antihistamines (Loratadine), enzyme agents (Creon, Mezim) and choleretic agents (Ursosan). To remove protozoan parasites from the liver, antiprotozoal drugs are prescribed: Trichopolum, Nimorazole, Ornidazole, Tiberal. Doctors recommend two courses of therapy with a short interval between them. After a course of treatment, control blood and stool tests are necessary.
The recovery stage is characterized by the administration of vitamin-mineral complexes, immunostimulants (Amiksin, Cycloferon), prebiotics (Lactulose) and enterosorbents (Enterosgel, activated carbon), which accelerate the recovery period.
Traditional methods
This type of treatment can complement primary therapy, but is not the primary way to combat parasites. All folk recipes have low effectiveness in the treatment of hepatic giardiasis.
Most often, patients use a mixture based on pumpkin seeds, an infusion with vegetable juices or calendula flowers, vegetable oil with vegetables, and an infusion of birch leaves.
Why is Giardia infection dangerous?
Giardia are the smallest protozoan parasites that live in the human body. Indiscriminate and incredibly tenacious helminths are absolutely resistant to any environmental influences, and when in a suitable environment, they multiply almost every minute.
Giardia not only lives in the human body, but also feeds on the breakdown products of food, and the results of their vital activity are absorbed into the blood. This causes serious toxic reactions in the nervous system, gastrointestinal tract and critical organs.
How can you become infected with Giardia?
You can become infected with giardiasis in different ways, because not only people, but also cattle, birds, dogs, rats, and horses can be carriers of the disease. Communication with infected animals and failure to comply with personal hygiene rules lead to infection and spread of Giardia in the liver.
Routes of infection:
- in close contact with an infected person or animal, through the use of the same dishes, bedding, clothing, personal hygiene products;
- when consuming unwashed or poorly washed vegetables, fruits and herbs, on the surface of which there may be cysts;
- when drinking raw contaminated water.
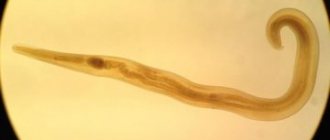
Signs and treatment of giardiasis of the liver
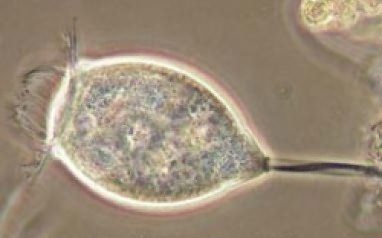
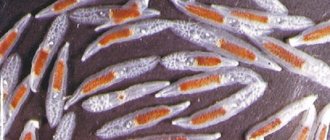
Parasite under a microscope
Giardiasis or giardiasis (giardiasis) is a fairly common infectious, parasitic disease, which, according to WHO, infects 8 to 20% of children and adults.
The disease received both names after scientists who studied this type of human infection and described the symptoms of Giardia in the liver and intestines and were looking for ways to treat the disease - this is the Czech D.F. Lambl (professor at Kharkov and Warsaw universities) and the Frenchman Alfred Giard.
Giardia are parasites that “settle” on the walls of the intestines and (or) liver, attaching to the epithelium with a suction disk and rapidly multiplying in large numbers. As for their damaging effect, it consists of repeated attachment and detachment, which causes mechanical irritation of the walls of organs, affects the nerve endings and, sooner or later, leads to pathological reflex reactions of the affected organ.
Ways of infection with Giardia

Be sure to boil tap water, as chlorine does not kill Giardia
The highest prevalence rates of giardiasis in the world (up to 35%) are registered in developing countries. This is almost always a “disease of dirty hands”, the risk of infection of which is largely related to personal hygiene, the level of communal amenities and the quality of drinking water. Children with the habit of biting their nails or any foreign objects (pens, pencils, etc.) have a high risk of getting Giardia.
Giardia during its life cycle has vegetative and cystic morphological forms - trophozoites and cysts. The vegetative form exists only in the infected organism and is unstable when moving into the external environment (it dies after 5–10 minutes). Cysts retain their vital activity much longer: at room temperature, on objects - up to 2 weeks, and in water even more - up to 80-90 days. Moreover, chlorination of water does not affect Giardia, but when boiled, Giardia cysts die instantly.
There are three main routes of infection with Giardia:
- water;
- contact-household;
- food.
In the first route of transmission of giardiasis, most often the source of infection is tap water. In the second case, infected children, adults or mammals (even flies can be mechanical carriers for cysts). Well, in the third case, accordingly, products that have not undergone heat treatment.
Diagnosis of giardiasis

Do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor
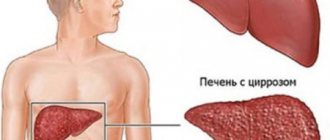
It should be noted that even if you encounter all the symptoms listed below of the presence of Giardia in the body, in order to confirm the appropriate diagnosis, consultation with an infectious disease specialist and laboratory confirmation of tests are required. You should not self-medicate; more serious diseases become frequent companions of Giardia in the liver: enteritis, cholecystitis, cholangitis and others, including cirrhosis of the liver or hepatitis. Correct diagnosis of symptoms and effective treatment is only possible under the supervision of a specialist.
The disease process of giardiasis has two stages: acute and chronic. The acute form (most often observed in children) lasts only a few days, after which it passes into the subacute stage or into the chronic stage.
Symptoms of the acute stage
- increased body temperature (fever);
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- allergic dermatitis (rash similar to measles or rubella);
- lack of appetite.
Symptoms of the chronic stage of giardiasis
- persistent tongue coating;
- stable weight loss;
- pale skin;
- thinning hair, slower growth;
- general apathy;
- frequent weakness and fatigue;
- headache;
- nausea;
- constant irritability;
- prolonged deterioration of sleep;
- frequent dryness and/or bitterness in the mouth;
- spasms and pain on the right side of the abdomen;
- flatulence;
- liver enlargement;
- alternating diarrhea and constipation.
In addition to the listed symptoms, both stages of the disease in children are characterized by damage to the lip border. The degree of manifestation of this symptom can vary: from mild dryness and flaking to severe manifestations with cracks and jams.
Treatment of giardiasis
To completely get rid of the parasites - lamblia in the liver, it is not enough to just “take a pill”. Successful treatment of this disease is only possible in a comprehensive manner. Necessary:
- Careful observance of personal hygiene by the patient and those around him.
- Strict diet. It is necessary to completely exclude foods high in simple carbohydrates and sugars: milk, sweets, bread and pastries, pasta and all kinds of sausages. Any other products must be heat treated. Vegetables and fruits must be washed well with warm water. The main food should be porridge with vegetable oil, vegetables, baked apples, dried fruits, sour berries (cranberries, lingonberries).
- Use of enterosorbents: smectite, activated carbon, lactofiltrum. They remove toxins that are formed during the life of lamblia.
- Treatment of vitamin deficiency (B-vitamin complexes) to increase the stability of the nervous system.
Important! Basic treatment: antispasmodic, cleansing, restoring digestion and other medications should be strictly prescribed only by a specialist - an infectious disease doctor. Self-medication can have serious consequences and side effects: from intoxication and allergies to neurological disorders.

netglista.ru>