Stomach neurosis (gastroneurosis) is a recurrent psychopathological condition of the digestive organs, manifested by a complex of symptoms of a functional dyspeptic disorder and arising due to a violation of nervous regulation. Gastroneurosis occurs to one degree or another in every fourth adult representative of the human population, but the occurrence and progression of pathology is also possible in children.
Subjectively, gastric neurosis has the same symptoms as other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which can make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis and delay treatment. Optimal correction of gastroneurosis at any age includes not only drug treatment, but also auxiliary physiotherapy, diet therapy, spa treatment and psychotherapy (in the case of a burdened neurotic history).
What is gastric neurosis
Gastroneurosis is an inorganic dysfunction of the stomach and the initial parts of the small intestine and, according to pathomorphological criteria, is a somatoform disorder of the autonomic nervous system.
With gastroneurosis, the morphological structure of the organ does not change
The main feature of neurotic gastric dysfunction is the absence of structural and organic changes in the epithelial lining of the stomach. This means that the patient experiences most of the symptoms characteristic of functional dyspeptic stomach disorders (epigastric pain, nausea, loss of appetite, stomach discomfort). Gastric neurosis is also called “pseudo-ulcer syndrome” and “non-ulcer functional dyspepsia.”
The mechanism of development of the pathogenetic reaction in response to stress factors (including physical stress) is usually represented by the following changes:
- Increased tone of the sympathetic nervous system.
- Slowing down parasympathetic transmission.
- Activation of the effects of the paired vagus nerve, which runs from the brain to the abdominal organs and is responsible for the functioning of the organs of the head, neck, chest and peritoneal space.
The main mediator of somatoform gastric dysfunction is stress. In response to the influence of stress factors (both emotional and physical, for example, prolonged fasting), the most important processes necessary to maintain human life are disrupted.
With gastroneurosis, the contractility of the muscles that move partially digested food (chyme) into the intestines for further processing is impaired. The secretion of the main components of gastric juice changes naturally: enzymes, pepsin, hydrochloric acid, etc. This leads to indigestion, retention of the food bolus in the stomach cavity and the emergence of a typical symptom complex of functional dyspepsia of inorganic origin.
Note! A stress factor itself can provoke monofocal inflammation of the epithelial lining of the stomach, since in response to stress the body increases the synthesis of prostaglandins, mediators of inflammation.
Preventive measures
Of course, it is impossible to predict the occurrence of the disease.
Someone is predisposed to gastrointestinal ailments, but will never encounter stomach neurosis. And some people have enough health for ten people their entire life, but suddenly, overnight, an illness changes the person beyond recognition, plunging him into the abyss of pain and suffering. General preventive recommendations for all people:
- normal balanced nutrition - varied, on schedule (it is easier for the stomach to cope with material that comes in doses);
- do not forget to drink 1.5-2 liters of water daily (in addition to soups);
- priority food is boiled, stewed, steamed (smoked, fried and over-salted are undesirable);
- physical activity (guarantees proper blood circulation and oxygen supply to all cells of the body, including the digestive system);
- consciously avoid stress, accept the realities of the day with wise fortitude, a strong-willed decision to avoid neurotic reactions to negative events.
It is advisable to prevent the disease in advance, because fighting it will take up your energy and your time. Love yourself, take care of your body not only on a physiological, but also on a mental and mental level. Then the disease is guaranteed not to affect you.
Causes and predisposing factors
Gastric neurosis, that is, inflammation of the gastric mucosa not associated with Helicobacter pylori bacteria, is considered by many experts to be a borderline somatoform disorder that requires complex gastroenterological and psychotherapeutic correction. The disease can occur at any age.

Groups of people most susceptible to gastroneurosis
The maximum risk group includes women, as the most vulnerable category of patients in terms of emotional lability. The second category at risk is children of primary preschool and school age, who often experience stress due to difficulties with social adaptation when entering kindergartens and schools.
Chronic neurotic dysfunctions of the stomach in most cases occur in individuals with various types of psychopathologies. Such patients often experience feelings of irritation, anger, and sudden attacks of aggression.
In children, risk factors include asthenic syndromes, autism, and various neurotic disorders. In infancy, possible manifestations of gastroneurosis can be provoked by the syndrome of traumatic shaking of the child.
