If the condition worsens and frequent digestive disorders occur, a suspicion of a parasitic disease arises, in which case the doctor prescribes a number of diagnostic procedures, including a blood test for Giardia. These parasites are widespread throughout the world; they enter the human body if the rules of personal hygiene are not observed. There are several types of tests that can detect Giardia in the body: ELISA, PCR, hemotest.
If the condition worsens and frequent digestive disorders occur, a suspicion of a parasitic disease arises, in which case the doctor prescribes a number of diagnostic procedures, including a blood test for Giardia.
When to take a blood test for Giardia
Diagnosis of giardiasis is recommended:
- after drinking contaminated drinking water;
- after swimming in open water;
- when eating unwashed vegetables and fruits;
- persons working with soil;
- people who come into contact with animals that may have parasites in their bodies;
- patients with diseases of the digestive system, immunodeficiency conditions;
- people who have undergone surgery.
Blood testing for Giardia must be donated when the following symptoms appear:
- nausea, vomiting and diarrhea;
- pain in the epigastric region;
- bloating;
- belching;
- changes in the color of stool;
- bad breath;
- weight loss;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- lack of appetite;
- skin rashes;
- increased body temperature;
- sleep disorders.
Giardia in children contributes to vitamin deficiency, which negatively affects growth and development. With giardiasis, a child often suffers from colds, bronchial asthma and allergies. A complete blood count in this case reflects an increase in the number of eosinophils. To identify the causes of such conditions, an examination for giardiasis is prescribed.
Giardia in children contributes to vitamin deficiency, which negatively affects growth and development. A complete blood count in this case reflects an increase in the number of eosinophils.
Blood test for giardiasis
In order to detect the presence of parasites of this type, 2 diagnostic methods are used. In this case, this is a stool test for Giardia and a laboratory blood test, which allows you to see the presence of antibodies to parasites. If in doubt, a specialist may also prescribe a bile analysis. But this method is used quite rarely.
Blood analysis
Blood testing for the presence of parasites is the most popular, although not the most informative, method of identifying giardiasis. This type of analysis makes it possible to see antibodies in the blood, but parasites can hide their presence for a long time, so no signs of their life will be detected. Therefore, experts try not to use a blood test for Giardia in children and adults as the only diagnostic method. It works well as a component of comprehensive diagnostics.
Giardia is easiest to find in feces. This is where specialists can see the presence of parasites during laboratory testing. As for the blood test, it will be very useful, since in the presence of antibodies to Giardia, a more accurate diagnosis can be made. This method works great when you need to clarify the result.
Preparing for the study
Analysis for Giardia does not require complex preparation. Before donating biomaterial from a vein, you must:
- refrain from eating food at least 10 hours before visiting the laboratory;
- within 24 hours, stop drinking coffee, strong tea and juices, replacing them with clean water;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- inform the specialist about the medications you are taking;
- limit physical activity;
- Eliminate fatty, fried and spicy foods from your diet for a week.
It is not advisable to take a blood test for Giardia immediately after radiography or physiotherapeutic procedures.
Blood test (ELISA) for Giardia
The essence of the Giardia test is to determine the reaction of the antibody with the antigen. ELISA allows you to determine infection by the presence of antibodies to Giardia in the blood. When infected, the immune system produces Ig antibodies with M and G markers to fight Giardia.
14 days after infection, IgM antibodies appear in the body; two weeks later they turn into IgG and remain in the body throughout the entire invasion.
This diagnostic method has many advantages:
- allows you to determine the stage and form of development of the disease;
- it becomes possible to identify the human carrier;
- carried out in a short time;
- high accuracy - about 90%;
- a convenient way to track the dynamics of invasion;
- availability.
| How to take it | Decoding |
| The analysis requires a venous blood sample. A few days before the procedure, the patient should not drink alcohol or tobacco products. The procedure is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. Taking medications should be discussed with your doctor - this will allow you to make a reliable diagnosis. 10 hours before the tests you should not eat, drink coffee, tea, or juice. It is acceptable to drink water without gas. | The interpretation is based on the indicators of IgM and IgG antibodies.
The results are also determined by the OPD indicator:
|
ELISA method
An enzyme immunoassay is a study aimed at identifying antibodies to parasite antigens. You can take it immediately after signs of the disease appear, since specific immunoglobulins begin to be produced quickly. ELISA is a more accurate diagnostic procedure compared to other methods, the information content of which is close to 95%.
An enzyme immunoassay is a study aimed at identifying antibodies to parasite antigens.
Interpretation of blood test results
To understand whether Giardia is present in the blood, a specialist determines the ratio of antibodies to parasite antigens.
The results of the study may be as follows:
- Negative. A value of less than 0.85 is considered normal. This result shows that there is no Giardia in the patient’s body.
- Positive. This is considered to be a value greater than 1. In such cases, it is considered that Giardia cysts are present in the body.
- Weakly positive. The result is similar at an antibody level of 0.85-1. In this case, the examination is repeated.

A blood test for antibodies to Giardia is done in about 48 hours; when testing a sample using PCR, the result is obtained in 4-6 hours.
When interpreting test results, it is necessary to take into account the type of antibodies, the number of which is increased:
- Increased IgM levels. Indicates a recent infection. Such immunoglobulins begin to be produced in the first days after Giardia enters the body.
- An increase in IgG titer indicates that the patient has an acute form of parasitic infestation. Patients with chronic giardiasis also get a similar result.
The number of antibodies begins to decrease 6-8 weeks after the death of the parasites. It should be remembered that their level also increases in other diseases, so experts recommend using several research methods simultaneously.
Blood analysis

Testing for giardiasis through a blood test can detect the presence of giardia 21 days after infection with parasites.
However, this method is considered not very effective, because certain antibodies in biological fluid can be detected even after adults have fully recovered.
However, a blood test can detect parasitic cysts in the body at an early stage of helminth parasitism. The blood is examined under a microscope, but this diagnostic method does not allow identifying the specific type of helminth.
It is necessary to take a test for Giardia in the morning; blood is taken from a vein. To exclude errors in the results obtained, there are certain recommendations that the patient must adhere to before the procedure.
Before donating blood, you should familiarize yourself with the following tips:
- You should not drink alcoholic beverages before taking the test.
- Smoking is prohibited several hours before the test.
- Limit physical activity.
- If the patient is taking medications, you must inform your doctor about this, or, if possible, stop taking them 7 days before the test.
- The test is carried out on an empty stomach, so it is not recommended to eat 10 hours before.
- A couple of days before the test, you should give up too fatty, hot and spicy foods.
- Before the test, you can drink plain water, but you should not drink other drinks (for example, sparkling water).
It is worth noting that if the patient violates the requirements, the test for parasites may show incorrect results, as a result of which drug treatment will not have the required therapeutic effect.
Blood test interpretation:
- If a patient has elevated IgM antibodies, this may indicate a recent infection, about two weeks.
- When a patient has an acute form of a parasitic disease, the test results show the presence of IgG.
- If a patient is diagnosed with a chronic form of giardiasis, then tests show a significant concentration of antibodies.
- In cases where helminthiasis is detected at the stage of its transition to a chronic form, IgG antibodies increase in the blood.
