The term worms is used to unite a large group of lower worms that can enter the human body and parasitize it. Depending on the habitat they choose, the invasion will be accompanied by a lot of unpleasant symptoms. Most often, worms settle in the intestines. The gastrointestinal tract and immune system suffer greatly from this. Therefore, it is important to recognize the problem in time and begin treatment.
About roundworm infection
Roundworms cause a whole group of diseases.
Nematodes are a whole group of specific diseases caused by the same pathogen - roundworms.
Symptoms of such ailments can be very different, depending on the type of parasite that has entered the body. In general, all nematodes can be divided into two large categories:
- acute, characterized by a clear manifestation of symptoms from the very first days of the development of the disease;
- chronic, sluggish and passing, as a rule, almost asymptomatic.
Diagnostics
Since helminthiasis is a whole group of different diseases, its diagnosis requires many research methods. These include:
- stool analysis;
- macroscopic and microscopic diagnostics;
- coproovoscopy;
- laboratory bile analysis
- biopsy of the patient’s soft muscle tissue;
- blood test for the presence of microfilaria;
- ultrasound examination, fibrogastroduodenoscopy and x-ray.

Diagnosis of helminthiasis
Based on the number of procedures listed above, we can say that analysis for helminth infections is a very complex operation, consisting of many steps. A doctor may prescribe it if he suspects the presence of a particular type of disease.
Roundworms
The most common causative agent of nematodes in humans is roundworm. Typically, the first signs of infection with this worm appear in the second week, when the larvae of the parasite begin the migratory phase.
Most patients suffering from one type or another of ascariasis exhibit the same characteristic symptoms of this condition. Thus, with helminthic infestation of the lungs, patients usually complain of:
- temperature increase;
- paroxysmal asthmatic cough accompanied by chest pain;
- discharge from the lungs of a small amount of mucous sputum (sometimes streaked with blood).
Due to the ambiguity of symptoms, the described type of ascariasis is often confused with allergies, bronchitis, ARVI, asthma or even pneumonia. This kind of invasion is generally the last thing to be suspected, since the adult parasite does not take root in human lungs.
In other words, such a condition can arise only during the period of migration of roundworm larvae. As a result, only an x-ray showing a large number of infiltrates (that is, accumulations of eosinophils reacting to helminth toxins) in the patient’s lungs usually helps to establish an accurate diagnosis. With helminthic infestation of the intestines, the symptoms of the disease become more specific:
- a sharp increase (or, conversely, decrease) in appetite;
- increased salivation, especially pronounced in the morning, on an empty stomach;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- cramping pain in the abdominal area, aggravated by palpation;
- flatulence;
- enlarged peripheral lymph nodes;
- sometimes - in cases where the number of parasites in the body goes off scale - there is a clear sensation of movement in the intestines.
Characteristics of biohelminths
The class Tapeworms (Cestoda) has about 3000 species. All without exception are parasites. They most often parasitize the small intestine of chordates. Length - from 0.5 mm to 30 m. The body is flat, ribbon-shaped, consists of a scolex, neck and strobila. The scolex carries fixation organs - hooks, proboscis, suckers, bothria, botridia, etc.
The neck is the zone of budding of segments. The strobila consists of many segments called proglottids. Only in a few species the body does not have visible division. The skin-muscle sac corresponds to that of flukes, but unlike them, the submerged epithelium is equipped with microscopic villi - microtrichia.
There is no digestive system, absorption occurs over the entire surface of the body. The excretory system is of the protonephridial type, the most developed are two canals on the sides of the body, connected in each segment by a transverse canal. The reproductive system is hermaphrodite type. Each segment contains one or two sets of gonads.
The male reproductive system is represented by vesicular testes (from 1 to 1200), seminiferous tubules extending from them, which in turn flow into a large canal opening into the cirrus. The female reproductive system consists of an ovary (usually a pair), an ootype, a vitelline and a uterus.
The ootype is connected to the female genital opening by the vaginal canal, which has an extension - the spermatic receptacle. The genital openings of both the male and female reproductive systems open into the genital cloaca, located on the side of the joint or on its flat side.
Echinococcal vesicle - consists of several layers, the inner of which is germinative, that is, capable of budding both scolex and daughter vesicles, and those, in turn, grandsons. Bubbles form in parenchymal organs.
