Man lives in a huge ecosystem; both large and very tiny animals live with him on the same territory. Microorganisms always accompany a person, no matter where he is.
Of course, there are both beneficial bacteria and parasites, which include helminths. Many people think that they most often affect the intestines in the body, but parasites can take root in any organ; helminths in the liver are especially dangerous.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
Types of parasites
There are many varieties of parasites that can infect the human body, and if this happens, it is impossible to do without treatment aimed at destroying them.
However, before starting therapy, it is important to determine the type of worms:
- Roundworms . Even one worm can cause serious consequences, namely provoke necrosis or abscess.
- Schistosomes . They can lead to hepatitis; in the absence of timely treatment, liver cirrhosis develops.
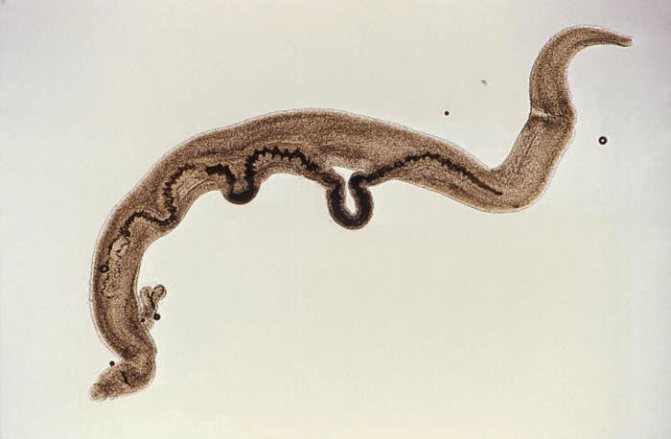
- Opisthorchia . The size does not exceed 2 cm, while the roundworm can be about 40 cm. They affect the gallbladder, blood circulation in it is disrupted, the temperature rises, if they get into the liver, they disrupt its functions and can lead to hepatitis.
- Unilocular echinococcus . Affects bile ducts and blood vessels.
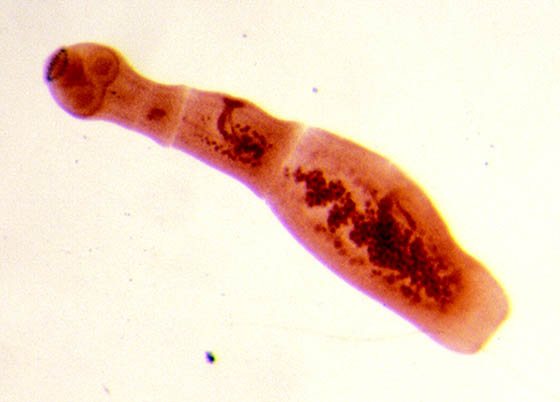
Echinococcus
- Alveolar echinococcus . It can develop in the human body up to 10 years and provokes the development of malignant tumors in the tissues and organs adjacent to the liver.
Liver parasites: diagnosis, treatment, prevention
Worms in the liver are a serious disease that can lead to serious consequences, sometimes even death. Therefore, diagnosis of the disease is one of the important stages in getting rid of liver parasites.
Diagnostics
First of all, blood and stool tests are prescribed. A scraping is taken from the anus. It is not recommended to take a shower or wash yourself before diagnosis, otherwise the tests will show incorrect results.
Additionally, ultrasound and endoscopic examinations may be prescribed. They may also prescribe a test for antibodies to parasites.
Treatment
To get rid of the parasitic organism, drug therapy is prescribed. Medicines differ in the type of action and affect one type of worm.
So, roundworms are treated with Albendazole, Levamisole or Pyrantel. Schistosomes - Albendazole, Metrifonate, Niridazole. If treatment is complicated by kidney stones, then a surgical method can be used.
The doctor may also prescribe the innovative German drug Diethylcabamazine.
Liver opisthorchia parasites are treated with the following medications:
- No-spa, as a preparatory agent;
- Mezim forte to improve digestion;
- Metronidazole (antibiotic), to prevent inflammation;
- Praziquantel, Albendazole, Chloxyl (not recommended for children under one year old).
Echinococci can be treated with Albendazole. For cysts in the liver - surgical method. Symptomatic therapy is also used.

Popular recipes among folk remedies:
- Grind a spoonful of wormwood and pour boiling water over it (use only fresh water), let it brew. Drink 1 tsp. 3 times a day for a week.
- Garlic. Can be consumed as a stand-alone product or mixed with milk and drunk in the morning
- Make a tincture of onions, take 0.5 tbsp on an empty stomach. in a day. The course is at least 7 days.
Roundworms in the liver
Ascaris can be considered one of the most dangerous types of liver parasites. Diagnosis of ascariasis is complicated by the fact that the symptoms of the pathology differ little from cholecystitis.
Most patients, just as with inflammation of the gallbladder, experience nausea, and roundworms may be expelled when vomiting. When helminths penetrate the bile ducts, jaundice develops.
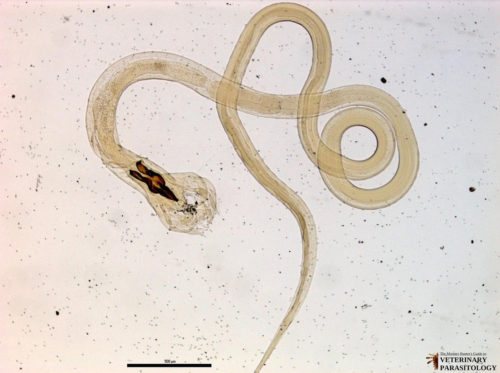
The body shape of the roundworm is spindle-shaped, the length of the female reaches several tens of centimeters, the males are slightly smaller. Typically, adult females parasitize the small intestine of humans. The question of how roundworms penetrate the liver still remains controversial.
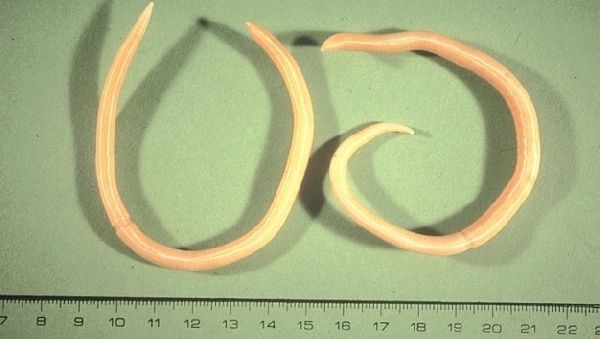
Ascaris
Scientists suggest that the embryo emerges from the egg in the intestine and damages its shell. With the blood flow in the portal vein, the larva enters the liver and spreads through the blood vessels to the heart, lungs and bronchi. Neurotoxins secreted by roundworms cause weakness, dizziness, sore throat, runny nose, and itchy nose.
Ascaris larvae during migration enter the parenchyma of the organ and injure the liver tissue. Foci of inflammation arise, hepatitis, cholangitis and cholecystitis develop.
Symptoms of ascariasis are nonspecific:
- pain in the right upper abdomen;
- bluish circles under the eyes;
- skin rashes, itching;
- diarrhea;
- vomit.
Anthelmintics for intestinal and liver damage by roundworms are used with great caution. Such drugs cause mass death and migration of parasites, which is dangerous due to severe intoxication and penetration of larvae into deep bile ducts.
Treatment of liver ascariasis is surgical. In the absence of medical care, the patient’s lungs are affected, the immune system suffers, and signs of intoxication of the whole body appear.
Larvae that penetrate the brain and spinal cord cause various disorders of the central nervous system. Possible complications of ascariasis include necrosis and liver abscess. In case of perforation of the intestinal lining, peritonitis may develop.
Signs of worms
There are a large number of signs by which one can suspect the presence of a helminthic infestation. First of all, you should pay attention to the person’s appearance:
Signs of helminthiasis in children
- seborrhea;
- acne;
- freckles;
- dark spots;
- early wrinkles;
- papillomas;
- brittle nails;
- cracks on the heels.
You should also pay attention to the following symptoms:
- causeless weight loss;
- pain in the right hypochondrium radiating to the right shoulder;
- nervousness. The fact is that parasites secrete toxic substances that irritate the nervous system;
- sleep disturbance;
- itching in the anorectal area, which occurs due to attempts by parasites to exit through the anus;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- constant feeling of hunger;
- headache.