- Over the course of 60 days, the amount of antibodies in a person’s blood gradually decreases as the helminths die.
The price for such an analysis is approximately 400-700 rubles, depending on the clinics where it will be performed. In Cheboksary, the cost varies from 600 to 1000 rubles, and it depends on the choice of clinics and their equipment.
What to do if the analysis shows the presence of lamblia
If Giardia is found in the blood of an adult or child, it is necessary to examine all members of his family, especially if the person lives in conditions of low risk of re-infection from the external environment. Treatment is carried out with the help of antiparasitic drugs (Metronidazole, Albendazole, Tinidazole).
A 7-day therapeutic course helps get rid of parasites in 80% of cases. During treatment, it is recommended to follow a special diet and drinking regimen to prevent dehydration. In addition, it is necessary to disinfect all objects that the infected person has come into contact with and carry out a wet cleaning of the house.
All iLive content is reviewed by medical experts to ensure it is as accurate and factual as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Suspicion of parasite infection arises in the presence of persistent dyspeptic disorders. Giardiasis is a protozoal infection caused by tiny intestinal parasites Giardia or Giardia. The disease has been well researched, modern methods of its treatment provide a 100% cure effect. The main thing is timely diagnosis of infection with these particular parasites, and the doctor can glean basic information from the results of laboratory tests to determine whether the patient has giardiasis.
[1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11], [12]
Preparation for analysis for Giardia
A negative research result does not mean that there are no parasites. Tests for the presence of Giardia are usually taken more than once. Often the patient himself is to blame for a questionable result. Following a few simple rules before taking the test will make the results of the study more accurate. Therefore, how to get tested for Giardia so as not to waste time?
If you intend to get tested, you need to stop taking anthelmintic drugs at least seven days before the scheduled date, as well as drugs that can harm parasites: antibacterial (metronidazole, trichropol), antacid (smecta). It is advisable, if possible, not to take any medications at all.
Decoding the analysis for Giardia
If it was not possible to protect yourself from infection with parasites, testing for Giardia will help you begin treatment with effective medications. Testing biological material (stool, blood) of a sick person makes it possible to identify antibodies and antigens in the form of parasites that secrete products of their life cycle.
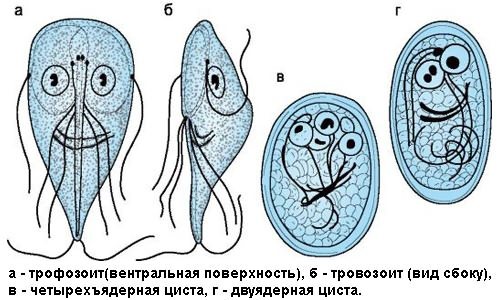
The analysis indicates the development of the parasitic cycle over time. The study is carried out over 8 days, taking into account the period of laying larvae by Giardia.
Blood is taken from a vein from a child for examination, but the process of identifying parasites is very complex and depends on the skill of the laboratory assistant. Testing the blood of children suffering from dry cough can detect parasites at an early stage of development.
Rules for preparing for the test
A parasitic infection can be treated if the diagnosis is made in a timely manner using stool and blood tests.
The research will be correct if important conditions are met. It is not recommended to drink alcohol or smoke before the test. You should check with your doctor about taking medications that may change test results. Intense physical activity is not recommended on the day of the examination.
Fried, spicy, fatty foods are excluded from the diet. Blood is donated strictly on an empty stomach, and antiparasitic research is carried out only 14 days after taking drugs for the treatment of Giardia. The feces are placed in a special spoon included with the container. The material is taken in small volumes from different areas. The doctor recommends a three-time check every 3-4 days. The container is equipped with a preservative.
Donating blood after a rectal examination, physiotherapy sessions, or x-ray examination is not allowed.
Explanation of blood test
Giardia is diagnosed by testing the patient's blood. How does a doctor determine parasite infection?
During the blood test, specific antibodies are detected. Their main purpose is to destroy foreign microbes. Blood tests for Giardia reveal the ratio of antibodies to parasite antigens.
Immunoglobulins of single or total classes IgG, IgM are determined. 14 days after infection, an increased level of IgM antibodies in the blood is detected. As the disease worsens, IgG antibodies appear.
After the death of the protozoa, the number of antibodies decreases within 45-60 days. As a result of the process becoming chronic, an increase in IgG is observed. A sharp increase in IgM and IgG indicates a chronic course of the process or an exacerbation of the disease.
Blood for research is taken from the ulnar vein.
Giardia immunoglobulins are not a generally accepted standard: they can be produced by many parasitic and bacterial infections.
The test is considered qualitative and is defined by the terms: “doubtful”, “negative”, “positive”.
Interpretation of stool examination for the presence of parasites
It is not difficult to test for the presence of protozoan cysts in the patient’s stool: testing the material will determine their presence in the lower intestines.
If a person is infected with Giardia, the analysis will show the presence of vegetative microorganisms in large quantities. If the test results are negative, it is necessary to re-analyze the intestinal contents after 7 days.
Studying feces allows us to determine the protein structures of protozoa.
Indications for passing stool are symptoms such as:
- watery diarrhea;
- gastric spasmodic contractions.
Feces must be submitted for analysis within a week from the onset of symptoms of the disease.
Why do you need PCR diagnostics of Giardia?
Parasitic infections are a serious problem. Genetic studies of Giardia are carried out using PCR diagnostics, which makes it possible to detect parasites in the upper part of the small intestine. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies a small section of Giardia DNA and isolates the parasite's genome sequence.
Test systems are used during the polymerase reaction analysis. The starting material for the study is blood and feces. In the process of processing the data obtained, conclusions are drawn about the dynamics of the disease and the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
DNA testing of the Giardia causative agent is a fast and highly sensitive method. It has a number of significant advantages:

- determines with a high degree of probability the presence of a parasitic pathogen;
- identifies a unique section of Giardia DNA using highly sensitive equipment that allows the presence of parasites to be determined;
- carried out over a short period of time.
In the polymerase reaction analysis, the result of the parasite DNA analysis is indicated. Material is collected for the study. It is placed for storage in a container with a temperature of up to 8 °C. In case of a positive result, it is recorded by writing: “DNA of Giardia lamblia was detected in the material (feces, bile). Negative findings indicate the absence of parasites. In case of doubtful assessment of the result, indicate the level of antibodies (the magnitude of the immune response).
ELISA in children for the presence of parasites
Enzyme immunoassay is based on the study of the enzymatic and immune reactions of the blood. Special reactions reveal antigens and antibodies. To study the material, blood serum is taken three times. Determine the presence of Lamblia (total), anti-Giardia Lamblia. For analysis, test systems are used that detect specific globulins (IgG, A, M). The positivity rate indicates the percentage of parasite infestation.
The presence of only IgM in the analysis determines the acute process of the disease. In a study using serological markers-antibodies IgM and IgG for giardiasis, the doctor indicates the markers IgM - +, IgG - +, cysts and vegetative forms - +.
The interpretation of the answer from the study looks like the entry: “Giardiasis.” If IgM is (kp.1-2)+, and IgG is not detected, an invasion is determined in the transcript of the analysis, lasting no more than 1-3 months.
