Basic principles
Basic principles of nutrition for chronic gastritis:
- eating quickly digestible food in small portions up to 6 times a day;
- It is allowed to steam, boil, bake or stew dishes - frying is completely prohibited;
- food should be warm and served in crushed form;
- It is necessary to completely exclude spicy/fatty/rough dishes and foods, salted and smoked foods, alcohol, and carbonated drinks from the menu.
The diet should contain products that provide the patient’s body with all the necessary vitamins and microelements.
General rules
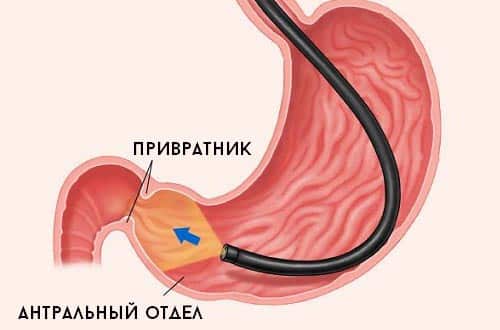
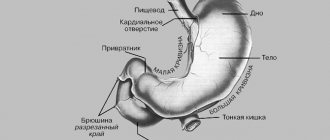
Antral gastritis (or gastritis type B, bacterially caused) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the outlet of the stomach, which in Latin is called antrum.
In this part of the stomach, food chyme is alkalized by the bicarbonates produced before passing into the intestine. Antrum gastritis is closely related to Helicobacter pylori infection, since Helicobacter pylori is detected in 80-85% of cases. What is this connected with? In individuals with normal or high secretion hydrochloric acid suppresses the growth of this bacterium, and in the antrum, where acidity is reduced by bicarbonates and the effect of the acid factor is not expressed, H. pylori multiplies intensively, causing limited antral gastritis. In turn, inflammation in the antrum causes hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid, acidification of the duodenum, development of bulbitis and the risk of duodenal ulcer. We can say that Helicobacter pylori infection and antral gastritis are constant companions of ulcers.
Infection with H. pylori occurs in adolescence, which is when acute gastritis , and after a few months - chronic gastritis with the formation of antral gastritis. This form can be considered an early stage of gastritis. Over time, H. pylori, especially when hydrochloric acid levels are low, colonizes the lining of the entire stomach, causing pangastritis .
Since this form of gastritis disrupts the evacuation of food from the stomach, increases the pressure inside it, and intensifies gastroesophageal reflux, patients are bothered by belching , regurgitation, nausea, and heartburn . Thus, there is a combination of chronic antral gastritis with reflux esophagitis. The appearance of an “ulcer-like” symptom complex is characteristic: epigastric pain on an empty stomach (hunger pain) or two hours after eating. Patients are also concerned about constipation . Complex treatment, which includes anti-Helicobacter therapy (three-component or four-component regimen), also includes dietary nutrition.
The diet for antrum gastritis during severe exacerbation corresponds to treatment Tables No. 1A and 1B (they are prescribed for several days). They exclude:
- Causative agents of secretion (this applies to broths, caffeine-containing drinks) and irritants of the mucous membrane (any rough foods, including vegetables in any form).
- Difficult to digest dishes: mushrooms and tough meat with tendons and skin. All products must be boiled, pureed and brought to a semi-liquid (mushy) state.
- Excessively cold and hot dishes that adversely affect the gastric mucosa.
Meals during this period include pureed cereal soups without vegetables, meat and fish pates or souffles, milk jelly, cream, pureed cottage cheese, steamed omelet, diluted juices, rosehip infusion. At the same time, the calorie content of the diet is reduced due to simple carbohydrates and fats, meals are organized 6 times a day while simultaneously reducing the amount of food taken once. All this has a gentle effect on the stomach.
As the condition improves, mechanical and chemical sparing decreases, and for some patients the main Table No. 1 . It includes boiled meat and fish, which can be eaten in pieces; stewing and baking of foods is allowed. Thermally processed vegetables and fresh fruits are introduced, preferably without peels. Preference is given to soft fruits and berries: blueberries, cherries, bananas, strawberries, raspberries, sweet apples. The amount of protein, fats and carbohydrates in the diet is increased and, in general, the diet is balanced, which allows you to stay on it for a long time.
Diet without exacerbation
The diet for chronic gastritis, accompanied by normal/high acidity outside the period of exacerbation, is based on treatment table No. 1. When diagnosing low acidity, table No. 2 is taken as the basis for dietary nutrition.
