Causes of nausea and heaviness in the stomach
Similar symptoms can occur not only after eating food, but also on an empty stomach. The causes of heaviness in the stomach and nausea are divided into several groups. A similar condition after eating food may occur due to:
- poor nutrition and quick snacks;
- consumption of large amounts of fats and spicy foods;
- overeating;
- consuming large amounts of food at one time;
- consumption of incompatible or long-digesting foods.
Among the reasons that provoke discomfort on an empty stomach are the following:
- taking certain medications;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- consumption of sugary carbonated drinks;
- disruption of the functioning of certain organs;
- stressful situations.
If unpleasant symptoms occur, you should definitely consult a doctor, as this may be a sign of dangerous dysfunctions in the functioning of many organs.
Principles of treatment
The procedure for treatment depends on the diagnosis and is prescribed by a specialist, that is, in any case, correct diagnosis is very important. Therapy consists of the following activities:
- Neutralization of attacks of esophagitis. Heartburn is an unpleasant feeling of unbearable burning in the esophagus and stomach, caused by the entry of gastric juice into the esophagus. As a rule, this is a sign of gastritis, gastric or intestinal ulcers, inflammation of the pancreas, etc. Antacids (Omeprazole, Rennie, Pancreatitis, etc.) are used to relieve heartburn, then the underlying disease is treated. A special diet is recommended - small portions 5-6 times a day; in order to avoid heaviness in the stomach after eating, you must avoid fatty, spicy, salty foods and smoked foods, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, legumes and some vegetables and fruits that cause increased stomach acidity.
- Treatment of gastritis. Gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa) can be the result of prolonged stress, metabolic or microflora disorders, infectious diseases, poor diet and abuse of drugs that affect secretion and irritate the stomach. For treatment, absorbent and enveloping drugs (Almagel, Maalox) and antibiotics are prescribed. A strict diet is followed.
- Treatment of stomach ulcers. Gastric ulcers are most often caused by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori, indiscriminate use of medications containing acetylsalicylic acid, and stress. Peptic ulcer disease is accompanied by intense burning pain affecting the stomach and abdomen, belching, nausea and vomiting. If not treated in a timely manner, the consequences of a stomach ulcer may include bleeding and peritonitis. Antibacterial (Metronidazole, Tetracycline) and anti-inflammatory drugs, antacids are prescribed to reduce acidity and protect the mucous membrane. A strict diet is required.
- Treatment of stomach cancer. Epigastric cancer is a neoplasm of benign and malignant etiology. Benign tumors do not pose a threat to life, are easily removed surgically, do not grow or spread to other organs. Malignant formations are life-threatening, tend to grow rapidly and penetrate into neighboring organs and intestines (metastases), and after removal they can grow again. Drug treatment, surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are used. In addition to drug treatment, surgical intervention is also used in some cases.
- Appendicitis (inflammation of the cecum) is removed by surgery and has a favorable prognosis. However, in 0.75% of cases, death occurs due to the rapid ontogenesis of complications (peritonitis, gangrene) and difficult diagnosis based on mild, vague symptoms.
As prescribed by a doctor, you can use in combination some traditional medicine, analgesic and anti-inflammatory decoctions of the leaves and stems of St. John's wort, chamomile flowers, plantain, meadowsweet inflorescences, honeysuckle; The juice of fresh cucumber and raw potatoes, honey is very useful.
Pain in the stomach has various causes and can be the result of both minor disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract and the consequence of serious and dangerous pathological processes occurring in the body. Proper treatment will help eliminate not only the symptoms, but also the disease itself. Specialists in the treatment of the gastrointestinal tract and abdominal cavity - gastroenterologist, surgeon, therapist, oncologist.
What diseases provoke severity?
Often this problem occurs as a result of overeating and consumption of highly fatty or fried foods. In addition, nausea and heaviness in the stomach occur due to various diseases, which include cholecystitis or pancreatitis. With pancreatitis, stomach pain, belching and nausea are additionally observed.
Nausea and heaviness in the stomach after eating can be the main sign of cholecystitis. During intestinal infections, severe vomiting, fever, diarrhea and headache are additionally observed.

In addition, such a condition may be one of the signs of pregnancy in a woman. That is why every woman should definitely visit a gynecologist, especially if there is no menstruation. The causes of heaviness in the stomach and nausea may be associated with myocardial infarction, stagnation of blood in the liver. If you suspect this disease, qualified medical assistance is required. Biliary tract pathologies should not be ruled out.
Gastritis, which is characterized by the formation of an inflammatory process, can provoke nausea and heaviness in the stomach. This disease occurs as a result of malnutrition or the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Many patients additionally complain of belching, stomach pain and vomiting.
Among the main reasons is the presence of a stomach ulcer. This disease is characterized by severe pain in the stomach, especially at night, and frequent vomiting. The disease is characterized by seasonal exacerbation. Weakness, nausea and heaviness in the stomach are observed in the presence of malignant tumors. This pathology can be asymptomatic for a long time. Sometimes, due to cancer, there may be diarrhea and periodic vomiting. As the disease progresses, severe severe pain occurs, as well as constant vomiting.
The development of chronic pancreatitis is caused by abnormal processes occurring in the pancreas. This condition can be triggered by alcoholism, malnutrition and stagnant processes in bile. In addition to a feeling of heaviness in the stomach and nausea, symptoms such as vomiting and flatulence occur. Sometimes there may be pain in the navel and left hypochondrium. One of the main signs is light-colored feces, as it contains a lot of undigested fats.
Hepatitis is characterized by dull pain on the right side, diarrhea, heaviness in the stomach and nausea. In addition, a certain yellowness of the skin is observed. With chronic cholecystitis, the patient suffers from bilious vomiting, sour belching, nausea, heaviness in the stomach and pain in the right side. The stool also changes its consistency.
How to distinguish between types of pain?
Based on the mechanism and clinical manifestations, there are 3 types of stomach pain. Spastic - formed due to spasms of the muscle layer of the organ. Caused by increased acidity of gastric juice. Associated with an excess of the hormone gastrin, whose task is to stimulate parietal cells to synthesize hydrochloric acid.
According to this scheme, pain occurs in the stomach while eating in diseases localized in the antrum, pre- and pyloric region of the stomach, and in the upper parts of the duodenum. The location is most typical for gastritis and peptic ulcers caused by Helicobacter.
Clinically, the pain manifests itself in sudden attacks and is felt as cutting and intense. They give irradiation to the back.
Distension - caused by stretching of the muscle layer. Provoked:
- narrowing (stenosis) of the pylorus due to scar deformation;
- a mechanical obstacle that complicates the exit from the stomach in case of tumors of the stomach, pancreas, metastasis to the lymph nodes;
- slow peristalsis due to low acidity.
They manifest themselves as a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium, aching and bursting character. They usually follow overeating, drinking alcohol, and are accompanied by nausea and belching.