Causes of neuroses
Among patients with diagnosed neuroses, there are more women; the average age of patients is 35-37 years. In the group of people suffering from gastrointestinal disorders due to psychosomatic problems, three areas are distinguished:
- neurosis-like disorders;
- neurotic fixation of the pathology of the digestive system;
- neurotic disorders.
Since a clear mechanism for the formation of systemic neuroses has not yet been identified, that is, there is no obvious understanding of which area of the body’s functioning will be affected by the reaction to stress, it is necessary to determine the specificity of the neurosis. Problems of a psychological nature can lie in one or several areas at once: hidden conflicts, defects in upbringing, emotional experiences, psychological trauma, etc.
Neuroses can be different in nature; there are some statistics regarding patients with neurotic gastrointestinal disorders:
- 70% - hysterical neuroses;
- 22% - neurasthenia;
- 8% - obsessive states.
Many patients complain of dissatisfaction with themselves, dependence on third parties, increased conflict, manifestations of aggression, susceptibility to outside influence, which leads them to a stage of severe emotional discomfort and dissonance.
Risk factors for the development of gastric neurosis
The following risk factors for the development of gastric neurosis are identified:
- Various neurotic conditions (neuroses) in the anamnesis.
- Severe emotional shock or stress, provoked by a change in the usual conditions of the environment and the team.
- Violation of the conditions of “comfort eating” (watching TV shows, sitting at the computer, using various electronic devices and gadgets, reading books and newspapers while eating).
- Eating immediately after sports or heavy physical work.
- Neurological and other diseases that significantly affect autonomic regulation and the balance of sympathetic and parasympathetic transmission.
- Taking psychoactive, psychotropic, sedative and hypnotic medications without a doctor’s prescription or in a dosage exceeding the maximum permissible dose.
The situation is aggravated if the patient suffers from eating disorders, smokes, or abuses alcohol.
Nervous pain in the stomach - causes of concern
According to Freud, the main reason for the emergence of neurotic states is associated with the discrepancy between human moral and animal instincts. This entails the emergence of a conflict of values. According to Adler, neuroses in humans begin in childhood, and over the years this condition develops more strongly. The great scientist Pavlov studied neurosis and its symptoms. He believed that neurosis occurs at a moment of prolonged nervous excitement.
All experiments were carried out on dogs, which were given very difficult living conditions. They reacted differently to each stimulus. According to the famous psychologist of the last century, Myasishchev, the signs of neurosis for a person are distinguished by their individuality. For some this is due to the onset of a serious illness, but for others it is an ordinary life situation.
Medical statistics record only cases when a patient requires medical attention. According to doctors, most of the population experienced the symptoms of the disease in question.
In principle, this phenomenon is not surprising, because such a reaction of the body is associated with a variety of factors:
- hectic life;
- constant lack of sleep;
- unbalanced psyche;
- stress;
- overvoltage;
- psychological trauma;
- poor nutrition;
- low quality products.
Quite often, the appearance of this pathology can be caused by other diseases - ulcers, gastritis or tumors. Changes in the functioning of the stomach can also be affected by harmful substances that enter the human body with food. A neurotic reaction can occur even after final recovery from severe food poisoning.
Other diseases also have a serious impact on the appearance of symptoms of gastric neurosis:
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- colitis.
The cause of a neurotic condition may be a viral or infectious disease.
Low resistance to stress, emotional overstrain and other psychosomatic factors can cause burdensome pain in the digestive system. Gastrointestinal neurosis is the result of a nervous system reaction to prolonged, intense stress, chronic anxiety or depression, or traumatic events or sensations.

The cause of severe abdominal pain may be gastric neurosis
Stomach neurosis is a fairly common disease. About 87% of people have suffered from it at least once in their lives. It is often confused with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastritis or stomach ulcers.
Causes of neurosis:
- Hard work with nervous tension and stress.
- Systematic, regular lack of sleep.
- Mental disorders.
- Fast and fast paced life.
- Mental overstrain.
- Poor nutrition.
- Consumption of low-quality products.
- Viral diseases.
- Some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other organs.