- limiting dishes that increase the secretion of gastric juice - rich broths, foods with a spicy taste, all seasonings without exception, fresh vegetables;
- refusal of difficult to digest dishes/products;
- food is served boiled, pureed - exception: fish;
- food should be comfortably warm - cold/hot dishes are prohibited;
- salt restriction;
- 5-6 meals a day in small portions - a glass of warm milk before bed is required.
The duration of diet number one is two to three months. After this, when stable remission is achieved, the patient is transferred to the general table. But many recommendations for restriction must continue to be followed. This applies to avoiding spicy foods/seasonings/sauces. If the acidity level is high, you should not eat a lot of easily digestible carbohydrates. This includes any sweets. This helps reduce the secretory activity of gastric receptors.
Permitted and prohibited products
The list of permitted products is quite large, which provides variety in the patient’s menu. In case of erosive gastritis, occurring with an increased/normal level of gastric acidity, the patient is prescribed diet No. 1 according to Pevzner.
The first table according to Pevzner allows:
- Vegetable soups. Potato and vegetable decoctions are used for preparation. To thicken, you can take pureed vegetables, thoroughly boiled rice, semolina, rolled oats and buckwheat.
- Milk soups with pasta.
- Puree soups with chicken or other dietary meat. Adding butter is allowed to all dishes.
- Steamed/boiled meat dishes. For chronic gastritis without exacerbation, beef, lamb, pork without fat, poultry, liver, and tongue will be allowed. It can be used to prepare any dishes.
- Lean fish with skin removed. Before serving, the product is boiled or steamed.
- Yesterday's wheat bread or homemade crackers made from fresh. Biscuits, baked goods without baking (no more than once a week).
- Side dishes – semolina, buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, pasta.
- Porridge with milk/water. The cereal must be thoroughly boiled (it should be viscous when serving) or pureed (a mandatory rule for buckwheat).
- Steam souffles and cottage cheese puddings.
- Vegetables - potatoes, carrots, cauliflower, peas, beets. Be sure to boil. Wipe clean before serving. Used for garnishing. Boiled pumpkin, zucchini, and ripe sweet tomatoes can be served in pieces.
- Dairy products - milk, cream, yogurt, cottage cheese and kefir (both non-acidic), cottage cheese curds, sour cream.
Acceptable appetizers are salads of boiled vegetables and meat, liver pate, doctor's/boiled sausage, and fish aspic. Desserts should have a sweet taste without sourness; for example, you can serve pureed berries with semolina, previously cooked in a double boiler. Berries and fruits must be baked in the oven or boiled. They are used to prepare purees, compotes, jelly, and jelly.
Drinks you can serve at the table include sweet fruit juices, rosehip decoction, tea with added milk/cream, and weak coffee with milk. The following products/dishes should be completely excluded from the menu or significantly limited:
- high fiber vegetables;
- fatty meat - pork, lamb, goose/duck;
- smoked meats;
- fatty broths;
- cabbage soup, okroshka, borscht;
- sorrel, dill, parsley, onion - can cause irritation of the gastric mucosa;
- mushrooms;
- pickled vegetables, marinades - increase secretion;
- cereals – millet, pearl barley, corn, egg;
- fresh bread, pastries;
- ice cream, chocolate;
- fruits/berries that are sour to taste;
- sour cream (limited).
Following a diet helps minimize the risk of relapse of the pathology. Antral chronic gastritis during the period of exacerbation is treated with diet No. 1 A. After the symptoms subside, the patient is transferred to treatment table No. 1.
Causes of the disease
Antrum gastritis is caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. In rare cases, the disease is caused by the activity of other microorganisms or fungi. Antrum gastritis develops under the influence of external and internal factors. Causes:
- eating disorder;
- alcohol consumption;
- smoking;
- long-term therapy with hormonal agents, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- contact of chemical compounds with mucous membranes;
- radiation;
- parasitic, viral infections;
- psychological stress;
- physiological characteristics - increased pressure in the duodenum leads to the reflux of its contents into the pyloric region;
- oxygen starvation;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- hormonal disbalance;
- avitaminosis.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane usually occurs due to a combination of several factors.
Nutrition during an exacerbation
In case of exacerbation of chronic gastritis - within several days - the patient is recommended to follow diet No. 1A and No. 1B. Nutrition minimizes the negative impact of food on the inflamed gastric mucosa. Treatment table No. 1A is physiologically inferior and has a reduced caloric intake: a person receives no more than 2000 Kcal per day. The volume of table salt is 8 grams.
