| At home | In the center | On one's own |
| Deoxygenated blood |
At home
: it is possible for a mobile service employee to take biomaterial.
At the Diagnostic Center
: collection or independent collection of biomaterial is carried out at the Diagnostic Center.
On one's own
: collection of biomaterial is carried out by the patient himself (urine, feces, sputum, etc.). Another option is for the doctor to provide samples of biomaterial to the patient (for example, surgical material, cerebrospinal fluid, biopsies, etc.). After receiving the samples, the patient can either independently deliver them to the Diagnostic Center or call a mobile service at home to transfer them to the laboratory.
* The price does not include the cost of taking biomaterial. Services for collecting biomaterial are added to the pre-order automatically. When ordering several services at a time, the biomaterial collection service is paid only once.
source
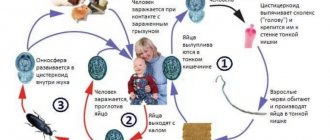
Parasites in the human body
Not all people understand why they are recommended to donate blood for helminths. Namely, such an examination allows you to detect infection at the initial stage. Helminths are parasites that live in the human body. Several dozen such parasites have now been discovered - from microscopic microorganisms to large worms. All of them cause serious harm to health. The most common parasites are several types.
- Roundworms are long roundworms. They live in the human intestines, causing various unpleasant symptoms. The eggs of these parasites are transmitted through unwashed hands, vegetables and fruits.
- Pinworms cause the disease enterobiasis. These are small parasites that live in the intestines.
- Toxocara is transmitted from domestic animals. Toxocariasis can affect not only the intestines, but also other internal organs, as well as the eyes.
- Trichinella can penetrate the muscles, causing serious pathologies.
- Echinococci, entering the body, form a cyst. Their penetration into the brain is especially dangerous.
- Giardia enters the body through dirty hands and food. This is a highly contagious disease that causes unpleasant symptoms.
Indications for prescribing tests for worms
Most often, infection with helminths occurs during food intake. Unwashed vegetables and fruits, touching food with dirty hands, poorly purified water, insufficient heat treatment of fish and meat - all this causes the appearance of parasites in the body. Helminth eggs are also transmitted through bedding and underwear. Having pets in the house requires strict adherence to hygiene rules: cats and dogs are often carriers of helminths, and petting a pet that comes up to you during dinner can become a carrier of parasites.
For the timely detection and destruction of helminths, it is necessary to undergo studies that detect the presence of parasites in the body. Usually, a simple and painless analysis is enough for this.
Tests for worms, depending on the reasons for the appointment, are conventionally divided into the following types:
- Preventive – carried out with the aim of promptly detecting the presence of parasites, even in the absence of symptoms. The procedure is carried out both on their own initiative and as part of a medical examination. The recommended frequency is at least once a year.
- Barrier - prevent the spread of the disease among population groups. So, when a child enters a kindergarten or swimming pool, he will need a certificate that includes information about the absence of helminths. Workers in the field of sales and food production must be tested for worms annually when applying for a medical certificate. As with preventive tests, the examination usually consists of laboratory examination of stool.
- As prescribed by a doctor - when visiting the clinic with symptoms such as weight loss, itching in the anus, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, increased fatigue, or when diseases often caused by parasites appear, the patient is prescribed a stool test for helminth eggs, as well as a blood test for antibodies. In these cases, the examination is carried out more thoroughly; if there are doubts about the reliability of the results, the tests are ordered again.
Regularly checking all family members for worms is an important part of staying healthy. This is especially important if there are risk factors: the presence of children and animals in the house, gardening, swimming in natural bodies of water, drinking water from springs, wells and wells, eating foods without proper heat treatment (rare steaks, lard, sushi, stroganina, etc.). The consequences of untimely detection of the presence of helminths in the body can be very serious: some types of these parasites damage the intestinal walls, causing sepsis, cause disruption of the central nervous system and destroy internal organs.
There are several types of tests that can reliably identify the presence or absence of parasites in the body: stool analysis for helminth eggs, scraping, blood test for antibodies. Also, indicators of a general blood test can indicate the presence of helminths - the patient has increased hemoglobin and ESR.