Unfortunately, in the modern world people forget about peace and measured life, trying to be on time everywhere. Many people eat processed foods or food from cafes, often snacking on stale and low-quality products on the go. This usually results in health problems, including the gastrointestinal tract.
Neurosis of the stomach with irritable bowel syndrome
Gastric neurosis is the main clinical manifestation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome) - a chronic intestinal disorder in the absence of visible organic causes. This type of intestinal pathology manifests itself as constant pain in various parts of the abdomen, flatulence, rumbling, discomfort, and stool disturbances. Histological examination reveals predominantly dystrophic changes; there is no objective clinical picture of inflammatory processes.
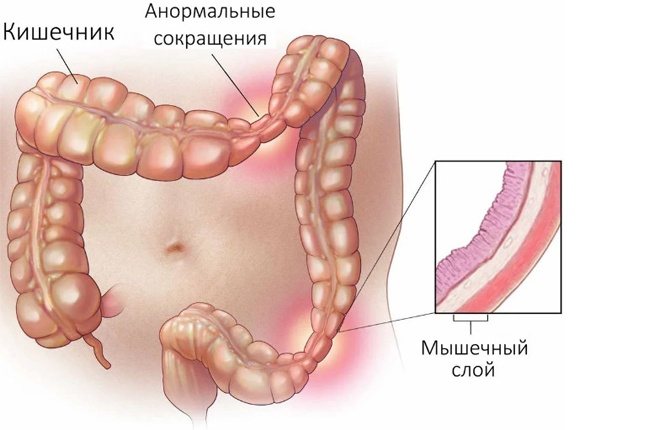
State of the intestines in the presence of the syndrome
The main reasons influencing the development of such symptoms are considered to be psychological and social factors. In 90% of cases, IBS is accompanied by somatoform neurotic digestive dysfunction (in some sources, neurosis of the stomach and intestines and IBS are even used as synonyms).
Objective clinical picture of gastric neurosis
With gastric neurosis, patients usually complain of epigastric pain, nausea, poor digestion of food, and stomach discomfort after eating. It is important that with gastroneurosis, such disorders occur after eating any food, even if it is prepared in compliance with all the principles of dietary sparing recommended for gastroenterological patients.
Gastroneuroses are divided into three groups:
- with a predominance of epigastric and distress syndrome;
- with a predominance of functional dyspeptic syndrome (after eating there is a feeling of fullness, bloating, heaviness, the amount of intestinal gas increases);
- with a predominance of intestinal disorders (constipation, diarrhea, various changes in the consistency, appearance and texture of stool).
In almost 80% of cases, gastric neurosis with a predominance of intestinal disorders manifests itself as constipation, the duration of which can last up to 3-4 days. This category also includes painful straining during bowel movements, imperative (false) urges that do not end with the release of feces, and the appearance of the so-called fragment-like “sheep” feces (hard spherical fecal lumps of dark brown or black color).
Symptoms of gastric neurosis
Typical complaints of patients suffering from gastroneurosis are:
- pain in the epigastric region that occurs after a strong emotional experience or consumption of any foods;
- intestinal disorders;
- increased gas formation, bloating, release of large amounts of intestinal gas with an unpleasant odor, stomach discomfort;
- feeling of incomplete evacuation after defecation;
- nausea.
Neurotic gastric dysfunction is characterized by the appearance of all these symptoms after exposure to stress factors or consumption of food, even if it complies with the norms of healthy and dietary nutrition of patients with gastroenterological pathologies.
In addition to gastroenterological symptoms, extragastric symptoms (i.e. caused by other disorders) are distinguished. These include autonomic dysfunction, psychopathological condition and other associated syndromes. The table below provides examples of complaints for certain groups of symptoms.
Symptoms of the pathological condition
Belching may be a symptom of a compromised digestive organ.
An undermined stomach manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- unstable appetite;
- heaviness and discomfort after eating;
- desire to eat spicy food;
- refusal of dairy products;
- nausea and belching;
- increased gas formation;
- problems with stool;
- abdominal pain, especially in the navel area;
- dizziness and weakness;
- irritability and moodiness, if more than a child;
- acceleration of heartbeat.