The alveococcal bladder has a cellular structure. Each cell contains several scolex. In the lungs and liver of mammals.
Parasitization of tapeworms in the small intestine leads to various pathological changes in the host body. Significant competition for food leads to a sharp weight loss of the owner. In addition, the worm adsorbs vitamin B12 and vitamin deficiency occurs. The helminth also releases toxins. Anemia, nausea, and pain in the intestines are also typical. People may experience parasitic psychosis.
The following genera and species pose the greatest danger to human and animal health.
Diphyllobothrium latum (wide tapeworm)
Systematic position: order Pseudophyllidea, family Diphyllobothriidae.
The strobila is up to 20 m, the scolex is armed with two suction slits - bothria. The segments are very wide - up to 15 mm and short - 6-8 mm. The uterus is a highly convoluted tube that looks like an irregular spot in the central part of the segment. Eggs (68-71 µm long and 45 µm wide).
Parasitizes humans and piscivorous mammals. Eggs are laid either in the intestines, or they are released along with the segments. At the same time, strobila fragments ranging in length from 2-4 to 60 cm are periodically released. When infested by a large specimen of the helminth, an infected person can secrete up to 2 million eggs in 1 g of feces. For further development, the egg must fall into fresh water, where after 3-5 weeks the coracidium larva emerges from it.
This larva is swallowed by the first intermediate host - the crustacean diaptomus or cyclops, in which a procercoid is formed after 1-2 weeks. If an infected crustacean is eaten by a fish (additional host), then within a month a larva, a plerocercoid, develops from the procercoid, which is invasive.
If this fish is eaten by a pike, pike perch or other predatory fish, the plerocercoid passes into the muscles and internal organs of this predator (reservoir host). In large pikes there can be up to several tens or hundreds of plerocercoids.
Human infection most often occurs through consumption of raw pike caviar. Symptoms: nausea, dizziness, abdominal pain, anemia, discomfort on the tongue while taking medications, sour and salty foods, then the papillae of the tongue atrophy, and the edge of the tongue appears varnished. There is a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid by the stomach, disruption of the heart, and vitamin deficiencies. When infested by several helminths or one large one, intestinal blockage may occur.
Foci of diphyllobothriasis exist in large river basins. Thus, in Lakes Ladoga and Lake Peipus, as well as in the Vuoksa system, most pikes are infected. At the beginning of the twentieth century, 10% of the population in St. Petersburg was sick. Now the average incidence in Russia is 11.7 per 100,000 population, in the Leningrad region - 15.6; in Karelia - 35.5; Komi - 49%; In the Nenets Autonomous Okrug - 258.5; Evenki Autonomous Okrug - 534.9. More than 90% of patients are adults.
Ligula intestinalis (Little Ligulp)
Systematic position: order Pseudophyllidea, family Ligulidae.
The belt-shaped strobila reaches 1 m. The scolex is very poorly developed. The segments are very short, their boundaries are unclear.
Testes and vitellaria are numerous. The uterus occupies a central position.
As an adult, it lives in the intestines of fish-eating birds for a very short time - from 2-5 days to 2 - 4 weeks. Eggs that fall into water develop and coracidia emerge from them after 1-3 weeks. They are swallowed by cyclops crustaceans - the first intermediate hosts. In cyclops, a procercoid forms after 2 weeks.
If an infected cyclops is eaten by a fish, then in its body the procercoid turns into a plerocercoid, which develops over 1-3 years and grows up to 1 m in length. During this time, the larva develops many parts of the reproductive system. Infected fish are inactive, emaciated, weakened, their abdomen is greatly swollen, they swim poorly and become easy prey for gulls, terns and other birds.
Sometimes the body wall ruptures and the ligula emerges into the water. In some small reservoirs of the Leningrad region, crucian carp are 90-95% infected.
In economically valuable fish, the larva of L. intestinalis (ligamentum) causes a dangerous and widespread disease - ligulosis. Prevention of ligulosis is carried out by scaring away fish-eating birds and catching diseased fish as much as possible. Ligula are absolutely safe for humans. The closely related species Digramma interrupta is very similar to Ligula.
