Bovine tapeworm is a tapeworm that causes the disease teniarinhoz. This worm enters the human body at the larval stage, and the previous stages of its life cycle take place in the skeletal muscles of cattle. However, the cow is only an intermediate host, and the parasite does not cause any particular harm to it, which cannot be said about humans.
Helminths are dangerous to humans not at all stages of their life cycle. There are only 3 forms that change inside the animal’s body:
- an egg that enters the cow’s gastrointestinal tract with herbal food;
- oncosphere or cyst - the first stage of the larva, which is freed from protective shells already in the food system;
- Finna is the second larval stage, the transition to which is possible only in the muscle tissue of cattle.
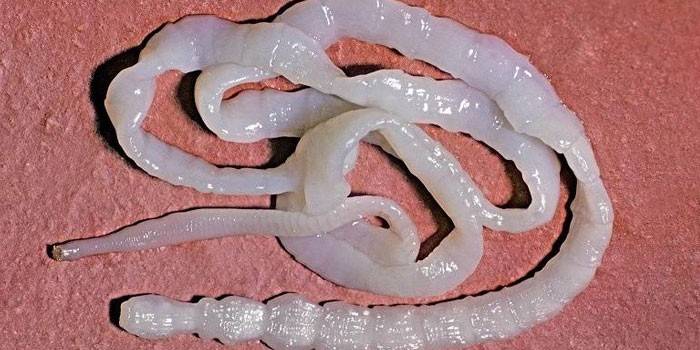
Bull tapeworm eggs
The first stage of the existence of a bovine tapeworm is the eggs, which are released outward in segments from the human body in which the worms live.
Tapeworms are hermaphrodites, so one adult is sufficient for reproduction, i.e. their life cycle does not depend on the simultaneous presence of a female and a male. Nature also took care of preserving the normal genotype. If there are two or more individuals in the human intestine, then cross-fertilization occurs: the testes of one worm fertilize the egg of another. If so far only one helminth parasitizes the esophageal mucosa, then fertilization of the eggs will occur in different segments of the same parasite.
Bovine tapeworm eggs, photographs of which can only be taken under an electron microscope, are very small in size. Considering that just one segment (which reaches only 6 mm in length) contains up to 180 million eggs, it is impossible to eliminate them from livestock pasture. Therefore, to prevent infection, it is necessary to follow the rules of individual prevention.
Helminth eggs are colorless and oval in shape. The shell is smooth, it contains two processes in the form of short threads, with which the future worm is attached to the plants. The egg consists of a bovine tapeworm cyst in the form of an oncosphere, and several transparent membranes.
The shell of the egg released from the body of the final host is quickly destroyed due to contact with oxygen. The oncosphere can exist independently in the open air for up to 5 days, and then it dies.
If you visually detect very small bead-like eggs in beef, eliminate them, however, remember that they cannot infect you with worms. They cannot skip 2 stages of transformation, so they will simply die. But for domestic animals, bovine tapeworm eggs can cause illness and a weakened immune response.
Bovine tapeworm larva
The oncosphere is called the first larval stage of helminth development. It is released from the protective membranes and enters the lymph or blood through the thin walls of the stomach. Next, the larva enters the skeletal muscles (the area of the back, sternum or neck), where it spends the next 2-3 months.
When wondering what bovine tapeworm larvae look like in meat, the answer will be ambiguous. This stage of the life cycle can indeed be found in beef, but it is difficult to see the structural features with the naked eye. The oncosphere of the bovine tapeworm, unlike the eggs, is not transparent, but yellowish-brown. On its surface there are 3 pairs of hook-shaped processes, which will then be located on the head of the helminth (as shown in the photo).
The first-order larva itself is not dangerous for humans, just like the eggs of the worm. However, if yellowish ovals up to 0.5 cm long are found, it is better to remove them from the meat.
Finn's bull tapeworm
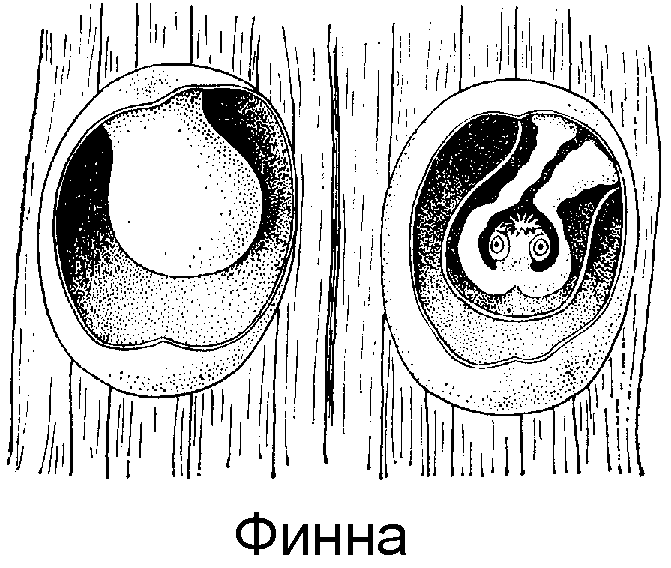
Finna is very similar to an everted larva, and it is this stage that poses the greatest danger to the human body. Finna looks like a smooth yellowish oval up to 1 cm long, filled with a cloudy liquid. At one end there is a cavity in the form of a bovine tapeworm's head turned inward.
Recognizing Finna in the skeletal areas of a beef carcass is quite simple. In addition, you should be careful not only with the muscles, but also with the cow’s tongue, as well as the heart - the Finn can be in any part of the body of cattle where there is good blood flow, with which it enters the organ.
It is not necessary that if you do not heat-treat the meat well, infection with bovine tapeworm will occur. Finna remains viable only for a year after transformation from the oncosphere. It is impossible to go to the helminth stage in the body of an intermediate host, so it will not be possible to detect worms in meat.
If you notice flat or annelid worms in the animal’s muscles, it is better to throw away the beef, as this indicates that it is no longer fresh. But the Finns are not an indicator of spoilage of the meat, and after removing them, the product can be used.
The second larval stage is always attached between muscle fibers, so the meat needs proper heat treatment. The life cycle of the bull tapeworm is depicted in detail in the photo.
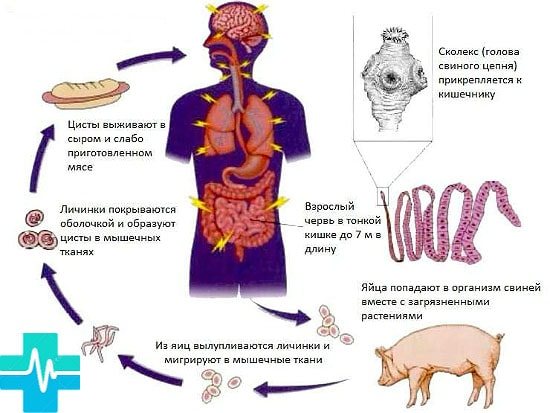
What is pork tapeworm? The pork tapeworm (Taenia solium), also known as the pork tapeworm, or the armed tapeworm, is a tapeworm that is a parasite of mammals.
Its final owner can only be a person, and dogs, hares, rabbits and camels also act as intermediate hosts, along with domestic and wild pigs.
What to do? To begin with, we recommend reading an article from the main institute of parasitology of the Russian Federation. This article reveals a method by which you can cleanse your body of parasites, without harm to the body. Read the article >>>
Depending on the stage of development of the pork tapeworm at which infection with this parasite occurred, a person may develop:
- taeniasis, if there is an adult parasite in his body;
- cysticercosis, if eggs or cysticerci (the so-called larvae of this worm) have entered the body.
Cysticercosis is considered a complication of taeniasis. This disease develops when pork tapeworm in the form of eggs enters the human gastrointestinal tract.
Gastric juice dissolves their dense shell, and with the bloodstream, the embryos of the worm enter various human organs.
The main distribution area of taeniasis is in regions and countries with developed pig production. Thus, in China, Taiwan, India and South Korea, African and Latin American countries, the number of pigs that have pork tapeworm is more than a third.
Knowing who the intermediate host is, it is not difficult to imagine the prevalence of taeniasis among the local population.

