Bile is a yellow-green liquid that is synthesized by hepatocytes (liver cells) and accumulates in the gallbladder. It is involved in the digestion of food in the small intestine. Stagnation of bile in the organs of the biliary system leads to digestive disorders, increased levels of bile acids and enzymes in the blood. Because of this, dangerous diseases arise - cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, cholangitis, etc. Before removing bile from the body, the cause of the pathology is determined. Elimination of provoking factors restores the functioning of organs.
Who needs to remove bile
Removing liver secretions from the body is indicated for people who suffer from obstruction (narrowing) of the bile ducts or catarrhal inflammation of the bladder.
Removing excess bile from the body, even at home, should be carried out under the strict supervision of the attending physician. Traditional medicine in this matter is only an addition to complex treatment, which is always based on drug therapy that helps remove excess fluid from the body.
Conservative and surgical treatment is prescribed for:
- cholestasis;
- cholelithiasis;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- cholecystitis.
Choleretic medications should be taken only after consulting a gastroenterologist. Their irrational use in the presence of stones in the cavity of the bladder is fraught with hepatic colic, exacerbation of calculous cholecystitis, and peritonitis.
Who is indicated for the removal of bile and the use of medications?
Removal of bile from the body is indicated for patients diagnosed with biliary dyskinesia . This is a pathology in which the physiological outflow is disrupted or complicated. Cleansing is also prescribed for chronic inflammatory processes in the liver.
Choleretic drugs are mandatory for people after cholecystectomy - surgical removal of the gallbladder, so that it is not deposited in the liver.
It is strictly forbidden for patients who have stones in the bladder to expel bile on their own. A sharp outflow of fluid can provoke active advancement of stones, which will lead to blockage of the ducts. This condition is dangerous, and if it occurs, it requires emergency surgery.
To effectively expel bile from the body, medications, diet and traditional medicine are simultaneously prescribed.
Choleretic agents
Cleansing preparations help get rid of many negative symptoms. They relieve nausea, bitterness and unpleasant taste in the mouth. Medicines relax the smooth muscles of the bile ducts and relieve their spasm, which helps relieve pain symptoms. After taking the drugs, digestion processes improve and appetite increases .
Preparations:
- Allochol is a product based on dry bile, activated carbon, garlic and nettle. Stimulates the motor activity of the ducts, enhances the production of gastrointestinal enzymes, inhibits fermentation and putrefaction in the large and small intestines.
- Cholenzym – the basis of the drug – is dry bile. Promotes its removal from the liver, improves the functioning of the entire gastrointestinal tract.
- Hologon – irritates liver cells and stimulates the formation of bile. Has a pronounced choleretic effect.
- Ursoliv is a choleretic agent that partially dissolves stones in the bladder and removes cholesterol from the liver and intestines. Indicated for reflux of bile into the stomach.
- Urdoxa - reduces the concentration of cholesterol in bile, stimulates its evacuation from the bladder.
- Choludexan - reduces cholesterol secretion, gradually dissolves stones, promotes the outflow of bile.
Herbal choleretic agents:
- Berberis plus - homeopathic medicine based on berberis.
- Datiscan – Datiscan hemp extract.
- Solaren – curcuma longa extract.
- Travochol - immortelle, tansy, licorice, mint, bird cherry, currant, rosehip.
- Phytohepatol is a herbal mixture that includes marigold, tansy, mint, and chamomile.
- Holagol – turmeric root, mint, eucalyptus.
- Tanacehol is a drug based on tansy flowers.
- Urolesan – urolesan extract, wild carrot fruits, hop cones, oregano, fir and mint oil.
How to expel bile from the gallbladder
With cholestasis, changes occur in the body that cause severe pathologies. To prevent them, they resort to conservative, physiotherapeutic or surgical treatment. The choice of technique is determined by the reasons for the accumulation of bile in the bladder or ducts.
Pharmacy drugs
To restore the functioning of the body and prevent dangerous diseases, drug therapy is prescribed. It includes medications that normalize the outflow of liver secretions into the duodenum:
- Ursohol - accelerates the dissolution of cholesterol, thereby reducing the risk of stone formation in the bladder;
- Hophytol – stimulates the movement of bile through the biliary system, protects hepatocytes from destruction;
- Cynarix – stimulates the restoration of hepatocytes and the secretory activity of the liver in the body;
- Odeston - accelerates the synthesis of liver secretions and its outflow into the intestines, due to which the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is restored;
- Gimecromone - enhances the biosynthesis and promotion of bile enzymes into the duodenum.
The removal of bile from the body has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Patients note normalization of stool, disappearance of pain in the right side and nausea.
To expel liver secretions from the gallbladder, you need to eat right. For cholestasis and dyskinesia, the diet includes:
- vegetables and fruits after heat treatment;
- cereals (buckwheat, oatmeal);
- pumpkin seeds;
- dried fruits;
- herbal teas;
- cashew nuts;
- white crackers;
- vegetable stew;
- dietary meat;
- artichokes;
- cabbage;
- celery;
- corn bran;
- cauliflower.
Choleretic procedures accelerate metabolism in the body, eliminate constipation and symptoms of intoxication.
Home Remedies
Herbal remedies from traditional medicine accelerate metabolic reactions in the body and stimulate the movement of liver secretions into the intestines.
To combat bile stagnation, the following are used:
- Rosehip decoction. 2 tbsp. l. dried fruits are poured into a thermos and 1 liter of boiling water is poured. Leave for 3 hours and drink 100 ml before meals three to four times a day.