With helminthic infestation, pain may occur in the liver area
Specifics of opisthorchiasis
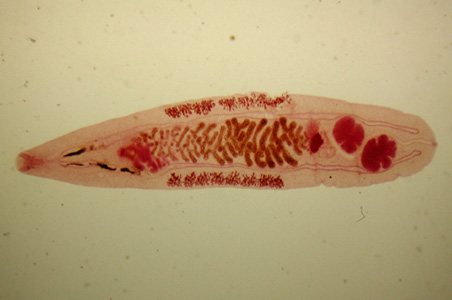
Small flukes belonging to the genus Opisthorchis infect the liver and bile ducts. Dangerous worms destroy liver tissue, absorb biologically active substances, and produce toxins that suppress the immune system. Infection with flukes is associated with allergic reactions and biliary colic.
The cat fluke has a leaf shape, up to 1.8 cm long and up to 2 cm wide. It is found in river basins from China to the Volga. Opisthorchiasis can be contracted by eating fish, meat of domestic and wild animals that feed on fish. The average duration of incubation is 28 days. The immature fluke migrates into the bile ducts and develops until sexual maturity.
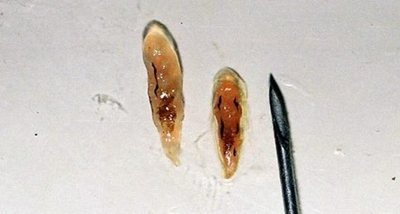
Opisthorchis
The onset of opisthorchiasis is rapid. After a week, symptoms of the acute stage may disappear without treatment. A chronic disease is characterized by exacerbations and complications. The main symptoms of opisthorchiasis:
- abdominal pain and other manifestations of dyspepsia;
- fever;
- increase in liver size;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
Fascioliasis is caused by flukes of the genus Fasciola. The leaf-shaped body is up to 3 cm long and about 1 cm wide. Infection occurs when contaminated water enters the stomach: during bathing, when using it for watering and washing greens and fruits.
Fasciola larvae penetrate from the intestines into the liver and gall bladder. At an early stage, symptoms of an allergic disease appear. The temperature rises, abdominal pain occurs, and the liver enlarges. Adult helminths injure the bile ducts and disrupt the flow of bile.
Fluke eggs are passed in the stool. Blood tests reveal eosinophilia. Treatment consists of taking a medicine with the active ingredient praziquantel. The patient needs to take adsorbents, enzyme and choleretic drugs.
Without therapy, the patient develops purulent cholangitis, gallbladder dyskinesia and gastroduodenitis. Later, fibrosis, cirrhosis and portal hypertension may appear. The most serious complication of opisthorchiasis is cholangiocarcinoma.
Treatment of worms
A specific medicine for worms is prescribed depending on the type of parasite that has settled in the patient’s liver. When infected with amoebas, the drugs “Metronidazole”, “Tinidazole”, “Nifuratel”, “Delagil” are used. The tablets are a complex that removes tissue worms in the liver and a wide range of drugs. For giardiasis, Furazolidone, Tinidazole, Trichopolum, Albendazole are prescribed. Schistosomas are removed with Praziquantel. As a result of treatment, dead individuals will be removed during defecation. Ascaris infestation is treated with Levamisole, Mebendazole, Albendazole, Pyrantel, additionally using drugs to strengthen the immune system and restore the level of nutrients in the body. This therapy kills the worms and restores the liver.
After taking antibacterial and antiparasitic drugs, the patient is prescribed probiotics to normalize the intestinal microflora. To cleanse the body of residual helminth poisoning, enterosorbents and antihistamines are used. Remember that only a doctor can prescribe any medications for treatment. He will help determine the required dose of anti-worm medication and the course of treatment, depending on the patient’s age, weight and other individual characteristics.
Symptoms of liver damage
Worms that live in the human liver cause the following symptoms of the disease:
- icteric tint of the mucous membranes and skin, severe itching of the skin, which can be confused with allergic;
- dyspeptic disorders: nausea, vomiting, indigestion;
- pain and pathological enlargement of the liver - hepatomegaly;
- general weakness, feeling of exhaustion, deterioration in performance, sleep disorders, bad mood, decreased learning ability;
- pain in the area of the right hypochondrium, usually of a dull, periodic nature.
Very often a person develops a rash. It is not diagnosed in all cases, but its appearance is the result of an allergic mechanism of development of helminthic infestations, which, when the process becomes chronic, cause a process of hypersensitivity in the body to its poisons and toxins.
As a rule, the increase in temperature in this case is of a long-term nature, like a low-grade fever, that is, the temperature can increase to 37–37.5 ° C.
These were the general signs of parasites in the liver; we will look at how they affect the organ collectively in the table.
| Type of helminthiasis | How does the disease manifest itself? |
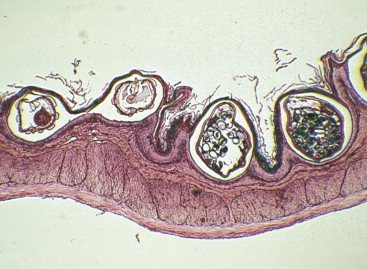
| ECHINOCOCCOSIS | With this disease, several cystic formations containing parasites form in the liver. The disease proceeds latently for a long time, then causes general symptoms. The cysts gradually increase in size, causing a lot of discomfort for the patient. Large cysts require surgical treatment. |
| ASCARIDASIS | The causative agent of the disease usually lives in the intestines; roundworms in the liver usually appear to be migratory. In organ tissues they create eosinophilic infiltrates. People complain of itching and skin rashes. |
| Opisthorchiasis | Trematodes or opisthorchises parasitize the ducts of the liver and gall bladder. They cause cholangiohepatitis, which occurs with abdominal pain, signs of jaundice and low-grade fever. |
| STRONGYLOIDOSIS | The presence of these worms in the liver provokes damage to the organ with dyskinesia of the biliary system. Signs: loss of appetite, bitterness in the mouth, yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, pain in the hypochondrium. Perhaps the most painful form of the disease among all others. |
| GIARDIASIS | Giardia causes biliary dyskinesia. Signs: pain in the hypochondrium, nausea, jaundice. |
| AMOEBIAS | The disease occurs as an acute form of hepatitis. The liver increases in size and abscesses form in its tissues. Signs: fever, jaundice, abdominal pain, damage to organ tissue with the prospect of developing cirrhosis. |
| BALANTIDIASIS | Ciliates lead to a painful reaction of the liver to palpation, diarrhea streaked with blood and mucus, dehydration, fever and other unpleasant symptoms. |
If proper treatment is not available, the disease quickly becomes a chronic process. In this case, a disruption of the central nervous system occurs, the person begins to complain of increased headaches, dizziness, and increased irritability.
In advanced cases, there may be increased sweating, tremors of the eyelids, hands and tongue. Being in this condition, not all doctors suspect helminthic infestation in the patient as the root cause of the disease, and carry out therapy for neuroses, vegetative-vascular dystonia and other diseases.
Symptoms of worm infection
When infected with worms, the patient experiences a number of general symptoms of body poisoning. They do not directly indicate the presence of worms, since they are easily confused with manifestations of another infectious or cold disease. The list of symptoms includes:
- increased body temperature;
- feeling of aching muscles;
- the occurrence of itchy skin lesions;
- nausea and subsequent vomiting;
- problems with stool, including diarrhea;
- decreased appetite.
Manifestations of the disease worsen when toxins secreted by the worm accumulate in the body. The infected person experiences severe allergic reactions, which manifest themselves in the form of redness, ulcerative and erosive lesions of the skin. As the worms consume silicon, the skin dries out and psoriasis develops. Due to the effects of toxic substances on the central nervous system, the patient experiences attacks of irritation, sleep deteriorates, and chronic fatigue appears. Liverworms cause weight problems in humans. Moreover, both weight loss and weight gain are possible.
Intoxication with waste products of worms can cause pathological changes in the liver.
Together with damage to the liver and bile ducts, parasites provoke blood loss and reduce the amount of absorbed nutrients. As a result, the patient suffers from vitamin deficiency and anemia. Toxins that poison the liver can also affect the bronchi, so along with liver problems, asthma develops and bronchitis becomes more frequent. Pathological changes occur in the liver, which leads to jaundice, hepatitis and subsequently cirrhosis. The longer helminths are in the body, the more serious the consequences will be. Usually, with prolonged exposure to toxins on the body, obvious diseases become chronic. Since immunity is significantly reduced, it is much easier to become infected with anything.