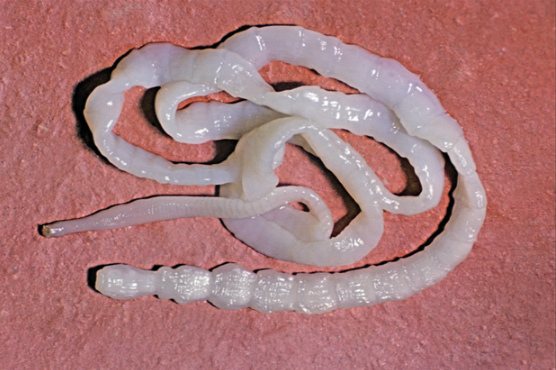
The structure of the bull tapeworm
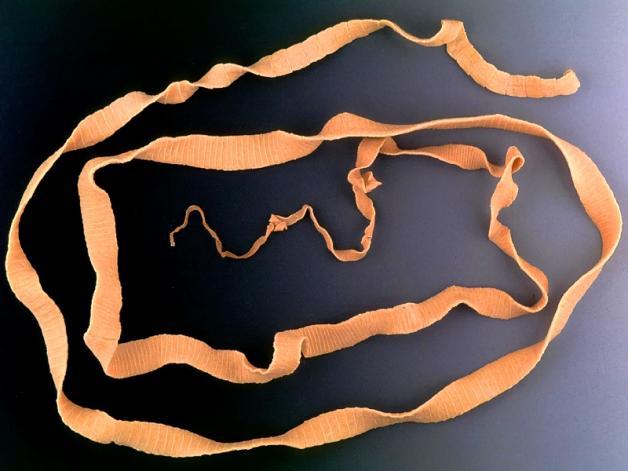
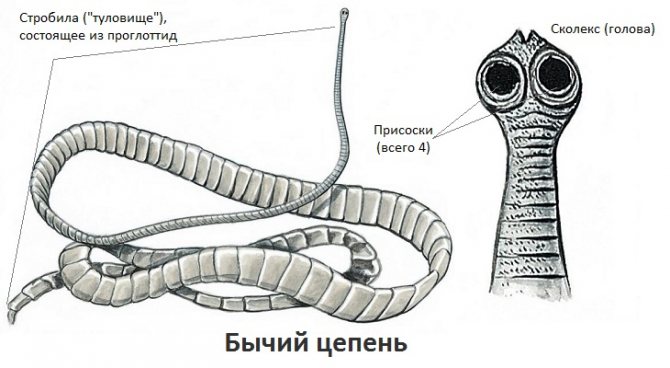
The bovine tapeworm belongs to the class Cestoidea, order Cyclophyllidea, family Taeniidae. The helminth has a ribbon-shaped flat body, consisting of huge (up to 2 thousand) segments (proglottids), reaching an average length of 7 - 10 meters. Cases have been described in the literature when the length of the parasite was 22 meters.
The body of the parasite (strobilus) is light gray in color. It is connected to the head by a small neck. The segments of the helminth are thicker, their shell is rougher and less transparent than that of the pork tapeworm. As a rule, one individual parasitizes the human body. The bovine tapeworm produces about 600 million eggs per year, or 11 billion over its entire life. Without treatment, the lifespan of the helminth is 18 - 20 years.

Rice. 8. Bovine tapeworm in humans. Its length reaches an average of 7 - 10 meters.
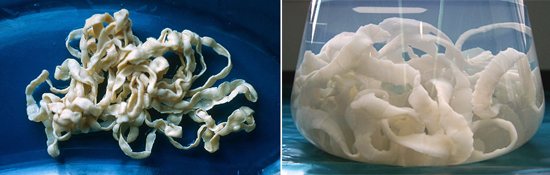
Rice. 9. Bovine tapeworms extracted from human intestines. The literature describes cases where the length of the parasite was 22 meters.
Rice. 10. The figure shows the body (strobilus), head (scolex) with suckers, and mature segments of a bovine tapeworm.
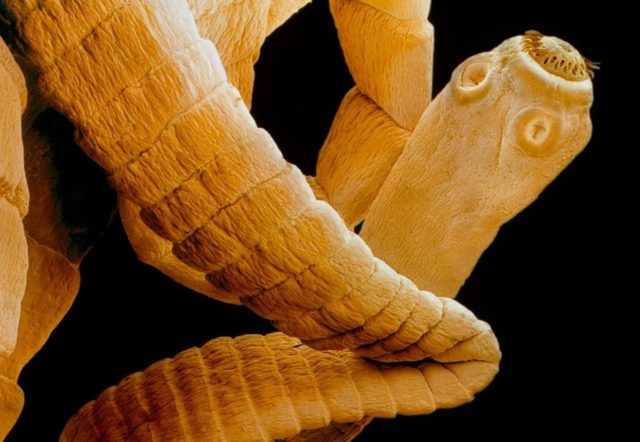
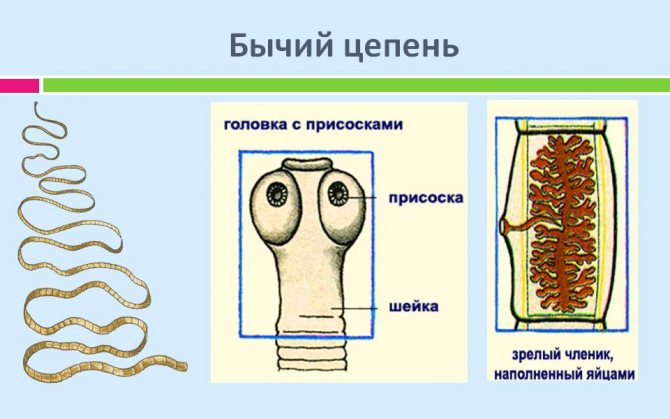
Head (scolex)
The head of the parasite is square-oval, 1.5 - 2.0 mm in diameter. It has 4 well-developed muscular suckers, with the help of which the parasite is fixed to the intestinal wall, and a pigmented rudimentary proboscis without hooks (hence the second name of the helminth - unarmed tapeworm). Pork tapeworm has hooks on its proboscis.
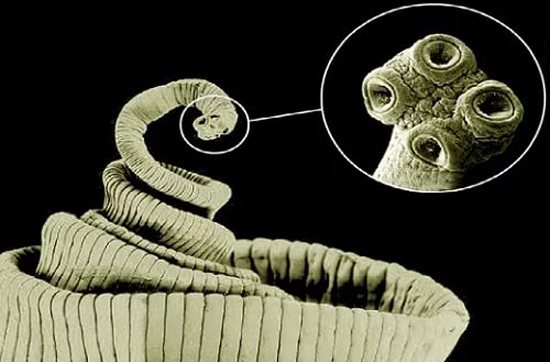
Rice. 11. Body and head of a bull tapeworm.
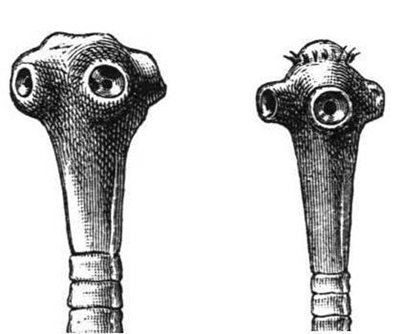
Rice. 12. Head of a bovine (left) and pork (right) tapeworm.
Digestive organs
The parasite has no digestive organs. It receives nutrients from the food consumed by the patient, absorbing them through the surface of the entire body.
Reproductive organs
The bovine tapeworm, like all tapeworms, is a hermaphrodite. Each segment has its own reproductive system. In the segments located next to the neck, the reproductive system is just emerging. In the middle of the worm's body, in the segments, the female and male reproductive systems are already developed and fertilization is intense. In the terminal segments the reproductive system is reduced. Only the uterus, filled with eggs, remains in them.
The ovary, located in the segment, is bilobed. It is located at the back of the proglottid. The lobe located under the vas deferens is smaller in volume than the second lobe. A tubular-shaped vitelline is located parallel to the posterior edge of the segment.
As the segment matures, the uterus forms in it. Initially, it is a stem formed from the fusion of the common duct of the vitelline duct and the oviduct. Next, lateral branches are formed on both sides, 17 - 35 on each side. At the end, the body of the parasite narrows and the segments lengthen. Their cavity is completely filled by the uterus with eggs. Every day, a sexually mature helminth individual secretes up to 10 proglottids filled with eggs, which are released spontaneously or with feces into the external environment. Each segment contains up to 175 thousand eggs, inside of which are located oncospheres (larvae).
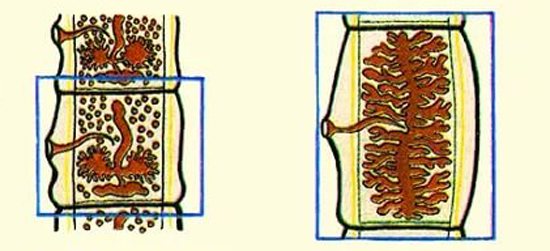
Rice. 13. The figure on the left shows the reproductive organs of the bovine tapeworm; the figure on the right shows a uterus filled with eggs.
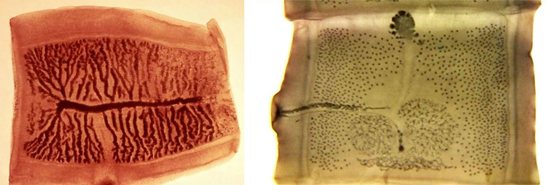
Rice. 14. In the photo on the left is a segment, the volume of which is completely filled by the uterus with eggs. In the photo on the right, the bilobed ovary, vas deferens and vitelline are clearly visible.
Segments (proglottids)
The segments of the bovine tapeworm grow from the side of the neck. Mature proglottids are 16–30 mm long and 8–10 mm wide. Each segment has its own reproductive system. Proglottids, located in the middle third of the parasite's body, have a hermaphroditic structure. The segments located in the distal part of the strobili have different sizes. Their length is greater than their width. The volume of the segments is filled by the uterus, inside which up to 175 thousand eggs with oncospheres accumulate inside.