If your stomach hurts, this does not necessarily mean that the food organ is torn. Symptoms of a torn stomach appear based on the stage of prolapse of the organ. Only appropriate diagnosis by a specialist will give an accurate picture of the disease. Men who lift heavy things often experience a feeling of soreness. They have a higher risk of tearing their abdominal muscles. Symptoms depend on the number of years, the presence of underlying illnesses and the physical fitness of the person. Pain in the navel area cannot be ignored; a diagnosis must be made, based on the results of which treatment will be prescribed.
Diagnosis of gastric neurosis
To carry out differential diagnosis, a set of measures is carried out. The patient is prescribed ultrasound of the abdominal organs, FGDS, electrogastrography, sonography (if necessary). Laboratory diagnostics include stool testing for occult blood (to exclude gastrointestinal bleeding), general urine and blood tests.
The table below provides a description of the differential diagnosis based on the study of the primary anamnesis.
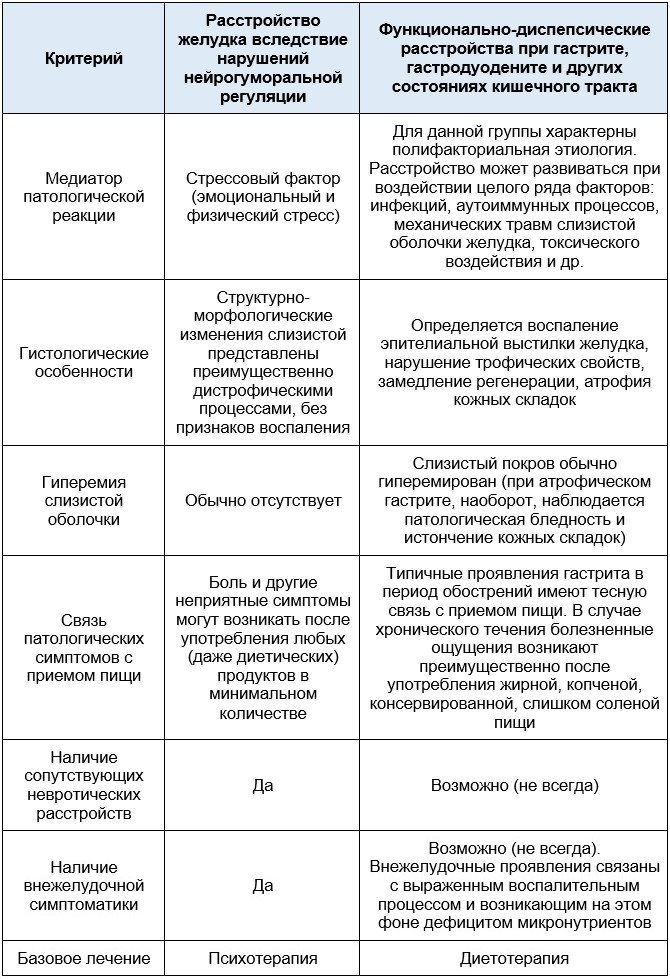
Treatment of gastric neurosis
Gastroneurosis must be treated comprehensively (unlike infectious gastritis, which requires step-by-step therapy).
Psychotherapy
For neurotic gastric dysfunction, the basic treatment is psychotherapy (and not diet therapy, as with other forms of gastritis and gastroduodenitis). To work through the underlying cause of pseudoulcer syndrome, cognitive-behavioral and psychoanalytic therapy techniques are used.
Against the background of psychocorrection, it is important to ensure a sufficiently restrictive regime that allows you to eliminate as much as possible all sources of possible stress. The patient should take daily walks away from busy streets, highways, and large industrial facilities. It is useful to practice aromatherapy and audiotherapy techniques, and if there are no contraindications, regularly take relaxing baths with chamomile or lavender infusions.

Yoga or Pilates also have a good calming effect.
Drug treatment
Sedatives are used to correct the psycho-emotional state. For mild or moderately expressed disorders, it is preferable to use herbal remedies: valerian tincture and syrup, motherwort, hawthorn tincture, herbal preparations (Tenoten, Persen, Novo-PASSIT).