Products/dishes that can enhance the secretory function of the stomach and irritate its surface are completely excluded from the menu. The food served should be moderately warm, but in no case hot or cold. Dishes should have a liquid consistency, which facilitates the digestion process. You need to eat fractionally - up to 6 times a day - in small portions so as not to overload the stomach.
During an exacerbation, you should not eat:
- bread;
- sour cream;
- cheese products;
- fat meat;
- sour milk;
- cottage cheese;
- fresh vegetables/fruits;
- seasonings/spices;
- strong brewed teas;
- carbonated drinks.
The patient is transferred to therapeutic diet No. 1B on the fourth or fifth day from the onset of the disease - when the pathological symptoms subside. Daily caloric intake – up to 2500 Kcal. The diet is characterized by a reduced carbohydrate content, but the protein content meets physiological needs.
What can you include in your diet? The menu is expanding due to the introduction of new products. These are homemade crackers, slimy cereal soups, boiled, pureed dietary meat, dairy products, soft-boiled eggs, white fish, boiled vegetables, sweet juices, previously diluted with water. The duration of diet No. 1B is three to five days. Then the patient is transferred to table No. 1.
Treatment
Treatment of antrum gastritis is always complex. It includes not only taking certain medications, but also following the nutritional rules prescribed by the doctor, as well as the use of certain folk remedies.
In the overwhelming majority, patients are prescribed antibacterial therapy. If Helicobacter is detected in the patient’s body, doctors prescribe antibiotics. Among them:
- Amoxicillin;
- Metronidazole.
To reduce acidity and protect the stomach by coating it, the following series of drugs are prescribed:
- Omez or Omeprazole;
- De-nol;
- Renicidin;
- Almagel;
- Alugastrin.

Antispasmodics in the treatment of antrum gastritis are also quite common. In case of severe and pronounced pain syndrome, patients are prescribed No-shpu and Platyfillin.
To improve digestion and intestinal motor function, the following are used:
- Festal;
- Mezim;
- Penzinorm forte.
If the patient has vomiting or severe nausea, Metoclopramide and Domperidone are prescribed.
Treatment is always complex, and therefore, some doctors recommend that their patients take herbal decoctions that have a calming effect and honey. It is this medicine that is considered a natural enveloping agent that can protect the stomach from the negative effects of an aggressive environment.
Diet for atrophic form
Atrophic gastritis is accompanied by significant changes in the gastric mucosa. The pathology is characterized by reduced acidity of gastric juice. Nutrition for this form of inflammation is based on treatment table No. 2 according to Pevzner. Its main task is to stimulate the secretory function of the stomach and normalize the motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract.
Basic principles of diet No. 2:
- the presence in the diet of broths that enhance secretion;
- food is not served in a puree state, but cut into small pieces;
- refusal to eat foods that are difficult to digest;
- frying is allowed;
- moderate salt restriction;
- five meals a day, including an evening glass of kefir.
Most of the rumors associated with atrophic gastritis are true. In the presence of a disease, the gastric mucosa becomes inflamed, and its renewal process loses functionality. Digestion becomes difficult, secretion production decreases, and the gastric glands are replaced by epithelial tissue.
Diet for atrophic gastritis of the stomach is a fundamental part of recovery, so you should follow nutritional recommendations. This will help cure the disease more effectively, increase the absorption of medications and eliminate sludge from the body.
Therapy of non-atrophic gastritis
Treatment of non-atrophic gastritis consists of a combination of medications selected by a specialist, adherence to a dietary diet and reorganization of the overall lifestyle. Only together will these measures lead to recovery and prevent further development of the disease.
Medicines are selected based on the root cause that provoked the disease.
- In the case of infection with Helicobacter pylori, eradication is carried out - a set of measures aimed at destroying the bacteria and normalizing the functioning of the stomach. There are several eradication lines, each of which is represented by certain schemes. The choice of a specific treatment plan should be made only by a specialist in accordance with the severity of the disease, the duration of its course and possible concomitant ailments. As a rule, the eradication regimen includes antibacterial agents, bismuth preparations and proton pump inhibitors that regulate the secretion of secretory fluid.
- In a situation where the disease was provoked by other pathologies of the digestive system, complex treatment of all ailments is carried out, and not separately. Therapy may include antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs that normalize stomach acidity.