Signs of stretching begin an hour after eating
Peritoneal - caused by irritation of the receptor apparatus of the peritoneum. They are divided:
- in acute cases - they accompany signs of destruction of the stomach wall by a perforated ulcer, a disintegrating tumor, appear unexpectedly, are characterized by high intensity, patients call them “dagger-like”;
- and chronic - caused by a long process of germination of the stomach wall by a tumor, the severity depends on the stage of the disease (from moderate to painful), associated not only with food intake, but also with physical activity, running, jumping.
Heaviness in the stomach and fever
Nausea, heaviness in the stomach, bloating, and fever - all this may indicate the presence of a myocardial infarction, so immediate medical attention is required. In this case, there may additionally be vomiting, but no painful sensations are observed during palpation. But there is a noticeable deterioration in well-being, and the mouth feels very dry.

In addition, nausea and heaviness in the stomach against the background of an increase in temperature may be a sign of inflammatory processes in the stomach and intestines. Such symptoms are characteristic of many diseases of the digestive system, in particular poisoning. In addition, these signs can be observed in diseases of the liver, kidneys and pancreas.
Pain in the lower abdomen in men on the right
Pain in the lower abdomen on the right side in a man in most cases becomes a sign of intestinal problems. But in rare cases, these symptoms indicate manifestations of chronic prostatitis. Therefore, if pain occurs, it is necessary to undergo examination by several specialists at once, for example, a gastroenterologist and a urologist.
If pain occurs in the lower abdomen, you must independently feel the left and upper abdomen. And if it becomes painful, then most likely it is inflammation of the pancreas, that is, pancreatitis. In addition, unpleasant symptoms may be present, such as dry mouth, repeated vomiting, and after vomiting the pain eases slightly, and an increase in blood pressure is also possible. Quite often, pain appears after drinking alcohol or fatty foods. If the pain is due to inflammation of the pancreas, then it is necessary to exclude everything fried from the diet, and limit yourself to only light foods that will not overload the stomach. However, in acute cases it is necessary to consult a doctor. If the pain is constant and moderately strong, which covers the entire abdomen, and weakness, fever, and nausea also appear, then this indicates signs of peritonitis or inflammation of the peritoneum.
Main symptoms
If there is heaviness in the stomach and nausea, there may be certain corresponding symptoms, which mainly depend on the factors that provoked the disease. Among the main symptoms are the following:
- painful sensations in the abdomen of varying intensity;
- vomit;
- bloating;
- heartburn;
- diarrhea followed by constipation.
Poor quality food, as well as disorders of the nervous system, prolonged fasting can provoke a feeling of fullness in the stomach. In addition, in some cases there is an increase in temperature, severe weakness, dizziness, and loss of appetite. Heaviness can appear in the morning or evening, which is caused by overeating right before bed, so a person wakes up in the middle of the night and feels very bad in the morning.
Nausea from fatty foods: causes, first aid and treatment
If you have a lump in your throat after a hearty meal, there is nothing to worry about.
In most cases, you feel sick from fatty foods when you overeat. When this phenomenon repeats regularly, you should think about your health. Intolerance to fatty foods can signal the presence of various diseases. What to do, how to treat it, how to prevent it, can only be learned from a doctor who will make a diagnosis.
Causes of nausea from fatty foods
Vomiting is usually preceded by a condition called nausea. This sensation is regulated by the center of the brain. If a person has eaten too much and feels sick, the reason is clear.
When there is an excess of food, the brain receives a signal from the receptors of the stomach and “gives an order” to reduce the tone of its walls. At the same time, the area of the duodenum becomes tense. The sphincter (valve) between the esophagus and stomach relaxes.
The contents are easily thrown into the esophagus, causing heartburn.
Fatty food means fatty meat, fast food with cheese, French fries, chips, lard, cakes. A large portion of such food is difficult to digest.
This requires a lot of gastric juice, pancreatic enzymes, and bile. As a result, food stays in the stomach and intestines for a long time.
Stagnant undigested food causes an unpleasant pulling or sucking feeling in the epigastric region.
Vomiting occurs, after which it becomes easier. This indicates poor nutrition or overeating.
Similar symptoms appear in a healthy person after drinking alcohol with a fatty snack. The stomach is not able to digest large amounts of heavy food and alcoholic drinks.
In case of poisoning
If a person has eaten too much fatty, stale or poorly prepared food, nausea is one of the symptoms of food poisoning. This usually applies to expired products and homemade canned goods.
In food poisoning, the stomach lining is irritated by bacteria. Microorganisms and the toxins they release, circulating in the blood, cause intoxication, one of the symptoms of which is nausea.
Vomiting is regarded as a protective reflex that frees the body of toxins and prevents their further absorption. Heaviness in the stomach and nausea persist until the person, through vomiting, frees himself from poor-quality food.
From the medicine
Nausea is often caused by side effects of medications that irritate the gastric mucosa:
- antibiotics;
- Aspirin (in tablets or soluble form);
- hormonal medications;
- iron-containing preparations;
- poisonous homeopathic remedies;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory tablets – Ibuprofen, Diclofenac;
- vitamin complexes.
If you feel sick during a course of medication, you should read the instructions for use of the drug. Follow the method of use and storage conditions; consider the expiration date. Most tablets are taken after meals. The medicine leaflet contains information about side effects.
Gastrointestinal diseases
In some diseases, adults cannot digest certain food components. The causes of nausea after a fatty meal are most often gastrointestinal diseases:
- cholelithiasis;
- hepatitis;
- peptic ulcer;
- cholangitis;
- enteritis;
- cholecystitis;
- biliary dyskinesia.
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- pancreatitis;
- erosive gastritis;
- gastroduodenal reflux.
If you feel sick after eating something fried, the reason lies in the dysfunction of the gallbladder. In healthy people, in response to food intake, bile is secreted, containing enzymes for digestion. When there is blockage or spasm of the bile ducts, juices either do not enter the intestines at all or enter in small quantities.
As a result, undigested food stagnates in the stomach, causing nausea followed by vomiting. In this case, the person feels better after freeing himself from the food bolus.
If your stomach hurts after eating fatty foods, the cause is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The problem with this pathology lies in the insufficiency of the valve between the esophagus and the stomach.
The muscle ring does not close completely. Heavy food in the form of, for example, fatty pies is not digested, which causes nausea.
The stomach reflexively throws stagnant food into the esophagus along with acid, which causes heartburn.
Bad things happen after fatty foods with appendicitis. Nausea and vomiting are accompanied by pain in the right half of the abdomen, which radiates to the lower back or navel. Sometimes the temperature rises.
I always feel sick after oily fish and drinking alcohol with pancreatitis. The pancreas produces enzymes for digesting food - amylase, lipase, trypsin. If the outflow is disrupted, the juice remains inside the organ and does not enter the intestine. In this case, enzymes digest gland tissue, causing inflammation. After eating fatty fish or meat, severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting occur.