Strobila 0.2 cm - 1 m. The scolex has 4 suckers and a proboscis armed with hooks. In different representatives, the hooks and proboscis are developed to varying degrees. Semennikov 1-3, well developed spermatic receptacle. The ovary is large. Parasites of mammals and birds cause hymenolepiasis, which occurs as enteritis.
H. nana (dwarf tapeworm)
Often found in humans, less commonly in mice and rats. The length of the strobila is 2 cm. The scolex has a proboscis with a rim of hooks. The three testes in the hermaphroditic segment are arranged in a row at the bottom of the segment. The uterus is saccular. The eggs are oval, colorless, 40-50 microns in size. Inside there is an oncosphere, from the poles of which 2 pairs of long wriggling processes extend. It develops most often without an intermediate host (sometimes an insect wedges itself into the cycle).
Oncospheres immediately emerge from the laid eggs, which penetrate the intestinal villi, where the further development of larvae - cysticercoids - occurs. The larva matures within 102 hours. After this, the cysticercoid falls into the intestinal lumen and a new tapeworm grows.
With this disease, superinvasion quite often occurs, in which the number of parasites amounts to tens of thousands.
Children are more likely to get sick, but self-healing occurs by the age of 12-14, and re-infection occurs very rarely. Occurrence is 0.1-0.4 per 100,000. The basis of preventive measures is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
H. diminuta (rat tapeworm)
It parasitizes synanthropic rodents and sometimes humans. The strobila is up to 60 cm long. The proboscis on the scolex is underdeveloped. In the hermaphrodite segment, the ovary and vitelline occupy a central position; one testis is located on one side of the ovary (the genital opening opens on the same side), and two are located on the other. The uterus is saccular. The eggs are round with a double-circuit shell with a diameter of 60-70 microns, containing an oncosphere. Intermediate hosts are mainly insects (stock pests), in which cysticercoids are formed. A person becomes infected by eating baked goods prepared in violation of technology from flour containing infested insects. Human infection in one third of cases does not produce significant symptoms. Main symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, unstable stool, general weakness, dizziness. Acidity in the stomach also often decreases. When parasitized by rat tapeworm, nervous seizures can occur.
Hymenolepididae often parasitize the intestines of waterfowl. Drepanidotaenia lanceolata is of veterinary importance. The strobila size is up to 23 cm. The scolex is equipped with 4 suckers and a proboscis with 8 hooks. The genital openings are located on one side of the strobile.
Three testes lie in one line. The eggs are oval in shape, up to 106 microns in length and up to 46 microns in width.
Intermediate hosts are Cyclops and Diaptomus, in which the oncosphere penetrates the body cavity and after 11-12 days turns into a cysticercoid. After another 3 weeks, the larva becomes invasive. Ducks and geese become infected by ingesting crustaceans along with food. In the body of a bird, the helminth reaches sexual maturity in 2-3 weeks. If a cyclops infested with a cysticercoid is accidentally eaten by a mollusk, the helminth larva retains its invasiveness. The sick bird is emaciated, the feces are liquid. Paralysis of the legs is often observed.
Taeniarhynchus saginatus, bull tapeworm
Systematic position: order Cyclophyllidea, suborder Taeniata, family Taeniidae, subfamily Teniinae.
Powerful strobila (sagina - obesity) reaches 10-14 m in length. The scolex is equipped with 4 powerful suction cups. In the hermaphroditic segment, the testes are small, numerous, and the ovary is biramous. In a mature segment, the central canal of the uterus has from 13 to 35 lateral branches on each side. The muscular system is highly developed. The eggs are oval, 30-40 microns in size. They are covered with a thick shell with radial striations and contain a mature oncosphere.
The final host of the bovine tapeworm is only human. Mature segments can crawl out of a person’s anus on their own, 6-11 pieces per day, but more often they come out with feces. They crawl for quite a long time, dispersing their eggs. Thus, the grass and hay become contaminated. The eggs remain viable for a long time. The intermediate host is cattle, which ingests eggs along with food. An oncosphere emerges from them in the intestines, which is carried into the muscles through the bloodstream. There, after 5-6 months, cysticerci (Finns) are formed.
A person becomes infected by eating poorly processed Finnish meat. Causes the disease teniarinhoz in humans (in Russia - 0.2-0.4 per 100,000 population). Symptoms of teniarhynchosis: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, flatulence, abdominal pain, drooling. There is irritability and restless sleep.
