Kinds
The disease is divided into types with characteristic features for each:
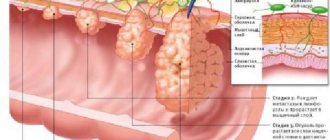
- Unexpressed hepatomegaly is expressed in a slight increase in the size of the liver. The disease is diagnosed in young children. If the child does not have negative symptoms and his health does not cause him discomfort, the doctor does not prescribe treatment. Most often, this type of hepatomegaly goes away on its own over time. If, over time, an increase in the organ is observed, the doctor selects complex therapy.
- Severe hepatomegaly is diagnosed if the organ has increased to 5 cm or more. Because of this, there is an increase in the volume of the abdominal cavity, which can be observed upon visual examination. As the disease progresses, a person develops leukemia or hemoblastosis.
- A moderately pronounced form is characterized by a slight increase in size, which exceeds the norm by up to 2-5 cm. In this case, the patient rarely experiences negative symptoms. If you follow a diet and do not drink alcohol, the organ can recover on its own and eventually return to its normal size. If the liver is moderately enlarged, drug therapy is prescribed only when negative symptoms begin to appear over time.
Enlarged liver: what to do and how to treat?
Treatment of an enlarged liver is not limited to reducing the volume of the liver. Usually it is necessary to carry out complex therapy, which is aimed at curing a specific disease (if this disease can be treated). But at the same time, special vigilance must be shown when drawing up a menu for the patient (this is especially true for children: no chocolate, fast food, fried food).
Adults also need to refrain from junk food, drinking alcohol, and smoking. You need to move more, eat foods that are healthy for the liver and gastrointestinal tract, rich in fiber and vitamins. For detailed advice on supporting liver health, consult your doctor; do not try to treat your liver yourself, as this can only harm your health.
What are the features of pathology in children?
In an infant, changes in liver size may be associated with jaundice.
The presented condition does not require separate therapy, because it goes away on its own within one month.
The reasons for this in childhood may be birth injuries, diabetes mellitus and other problems in the functioning of the endocrine system in a woman. Next, I would like to draw your attention to the following:
- if a child has an enlarged liver and is no more than seven years old, this condition can be considered quite normal from a physiological point of view;
- the norm should be considered a case in which the baby’s organ protrudes slightly beyond the edges of the costal region, but no more than a few cm;
- As the baby grows, the liver will become normal in size.
An increase in the right lobe of the liver or the left may well indicate inflammatory algorithms in the body.
We can also talk about congenital TORCH infections (toxoplasma lesions), effects on the organ of toxins or medicinal names.
An enlargement of the left lobe of the liver, as well as the right one, may well be associated with pathology within the framework of metabolism, or any disturbances in the functioning of the biliary tract. Another factor may well be blockage of the bile ducts.
How to remove and get rid of gallstones forever without surgery
In childhood, the liver is most rarely enlarged due to the influence of metastases or any neoplasms. It is also necessary to understand that a change in the size of an organ in combination with other alarming signs is a cause for alarm.
For example, special attention should be paid to the increase in temperature indicators and the appearance of a venous network in the peritoneum. Symptoms such as vomiting and rashes on the skin will most likely help determine the causes of liver enlargement. We should also not forget about weight loss and yellowness of the mucous membranes.
After the answer to the question of why the liver is enlarged has been given, it is necessary to understand the problem in more detail and what to do about it.
Treatment
Having found out why the liver is enlarged, treatment for hepatomegaly is required. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the provoking factor. Treatment involves taking medications prescribed by the doctor, diet, and auxiliary therapy using traditional methods.
Drug treatment
The effectiveness of the drugs depends on the nature of the disease and the specific clinical picture. In the early stages, treatment helps relieve symptoms of the disease and restore organ function. In severe cases, medications are used only to maintain liver function (late stages of cirrhosis, hepatosis, hepatitis, cancer).