Features of helminthiasis in children
Due to the fact that children do not always adhere to the rules of hygiene, they are more susceptible to helminthic infestations. The very first signs of infection in children:
- lack of appetite;
- sleep problems;
- absent-mindedness;
- feeling of nausea;
- pain on the right side.
Since such manifestations in a child can be caused by a number of different diseases, it is necessary to visit a doctor. The baby will be prescribed tests and examined to make sure that there is a helminthic organism in the liver. If you delay going to a specialist, serious complications will develop, which are much more difficult to cure than simply removing worms.
How does infection occur?
Worms can settle in the human body - a child or an adult, and subsequently infect the liver in the following ways:
- in the process of contact with the ground, since the eggs of nematodes, liver flukes, roundworms and pinworms can live in the soil substrate, as a result of which they easily enter the human body along with poorly washed vegetables and fruits, through bare feet and dirty hands;
- through direct interaction with an infected person, for example, pinworms are easily transmitted in a group through household items, such as bedding, or dirty hands;
- from pets - through saliva, fur, contact with feces, etc.;
- when drinking obviously unboiled infected water, liver fluke, nematodes and other helminths can be transmitted;
- in case of improperly processed food, for example, violation of the cooking process of fish, cutlets or undercooked kebabs, as well as recently popular rolls and sushi - in this case, parasites such as flukes, liver fluke, roundworms and echinococci easily settle in the body of an infected person;
- after an insect bite.
It is no secret that children are most often carriers of helminthic infestations. It is not difficult to explain: the immune system in childhood is not sufficiently formed, the body continues to grow and develop, requiring a large amount of strength and energy.

As a result, a weakened immune system, as well as age-related weak acidity of gastric juice, compared to adults, makes the body more susceptible to various types of helminthic infestations.
Moreover, from an early age, a child rushes to actively explore the world around him, and he tries to do this not only by touching with his hands, but also with his mouth, tasting absolutely everything - both at home and on the street.
Even despite the comprehensive care that most children receive, not all parents can teach a preschool child basic hygiene rules. Therefore, no one is safe from infection with worms in a family with small children.
What are the routes of infection?
The main route of infection with worms is through the mouth, i.e. helminths enter the organ through food intake. Most often, this is low-quality or poorly thermally processed fish. When drinking water from reservoirs and rivers, without boiling.
Cases of infection through pets (cats, dogs) are not uncommon, because parasites can live on animal fur. If your pets walk outside, you should regularly treat them with a special shampoo.
One of the most common ways of infection is dirty hands, as well as poorly washed vegetables and fruits.
Liver damage by worms can occur in both adults and children. The latter are at risk because they often put dirty hands in their mouths, touch stray animals, etc.
Helminths in the liver cause a number of changes that immediately affect human health. Body temperature rises, colic appears, red spots and other allergic reactions may appear; these are only the main symptoms of the disease.
Tests and other diagnostics
In many ways, what worms live in a person’s liver depends on the region of residence, since in some countries there is an increased risk of helminthic infestation. In addition, it is important to consider the person's occupation when making a diagnosis. Important information is the presence of contact with animals. In addition to collecting an anamnesis about the patient’s condition and information about his life, it is necessary to conduct a number of laboratory tests. Therefore, the patient undergoes blood, urine and stool tests. In addition to a general blood test, a biochemical study is carried out to determine the presence of antibodies to certain types of parasites. Feces are donated only if the test is carried out no more than 2 hours after collection.
The list of basic diagnostic procedures includes:
- collecting bile using a probe;
- PCR diagnostics (polymerase chain reaction) is one of the methods for determining infectious diseases;
- endoscopy;
- X-ray examination;
- ultrasonography;
- computer (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Return to contents
Clinical picture
The main symptoms of helminths that affect the liver in adults and children.
In adults:
- Roundworms - weakness, headache, decreased blood pressure, nausea, itching near the anus.
- Schistosomes - cough, hemoptysis, itching, muscle pain, headache.
- Opisthorchia - lack of appetite, high temperature, pain in the right hypochondrium.
- Unichamber echinococcus - pain in the epigastrium, dull and nagging pain, problems with digestion of food.
- Alveolar echinococcus - weight loss, pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea and vomiting, decreased performance.
In children:
- Roundworms - the temperature rises to 38 C, upon palpation the liver is enlarged and painful. Lymph nodes are larger than normal, dermatitis on the arms and legs. It is recommended to begin drug therapy as soon as possible.
- Schistosomes - allergies, urticaria type, anemia, blood in urine and feces. The symptoms are similar to amoebiasis.
- Opisthorchia - a feeling of aching, urticaria, fever, pain in the stomach, vomiting.
- Unilocular echinococcus - Pain in the chest, weakness, no appetite, nausea and vomiting.
- Alveolar echinococcus - Diarrhea, poor appetite, vomiting, fatigue, jaundice.
The appearance of helminths is not immediately noticeable. In some, development in the liver occurs within a few days, in others within a few days, and there are types that may not cause any symptoms for several years.
If any signs appear, you must consult a doctor and undergo all the necessary tests. First of all, drug treatment should be carried out, but for prevention, as well as to enhance the medicinal effect, folk remedies can also be used.
Pumpkin seeds are a good preventative measure. Children up to 75 g per day, adults - 150 g. Consume on an empty stomach along with the peel, it contains substances that will help get rid of worms.
Medicinal herbs (tansy, wormwood, dandelion) also help with the disease. At the pharmacy you can purchase a special collection of medicinal plants for worms.
Treatment of parasites in the liver: drugs and the order of their administration
The main types of worms that infect the organ are as follows:
- Liver fluke: fasciola (liver and giant);
- cat fluke;
- lanceolate fluke;
- Chinese;
- American.
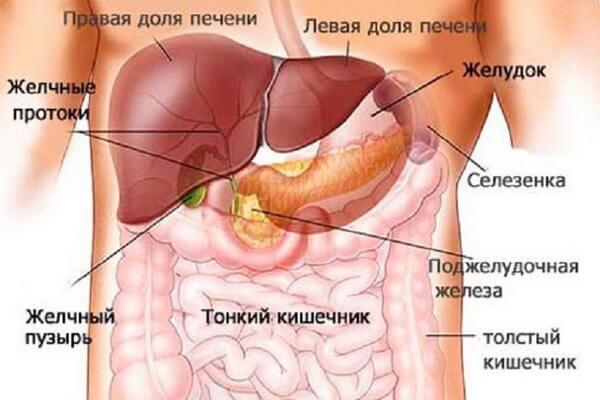
The main functions of the liver and gall bladder in the human body:
- cleansing the blood composition of toxins, breakdown products of alcohol and drugs, medicines, processing excess fats from food;
- participation in the digestion process - production of bile;
- participation in all types of metabolism in the body - in particular, if the pancreas produces insulin, the liver “processes” the products of the breakdown of nutrients in the human body;
- the liver cells synthesize albumins and partially globulins;
- the liver is responsible for the production of special proteins that play a role in hematopoiesis - thus, without normal functioning of the liver there can be no talk of normal blood clotting;
- the liver takes part in the absorption of vitamins, minerals, and amino acids from food and medicines; The liver is also a kind of “transshipment point” in which the body stores glycogen reserves and a number of vitamins.
The liver is the largest gland in the human body. It also leads in weight among other organs. There are no nerve roots in the liver, so this organ does not hurt. Patients often complain of a feeling of heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium, being sure that the liver is hurting.
In fact, this organ can only increase in size, but cannot hurt. If the liver is enlarged, it puts pressure on nearby organs, as a result of which the patient experiences discomfort in the right hypochondrium. Pain in this area of the body may also indicate a violation of the outflow of bile or cholelithiasis.
The liver is divided into four lobes - right, left, caudate and quadrate. The liver is often called the “biochemical laboratory of the body”, since many metabolic processes are carried out in the cells of this organ. Its functioning is closely related to the functioning of the gallbladder. It regularly produces bile, and from here it flows through the bile ducts into a kind of reliable “storage” - the gallbladder.
It is often necessary to make sure that there are no other chronic diseases when symptoms appear indicating the presence of worms in the human liver. Treatment (photos of a liver infected with helminthic infestation is an unpleasant sight, and therefore we will refrain from publishing such materials) will depend on what concomitant diseases are present.
Most adults are well aware of simple steps to prevent helminthic infestations. This means washing your hands with soap before every meal, after visiting the toilet, and after traveling on public transport. It is also the thorough washing of food that a person is going to eat.