Anemia is also observed. Women get sick more often than men by almost 40%. The crawling out of mature proglottids greatly depresses the psyche of patients. Tapeworm larvae (finns) parasitize cattle and cause bovis cysticercosis (finnosis), which is usually asymptomatic. This bovine disease is found in 0.3-0.4% of slaughtered animals in Europe, and in 30-80% in East African countries.
Pork tapeworm (T. solium)
Strobila up to 3 m long. Scolex with 4 suckers and a double crown of hooks. The hermaphroditic segment is similar in structure to that of the bovine tapeworm and is distinguished by the presence of a third (additional) ovarian lobule. In a mature segment, the central canal of the uterus forms 4-10 branches on each side. A mature segment contains up to 100 thousand eggs, which in morphology are indistinguishable from the eggs of a bovine tapeworm (Fig. 14).
The final owner is only human. The intermediate host is the wild boar and domestic pig, in whose muscles cysticerci (Finns) are formed. The heart is especially often affected. Human infection occurs when consuming lightly salted or raw pork meat and especially lard, which contain viable finches. The larvae are stored in meat for quite a long time - in the freezer of the refrigerator for up to 2 weeks. The tape stage causes taeniasis in humans. Mature proglottids never crawl out spontaneously.
The symptoms are the same as with teniarynchosis. Once, more than 100 tapeworms with a total length of 128 m were expelled from a person. The larval phase causes cellulose cysticercosis in pigs, which, as a rule, is asymptomatic. When the finca enters the human intestine, the head turns out of the bladder and attaches to the intestinal mucosa.
When parasite eggs enter the human stomach (for example, through ingestion or reverse intestinal peristalsis), the person can also become an intermediate host: an oncosphere emerges from the egg and is carried through the bloodstream into different organs where fins are formed.
Damage to the brain and eyes is especially dangerous. Brain damage by larvae is accompanied by headaches, vomiting, memory loss and nervous attacks. When the eyes are affected, complete or partial loss of vision occurs. Human cysticercosis is treated either conservatively (with the drug praziquantel) or surgically.
Pinworms
Pinworms - cause severe swelling in the anus.
In general, pinworm infection is characterized by the same specific symptoms as ascariasis. In addition, the patient may feel severe itching in the anus, noticeably increasing in the evening and at night.
Read: Cleaning from parasites at home, signs of infestations and methods of combating them
The nervous system suffers especially greatly with this type of helminthic infestation: the patient becomes restless and irritable; suffers from sleep disorders.
Typically, all the described symptoms begin to appear at the moment when the parasite that has settled in the body fully matures and begins the active process of reproduction and laying eggs.
Young children are most often infected with pinworms. The disease caused by these parasites, enterobiasis, in some cases can manifest itself in the form of urinary incontinence or suspicious heavy vaginal discharge (in women) or a rash similar to hives that occurs in the genital area (in both sexes). This is due to the fact that, in attempts to lay eggs in the perianal area, worms can penetrate the urethra.
It is curious that pinworms never begin to reproduce directly in the intestines. That is why the fact of infection with these helminths is so difficult to establish using a standard stool analysis, while eggs or even adult individuals of other parasites can often be seen in the stool with the naked eye.
Methods for treating helminthiasis
To treat helminthiasis, medication is most often used, but in rare cases, doctors may insist on surgery. Taking medications on your own is not recommended, as this may not only not help get rid of parasites, but also harm your health . First of all, the doctor must determine the type of helminths, and only then prescribe the appropriate treatment. For this purpose, they can use not only pharmacy, but also folk remedies, which, having passed the test of time, have managed to win the trust of many people. Let's consider each method of treating pathology separately.

Remedies for worms
Medicines
To combat any type of helminthiasis, pharmaceutical drugs are most often used; the least toxic of them (and at the same time effective) include:
- "Diethylcarbamazine";
- "Praziquantel";
- "Medamin";
- "Pyrantel";
- "Mebendazole";
- "Albendazole";
- "Levamisole."