Terminal proglottids in the amount of 7 - 10 per day are regularly separated one by one from the scolex and with feces or come out on their own. The segments of the bovine tapeworm are capable of independent movement. After exiting, they squeeze out eggs from the uterus, which are dispersed into the external environment. Producing and dispersing eggs is their sole purpose.

Rice. 15. The photo shows a segment of a bovine tapeworm in the distal part of the strobila with a well-developed uterus.
Bull tapeworm eggs
Bovine tapeworm eggs are produced and accumulate inside the distal segments. The uterus simultaneously contains up to 175 thousand eggs with oncospheres (larvae) inside. They have a spherical shape. The outside is covered with a thin shell that has a yellow-brown color. The size of the eggs is 28 - 44 x 28 x 38 microns.
Every day, 7 to 10 segments separate (one at a time) from the body of the parasite and come out. In one year, the helminth releases up to 600 million eggs. Over your entire life (18 - 20 years) - up to 11 billion.
Only cattle are infected with bovine tapeworm eggs. They are not dangerous for humans.
Eggs exhibit resistance in the external environment. In hay at temperatures from 10 to 300C they are stored for 21 days, in water - up to 33 days, in liquid manure - up to 70 days, in grass - more than 150 days, and can withstand wintering in manure. Eggs die at temperatures above 300C and from exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Oncospheres
Oncospheres are located inside the eggs. They have 6 hooks designed for attachment to the intestinal wall of the animal. The outside is covered with a thick, radially striated brown shell (embryophore). Their size is slightly smaller than an egg and is 30 - 40 x 30 - 30 microns.
Rice. 16. The photo shows the egg and oncosphere of a bovine tapeworm. The oncosphere is surrounded by a thick, radially striated brown shell (embryophore).
Finns (cysticerci)
The eggs of the bovine tapeworm, entering the intestines of the animal, lose their outer shell. Oncospheres are attached to the intestinal wall using hooks, then penetrate the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, settling in the intermuscular connective and muscle tissue of the tongue, heart, skeletal and masticatory muscles. Here the oncospheres transform into invasive larvae that form fins (cysticerci). Finns are covered with a thin membrane, through which the head (scolex) of the future tapeworm and the rudiment of the neck are visible. Cysticerci live 8 - 9 months and then die. There are different life expectancies for Finnfish in different regions: in Kenya, invasive larvae live for life, in Yakutia - up to 9 months, in Azerbaijan - 15 months.
If the infection is severe, the animal suffers: it refuses to eat, its body temperature rises, muscle soreness appears, and respiratory and cardiac function are impaired. Next comes an imaginary “recovery.” Some animals die.
Finns (cysticerci) or invasive larvae have the appearance of a bubble, the size of a pea or slightly larger (4 - 10 mm in diameter), with a head screwed inward.
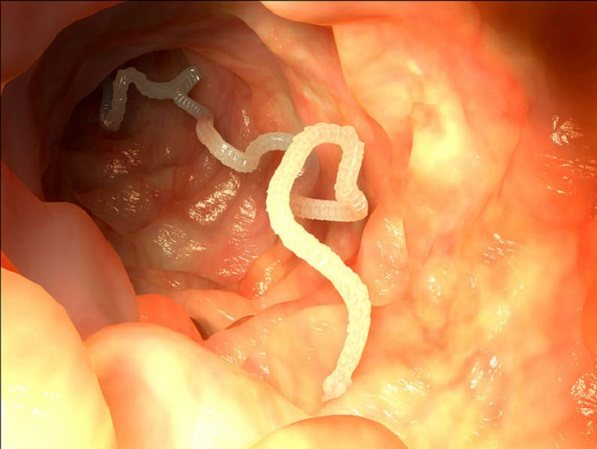
Finns that enter the human intestine turn their heads out, stick to the wall of the organ and begin to grow segments. They soon turn into adult worms.
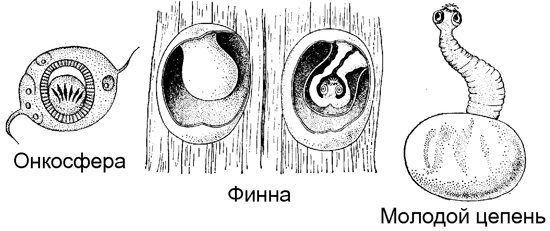
Rice. 17. Scheme of the transformation of an oncosphere into a young tapeworm.
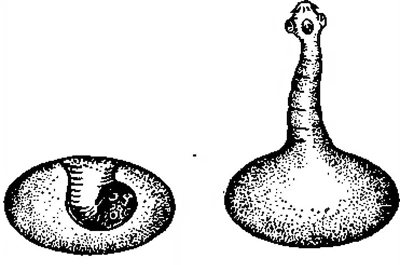
Rice. 18. The figure shows a Finn with a screwed-in (left) and turned-out (right) head.
How does a bull tapeworm come out of a person?
The release of segments into the external environment begins on the 80th day from the moment of invasion of the bovine tapeworm. The end segments (proglottids) in the amount of 7 - 10 per day are regularly separated from the scolex one by one and come out with feces or independently (in 98% of cases). When crawling out, the integrity of the outer cover of the segment is violated, the uterus ruptures and eggs are squeezed out of it. They remain on the linen and end up in the patient’s hands.
The crawling of proglottids from the anus and their movement along the surface of the body is accompanied by constant itching in the anus, which negatively affects the patient’s psyche.

Rice. 19. In the photo are segments of a bovine tapeworm that randomly came out of a person.
Rice. 20. Bovine tapeworm, accidentally removed by doctors through the nasal passage. The parasite got caught on the nasogastric tube during manipulation.
The structure and life cycle of pork tapeworm
The pork tapeworm can reach a length of up to 4 m. Its flat, “ribbon-like” white body consists of a scolex and many small segments - segments, the number of which can reach up to a thousand.
The scolex is the head part with fixation organs - four muscle suckers.
A special feature of the parasite is the presence of two rows of hooks on its body (there are more than 30 of them); Apparently, this is why it is called an “armed tapeworm.”
In a close-up photo, the pork tapeworm, at least its “head end” (scolex), looks like a cute soft children's toy, but the whole specimen is disgusting.
Pork tapeworm infection
Infection with pork tapeworm occurs through the alimentary, that is, fecal-oral route: parasite eggs are released from the body of a patient with taeniasis into the external environment and, through intermediate hosts (mainly through meat), enter the body of another person - this is how pork tapeworm is transmitted from person to person, not directly, but indirectly.
In this case, cysticercosis occurs because the pork tapeworm is in the larval stage. If personal hygiene rules are not followed, self-infection is possible.
Pork tapeworm in humans
The causative agent of the parasitic disease is a parasitic tapeworm from the Taenia solium family. Pork tapeworm causes digestive upset and neurological disorders. The disease is dangerous due to cysticercosis of the eyes, brain, skin, lungs, and heart muscle. The pork tapeworm is large in size, its length can reach 4 m. There are 4 suckers on the head of the parasitic worm.
The helminth is a hermaphrodite. Each fertilized segment of the worm can contain 50 thousand eggs with embryos, or oncospheres. Adults parasitize the human digestive tract, excreting segments of the worm's body along with feces. The role of the intermediate host of the worm is played by a pig or wild boar. The main place of residence for the parasitic worm is the human intestine.
Infestation of pigs by worm larvae occurs when animals eat contaminated waste or drink contaminated water. Having penetrated the stomach of the intermediate host, the pork tapeworm is freed from its protective shell and spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream. The larvae of the parasitic worm mainly settle in the muscles. After 2-3 months, the embryos of the worm turn into peculiar vesicles with eggs - cysticerci. The latter remain viable for 4-6 years, after which they calcify and die.
When invasive meat is consumed in the human small intestine, the head of the worm is released from the vesicles, which is attached to the wall with the help of hooks and suction cups and begins to release body segments with eggs into the external environment. During invasion, the oral-fecal mechanism of transmission of the pathogen is realized. The route of infection of a person by worm larvae is food or water (by drinking contaminated water). The disease is common in areas with unfavorable sanitary conditions. Employees of meat processing plants and pig farms are at risk.
- Solyanka with sausages: recipes with photos
- How to make honey cake for cough
- Psychotherapy for depression
Symptoms
Infection with pork tapeworm is accompanied by various clinical manifestations. The symptomatic picture can be both pronounced and hidden. Signs of invasion appear 1.5-2 months after ingestion of the larvae of the parasitic worm. The extraintestinal form of taeniasis (cysticercosis) can lead to damage to the eyes, heart, lungs and other organs. Depending on the location of the pork tapeworm in the human body, the disease manifests itself:
For intestinal form:
- nausea, vomiting;
- weakness;
- indigestion;
- increased appetite;
- abdominal pain of varying intensity;
- anal itching;
- iron deficiency anemia;
- decreased immunity.
For extraintestinal form:
- cerebral hypertension, hydrocephalus, severe headaches, epileptic seizures (damage to the larvae of a parasitic brain worm);
- chronic inflammation of the eyes, blurred vision (infection of the retina, conjunctiva);
- heart rhythm disturbances (penetration of parasitic worm larvae into the myocardium);
- tumors on the surface of the skin (damage to epidermal structures by parasitic worm larvae).