However, for some reason, it is very rare that even adults (not to mention children) scrupulously adhere to these simple rules. Should we subsequently be surprised at the appearance of symptoms signaling the presence of worms in the human liver? Treatment, as a rule, is not cheap: in addition to taking special medications, the patient will be forced to undergo tests several times to make sure that the parasites have left the organ.
There is an opinion that only worms can “settle” in the liver. This is a misconception; in fact, the following parasites can gain a foothold in the organ:
- roundworms;
- schistosomes;
- opisthorchia;
- unilocular echinococcus;
- alveolar echinococcus.
Delving deeper into medical terminology, it should be clarified that roundworms are a type of worms, since their size and structure fit a number of criteria. But other parasites no longer belong to the class of worms, since the principle of their life activity is different. Therefore, the symptoms of worms in the human liver are somewhat different depending on what kind of parasite has taken hold.
How to remove parasites is an important question. But everything should be approached wisely and thoroughly. It is important to remove not the symptom, but the cause. In our case, to achieve a positive result, you need to have information about the etiology of the disease.
What indicates the presence of worms in the human liver? The signs of invasion are different: it all depends on which particular “invader” has established itself in the tissues of the organ and left eggs there. It will not be possible to determine the type of parasite on your own, but thanks to the information presented below, you can draw some conclusions.
So, how can you tell if there are worms in your liver? Symptoms in a person over 15 years of age may include:
- If the organ is attacked by roundworms, then the person suffers from weakness and apathy. After eating, he may often experience nausea, although the internal organs on ultrasound are normal. In older people, blood pressure may drop for no apparent reason. Itching develops in the anal area.
- If schistosomes have taken hold, the patient suffers from a cough, and hemoptysis may develop. A person suffers from headaches of unknown origin, he often experiences drowsiness and weakness, which the usual methods do not help to fight (taking energy drinks, vitamins, etc.).
- When the liver is damaged by opisthorchia, the patient suffers from lack of appetite and a pulling sensation in the right hypochondrium. In some cases, the patient may suffer from a constant low-grade fever.
- Unichamber echinococcus makes itself felt by dull and nagging pain in the right hypochondrium, pain in the stomach, and digestive problems. The patient switches to a gentle diet, but even in this case he suffers from diarrhea, bloating, and pain in the epigastric region.
Symptoms of infection in children:
- When a child is infected with roundworms, the liver becomes enlarged and can be felt by palpation. Lymph nodes enlarge. Atopic dermatitis appears on the surface of the skin of the arms, legs, and back.
- When infected with schistosomes, iron deficiency anemia develops. The skin turns pale and there is blood in the urine and feces. You should consult a doctor as soon as possible if you have these symptoms.
- When infected with opisthorchia, the child suffers from itchy skin. The skin becomes yellowish and pale.
- Unichamber echinococcus makes itself known by painful sensations in the chest and cough. The child loses his appetite. Digestion is disturbed, after eating, nausea and vomiting may occur.
These are the symptoms indicating the presence of worms in the human liver. We will talk about the treatment further.
Why do symptoms indicating the presence of worms in the human liver appear? It is obvious that the parasite or its egg reached this organ through the bloodstream and became entrenched in its tissue. Worms living in the human liver often make the patient’s life literally unbearable. The easiest way to prevent invasion is to follow safety rules, and to do this you need to know the ways of infection by parasites.
So, the most common causes of the development of parasitic liver infestations are:
- parasites enter the body through food intake, so you should thoroughly wash food before processing and cutlery immediately before eating;
- when water from dirty reservoirs enters the body (and it is not necessary to drink it - it can get, for example, through the nose into the larynx);
- infection is also possible through contact with stray animals - you must wash your hands as thoroughly as possible after such contact has taken place;
- working in the soil with unprotected hands allows helminth eggs to enter the skin and then into the body; It is optimal to carry out work in the soil wearing special gloves.
How to get rid of worms in the human liver? The process may not be quick. If the first “blow” of therapy destroys the adults, the eggs may still remain in the tissues of the organ. How to remove worms from the human liver forever? You will have to undergo several courses of therapy. Sometimes the process is limited to one course, but after it it is necessary to verify with the help of tests that the organ has been completely cleansed.
Treatment for worms in the human liver is carried out with the following drugs (it is important to remember that the duration of therapy and optimal dosages are prescribed only by the attending hepatologist or gastroenterologist):
- roundworms are removed with Albendazole, Levamisole;
- schistosomes - “Metriphonate”, “Niridazole”;
- opisthorchias are treated with Metronidazole, Praziquantel, Chloxyl;
- Echinococci are sensitive to the action of Albendazole.
If there are cysts or hemangiomas in the liver, then surgical intervention is often necessary.

Patients often ask: “Is it possible to remove worms that have settled in the human liver on their own? How do you know if therapy was successful? At home, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis (even if the totality of symptoms most eloquently indicates the presence of parasites in the liver), nor to get rid of the infestation.
There is an opinion that the popular folk method - two raw cloves of garlic on an empty stomach - will help remove all parasites and even their eggs from the body. Unfortunately, the effectiveness of this method has not been confirmed. Attempts to treat parasitic infestations using traditional methods in children are especially dangerous. In the future, such amateur activity can lead to very serious consequences, including the development of chronic pathologies of internal organs for the rest of your life.
Worms can enter the human body through the fecal-oral route. Unwashed hands, contact with animals - all this leads to the process of contracting a dangerous infection. It is difficult to determine the presence of parasites in the human liver by eye. The main symptoms of the development of worms and liver amoebas include poor condition of the skin and nails, pigment spots, and chapped lips. Such indicators are subjective for determining the disease, so you should pay attention to the following changes:
- weight loss;
- irritability;
- poor sleep;
- headache;
- nausea;
- bad breath.
Echinococcus
Diagnosis and treatment of liver helminthiasis
Adult women and men, elderly people and children need to undergo a differential diagnosis before prescribing a specific treatment method. Detecting helminths in the liver is very difficult, as they can migrate to other organs.
First you need to take an enzyme immunoassay blood test. Ultrasound of the liver, endoscopy, liver biopsy, ultrasound of the bile ducts and gallbladder, general blood and urine tests, and blood tests for liver enzymes are also prescribed. Optionally, FGDS, stool analysis for oocytes and occult blood may be recommended.
Principles of treatment of hepatic helminthiasis:
- Taking medications that have a detrimental effect on parasites. The most effective drugs are Tinidazole, Nifuratel, Praziquantel, Albendazole, Mebendazole, Furazolidone, Levamisole, Piperazine, Pyrantel. Dosages and course duration are determined individually, based on the type of helminthiasis.
- Use of antihistamines, enterosorbents, immunomodulators, multivitamin complexes. They help eliminate the symptoms of helminthic infestations, remove waste products of parasites and normalize the general condition of the patient.
- Taking hepatoprotectors. They help support the organ and prevent the development of complications in the form of cirrhosis, hepatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, and diarrhea.
- Dieting. Pickles, sweets and any other foods that are difficult to digest in the body are removed from the menu.
In case of massive liver damage and the development of complications that are life-threatening, surgical intervention may be prescribed. Most often, surgical procedures are used for amoebiasis, echinococcosis and fascioliasis.
It is completely pointless to use traditional methods in the presence of parasites in the liver. Decoctions and tinctures will not help remove helminths from the parenchyma. Homemade drugs can only be used for preventive purposes.
Diagnosis of the disease
In order to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor first conducts a conversation with the patient or his parents if a child has become infected with worms. This is done to find out his lifestyle, the presence of animals in the house, whether the child ate unwashed fruits and vegetables from the dacha, or swam in unfamiliar bodies of water.
Next, the doctor gives a referral for stool, blood and urine tests. Then a modern analysis for antigens and antibodies is carried out, which even makes it possible to determine not only the degree of infection, but also the type of helminthiasis. You may also need a biochemical blood test and an ultrasound of the internal organs to see the damage caused by worms.
For a more accurate result, the analysis is carried out several times.
If there is a suspicion of helminth damage to the liver, it is recommended to consult an infectious disease specialist or parasitologist, and consultation with a gastroenterologist and hepatologist is also necessary. The following diagnostic methods will help you check and identify parasites:
- general blood analysis;
- stool examination for oviworm;
- linked immunosorbent assay;
- serological tests for antibodies;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- analysis of duodenic fluid;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- CT or MRI.