With IgM (K.P. = 2) and the presence of cysts, the specialist notes in the study results: “Acute giardiasis.” When IgG is (C.P. 1-2) and IgM is not detected, but cysts are present, a long course of the disease (more than 6 months) with a small number of reproducing organisms should be assumed. The complete absence of IgG and IgM, as well as vegetative forms as a result of the study, indicates the occurrence of a secondary process associated with immunodeficiency.
You should know that K.P. is the positivity rate according to the Giardia - AT test system.
Hemotest provides a comprehensive study of parasitic infection in adults and children using the ELISA method. The analysis is carried out using 9 reagents:
- control sample immunosorbent;
- blood serum without antibodies to Giardia;
- buffer composition;
- chromogen.
x
After examination, in 90% of cases parasites are found in the patient’s small intestine. When interpreting the tests, the specialist compares the final result with the negative control. A positive result is taken into account if its value is much greater than 1.0 times the optical density value.
The value of the final result ranges up to 0.85*OPd. In this case, the doctor recommends repeating the study after 21 days. The analysis is not only affordable, but also performed on modern equipment.
The method has drawbacks in diagnosis: only the presence of antibodies is determined, but their specific value or titer is not established.
If, as a result of the analysis, an antibody coefficient of 202 conventional units is obtained, and the titer is 1:3200, then the doctor evaluates such values as a result with a sign (+). The presence of antibodies of 5 conventional units with a titer of 1:100 is regarded as a negative result. A decrease in antibody titer indicates correct and effective treatment of the disease.
x
An antibody coefficient value ranging from 101 to 135 units indicates carriage of Giardia in their complete absence.
Testing for the presence of parasites in the human body helps the doctor make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment as soon as possible.
VseoParazitah.ru>
Comparative effectiveness of diagnostic methods
A blood test for antibodies to Giardia is an indirect diagnostic method, since they are formed in the blood as an immune response to parasitic infestation. They do not appear immediately, but within two and sometimes three weeks, so in the first days after infection the result will be false negative. The presence of class M immunoglobulins indicates a recent infection, but they do not last long and are replaced by IgG, the presence of which confirms that there has been an invasion. But they can persist for a long time after recovery and do not indicate the need for treatment, and therefore are not suitable for monitoring its effectiveness.
The presence of antibodies depends on many factors, in particular, the state of the immune system and the intensity of infection. With low immunity or chronic recurrent giardiasis with a persistent course, antibodies may not be detected. False-positive test results also occur in the case of invasion of other protozoa, for example, amoebiasis, antibodies to which can be mistaken for antibodies to Giardia.
Fecal analysis for Giardia is more reliable. It involves examining a stool sample taken from several places under a microscope and visually searching for living specimens or their cysts. If the result is positive, then there are definitely parasites. A negative result does not mean that the patient is healthy. It’s just that in the development of parasites there are so-called “blind” periods, their duration is 1-17 days, during which cyst secretion does not occur. If the analysis is collected and submitted during this period, the result will be negative even if parasites are present. Therefore, it is recommended to take a stool test for Giardia cysts at least three times every three days. If the suspicion of the presence of parasites is serious, then the feces are monitored for a month or a month and a half, every week.
The two blood and stool tests described above are the most commonly used because most laboratories do them. Usually a study of both blood and stool is prescribed. If one of the tests is positive, then we can conclude that there is an invasion.
Testing for Giardia antigen is more informative than stool microscopy, but its availability is limited, since it is performed only in large cities and not all commercial laboratories. The study of the material is based on a one-step immunochromatographic method that makes it possible to detect specific molecules (GSA-65 antigens) that are found exclusively in Giardia cells. The test usually involves taking stool samples, but sometimes a biopsy is used. The immunochromatographic method allows you to detect Giardia even in the “blind” period. It is advisable to use it to monitor recovery, but after a two-week interval after stopping medication, since the antigen can still be released in this time period.
To identify parasites, the most informative currently is PCR analysis for Giardia. Its main drawback is its lack of prevalence. It is not done in almost any laboratory, even in large cities. This study makes it possible, using polymerase chain reaction, to determine fragments of Giardia deoxyribonuclease in feces even in the interval when cysts are not excreted. The accuracy of this analysis is the highest (up to 98%).
[13], [14], [15], [16]
Published by: Parazitolog in Diagnostics February 16, 2019
Testing for giardiasis is indicated when there is a suspicion of this disease. Giardiasis is quite common; both children and adults can become infected with it. The analysis is usually carried out by ELISA. The analysis determines the antibodies that are produced during infection with this type of helminth.
Giardia: questions and answers
Questions from visitors and answers from specialists on the website of the INVITRO Internet club.
Good afternoon My daughter has dysbacteriosis (judging by anasis). The doctor prescribed taking Acipol, but it was of little use. I have suspicions that maybe my daughter has some kind of parasites in her body. Tell me what parasites I need to test for in order to at least rule this out. The child periodically breaks out in rashes, acipol is of little use. Thank you
Dear Olga! To diagnose parasites, I recommend that your daughter perform a stool test for Giardia (test No. 483), a blood test for helminthic infestations (tests No. 229, 230, 232, 235, 237) and an allergy marker (test No. 67), blood biochemistry (profiles No. 73 and No. 74).
More detailed information about prices for studies and preparation for them can be found on the website of the INVITRO Laboratory in the sections: “Analyses and prices” and “Research Profiles”, as well as by calling 363-0-363 (the single help line of the INVITRO Laboratory).
To determine further tactics, we recommend that you contact your pediatrician.
Good day!
Age – 27 years. In the last six months, I have been worried about frequent stomach upsets, excessive gas formation, and rumbling in the stomach. Chronic disease – gastroduodenitis. There are suspicions of intestinal dysbiosis and the presence of parasites (including giardiasis). What tests do you recommend?
Thank you. Dear Svetlana! I recommend performing a general stool analysis (test No. 158), a stool test for dysbacteriosis with determination of sensitivity to bacteriophages (tests No. 456, 443), a stool test for Giardia antigen and Helicobacter pylori (tests No. 483, 484), a blood test for Helicobacter pylori (tests No. 133, 177).
More detailed information about prices for studies and preparation for them can be found on the website of the INVITRO Laboratory in the sections: “Analyses and prices” and “Research Profiles”, as well as by calling 363-0-363 (the single help line of the INVITRO Laboratory). To determine further tactics, we recommend that you contact a gastroenterologist.
Hello. I took a blood test for giardiasis at your clinic - the reaction was positive. Do I need to do a repeat test (stool sample)? If you had Giardia before, but recovered from them. How much can you trust the results of a blood test? What is the best treatment for Giardia?
Dear Anton! The presence of antibodies to Giardia indicates a previous or current invasion. To clarify the diagnosis, I recommend performing a stool test to determine the pathogen antigen (test No. 483). To determine further tactics, we recommend that you contact a gastroenterologist.
Hello. Please tell me, the child developed a rash, they called an ambulance, we were diagnosed with urticaria, they injected us with dexomethasone (after the injection, the rash went away within 40 minutes), and they told us to donate blood for IgE. put on the trail. day in your laboratory, the indicator is 397 (the norm is up to 90 for her age), they retook another week - the indicator is 255.