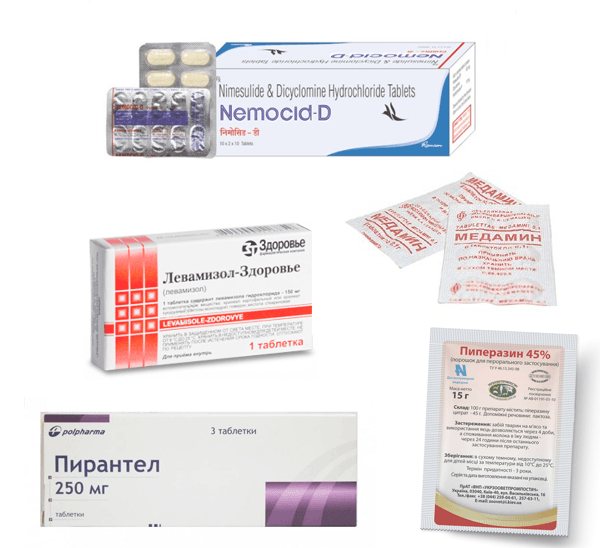
Medicines for worms
Depending on the physiological characteristics of the patient, the dosage or frequency of taking a particular drug may vary. In parallel with taking the above medications, doctors prescribe treatment that is aimed at eliminating other symptoms that arise as a result of the influence of parasites on the patient’s body.
Folk remedies
Despite the great popularity of drug treatment, many are in no hurry to use them due to the high toxicity of the drugs and the presence of side effects. To get rid of parasites, you can use alternative medicine methods.
Table. Traditional medicine for helminthiasis.
| Product name, photo | Application |
| Papaya seeds | The seeds contain various beneficial components that have a negative effect on worms. These are myrosin, sitosterol, carpain and other substances. Regular consumption of seeds helps normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. They can be eaten whole or added to other dishes in already ground form. For example, papaya seeds can be mixed with yogurt or honey. |
| A pineapple | It is no secret that pineapples contain bromelain, a substance that has a negative effect on parasites. Daily consumption of dishes with pineapple will not only destroy helminths and other types of parasites, but will also prevent their further occurrence. This is due to the fact that this fruit is quite sour, and increased acidity in the stomach helps lower blood sugar levels. This habitat is not suitable for parasites. |
| Lemon-banana juice | To prepare this product, you need to grind one peeled banana in a blender, then mix the resulting slurry with 1 tbsp. l. lemon juice. Banana contains special components that have a laxative effect on the body, and lemon, in turn, has antiprotozoal and antibacterial properties. The combination of these qualities makes lemon-banana juice destructive to various types of worms. |
| Pomegranate juice | In folk medicine, pomegranate is used to treat many diseases. It also helps get rid of parasites. To do this, you need to drink 3-4 glasses of fresh juice on an empty stomach, that is, 600-800 ml. After this, the helminths will leave the intestines on their own. The product is not recommended for use by people suffering from high blood pressure. |
| Pumpkin seeds | These seeds contain cucurbitacin, which, when it enters the human body, negatively affects the nervous system of parasites. As a result, the worms stop growing and eventually die. For treatment, it will be enough to consume 12-15 seeds per day. This is enough to cleanse the body of unwanted guests. |
| Castor oil | Take 1 tsp daily. castor oil on an empty stomach and soon you will be able to forget about worms. The substance has laxative properties, which is why all parasites leave the human body naturally. But castor oil does not help in all cases, since some types of helminths can cling to the patient’s intestinal walls, which is why diarrhea will not help get rid of them. |
Trichinella
Trichinella disrupts heart rhythm.
Trichinosis, or infection of the body with roundworms - Trichinella, usually occurs in three phases:
- an asymptomatic incubation period, which usually lasts no more than one and a half months;
- phase of disease development, accompanied by characteristic clinical symptoms (fever, chills, general weakness, muscle pain and swelling);
- peak of the disease, characterized by persistent fever, myalgia of the muscles of the neck, calves and lower back, puffiness of the face and allergic skin rashes (the latter appear as a result of an allergic reaction to helminths, accompanied by an increase in the level of eosinophils in the blood).
If trichinosis reaches its peak stage, the active development of accompanying respiratory tract diseases, such as bronchitis, pleurisy or even pneumonia, begins. The cardiovascular system suffers no less.
Thus, for carriers of Trichinella, heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia and arterial hypertension are very typical. As is the case with damage to the body by other helminths, prolonged presence of parasites in the body of the carrier can ultimately lead to appendicitis and peritonitis, anaphylactic shock, internal bleeding, the initiation of oncological processes, or even brain damage.