About the inadmissibility of self-medication
The first rule of successful therapy is to never self-medicate. Indeed, symptoms may clearly indicate the fact that the liver is infected with a parasitic infestation. But only an experienced doctor will be able to correctly classify the symptoms of worms in the human liver.
Treatment (in the photo below you can see a schematic representation of cysts formed as a result of infection with echinococcus) cannot be the same for everyone. A number of drugs for helminthic infestations have many side effects, and if the patient himself attempts treatment, the situation can end in disaster.
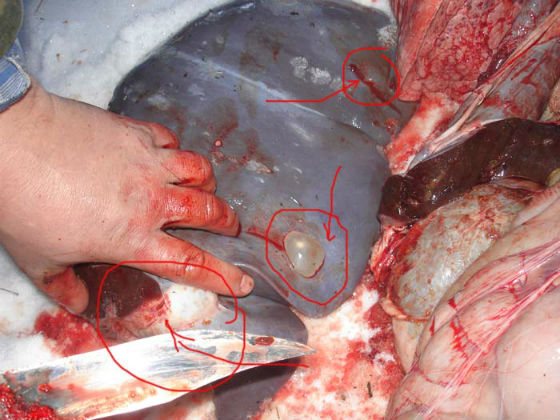
Tumor due to echinococcosis
Moreover, many patients try to choose hepatoprotectors for themselves when they feel heaviness in the right hypochondrium. The cause of discomfort in this case is not directly in liver pathologies, but in the fact of parasitic invasion.
Traditional treatment
In order to quickly cleanse the body of parasites at home and normalize the functioning of the digestive tract, you can supplement conservative treatment with folk remedies.
Using burdock rhizome. To eliminate signs of intoxication in the body, as a result of which the liver will be better cleansed, you will need a teaspoon of burdock rhizome extract, which must be diluted in a glass of clean water and drunk in one gulp. Repeat 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 7 days.
Fir remedy. Fir extract has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, disinfectant and hepatoprotective effects. How to cleanse the liver of parasites using fir extract? For a month, take 50 ml of the product daily orally 3 times a day, previously diluted with clean water.
Tansy recipe . Effective liver cleansing at home using folk remedies can be done using tansy. The unique composition of tansy can not only remove parasites from the liver, but also cope with the signs of cholecystitis and inflammatory changes that have arisen in the organ as a result of the parasitic activity of helminths and protozoa.
Tansy should be brewed at the rate of one teaspoon of dry raw material per 200 ml of water, consumed in 3 doses during the day. Additionally, before going to bed, you can chew the crushed flowers of the plant and wash it down with a glass of water. In the morning, it is necessary to supplement treatment with the use of laxatives to speed up the elimination of parasites and their waste products.
Author's methods of cleansing the liver from parasites
There are many proprietary methods for getting rid of parasites in the liver. Yu. A. Frolov even held entire conferences on this topic. However, the most popular are the methods of Semenova and Hilde Clark.
By H. Clark
Cleansing the liver of parasites according to H. Clark involves the simultaneous intake of such ingredients as:
- wormwood herb powder;
- tincture of green black walnut peels;
- clove powder (spice).
Drink the nut peel tincture on an empty stomach, starting with one drop per day, and gradually, adding drop by drop, bring the daily dose to 2 teaspoons. Dissolve the tincture in 1/2-1 glass of water.
Wormwood powder is also taken on an empty stomach, starting with one pinch and increasing to 1/2 tbsp. spoons a day. Clove powder is used in the same way, but the initial dose (½ teaspoon three times a day) is not increased, but reduced to 1/4, then to 1/3 teaspoon. After the 10th day of treatment, it is recommended to take 1 teaspoon per week.
This method is highly effective and can eliminate not only adults, but also their larvae. However, it has many contraindications and nuances, so it is not recommended to use it in practice without the knowledge of a doctor.
According to Semenova
This cleansing technique takes place in 3 stages:
- the first – lasts 3 days and consists of the use of cleansing enemas from an infusion of wormwood and garlic broth;
- second - cleansing occurs by ingesting pumpkin seeds and herbal teas;
- the third requires the ingestion of vegetable oil with lemon juice.
Liver cleansing according to Semenova also has a number of contraindications . Therefore, it cannot be used without a doctor’s permission.
What to do if nothing helps
Unfortunately, sometimes cleansing the liver of helminths that parasitize its tissues is not always successful. In this case, the task of removing parasites from the liver turns into a labor-intensive process that requires a lot of patience. You will need not only a specific anti-parasite pill or folk remedies, but also a diet and special cleansing procedures.
To get rid of parasites from the human liver, many methods have been developed by many specialists in both official and alternative medicine. Let's consider a proven method of cleaning the organ, Gennady Malakhov, Anatoly Malovichko and other specialists.
It is advisable to begin cleansing procedures against parasitic organisms in the liver before the onset of the full moon phase, from the 10th to the 13th day of the lunar cycle. For 5 days, it is necessary to carry out water thermal procedures that have a relaxing effect: this can be a regular hot shower, bath, sauna or bath. The main condition for their implementation is that after completing the procedure it is necessary to rinse the body with cold water.
It is important to follow a vegetarian diet during the cleanse. It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, including apple and beet juice, which can be drunk separately or mixed.
Once a day it is necessary to do a cleansing enema, preferably in the morning. This course of treatment must be followed for at least 2 weeks; it can be combined with any type of medication or folk therapy.
Preparing to cleanse the liver of parasites
In order for the process of removing worms from the liver to occur as efficiently as possible, it is necessary to prepare the body before starting the treatment course. To do this, you need to adhere to a special diet for 2 weeks, which involves excluding the following foods from your diet:
- meat;
- fried and fatty foods;
- sweets (including diet cookies);
- refined vegetable oil.
Cleansing the liver of parasites with tablets or alternative medicine also involves drinking plenty of fluids. A person needs to drink at least 2 liters of water per day. Additionally, doctors prescribe enemas or laxatives.
Without the preparatory stage, the process of removing helminths from the liver becomes more complicated. Following a diet and cleansing the intestines creates unfavorable conditions for the proliferation of parasites.
Liverworms in cows
Cows and other cattle, like all animals, are susceptible to helminthic infestations. Depending on the types of helminths themselves and the infectious load, diseases can be asymptomatic or lead to weight loss, milk yield and even death of the entire herd, which has a large negative economic effect in livestock farming.
However, helminthiasis is not always accompanied by characteristic symptoms and signs. It is important to take preventive measures to avoid the spread of infection. This is the best way to avoid serious consequences, since when cows are seriously damaged by worms, sometimes the only way out is slaughter. More often, visible clinical signs appear in calves.
Worms that parasitize the body of cows and other cattle (cattle) are very diverse. Therefore, treatment and prevention methods may differ.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment can also help cope with liver diseases. Unlike pharmacological agents, they are safe for the body. A person can use alternative medicine recipes at the first sign of a parasitic infection. In this case, the likelihood of a quick recovery without the use of potent drugs increases.
300 g of seeds are crushed and mixed with 20 g of beekeeping product. The mixture is poured with 50 ml of boiled water and infused. You must take the medicine before breakfast. After 2 hours, drink a laxative and cleanse the intestines with an enema. The procedure is repeated once a month.
Fir extract
It can be bought at a pharmacy. The product is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:1 and consumed before meals, 50 ml. The extract is allowed to be consumed no more than 3 times a day.
Tansy tincture
10 g of plant material is poured into 250 ml of boiling water and left to cool. The tincture is divided into 3 equal parts and taken in the morning, lunch and evening. To increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is recommended to chew tansy flowers before going to bed. The course of therapy is 7 days. Every morning you need to cleanse your intestines with laxatives or enemas.
Mainly gastrointestinal roundworms (nematodes)
Various types of nematodes often cause helminthiasis in cattle. All of them are similar in morphological characteristics and affect the heart, lungs and other organs of animals.
Genus Bunostomum
Spreading. It is more common in regions with warm and humid climates. The following species parasitize livestock: B. phlebotomum, B. trigonocephalum.