Groups of drugs used:
- Antiviral drugs (Daklatasvir, Sofosbuvir, Sovriad, Ribavirin)
- Hepatoprotectors (Gepabene, Hepalex, Karsil, Legalon, Silibor)
- Choleretic agents (Allohol, Odeston, Cholenzym)
- Diuretics (Furosemide, Veroshpiron, Oxodolin)
- Enzyme preparations (Pancreazim, Creon, Mezim, Festal)
- Glucocorticosteroids (Beclomethasone)
When treating an enlarged liver, drugs are used whose action is aimed at eliminating toxins and vitamin complexes. Admission is allowed only according to indications. Oncological pathologies are treated with chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
This is interesting: Liver hepatomegaly: what is it and how to treat it?
Folk remedies
When studying the question of why the liver is enlarged, it is necessary to pay attention to an alternative method of therapy - alternative medicine. It is recommended to use them after consultation with a doctor, in the absence of contraindications. It is important to remember that such methods do not normalize the size of the enlarged organ, but they do help normalize its basic functions.
Popular traditional medicine methods:
- Milk thistle meal. Prepared from the seeds of the plant. They should be ground using a coffee grinder until a homogeneous powder is obtained. This remedy is taken 3-4 times a day, half a spoon. In this case, you should drink the meal with water. The course of treatment lasts 40 days.
- Dandelion juice. It is recommended to take it for cirrhosis and fatty hepatosis. The freshly cut plant is crushed, placed in gauze, and squeezed. The resulting juice is taken 2 tablespoons in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Corn silk. To prepare the decoction, add 1 spoon of crushed stigmas to 1 liter of water. The mixture is brought to a boil and simmered in a steam bath for 30 minutes. Then the container with the decoction is infused for 1 hour. Take 100 ml 4 times a day.
- Milk thistle decoction. To protect the enlarged organ from toxins, it is recommended to take a decoction. To prepare, pour 1 spoon of raw material into 500 ml of water, boil, cook until half of the liquid has evaporated. Cool the resulting medicine and drink 20 ml each time before meals. Treatment lasts 1 month.
Diet
During the treatment period, you must follow a diet. The basis of the diet is protein foods and carbohydrates. Fat consumption is kept to a minimum. It is strictly forbidden to eat fried foods, spicy foods, smoked meats, sausages, fatty fish, and dairy products. The daily amount of calories should not exceed 2500 kcal.
It is recommended to include cereals and pasta in the diet. Oats have hepatoprotective properties. It is recommended to use milk thistle oil as an additive to salads. It is important to maintain a drinking regime and avoid alcoholic beverages.
This is interesting: Causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention of splenomegaly
Therapy methods
Treatment of hepatomegaly is most often carried out with the help of medications; in exceptional cases, surgical intervention is possible. To enhance the effect of traditional therapy, it is recommended to use folk recipes based on herbs.
The duration of therapy depends on the stage of the disease and the nature of liver damage. It is important to prevent relapse of the disease if the disease is viral.
The use of medications in the treatment process depends on the type of underlying disease:
- if the body is affected by hepatitis A or B, the use of antiviral medications is necessary;
- antibiotics are used to treat listeriosis and other infectious diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria;
- if echinococcosis is detected, anthelmintic drugs are used;
- if the cause of changes in liver size is a neoplasm, chemotherapy is required;
- for heart failure, drugs from the group of glycosides are used;
- To protect and regenerate damaged liver tissue, hepatoprotectors and essential phospholipids are used, and taking vitamin complexes is also recommended.
Causes of enlargement of the left lobe of the liver
There are three groups of factors that cause changes in the volume and weight of the parenchyma:
- pathologies associated with changes in the functioning of hepatocytes (parenchyma cells);
- chronic or past infectious diseases;
- cardiovascular disorders; with heart failure, blood stagnates, metabolism slows down, and there is cardiac cirrhosis that occurs against the background of myocardial dysfunction.