This type of analysis is the most popular way to determine the presence of worms (parasites of all types) in the body. When examining feces, a specialist does not see the parasites themselves, but only helminth eggs.
In general, taking a stool test for worm eggs does not require any special preliminary preparation. The only limitation: it is not recommended to take antiparasitic drugs, antibiotics, or anti-diarrhea medications before it. A special sterile container for biomaterial can be taken in advance from a laboratory, clinic or regular pharmacy. Immediately after defecation, feces are collected in a jar, which must be immediately transferred for examination or stored in the refrigerator for no more than 8 hours.
If the test result is good (normally, worm eggs should not be found in the stool), it is better to take the sample twice more on other days. The accuracy of the first study for many parasites is only 50%, while the same result obtained three times indicates a 99% absence of helminths.
Despite its simplicity and popularity, stool analysis is inferior in its information content to a more modern method - testing blood for antibodies. Below we will look at ways to more effectively recognize the presence of the most common types of parasites.
Enterobiasis occupies a leading position in prevalence among helminthiases. It is caused by pinworms - small white worms. The disease is especially common in children of preschool and primary school age. The main symptom is severe itching in the anal area, especially in the evening and at night.
The most effective method for identifying roundworms in the body is a blood test for antibodies. It does not require special preparation, but it is advisable to abstain from eating for four hours before the test.
Opisthorchiasis is caused by flatworms - the cat fluke. The disease has a pronounced local spread: the majority of patients live in Russia and the CIS countries. You can get opisthorchiasis by eating infected fish, which is an intermediate host for the parasite. Worms develop in the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, causing infections, allergic reactions, liver disease, flank pain and fever. Lack of timely treatment can lead to damage to the central nervous system, chronic gastritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers.
The most effective way to identify cat flukes is a blood test for specific IgG antibodies. A reliable result can be obtained by conducting the study between the sixth and eighth weeks after infection. When entering the chronic stage, the indicators may return to normal; in this case, it will not be possible to determine opisthorchiasis using this method.
Trichinosis is caused by Trichinella - helminths that enter the human body with contaminated meat and lard. Products in large stores must be tested for the presence of the parasite, so private farmers, hunters and people who buy meat in unverified places usually fall victim to Trichinella. Conventional heat treatment cannot destroy the eggs of this parasite; salting and smoking do not help either. One small piece is enough for infection.
Symptoms of the disease in the first two to three weeks are allergic reactions of the body, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. Then a disease occurs in the organ in which the worms have developed: the parasites can choose any part of the body and destroy it over many years. Ultimately, trichinosis can lead to the death of the patient or to irreversible disturbances in the functioning of the body.
If the presence of Trichinella is suspected, the patient is sent for a blood test for specific antibodies. If the result is negative and symptoms continue, it is recommended to undergo a re-examination after a couple of weeks: in the early stages, the disease may not be detected, but a blood test from the second to fourth week after infection provides high accuracy.
Strongyloidiasis is caused by white worms called eels intestinalis. This parasite lives mainly in places with a tropical climate; gardeners and farmers often suffer from it. The helminth can enter the human body through any contact of open skin with the ground, for example, when walking barefoot or when weeding a garden bed.
Once in the body, the blackhead leaves a red mark on the skin that lasts up to several days and causes severe itching. Subsequent symptoms can be either classic (itching in the anus, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain) or completely unexpressed. The parasite can live in the host's body for many years without causing severe inconvenience. However, with weakened immunity, strongyloidiasis leads to the death of the patient in more than half of the cases.
To identify strongyloidiasis, stool analysis is effective: when examining feces, it is not the eggs of worms that are visible, but the larvae. A blood test for antibodies, however, gives more accurate results - up to 85%.
Helminth infections are parasitic diseases that are dangerous to health and life and can lead to disability or even death. Timely consultation with a doctor and subsequent treatment are the key to ensuring that the patient avoids possible complications. Tests for worms must be taken at least once a year and only in a modern laboratory where the most effective research methods are used.