If taeniasis is suspected, the patient is prescribed a stool test and perianal scraping. If segments of a parasitic worm are detected, the patient is advised to undergo a comprehensive examination. For this purpose, he is sent for ophthalmoscopy, lung X-ray, CT scan of the brain and other diagnostic procedures to identify damage to other organs. Antibodies to pork tapeworm are detected using serological methods:
- RNGA;
- ELISA;
- RSK;
- NRIF.
Treatment
Therapy for taeniasis is carried out in a hospital in compliance with specific conditions for preventing self-infection of the patient. Treatment of parasitic infestation involves the use of anthelmintic drugs (Praziquantel, Niclosamide), and a saline laxative. The patient is recommended to eat a diet. Upon completion of anthelmintic therapy, at least 4 control stool tests are performed with an interval of 30 days. In parallel with drug therapy, it is allowed to treat taeniosis using traditional methods:
- Pumpkin seeds. The product (300 g) is peeled from the white peel, leaving a green inner shell. Then the seeds are crushed and diluted with a small amount of honey and water until a creamy mass is formed. The mixture is consumed on an empty stomach in one dose. After half an hour they drink a laxative, and after 3 hours they do an enema.
- Troychatka Ivanchenko. The prepared mixture of wormwood, tansy flowers and cloves is ground in a coffee grinder. Take 1.75 g of the composition on an empty stomach with water. On the first day, the drug is taken only in the morning, on the second - in the morning and at lunch. A full course of treatment for pork tapeworm can begin no earlier than the third day.
In a situation where single segments of a parasitic worm are found in the brain and eyes of an infected person, surgical intervention is performed followed by etiotropic treatment. The intestinal form of taeniasis usually has a favorable prognosis. The outcome of the disease in relation to the life and health of the patient in case of damage to the brain and other vital organs depends on the massiveness of the invasion and the location of the pork tapeworm larvae.
| Drug treatment | ||||||
| A drug | Active substance | Dosage | pharmachologic effect | Indications | Contraindications | Side effects |
| Praziquantel | Praziquantel | Therapy for cestodoses – 10-25 mg/kg once. Dosage for cysticercosis – 50 mg/kg in three doses. The course lasts 1-4 days. | The drug causes paralysis of the muscle structures of the parasitic worm, which leads to the destruction of the tapeworm's protective shell. | Schistosomiasis, trematodiasis, cestodiasis, neurocysticercosis and cysticercosis. | Pregnancy, lactation, children under 4 years of age, ocular cysticercosis, liver pathologies, individual intolerance | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, sweating, headache, vomiting. |
| Niclosamide | Niclosamide | The daily dose for adults and children over 12 years of age is 2-3 g. For children 5-12 years of age – 1.5 g. Young patients under 5 years of age are prescribed 0.5-0.7 g of Niclosamide per day. The daily dose is taken in one dose. The average duration of treatment is 4 days. | The drug slows down the life processes of the pork tapeworm, causing the death of the parasitic worm. | Hymenolepiasis, teniarhynchosis, taeniasis, diphyllobothriasis. | Pathologies of the liver, kidneys, lactation, pregnancy, stomach ulcers, individual intolerance. | Stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, dizziness, drowsiness. |
| Fenasal | Niclosamide | Treatment of taeniasis in adults is carried out by a single dose of 8-12 tablets (2-3 g each) of Fenasal. Dose for children 5-12 years old – 4-6 tablets of 1-1.5 g each. | The drug has a paralytic effect on the parasitic worm, as a result of which it completely loses the ability to attach to the intestinal wall. | Taeniarinhoz, hymenolepiasis, dwarf tapeworm, diphyllobothriasis. | Pregnancy, lactation, individual intolerance. | Nausea, abdominal pain, itching, urticaria. |
| Male Fern Extract | Phylixic acid, filmaron. | Orally on an empty stomach, 4-7 g per dose. The daily dose should be taken within 20-30 minutes. | The drug paralyzes the muscles of the pork tapeworm and promotes the exit of the worm from the body along with feces. | Tenidosis, hymenolepiasis, diphyllobothriasis, enterobiasis. | Circulatory failure, pathologies of the liver, kidneys, stomach ulcers, duodenal ulcers, acute gastrointestinal diseases, fever, anemia, exhaustion, pregnancy, children under 2 years of age. | Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, diarrhea, headache, convulsions, respiratory depression, optic atrophy, collapse, hepatitis. |
- The highest paid professions in the world and Russia
- Homemade anti-aging hand mask
- Pepper patch: instructions for use
What is the difference between bovine tapeworm and pork tapeworm?
What doctors say about treating parasites
Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor German Shaevich Gandelman
Work experience: more than 30 years.
I have been detecting and treating parasites for many years. I can say with confidence that almost everyone is infected with parasites. It's just that most of them are extremely difficult to detect. They can be anywhere - in the blood, intestines, lungs, heart, brain.
Parasites literally devour you from the inside, at the same time poisoning your body. As a result, numerous health problems appear, shortening life by 15-25 years.
The main mistake is delaying! The sooner you start removing parasites, the better. If we talk about medications, then everything is problematic. Today there is only one truly effective anti-parasitic complex, this is TOXIMIN. It destroys and sweeps out all known parasites from the body - from the brain and heart to the liver and intestines. None of the drugs existing today is capable of this.
Within the framework of the Federal program, when submitting an application before June 10. (inclusive) every resident of the Russian Federation and the CIS can receive one package of TOXIMIN FOR FREE!
Although the size of the pork tapeworm is smaller than that of the bovine tapeworm (it reaches up to 10 m), the pork tapeworm is more dangerous due to its hooks - the bovine tapeworm does not have them.
Although the eggs of both parasites are similar in appearance, in the pork tapeworm they are infectious to humans, but in the bovine tapeworm they are not.
The main way to distinguish these parasites in the laboratory is by the end segments, which are elongated in the pork tapeworm; in addition, they have an ovary with a third (accessory) lobule.
Laboratory analysis is necessary to select treatment tactics, since there are differences depending on the type of parasite.
How does teniarhynchosis affect health?
The presence of bovine tapeworm leads to the following health problems:
- The parasite attaches to the intestinal mucosa with the help of segments and special suction cups, as a result of which the integrity of the tissue is disrupted, and infection can penetrate through tiny wounds. Mechanical injury leads to disruption of motor and secretory functions and the development of the inflammatory process.
- With multiple infections, intestinal obstruction may develop.
- Living in the human body, the parasite feeds on substances entering the intestines. As a result, the host body experiences a significant nutritional deficiency.
- Bovine tapeworm waste products often cause an allergic reaction.
The characteristic symptoms of bovine tapeworm in humans will help to identify the pathology and carry out appropriate treatment.
Taeniasis
Taeniasis is a disease caused by mature pork tapeworm, which parasitizes the patient’s intestines. Symptoms in humans are as follows:
- the appearance of allergic reactions due to the toxic-allergic effects of the parasite on the body;
- inflammation of the intestinal mucosa due to mechanical irritation caused by hooks attached to it;
- astheno-neurotic syndrome with headaches, dizziness, fainting, increased nervousness) due to a deficiency of nutrients that the pork tapeworm absorbs;
- dyspepsia, loss of appetite, discomfort in the intestines after eating, belching;
- abdominal pain of varying intensity.
The organs affected by taeniasis are mainly the digestive system.
To identify signs of the parasite, laboratory diagnostics are performed after an epidemiological history:
- fecal analysis for the presence of end segments (strobilae) of the pork tapeworm, which are not able to crawl out of the host’s body on their own;
- ovoscopy of perianal scraping - for the same purpose;
- blood test: general and for specific antibodies of pork tapeworm;
- coprogram;
- radiography and fluoroscopy.
Diagnosis of bovine tapeworm
If teniarhynchosis is suspected and there are obvious presence or absence of tapeworm symptoms, the diagnosis of a parasitic infection is carried out using the following methods:
- Patient's blood test. If there is a parasitic infection, the patient will have anemia and eosinophilic leukopenia;
- Stool analysis. Here, tapeworm eggs are detected in feces;
- Radiography. Allows you to see an individual tapeworm in the patient’s small intestine;
- Scraping or rinsing the patient's perianal folds. It also makes it possible to identify parasite eggs.
Treatment of taeniasis
Tips from our readers
I got rid of parasites in just a week! I was helped by a remedy that I learned about from an interview with a parasitologist.
Treatment of taeniosis is carried out only in a hospital in order to exclude the occurrence of cysticercosis due to the destruction of the egg shell and the entry of oncospheres into the circulatory system.
Treatment includes:
- strict adherence to a diet with reduced energy value (table No. 13) and 4-5 meals a day;
- the use of medications to expel the parasite: biltricide - a one-time dose to paralyze the parasite, which will not be able to cling to the intestinal walls and will be released during defecation;
- treatment with folk remedies: male fern extract and pumpkin seeds (have a similar effect).
Self-medication can cause cysticercosis, so you must strictly follow your doctor's instructions. Drugs that cause the collapse of strobili are contraindicated.