: Enlarged liver on ultrasound: causes, prevention and treatment
When the left lobe of the liver is enlarged, the cause is determined by general history. A blood test reveals inflammatory processes in the body, liver diseases:
- hepatitis of various nature (alcoholic, toxic, allergic);
- benign neoplasms;
- proliferation of cancer cells due to the left lobe;
- fatty chronic hepatosis (organ degeneration);
- the presence of parasites in the organ;
- atherosclerotic or varicose changes in the vessels of the right and left lobes of the organ.
Metabolic diseases include:
- autoimmune pathologies;
- amyloidosis – a disorder of protein metabolism;
- hemochromatosis is a genetic disease characterized by the accumulation of iron in the body;
- diabetes;
- obesity.
An increase in the left lobe occurs due to toxic lesions, why they occur:
- due to taste preferences for preservatives, prepared with vinegar, fatty, salty foods;
- drinking alcohol, smoking, drug addiction;
- excessive and uncontrolled use of medications, dietary supplements, phytocomponents used in folk medicine;
- exposure to harmful production factors;
- allergy;
- hormonal disruptions during pregnancy, age-related changes typical for men and women after 40 years.
Symptoms
The weight of a healthy liver does not exceed one and a half kilograms. During various pathological processes, the weight of the organ can increase several times, as bile fills the cellular spaces.
If left untreated, connective tissue grows in the cavity and scars form. Clinically, hepatomegaly manifests itself in advanced forms of pathology, when the organ protrudes from the right hypochondrium.
In the initial stages, the disease manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- impaired digestion of food, which manifests itself in the form of nausea and vomiting;
- discomfort in the right hypochondrium;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- violation of the act of defecation;
- loss of appetite;
- apathy;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- change in color of the skin and sclera of the eyes to a jaundiced tint.
Ultrasound diagnosis of liver enlargement
Ultrasound examination is an accessible, safe and informative method that helps to identify changes in size and pathology of the liver parenchyma. To determine the size, the diagnostician measures the lobes of the liver in various sections.
Normally, the main indicators are as follows:
- right lobe 110–140 mm length, 111–125 mm width, up to 150 mm height (VKR);
- left up to 60 mm thickness, less than 100 mm height (KKR);
- total length 140-180 mm, width up to 225 mm;
- sagittal size 90-120 cm.
The diameter and patency of the bile ducts and main vessels are also determined. For the portal vein it is up to 15 mm, and for the hepatic artery up to 6 mm.
There are many reasons why a person’s liver enlarges. Among them are viral parasitic infections, toxic effects, and metabolic disorders. Therefore, after diagnosis, treatment of the disease is carried out in two directions:
- treatment of the underlying pathology;
- restoration of liver cells.
The regenerative function of hepatocytes is increased by prescribing vitamin complexes that cleanse, remove waste, and toxins, substances that stimulate regeneration. Most of them include natural substances, medicinal herbs (milk thistle), and choleretic agents. Dietary nutrition is required.
An enlarged liver is a serious sign that requires medical attention. Any discomfort in the right hypochondrium region needs to be studied, and the most informative and inexpensive method for this is ultrasound. The diagnosis is made based on a combination of signs and test results.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnostics involves a set of procedures aimed at studying and assessing the condition of the organ and identifying precipitating diseases. To find out why the organ is enlarged, laboratory and instrumental research methods are used.
The exact size of the liver can be determined using ultrasound. During the examination, the gland is measured in length, width, and thickness. The contours of the organ and structure are examined. On average, the weight of an adult’s liver is 1.5 kg. Ultrasound can detect diseases, including those of a vascular nature.
For diagnostic purposes the following is also carried out:
- Palpation
- Tomography methods (CT, MRI)
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
- Contrast radiography
- Scintigraphy of the hepatobiliary system
- General and biochemical blood test
- Coagulogram
- Needle biopsy
- Analysis of urine and feces samples
To make and confirm a diagnosis, specific samples and tests are used.