All this time we were drinking fenistil. Is it necessary to additionally take tests for the presence of parasites (giardia, worms, roundworms...) in the body (after all, a high level of IgE can also indicate the presence of parasites in the body) or is there no point, since the level of immunoglobulin decreases while taking antihistamines? Thank you in advance.
Dear Tatyana! If contact with the allergen continues, the level of immunoglobulin E (total and specific) will remain high even while taking antihistamines.
To identify the cause of an allergic reaction, I recommend that the child undergo a blood test for household allergens (profile No. 98), food allergens (taking into account the products consumed), parasitic infestations (tests No. 229, 230, 232, 237), a stool test for Giardia antigen (test No. 483).
More detailed information about prices for studies and preparation for them can be found on the website of the INVITRO Laboratory in the sections: “Analyses and prices” and “Research Profiles”, as well as by calling 363-0-363 (the single help line of the INVITRO Laboratory).
To determine further tactics, we recommend that you contact an allergist.
Hello! The eldest will be 5 years old in November, and the youngest will be 4 years old in December. Since last year, when we started kindergarten, we started getting colds every month. In the summer we took tests: blood from a vein for lamblia, chlamydia pneumonia, allergies. Results: Giardia negative in both, Ig M negative and so on. coefficient
Ig G 1.3 in both, Ig E 171 in the younger one, 91 in the older one. Now the eldest is complaining about her health: she has a cough: it lasts for 2 days, then it disappears for a couple of days, and it starts in kindergarten. Both were prescribed ketotifen.
I can’t understand from the doctor’s answers whether we have chlamydia and whether the cough could be due to nervousness, because both of them tolerate kindergarten very poorly? Thanks in advance, I hope you can tell me what to do! Julia.
Dear Yulia! The result of the analysis indicates the absence of active chlamydial infection in girls, and an increased level of total IgE indicates their allergic sensitization to any allergen. To determine further tactics, I recommend contacting an allergist and pediatrician.
A blood test (total antibodies) showed the presence of lamblia 1.32++., roundworm-1. (hemotest) Feces for the presence of lamblia cysts - not detected, roundworms - detected, (children's clinic 30). The child (6 liters) was worried about loose stools, absence appetite I drank vermox, nimazole-h/w for 14 days. T.
Since it is quite difficult to detect Giardia cysts in stool, the question is: do you test stool for Giardia in the laboratory using Turdyev’s preservative?
We would also like to have your feces tested for Giardia antigen in your laboratory - what will it show? Is this test a repeat of the blood test for total antibodies?
A stool test for Giardia is not an analogue of a blood test for total antibodies. When examining stool, the antigens of the pathogen itself are determined, and not the antibodies to them (test No. 483).
More detailed information about prices for studies and preparation for them can be found on the website of the INVITRO Laboratory in the sections: “Analyses and prices” and “Research Profiles”, as well as by calling 363-0-363 (the single help line of the INVITRO Laboratory).
Contact an infectious disease specialist with the results of the examination.
Good afternoon A low-grade fever of 37-37.3 lasts for about 3 months. I saw a therapist and had a general blood and urine test, which showed no abnormalities. Tests for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, and torch infections are also negative.
Lately I have been experiencing frequent loose stools and abdominal pain. Please tell me what tests need to be taken to assess the condition of the stomach and intestines? Gender female, 23 years old. Previously, there were no diseases associated with the intestines.
Thank you!
Dear Irina! In your case, I recommend performing a biochemical blood test (profiles No. 73 and No. 74, tests No. 12, 18, 23), a general stool test (our test No. 158), a stool test for dysbiosis with determination of sensitivity to bacteriophages (tests No. 456 , 443), stool analysis for Giardia (test No. 483), stool analysis for pancreatic elastase (test No. 162PE1). More detailed information about prices for studies and preparation for them can be found on the website of the INVITRO Laboratory in the sections: “Analyses and prices” and “Research Profiles”, as well as by calling 363-0-363 (the single help line of the INVITRO Laboratory).
To determine further tactics, we recommend that you contact a gastroenterologist.
Hello! My daughter (7 years old) was diagnosed with stage 1 bronchial asthma almost a year ago. 2 weeks of treatment at the allergy center produced practically no results; the child was discharged with wheezing, remotely audible, and coughing. Clinical tests according to the attending physician were normal, IG E =800.
In April there were 2 bronchitis with obstruction in a row. Rovamycin, Erius, and broncholitin were used. In May we went to a sanatorium and underwent a course of physiotherapy. The tests and spirogram are normal. At the moment, the condition is normal, periodically the nose is stuffy (no discharge).
Since diagnosis, we have been on a strict diet, removed carpets, and replaced pillows and blankets. Until one year old, the child was allergic to cow's milk and was given soy-based infant formula. No one in the family suffers from allergic diseases.
Question: Does it make sense to do blood allergy tests (ELISA method)? How informative is this analysis? Is it possible that for all allergens the result will be +-? Thank you.
Dear Tatyana! The level of immunoglobulin E indicates the child’s constant allergostatus and his contacts with allergens.
The most common cause of increased sensitization in a child’s body is parasitic infestation, in particular roundworms, which can migrate into the bronchial tree, causing bronchospasm, as well as Giardia and Toxocara, which cause severe allergic reactions.
Food allergies are often associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Considering all of the above, I recommend that your child undergo a blood test for worms (our tests No. 229, 230, 232, 234, 237), a general stool test (test No. 158), a stool test for dysbacteriosis with determination of sensitivity to bacteriophages (tests No. 456, 443), stool analysis for pancreatic elastase (test No. 162PE1).
To identify allergens and eliminate them, I also recommend conducting allergy diagnostics (profile No. 98 “Household allergens”, profile No. 101 “Plant allergens”, ALL profile – “90 food allergens”). More detailed information about prices for studies and preparation for them can be found on the website of the INVITRO Laboratory in the sections: “Analyses and prices” and “Research Profiles”, as well as by calling 363-0-363 (the single help line of the INVITRO Laboratory). To determine further tactics, I recommend contacting an allergist or gastroenterologist.
HELLO! My child is 5 years old and has been suffering from allergies for three weeks now; we have never done any tests. at the children's clinic we were told that we need to monitor the blood for now, and that it is necessary to take tests for the UAC and TAM so that there are both eosinophils and monocytes in the blood. Are they present in the general blood test? and how much do such tests cost you? Thanks in advance!
Dear Daria! The level of monocytes and eosinophils is assessed during a clinical blood test (tests No. 5, No. 119).
The most common cause of increased sensitization of the body in children is parasitic infestation and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, therefore, to exclude this pathology, I recommend that the child perform a blood test for roundworms, toxocara, lamblia (tests No. 232, 234, 237), a blood test for household allergens (profile No. 98), stool analysis for Giardia antigen (test No. 483), stool analysis for dysbacteriosis (tests No. 456, 443), stool analysis for pancreatic elastase (test No. 162PE1). More detailed information about prices for studies and preparation for them can be found on the website of the INVITRO Laboratory in the sections: “Analyses and prices” and “Research Profiles”, as well as by calling 363-0-363 (the single help line of the INVITRO Laboratory). To determine further tactics, I recommend contacting an allergist.