The diet is quite strict and includes the exclusion of fatty, smoked, canned foods, sour cream, cheeses, pasta, fiber-rich fruits, a number of vegetables (onions, garlic, white cabbage, etc.), fresh bread and baked goods, some cereals, chocolate, etc.
It is recommended to include low-fat and low-fat foods in the diet, pureed porridge (rice, buckwheat, semolina), cottage cheese and lactic acid drinks, some vegetables (carrots, beets, potatoes, ripe tomatoes, cauliflower), ripe fruits, etc.
Medications and folk remedies are combined with laxatives and cleansing enemas, which are carried out according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor.
How a worm emerges from a person is not a pleasant sight, but after this it must be examined for integrity so that there are no end segments left in the intestine. That is why treatment of diseases caused by pork tapeworm is carried out in a hospital.
After expulsion of the parasite, the patient is under clinical observation and undergoes a stool test every month for 4 months.

Cysticercosis
Unlike tyneosis, which occurs due to a sexually mature parasite, cysticercosis is caused by larvae of the pork tapeworm.
When they enter the gastrointestinal tract, their shell dissolves, with the help of hooks they are attached to the intestinal mucosa, and then seep into the bloodstream and spread throughout the body.
Their location can be the eyes, lungs, heart, skin, brain and spinal cord; The symptoms and treatment of the disease also depend on this.
The development of larvae causes an increase in their size, and pressure on neighboring cells may cause pain in the host, and their waste products have a toxic effect.
But even if the pork tapeworm dies at this stage, the dissolution (leasing) of its body causes the release of particularly dangerous substances, often causing allergic shock, which is fatal in 20% of cases.
Symptoms and diagnosis of cysticercosis
The viability of cysticerci (Finns) persists for 5 years. Around these bubble-shaped larvae with a diameter of 5 to 8 mm, an inflammatory process occurs, causing degenerative changes in tissue.
As already mentioned, pork tapeworm larvae can be located in many organs.
Brain. This is the most dangerous type of cysticercosis, which occurs in 60% of cases; larvae can live in the brain (its cortex and meninges) for up to 18 years!
Symptoms:
- weakening of muscles, sluggish movements;
- depression,
- the appearance of hallucinations;
- alternation of mental attacks and enlightenment;
- delirium, memory gaps;
at a later stage:
- cerebral edema;
- headaches up to vomiting;
- epileptic seizures;
- sometimes breathing problems and heart failure.
To differentiate cysticercosis from brain tumors, meningitis, epilepsy, it is necessary to examine the cerebrospinal fluid and blood (for eosinophils), as well as perform X-rays, MRI and RCT.
Treatment is surgical if few larvae are found in the brain. If there is a large amount of them, take Praziquantel tablets.
In some cases, nemozol is prescribed to treat neurocysticercosis caused by pork tapeworm larvae. However, if pork tapeworm larvae have infected the ventricles of the brain in large numbers, the prognosis will be extremely unfavorable.
Spinal cord . Because of the larvae, adhesions and cysts appear on the roots and membranes of the spinal cord, which can compress it. MRI, serological reaction and myelography are used for diagnosis.
Symptoms:
- pain in the legs, arms and back;
- girdle pain in the abdomen and chest;
- possible impairment of motor functions;
- in especially severe cases, paralysis occurs.
There is no specific treatment.
Eyes . The locations of larvae in the eyes are the eyeball, retina and vitreous body. Vision gradually deteriorates with short periods of remission until complete blindness.
Symptoms:
- retinitis, uveitis (inflammation of eye tissue);
- degenerative changes in eye tissue;
- conjunctivitis.
Diagnostics : ophthalmoscopy and biopsy; RSC of blood and cerebrospinal fluid; specific blood test.
Treatment is surgical; if this is not possible, Praziquantel is prescribed.
Leather _ Cysticercosis of the skin is a fairly rare disease, only 6% of the total
Pork tapeworm infections. Its larvae are localized in the fatty layer under the skin (most often in the muscles, chest, palms, etc.), as a result of which small tubercles appear in this place.
Although they feel hollow to the touch, there is liquid inside them in which the larva floats. In such conditions it can grow up to 2-10 cm in length. Sometimes urticaria occurs, but in general the disease is asymptomatic.
Treatment is surgical.
Lungs . Localized in the interstitial, less often in the peribronchial tissue, the larvae encapsulate and, as they grow (up to 2 cm), compress the lumen, which leads to inflammation with symptoms characteristic of pneumonia.
When the parasite dies, either it dissolves or becomes calcified, which again causes deformation of the lungs.
For diagnosis, an x-ray, a blood test for eosinophils, and a stool test for helminths are performed.
Treatment is medicinal.
Cysticercosis during pregnancy is extremely dangerous, since it can penetrate the placenta and damage the fetus, which leads to stillbirth or significant developmental abnormalities.
Spontaneous termination of pregnancy is also possible. If infestation with pork tapeworm larvae is detected in the early stages of pregnancy, abortion is often recommended for medical reasons.
How to diagnose bovine tapeworm?
At the initial stage of teniarynchosis, erased symptoms are observed, since the larvae do not yet reproduce. Symptoms begin to appear starting from 3-4 months of infection, when the worm has turned into an adult. There are several ways to diagnose bovine tapeworm:
- analysis of epidemiological history;
- stool analysis for the presence of adult tapeworm worms or larvae;
- ovoscopy and perianal scraping;
- blood test for the presence of specific antibodies;
- X-ray examination of the intestines.
Sometimes the diagnosis gives a negative result, but for a reliable result it is necessary to undergo the examination again after 3-4 weeks. Also, to obtain an accurate result, several diagnostic options are used, which makes it possible to identify not only adult individuals, but also their eggs.
Prevention of pork tapeworm infection
Now you have an idea how to get rid of pork tapeworm.
But it is much better to prevent infection with it and do everything to prevent this disease:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene, be sure to wash your hands after using the toilet;
- purchase meat only in large or specialized stores and carefully inspect it for the presence of suspicious inclusions (which may include pork tapeworm);
- store meat in proper conditions, for long-term storage - in the freezer;
- When preparing meat dishes, carry out thorough heat treatment;
- do not taste raw minced meat when cooking;
- If suspicious symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately.
Bovine tapeworm infection
After being released into the environment with feces, the tapeworm proglottids, tapeworm segments, do not lose their motor function. They can move around for some time, spreading eggs around. The larvae, fincas, are already inside and are ready for the onset of infection.
They can survive sharp temperature fluctuations of up to 30°C, cold and heat, and do not die under snow. Animals become the first victim, a temporary host into which the parasite penetrates. They can become carriers for up to 2-3 months.
How does tapeworm enter the human body:
- raw, poorly processed, low-quality cattle meat;
- female horsefly. Feeds on the blood of mammals and infects humans;
- vegetables, greens from the garden;
- contaminated sand, grass, soil.
Most often, the parasite is observed in women, since they spend most of the time in the kitchen and prepare food. Even dirty hands and clothes can carry tapeworm eggs.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Toximin® - a remedy for parasites for children and adults!
- Dispensed without a doctor's prescription;
- Can be used at home;
- Clears parasites in 1 course;
- Thanks to tannins, it heals and protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, and skin from parasites;
- Eliminates rotting in the intestines, neutralizes parasite eggs thanks to the F molecule.
A certified remedy recommended by helminthologists for getting rid of parasites at home. It has a pleasant taste that children will like. Consists exclusively of medicinal plants collected in environmentally friendly places.
There is a discount now. The drug can be obtained free of charge.
Hello, readers of the site about parasites Noparasites.ru. My name is Alexander Lignum. I am the author of this site. I am 23 years old, I am a 5th year student at the Kemerovo State Medical Institute. Specialization "Parasitologist". Consultation by phone: +7. More about the author>>

The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
I have felt very bad for the past few years. Constant fatigue, insomnia, some kind of apathy, laziness, frequent headaches. I also had problems with digestion, and in the morning I had bad breath.
And here is my story
All this began to accumulate and I realized that I was moving in some wrong direction. I began to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right, but this did not affect my well-being. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
Then I went to an expensive clinic and had all the tests done, and in one of the tests I was found to have parasites. These were not ordinary worms, but a specific type, with which, according to doctors, almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent. It is almost impossible to remove them from the body. I took a course of antiparasitic medications that were prescribed to me at that clinic, but there was almost no result.