The danger of helminthiases
Despite the fact that the vast majority of the population is infected with parasites to one degree or another, for some reason these pathologies are not considered serious. Although helminthiasis can actually cause quite unpleasant symptoms and lead to serious consequences. Their main danger is that they are often asymptomatic at the initial stage. And it is quite difficult to detect them; the now widespread diagnosis through stool analysis is not always informative. Moreover, parasites often live in other internal organs, the brain, and muscles. Therefore, a blood test for helminths will be the most effective for diagnosis. It is recommended to do it not only according to indications, but also for preventive purposes in order to prevent complications.
The presence of parasites in the human body greatly disrupts its vital functions. They take nutrients, release decay products into the blood, poisoning it, reduce immunity and disrupt metabolic processes. People infected with helminths may experience vitamin deficiency and anemia, various pathologies of the digestive tract and decreased performance. It is especially dangerous when parasites penetrate the brain, eyes or heart. However, they can cause serious illness. The consequences of helminthiasis can be decreased vision, movement disorders, and severe intoxication of the body. Serious complications arise when children become infected with parasites. Their growth and development may slow down, and the functioning of internal organs may be disrupted.

What diagnostic methods are the most effective today?
Which method is the most accurate?
Both a smear from the perianal folds and a stool analysis have approximately the same specificity and sensitivity.
They do not lose their relevance in the diagnosis of enterobiasis and other parasitoses caused by roundworms.
In addition, stool examination is informative for screening for parasitosis.
Therefore, the use of this method has not yet lost its significance.
- For an adequate diagnosis of giardiasis (giardiasis), it is necessary to examine not only blood and feces. Analysis of duodenal contents reacts very sensitively to Giardia. After all, the intestinal chyme in the lumen of the duodenum is the favorite habitat of pyriform parasites. For a long time, it is there that they parasitize, causing clinical manifestations of liver damage and cholecystitis.
- A blood test for helminths (enzyme immunoassay) is considered promising today. Immunological diagnostic methods are more advantageous because they have high sensitivity and specificity. Moreover, these techniques make it possible to differentiate chronic, long-standing manifestations from fresh, acute parasitoses. The only negative is the higher price and the presence of a period when antibodies in the blood are not yet detected, because they have not yet been synthesized in quantities that can be detected by existing analyzing systems. Also, a blood test for helminths, in contrast to stool examination (ovomicroscopy), is rarely used in evaluating treatment.
- Specific diagnosis of parasitosis pathogens also includes the polymerase chain reaction or PCR method. This is an immunogenetic determination of the presence of parasitic cell deoxyribonucleic acid particles (DNA). The method is the most revealing and most effective for diagnosing any infectious or parasitic pathology. Its use is limited by its very high price. Therefore, its use is resorted to only in very complex clinical and controversial cases.
- In addition to specific verification methods, instrumental methods have not lost their relevance. They are better suited for diagnosing the pulmonary localization of parasites. Diseases such as echinococcosis, alveococcosis, trichinosis and opisthorchiasis with lung damage are often visible during radiographic examination of patients. The allergic Casoni method is rarely used to determine possible infection with echinococcus. But in controversial situations it finds its application. Duodenal contents are analyzed for the detection of lamblia (giardia).
The choice of the most effective method for searching for pathogens among worms and protozoa is carried out taking into account the clinical manifestations and complaints of the patient. Therefore, by contacting your doctor, you can receive clear instructions on the diagnostic examination plan.
He will help to structure all the methods, assigning them according to the principles “from simple to complex” and “from cheap to more expensive”. Independent selection of diagnostic procedures will only prolong the process and, most likely, will require unnecessary and unnecessary expenses.
Symptoms of parasitic diseases
To prevent serious consequences of parasitic diseases, many doctors recommend doing blood tests for helminths and giardia. This diagnosis is more informative than stool tests. It allows you to identify pathology at the initial stage and detect those parasites that do not live in the intestines. Indications for such an examination may include the following problems:
- indigestion;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea, flatulence, bloating;
- decreased or, conversely, increased appetite, weight loss;
- sleep disorders, decreased performance, drowsiness;
- enlarged liver, pain in the right side;
- decreased vision, brittle nails and hair;
- headaches, abdominal cramps;
- muscle pain, weakness;
- irritability, depression;
- decreased immunity, frequent colds;
- skin rash, allergic reactions;
- itching in the anal area.