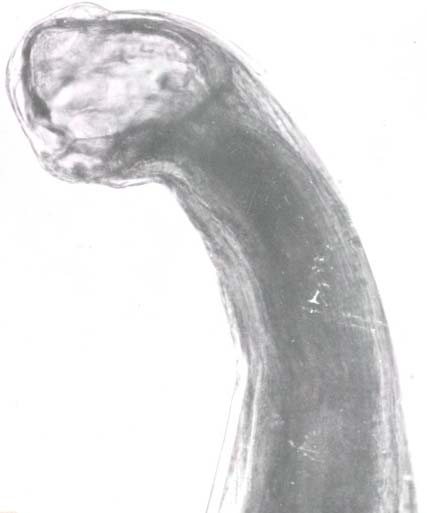
Infection. The larvae enter through the skin or by ingesting contaminated soil or water.
What does it look like? The body is grayish-whitish in color, length from 1 to 3 cm. Covered with cuticle.
Symptoms and signs. Diarrhea, dehydration, loss of appetite, weakness, weight loss and slow growth, submandibular swelling. The larvae, penetrating the skin and migrating under it, can cause dermatitis (itching, swelling, redness, thickening), hair loss, and damage to the hooves. When the lungs are affected, a cough occurs.
Genus Cooperia
Spreading. Found everywhere. Main species: C. curticei, C. oncophora, C. pectinata, C. surnabada.
Infection. Through food or water, where helminth eggs can enter with contaminated feces.
What does it look like? The body is reddish in color, up to 10 mm, and females are larger than males. Covered with cuticle.
Symptoms and signs. Typical clinical manifestations are diarrhea (watery, green or black) followed by dehydration and weight loss. Other signs are apathy, loss of appetite, anemia.
Genus Gongylonema
Spreading. The following types are found:
- Gongylonema pulchrum – distributed throughout the world;
- Gongylonema verrucosum is found in parts of Asia, Australia, South Africa and North America.
Infection. By eating dung beetles and cockroaches that feed on excrement.
What does it look like? Length - about 6 cm (males), 14 cm (females). The body has a yellowish-brownish-reddish color and is covered with a cuticle.
Symptoms and signs. Minor inflammation of the esophagus or stomach walls. It is often asymptomatic.
Common parasitic infections
The disease is caused by a certain type of worm or protozoan. Regardless of the type of pathogen, the start of therapy cannot be delayed: parasitic infections weaken the body, toxins are actively distributed throughout all departments. In the absence of proper treatment, the patient's condition noticeably worsens.
Characteristics of common parasitic diseases:
- ascariasis. When parasites colonize, a microabscess of the liver occurs and the tissues die. The causative agent is roundworms (roundworms). Helminths up to 40 cm long actively migrate throughout the body, poison the liver and bile ducts, and inflammation often develops. In severe stages of ascariasis, damage not only to the gastrointestinal tract is observed, but also to nervous disorders, hallucinations, and the patient has nightmares;
- echinococcosis. The disease is often observed among pet owners, veterinarians, zoologists, and hunters. Parasites enter the body from the fur of wild animals, cats or dogs, but fortunately they are not transmitted to other family members. Echinococcus eggs rupture in the stomach, helminths penetrate into the bloodstream and spread to various organs. In severe stages, dangerous complications are possible, including anaphylactic shock. The duration of the first stage is from 5 to 15 years, later the disease becomes more active;
- Giardiasis Tiny flagellated parasites attach to the intestinal wall. Many researchers believe that half the world's population is infected with Giardia. With active division of parasites, intestinal function is disrupted, and liver damage is often noted. The ducts become clogged, an inflammatory process develops, and hepatocytes are depleted. Skin rashes often appear. The main category of patients with acute symptoms are children;
- schistosomiasis. A dangerous disease develops after the penetration of trematodes. Blood flukes migrate to the bladder and liver. The parasites are small – up to 20 mm in length. Schistosomes enter the body through the skin after swimming in an infected body of water. The danger of liver damage is blockage of venules, increased pressure. Against the background of schistosomiasis, portal hypertension is often recorded;
- amoebiasis. Single-celled organisms enter the human body through dirty water, unwashed hands, and poor hygiene when visiting the toilet. Protozoa penetrate the liver from the large intestine, and acute amoebic hepatitis or amoebic abscess develops. The temperature rises to 38 degrees and higher, the liver becomes denser, and the organ is painful to the touch.
Liverworms in broilers
Chickens, like other types of poultry, are susceptible to helminthiasis. The most important reason for parasite infection is violation of sanitary standards during maintenance. In addition, poultry can become infected with helminthiasis after eating contaminated feed.
Helminths pose a threat to the health of chickens, which necessitates the need to quickly take measures to treat them. You can get rid of parasites in chickens using both folk remedies and special preparations.
Treatment
When the first symptoms of a parasitic infection appear, you should seek medical help, since it is impossible to get rid of parasites on your own. Otherwise, the parasitic infection can become chronic and cause serious and life-threatening complications.
An infectious disease doctor establishes a treatment method taking into account the type of worms, their life phase, the individual needs of the body and the general well-being of the patient. Basically, getting rid of helminths occurs in 3 stages.
Let's look at how to cleanse the liver of worms:

Initially, therapeutic therapy is aimed at relieving a person of the symptoms of intoxication and stabilizing the functioning of the liver and digestive tract. The patient is prescribed a healthy diet, taking choleretic drugs such as Hofitol, Galstena and antihistamines - Suprastin, Zodak. Toxic substances are removed by sorbents, and digestion is improved by enzymes.- After the preparatory stage of the body is completed, an intensive effect on the worms is carried out. The destruction of parasites occurs with the help of special drugs, many of which are toxic. Any medicine against parasites - Nemozol, Vermox, Pirantel - is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician, taking into account individual characteristics.
- The final stage is aimed at strengthening the immune system and preventing relapse. For this purpose, vitamins and immunomodulators are prescribed.
When all 3 stages are completed, follow-up studies are carried out to ensure that the patient has fully recovered. If the helminths are not completely eliminated, then the treatment regimen is repeated, but with different medications.
Traditional methods
To make treatment more effective, you can add traditional methods to drug therapy. But this must be done exclusively with the permission of the attending physician.
Let's consider several effective methods of treatment with folk remedies:

300 g of pumpkin seeds are cleaned, crushed and mixed with 20 g of honey. 50 ml of boiling water is added to the resulting mass. After the medicine has infused, it is ready for use. The product is drunk on an empty stomach before breakfast, after 2 hours a laxative is taken, after which an enema is performed to cleanse the intestines.- Take 10 g of dried fir needles, add 250 ml of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. After the allotted time has passed, the infusion is filtered and drunk during the day in 3 doses. To increase effectiveness, chew tansy inflorescences before going to bed and wash down with clean water. In the morning, the intestines are cleansed using an enema.
- Inflorescences of chamomile, tansy, yarrow, wormwood and oak bark are mixed in equal proportions. 50 g of the plant mixture is selected, poured with 1 liter of boiling water and left to infuse for 2 hours. After the allotted time has passed, the medicine is ready for use. Use half a glass before breakfast for 14 days.
- Take a large onion, chop it, pour a liter of boiling water, and leave it in a thermos for 12 hours. After this time, the infusion is filtered and 2 tablespoons are taken every morning after waking up for 10 days. For preventive purposes, it can be used once every six months.
We suggest you read How to get rid of parasites at home
Traditional medicine does not guarantee getting rid of parasites in the liver and can be dangerous to health, so you should consult your doctor.
The first stage of therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of intoxication, normalizing the functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
During therapy, the patient will have to follow a strict diet. The rule will speed up the healing process. The infected person excludes spices, smoked meats, fatty and sweet foods from the menu. The diet includes fruits, vegetables, cereals, fermented milk products, low-fat fish and meat.
In addition to diet, the preparatory stage includes taking medications aimed at suppressing the symptoms of the infectious disease. The patient is recommended to take choleretic drugs (Hofitol, Galstena) to relieve abdominal pain and normalize digestion processes. To eliminate skin itching and rashes, treatment is supplemented with antihistamines (Zodak, Zyrtec, Suprastinex).
To remove waste products of worms from the body, sorbents are used: Lactofiltrum, Neo-smeptin. Fermented preparations can normalize appetite and improve digestion: Creon, Pasinorm.
After initial preparation, patients are recommended to take drugs that act on parasites. Many of the drugs in this group are toxic, so they should only be taken with the permission of a doctor. Exceeding standard dosages of anthelmintic drugs is not allowed.
List of effective medications for parasites:
- Pyrantel;
- Nemozol;
- Dekaris;
- Wormil;
- Piperazine.