- With reduced secretory activity and insufficient acidity, medications are prescribed that increase the pH and stimulate the production of hydrochloric acid.
- In cases where non-atrophic gastritis is accompanied by B12-deficiency anamnia, the patient is advised to take anti-inflammatory drugs high in essential minerals. In some cases, these medications can be replaced with herbal infusions and decoctions prepared from medicinal herbs - chamomile, St. John's wort, mint, valerian, plantain leaves.

In no case should a patient with non-atrophic gastritis independently select, replace or change medications at his own discretion or on the advice of a pharmacist from a pharmacy, a neighbor, or loving relatives. The same applies to medicinal herbs: the decision to replace a medicine with a specific herbal decoction is made only by a doctor who knows the characteristics of the course of the disease, possible side effects and complications.
Symptoms of atrophic gastritis of the stomach
At first, it is impossible to detect atrophic gastritis. The disease does not cause visible symptoms. The mucous membrane thins along the bottom of the stomach, then the process moves higher, affecting the upper and middle part of the organ. After atrophy, the first signs of the disease become noticeable, which are divided into 2 syndromes that have their own symptoms.
Anemic syndrome
Indicates a decrease in hemoglobin in a general blood test. This leads to a decrease in red blood cells, which are responsible for supplying oxygen to the internal organs. Anemic syndrome occurs when there is a lack of vitamins B12, B9, and iron. The listed elements may be absent due to low digestibility or absence from the diet. Signs of anemic syndrome:
- increasing weakness, feeling of depression, drowsiness;
- pale skin;
- feeling of pain in the stomach, burning sensation in the mouth;
- high fatigue, sleep duration more than 9.5 hours;
- lack of sensation in the limbs.
Dyspeptic syndrome
Occurs due to disturbances in the digestive tract. Has the following symptoms:
- Heaviness in the stomach, burning under the ribs;
- Heartburn after consuming acidic drinks or foods;
- Decreased appetite;
- A white coating appears on the tongue, teeth are imprinted;
- Salivation;
- There is a constant presence of bad breath;
- Belching;
- Regurgitation, which occurs after accidental entry of stomach contents into the oral cavity;
- Vomiting of mucus, bile and pieces of undigested food, nausea, and discomfort in the abdomen;
- Loose stools;
- Occasionally, patients report pain, the duration of which reaches 3-6 hours. After eating, the pain intensifies, but after vomiting it decreases.
NOTE! Atrophic gastritis is a provocateur of cancer diseases associated with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. A connection has been established between the disease and the formation of cancer in patients suffering from atrophic gastritis from a young age.
Causes, risk factors and mechanism of disease development
The mechanism of development of chronic non-atrophic gastritis is very simple: disruption of normal digestive function leads to destruction of the gastric epithelium. At the initial stage, degenerative changes occur only in the upper layer of protective mucus. The main cause of pathological processes: an unbalanced diet. Low-quality processed foods, alcohol, salty and sweet snacks, especially eaten on an empty stomach, can trigger a destructive mechanism.
Constant breakdowns from diets are also dangerous: alternating hunger and subsequent consumption of excessive amounts of food is extremely harmful to the lining of the stomach. Sometimes the cause of the disease is stress .
The trigger of the disease can also be a bacterial infection Helicobacter pylori . The pathogenic bacterium enters the body during close physical contact, kissing, or sharing cutlery between two people. Experts emphasize that many people are carriers of Helicobacter pylori, but not everyone suffers from gastritis. The following risk factors contribute to the development of pathology:
- hereditary predisposition to the disease;
- smoking;
- drinking alcoholic beverages in large quantities;
- regular consumption of spicy, salty foods;
- constant failures from strict diets;
- the presence of other diseases of the stomach and pancreas.
That is why those people who know about the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the body should adhere to healthy eating principles.
Nutritional features for types of atrophic gastritis
If it’s time to start treatment, then one of the means of complex therapy will be diet. Atrophic gastritis forces you to give up food with an abundance of flavors and replace it with more bland dishes. The main requirement for the diet is the stimulation and restoration of cells in the gastric mucosa. It is necessary to ensure that the diet does not contain food that can damage the walls of the organ.
If the acidity in the stomach is increased, then it is recommended to eat foods that can reduce secretion production (flax porridge, low-fat soup, vegetable purees, pears, bananas). If acidity decreases, you will have to include in the daily menu food and drinks that increase secretion (natural juices, still water).