It is especially important to identify helminthiasis in a child in time. This is difficult, since children cannot always talk about their feelings. Parents may suspect a pathology based on the baby's restless behavior, loss of appetite, excessive salivation, and itching in the anus. Allergic reactions, diarrhea, and frequent colds may occur.

How long are tests for eggworm and enterobiasis valid?
Having described the examinations for the presence of worms, let us summarize briefly about how valid tests for worms and enterobiasis are. In both cases, the validity period of the tests is the same.
Having read the article up to this point, you already know how valid the results of stool tests for pinworms and scrapings for enterobiasis, as well as an analysis for eggworms are valid:
The shelf life of the listed tests is only 10 days. Find out what other tests you can take to get a reliable answer: do you or your child have parasites or not? To do this, you can follow the link to a blood test for parasites, where there is a description of the various methods for determining them and the characteristics of each.
Why do they do a blood test for helminths?
Diagnosis of helminosis must be comprehensive. It is very important to accurately identify the type of parasite so that treatment is more effective. Many helminths cause the same symptoms, and in the initial stages the disease may not manifest itself at all. If the parasites live in internal organs or muscles, stool tests will not be able to detect them. Therefore, it is recommended to donate blood for helminths - this is the most informative examination. It allows you to identify the disease at the initial stage and begin treatment on time.
The effectiveness of this analysis is explained by the fact that in the presence of parasites in the body, special substances - antibodies - begin to be produced. This happens almost immediately after infection. And the release of worm eggs in feces occurs already in the later stages, when the parasites have colonized the intestines. Moreover, this does not always happen. For such an examination to be informative, you need to take stool samples at least three times.
Who needs to donate blood
It is recommended to take a blood test for antibodies to helminths when symptoms of illness appear that cannot be explained by other pathologies. This may be anemia, the occurrence of uterine fibroids, painful periods, causeless inflammation of the kidneys or bladder, prostatitis or prostate adenoma in men. In addition, a blood test for helminths is always prescribed in a child with signs of intoxication and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. For preventive purposes, they are needed when a child enters a child care facility, before visiting a swimming pool, or when registering for a sanatorium.
How to diagnose enterobiasis?
A blood test for worms involves mainly assessing the level of eosinophils, since with any helminthic infestation their number increases. Normal eosinophil counts are as follows:
- in adults - 0-0.45 x 10⁹/l;
- in children under 1 year - 0.0 -7 x 10⁹/l;
- in children from 1 year to 7 years - 0.0 -0.7 x 10⁹/l;
- at the age of 8 to 16 years - 0-0.6 x 10⁹/l.
With severe enterobiasis, a decrease in hemoglobin levels is possible, the normal values of which are:
- in men - 132 -164 g/l;
- in women - 115-145 g/l;
- in children from 1 year to 6 years - 110-140 g/l;
- at the age of 7 to 12 years - 110-145 g/l;
- at the age of 13 to 15 years - 115-150 g/l.
The fact that inflammatory reactions occur in the body is indicated by an increase in the level of leukocytes and ESR of varying degrees of severity.
However, the decisive role in making a diagnosis is played not by a blood test, but by examination under a microscope of scrapings from the perianal area, in which pinworm eggs are searched. It is often advisable to conduct such a study for enterobiasis several times with an interval of 3-4 days, since false negative results can be observed with low-intensity invasion.
Benefits of such a study
Various methods are now used to identify parasitic diseases. The doctor decides which one to choose. But recently it is more often recommended to donate blood for antibodies to helminths. This test has advantages over stool testing. First of all, worm eggs are not always excreted in feces. Only a three-time analysis is informative. In addition, the laboratory technician may simply not notice them in the collected samples.
But blood tests do not depend on the human factor and detect parasites already at the initial stage. In addition, with their help, you can assess not only the presence of worms in the body, but also the severity of infection - this increases the number of antibodies. But there are also disadvantages to such an examination. First of all, it is not always available in public clinics, and the fees are quite expensive - about 400-500 rubles to identify each parasite. In addition, this is an invasive examination, and you need to donate blood from a vein, which children especially do not like.