- Birch decoction. 10 g of leaves are brewed in 500 ml of water. The strained liquid is taken 150 ml before meals three times a day.
- Phytocollection. Dried peppermint and chopped chicory root are mixed in equal proportions. 10 g of the mixture is poured into 250 ml of water and boiled for 4 minutes. During the day, drink 500-600 ml of decoction.
Folk remedies cleanse the body not only of bile, but also of toxins.
It is recommended to take medicinal decoctions in courses of 2 weeks.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures ensure rapid removal of bile from the body. To combat diseases of the biliary system, the following are used:
- Paraffin and ozokerite applications are a thermal procedure that improves blood flow to the liver and bile ducts. Cleanses the body of toxic substances, restores the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Phototherapy – neutralizes bile pigment, which causes yellowing of the skin. By reducing the level of bilirubin, metabolism is restored.
- Plasmapheresis is a hardware cleansing of the body from poisons contained in the blood. Removes toxic components of bile (bilirubin, cholesterol) from plasma.
Hardware techniques are used only in the absence of acute inflammation in the body.
Physical activity
To stimulate bile drainage naturally, resort to moderate physical activity. Exercise therapy, swimming, fitness, gymnastics, and yoga increase muscle tone in the body and improve blood circulation in the liver. Due to this, the motility of the bladder and the movement of bile acids into the duodenum are restored. They resort to sports activities only in the absence of acute inflammation in the biliary system.
Surgery
If the body cannot cope with the removal of bile on its own, surgical treatment is prescribed. For dyskinesia, cholecystitis and cholestasis, the following surgical techniques are used:
- cholecystodigestive anastomosis - the formation of alternative pathways for draining the contents of the gallbladder into the intestine;
- choledochostomy - continuous removal of liver secretions from the bile ducts using drainage instruments;
- cholecystectomy - excision of the bladder in case of irreversible impairment of its functions.
If bile stagnation is caused by obstruction of the bile ducts, laser or ultrasound destruction (destruction) of stones is resorted to.
When do you need a liver and gallbladder cleanse?
Cleaning the liver and gallbladder at home is a good preventative measure to prevent the formation of stones, inflammation, cysts, and cancer. You can use different cleaning methods to suit your needs.
Impaired bile flow leads to destructive processes in hepatocytes, which is fraught with cirrhosis, intoxication, and liver dysfunction.
Cleaning can be done on the recommendation of a doctor or on your own. It is necessary in cases where the patient is bothered by the following symptoms:
- Excessive pallor or yellowing of the skin.
- Deterioration/loss of appetite.
- Sharp weight loss.
- Sleep disturbance (drowsiness or insomnia).
- Bitterness in the mouth (especially in the morning).
- Lethargy, weakness, constant fatigue for no reason.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Heaviness, pain or discomfort in the right side.
- Skin pigmentation.
- Clarification of feces and urine.
Such symptoms indicate a decrease in the functionality of the liver; it cannot cope with the task of neutralizing toxic compounds, so they enter the blood.
Precautions and contraindications
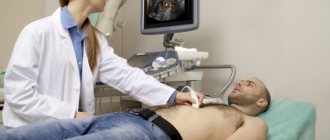
Home cleaning needs to be done carefully. It is recommended to do an ultrasound to assess the condition of the liver, the absence or presence of stones. In the latter case, cleansing will only bring harm; you may end up on the operating table.
Cleansing the gallbladder and liver is not carried out in the following cases:
- Impaired absorption of sugar in the body.
- Lactation, the time of bearing a child.
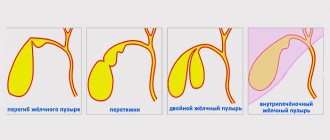
- Congenital inflection of the gallbladder.
- Calculous form of cholecystitis.
- Disorders of the digestive system.
- Chronic pathologies during exacerbation.
- Liver cirrhosis, ascites.
- Infectious and colds, accompanied by an increase in body temperature and a febrile state.
- Parasites in the liver.
In order for the procedure to be painless and give a good therapeutic effect, you need to cleanse the liver and gall bladder correctly, following all the recommendations.
How to remove bile from the body if there is no gallbladder
The secretion secreted by the liver is stored in the bladder, but after its removal it continuously enters the intestine through the bile ducts. Therefore, after surgery, patients are advised to eat frequently, but in small portions.
Regular eating disorders can also lead to bile reflux. As a rule, this phenomenon is observed in lovers of physical activity immediately after eating.
After cholecystectomy, the removal of bile from the body is ensured by the sphincter of Oddi, which is located between the duodenum and the bile duct. It opens when food enters the small intestine. This ensures that bile also enters the intestine.
Many patients have a question about why they need to take choleretic drugs after cholecystectomy. The organs of the biliary system do not always function without failures. If the contractile activity of the sphincters is impaired, medications help remove bile from the body:
You need to take choleretics in the dosage prescribed by your doctor. Drug abuse disrupts digestion, which causes abdominal pain, flatulence, loose stools, dehydration, weakness, etc.
How to understand that bile has begun to come out
Stagnation of bile leads to digestive disorders and the appearance of the following symptoms:
- bitterness in the mouth;
- fast saturation;
- pain in the right side;
- flatulence;
- frequent constipation;
- stool discoloration;
- fast fatiguability;
- yellowness of the skin;
- lack of appetite, etc.