Diet No. 2 for atrophic and hyperplastic gastritis of the stomach
The diet has another name - “Healing table No. 2”. Nutrition is based on the intake of all necessary substances in the body in a certain quantity. Within a short time, the digestive system returns to normal, but sometimes the diet is prescribed for life.
Food can be prepared in several ways:
- boil;
- steam;
- stew;
- cook;
- bake - less often, but possible.
It is necessary to ensure that the dish can be cooked for as little time as possible. The smaller the food, the easier it is to digest, so it is important to grind all products used in food. You should avoid fatty, spicy, sour, salty, smoked, fried, hot or cold foods.
The amount of preservatives and artificial colors will have to be reduced to the maximum, since they provoke gastritis. The portion of food should be small - no more than 250 grams. for one meal. The ideal option would be to eat food every 2-2.5 hours.
A diet for hyperplastic gastritis involves reducing the level of carbohydrates to 200 grams. per day, and the amount of fat and protein can reach up to 100 grams. Kilocalories are counted only in their pure form, that is, until the moment of preparation. The temperature of the food consumed should not exceed 50 ºС, but completely cold food should not be eaten. There should be at least 6 meals a day without excess salt or other spices.
NOTE! Hyperplastic gastritis is the most dangerous type known. If treatment is not started on time, metastases will appear in the gastric mucosa.
Therapeutic diet for chronic gastritis of the antrum of the stomach
There are categories of products necessary to follow a diet for antral atrophic gastritis:
- Probiotics - reduce inflammation in the stomach, help maintain acid-base balance;
- Ginger - inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria. You can eat it or add it to tea. Garlic has similar properties, with the exception of being an additive to tea. You can eat no more than ¼ tbsp per day;
- Fiber - contains a large amount of dietary fiber, which has a beneficial effect on digestion. Fiber is quickly absorbed. Flax seed, oatmeal, buckwheat, rice, and legume porridges can boast a high content of dietary fiber.
- Fats and proteins are healthy foods because they can restore damaged stomach walls. Animal protein can be obtained together with chicken eggs, red fish, poultry meat (chicken or turkey). Olive oil or avocado are healthy plant sources of fat.
Focal atrophic gastritis and colitis - principles of diet
In the treatment of focal atrophic colitis, diet is the main remedy. The mucous membrane of the stomach is partially affected, while affecting the intestines. Pepsin and hydrochloric acid begin to be produced in small doses, which leads to a gradual deterioration of the stomach. Inflammatory plaques appear on the walls. Focal atrophic gastritis implies the following diet:
- 6 meals a day;
- Cooking must be carried out according to all the rules - dishes are prepared without adding fat. Salt food should be kept to a minimum. Among the types of heat treatment, you can use boiling, stewing, baking, steam;
- All food must be thoroughly ground or crushed;
- Products that affect gas formation in the intestines are eliminated from the diet;
- The food temperature should be 45-55 degrees;
- You should drink 2 liters daily. clean water. Other liquids are not taken into account.
What symptoms can be used to suspect the disease?
At an early stage, characteristic symptoms appear quite rarely, but pain is usually characterized as mild or moderate. At the earliest stage, the patient may experience nausea, heartburn and an unpleasant taste in the mouth a couple of hours after eating.
Also, after drinking even a small amount of a highly carbonated sweet drink, obvious bloating may occur. Other signs of chronic non-atrophic gastritis:
- loss of appetite;
- constant belching ;
- general weakness;
- gray or whitish coating on the tongue ;
- dry mouth.

Of course, all of the above symptoms do not develop unexpectedly. They are preceded by long-term stress, or constant consumption of “dangerous” foods. Unpleasant painful sensations often last no more than a week in a row, because with adequate therapy, the walls of the stomach are restored very quickly. But if no measures are taken, superficial gastritis may worsen. pain in the stomach and vomiting occurs .