Where to donate blood for helminths
Not all medical institutions have equipment for this type of research. Therefore, it is usually recommended to take such tests at paid medical centers, which are available in every city. But the peculiarity of such an examination is that tests are done separately for each type of parasite. Not all clinics provide a comprehensive examination, although it will cost less. Usually, each type of parasite is estimated at 400-500 rubles. The turnaround time for results also varies, depending on the institution. Usually tests are ready in 5-7 days.

How long is an eggworm test valid?
Having gone through the test procedure and received an official laboratory form with the test results, a person naturally wonders how long the test for worm eggs is valid, how many days it is valid for.

This is important to know because the test for eggworms is valid for only 10 days. The tests are also valid for kindergarten and camp, when hospitalized in a hospital and for visiting a swimming pool, when receiving a voucher to a sanatorium. If a child is undergoing an examination for kindergarten, it is recommended to take tests after visiting the main list of specialists, so that the deadline does not expire at the time of signing the conclusion and issuing the certificate. A ten-day period is the minimum possible time during which the parasite (pinworm) can lay eggs.
It is worth recalling the obvious - the doctor, having received a response from the laboratory, can sign positive recommendations or issue a certificate only in the case of a negative response to eggworm and enterobiasis.
If there is a suspicion of infection of the gastrointestinal tract with helminths, the received negative answer should not be interpreted as the absolute absence of parasites. The fact is that various parasites of the intestinal group have complex development cycles and their eggs are not always present in the feces.
A reliable analysis for these pathogens is the key to their successful expulsion, because the final diagnosis for them is made precisely by examining stool. The result of stool for worm eggs and scraping analysis is also valid for 10 days. After this period, if you did not have time to obtain an official certificate from a doctor, then you must take a second stool or scraping test to diagnose the presence of parasites.
Methods of such research
Most often, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is used to identify parasites. This is the most reliable survey. It evaluates the reaction of the immune system and the presence of antibodies in the blood. They are produced when foreign substances are present in the body. Antibodies are needed so that the immune system receives information about the type of these microorganisms and is able to fight them more efficiently.
Sometimes a more complex examination is also performed - polymerase chain reaction - PCR. It allows you to detect DNA fragments of microorganisms and accurately identify their type.
Tests to detect ascariasis
In order to assume the presence of helminths in the body and assess the extent of the negative impact that parasites have had on the body, a general blood test is performed. In acute ascariasis, it reveals, first of all, an increase in the number of eosinophils.
However, in addition to the number of eosinophils, the doctor pays attention to the number of leukocytes, since with ascariasis it is also increased. Normally, an adult contains - 4-8.8 x 10⁹/l of leukocytes, in newborns - 9.2-13.8 x 10⁹/l, in children from 1 to 3 years old the norm is considered to be 6 - 17 x 10⁹/ l, and in a child from 3 to 10 years old the blood contains 6.1-11.4 x 10⁹/l leukocytes. Accordingly, the more eosinophils and leukocytes in the blood, the more massive the invasion.
To assess the extent of damage to the body due to ascariasis, the doctor may additionally prescribe a biochemical blood test. With this disease, it reveals an increase in the activity of ALT and AST (normal concentration is 7 - 41 IU/l and 10 - 38 IU/l, respectively), an increase in alkaline phosphatase (normally in women up to 240 U/l, and in men up to 270 U/l), increased bilirubin (normally 8.5 - 20.55 µmol/l).
In chronic ascariasis, the number of eosinophils is also increased, but there is a tendency towards leukopenia - a decrease in the number of leukocytes, since the parasites inhibit the functioning of the immune system. In addition, there is a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin. A general blood test for chronic ascariasis shows an increase in ESR to 15-20 mm/h.
It should be noted that a general blood test is not enough to establish an accurate diagnosis, namely, to determine a specific helminth. Therefore, along with it, an indirect hemoagglutination reaction (IHA) or an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using special diagnostic kits must be carried out. For such studies, blood is taken from a vein; they allow the parasite to be accurately identified in order to prescribe appropriate treatment.
Express tests
If helminthiasis is suspected, the patient may be prescribed a hemotest. In this case, blood for helminths is also taken from a vein, but the analysis is carried out more quickly, by mixing with certain reagents. The following methods are used for express diagnostics:
- latex agglutination;
- indirect hemagglutination;
- antigen-antibody test.