A couple of weeks later I came across an article on the Internet. This article literally changed my life. I did everything as it was written there and within a few days I felt significant improvements in my body. I began to get enough sleep much faster, and the energy that I had in my youth appeared. My head no longer hurts, my mind became clearer, my brain began to work much better. My digestion has improved, despite the fact that I now eat haphazardly. I took tests and made sure that no one else lives in me!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
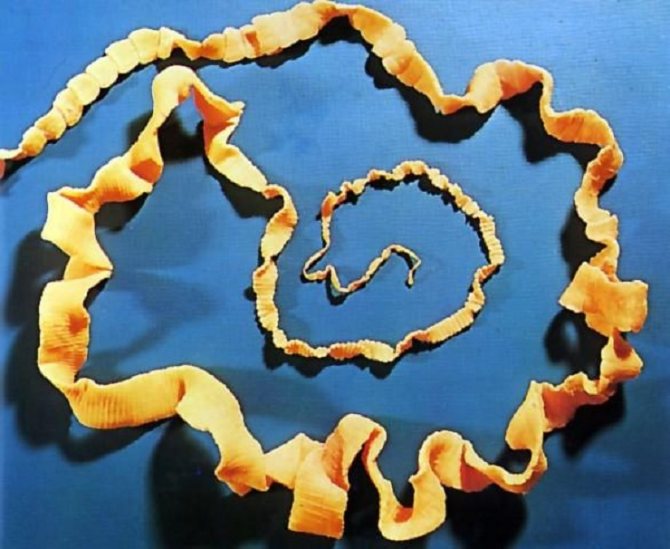
Each segment (proglottid) of the bovine tapeworm includes male and female genital organs. The head (scolex) is located in the center in the photo
The bovine tapeworm (Latin: Taeniarhynchus saginatus) is a helminth representing tapeworms of the family Taenia, which, together with other worms of this family, causes parasitic infections called taeniasis. In case of infection with this particular type of tapeworm, the disease is called teniarinchiasis.
Morphology
The bull tapeworm has a very distinctive morphology. This representative of flatworms can grow from 4 to 12 meters in length, 5-7 mm in width and 2 mm in thickness. But individual specimens more than 22 m long have been reported. Its body consists of a scolex, neck and strobila. Adults have a flat, ribbon-like shape, which is important for absorbing nutrients from the intestines of their hosts. Bovine tapeworm worms do not have a digestive system: no mouth, no anus, or gastrointestinal tract. They receive nutrition by absorbing carbohydrates from the host’s body through the flat membrane of the body (primarily this concerns polysaccharides, in particular glucose, which are the most important for the life of parasites). Tapeworms also do not have a body cavity.
Proglottids . The strobila consists of a chain of proglottids (segments), which are mainly filled with eggs. New proglottids are produced at the neck and this growth pushes the more mature segments towards the posterior end, where they break off and thus release thousands of eggs. This process is very important in the complex life cycle of this tapeworm. The bovine tapeworm is the largest human helminth of its kind, consisting of 1,000 to 2,000 segments, which can remain viable in the human intestine for up to 25 years.
Scolex . The scolex of the bovine tapeworm has a diameter of 1.5 - 2 mm and consists of four suckers at the anterior end of the flatworm, which are used as a means of attachment to the intestinal wall of the host. The bovine tapeworm lacks hooks on the scolex, unlike its close relative the pork tapeworm, which infects domestic pigs and then humans. The eggs of both types of tapeworms are indistinguishable. They have a round or oval shape, covered on top with a thin (approximately 31-43 microns), colorless shell.
The egg contains the larval form (oncosphere) of T. saginata, surrounded by a double-edged yellowish-brown shell, which is destroyed after the eggs are released. The oncosphere has 6 hooks.
Bull tapeworm - symptoms in humans when infected with teniarinhoz
Nausea persists, you suffer from abdominal pain and have no appetite? Perhaps you drew an unlucky ticket in the lucky lottery, and a bull tapeworm has taken up residence in your body. The symptoms of a person who has “caught” this helminth may “dormant” for a long time, but their manifestation is extremely uncomfortable.
What is bovine tapeworm
Bull tapeworm is a white tapeworm. And this is not some tiny pinworm; its average size ranges from 4 to 10 meters. Cases have been recorded when particularly voracious parasites reached 22 meters. The width of the bull tapeworm is 5-7 millimeters.
On the round head of the parasite, about three millimeters in diameter, there are suction cups - four “fixtures” that help it attach to the donor’s intestinal wall and crawl. The smallest “detail” of a bovine tapeworm’s body is the neck. It consists of underdeveloped segments and serves as a “growth zone” for the helminth.
The neck passes into the body, which consists of individual segments - proglottids. The division of the body into separate parts ranging from 16 to 30 millimeters in length is a feature of the bovine tapeworm. Proglottids form in the neck area. Having reached their maximum size, they become part of the main body (strobili).
And the segments that are at the end of the strobile are separated.
Once separated, the segments are able to move independently of each other for some time. Young proglottids, located near the neck, have their own digestive system. The segments that “advance” closer to the end of the “tail” of the body become “containers” for eggs. Oval or round eggs covered with a thin shell contain embryos (oncospheres) equipped with three pairs of hooks.
Bovine tapeworm causes a disease called teniarinchiasis. The total number of helminth segments reaches two thousand. The segments detached from the strobila crawl out of the intestine, but due to the action of the “growth zone,” the “extent” of the bovine tapeworm does not decrease.
On the contrary, over two decades of life it grows to a huge size, filling the donor’s intestines. At the same time, two and a half thousand segments are separated from the body per year, carrying millions of eggs. “Autonomous” segments can move throughout the human body and crawl out of the anus.
Some of the proglottids are excreted in the feces. Sometimes “travelers” are found:
- in the ear;
- in the respiratory tract
- in the gallbladder;
- in vessels.
Important! Once outside the “host,” the eggs are viable for a month, infecting the ground and water bodies.
Ways of infection with bovine tapeworm
The helminth is unique in that it lives in the body of two hosts:
- intermediate;
- final.
Having left the human body, the segments of the bovine tapeworm crawl on the ground until they die, “float” in the water, scattering eggs with oncospheres - infectious larvae.
Sooner or later, one or more oncospheres along with the grass will be swallowed by a cow. The larva, with the help of its hooks, will drill through its intestines and move along the circulatory and lymphatic systems.
The bovine helminth received its name precisely because it uses bulls and cows as intermediate hosts.
The oncosphere can spread throughout the body of the intermediate host. At a certain moment, the larva enters the next phase: finna - a bubble with a head twisted inward.
In order to live and develop, contaminated meat must reach the final owner, a human. Already in his intestines, the finna turns its head outward and attaches to the wall.
She already looks very much like a real tapeworm.
As soon as the vesicle falls off, the process of producing proglottids will begin - the helminth will “grow up.” This takes about three weeks. And then the “evacuation” of sexually mature worm segments filled with eggs begins. A new round of the life cycle of the bull tapeworm begins. But you can only “catch” the parasite by eating undercooked or undercooked beef.
For humans, bovine tapeworm is dangerous because it causes:
- discomfort (movement of joints);
- lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (inflammation of the mucous membrane);
- pain (penetration of proglottids through the ileocecal valve);
- intestinal obstruction (excessively long tapeworm);
- lack of nutrients;
- allergic reactions.
Important! Finns live in the body of an intermediate host for no more than two years. Having not found a final host during this period, the larvae die.
Symptoms of teniarinhoz
The discharge of proglottids from the anus sometimes becomes the only sign that bovine tapeworm is “registered” in the body. Symptoms in humans , however , are very diverse:
- itching and discomfort in the anus;
- colic in the abdomen, reminiscent of an attack of pain due to appendicitis;
- nausea and vomiting;
- salivation;
- weakness;
- high or low appetite;
- stool disorders (diarrhea and constipation);
- dizziness;
- seizures;
- rash surrounded by crusts;
- anemia;
- inexplicable thinness;
- decreased immunity;
- manifestation of atypical pathologies (in cases of helminth larvae entering “inappropriate” organs).
Teniarinhoz develops in two stages. In the early stages, the disease is asymptomatic. As it becomes chronic, the number of symptoms increases and they become more pronounced.
Important! The head and proglottids of the helminth should not be thrown away or buried. Under certain conditions, they are able to enter the body of a new “host”. The “remains” of the tapeworm must be burned.
Diagnosis of infection
It is not easy to determine infestation with bovine tapeworm because of the mild symptoms at the initial stage of the disease. To make a diagnosis, use:
➡ interviewing the patient (it is found out whether the patient has consumed raw, dried or undercooked meat);
➡ feces analysis, scraping (allows you to detect helminth segments);
➡ blood test (will indicate a decrease in the number of red blood cells, leukocytes, sometimes hemoglobin and an increase in the number of eosinophils);
➡ radiography (the image shows the presence of a helminth in the form of a light stripe about a centimeter wide);
➡ analysis of gastric juice (after infection, its acidity decreases).
Treatment of teniarynchosis
Therapy for the disease is designed to remove the parasite from the patient’s body. The results of treatment depend on the length of time the bovine tapeworm remains in the host’s body and on the number of helminths. The treatment regimen consists of three stages:
- preparation (cleansing the body of toxins released by parasites during life) - involves the use of sorbents;
- antiparasitic therapy - dewormers (anthelmintics) are used, which promote the detachment of the worm from the wall of the small intestine and provoke its “evacuation”. The drugs have side effects similar to the symptoms of the disease itself. During endoscopic treatment, the drug is injected directly into the small intestine;
- recovery (diet, immunization).
Treatment is carried out in a hospital or on an outpatient basis - after consultation with a doctor. Drug treatment is supplemented with enemas, the use of laxatives and herbal medicines. The results of therapy are assessed after three months - by the presence or absence of bovine tapeworm proglottids in the feces. Surgical intervention is extremely rarely used.