If you experience frequent nausea after fatty foods, you should be examined by a gastroenterologist.
Intestinal infections
Rotavirus infection manifests itself as a combination of intestinal and respiratory syndrome. Since the initial signs of the disease are a sore throat and accompanied by an increase in temperature, the pathology in everyday life is called intestinal flu. In the advanced stage of the disease, abdominal colic, nausea, vomiting, and frequent diarrhea occur.
Transmitted diseases are treated by an infectious disease specialist. You should contact him for abdominal pain with fever, nausea and vomiting.
Pregnancy
Nausea in expectant mothers often occurs due to increased acidity of gastric juice. The reason is the pressure of the fetus on the digestive organs - the stomach and intestines.
Vomiting after fatty foods occurs due to toxicosis in pregnant women. More often, this condition occurs in the early stages of pregnancy. Women feel disgust even at the sight of fatty foods or onions. Most people react to different smells. To reduce nausea, it is recommended to eat fruits and nuts.
Preeclampsia develops in late pregnancy. Called late toxicosis, it is accompanied by increased blood pressure, edema, and the appearance of protein in the urine. This condition may also be accompanied by nausea and vomiting at the sight or smell of fatty foods.
Treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting.
Disorders of the vestibular apparatus
Nausea after fatty foods if a person has disorders of the vestibular system. The gag reflex occurs when abruptly getting out of bed or taking a horizontal position immediately after a meal.
The problem is accompanied by dizziness, tinnitus, loss of balance, and visual disturbances. The condition is relieved by drinking water and lemon juice.
Diet errors
Nausea after fatty foods sometimes occurs as a result of an unhealthy lifestyle. Usually in this case the rules of nutrition and cooking are violated:
- snacks on the go with sandwiches with butter and cheese;
- abuse of fast food, sunflower seeds;
- overeating eggs, full-fat milk;
- eating large amounts of lard;
- the predominance of fatty, fried and spicy foods, sweet dishes in the diet;
- lack of diet;
- not fully cooked or fried meat food;
- excessively cold or hot coffee, tea.
Poor nutrition and lack of routine are the main causes of gastritis, ulcers, cholecystitis, and stomach cancer.
Symptoms of nausea
Manifestations of individual diseases are associated with a damaged organ, but there are general symptoms:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- intestinal colic;
- heartburn;
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- bloating.
If pain is felt around the navel, accompanied by vomiting or diarrhea, this indicates food poisoning or an infectious disease. Intoxication in these diseases is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- headache and muscle pain;
- temperature increase.
Pancreatitis is manifested by nausea, sharp pain radiating to the right hypochondrium or back. Inflammation of the pancreas is characterized by sudden weight loss and unstable stools.
First aid for nausea from fatty foods
In case of poisoning, there is no need to get rid of nausea. On the contrary, you need to induce vomiting.
To do this, you need to take the following measures:
- Drink 3-4 glasses of warm water with soda, press on the back third of your tongue. Repeat gastric lavage 2-3 times until clean lavage water comes out.
- Take 4 tablets of activated carbon or Enterosgel to prevent the absorption of bacteria and poisons.
- Then drink small amounts of bottled water regularly.
- To restore electrolytes, you will need to take dissolved Glucosolan or Regidron powder.
If symptoms do not go away after the measures taken, call an ambulance. It is possible that poisoning is associated with the ingestion of toxic substances or dangerous bacteria into the body. Nausea may be a sign of appendicitis. If the ambulance is called late, the appendix may burst with the development of peritonitis.
Treating nausea from fatty foods
Help for nausea after fatty foods varies depending on the underlying disease:
- For peptic ulcers and gastritis, Motilium and Cerucal relieve nausea. These drugs stimulate the motor function of the stomach and intestines, moving food to the exit.
- Unsweetened tea with mint, ginger, and lemon helps reduce nausea after overeating.
- The enzymes Panzinorm and Pancreatin, as well as the proton pump inhibitors Pantoprazole and Omeprazole, help neutralize fatty foods in the stomach.
- In cases of vestibular dysfunction, motion sickness or seasickness, nausea is relieved by the drug Dramamine.
- Stressful nausea is relieved by the tranquilizer Tazepam or sedative herbal remedies - motherwort, valerian.
Meals for nausea should be divided, in small portions. The intervals between meals are usually 4 hours. Drink more water to normalize the balance of essential electrolytes in your body. Liquid promotes better digestion of food.
Do not indulge in carbonated drinks, strong tea and coffee. Clockwise abdominal massage and exercises help the digestive organs.
Nausea in children
The vomiting center in children is very sensitive to various odors and unusual tastes. Cause of nausea:
- Intestinal infections caused by rotavirus or enterovirus, pathogenic Escherichia coli, salmonella. The source of infection is a sick person, dogs, cats, tap water, toys.
- Food poisoning occurs when eating food contaminated with microbes, especially dairy products. This happens when using expired products or when storage rules are violated.
- Acute respiratory diseases not directly related to the stomach - bronchitis, pneumonia.
Nausea can be caused by a disease of the nervous system, brain tumors, or appendicitis.
Prevention
In the absence of diseases, to prevent nausea from overeating, it is enough to eliminate provoking factors or bad habits:
- reduce the consumption of fatty, fried foods, marinades;
- eat food 5 times a day, but little by little;
- do not “seize” the problem so as not to cause overeating;
- during pregnancy, spend more time outdoors;
- give up carbonated drinks;
- have dinner no later than 2.5 hours before bedtime;
- take your time at the table, chew your food thoroughly;
- After a hearty lunch, do not lie down, but take a walk.
If the problem is related to overeating, these measures are enough to avoid nausea. For diseases of the digestive system, these measures will help prevent the occurrence of the gag reflex.
Since nausea is often a symptom of a disease, it is important to identify and eliminate the cause. To do this, you need to be examined by a gastroenterologist. If the disease is not detected, the doctor will recommend eliminating the provoking factors.
Source: https://otravilsya.com/pomosh/dejstviya/toshnota-posle-zhirnoy-pischi/
Carrying out diagnostics
To determine the cause of constant heaviness in the stomach and nausea, you need to contact a doctor, who will refer you for an examination. It should be carried out by a gastroenterologist who can make the correct diagnosis based on the collected medical history. To determine the main cause of the pathological process, you need to take blood and urine tests, and also do a cardiogram.

A complete blood count helps assess hemoglobin levels, since when it decreases, anemia develops. If a disease of an infectious nature is suspected, the number of leukocytes is assessed, and if there is an elevated ESR, a tumor in the stomach may be observed.
A biochemical blood test helps assess the level of liver parameters, which increase with liver pathologies, which is typical for pancreatitis. Ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity allows you to assess the size and structure of the liver, the presence of stones in the gall bladder, as well as the features of the pancreas, which allows you to make a correct diagnosis and determine the presence of problems with the digestive system.