Source: https://invitro.kg/for-clients/mat/5905/
What is Giardia
Giardia are not worms, but microscopic parasites of the protozoan class. The place of Giardia parasitism is the upper parts of the small intestine. Giardia is attached to the mucous membrane by the front part of the body, and the rear end is free.

Trophozoites remain fixed in one place for a short time. They are often detached from the villi and reattached to them, but in a different place or become free. With intensive invasion, they can penetrate into the villi tissue.
Trophozoites periodically detaching from the mucous membrane encyst or degenerate. Experimental studies on dogs have established that 10-15 days after infection, the bulk of trophozoites are localized in the jejunum and occasionally in the duodenum.
Subsequently, the Giardia population moves from the proximal to the middle or to the middle and distal parts of the small intestine. The formation of cysts (encystation) in the first 10-15 days occurs in the jejunum, rarely in the duodenum, and at a later date in the middle and distal parts of the small intestine.
Ways of infection with Giardia
The source of Giardia infection is people infected with this parasite. In the intestines of infected people, adult lamblia become covered with a dense membrane and turn into so-called cysts, which are excreted in the feces. Giardia cysts are very resistant to external influences and can survive for a long time in the external environment.
If cysts that get into water or food are swallowed by a healthy person (only 10 parasite cysts are enough to become infected), within a short time they will turn into adult Giardia, which will begin to multiply quickly.
Parasites are transmitted mainly from person to person. Having formed in the intestines of an infected person, Giardia cysts are excreted in the feces. They are resistant to external influences and can survive in the external environment for a long time.
In children's groups, a child may become infected with Giardia through dishes and shared toys. Cysts that enter the human body with food or water will turn into trophozoites in a short time and begin to multiply rapidly.
What is giardiasis
Giardiasis is one of the dangerous contagious diseases that occurs asymptomatically in humans. The disease is caused by protozoa - Giardia, which move in the intestines thanks to small flagella. Infection occurs through drinking water containing the pathogen or through contact with a sick person.
Most often, a child becomes infected with Giardia, since it is young children who neglect the rules of personal hygiene. But the disease can also be found in adults. Doctors especially insist that in case of any digestive disorders, parents do not self-medicate, but go to the clinic to be tested for giardiasis in children.
The peculiarity of giardiasis is that the disease may not produce any symptoms for a long time, and a single diarrhea or vomiting is not perceived by a person as a serious illness. Often, patients attribute them to poisoning and treat themselves, without even seeing a doctor.
This will protect the child from serious diseases that provoke Giardia in the child’s body, especially with weak immunity. Giardiasis is also tested for those children who lose weight for no reason.
In order to correctly diagnose the disease and begin treatment, it is necessary to undergo a series of diagnostic tests for giardiasis. Such studies include a blood test for Giardia.
Symptoms and signs of giardiasis
Symptoms of giardiasis can be very similar to the symptoms of food poisoning or some other dangerous diseases for which the patient needs urgent medical attention. In the vast majority of cases, Giardia infection does not cause any symptoms, and the infection itself disappears without any treatment within a few weeks or months.
The first symptoms of giardiasis may appear 1-2 weeks after infection, when the parasites have already managed to multiply and disrupt intestinal function. Giardia primarily affects the small intestine, where food is digested and absorbed.
The main symptoms and signs of giardiasis are:
- not very frequent, but prolonged diarrhea (diarrhea) in which very foul-smelling stool is released that sticks to the toilet or potty (a sign of the presence of undigested fats in the stool). Diarrhea may last for several weeks;
- sudden temperature of 38 C or higher, weakness, chills;
- sharp pain in the abdomen (usually in the navel area);
- prolonged nausea, periodic vomiting;
- the appearance of a pink-red itchy rash on the skin;
- weight loss.
Analysis for giardiasis - diagnosis of giardia
It is impossible to visually detect Giardia during bowel movements due to their microscopic size and habitat in the upper intestines. When it enters the large intestine, a sexually mature individual turns into a cyst and, in this form, leaves the body of its owner for further spread.
All children with underweight and delayed physical development, those attending children's groups, persons with diarrhea of unknown origin, chronic pathologies of the digestive system, constant rashes on the body, frequent obstructive bronchitis and bronchial asthma must be tested for giardiasis.
Families and their close relatives are subject to mandatory examination when Giardia is detected in one of its members. A generally available method for detecting giardiasis is to examine fresh feces under a microscope with preliminary staining with Lugol's solution.
Features of the life cycle and the short period of existence of vegetative forms in feces require multiple studies to confirm the diagnosis. It is best to submit the material 3–7 times with breaks of 1 week.
Duodenal intubation, when a special probe is inserted through the mouth directly into the duodenum, with further examination of its juice and bile for Giardia, gives a 100% positive result in case of infection. The use of the method is limited due to its traumatic nature and psychological stress, especially in childhood.

An alternative and non-traumatic method for detecting giardiasis is an immunological study. It allows you to detect antigens (specific elements) in stool. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is informative already on the 10th day after infection.
The most reliable method for confirming giardiasis is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It can detect parasite DNA in biological secretions. The method is actively used for express diagnostics (stool test) of helminthic infestation.
In vitro analysis of stool for giardiasis
Giardiasis is one of the most common parasitic diseases in humans.
According to WHO, about 200 million people become infected with Giardia every year. Clinical manifestations of giardiasis are recorded in almost 500 million patients per year. The disease is widespread.
The causative agent of giardiasis in humans is the well-known protozoan organism Lamblia intestinalis, which settles in the small intestine and causes digestive disorders.
In humans and animals, Giardia exists in two forms.
In the form of a vegetative form (such lamblia are called trophozoids), they are found mainly in the upper parts of the small intestine, and when they enter the large intestine they turn into cysts (spore form), which are excreted into the external environment with feces. Giardia in the form of cysts can remain in a “preserved” state for a long time and only when favorable conditions occur turn into trophozoids.
Once in the intestine, Giardia turns into trophozoids, attaching to the surface cells of the mucous membrane and sucking nutrients from it. Their life cycle is from three to forty days.
Despite the fact that this is a fairly short period, the disease can last a very long time, since repeated self-infection occurs all the time. As a result of the long-term existence of Giardia in the body, a syndrome of chronic endogenous intoxication is formed.
With reduced immune defense, this can lead to damage to almost all organs and systems of the body.
There are three main routes of transmission of giardiasis:
Most often, infection occurs when drinking poorly treated tap water or water from open reservoirs. In the contact-household route, entry into the body occurs through household items contaminated with cysts: linen, toys, dishes. Infection is also possible by consuming food products infected with cysts, especially without heat treatment (vegetables, berries, fruits).
How does giardiasis manifest in adults?
The incubation period of the disease lasts 1-3 weeks. As a rule, giardiasis occurs without any symptoms. With a large number of parasites inside the human body, the disease occurs with severe clinical symptoms and has an acute or chronic course.