Prevention measures
First of all, you need to follow the rules of hygiene. Also, prevention of helminthiasis implies timely identification of infected patients so that the disease does not spread even more. For this purpose, it is necessary to regularly undergo special examinations for helminths.

Wash your hands regularly and thoroughly
Compliance with these preventive measures will prevent the body from becoming infected with parasites.
Infestation by flatworms
Bloating and nausea are signs of flatworm infestation.
Flat tapeworms are also capable of parasitizing the human body. Cases of infection with such helminths are collectively called “cestodiasis.”
Some parasites in this group, such as bovine tapeworms and pork tapeworms, can be especially dangerous.
Read: Worms in infants: symptoms, information about pathology, diagnostic methods and treatment
The main danger of infection with flatworms is that during the incubation period such helminths do not manifest themselves in any way.
The first symptoms of infection in patients, as a rule, begin to appear only one and a half to two months after infection. What signs can be used to determine the fact of infection? As a rule, the presence of parasitic flatworms in the body is indicated by the following alarming symptoms:
- bloating, nausea and vomiting, as well as other dyspeptic disorders;
- dizziness and headaches;
- various types of allergic reactions;
- sudden weight loss;
- periodic abdominal pain.
When infected with a bovine tapeworm, there is also some probability of finding detached segments of the parasite in the stool after defecation, similar to small white worms.
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.

The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
Other tests
We recommend reading

Pinworms in women: symptoms, treatment and how they leave the body
10 hours ago 03.09.202003.09.2020ecoliv94
Necatoriasis: what kind of disease is it, what are the symptoms and treatment methods
10 hours ago 03.09.202003.09.2020ecoliv94
Ascariasis in children: symptoms, causes, drugs and treatment regimens for roundworms
1 day ago 02.09.202002.09.2020ecoliv94
What is helminthic infestation in children and adults, causes and symptoms
07/29/202007/29/2020ecoliv94
Wide tapeworm
In severe cases of tapeworm infection, high fever and nausea occur.
Another dangerous flat parasite for humans, the broad tapeworm, causes a rather specific type of helminthiasis. We are talking about a disease called diphyllobothriasis.
This helminthiasis is distinguished by the long incubation period of its pathogen (it takes, on average, about two months for the worm to “take root” in the body). How is diphyllobothriasis diagnosed?
As a rule, the general condition of the patient with helminthiasis of this type is only slightly impaired. In some cases, the infected person may complain of slight dizziness or malaise, which appears only occasionally.
With a more severe form of infection that occurs with complications, the symptoms of diphyllobothriasis become more pronounced. The patient experiences an increase in body temperature (usually up to 37.5 degrees), nausea and diarrhea. Unpleasant, crusty rashes appear on the skin.
Most patients also complain of pain in the upper abdomen.
The easiest way to diagnose diphyllobothriasis is by assessing the condition of the patient’s oral cavity. Thus, when infected with a wide tapeworm, the mucous membrane of the host’s mouth becomes covered with bright red painful spots. A similar picture is observed in the tongue, where, in addition, atrophy of the taste buds can be noticed.
Medicines for intestinal parasites

Properly selected medications play an important role in quickly removing worms from the body. Tablets against intestinal parasites, which cause severe complications and cause enormous harm to health, must be as effective as possible and have a wide spectrum of action.
"Vermakar". Used for pinworms, whipworms, roundworms. Inhibits the cellular structure of helminths. It is prescribed in a daily dosage of 100 mg once. Children under 10 years old - 50 mg.
"Biltricide." An effective anthelmintic agent for diseases: schistosomiasis, teniarinchiasis, taeniasis, diphyllobothriasis. It provokes the penetration of calcium into the structure of the parasite, which leads to its paralysis and death. For a single dose, the recommended dose of the drug is 40 mg per kilogram of body weight.
"Fenasal". Recommended for helminthic infestations caused by bovine and dwarf tapeworms and the tapeworm parasite. The norm per day should not exceed 8-12 tablets for adults, 4 tablets for children.
"Dekaris." Indications for use: ascariasis, trichocephalosis, enterobiasis. Stimulates the restoration of the immune system and the production of antibodies to helminth antigens, disrupts the course of important biological processes in parasites. Used once at 150 mg.