Therapy with anthelmintic drugs is carried out in conjunction with the intake of enterosorbents. First, they take medications for parasites, and after 15-20 minutes, sorbents. Thanks to sorbents, you can quickly cope with the signs of liver damage by parasites. To completely cleanse the body, antiparasitic drugs are taken in courses (with breaks of 3 weeks).
After completing the drug course, the person will be scheduled for repeated tests to detect helminths. The doctor will be able to begin the last stage of treatment only after confirming the absence of helminths in the patient’s body. If after taking medications the parasites remain in the body, the treatment regimen is adjusted.
The last stage of treatment includes strengthening the immune system. To restore the body's defenses and prevent a relapse of the parasitic infection, the patient is prescribed a course of vitamins (Supradin, Complevit) and drugs with an immunomodulatory effect (Interferon, Kipferon).
Specifics of the disease
Helminthiasis refers to an invasive disease, the source of which is helminths.
Most often, worms settle in chickens and continue to develop in the following organs:
Parasites absorb blood from the internal tissues of an infected animal and cause deformation or rupture of organ walls. Toxic substances released by helminths poison and deplete the bird's body.
Helpful information. Worms reproduce in a very short time - one individual chicken roundworm produces 50,000,000 eggs every year.
Parasites help weaken the immune system of a sick animal, which increases the likelihood of contracting a dangerous infection. Poultry begins to suffer from anemia, and the quality of meat decreases significantly.
Note! Since the larvae of worms from sick chickens enter the egg, when this type of animal product is consumed, the parasites are transmitted to humans.
Among the causes of worms are the following:
- damp soil in the room where birds are bred;
- rare replacement of flooring;
- low quality food;
- dirty water;
- insects that carry parasites;
- animal carrier of parasites;
- purchasing sick birds;
- refusal of quarantine.
Another source of worms may be a farmer who takes care of birds, introducing them through dirty shoes. The most susceptible to infection with worms are chickens released outdoors, representatives of light breeds, as well as birds that consume food primarily of animal origin.
Keeping different varieties together with young animals also increases the risk of disease. For example, turkeys transmit parasites to their young - chickens are more resistant to this type of worms.
Helpful advice. It is recommended to release young birds separately from adult birds, ensuring that the chicken walks in a place where there is no droppings.
Preventive measures
Prevention of infection with worms requires compliance with certain rules. They mainly concern hygiene, since most parasitic infestations occur due to dirty hands. Therefore, it is necessary to wash your hands after each visit to the toilet, public places, transport, walks in nature or work in the country. It is recommended to regularly wet clean the house and ventilate the rooms. If a person has pets, it is necessary to take care of their regular anthelmintic therapy.
It is important to monitor the food you eat. Vegetables and fruits must be thoroughly washed and only after that they can be eaten. When preparing dishes from fish and meat, you should observe the temperature regime and do not consume raw, half-raw, lightly salted or smoked products. Drinking water should not be collected from standing sources. In addition, water taken from unfamiliar sources should be boiled and filtered.
Types of helminths and list of symptoms
An infected chicken can be identified by the presence of the following signs that characterize the general symptoms of helminthiasis:
- lack of appetite;
- low body weight;
- weakness;
- sluggish state.
Note. Severe infestation can lead to the death of the animal.
When cutting up a carcass, certain types of helminths are visible to the naked eye. Accurate diagnosis is carried out by examining infected chicken droppings in a veterinary laboratory.
List of parasites living in the chicken body and characteristic symptoms:
- Capillariasis is a disease caused by threadworms that live in the intestines of poultry. With capillariasis, the chicken lags behind in development, has lethargic behavior, may lay eggs weakly and refuses to eat.
- Syngamosis is a disease transmitted by nematodes and syngamos that live in the respiratory organs. With syngamosis, the chicken has no appetite, which is accompanied by severe exhaustion and wheezing when breathing.
- Ascariasis is a disease caused by roundworms that settle in the intestines. With ascariasis, the bird refuses water and feed, which is accompanied by paralysis and a decrease in egg production.
- Cestodosis is a disease transmitted by a tapeworm parasite that lives in the gastrointestinal tract. The disease is accompanied by symptoms such as weakness and weak appetite.
- Histomonosis is a disease transmitted by histomonas that live in the liver. Accompanied by apathy, liquid droppings of yellow or green color.
- Amidostomiasis is a disease transmitted by nematodes and the amidostoma helminth that live in the stomach. A sick laying hen is apathetic and refuses to feed. Another sign of the presence of amidostomiasis is that young chickens develop slowly.
- Trematodosis is a disease caused by almost microscopic parasites, characterized by a pear-shaped shape and a yellowish tint to the body, that live in the oviduct. Infection occurs by eating shellfish. The presence of this disease can be recognized by the deformation of the shape of the oviduct and the absence of a shell or yolk.
- Nocotilidosis is a disease transmitted by parasites with a rounded body that live in the rectum of a bird. Infection occurs when the larvae are ingested in a swampy area. The list of symptoms includes a decrease or lack of response to food, and slower weight gain. The young may die altogether.
- Daveniosis is a disease caused by small-sized cestodes. Symptoms of this disease include symptoms such as low mobility of the animal and refusal to eat feed. Severe consequences include the death of 65% of the population or the death of certain individuals, before which the sick birds remain in a paralyzed state for some time.
- Heteracosis is a disease transmitted by chickens pecking at the eggs of this type of worm. The disease is indicated by low mobility of chickens, lack of response to food and diarrhea. In addition, the area of the digestive tract is subject to deformation.
Infected chickens produce a small number of eggs, which have thin shells. If the respiratory organs are affected, the scallop may become pale in color and wheeze.
Parasitic species and diseases
Among all the known forms of parasitic worms, during the entire period of research, scientists were able to identify the most common types found in the human liver. Each of them has a specific effect due to the production of toxic poisons that damage tissues and cellular structures. It will be useful to find out what parasites live in the human liver, as well as what danger they pose in terms of the development of diseases.
Amoebas
The simplest parasitic microorganisms live in most bodies of water, and enter the liver with lymph and blood from the gastrointestinal tract. Their danger is that by releasing a certain toxin, they lead to the degeneration of cellular structures, provoking the formation of blood clots and areas of necrosis. Diseases associated with amoeba damage - amoebiasis - often end in liver abscess and often cause hepatitis.
Giardia
They choose to live in the gastrointestinal tract, brain, and lungs, but are mainly found in the liver. The giardiasis they cause is also called the “disease of dirty hands,” and its insidiousness lies in the fact that adult lamblia are capable of becoming covered with a dense keratin shell that is resistant to the effects of most drugs. It is not easy to get rid of parasites in a protective cocoon, so they can live in the body for years, causing hepatitis and cholecystitis.

Roundworms
Roundworms
Roundworms enter the body most often through contact with an infected person or pet. Roundworms are not particularly selective in their habitat and can live in the intestines, gall bladder and liver, moving depending on the conditions of the internal environment with the flow of blood and bile. The migration of parasites leads to the fact that it is most often possible to recognize the fact of their presence only during surgical operations. In addition to intestinal disorders, they often cause ascaris liver abscess, the breakthrough of which threatens peritonitis. With a long and protracted course, the disease manifests itself in the form of hepatitis, cholecystitis and cholangitis.
Echinococcus
A terrible parasite with a tape-like body structure appears in the human body after communicating with animals and if preventive measures are not followed. The adult looks like a sphere with the head and body of the parasite inside. It lives in colonies, the lifespan of which is more than 10 years, and forms a cluster of alveoli or, in other words, cysts. Extensive alveolar growths lead to pressure on internal organs, disrupting their functioning mechanically and poisoning them with toxins. It looks no less threatening than the consequences of the development of the alveolar form of echinococcosis. Toxic poisons provoke parasitic liver diseases, complications of which are obstructive jaundice, hepatitis, ascites, and allergic reactions.
Alveococcus
Another representative of the ribbon species, living in colonies. Infection occurs through the consumption of poorly processed meat of wild and domestic animals; individuals are found in mushrooms, berries, and vegetables, and the carriers are domestic animals, on whose fur eggs can be attached. Liver worms in humans provoke the development of necrosis, hepatitis, obstructive jaundice, easily enter the lungs and can parasitize the structures of the nervous system. The main danger is their prolonged growth and resistance to many antiparasitic drugs.
Cat (Siberian) fluke
A flat-type liver helminth with a shape resembling a leaf often enters the human body with raw river and lake fish, and can also be transmitted by contact. It causes the development of opisthorchiasis, which leads to compaction of the liver structure, the development of inflammation and abscesses.