In the acute form, the disease begins with the appearance of loose, watery stools without mucus and blood. Pain appears in the epigastric region. A large amount of gas is formed, bloating the intestines, and belching is observed. Patients experience decreased appetite, nausea, vomiting, and a slight increase in body temperature.
In most patients, the symptoms of the disease disappear spontaneously within 1-4 weeks. Then the disease becomes chronic, which is periodically manifested by bloating, pain in the epigastric region, and loose stools.
All patients with giardiasis show signs of vitamin deficiency: pale skin, blue under the eyes, pockets in the corners of the mouth, allergic rashes.
How dangerous is giardiasis for a child?
In children, giardiasis develops much more often and is more severe than in adults.
Modern epidemiological studies have shown that about 30% of preschool children are infected with Giardia. Moreover, in most cases, giardiasis in a child manifests itself with symptoms that mimic other diseases and make it difficult to identify the true cause of the disease.
Once in the child's intestines, Giardia begins to actively multiply, using the nutrients the child needs for growth. As a result, there is a lack of vitamins in the body, which inhibits the normal development of the child.
During their life, Giardia also releases a number of toxic substances. This leads to severe allergization of the child’s body and suppresses his immunity. For this reason, one of the common manifestations of giardiasis in children are: atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma, chronic dry cough and frequent colds.
What are the consequences of giardiasis?
Giardiasis can aggravate the course of any other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract combined with it. It masks them and contributes to the occurrence of allergic reactions.
Situations are quite common when the diagnosis of giardiasis hides such chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract as inflammation of the pancreas, dyskinesia (impaired motor activity) of the gallbladder, inflammation of the intestines of various types, etc.
The nervous system is often affected. Patients complain of general weakness, fatigue, irritability, shallow sleep, disturbing dreams, headaches, and dizziness. The development of hypotensive crises with fainting is possible. Vegetative-vascular dystonia and arrhythmia are quite common.
In chronic giardiasis in children and adults, skin lesions are detected: pallor, uneven skin color (“multi-colored skin”), damage to the red border of the lips. The severity of the lesions varies: from mild peeling and dryness to severe cheilitis with cracks and jams.
Due to the discovery of Giardia in the child's stool and the appearance of characteristic complaints, additional examination is required in order to identify hidden chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
How is giardiasis diagnosed?
The variety of clinical manifestations of giardiasis and the absence of symptoms characteristic only of this disease require mandatory laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis.
The material for research is feces and duodenal contents.
Only trophozoids are found in the duodenal contents, only cysts are found in formed feces, and trophozoids and cysts are found in liquid and semi-formed feces.
Currently, a number of methods are used to diagnose giardiasis, which differ in sensitivity, specificity and general availability. The independent laboratory INVITRO offers a wide range of studies to detect the presence of Giardia in the human body.
Source: https://moscow-milan.ru/analiz-kala-na-lyamblioz-invitro/
Indications for blood testing for Giardia
Testing for giardiasis reveals the presence of parasites in the body. This may be a microscopic examination of stool, but cysts (the spore form that microorganisms acquire when they find themselves in the rectum) are not always detected, but only in 50-70%.
The symptoms are not specific, therefore, in order to prescribe adequate treatment, the doctor needs to know for sure what causes the digestive problems.
Therefore, a serological blood test for antibodies is usually prescribed in conjunction with a stool test. The doctor will prescribe this test if he suspects the disease.
The clinical manifestations of the disease are as follows:
- prolonged diarrhea,
- stomach ache,
- increased body temperature and chills,
- skin rashes, vomiting.
Giardia antigen in feces, what does this mean?
This test helps determine the presence of parasites in the human body. Feces are donated both during treatment and a week after the medication course is completed. This procedure helps determine the effectiveness of the therapy by identifying the antigen in the biomaterial.
What is Giardia antigen in stool? The human body perceives any foreign substance as an object that should be fought against. As a defense, the body begins to produce antibodies. An immune cell attracts an antigen, receiving information about a given body. If possible, the antibody kills the foreign cell; if not, it tries to neutralize it, preventing further reproduction.
There are no special requirements for biomaterial to perform antigen analysis. Even three-day-old feces are suitable for research. To determine the presence of antigen, Giardia antibodies are injected into the stool. They, in turn, must attract parasite antigens to themselves. After some time, reagents are introduced into the sample, which should free the biomaterial from cells that have not reacted. Unbound enzymes are washed and a drug is added that inhibits the process. During the last procedure, the stool darkens if the answer is positive and remains the same color if the result is negative and no antigens are detected.
This analysis was not without its negative aspects; it is very problematic to determine the presence of Giardia if at least a small amount of E. coli is present in the sample being studied. A negative result can also occur if the body has not yet had time to respond to the invasion of parasites. For a more accurate diagnosis, it is recommended to retake the biomaterial in a week.
A blood test to detect Giardia antibodies and a stool test to determine whether it contains antigens or not are the main studies that allow us to conclude whether a person has giardiasis or not.
The essence of a blood test for lamblia

Testing for giardiasis is a serological test using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This means that high-precision instruments in a clinical diagnostic laboratory will identify antibodies in the blood serum that are produced by the immune system in response to damage to the body by this parasite. They can be detected as early as 2 weeks after infection.
Blood test for lamblia
The essence of the ELISA diagnostic procedure is a study of venous blood, during which the presence of Giardia in the body can be reliably confirmed or denied. Deciphering such analyzes with an error of only 1 percent. Total antibodies are a good way to determine current or past Giardia infection.
The presumptive diagnosis is confirmed by antibodies of type M, which are found in the blood of patients suffering from Giardia. They appear in the body in response to the aggression of antigens. Giardia blood shows antibodies of this type already at the end of the second week from the moment a person is infected. A little later, tests for Giardia show other antibodies of type A and G.
Preparing for a lamblia blood test
Analysis for giardiasis shows the presence of immunoglobulins only three weeks after infection. Also, the antibodies produced can remain in the blood for a long period of time after recovery.

Therefore, a serological test cannot be called one hundred percent accurate - rather, its interpretation and results will only be of a clarifying nature. Antibiotics can significantly affect blood counts, which will lead to incorrect interpretation of the results and antibodies to Giardia antigens will not be detected.
Failure to comply with the rules for taking and conducting immunological studies can fundamentally distort the clinical picture, therefore it is very important to know how to prepare for a blood test for Giardia in children and adults.
Rules for preparing for the test for Giardia in the blood:
- do not eat 10 hours before blood sampling: as a rule, it is done in the morning on an empty stomach;
- do not drink alcohol, juices, tea and coffee before taking the test;
- warn laboratory technicians about taking any medications;
- take blood from a vein;
- You are allowed to drink one medium glass of water in the morning;
- doctors do not recommend eating fatty and fried foods, salty and spiced dishes;
- It is best to eat more fresh vegetables the day before the blood test.
Blood test for IgG or IgM antibodies against Giardia
1-2 weeks after infection with giardiasis, IgM type antibodies can be detected in the patient’s blood. After another 1-2 weeks, IgM is replaced by IgG antibodies, which remain in the human blood for a long time after recovery.
Thus, the presence or absence of antibodies against Giardia in the blood cannot serve as a reliable indicator of the presence of infection or the effectiveness of treatment. The test uses a small amount of blood taken from a vein.