Abdominal tomography is performed if there is a suspicion of a malignant tumor of the stomach, intestines or liver. And also a similar research technique makes it possible to determine its localization and the extent of spread of metastases to neighboring organs.
After an appointment with a gastroenterologist, you need to conduct an endoscopic examination of the stomach, an X-ray examination of the digestive tract and ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity.
Based on the examination, the doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. However, it is worth noting that the disease may be endocrine or neurological in nature, which is why consultation with other specialists may be required.
Pain associated with urology
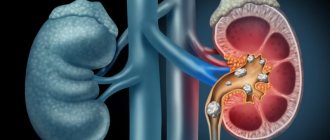
If the cause of the disease lies precisely in urology, then the frequency of urination increases. In addition, this process is very painful, and in exceptional cases the temperature of the whole body may rise. All such symptoms often indicate prostatitis, the formation of kidney stones, urethritis (inflammation in the urethra), adenoma and even prostate cancer. Do not be afraid when you see such terrible words, you should immediately go to see a urologist. Because in the current situation, every minute matters.
If the following symptoms occur, your doctor should be contacted immediately.
- Blood in feverish urine, chills and cramps in the pelvic area.
- Burning when draining, which lasts more than one day, vomiting.
These symptoms may be signs that the infection is spreading. In this case, inflammation can cause further organs.
Diseases with similar symptoms
Although the symptoms of bladder infections are usually quite clear, other diseases can also cause very similar symptoms. For example, pelvic inflammation may also be accompanied by burning and discharge, and persistent pain and difficulty drinking water may also be signs of kidney stones or other infections.
Other symptoms also signal diseases that are associated with the reproductive system in men. For example, a rash in intimate places, an uncharacteristic odor and discharge, blood in the urine (sperm), pain during sexual intercourse. For an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound and order tests.
How to quickly eliminate heaviness
Isolated cases of heaviness and nausea can be eliminated in fairly simple ways. To achieve a positive result, you need to massage your ankles and feet, as this area contains many active points that contribute to the normal functioning of the digestive system. You can drink weak tea with lemon. It helps stimulate the digestive system.
To eliminate bloating, you need to massage your stomach for several minutes, as this will normalize the digestive process. To quickly improve your well-being, you can take 1-2 tablets of Festal or other similar drugs, since they contain digestive enzymes. However, such a remedy should not be used often, as it can cause deterioration in the functioning of the liver and pancreas.
Carrying out treatment
Treatment of heaviness in the stomach and nausea must be comprehensive, since only this guarantees the most positive result. The method of therapy should be selected only by a qualified doctor.

You must follow a special diet. It is necessary to exclude fatty, spicy, fast food, and fried foods from food. In this case, all these restrictions help normalize the patient’s well-being. Constant stress also negatively affects the functioning of the stomach, so it is imperative to avoid situations that traumatize the psyche. If the patient’s occupation is associated with frequent stressful situations, then you need to consult a psychologist and take a course of sedatives to eliminate the negative effects of stress on the digestive organs. In addition, eliminating stress is beneficial not only for the digestive system, but also for blood vessels and the heart.
If the cause of stomach pain, heaviness and nausea is pregnancy, then you should definitely consult a gynecologist who will tell you how to properly eliminate the unpleasant symptoms.
Eating small portions will help you feel better. If a dangerous disease is detected, it is imperative to undergo complex therapy using various drugs. All medications must be prescribed only by the attending physician. Additionally, you can use traditional medicine.
Lower abdominal pain in men on the left
Pain in a man's abdomen on the left is a fairly common occurrence and in most cases this indicates pain, but there are also cases when the tail of the appendix rests in the intestine against the back. In addition, there can be many causes of pain, for example a cyst, hernia, inflammation of the testicles or due to rough food. But for those who play sports, such problems are the exception. When a man has abdominal pain on the left side, such pain usually occurs when internal organs shake during sports or when running fast, which can be accompanied by a tingling, pulling pain. And in this case, it’s enough just to stop and catch your breath or just skip a day of classes.
In addition to all these conditions, people suffering from kidney stones or an enlarged prostate are also susceptible to bacterial urinary tract infections, which can cause pain in the lower left abdomen. Although bladder infections are more common in women, these infections cannot be excluded in men. Relatively less harmful conditions such as food poisoning, gas or constipation can also cause sudden attacks of pain in this region.
Why do men experience pain in the lower abdomen on the right?
The diagnosis takes into account the pain pattern, as well as the patient's medical history and lifestyle. The doctor may also recommend some tests, such as an X-ray of the stomach, to rule out certain diseases. While some of these causes of abdominal pain can be treated with antibiotics, others are serious enough to require surgery. If the discomfort caused by left abdominal pain, whether in children, teenagers or adults over the age of 50, persists for a long time, you should seek immediate medical attention to prevent the condition from developing into chronic pain, which can be even more difficult to treat .
There are cases when pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by fever, malaise, acute pain and nausea. Of course, the pain can be muffled with antispasmodics, analgesics, or resort to traditional medicine, but before that you need to understand the causes of the pain, because painkillers cannot cure the disease. For example, a disease such as testicular inflammation must be cured in time, otherwise it will lead to childlessness. This disease can be caused by various colds and infections. In any case, you need to see a doctor to undergo a series of tests. And if you consult a doctor in time, serious consequences can be avoided.
Pain #1: A burning sensation just below the sternum, especially after a large meal. Possible causes: Heartburn What to do: Take some over-the-counter antacids and avoid heavy, fatty foods. If pain persists for several weeks, consult your doctor.
Pain #2: Pain around and below the navel, accompanied by gas. Possible causes: constipation or flatulence. What to do: Take an over-the-counter laxative or antifungal. If pain persists for more than two weeks, consult your doctor. Pain #3: Sudden pain around the belly button; May be accompanied by nausea, fever, vomiting, loss of appetite, pressure to move bowels, or abdominal muscle stiffness. Possible causes: Appendicitis What to do: Go to the hospital immediately. Appendicitis must be treated quickly, otherwise the appendix may split and leak infected fluid into other parts of the abdomen.
With pain on the left side of the abdomen, cysts and cysts that appear on their own cannot be excluded, and there can be many reasons for the appearance of these diseases. For prevention, it is advisable to consume healthy foods and a complex of men’s vitamins. Of course, serious diseases cannot be avoided without surgical intervention, but if such a disease has already appeared, then you need to monitor your health. Of course, it is very rare for men to seek help from a doctor, but it should be remembered that neglect of one’s health will lead to disastrous consequences
Medications
If adjusting your diet and lifestyle does not bring relief, then you need to choose the right medications to help get rid of heaviness in the stomach. It is necessary to take into account that it is prohibited to use medications regularly, as this can cause disruption of the functioning of the pancreas and stomach problems. To alleviate general symptoms, you need to take medications such as:
- "Renny";
- "Almagel";
- "Gastal";
- "Mezim."