Some of the bile components leave the body in the urine, so it acquires a dark brown tint. When the functioning of the biliary system is restored, the symptoms disappear completely or partially. If bile leaves the body, this is indicated by:
- regular bowel movements (once every 1-2 days);
- no pain in the side;
- increased appetite;
- no gas formation;
- improved mood;
- reduction of yellowness of the skin.
The results of choleretic therapy appear within 1-2 weeks. If the cause of cholestasis is not addressed, symptoms will return. For bile duct dyskinesia, cholecystitis and cholestasis, it is recommended to repeat the course at least once every 3-4 months. Periodic cleansing of the body prevents complications and the need for surgical intervention.
Are there any specific features of collecting urine for analysis?
When collecting urine, general requirements should be met:
- mandatory hygiene of the external genitalia;
- Only the average portion of morning urine is suitable for research;
- the container with urine should not be stored for more than two hours, there is no need to leave the transparent jar in the light;
- 50 ml is enough for analysis.
Bile pigments in urine are involved in the metabolism of important organs and the hematopoietic system. Their determination in urine plays a significant role in diagnosis.
Source: 2pochki.com
The most interesting:
Who is prohibited from performing cleansing?
Accelerating the outflow of bile with pharmaceuticals and physiotherapeutic procedures has its contraindications. Taking medications and stimulating the synthesis of bile enzymes puts a strain on the liver and reduces the concentration of antioxidants in it. Because of this, dystrophy of the liver tissue and associated complications occur.
Overeating, excess body weight, chronic pancreatitis - all this affects the secretion of gastric juice and the production of bile secretion.
Taking cholekinetics is contraindicated in case of stone formation and certain gastrointestinal pathologies. Therefore, doctors do not advise resorting to cleansing the body when:
- pancreatitis;
- obstruction of the bile ducts;
- calculous cholecystitis;
- duodenitis;
- acute kidney inflammation;
- cholelithiasis;
- diarrhea;
- cholangitis;
- acute hepatitis;
- suppuration of the gallbladder;
- liver inflammation;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
Treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies with medications is prescribed only by a gastroenterologist if indicated. It is not advisable to take choleretic tablets to prevent diseases without the knowledge of your doctor.
- How to remove bile from the stomach
- How to treat bile stagnation
- Why can there be bile in the stomach?
- Wormwood tincture, honey, plantain, immortelle herb, thyme herb, St. John's wort herb.
- how to expel bile from the body
- - examination by a gastroenterologist-hepatologist;
- - a course of treatment prescribed by a doctor;
- — dietary food;
- - repeated examinations.
- how to get rid of bile reflux into the stomach
- bear bile tincture
- - immortelle flowers, coriander fruits, watch leaves, mint leaves;
- - angelica roots, buckthorn bark, mint leaf, caraway fruits, sage leaf;
- - sunflower oil;
- - carrot juice, celery juice, parsley juice;
- - Dill seeds.
- bile how to treat it
Stagnation of bile leads to the development of cholelithiasis. How to remove bile from the body using folk remedies and medications if there are functional disorders. We will also analyze the causes and symptoms of the disease that contribute to cholestasis in pregnant women.
When is the level of bilirubin in urine impaired?
Unconjugated bilirubin appears in the blood in liver diseases:
- viral hepatitis;
- toxic hepatitis due to poisoning with toxic substances (medicines);
- severe consequences of allergies;
- cirrhosis;
- oxygen hypoxia of liver tissue in heart failure;
- metastatic damage to cancer cells from other organs.
But it does not pass into urine due to the impossibility of filtration. Only in the case of renal and hepatic failure with destruction of the nephron membrane can it be detected in urine.
These same diseases are accompanied by the accumulation of conjugated bilirubin. Its level in the blood determines the degree of damage to the liver tissue. The “renal threshold” for bilirubin is considered to be a level of 0.01-0.02 g/l.
If the liver function is not impaired, but the outflow of bile into the intestines is hampered, then a significant amount of conjugated bilirubin enters the blood and its excretion in the urine increases accordingly. This variant of pathology develops when:
- cholelithiasis;
- compression of the bile duct by a tumor of the head of the pancreas or swelling in acute pancreatitis.
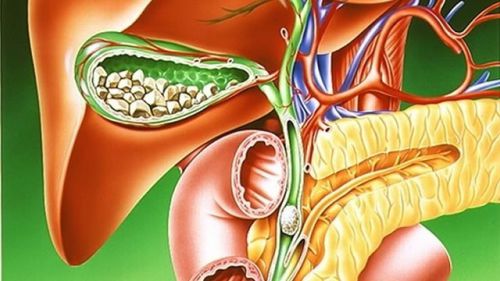
Impaired bile outflow leads to high levels of bilirubin in urine
Protein in urine with pyrogallol red
Bilirubinuria occurs as a result of a slow flow of bile in the interlobular ducts (cholestasis), leakage of bile into the blood vessels. The patient is expressed in yellowness of the skin and sclera. The type of jaundice (mechanical or parenchymal, subhepatic or hepatic) is determined by the ratio of free - bound bilirubin in the blood and urine.
An important distinguishing feature of hemolytic conditions is the absence of bilirubinuria.
Reasons for the formation of bile stagnation and why it is dangerous
One of the functions of hepatocytes is the synthesis of bile, a fluid that helps digest food. The mechanisms of its formation, promotion and outflow must be clearly regulated, otherwise bile stagnation processes develop, ending in some cases with the intervention of a surgeon.