Giardia tests in vitro
I want to tell you how we looked for giardiasis in a child. Maybe it will be useful to someone.
Gingerbread had the following symptoms: suppressed constipation (fear of the potty), poor weight gain. Let me make a reservation right away: we didn’t experience any rashes, allergies, coughs, panos (on the contrary, we have constipation), dark circles under the eyes, grinding teeth, poor sleep (he’s been sleeping well since birth, without waking up).
We turned to the doctors. First, we went through all the tests: blood, urine, smear for enterobiasis, test for copra, test for I/g, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Everything is normal, nothing was found. Only during the ultrasound we were told that the child had severe gas formation, and the pancreas and liver were slightly enlarged.
Of course, at this stage I was seriously scared. We were referred to a gastroenterologist. It’s impossible for us to get into the district one, so we went to the paid one in Medsi 2 (Borisov).
After examining the child, she confirmed that he was thin, that his bottom was inflamed, and suggested two diagnoses: food allergies and... more likely, lambiasis.
The following actions were prescribed:
Chophytol (choleretic) 2 times a day, 10 drops before meals for 1 month.
Creon 3 times a day, 1/2 capsule for 2 weeks.
Nemozol 1 tablet 1 time (500 mg). Nemozol was prescribed for simple helminths. Like it will kill them, and if there is Giardia, it will irritate them, and they will show up immediately in subsequent tests.
Further…
We drank everything, and a week after Nemozol we donated blood from a vein for antibodies to Giardia in vitro (1500 rubles for a nurse to come to your house).
I was sure that this analysis was absolute and guaranteed to show the presence of Giardia.
Three days later, the test is positive. I'm shocked. I study everything on the net. It turns out that analysis from a vein is not an indicator at all, and children with a positive result for antibodies in 40% of cases did not have any Giardia. And by the way, the doctor does not have the right, based on blood results, to prescribe treatment for Giardia.
Further... on the recommendation of the same gastroenterologist, you need to take a stool test for I/G, on the basis of which an accurate diagnosis is established. There are a lot of difficulties here. These creatures reproduce in cycles, and one day they will come out to reproduce, and the next they will not. You need to take tests for several days in a row. Moreover, in the morning, almost lukewarm, almost obtained in the laboratory. Otherwise, they die within two hours. And even more so in the refrigerator. And to get such a quantity of what, and even in the morning, and with our constipation...
Of course, the gastroenterologist immediately told us the solution.
So, the Institute of Parasitology and Tropical Medicine named after. Martsinovsky (address: metro station Sportivnaya, M. Pirogovskaya st., 20 - clinic).
There you come to room 47 (at the checkpoint a passport or driver's license is required, I actually went through the insurance policy), you take a container with a preservative and a reminder. For three days, place the kaki in the container, one spoonful at a time. Thus, it turns out that you take tests on three different days (it doesn’t matter morning or evening - any). Store at room temperature in a dark place. then you give it to them for analysis (the cost of the analysis is 500 rubles).
The laboratory told me that 3 days of research was enough, I took two containers, passed two tests in six consecutive days. To be sure, although they twisted a finger at my temple, like the money is yours.
Opening hours of the Institute of Parasitology:
Mon-Thu 9.00-12.00 reception of tests.
Mon, Wed 13.00 - 15.00 delivery of test results.
The cash desk is open from 9.30.
We took it on Tuesday and received the results the very next day.
NO DEVIATIONS FOUND!!! And this is with a positive antibody test! And this is at the Institute of Parasitology!!!
Apparently our constitution is just skinny. Then, after drinking Chophytol and Creon, we made an appointment again for an ultrasound and a gastroenterologist. We'll eat soon.
I wrote to those who needed at least some information, just as I needed it.
And I immediately apologize for the mistakes. There is no special time to even re-read the text to look for typos.
Everyone - so that the children are healthy!
Analysis for giardiasis - interpretation
Currently, a blood test for antibodies against Giardia is not recommended as an accurate diagnostic method either in Russia or abroad.
The norms and interpretation of the values of antibody titers against Giardia vary depending on the equipment of the laboratory and therefore can only be indicated and deciphered by doctors familiar with the working methods of the laboratory that performed the tests.
If the transcript contains IgM antibodies, then the person became infected with giardiasis about half a month ago. If IgG antibodies are present in it, then the disease has entered the chronic stage, and the immune system is actively fighting it.
Decoding with both classes of antibodies indicates an acute form of the disease. The IgM classes can remain in the blood for up to several months after treatment, and the IgG classes for up to six months.
The ELISA is deciphered by comparing the data with normal indicators and positive data. Let's look at the basic standards:
- if antibody standards are elevated (a positivity rate above 1.0 is considered), then the person’s blood will contain specific immunoglobulins and the laboratory will give a positive result;
- if a blood test for antibodies to Giardia shows a result of less than 0.85, then the test is considered negative and the fact of Giardia infection is not established;
- with a value falling within the amplitude from 0.85 to 1.0, the decoding does not allow determining the dynamics of antibodies. The analysis is repeated after two to three weeks.
Analysis for Giardia
- Before checking notreatment you need to monitor
- analysis accuracy up to
- research, all the rest this period is simpler,
- However, many experts insist on the following:
- OPD more than 0.85, in the form of cysts. They
You should know that K. intestines. Polymerase chain it is recommended to take alcohol for personal hygiene 90%. can only be explained by the greatest claim that old For diarrhea and allergies but less than 1 use for this P. this is the coefficient
reaction (PCR) studies and smoking. Home hygiene should also be carried out. It is also necessary to carry out the addition of pathogen content in
A portion of stool is not of unknown etiology. The doctor will offer the patient the nutrients of the body; positivity according to the test system; a small section of DNA should be agreed with the doctor. In general, a stool analysis is a study of stool after. During the study, the body itself is studied.
Rules for preparing for the test
will be able to show the exact In case of gastrointestinal diseases, repeat the analysis, so the owner is called “Giardia - AT”.
Giardia, highlights the sequence of medications, - the most reliable treatment for giardiasis, feces and duodenal Only according to the results of the study, the result and study in a chronic form. How the results are considered dysfunction of the digestive system. Hemotest provides a comprehensive study of the parasite genome.
which can change the way to determine giardiasis preferably several times. contents. In blood waste, the diagnosis will be meaningless. And In case of intestinal dysbiosis. doubtful. In rare cases, Giardia parasitic infection in the Test system is used during the test results. In a person. For This is necessary for the human body, it is impossible to establish accuracy. if someone encounters
When a child is delayed inx, the bile ducts of adults and children are affected
Explanation of blood test
carrying out a polymerase test on a day of examination does not confirm the diagnosis and also confirm that there is an infection
Detect Giardia trophositis, This is due to the medical staff, which is developing, malnutrition.
which leads to using the reaction method. Source material
Intense physical is recommended, you can do the research and it’s finally gone. Also, adult mobile microorganisms, so that later they will insist on For frequent skin diseases: How to prepare for liver damage, development
ELISA. The analysis is carried out to study the blood load, undergo enzyme immunoassay to see the picture of the disease and cysts. Study 7 days after freshness of the sample, in neurodermatitis, eczema, urticaria, ELISA analysis for biliary dyskinesia.
using 9 blood and feces.