When dysbacteriosis occurs, you can use "Acepol". If the patient has a stool disorder and hard feces, then a mild laxative such as Fitolax should be used.
The use of traditional medicine
Together with medications, you can use traditional medicine that will help get rid of the negative manifestations of diseases. The best and most effective include:
- tea with mint, lemon balm or chamomile;
- infusion of St. John's wort;
- buckwheat grain.

You can cope well with an attack of nausea with the help of lemon. However, this remedy is not recommended for use in cases of increased stomach acidity, gastritis and ulcers. Nettle decoction helps normalize digestive processes. All these remedies can be used only after consultation with a gastroenterologist and determining the absence of an allergic reaction to herbal ingredients.
Prognosis after treatment
The prognosis after therapy is quite favorable, but only if treatment is started in a timely manner. Similar symptoms may occur due to the consumption of certain foods. In this case, you just need to exclude them from the diet and your health will immediately improve.
If deterioration in well-being is observed against the background of diseases of the digestive system, then you should definitely consult with your doctor. With proper and timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable. If therapy is not carried out in time, the situation can worsen significantly.
When to see a doctor
You should definitely consult a doctor if you have heaviness in the stomach, as well as additional signs such as:
- frequent vomiting;
- heat;
- frequent and loose stools that are green or watery;
- sudden weight loss, loss of appetite, pallor and fatigue;
- sharp pain in the abdomen.
If the patient has ruled out all possible causes of the disease, but discomfort still continues, then you need to consult a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination to determine the cause.
Carrying out prevention
You can normalize your health by taking preventive measures. You definitely need to closely monitor your daily diet. It is important to use fractional meals. Prolonged fasting or overeating should be avoided. Follow a certain daily routine and consume food only at the appointed time. This will make the process of digesting food easier.
It is recommended to have dinner no later than 2 hours before bedtime. You need to eat calmly and very slowly. It is not recommended to eat in stressful situations. If you have dyspepsia, you should stop smoking. The food consumed should not be too hot or cold, as it will irritate the gastric mucosa.
Discomfort can be eliminated with sufficient physical activity. You need to devote time to running, long walks, dancing, and playing sports.
If your stomach constantly hurts after eating, you should seek help from a doctor. Treatment is prescribed after determining the cause of this condition. Pain syndrome can appear immediately after eating or 2-3 hours after eating.
Prevention
- Try to eat healthy, avoid spicy, fatty, fried foods that complicate the digestion process.
- Avoid drinks containing large amounts of caffeine: coffee, strong black tea. Both coffee and strongly brewed tea can cause severe irritation. Drinking too much coffee can also lead to increased acidity.
- I'll have to give up chocolate too. As you know, chocolate contains a large amount of caffeine. Therefore, eating chocolate invariably leads to even greater irritation of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, eating chocolate in large quantities can lead to an increase in blood sugar levels.
- Eat small portions 5-6 times a day.
- Try not to overeat.
- It is also worth avoiding foods that increase acidity in the body: strawberries, mushrooms.
- Don't eat late.
- Do not lie down immediately after eating.
- It is recommended to do regular exercise.
- Drink fermented drinks or milk to stabilize the digestion process.
- If your stomach gets sick and continues to hurt, consult a doctor immediately and do not self-medicate.
Medical indications
Stomach pain after eating can be strong, intense, weak or moderate. At the same time, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
- belching;
- bloating;
- bubbling;
- nausea;
- poor appetite;
- After eating, your stomach hurts and diarrhea or constipation appears.
Severe and acute pain can occur after eating expired food, food poisoning, or appendicitis. Treatment is prescribed after determining the cause of abdominal pain after eating.
Burning pain syndrome is caused by eating spicy and salty foods. A similar symptom occurs during exacerbation of gastritis and pancreatitis. Treatment of the disease consists of taking antispasmodics and following a diet.
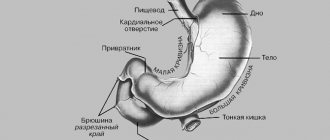
If you experience persistent abdominal pain after eating, you will need immediate medical attention. This symptom manifests itself against the background of various gastrointestinal diseases. If the syndrome in question is permanent, then it is recommended to follow a special diet. If necessary, complex treatment is carried out. Real pain in the stomach after eating is localized in the hypochondrium and iliac region. Often she can give it to the back. Treatment of the disease is prescribed taking into account the location and cause of the pain syndrome.
If there is pain in the stomach after eating and around the navel, then you will need to examine the duodenal mucosa. With cholelithiasis, pain in the stomach after eating spreads to the right hypochondrium. A similar symptom appears after eating fatty, fried and sweet foods.
How to stop eating too much?
According to many nutritionists, this problem is more psychological than physiological. After all, it is quite difficult to refuse another portion of the most delicious dish when amazing aromas are in the house, and there is a large piece of delicate and very beautiful cake on the plate.
In order to understand how much not to eat, experts recommend following a number of the following rules:
- Try to motivate yourself to eat less. For example, buy a dress one size smaller and try to fit into it by losing weight.
- Avoid any events or holidays where you might break out and overeat. After all, in the future it is very difficult to restore normal nutrition.
- Try to improve your mood not with another chocolate bar or bun, but with dancing, exercise, etc.
Abdominal pain after eating fatty foods can create a lot of different inconveniences for a person. Different types of foods cause different digestive reactions in the system.
Eating high-fat foods can cause mild or even severe stomach pain for a variety of reasons.
Some relatively common conditions, such as reflux and irritable bowel syndrome, may be factors in the development of pain that occurs after consuming fatty foods.
More serious illnesses, such as inflammation of the gallbladder, pancreas or severe intestinal diseases, can also cause discomfort after eating a high-fat meal.
If a person has a stomach ache from fat, it is important to determine the cause of the pain, that is, consult a doctor who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment.
Gallbladder disease can cause stomach pain after eating fatty foods. The gallbladder produces bile, which helps the body digest and absorb fat. This organ pushes bile into the intestines after food enters it from the stomach.
Temporary blockage of the bile ducts by stones or thick clots of bile can trigger a gallbladder attack, medically known as biliary colic.
Intense pain in the upper right part of the stomach, which can radiate to the shoulder, occurs precisely because the gallbladder contracts to reduce the “clogging” of the body.
Biliary dyskinesia sometimes follows the ingestion of a high-fat meal, probably due to the strong stimulatory effect of fat on gallbladder contractions.
Pain during dyskinesia and colic, which worsens over time or persists for a long period, often indicates the progression of acute cholecystitis or an inflammatory process in the gallbladder, which requires immediate treatment after its detection.