Produced in the liver, through ducts, bile enters the gallbladder, where it is stored until it needs to be used by the duodenum. The first portion is called “liver”, after leaving the bladder - “mature”, “vesical”. In 24 hours, the liver of an adult produces about 2 liters of this fluid.
It contains:
- bile acids (primary and secondary);
- bile pigments;
- cholesterol;
- phospholipids;
Potassium and sodium ions are present, as a result of which it is alkaline in nature.
Consequences of bile stagnation
Bile secretion is a physiological fluid that performs one of the important digestive functions. Bile plays a key role in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the cavity of the small intestine. Bile is produced by the glands of the liver structures, and is stored and accumulated in the gallbladder. If there is indigestion, inflammation of the stomach or parts of the duodenum, then bile stagnation occurs, leading to the following consequences:
- development of chronic cholestasis;
- cholecystitis;
- stone formation in the gland ducts;
- exacerbation of cholangitis.
Related Article: Breaking News: Chronic Kidney Disease Is Near Here
Biliary stasis is especially dangerous for young children due to the body’s inability to reflect pathological symptoms. Almost all disorders in the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract lead to the development of chronic diseases. Against the background of cholestasis, there is a violation of the acid-base balance, and the result may be the formation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites), inflammation due to the pathogenic activity of bacterial microflora.
Note! Persistent prolonged stagnation can lead to the death of hepatocytes - liver cells and partial localized necrosis of the parenchymal layer of the liver.
How can stagnation develop?
The movement of bile along physiological pathways ensures its entry into the duodenum. Here it is completely spent on the breakdown of food eaten and undergone gastric digestion. However, under the influence of certain factors, the process pattern changes. As a result of this it is possible:
- Movement of bile in the opposite direction and throwing it into the stomach (duodenogastric reflux).
- Stagnation in the gallbladder or canals.
The reasons for the first option are as follows:
- the duodenum is not able to accept bile due to compression of the ducts (for example, a tumor, hernia, mechanical damage, a growing fetus during pregnancy);
- the functioning of certain gastric valves is impaired;
- bad habits, non-compliance with diet (a lot of bile is produced at once and its excess is directed in the wrong direction).
Stagnation of bile in the gallbladder or biliary tract is often caused by a violation of its rheological properties (thickening) with subsequent stone formation, as well as a decrease in the motility of the smooth muscle fibers through which it moves.
How does bile enter the stomach?
Bile is involved in the digestive processes that occur in the duodenum. Therefore, part of this biological fluid, after being produced in the liver, immediately goes there. And the other part enters the gallbladder, which serves as a reservoir for additional bile needed by the duodenum.
The entry of bile into the stomach is prevented by the operation of special valves. Due to the influence of various factors, their functioning may be disrupted. And then a serious disease arises - duodenogastric reflux (DGR). Normally, it is present in healthy people, but if GHD exists for a long time, then we can talk about pathology.
The causes of valve malfunction may be:
Junk food
- Poor nutrition. An abundance of fatty, spicy foods causes increased production of bile, which subsequently cannot be stored in the gallbladder and is released into the stomach. This phenomenon can also be the result of eating spoiled foods.
- Violation of food rules. After a hearty lunch, you need to rest a little; you shouldn’t exhaust yourself with exercise. Due to intense physical activity on a full stomach, the valves cannot function normally, because... are subjected to strong pressure, and bile enters the stomach.
- Bad habits. Regular drinking and smoking can cause increased bile production, which also impairs the functioning of the valves.
How to get appendicitis: what causes the disease to develop
The entry of bile into the stomach has a detrimental effect on the condition of the mucous membrane: bile acids “corrode” it, which can subsequently lead to various inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of bile stagnation are formed as a result of functional digestive disorders. When bile is in the stomach, patients complain of epigastric pain, bitter-tasting belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, and deterioration in general condition. Bile has an alkaline environment.
Entering the “acidic” environment of the stomach, it triggers neutralization processes, which end in the formation of gases.
Heartburn and flatulence appear. The tongue becomes yellow. Subsequently, inflammation develops, accompanied by intoxication.
Fluid retention in the gallbladder is the first step to the development of cholecystitis, which is also painful, often paroxysmal. Due to the fact that bile ceases to participate in digestion, the digestion of incoming food occurs with defects, and the absorption of nutrients is impaired.
Patients note constipation, incomplete cleansing of the intestines, which also leads to intoxication and the development of pathogenic non-specific microflora.
Symptoms of the disease
Excess bile in the stomach is characterized by certain symptoms that can be independently identified:
Stomach pain
- Belching. Having accumulated in the stomach, bile begins to interact with gastric juice, which leads to the formation and release of gases. As a result, heartburn may occur, and a yellow coating may appear on the tongue, because... bile has a yellowish color.
- Stomach ache. Bile has an irritating effect on the walls of the stomach, which can cause severe sharp pain in the epigastric region associated with inflammation.
- Diarrhea and vomiting. Bile acids exhibit toxic effects in the stomach, so the body strives to remove this biological fluid as quickly as possible.
- Bloating and feeling of heaviness. Prolonged presence of bile in the stomach causes the formation of gases, as a result of which the patient suffers from flatulence.
These symptoms not only cause severe discomfort, but can also lead to more serious illnesses.
Stagnation of bile during pregnancy
Pregnant women may suffer from bile stagnation. The risk factors in this case are: physical inactivity, emotional imbalance, and simultaneous consumption of large amounts of food.