Folk remedies
The toxicity of antiparasitic drugs is sometimes a reason to refuse to take them. The secrets of traditional medicine are adopted:
- Infuse two tablespoons of immortelle in a thermos and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. After 12 hours, strain. Take 100 ml before meals 3-4 times a day;
- Eat a clove of garlic and drink a glass of carrot juice every day for a week;
- Pour two tablespoons of tansy with a glass of boiling water, leave for two hours, strain. Add milk and do an enema. Two days before it, do not eat meat;
- Chop four tablespoons of unripe walnuts and pour a glass of boiling water. Add a pinch of salt. After half an hour, strain. Drink during the day with a saline laxative;
- Peel the pumpkin seeds without touching the grayish skin. Eat in unlimited quantities until you feel disgusted. Do not eat or drink anything other than them. Two hours after the last use of the seeds, take a laxative;
- Pour a tablespoon of dried elecampane roots into 200 ml of boiling water. Let it brew. Every three hours, drink two tablespoons. Course – 4-5 days.
Important! When using tansy to make decoctions and infusions, strict adherence to dosages is necessary.
Life cycle
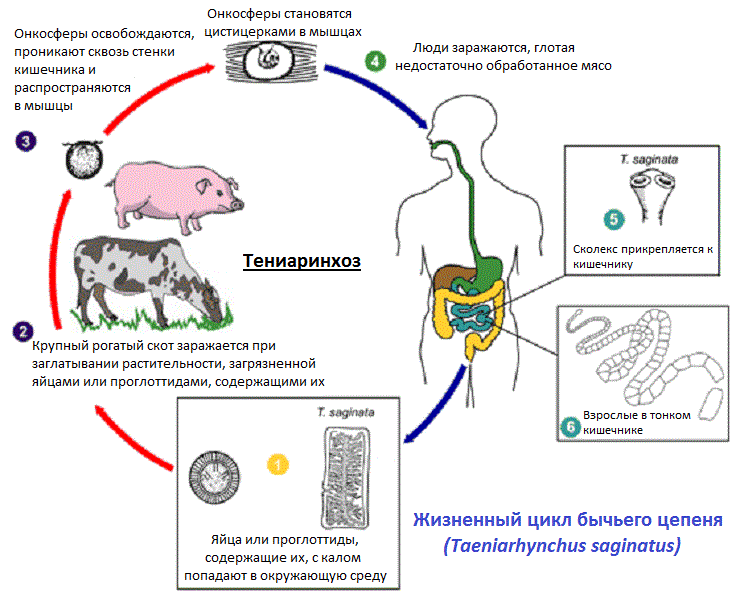
- Mature, egg-filled segments (proglottids), located in the intestines of the final host (human), are excreted into the environment along with feces. Each such segment contains up to 100 thousand eggs, which already contain infective larvae.
- These proglottids are able to move through the grass and soil for some time, spreading eggs, which are then absorbed by large horned cattle (cattle) along with contaminated vegetation and enter the gastrointestinal tract of their intermediate host.
- Enzymes and intestinal acids destroy the egg shell and release oncospheres (larvae), which, damaging the intestinal epithelium, can be transported through the bloodstream throughout the body of the cattle. After this, the larvae penetrate the muscle tissue, the oncosphere fills with liquid and turns into a fin (cysticercus).
- To complete the complex developmental cycle, raw or poorly cooked beef must be eaten by a person (the definitive host) and then enter the human digestive system. Digestive enzymes destroy the cysticerci, the larval cysts are released, and their inverted scolex is able to come out and attach to the walls of the host’s intestine.
- Next, the maturation of adult individuals occurs, during which the head and neck begin to grow rapidly, producing more and more new proglottids. The bull tapeworm increases in size, and within three months it can reach a length of up to 5 meters. After maturation, mature egg-containing proglottids separate from the tapeworm, and the life cycle restarts.
Epidemiology of bovine tapeworm
Infection and spread of tapeworm occurs through contact. The only distributor is man. The mechanism of infection by worms is called nutritional, and the route of penetration is called food. It is noteworthy that the bovine tapeworm is not transmitted from one person to another, since the horsefly must develop from an egg to a larva in the body of an intermediate host. The intermediate host is cattle. Oncospheres penetrate the body of the intermediate host. Next, the egg turns into a cyst or finna (adult larva), which is the source of infection. The main route of penetration of Finn into the human body is through the consumption of meat infected with cysts. The incubation period for teniarynchosis is 2-3 months, after which the larvae transform into adults. You can become infected with worms by eating meat that contains worms; there are no other methods of infection.
Bull tapeworm concept
Routes of infection
Bovine tapeworms enter the human body by consuming raw or undercooked beef. On average, 2-3 months pass from the moment of infection to the formation of a sexually mature individual. Helminths can maintain their vital activity in the body of the definitive host for up to 25 years.
In most cases, at a certain point in time, there is one sexually mature individual in the body of an infected person (the presence of two or more parasites is less often detected).
Cases of the disease are more common in adults than in children, which is explained by dietary habits. It is also noted that people working in meat processing plants, slaughterhouses or in various food establishments (cooks) suffer from teniarinhoz more often than others.
Bovine tapeworm parasitizes the human intestine
Bovine tapeworm, when entering the human body, provokes a disease such as teniarhynchosis, characterized by mechanical damage to the gastrointestinal tract. Chronic infection has pronounced symptoms and not the most pleasant consequences. This article will look at the developmental life cycle of the bovine tapeworm. The development cycle is well demonstrated by the pictures.
- What is bovine tapeworm
- Reasons for the development of infection and detailed description
- Life cycle of parasite development
- What processes does bovine tapeworm provoke?
Signs of cysticercosis
The gradual progression of cysticercosis leads to a significant impairment of the functional state of the affected organ. The pathological process is almost always accompanied by autonomic dysfunction and allergic reactions.
Symptoms of infection
It was previously agreed that a tapeworm can live for 20 years, poisoning the body of the intermediate host with toxic products of its own vital activity. Anyone who is at risk (eating meat of questionable quality or poorly processed offal) should be tested regularly, even if there are no obvious symptoms of infection.
At the very beginning of the invasion, the bovine tapeworm becomes a parasite in the human body, without causing serious disturbances in the general condition. The only unpleasant sensation is the exit of strobili from the anus with feces and/or as a result of their crawling out of the anus. But the imaginary well-being does not last long.
Beginning of infection
Many people, out of ignorance, think that helminthiasis will bypass them because they adhere to the rules of personal hygiene, constantly wash their hands before eating and are careful with their pets. But there are parasites that can infiltrate a person, regardless of these preventive measures.
These include bovine tapeworm. It’s worth eating an undercooked piece of meat for this dangerous neighbor to take up residence in your body.
Teniarinhoz has 2 stages of progression: early and chronic. The early stage of infection is practically asymptomatic. The owner of the bull tapeworm may not complain at all about deteriorating health; there are no obvious signs of infestation. As the disease progresses to the chronic stage, the situation changes.
The main symptoms of damage to the chronic stage of the disease:
- Unreasonable nausea, vomiting, problems with stool, heartburn, flatulence.
- Increased salivation.
- Dizziness.
- Fatigue, sleep problems, general weakness.
- Irritability, nervousness.
- Frequent pain in the abdominal area, the exact location of which is difficult to determine.
- Allergic reactions.
- Sharp fluctuations in appetite: from poor to excessive.
The human body is an ideal habitat for parasites. They infect absolutely any organ, deplete the body and are difficult to eliminate. The worm is the most famous parasite dangerous to humans.
Who is a tapeworm?
Tapeworm is a parasite belonging to the class of tapeworms. Tapeworms have a flattened rather than round body shape that resembles a ribbon.
- Types of tape parasites
- How does the disease manifest itself?
- Preventive measures
Cramping abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting may indicate bovine tapeworm in a person, the symptoms of which accompany the patient for several years. The danger from finding such a parasite in the body is enormous, because the length of the worm alone reaches 6-8 m. The tapeworm wanders through the gastrointestinal tract, thereby causing constant pain, sucking strength from a person and reducing his immunity.
A person can become infected by consuming cattle meat, in which, due to poor heat treatment, bovine tapeworm larvae live. Entering the body with food, the parasite larvae adhere to the walls of the small intestine and feed on processed food, which contains elements and substances necessary for life.
Instead, the parasite poisons its “host” with feces, which causes vomiting and nausea in the person.
Types of tape parasites
Among the large number of worms that live in the human body, the most dangerous is bovine tapeworm, since it causes a serious disease, Teniarinhoz, and it is very difficult to diagnose it in the early stages. Therefore, it is extremely necessary to know information about this parasite, the symptoms and consequences of its presence in the human body, for timely detection and treatment.
Description of the parasite
Bovine tapeworm, otherwise called tapeworm, is a tapeworm found in humans and animals (cattle). Once in the human body, the helminth causes the disease Teniarinhoz. Tapeworm is most common in the following geographic areas:
- Latin America.
- Equatorial Africa.
- Selected regions of Eastern Europe.
- Philippines.