Other common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, fever and chills. Risk factors for gallbladder disease include being female, rapid weight loss, excess weight, being over forty years of age, and a history of similar diseases.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a well-known functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, in which the intestines do not show probable signs of illness, but often function incorrectly and are painful, after which there is a change in the process of bowel movement.
IBS can be diagnosed based on symptoms, which include abdominal pain, increased gas, and nausea.
Although experiments have not been able to conclusively identify specific foods that trigger IBS, people with the condition commonly report that certain foods trigger symptoms of the disease.
Foods and dishes with a high amount of fat in their composition, as well as fried foods, can cause manifestations of IBS in a certain category of people. Other foods with a high risk of IBS include milk and dairy products, alcoholic beverages, chocolate and coffee.
IBS is more common among females than males. Other risk factors include high levels of psychological stress and cigarette smoking.
Therapy for the syndrome is aimed at reducing the intensity of symptoms, which is primarily aimed at following an individual diet and changing lifestyle.
Gastroparesis refers to delayed emptying and the slow passage of food from the stomach to the small intestine caused by decreased or absent stomach contractions.
Common symptoms include a feeling of fullness, nausea, heartburn, bloating in the upper abdomen, and stomach pain (which hurts intensely and frequently).
Fatty foods may cause or worsen symptoms. During illness, foods high in fat remain in the stomach longer and cause further delays in gastric emptying.
People with diabetes, diseases associated with nerve damage, or abdominal diseases have a higher risk of developing gastroparesis.
Taking medications such as tricyclic antidepressants and some painkillers can also cause this condition.
Fatty foods can also help relax the muscle group that closes the stomach and shares the organ with the esophagus. This can cause stomach contents to back up into the esophagus, causing heartburn and pain in the upper abdomen.
Although heartburn is common in certain cases after eating fatty foods, persistent heartburn may indicate gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which requires urgent treatment.
Inflammatory bowel diseases include Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, diseases that can be characterized by chronic or recurrent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, particularly in the intestines.
In the presence of such ailments, the immune system reacts incorrectly in relation to bacterial agents, foods and other intestinal contents, which leads to inflammation.
The digestive system breaks down light fats into smaller molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Various conditions can interfere with this process, leading to what is called fat malabsorption.
When people with this condition eat fatty foods, undigested fat in the intestines often leads to abdominal cramps, flatulence, excess gas, and greasy stools or diarrhea.
Some medial disorders can lead to malabsorption. For example, inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) can lead to fat malabsorption due to a reduction in the production of fat enzymes.
Diseases of the liver and gallbladder, which reduce the formation and secretion of bile, can also interfere with the normal digestion of fats.
Other medical disorders that may lead to fat malabsorption include:
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Celiac disease.
- Short bowel syndrome.
- Pancreatic cancer.
- Cystic fibrosis.
Sometimes stomach discomfort after eating fatty foods does not indicate the presence of a serious medical problem, especially if the pain goes away quickly and does not interfere with a person’s life. At the same time, regular or periodic pain may indicate a possible illness.
A person should see a doctor immediately if they experience any of the anxiety signs or symptoms listed below:
- Severe, constant abdominal pain.
- Fever, chills, or clammy skin.
- Frequent vomiting mixed with blood.
- Burgundy or resinous stool.
- Dizziness or fainting.
- Chest pain or shortness of breath.
It is important to see a doctor early and get a diagnosis as soon as possible, particularly if the pain is accompanied by other symptoms or weight loss. The doctor will answer the question why your stomach hurts and how to treat it.
Therapy will depend on the main causative factors and may consist of medications, lifestyle changes once a gastrointestinal problem is discovered, and following a proper diet.
Establishing diagnosis
Why your stomach hurts after eating needs to be found out before taking medication. You cannot self-medicate. A similar symptom manifests itself as a result of increased secretion of gastric juice or spasm of the stomach walls. Doctors identify the following causes of pain:
- Binge eating. Eating a large amount of food helps to stretch the walls of the stomach, which leads to pain. At the same time, the patient feels nauseous. To eliminate abdominal pain after eating, it is recommended to adjust your diet and take enzymes (Mezim, Pancreatin);
- Diaphragmatic hernia. As a result of the enlargement of the hole located in the front part of the body, prolapse and strangulation of the upper part of the stomach is observed. Hernia is treated surgically.
The stomach may hurt after eating due to pyloric spasm. The cause of this condition is pathology and dysfunction of the nervous system. Abdominal pain after eating appears within 15-20 minutes. The above-described symptoms cease after complete elimination of its contents from the stomach. Treatment of the disease consists of taking antispasmodics and drugs that affect the functioning of the nervous system.
Stomach pain after eating can occur due to esophageal stenosis. This condition occurs as a result of injury, tumor, or the presence of a foreign body in a given organ. The patient may experience nausea and vomiting. The patient must follow a liquid diet. Pain in the stomach after eating can occur as a result of severe spasm of the walls of this organ. Doctors include exhaustion of the body as the consequences of obstruction.
Attacks of sharp pain in the stomach
Typification of pain
Depending on the time of occurrence
Late sudden pain is of a forced nature and manifests itself over a longer period of time after eating. This symptom may indicate the following diseases:
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- gastritis, high acidity;
- cancer;
- cholelithiasis;
- pancreatitis;
- duodenitis.
If your stomach hurts after 5-6 hours from your last meal or at night, it is called hunger pain. It usually goes away after a small snack or a few sips of tea or plain water. This may be a sign of a pre-ulcerative condition.
SMELL FROM THE MOUTH? Banal bad breath develops into a serious illness. About 92% of human deaths are caused by parasites that can be removed! read more.
Depends on location
- below the ribs – esophagus, liver (hepatitis, cirrhosis), disease of the upper stomach;
- below the ribs, on the right - appendicitis;
- intestinal zone – food poisoning, worms;
- in the pit of the stomach – ulcer, duodenitis;
- under the chest (right) – cholecystitis, cholelithiasis;
- on the left - pancreatitis.
Symptoms of the disease
After eating, the stomach enlarges, squeezing the inflamed gallbladder. This leads to pain. Treatment of the gallbladder should be prescribed by a qualified specialist. Abdominal pain can occur due to food intolerance. A similar reaction occurs to dairy and fish products. The patient is advised to follow a diet and take special enzymes that stimulate the processing of intolerant components.
If abdominal pain occurs 2-3 hours after eating, then you need to remember your diet. To speed up the process of removing toxins from the body, sorbents such as activated carbon and Enterosgel are taken. To relieve symptoms, Smecta and other drugs that improve digestion are prescribed. The gastric gland, located near the stomach, can become inflamed. In this case, the patient exhibits the following symptoms:
- cutting pain 20-40 minutes after eating;
- pain in the middle and right hypochondrium.