Trematodes
Trematodes are capable of moving throughout the host’s body.
Fluke worms, trematodes, are perhaps the largest group of flatworms that infect humans.
Representatives of this class are distinguished by a wide variety of forms and a wide habitat in the host’s body. Depending on the location of the parasite in the victim’s body, the symptoms of infection vary.
Where exactly can fluke worms live? There are reliably known cases where trematodes moved freely throughout the host’s body, “traveling” along with the bloodstream. However, most often, parasites of this group settle:
- in the pancreas;
- in the lungs;
- in the liver;
- in the intestines.
In any of the described cases, the first signs of trematode infection begin to appear only a week after the parasite, which has completely “taken residence” in the victim’s body, begins to multiply. As a rule, helminths of this group choose the venous system as a place for hatching their eggs. The fact that the process of reproduction of the parasite in the host’s body has already begun can be judged by the characteristic symptoms, which include:
- pronounced swelling;
- skin allergic reactions;
- muscle pain and joint aches;
- headache;
- fever accompanied by chills and excessive sweating;
- severe cough (often with the release of blood clots from the lungs along with sputum).
Read: How to get rid of pinworms at home. Is it worth risking your own health?
In the event that a trematode decides to settle directly in the bloodstream, any systems that support the life of the host are threatened. This helminth especially often affects the genitourinary system.
Exacerbation of chronic diseases, kidney and bladder stones, inflammation of the prostate in men and vaginal bleeding in women - this is not a complete list of what the carrier of the parasite will have to face in the described case.
If the parasite infects the liver and gallbladder, the consequences for the carrier are no less sad. For example, in patients with opisthorchiasis (a disease caused by one of the types of fluke worms - the liver fluke), in addition to the standard symptoms of helminth infection, there is an episodic lack of coordination of movements, the development of cysts on internal organs, and even a complete failure of some body systems important for life.
Specific signs
How do worms even get into the human body? Who carries parasites? With serious vitamin deficiency and lack of nutrients caused by the vital processes of pests, serious inflammatory processes often develop in the human body. They are usually localized in the nasopharynx. Such signs appear in the form of sinusitis and sinusitis, sometimes even stomatitis develops.
Young women and girls often encounter complications in the functioning of the reproductive system, which can also be caused by the activity of worms. The presence of pests often causes vaginal dysbiosis, vaginosis, and inflammation of the appendages. These problems are often observed against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Associated signs of the presence of helminths in the body are diarrhea and vomiting. Some experts also include teeth grinding and heavy snoring as possible symptoms. It is also worth thinking about if you have been trying unsuccessfully to cure a cold for a long time. Perhaps a runny nose and cough are caused by the activity of parasites.
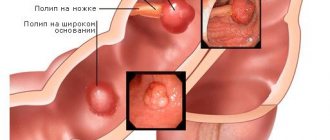
What else threatens tapeworm infestation?
Tapeworm infestation can cause intestinal blockage.
Adult tapeworms can reach enormous sizes, which, in some cases, can lead to a blockage in the host's intestines. The latter, in turn, threatens perforation with bleeding and the development of peritonitis in the abdominal cavity.
In addition, infestation by flat parasites has extremely negative consequences for the nervous system. In particular, the vast majority of patients infected with pork tapeworm reported a significant deterioration in their vision.
In severe cases of invasion, patients may experience epileptic seizures, as well as the development of dementia, meningitis and hydrocephalus. In each specific situation, the intensity of the progression of pathologies depends on which areas of the brain are already affected by flatworms.
Being in their larval stage, tape parasites, for the most part, are able to penetrate not only the intestines or brain, but also any other organs and systems of the body. In particular, cases of flatworms affecting the eyeballs are widely known. This kind of infection can be easily diagnosed by very specific symptoms:
- inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- uncontrolled lacrimation;
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity;
- the development of various inflammatory processes in the retina and both eyelids.
It should be understood that helminthic infestation of absolutely any type can lead to critical consequences for the patient’s health. Often, without proper medical intervention, cases of infection result in death for the parasite carrier. In order to prevent the irreparable, at the first signs of helminthic infestation, you should immediately visit an infectious disease specialist.
Read along with this article:
- Helminths in children - symptoms of helminthiasis and methods of combating...
- Signs of pneumonia in adults require special...