Sometimes a rapid hemoxcan is also performed. In this case, blood is taken from a finger and examined on a glass slide under a microscope. This way you can detect the larvae of parasites that live in the blood. In addition, the presence of some types of worms can be indicated by a general blood test from a finger prick. This is determined by the number of eosinophils. If their level is elevated, this indicates the presence of toxins or foreign microorganisms. In this case, you can continue the examination for a more accurate diagnosis.

When are tests prescribed and where to take them?

In most clinical pictures, infection with parasites occurs during food intake, through dirty hands. Worm eggs can be transmitted through household items and bedding. Having pets in the house is another factor leading to parasitic infection.
For your information, examining stool for helminth eggs is the most common and effective diagnostic technique that helps determine helminthic infestation in humans. This method helps to detect eggs of various types of parasites that infect tissues and internal organs. The test can detect infection with protozoan microorganisms.
Testing for helminth infections can be of the following types:
- Preventive analysis of stool for helminths. The attending physician prescribes a test for the presence of parasites in the human body, even if there are no complaints of alarming symptoms. The manipulation is carried out as part of a medical examination, as well as on the patient’s own initiative. It is recommended to carry out at least once a year;
- Barrier testing for helminthiasis. This option is necessary in those films when it is necessary to prevent the spread of the disease among certain groups of the team. For example, if a person wants to sign up for a swimming pool, or a child goes to kindergarten, school, etc. When visiting such places, a certificate is required indicating that the person is not sick. Most often, stool is analyzed for worm eggs and protozoan microorganisms. Blood is an additional test if the laboratory diagnostic result is questionable.
If a patient comes to a medical facility with symptoms such as weight loss, itching in the anus, loss of appetite, pain in the abdominal area, chronic fatigue, the doctor may recommend a test for helminths.
In the latter case, the research is carried out more thoroughly. In the vast majority of films, several methods are combined - human blood and feces are studied.
Where can I donate blood or stool? If you suspect a parasitic disease, you can contact your physician at your clinic. The doctor will give directions for tests and then decipher them for the patient. If there is an infection, then drug treatment using antiparasitic drugs is prescribed. You can also go to a private clinic and get all the tests done there.
Blood analysis
In order for the results to be reliable when examining blood for helminths and lamblia, you need to properly prepare for the analysis. It is given in the first half of the day on an empty stomach. It is not advisable to eat anything 12 hours before; you need to stop drinking alcohol and taking medications for several days, avoid stress and increased physical activity. You should not smoke a few hours before the test. The diet before the examination should exclude fatty, spicy foods, smoked foods and pickles - this will help make the analysis more reliable.
Blood is donated for helminths in the morning on an empty stomach. You need to properly prepare for the procedure, following all the doctor’s recommendations. Blood is taken from a vein, filling a test tube. Then it is sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Test results
The information content of this examination is based on the detection of antibodies to different types of helminths. They begin to be produced within a few days after infection. The amount of Ig A, Ig M and IgG antibodies is assessed. Acute helminthiasis with recent infection is manifested by a high level of Ig M antibodies. In the chronic long course of the pathology, a large number of Ig G antibodies are detected. If there are many different types of antibodies in the blood, this indicates an exacerbation of chronic helminthiasis and the presence of an inflammatory process.
Actions after detecting parasites
If tests show the presence of parasites, treatment is required. This must be done under the guidance of a doctor, as there are different techniques. Typically, treatment is complex and involves the use of different groups of drugs:
- special anthelmintic agents - “Nemozol”, “Dekaris”, “Vermox”, “Albendazole” and others;
- means for normalizing intestinal microflora, for example, “Linex”;
- adsorbents for removing toxins and waste products of parasites;
- immunomodulators and vitamins to increase the body's defenses.
Prevention of helminthiases
It is advisable for the patient to eat right, follow a daily routine, and avoid stress. It is very important to follow preventive measures after treatment to prevent re-infection. This is, first of all, thorough hygiene - washing your hands before every meal, after going outside and going to the toilet. It is also important to process food correctly, observe the duration of heat treatment of meat and fish, and drink only purified water. In addition, it is advisable to undergo such an examination annually. Timely identification of parasites will help to avoid serious complications.