Distinctive characteristics of the parasite:
- What is bovine tapeworm
- Symptoms of bovine tapeworm
- Diagnosis of teniarhynchosis: how to detect bovine tapeworm
- Treatment of bovine tapeworm
- Prevention measures
Diagnostics
Determining whether there is bovine tapeworm in the human body in the early stages is quite problematic due to weakly expressed signs. To find out an accurate diagnosis you need:
- Question the patient whether or not he ate undercooked or raw meat.
- Take feces and scrapings for examination.
- Take a blood test to check for anemia, eosinophilia and leukopenia.
- Tapeworm is a worm that can be seen on x-rays. Therefore, such a study is necessarily prescribed if teniarhynchosis is suspected. The patient is given a contrast solution to drink and an image is taken. The worm will be found on it in the form of a white stripe.
- Have feces scanned (ovoscopy).
You also need to not make a mistake in making a diagnosis, and not confuse the worms - bovine tapeworm and pork tapeworm. Their symptoms are very similar, but different diseases have to be treated.
Since proglottids with teniarhynchosis can independently move and crawl out of the anus, they can be easily detected, for example, in bed. This material must be collected and submitted to the laboratory to make a final diagnosis.
Once every six months to a year you need to donate blood and feces for worm eggs. If symptoms appear, it is necessary to urgently undergo all tests. Ultrasound and colonoscopy can also help detect tapeworms.
If suspicions are confirmed and bovine tapeworm is found in the body, then treatment must be started immediately. It must be prescribed by the attending physician after completing all examinations and tests.
Anthelmintics are usually prescribed to remove such parasites from the body. It is necessary to receive maintenance therapy that will gradually restore the body. It is necessary to take immunostimulating vitamin preparations in parallel.
It is also necessary to take into account that after a sharp release of the body from helminth proteins (worms), an acute allergic reaction may occur. Therefore, at the same time you need to start taking antihistamines. But it is the doctor who must prescribe this; you cannot self-medicate.
The parasites will leave the body gradually, and during treatment you need to constantly change bed linen and clothes, and wash everything at high temperatures.
Always wash your hands before eating. This is especially true for children. If you go to the village, constantly monitor the cleanliness of your child’s hands.
After treatment, you need to take tests again in two weeks to a month. And if they show the presence of a parasite, then undergo repeated treatment.
Important! If at least one person in a family is infected with Finnish bull tapeworm, then everyone living in this family must undergo diagnosis and treatment.
While undergoing treatment, you must follow a strict diet. Since the body is weakened, it is necessary to eat low-fat foods. You need to avoid all allergic foods. After the body has recovered, after a month, you can gradually begin to switch to your usual food.
Knowing the ways of infection with bovine tapeworm, you need to protect yourself: thoroughly boil and fry the meat, regularly wash your hands before eating and once a year undergo a thorough medical examination of the whole body to be sure that everything is fine!
Routes of infection
There are many parasites known in nature that, when they settle in the human body, cause enormous harm and inconvenience. These parasites include bovine tapeworm.
This type of worm is one of the most dangerous for the human body. It belongs to the class of tapeworms (helminths).
Over its long life cycle, this type of parasite reaches fifteen meters in length, and the size of the small intestine of an adult is six meters.
Bovine tapeworms enter the human body by consuming raw or undercooked beef. On average, 2-3 months pass from the moment of infection to the formation of a sexually mature individual. Helminths can maintain their vital activity in the body of the definitive host for up to 25 years.
In most cases, at a certain point in time, there is one sexually mature individual in the body of an infected person (the presence of two or more parasites is less often detected).
Cases of the disease are more common in adults than in children, which is explained by dietary habits. It is also noted that people working in meat processing plants, slaughterhouses or in various food establishments (cooks) suffer from teniarinhoz more often than others.
This dangerous helminth can enter the human body only through the fecal-oral route. To complete the cycle, the parasite necessarily needs an intermediate link.
This helminth can become infected in the following cases:
- If the required requirements are not followed correctly in the process of preparing food from raw beef.
- When taking samples from raw ground beef. The risk of helminthic infestation is greatest for cooks and housewives.
- The culinary preferences of some nationalities are noted. People who prefer shish kebab or stroganina should be aware that the tanks remain alive in poorly cooked meat.
As for the symptoms of bovine tapeworm, it may be completely absent and may, on the contrary, be pronounced with all the serious disturbances in the functioning of the entire body of an infected person.
Treatment of bovine tapeworm
The best way to prevent teniarhynchosis is thorough heat treatment of beef before consumption. For complete disinfection, the temperature inside the piece must be at least 80 0 C.
Source: https://tsitologiya.su/zheludok/v-kishechnike-cheloveka-parazitiruet-bychij-cepen
Geographical distribution
The disease is quite common in Africa, parts of Eastern Europe, the Philippines and Latin America. This parasite is found wherever beef is eaten, even in countries with strict sanitation policies. Estimates of the total global infection range from 40 to 60 million people worldwide: 100,000 in North America, 700,000 in Central and South America, and the majority in Asia and Africa. In Europe, Slovakia and Türkiye have the highest prevalence rates of bovine tapeworm.
Signs and symptoms
Most people infected with bovine tapeworm do not experience any symptoms unless the tapeworm grows quite large. In such situations, a person may experience a feeling of fullness, and sometimes (rarely) even nausea to the point of vomiting. The worm or worms can rarely cause acute intestinal obstruction, and individual proglottids can block the lumen of the worm, causing acute appendicitis.
In addition, with teniarynchosis the following may be observed:
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- headache;
- general weakness;
- itching in the anus.
Often patients become aware of the infection by finding a proglottid (or large segment of the worm) in the stool during bowel movements. These proglottids sometimes crawl down the thighs, usually when a person is active, and produce a tickling sensation.
Elevated levels of eosinophils and immunoglobulin E (IgE) may also indicate the presence of infection.
It should be noted that a significant difference between pork and bovine tapeworms is that the cysticercus stage does not occur in humans with T. saginata when eggs are ingested. Therefore, infection with a bovine tapeworm is less dangerous than with a pork one, since in the latter case, cysticerci can enter the central nervous system, eyes and other organs, developing into small subcutaneous cysts. Then they talk about cysticercosis.
Answers to questions related to bovine and pork tapeworms
What should you do if you or your child have tapeworm eggs in their stool?
"Hello. A few days ago, the doctor ordered my child (a 10-year-old boy) to be tested for worm eggs. Today we received the results: acarids - negative, opisthorchiasis - negative, tapeworm - positive! Please tell me what should we do?”
Pork and bovine tapeworm eggs are very similar in appearance. In this regard, doctors cannot determine by what kind of tapeworm (pork or bovine) they were laid just by the appearance of the eggs.
It is possible to distinguish one parasite from another if fragments are identified in the stool that are separated from its end (in medicine they are called segments or proglottids).
In this regard, if “tapeworm eggs” are found in you or your child’s stool, the doctor may suggest that you take a stool test several more times (on different days) and carefully examine the stool for the presence of segments of the parasite.
Every day, up to 6 new segments can be separated from the end of the tapeworm. They look like small (1-2 cm in length), slightly elongated, rectangular fragments, white-yellow in color. They may contract like a living worm trying to move.
| If you notice such a segment in the stool, carefully transfer it to a clean jar and show it to a parasitologist or infectious disease specialist. |
If the doctor determines that you or your child are infected with bovine tapeworm (teniarinhoz), he will be able to offer you a fairly simple and effective treatment, described below, which will help get rid of the parasite. You won't need to do anything else.
| A person infected with pork tapeworm can infect other people and can become infected with the larvae of this parasite themselves. In this regard, if the doctor determines that you or your child are infected with pork tapeworm (taeniasis), he will have to offer you: |
- Undergo additional examinations (including an examination by an ophthalmologist, a brain scan) to make sure that you have not been infected with pork tapeworm larvae and have not developed cysticercosis.
- The same examinations will need to be completed for all members of your family who could become infected with tapeworm eggs and develop cysticercosis.
- Get treatment (see below).
Under no circumstances should you begin treatment for tapeworm on your own initiative, without first consulting your doctor!
How can I check if I could have become infected with tapeworm?
“A few days ago I was at a barbecue with friends. I came across a poorly cooked piece of meat (blood was oozing from it). After that, I completely accidentally came across a message on the Internet that through poorly cooked meat you can become infected with worms and, in particular, tapeworm. Please tell me how to determine whether I could have become infected?”
Tapeworm larvae (pork or bovine) that may be found in meat develop into adults and begin laying eggs approximately 2-3 months after infection. Until this moment, they practically do not manifest themselves in any way (see symptoms ).
In this regard, if you suspect that you or your child may have become infected with tapeworm, you can, a few months after the suspected infection, consult an infectious disease doctor and have your stool tested several times for tapeworm eggs.
Treatment and prevention
The best way to prevent teniarhynchosis is thorough heat treatment of beef before consumption. For complete disinfection, the temperature inside the piece must be at least 80 0 C. An alternative to heat treatment is freezing: up to -5 ° C for 4 days, -15 ° C for 3 days or -24 ° C for 1 day kills the larvae parasite Freezing is not an effective method against pork tapeworm.
As with most cestodes, treatment involves the use of Praziquantel. Niclosamide is also effective in this situation.
Among the folk methods of getting rid of worms, the most popular are pumpkin seeds and garlic-milk mixture.