Due to the penetration of bile into the tissues and blood, the development of cholecystitis in pregnant women is accompanied by:
- itching, especially at night, of the palms and soles;
- darkening of urine;
- dry skin;
- sleep disorders;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes;
- the appearance of frequent and slightly loose stools.
Such disorders can be caused by alcohol consumption, viral diseases, chemical intoxications, and long-term use of certain medications. Cholestasis in pregnant women can occur in extrahepatic or intrahepatic types. Only a doctor can make a reliable diagnosis of the condition based on the results of examination and laboratory tests. The most likely period for making a diagnosis is after 2-3 weeks.
What to do in this case The described condition is an indication for the prescription of hepatoprotectors and glucocorticosteroids. In addition, rifampicin and ursodeoxycholic acid are prescribed (to relieve itching).
If extrahepatic cholestasis is diagnosed, regular radiation is used. In addition to specific purposes, plasmapheresis and blood purification from toxins - hemosorption - are used. Compliance with the prescribed diet and food intake is important.
Ways to remove excess bile from the body
When bile is thrown into the stomach, you can try to remove it mechanically. To do this, it is recommended to drink at least a liter of clean water in small sips.
The second method is washing the common bile ducts. One tablespoon of magnesia powder is dissolved in a glass of boiling water and left overnight. Drinking it at once, you need to lie down for an hour and a half, placing a warm heating pad under your right side.
Washing out bile can be done not only with water, but also with decoctions. This, in addition to mechanical leaching, enriches the body with vitamins and other useful components contained in natural plants. Suitable:
- rose hip;
- goji root and roadside grass (1:1);
- fruits of pharmaceutical dill;
- bitter Chernobyl and peppermint leaves;
- Sandy goldenflower herb.
The decoction is prepared according to a typical scheme: 25 g of crushed raw materials are poured with a liter of boiling water. Leave for a day (preferably in a thermos). The recommended intake is a third of a glass twice a day before meals.
During treatment, it is important to avoid heavy physical activity, rationally organize your daily routine, get rid of bad habits, and establish regular meals.
Surgical intervention
There are also surgical methods for treating bile stagnation. Among the most relevant:
- cholecystectomy (complete removal of the gallbladder);
- partial removal of its wall (if there is a tumor or compaction on it that caused stagnation);
- installation of special dilators in the bile ducts (if there is a decrease in the lumen, which was the cause of obstruction);
- drainage of bile ducts;
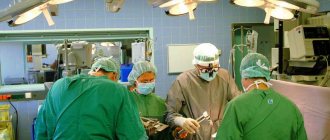
Surgical removal at the initial stage of the process can be done endoscopically. In this case, only a puncture is made on the skin into which special equipment (endoscope) is inserted. Removal control is carried out via a monitor, which displays an image of all actions on the internal organs. This is a laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
The second option for the operation is a cavity incision and removal using a laparotomy method. This method is good because it performs a complete audit of all nearby organs.
How to remove bile using tablets
Treatment of bile stagnation is also carried out with the help of medications. In this case, tablets are used for:
- cleansing the stomach;
- increased tone of gastric valves;
- normalization of the pH of the gastric environment;
- relieving signs of inflammation;
- relief of attacks of spasms;
- providing a choleretic effect.
Medicines prescribed:
- motilium;
- Maalox;
- no-shpa;
- papaverine;
- essentiale (or hepagard);
- ukrliv.
In each case, therapy is selected individually, taking into account concomitant diseases, allergy status, life history and illness.
Using herbs at home
Herbs are also of great importance in the home treatment of cholestasis. By selecting the right raw materials and preparing infusions or decoctions from them, ensure their regular use. Courses of such treatment can be carried out twice a year.
Recommended raw materials:
- dandelion;
- femoral rose;
- immortelle;
- red grass;
- mature birch leaves;
- calamus root;
- milk thistle;
- sagebrush;
- strawberry leaves;
- kolob;
- thistle.
The course of treatment can be up to three months.
Preparation of the decoction: 2 tablespoons of a mixture of crushed plants are poured with half a liter of boiling water and left for 15-20 minutes in a container covered with a lid. Strain and take after meals.
Bile removal from mineral water
It is useful to establish the function of bile secretion and flush the stomach with the help of special mineral waters. Hot magnesium sulfate and hydrocarbonate options are recommended.
Important: to make the effect more noticeable, drink water on an empty stomach, warm, in small sips. It is better to drink in two doses with an interval of 15 minutes. While drinking, you need to lie on your right side and place a heating pad under the bladder area. Under no circumstances should you drink alcohol or smoke during this treatment.
It is recommended to drink water for no more than one month, so as not to disturb the natural water-mineral balance of the body.
How to remove bile from the body
Home → Treatment of diseasesThe main purpose of bile is that it takes an active part in the digestion of food. Normally, the main location of bile in the body is the gallbladder. However, if digestion is impaired, bile can penetrate into the stomach and cause damage to the gastric mucosa. This is manifested by heartburn, pain in the upper abdomen, belching, nausea, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, a yellow coating on the tongue, and sometimes even vomiting with bile. If you have such symptoms, you need to seriously think about how to remove bile from the body, but first you should determine the cause.
The most common reason is improper diet. First of all, this means filling your stomach to capacity during a holiday dinner, as well as overeating at night. You should not consume food and drink at the same time, abuse alcohol, or exercise after eating - all this leads to disturbances in the normal digestion of food.
In case of digestive disorders, stagnation of bile often occurs in the gallbladder, which can cause various inflammatory processes, leading to acute or chronic cholecystitis, gastritis, pancreatitis, and the formation of stones. Therefore, if the above symptoms appear, you must consult a doctor and undergo a full examination of the digestive system, after which the doctor will prescribe treatment.