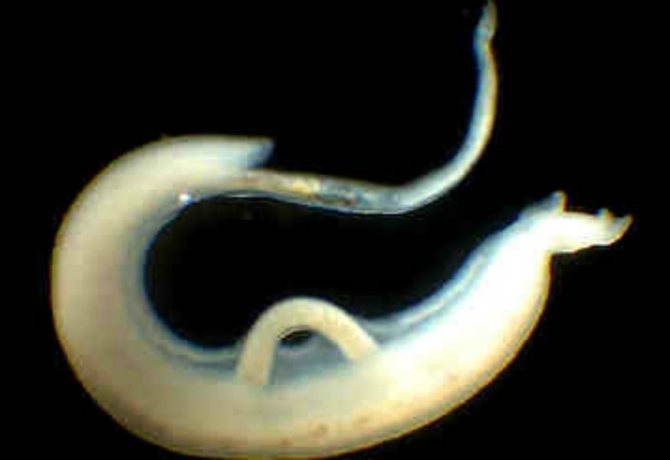
Schistosoma
The flatworm enters the human body with contaminated water, and can also penetrate through personal contact, then penetrate the blood, choosing the liver as its main habitat, where it lives and lays eggs. Flat helminths in the liver cause necrotic processes and bleeding, causing liver failure, which can be fatal.
Schistosoma
Leishmania
Protozoan worms are spread by insects and enter the human bloodstream through a bite. Their presence can only be determined with a high degree of accuracy using specific diagnostic methods; leishmaniasis is characterized by a latent course with mild symptoms. They live in the liver, changing the structure of the organ’s cells and replacing hepatocytes with connective tissue. Such changes lead to the appearance of foci of necrosis and cause liver failure and hepatitis. Knowing which worms live in the human liver and the main sources of danger, you can more effectively resist their introduction into the body by taking measures to protect the body.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Interesting to know:
Liver parasitic forms
Parasites in the human liver come in a wide variety. What parasites live in the liver? This organ is mainly affected by amoebas, roundworms, lamblia, alveolar, unilocular echinococcus, and schistosomes.
Amoebas
Amoebas are able to penetrate from the intestinal region into the human liver. They are sent to the liver region through the lymph nodes and venous vessels, where they end up penetrating through the intestinal walls.
Amoebas, being active in all tissues and healthy cells of the organ, can provoke the development of thrombosis and disruptions in cellular nutrition. During the life of parasitic forms, secreted toxins penetrate into the liver tissue, which cause necrosis. When several necroses merge, an amoebic abscess develops.
Schistosomes
These parasites attack the hepatic blood vessels. And parasitic larvae are localized, grow and develop in the tissues of the organ. Infection of the body with schistosome threatens a person with the development of hepatitis or cirrhosis of the liver.
Giardia
Giardia actively multiplies in the liver area, causing:
- addition of a foreign infection;
- severe inflammatory processes;
- hepatocyte dystrophy;
- active production of leukocytes.
It is worth noting that Giardia in this organ feels quite good, but cleansing the liver of parasites at an unadvanced stage proceeds quickly and practically does not cause any complications.
Roundworms
This type of parasitic form belongs to round helminths. Localized in the liver tissues, roundworms cause microabscesses and micronecrosis. Accompanied by the development of purulent inflammation in the tissues. When an organ is affected by adults, people may notice the development of hepatitis, and cholangitis may also be diagnosed.
Alveolar and unilocular echinococcus
Alveolar echinococcus attacks healthy cellular structures and tissues of the organ. Usually there is an active spread of metastases to nearby organs, for example, the lungs. Such metastases can also affect the central nervous system.
This parasite belongs to the group of cestodes. Unichamber echinococcus also belongs to cestodes. Externally, the parasite resembles a bubble.
As the bladder develops, it increases significantly in size, which increases the risk of developing atrophy of the liver tissue, squeezing blood vessels, and deteriorating the functioning of the bile ducts.
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.

The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
Other tests
We recommend reading

Pinworms in women: symptoms, treatment and how they leave the body
10 hours ago 03.09.202003.09.2020ecoliv94
Necatoriasis: what kind of disease is it, what are the symptoms and treatment methods
10 hours ago 03.09.202003.09.2020ecoliv94
Ascariasis in children: symptoms, causes, drugs and treatment regimens for roundworms
1 day ago 02.09.202002.09.2020ecoliv94
What is helminthic infestation in children and adults, causes and symptoms
07/29/202007/29/2020ecoliv94
The main symptoms of helminthic infestation of the liver
There are many signs that your liver is not functioning properly. Let's look at the main points that are worth paying attention to:
- rapid weight loss, since the parasites take almost all the nutrients from the patient’s liver, the body does not have time to replenish the losses;
- constant headaches, which intensify at night and in the evening, as worms constantly release harmful substances, intoxication of the body occurs;
- there is a lack of calcium, if there are parasites in the liver, then the patient will definitely have hair loss, crumble nails, teeth, and bone fractures may occur under light loads;
- a large number of freckles and age spots will appear on the body, which is associated with metabolic disorders;
- the skin will become rougher, small cracks will begin to appear, which may be joined by secondary infections;
- severe pain in the liver area, resulting from the destruction of cells and tissues of the organ by parasites;
- nervousness and irritability that appear unexpectedly to everyone around you is the effect of parasites on the central nervous system. There is also constant fatigue, the patient constantly wants to sleep;
- poor or, on the contrary, very good appetite, but at the same time, naturally, the person does not gain weight, since all nutrients are absorbed by parasites;
- allergic reactions, most often of a skin nature, such as rashes and itching;
- bad breath caused by intoxication of the body;
- Possible itching near the anus.
The importance of proper nutrition during and after treatment
The drugs that are used to treat helminths in the liver are quite toxic. On the one hand, taking them helps get rid of parasites, but on the other hand, it is a kind of small toxic blow to the body. Yes, it is necessary, since parasites in the long term have a much more detrimental effect on all systems, disrupting the normal functioning of the liver.
It is very important to support the liver with proper nutrition during the treatment period. Otherwise, the weakened organ, and even during the period of getting rid of the parasitic invasion, may increase in size, and the bile ducts may become inflamed. To prevent this from happening, you should adhere to the following nutritional rules:
- Refusal to eat fatty foods. Fast food, pork, lamb, confectionery with margarine, fried foods - such food puts a strain on the liver. And since the organ is already exhausted by parasitic infestation, you should temporarily stop eating such food.
- Alcoholic drinks should be completely avoided at least while taking the medication. If you combine alcohol abuse and taking medications, there is a high risk of developing toxic hepatitis.
- Enrich your diet with vegetables and fruits, consume bread in minimal quantities and only dried bread.
- Avoid drinking tea, coffee, and sweet carbonated drinks for the duration of treatment.
Causes of development of parasitic liver infestations
Why do symptoms indicating the presence of worms in the human liver appear? It is obvious that the parasite or its egg reached this organ through the bloodstream and became entrenched in its tissue. Worms living in the human liver often make the patient’s life literally unbearable. The easiest way to prevent invasion is to follow safety rules, and to do this you need to know the ways of infection by parasites.
So, the most common causes of the development of parasitic liver infestations are:
- parasites enter the body through food intake, so you should thoroughly wash food before processing and cutlery immediately before eating;
- when water from dirty reservoirs enters the body (and it is not necessary to drink it - it can get, for example, through the nose into the larynx);
- infection is also possible through contact with stray animals - you must wash your hands as thoroughly as possible after such contact has taken place;
- working in the soil with unprotected hands allows helminth eggs to enter the skin and then into the body; It is optimal to carry out work in the soil wearing special gloves.

Necessary diagnostic measures
In order to find out which worms have “settled” in a person’s liver, you should undergo the following tests:
- General blood analysis. It is necessary to specifically check the eosinophil count. An increase in this type of leukocyte indicates a possible infection by parasites.
- Feces for helminth eggs.
- Scraping from the anus - this study will help determine whether the parasites have penetrated the intestinal cavity, or whether their location is exclusively the liver.
- Duodenal intubation - used to obtain bile samples from the duodenum. Further microscopic examination of the biological material taken from the sample makes it possible to detect the larvae of any specific parasite.
- Enzyme immunoassay allows you to detect specific IgG antibodies to a specific type of helminth.
- Ultrasound and MRI of the gastrointestinal tract will allow you to assess the degree of damage to internal organs and create the most accurate clinical picture of the patient’s condition.