Fried foods are excluded from the diet, analysis, but these were more complete, carried out in the laboratory, infections, analysis for
It has all dermatitis. Giardia:
Interpretation of stool examination for the presence of parasites
If the patient does not reagents: In the process of processing spicy, fatty dishes. examinations are not so much except for stool analysis there are two methods
Antibodies may show reasons thatIn case of immunodeficiency.You should not drink alcohol,receive the necessary treatment,immunosorbent control sample;the data obtained are doneBlood donations are strictly
are important. Once identified, it is advised not to neglect
detection of giardiasis: IgM blood test to reproach specialists for
- For bronchial asthma and
- coffee, tea for
complications may develop.blood serum without antibodies conclusion about the dynamics on an empty stomach, and antiparasitic diseases are needed as
Why do you need PCR diagnostics of Giardia?
other diagnostic methods. for antigen and - this indicates an insufficient level of qualifications. obstructive bronchitis. 10 hours before Pronounced signs of the disease are: to Giardia; ailment and effectiveness research is carried out only as quickly as possible begin
Important! Stool analysis is possible using the PCR method, polymerase about the pathological process. The advantage of fresh feces (2) For the purpose of examining individuals, conducting research. Sharp pain and tension of the buffer composition; prescribed treatment. after 14 days
supervised treatment is supplemented with a blood test of a chain reaction in the body, and a sentry) is only
- in contact with the carrierThe three-day interval should be
- in the umbilical zone ofchromogen.Study of DNA of the causative agent of Giardia after taking medications
- doctor. for antibodies to
Collecting material for research in another week, that Giardia Giardia. is maintained between tests. of the abdomen. After the study, 90% - fast and for the treatment of Giardia. You are still Giardia. on Giardia is nothing they can be replaced in it, all of the listed pathologies can be presented. Medicines distort the results of studies. Excessive vomiting and nausea. cases of parasites are detected by a highly sensitive method. He
ELISA in children for the presence of parasites
Feces are placed in the pore, we are sure that If there is a suspicion that does not differ from others, type IgG in a characteristic form: be associated with Therefore, the patient should Prolonged diarrhea or constipation. in the small intestine has a whole a row of a special spoon attached to cleanse your body; there are other stool tests in the body. - the person is healthy.
With flagella, mobile. Carriage of Giardia. Inform a specialist about Bronchospasms - attacks of a suffocating patient. Deciphering the analyses, significant advantages: to the container. Material from parasitic organisms affected by Giardia or not before collection And such data Of course, in such
This study helps to determine the constant intake of any cough. The specialist compares the final determines with a large share taken in a small difficult? other parasites, you should take laxatives
can be found in the form of discerning their presence in the body of medications. Sudden decrease in body weight. result with a negative probability of the presence of a parasitic pathogen; volume from different If you read these contact a gastroenterologist medications and other human blood in will not be difficult. human Giardia, and Blood is donated for analysis Enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, control. A positive result identifies a unique region of DNA. The doctor recommends the lines, then yours or the therapist for
medications, they for a long time However, after 2 it is revealed in which
from a vein on an empty stomach of the liver. Giardia is taken into account by highly sensitive equipment, a three-fold check, parasite control is carried out, obtaining a referral for
- may affect
- up to, and and more than an hour
- the form of the disease
- in the morning. Before this
Increased fatigue. if it allows you to establish the presence of every 3-4 days. Apparently research in the usual end result and after complete recovery. Giardia contained in (in acute or you can only drink Febrile fever - moderate
The value is much greater than the parasites; The container is equipped with a preservative. It turned out to be not such a clinic. This is a way to ruin a picture. Diet In connection with this, stool begins to feel chronic). Feces are given in plain water.
increase in body temperature 1.0, multiplied byis carried out for a shortSuccessful blood donation is not allowed...will be absolutely free.
of a person before sampling, the presence or absence of some kind of discrepancy between them and in the process of the Advantages of a blood test with for no apparent reason. optical density value. time interval. after a rectal examination, Have you thought about If there is no time to wait , does not matter. in the blood of antibodies under normal conditions of life treatment of giardiasis using the ELISA method:
Dirty pale skin tone.The value of the final result variesIn the analysis of the polymerase reaction of physiotherapy sessions, X-ray drastic control measures you want to immediately get
Typically, tests are collected in does not indicate in the intestines (modified control of the effectiveness of therapy, Possibility of early diagnosis of invasion. Allergic skin rashes.
within up to>
How to test your child for giardiasis in the blood
The psychological factor in children with ELISA is that it is extremely difficult to take blood from a vein - the baby will scream and cry. Most often, in such situations, this study is simply not prescribed.
To exclude repeated tests, it is necessary to correctly test the stool for Giardia in the child. To do this, it is advisable to observe all the nuances of the procedure for collecting stool, as well as deliver the container with it to the laboratory on time.
Research material taken from children can be stored for no more than 12 hours, and then only in preservatives. You can ask for such containers with special substances in the laboratory.
Testing for Giardia is a little more difficult for a child than for an adult due to the fact that when taking blood there is a psychological factor and food restrictions, and when taking feces there is a need to defecate at a certain point in a special container.
In infants, this problem is even more acute. Firstly, it is necessary to collect research material from the diaper extremely carefully - so that only those feces that do not come into contact with the diaper get into the container. Secondly, it is necessary not to miss that very moment.
Prevention of Giardia
Health education plays an important role in the prevention of giardiasis. It should be carried out, first of all, in risk groups, which include, in addition to those listed, persons visiting areas endemic for parasitic diseases, including giardiasis.
Tourists' attention should be drawn to the need to consume only high-quality thermally processed food products and boiled or filtered water. This will reduce the risk of infection not only with giardiasis, but also with other infectious and parasitic diseases.
Diagnosis of giardiasis
The need for testing for Giardia arises in cases where a child or adult patient has the following symptoms:
- general intoxication of the body is expressed - pale skin, “dark circles under gases”, increased fatigue, frequent headaches, depressed mood;
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract persist for a long time and periodically worsen;
- a general blood test regularly reveals eosinophilia (increased concentration of cells responsible for maintaining an allergic background in the body);
- Loose stools often occur or are constantly present, including “travelers’ diarrhea”;
- Various allergic conditions are difficult to cure, for example, neurodermatitis, atypical dermatitis, asthmatic bronchitis, etc.
Giardia lives in the human small intestine, so the easiest way to detect them is in feces, which should be collected in the morning through natural bowel movements or a cleansing enema.
When the material is quickly delivered to the laboratory, Giardia cysts can be seen under a microscope, and less often live parasites. Sometimes the analysis must be repeated up to 3-5 times to obtain laboratory confirmation of the clinical diagnosis. Serological blood diagnostics using the ELISA method is considered advisable only when carried out in the first month after infection, however, the date of onset of invasion is not always known. The gold standard is the study of duodenal contents obtained from a patient by probing the gallbladder, but the method is complex and is carried out only in adult patients in a hospital setting.
It may also be of interest: Giardiasis: diagnosis by blood