First of all, medications are prescribed to remove bile, for example, Atropine, Choleritin, Magnesium Sulfate, etc., which depends on the diagnosis. The dosage and order of administration must be prescribed by the doctor. In addition to drug therapy, you can use traditional medicine. You can remove bile at home using folk remedies in the following ways:
- Rinsing the bile ducts - in the evening, dilute 1 dessert spoon of magnesia in a glass of hot water, let it brew overnight, and drink it in the morning, lie on your right side, place a heating pad under your right side and lie there for an hour and a half, this helps remove bile.
- You should eat food in small portions, but often. You can't overeat before bed.
- Products that remove bile - citrus fruits, greens, tomatoes, white cabbage, corn, spinach, celery, fruit and vegetable juices, avocado, olive and sunflower oil, chicory tea. Beetroot – It is recommended to consume 150 g of raw beets on an empty stomach. It is necessary to exclude fatty, spicy foods, mushrooms, alcoholic drinks, cola, limit flour dishes, mayonnaise, and rich broths.
- Decoction - take mint, sage, caraway leaves, buckthorn bark in equal proportions, pour boiling water over it, let cool. Take the decoction 1/2 cup 3 times a day.
- Infusion of St. John's wort - pour 10 g of St. John's wort into 1 glass of boiling water, leave for a couple of hours. Take 1/3 cup before meals 3 times a day for 1.5 months, the next day make a new infusion.
- Vegetable oil - take 1 teaspoon 3 times a day for 10 days.
- Infusion of immortelle - pour 1 tablespoon of the herb into 1 cup of boiling water, leave for a couple of hours, add another 250 ml of boiled water, drink 1/2 cup 2 times a day before meals.
Do not forget that you can use traditional medicine recipes only after consultation with your doctor. Folk remedies for removing bile can only be used as an addition to the main treatment, but not to replace it.
Additional articles on this topic:
How to remove lactic acid
How to remove potassium from the body
Proper nutrition and products to remove excess bile
Without a therapeutic diet, it is difficult, almost impossible, to cope with bile stagnation. This nutrition is aimed at reducing the viscosity of bile. It is recommended to take food in small portions.
Diet characteristics:
- not be too high in calories;
- quickly and easily digested;
- contain most natural products and not be saturated with preservatives or artificial taste improvers;
- have a balanced nutritional composition;
- exclude sour natural juices, fatty fried and smoked foods.
It is allowed to eat pasta, cereal or vegetable based soups, lean meat, fish, eggs, honey, jelly and compotes.
The following have a bile-liquefying effect: carrots, olives, avocado, dill, spinach leaves, corn oil, celery, whole grain porridge, bran, especially oatmeal. Also useful: grapes, watermelon, turmeric, rhubarb, beets.
Prevention measures
Prevention of cholelithiasis consists of a healthy lifestyle, uniform physical and mental activity, rational nutritious nutrition, getting rid of bad habits, strengthening the body's defenses, and combating physical inactivity. It is also important to undergo timely medical examinations and monitor your health.
Christina 36 years old, Vologda
I had a problem with stagnation of bile in the body, and if I didn’t eat, a bitter taste would appear in my mouth. Pumpkin oil helped very well, or you can take gelatin capsules based on pumpkin seeds. This product contains various biologically active additives, unsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, and carotenoids. I took 4 capsules after meals, three times a day, for one month. The average price of a bottle of oil is 100 ml. 750 rub. Gelatin capsules “Tykveol” 450 mg. 50 pieces per package 350 rub.
People suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract often ask doctors how to neutralize bile in the stomach.
This is a physiological state of the body, accompanied by extremely unpleasant sensations. In this case, the person feels a particular bitterness in the mouth and discomfort in the upper abdomen.
Experts call this phenomenon duodenogastric reflux. Appears as a result of the reverse flow of bile from the duodenum into the stomach.
How is urobilinogen formed?
Urobilinogen is a product of the subsequent processing of bilirubin in the intestine by:
- mucosal enzymes;
- bacteria.
More modern data indicate the presence of urobilinogen bodies, which include derivatives:
- mesobilirubinogen,
- i-ypobilinogen,
- urobilinogen IX a,
- d-urobilinogen,
- "third" urobilinogen.
The last two types and stercobilinogen are synthesized in fairly small quantities and are of no diagnostic value.
The formation of urobilinogen from conjugated bilirubin occurs in the upper part of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. Some researchers believe that it is synthesized by cellular dehydrogenase enzymes in the gallbladder with the participation of bacteria.
A small part of urobilinogen is absorbed through the intestinal wall into the portal vein and returns to the liver, where it is completely broken down. The other is processed into stercobilinogen.
Further, through the hemorrhoidal veins, these substances can enter the general bloodstream and are excreted into the urine by the kidneys. Most of the stercobilinogen in the lower intestine is transformed into stercobilin and excreted in the feces. This is the main pigment that provides color to feces.
The normal level in urine is considered to be no more than 17 µmol/l. If urine is briefly exposed to air, urobilinogen is oxidized by oxygen and converted into urobilin. This can be seen by color:
- urobilinogen is a colorless substance, fresh urine has a straw-yellow tint;
- after some time, due to the formation of urobilin, it darkens.