The standard treatment regimen for uncomplicated gastric neurosis is as follows:
- Anxiolytics and nootropics (“Phenazepam”, “Phenibut”, “Mexidol”, “Adaptol”).
- Antidepressants (Neuroplant, Fluoxetine, Velaxin) to combat depressive disorders, sleep disorders, irritability and anxiety.
- Antispasmodics (drotaverine, papaverine) for pain syndrome.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac, ketorolac) and analgesics (metamizole sodium) - for severe pain that is poorly controlled by myotropic antispasmodics.
- Prokinetics (“Motilium”, “Motilak”) for nausea and vomiting.
To correct conditions associated with long-term deficiency of essential vitamins and micronutrients, vitamin-mineral complexes are selected (after a biochemical blood test).
Important! For patients with severe forms of exhaustion and manifestations of anorexia, treatment begins with replacement infusion therapy and parenteral administration of nutritional mixtures.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a secondary treatment option for non-functional dyspeptic indigestion. Hydrotherapy, as well as procedures using alternating electromagnetic currents, have a good therapeutic effect. In the absence of contraindications, a course of relaxing massage is recommended: it has a positive effect on blood circulation and allows you to restore the motor-evacuation function of the digestive tract.
Diet
Diet for gastroneurosis is used as an auxiliary measure to prevent possible complications and prevent an acute inflammatory process. It is preferable to cook food using reactive, thermal and mechanical gentle methods.
Fried foods, smoked, canned and pickled foods, confectionery, sausages, and alcohol are limited or completely excluded.

Foods prohibited for consumption during gastroneurosis
Gastric neurosis is a serious psychopathological pathology in which the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for the functioning of the stomach and other digestive organs, is disrupted. The basic treatment for gastroneurosis (as opposed to infectious gastritis) is psychotherapy, which, depending on the clinical symptoms, is supplemented with medication, physiotherapeutic methods, and diet therapy. Once a year, sanatorium treatment at balneological resorts is recommended.
Treatment: what to do about the disease?
A prolapsed organ should be treated comprehensively. Prescribed:
- diet;
- physical therapy complex;
- traditional methods of therapy.
Synthetic medications are prescribed by a gastroenterologist, based on the diagnostic results and the general condition of the patient. The doctor prescribes the drug, dosage and regimen. The method of getting rid of pathology is based on the reasons for its occurrence. It is not the symptom of the disease that should be eliminated, but the factors that provoke it. Comprehensive therapy with proper nutrition and exercise is used. Treatment with recipes “from your grandmother” will help reduce symptoms and speed up the recovery process, but they cannot overcome the decrease in muscle tone on their own.
Principles of nutrition

There is no special diet for this pathology. It is important to eat food in small portions, but at least 5 times a day, avoiding overeating. The maximum interval between meals is 4 hours. It is necessary to exclude spicy dishes, white bread, semolina porridge, fatty and fried foods. You should avoid cocoa, baked goods and rice. The menu is enriched with fruits and vegetables to give the body the necessary amount of vitamins and easily digestible minerals. The first hour after eating, physical activity is contraindicated. It is recommended to eat bran bread, cereal porridge and lactic acid dishes.
Physiotherapy
Bed rest and lack of exercise can only make the situation worse. All loads should be moderate, correctly distributed and agreed upon with the doctor. Exercises are performed in a supine position, with limbs extended. Take deep exhalations and inhalations, while the air must be pushed out by the abdominal muscles - 10 repetitions. It is recommended to alternately raise the outstretched legs 5 times each. You can imitate riding a bicycle and do arm raises. Useful exercise: take a deep breath, exhale, press the right leg to the chest, exhale - lower it. This is done 5 approaches for each leg. All movements should be smooth, avoiding jerking and pain.
Traditional methods of therapy
With the help of tinctures of wormwood, chicory, yarrow, calamus or centaury, appetite is regulated. To do this, pour 25 g of dry herbs into a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. You need to drink 25 ml of the tincture every 30 minutes. before meals. Secretory function is normalized with plantain decoction. 75 g of medicinal plant are poured into 0.5 liters of water and boiled over low heat. Drink 100 ml half an hour before eating. You can make clay compresses. Mix the clay with water and apply the cake to the stomach for 3 hours.