- Worms in infants: symptoms, information about pathology, methods...
- Life cycle of human roundworm, diagnosis, symptoms and…
- How to identify parasites in the human body, who they are...
- Analysis for enterobiasis and worm eggs, indications and preparation rules
- What do worm eggs look like: appearance, routes and symptoms of infection
- Tapeworm: why is this worm dangerous? Symptoms of infection
- Types of worms in children, main routes of infection
What types of worms are there?
There are more than 200 types of helminthic infestations. Some of them pose no threat, others are life-threatening. Conventionally, modern parasitology distinguishes 2 groups:
- Tissue worms - live in the human body, preferably in the tissues of internal organs.
- Cavity helminths live in the abdomen, their habitat is the small and large intestines.
Headache
The degree of infection and damage to the human body is determined by the number of helminths that have entered the body. Signs of the appearance of worms are expressed in complex symptoms, which are characteristic of the following types:
- Roundworms. The most common worms living in humans. They enter the body through water and food and are transmitted in various ways. Characteristic of roundworms is damage to the intestinal mucosa, bile ducts and lungs.
- Pinworms. This type of helminth affects the rectum. This is characterized by itching of the anus. When scratching, there is a risk of pinworms penetrating under the nails, which can lead to re-infection.
- Tapeworms. This is one of the largest representatives of helminths. They enter the body through the consumption of half-raw meat and parasitize the large intestine.
- Trichinella. They appear in the body from insufficient heat treatment of meat or after contact with pets. They penetrate the muscles through the circulatory system and affect all muscle tissue.
How dangerous are worms for a child?
Helminths pose a particular danger to children. They aggravate the course of already formed pathologies, worsen immune defense, weaken the nervous system, and negatively affect the overall development of the baby and his activity. Children's worms - this is how you can call roundworms and pinworms, which are most often found in children.
For children, helminthic infestation is much more dangerous than for adults, since it can lead to significant problems:
If you ignore suspicious signs, they not only persist, but also develop longer, leading to complications, one of which may be anaphylactic shock. The organs of vision, lungs, kidneys and heart muscle, and brain may be affected.
Another “children’s” pathology is toxocariasis, since I diagnose it mainly in representatives of the younger generation. Its development is manifested by pulmonary, abdominal syndrome, eye problems, and impaired functionality of the nervous system.
What is an eggworm
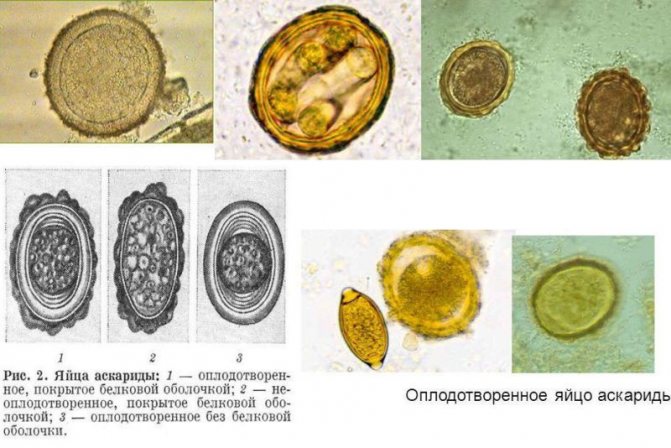
When diagnosing a pathology, the concept of “eggworm” appears - this medical jargon is used in the case of sending a patient’s biomaterial for laboratory testing in order to identify helminthic infestation. Helminth eggs are detected by examining stool or scrapings from the anal area. Carrying out such tests is one hundred percent confirmation of the presence of worms, and they are also designed to establish the type of parasites. Of these, the most common are pinworms, hookworms, and roundworms; they are especially often detected in children. Therefore, an eggworm test is mandatory when prescribing preventive medical examinations in children's institutions.
Worm eggs are small in size - less than one millimeter - so seeing them with the naked eye is problematic; this requires the use of a microscope. The parasites themselves look like small worms, their color and size depend on the type of helminth.
Most often, eggworm is found in the body of children, which is greatly facilitated by poor hygiene, close contact with animals, constant exposure to fresh air and playing on the ground and water. In addition, in young children the immune system is not as perfect as in an adult, and therefore it is more difficult for it to cope with the problem.