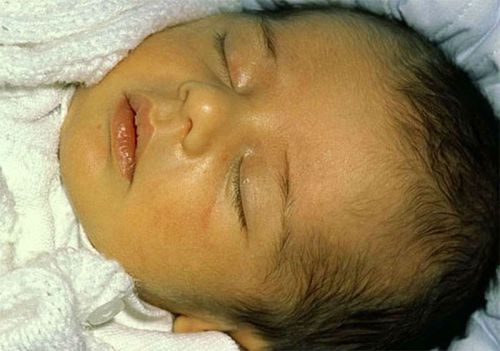
Jaundice in newborns is associated with increased breakdown of red blood cells and the transition to their own hematopoiesis
Properties of secretion
Bile is a special liquid of greenish, yellow or light brown color. It has a specific smell and bitter taste. It is produced by liver cells.
During normal functioning of the digestive system, bile accumulates in the gallbladder. The main function is digestive. Additionally takes part in the excretory system.
A few more important properties:
- assistance in the absorption of vitamins and microelements;
- breaks down foods, processes fats;
- destroys pathogenic bacteria that come from food;
- eliminates rotting processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
If there are any gastrointestinal disorders in the body, then the secretion goes straight into the stomach. However, disturbances can also occur in other body systems. This is discussed in more detail in the next paragraph.
Normally, digestion works to move food down the esophagus. Reverse movement is prevented by the sphincter muscles. If for some reason their functioning is impaired, the patient experiences reflux.
This often occurs after surgery to remove the gallbladder. Since it is a “vessel” for filling with bile, in its absence the secretion stagnates, the outflow is disrupted, and penetrates the stomach.
This reason is the most common, but there are others:
- Bad habits – smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Drink plenty of water during meals.
- Various formations near the intestines: tumors, hernias, polyps. They create pressure on the duodenum, causing bile to flow back.
- Poor nutrition. Eating unhealthy foods that are difficult to digest (fatty, salty, fried). The body begins to intensively secrete secretions to process food. As a result, the bladder overflows and excess bile is released into the epigastrium.
- Excessive workload, as well as sleeping immediately after a meal.
- Pregnancy. In the final stages, the uterus begins to enlarge and compress the internal organs of the abdominal cavity.
- Long-term treatment with drugs that relieve muscle spasms. They relax the muscles, including the sphincter.
- Inflammatory processes in the abdominal area.
- Hereditary factor.
Sometimes reflux can be triggered by a stressful situation. In this case, the phenomenon passes quickly, which means there is no reason to worry. Regularly recurring symptoms should prompt a person to seek help from a doctor.
Typical symptoms
Classic symptoms of bile reflux into the epigastrium:
- pressing pain under the ribs, may be vague, “blurry”. The severity depends on the degree of damage to the mucous membrane;
- heartburn;
- discomfort in the chest;
- belching;
- nausea, gag reflex;
- yellowish coating on the tongue;
- fetid “sourish” breath (especially noticeable on an empty stomach).
The caustic liquid can rise higher, entering the oral area. At the same time, a characteristic bitterness is felt.
The gastric mucosa and its microflora suffer from the too aggressive effect of bile acids on the walls. Therefore, the disease must be eliminated as soon as possible.
Diagnostics
Having noticed the first symptoms, a person should not self-medicate. This can only worsen the situation, so you should not delay contacting a medical facility for too long.
When you see a doctor, you will undergo several diagnostic tests so that the doctor can make the correct diagnosis and provide adequate therapy.
- Ultrasound examination of the gastrointestinal tract. The study allows you to identify the presence of stones, cystic and other formations.
- Radiography. This diagnostic method allows you to assess the condition, functioning and location of internal organs. Before the procedure, the patient needs to drink a contrast agent.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). A small camera is inserted into the esophagus. The doctor looks at the monitor and identifies any defects in the digestive system. It is possible to collect biological material: gastric juice, bile. If circumstances so require (the doctor makes a decision on an individual basis).
Treatment of the disease
If attacks occur rarely (once every 2 months), then there is no need to resort to radical measures. All bad habits are eliminated and the patient’s diet is normalized.
If there are other diseases that contribute to the reflux of bile, then 2 main principles of treatment are applied: eliminating symptoms and normalizing the outflow of bile.
Drug treatment
When treating pathology with medications, they use medications that relax smooth muscles, suppress mucous secretion, and improve the structure and motility of the bladder.
To stimulate the gastrointestinal tract, take the following tablets:
They activate digestion, accelerating the movement and excretion of feces. This cleanses the entire system.
The aggressive effects of hydrochloric acid are alleviated by antacids (Nexium, Maalox, Almagel). With their help, the pH balance of the microflora is normalized due to their effect on the secretory glands.
When there is a lot of bile, it is neutralized with ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk). The chemical substances included in its composition pass into a water-soluble form directly in the stomach, from where they are excreted from the body.
Pain syndrome is relieved with antispasmodics (No-spa).
Surgery
Gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by the release of bile often require surgical treatment. Modern medicine has reached a high level, so there are gentle treatment methods that avoid serious injuries:
- Laparoscopy . The operation is performed through a small hole with a diameter of no more than one and a half centimeters. The surgeon makes several punctures in the abdominal cavity. Next, an instrument and a probe with a camera are inserted. In most cases, patients tolerate this type of surgery well. Recovery occurs under the supervision of doctors. The necessary medications and procedures are prescribed. Seams are inspected regularly.
- Laparotomy . If it is impossible to carry out the operation described in the previous paragraph, doctors resort to this method. In this case, it is possible to remove the diseased organs. The risk of complications is high, rehabilitation is long. Medications are prescribed and physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out. Inspection and treatment of seams is carried out more often and more thoroughly.