List of permitted and prohibited products
Can
| It is forbidden | |
| Vegetable oil or butter | Preservation, pickles, marinades |
| Fruit juices, preferably homemade | Alcohol, sparkling water, coffee |
| All vegetables except prohibited ones | Fish and meat broths |
| Stale baked goods | Baking from butter and puff pastry |
| Porridge, better overcooked | Grape |
| Fermented milk products | Fatty meat or fish |
| Omelette | Lard, animal fats |
| Dried bread | Fresh baked goods |
| Soups with vegetable or low-fat chicken broth | Smoked and spicy dishes |
| Well-cooked pasta | Hard-boiled eggs |
| Low-fat milk | Whole raw vegetables – only pureed |
| Red lean fish, poultry – turkey, chicken | Rutabaga, radish |
| Ground berries | bell pepper |
| Decoctions - rose hips, thyme, St. John's wort | Legumes |
Menu for the week
1 day
| Boiled oatmeal, tea; Apple with cottage cheese, baked; Boiled breast, potato and carrot salad, homemade compote; Rice porridge with milk; Casserole with rice; Snowball 250 ml. | |
| Day 2 | Cheesecakes, tea; Banana; Steamed hake fish, boiled beets with olive oil, juice - be sure to dilute with plain water; cottage cheese with the addition of honey and sour cream; Zucchini in the oven; Kissel. |
| Day 3 | Vermicelli casserole with cheese, cocoa and low-fat milk; Pear; Creamy pumpkin soup; Steamed fish cutlets, compote; crackers with jam, tea; potatoes in the oven, salad (cucumbers, tomatoes, olive oil), mint decoction. |
| 4 day | Boiled buckwheat porridge, cocoa; Low-fat steamed fish, juice with water; Milk pumpkin soup, tea; Rice casserole with cheese; Green vegetable salad, kefir. |
How to diagnose
If signs of the disease are detected, consult a gastroenterologist. The specialist assesses the patient’s condition based on complaints and makes a preliminary diagnosis. After this, an examination is prescribed, which includes several stages. The purpose of diagnosis is to identify the cause and degree of antrum gastritis. Methods for diagnosing the disease:
- gastroscopy is an instrumental examination performed using an endoscope;
- biopsy - taking a tissue sample for study;
- breath test to detect helicobacteriosis;
- blood, urine, stool analysis;
- Ultrasound of the digestive system;
- determination of acidity level;
- assessment of the motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract;
- study of motility of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Additionally, X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging may be prescribed.
Popular recipes for dieting dishes
Milk pumpkin soup 400 gr. Pour water over the pumpkins and cook until you get a puree. Take another bowl, boil 3 cups of low-fat milk, add 2 tbsp. l. semolina, cook for 10 minutes, then add pumpkin puree. Add salt, sweeten and cook for another 15 minutes.
Puree rice porridge with milk Prepare a handful of rice, grind with a blender or coffee grinder. Pour 1.5 cups of low-fat milk into a saucepan, boil and gradually lower the resulting rice cereal. 5 minutes before readiness, add salt and sugar. Total cooking time is 15 minutes.
Potato and carrot salad Boil 4 medium potatoes and 2 large carrots. Wait for it to cool, peel and chop finely. Dilute lemon juice in a small amount of warm water, add sour cream and salt - this will be a salad dressing.
Dietary nutrition for gastrointestinal diseases
The diet presupposes full adherence to the doctor’s instructions regarding nutrition. Any arbitrary deviation from established norms can lead to the transformation of the disease into an acute form. During the diet, the following are completely excluded from the patient’s diet:
- alcoholic drinks and sodas;
- flour, chocolate, sweet, cream products;
- black and fresh bread;
- dried fruits;
- fast food;
- fat meat;
- coarse fiber (oats, corn, potatoes);
- dishes with spices and herbs;
- fried, smoked, spicy, canned, fatty foods;
- sour cream, milk.
Preference should be given to:
- boiled chicken, rabbit fillet and fish;
- steamed vegetables and cutlets;
- vegetable puree and soups;
- pasta, cereals, broths;
- sweet berries;
- pure mineral water with lemon;
- weak tea.
During exacerbations, it is necessary to completely switch to porridge and liquid dishes; they should be consumed in small portions up to 6 times a day with four-hour breaks. Returning rich broths, pickled cucumbers, herring, caviar and fried foods to the diet can only be done after the acute phase of the illness has passed.
Having answered the question of what antral gastritis is, it should be noted that the necessary help and additional information can only be obtained from a therapist or gastroenterologist after examination. The disease will have a positive prognosis only if the patient adheres to the diet, instructions and recommendations of specialists and eliminates bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking) from life.
«>
What is antrum gastritis and how to treat it?
Antrum gastritis is a disease in which inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the pyloric section of the stomach occurs. The affected area is located in the lower part of the organ adjacent to the spine. The pathology is often caused by the parasitic activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Gastritis of the antral type is characterized by disruption of the structure of the lower part of the stomach and malfunction of the glands.