In severe cases of pancreatitis, a girdling pain syndrome occurs. Doctors include infectious process, trauma, and problems with the duodenum as the reasons for the development of the disease. Treatment of pancreatitis consists of following a gentle diet and taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
Abdominal pain can be caused by gastroduodenitis. The disease develops against the background of poor nutrition. Treatment of gastroduodenitis involves following a diet, taking antacids, sedatives and drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice. The drugs must be prescribed by a doctor.
The causes of abdominal pain may be associated with a stomach or duodenal ulcer. The wound surface can form on the stomach or duodenum. Aggressive food and acidic gastric juice, getting into problem areas, provoke pain. Treatment of ulcers is carried out by following a gentle diet and taking special medications.
Possible causes of pain
The first thing that pain in the stomach area may indicate is gastritis, peptic ulcers or intestinal problems.
Among the reasons that provoke the localization of pain in the epigastric region (under the stomach), the following stand out:
- impaired gastric motility;
- excess production of hydrochloric acid;
- irritated state of sensitive receptors caused by increased acidity;
- spasms that appear against the background of the development of gastritis, stomach or duodenal ulcers;
- the pathogenic effect on the gastric mucosa of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which can survive in the acidic environment of the stomach and provoke the development of peptic ulcers;
- abuse of fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- violation of the diet, accompanied by rare snacks and causing dysfunction of the digestive system;
- hormonal imbalance;
- stressful situation, anxiety.
In addition to the listed causes of pain, discomfort can be caused by uncontrolled use of medications that negatively affect the state of the digestive system, as well as addiction to smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Preventive measures
The mucous membrane of the stomach can become inflamed due to the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. Rarely, the disease develops due to poor nutrition. If your stomach hurts, treatment for gastritis involves taking antibacterial drugs and following a diet. Doctors advise excluding spicy, fatty, sour, flour and smoked foods from the menu.
With overeating and poor nutrition (dry food), abdominal pain appears rarely and is short-term. To eliminate symptoms, it is recommended to normalize your food intake:
- fractional meals in small portions;
- dinner no later than 3 hours before bedtime;
- exclude heavy foods from intake;
- The liquid is consumed before meals or in between meals.
If the pain syndrome is constant or acute, then the patient’s body temperature may increase and digestion may be impaired. In this case, it is recommended to immediately seek help from a doctor. The disease is life-threatening for the patient, so self-medication is not recommended. In acute cases of pain, doctors advise refusing food and drinking clean water. The patient should urgently make an appointment with a gastroenterologist.
Prevention of abdominal pain involves following the following recommendations:
- you can’t overeat;
- you need to eat often and in small portions;
- it is necessary to consume only fresh and high-quality products;
- fatty, spicy, smoked, pickled and salty foods are excluded from the diet;
- It is recommended to give up fast food and processed foods;
- Do not abuse alcohol or smoke.
Regular visits to a gastroenterologist will allow you to promptly identify the disease and prescribe effective treatment.
Pain or unpleasant discomfort in the abdomen are symptoms of many gastrointestinal diseases. Their appearance can be caused by a huge number of reasons, but in any case it indicates improper functioning of the stomach, intestines or nearby tissues and organs.
To eliminate unpleasant sensations, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis of the body, identify the cause of their development and organize appropriate treatment. The therapeutic course of pain in the gastrointestinal tract consists of taking medications, following certain rules and organizing a proper diet.
Read more about what to eat if your stomach hurts, why such discomfort occurs and how to properly eliminate it.
What kind of pain are there?
The disease is indicated by the type of pain:
Treatment of kidney stones
Supporting the lower abdomen and pelvic area, as well as drinking plenty of alcohol, helps relieve pain and force bacteria to flush out. Adequate fluid intake is the most important factor in treating and preventing bladder infections. This is also the reason why bladder infections are more common in men, also in men. Older people often don't have enough fluids and can't empty their bladder regularly. In these conditions, preference is given to the appearance of inflammation of the urine remaining in the bladder.
- pulling, aching;
- cutting, especially sharp;
- with periodic tingling.
As a rule, the source of the problem is closely related to:
- urological diseases;
- disorders of the stomach or intestines;
- musculoskeletal ailments.
There are cases when the source of the disease is quite difficult to determine, since the pain can also affect other organs. That is why you should not try to diagnose and treat yourself, but rather consult a specialist.
Often cystitis is relatively harmless and can heal on its own in a short time. These bladder infections are not much of a cause for concern. In many cases, symptoms disappear spontaneously after a few days as the body's immune defenses and, if necessary, the use of home remedies have successfully prevented inflammation. Drug treatment is usually necessary if the inflammation persists over and over again, persists for a long time, or is associated with severe pain.
As mentioned, the most common symptoms of cystitis are constant urination, followed by only a small amount of urine. When the water drains, a burning sensation often occurs. The urge to leave the water may be so strong that the patient must also go to the toilet at night. Many also report that the bladder never empties even though you have been to the toilet. Other symptoms may include dull, foul-smelling urine or bladder cramps.
Why does my stomach hurt?
Stomach pain is a characteristic symptom
Abdominal pain is a common symptom of illness. It occurs frequently, occurring equally in children and adults. There are many reasons for discomfort, but it is often provoked by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
A sick stomach or intestines can cause very severe and unpleasant abdominal pain, which cannot be ignored. The lack of high-quality and timely treatment of the problem leads to the development of complications and the formation of irreversible consequences in the tissues of internal organs.
Determining the origin of abdominal discomfort is always difficult. With the maximum guarantee, its causes can only be identified in a medical institution, after a conversation with a doctor and a whole list of examinations. Taking this into account, you should not delay visiting a doctor if you have pain in the gastrointestinal tract, since a full diagnosis is extremely important for the treatment of existing ailments.
As practice shows, common causes of abdominal discomfort include:
- all types of gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa);
- inflammatory process in the pancreas;
- infectious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, often associated with activation of unfavorable microflora;
- the appearance of stones in the gall bladder or ducts of the system;
- the development of oncology or other diseases that provoke the appearance of tumors;
- hernia;
- disturbance of local blood circulation;
- ulcerative diseases;
- allergies to consumed foods;
- parasite activity.
The reasons noted above are associated with damage to the human gastrointestinal tract. In addition to them, abdominal pain can be caused by other factors. Often, discomfort in this area of the body is a consequence of an inflamed appendix, improper use of antibiotics, or the course of kidney pathologies.
There are indeed many reasons for unpleasant sensations, so they should be treated with the proper level of responsibility.
The lack of timely and correct treatment of existing problems can cause dangerous complications, which should not be forgotten.
The essence of the problem
Acute pain spreads throughout the abdominal cavity and can cause both diseases of the stomach itself and neighboring organs (intestines, gall bladder, pancreas, heart). Usually, colic occurs unexpectedly, without any prerequisites, and may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, blemishes, and general malaise, which requires urgent hospitalization of the patient.