Folk remedies for neutralizing bile
Traditional medicine can also be effective in combating large amounts of bile in the stomach. The main thing is to consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Prescriptions are prescribed that can drive away excess bile from the epigastrium, relieve pain and neutralize unpleasant bitterness in the oral cavity.
You can eliminate pain with a decoction of rowan or rosehip. At the same time, combining them with herbal infusions (birch, dandelion leaves, immortelle).
To cleanse the stomach, it is recommended to drink a decoction of flax seeds. The walls of the stomach are strengthened. To prepare it, you need to grind the seeds and pour warm water over them, leave to swell for a while. The resulting porridge is eaten for breakfast.
To eliminate the unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth, just drink a couple of glasses of warm boiled water. Thus, the gastric mucosa is cleansed and bile is removed.
If stagnation appears in the upper parts of the digestive tract, propolis is used. 10 grams should be dissolved in ½ glass of vodka, left for 3 days and strained. Take 60 drops half an hour before meals.
Ways to get rid of bile in the stomach
After examining and determining the cause of reflux, the doctor will tell you how to get rid of bile in the stomach at home. For this, a special diet, a course of medication, and folk remedies are prescribed.
Drug treatment
Conservative therapy consists of taking the following groups of drugs:
- Selective prokinetics, for example, Motilium and Cisapride tablets. Normalizes the process of digestion and cleansing. Medicines help clear the stomach of bile naturally. In addition, the drugs of the group help improve sphincter tone.
- Antacids such as Almagel suspension and Maalox tablets. They normalize the acidity of the stomach, neutralizing the negative effect on the walls of the bile organ.
- Drugs that reduce the negative effects of reflux, for example, Ursofalk capsules. The medicine makes bile components water-soluble. This reduces the aggressive effects of liver secretion acids and relieves the symptoms of reflux.
When it is impossible to cure the pathology with medications, the patient is prescribed surgery.
You can take any medicine only after consulting your doctor. Uncontrolled use of drugs can aggravate the situation and contribute to the occurrence of pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract.
Use of folk remedies
If bile is thrown into the stomach once, a person can cope with the problem on his own. It is enough to drink several glasses of water in small sips. The liquid will wash away bile from the walls of the stomach.
If reflux is observed constantly, folk remedies will help remove bile from the stomach:
- Tincture of barberry and chicory roots. You can buy them at the pharmacy or prepare them yourself. Both components are taken in equal quantities and mixed. Two tbsp. l. raw materials are poured into 1 liter of boiling water and infused under a tightly closed lid overnight. In the morning, strain the infusion and take 70 ml before meals. The course of treatment is from 2 to 3 months.
- A decoction of yarrow, peppermint, wormwood, and immortelle. Herbs are taken in equal quantities and mixed together. Two tbsp. l. raw materials are poured with 2 cups of boiling water and kept in a water bath for 5 minutes. Afterwards, the decoction should sit for about 10 hours. Drink 70 ml of the product half an hour before each meal. If desired, you can add honey to the broth.
- A decoction prepared from 3 tbsp. l. rose hips, 3 tbsp. l. corn silk, 2 tbsp. l. pharmaceutical chamomile and dill seeds, birch leaves, aspen bark, taken 1 tbsp. l. The ingredients are ground in a blender to a powdery state. Two tbsp. l. Add 1 liter of boiling water to the prepared mixture and leave for about 12 hours. The most convenient way to do this is in a thermos. Take the drug several times a day, immediately before meals.
If you take the medicine regularly, this will not only help you get rid of unpleasant symptoms, but also prevent the process of bile reflux into the stomach in the future.
Diet
Regardless of what treatment is carried out (medication or using traditional medicine), it is important to follow a special diet. You need to eat fractionally, in small portions.
Additionally, the following rules are followed:
- do not overeat and sit down at the table only with a feeling of hunger;
- reduce the serving size to a minimum (about 200 g);
- exclude from the diet harmful foods that stimulate the process of bile formation (fatty, fried, smoked, salty, alcohol).
The diet should be based on foods that promote normal digestion, for example, cereal porridge, kefir, jelly, fresh and also boiled vegetables and fruits.
In itself, the reflux of bile into the stomach is not an independent pathology, but only a symptom of disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, in order to completely get rid of reflux, it is important to identify and eliminate the cause of its occurrence.
Complications
If the phenomenon is constant and prolonged, then this becomes fraught with serious consequences.
Complications of the pathology include:
- development of stomach ulcers;
- reflux gastritis - develops with inflammation of the gastric walls;
- gastroesophageal disease is also characterized by inflammation and damage to the walls of the organ. In this case, its contents end up in the esophagus. This can cause Barrett's syndrome, which is considered pre-cancer.
Dietary recommendations
A proper diet serves both as a way to eliminate symptoms and as an excellent prevention of the disease.
- Eliminate products that enhance secretion.
- Drink enough water, but do not wash down your food in the process.
- The dish should be warm, and in no case hot or cold, so as not to irritate the mucous membranes.
- It is better to boil or steam.
- Eating small meals frequently.
Products should be selected based on standard rules of healthy eating (nothing fatty, spicy, sweet, etc.)
Pathology requires mandatory and thorough diagnosis. Timely seeking medical help, further compliance with the treatment plan and the recommendations of the attending physician will help you recover quickly, and if a complete cure is not possible, then reduce the manifestation of symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.