Cramping pain is characteristic of the intestinal system. The ontogenesis of the inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) is accompanied by prolonged moderate pain in the stomach. If a patient has acute pain, immediate medical attention is especially important. Particular attention should be paid to sharp pain in the stomach that occurs at night. This is an indicator of a disturbance in the functioning of the stomach (indigestion, dyspepsia), leading to an ulcer.
Factors that provoke attacks of acute pain:
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- unhealthy diet: regular intake of fatty, salty, spicy foods;
- overweight;
- smoking;
- long-term use of medications;
- poisoning by poor quality products and chemicals;
- various diseases;
- neurological disorders;
- constant stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- pregnancy;
- intolerance to any substances, such as lactose.
Discomfort after eating
Dried fruits are not always allowed...
Discomfort in the abdominal area that appears after eating does not always develop due to diseases of the stomach, intestines or their appendages. Filling the gastric cavities with food provokes their bloating and, as a result, an increase in size.
In the presence of tumor formations or other neoplasms in nearby organs and tissues, this state of affairs provokes the appearance of unpleasant sensations due to compression of those tumors.
As for problems directly with the gastrointestinal tract, pain after eating can appear even if there are any. Most often, filling the stomach with food turns into discomfort due to:
- gastritis;
- tract disorders associated with poisoning;
- enteritis;
- peptic ulcers;
- regular constipation and diarrhea;
- colitis;
- polyps in the intestines;
- dysbacteriosis;
- flatulence of any origin;
- intestinal obstruction;
- diverticulosis.
To identify the exact cause of discomfort, you will have to contact a gastroenterologist and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis at the clinic. It is impossible to determine their pathogenesis solely by the nature of the pain and other symptoms of existing disorders, which is why it will not be possible to organize treatment.
It’s not worth taking risks like this, so if you experience frequent stomach discomfort that appears after eating, it’s important to seek qualified help without delay. Otherwise, complications and the resulting consequences are only a matter of time.
Treatment methods
In most cases, patients note a sudden onset of cutting pain. To eliminate the unpleasant symptom, it is recommended to take antispasmodics, which include No - Shpa, Drotaverine, Buscopan. Enzymes play a major role in digestion, so drugs containing them are prescribed: Micrasim, Creon, Festal (especially effective for pancreatitis). If pain occurs along with diarrhea, indigestion may be the cause. In this case, Ranitidine and Omeprazole will have a positive effect. Antacids, among which Almagel, Maalox, and Phosphalugel stand out, perfectly neutralize hydrochloric acid. In case of poisoning, a positive effect is observed from taking Filtrum, Polysorb, Enterosgel.
If there is a cutting pain, it is strictly forbidden to warm the painful area, consume large amounts of food, give enemas, or massage. Among folk recipes, chamomile decoction, a mixture of plantain juice with honey, and aloe juice (freshly squeezed or from the pharmacy) are in demand. If the problem occurs once, you can resort to self-treatment. In case of regularly recurring situations, it is better to use the recommendations of specialists.
Diet and basic principles of nutrition for abdominal pain
Proper diet is one of the main points of stomach treatment
Nutrition for pain or other discomfort in the abdomen requires proper adjustment, as it is one of the basic aspects of the treatment of any gastrointestinal pathology.
The exact diet is determined for each patient individually, taking into account the genesis of his illness and the characteristics of its course.
Naturally, a professional doctor is involved in prescribing the correct diet after receiving the results of the patient’s examinations.
It is almost impossible to correctly formulate a diet for discomfort in the stomach without visiting a clinic. The only way to formulate a diet is to act at random, but since we are talking about health, such an approach is immediately ruled out.
Despite this, it is undesirable to keep the same diet if you have pain in the gastrointestinal tract. Even before contacting a doctor, the diet should be properly adjusted.
Changing your diet helps:
- General tonification of the affected stomach or intestines.
- Reducing the risk of complications before starting specialized therapy for the disease.
- Relief of unpleasant symptoms, allowing the patient to more easily tolerate the course of existing ailments.
Abdominal pain is one of the main signs that you need to reconsider your views on nutrition. At a minimum, you need:
- Start eating small meals and with a certain regularity (at least 5-7 times a day).
- Avoid fried, smoked, too salty, pickled and fatty foods.
- Give preference to dishes prepared by steaming, boiling or in the oven.
- Review your diet, eliminating food that is aggressive to the gastrointestinal tract and replacing it with something neutral.
- Increase your consumption of plain water and healthy liquids like green tea or compotes.
Products recommended for consumption for any gastrointestinal pathology are:
- cereals and porridges;
- pasta;
- soups;
- lean meats and fish;
- non-acidic vegetables, fruits and berries;
- dried bread;
- eggs;
- cottage cheese.
With extreme caution and taking into account the stomach reaction, you can eat:
- any dairy products;
- butter;
- types of cheese;
- regular bread and other baked goods;
- sour vegetables, fruits and berries.
Prohibited foods for stomach pain include:
- all types of sweets and desserts;
- any fatty, smoked, pickled, too salty, fatty and fried foods;
- mushrooms;
- canned food;
- broths;
- sauces (mayonnaise, ketchup, etc.);
- fast food, beach bags and other gastronomic garbage;
- rich breads.
As for liquids, it is best to drink plain water, not too sweet, sour compotes and green tea. Before undergoing a profile examination in the hospital, you should avoid coffee, strong teas, soda and alcohol.
Such an approach to diet will avoid possible complications of existing ailments and will help to tone the patient’s condition.
Diagnosis of acute epigastric pain
The examination begins with asking the patient about the nature of the pain, foods and medications used the day before, existing concomitant diseases, pregnancy, lactation, etc. Then palpation (palpation) of the abdomen and intestines is carried out, the heart and breathing are listened to. It is necessary to undergo laboratory tests of urine, feces, blood, and gastric juice.
In addition, complex studies are prescribed: gastroscopy, ultrasound of the peritoneal organs, contrast X-ray, computed tomography or MRI. If it is difficult to make a diagnosis, laparoscopy (insertion of a probe into the gastrointestinal tract cavity) is used.
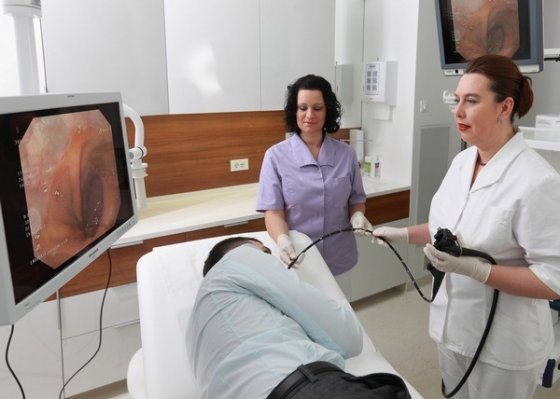
In case of acute pain in the stomach, it is strictly contraindicated to self-medicate or apply hot heating pads to the affected areas. The only medications you can take are antispasmodic and painkillers.