Surgery to remove hemorrhoids today is the only effective way to treat this disease when conservative methods have failed. In the initial stages of hemorrhoidal disease, specialists perform minimally invasive surgical interventions, which are painless and have a short recovery period. In advanced forms of the pathological process, it is possible to get rid of hemorrhoids only through radical surgery.
Treatment methods
04/09/201804/09/2018 0 Comment
- 1 Types of hemorrhoid surgery
- 2 Parkes hemorrhoidectomy
- 3 Indications for surgery to remove hemorrhoids 3.1 Indications for minimally invasive surgeries
- 3.2 Indications for radical operations
- 5.1 Preparation for minimally invasive surgery
Types of radical operations
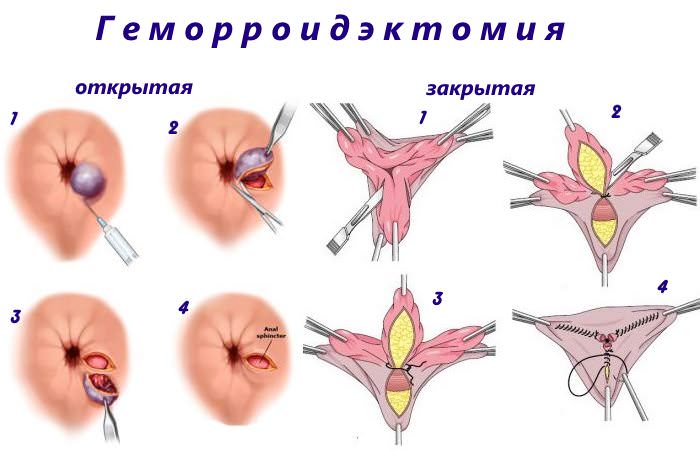
Classic hemorrhoid removal operations can be performed using two methods:
- open: during the operation, the surgeon does not suture the postoperative wounds, i.e. the places where the nodes were located heal on their own;
- closed: during the operation, the surgeon puts sutures on postoperative wounds and places where the nodes were excised, they heal much faster and more efficiently, as a rule, it is after such interventions that the disease is cured almost completely and the reappearance of hemorrhoids is possible only in a small number of patients only after 10 -15 years.
Radical operations to remove hemorrhoids can be performed in two ways:
- Hemorrhoidectomy according to the Milligan-Morgan method or its modification (they differ from the main method only in the way the intervention is completed).
- Transanal resection using the Longo method.
The above methods are carried out only after hospitalization and special preparation of the patient and require his rehabilitation in a hospital setting. To relieve pain, general anesthesia or prolonged epidural anesthesia is required.
Types of hemorrhoid surgery
offers several methods for removing hemorrhoids through surgery. Each method is effective for its specific case.
Sclerotherapy and ligation
Sclerotherapy and ligation are minimally invasive operations that are used in the treatment of hemorrhoids in the initial stages.
The principle of sclerotherapy is the introduction into the lumen of a vessel (hemorrhoidal vein) of a drug that reduces its tone. As a result of sclerosis, it loses its functional abilities, which further leads to disruption of the blood supply to the node and its subsequent degradation. Advantages of the method: low trauma, lack of pain and quick rehabilitation.
Ligation surgery is used to treat hemorrhoids at the initial stage of the disease and consists of pinching the problematic veins with a special latex material. For thrombosis, radio wave or laser therapy techniques are used.
Hemorrhoidectomy
Removal of nodes by surgical methods (hemorrhoidectomy, Longo operation, disarterization). Our clinic has improved the known surgical techniques for removing hemorrhoids, which has reduced the rehabilitation period and reduced the risk of complications. For example, during hemorrhoidectomy, nodal connections are removed, followed by ligation of the vascular bundles.
Operation Longo
The tactics of Longo's operation in the treatment of hemorrhoids involve excision of the mucous membrane, which is located above the node. The surgical intervention lasts up to half an hour and is performed under local anesthesia of the operated area and ultrasound control.
Desarterization
Arterial disarterization is the deprivation of a hemorrhagic node of blood supply. As a result of surgical intervention, large formations sclerotize and die. The operation is carried out under the control of radiation diagnostic methods (Doppler, ultrasound).
Hemorrhoidectomy
Indications
This technique for removing hemorrhoids can be used to treat any type of hemorrhoids, but, in most cases, it is used in the following clinical cases:
- internal hemorrhoids, starting from stage II of the disease, if the nodes are already too large to use ligation with latex rings;
- stage III hemorrhoids when it is impossible to reduce the hemorrhoids.
Most often, the operation is performed on patients over 40 years of age, since it does not always guarantee a long-term result when performed on patients under 35-40 years of age.
Contraindications
In some cases, hemorrhoidectomy may be contraindicated due to underlying conditions or diseases. These include:
- inflammatory bowel diseases (including Crohn's disease and immunodeficiency states due to AIDS and other diseases);
- cancer diseases;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- diseases affecting the composition of the blood that are not amenable to drug correction.
Preparing for surgery
Before hospitalization, the patient is recommended to improve bowel function. To do this, he needs to carefully consider his diet and include in it foods that help eliminate constipation. If it is impossible to eliminate them through diet therapy, the doctor may recommend taking laxatives, taking into account all the indications and contraindications for their use.
Also, if a hemorrhoidectomy is necessary, the patient may need to stop taking certain medications that he is taking regularly (for example, anticoagulants or hormonal agents). That is why, before surgery, the patient must tell the doctor the name of the medications he is using to treat other diseases.
Preparing the patient the day before and on the day of surgery should include the following:
- Before hemorrhoidectomy, the last meal should take place 10-12 hours before surgery.
- The night before, the patient should take a hygienic shower and put on clean underwear.
- Before the operation, the patient is given a cleansing enema to completely cleanse the intestines.
- During general anesthesia, it is recommended not to drink water or eat food.
Anesthesia
In most cases, hemorrhoidectomy is performed under general anesthesia or with prolonged epidural anesthesia, since the intervention lasts quite a long time and, if complications arise, may require additional time to prolong pain relief.
How is the operation performed?
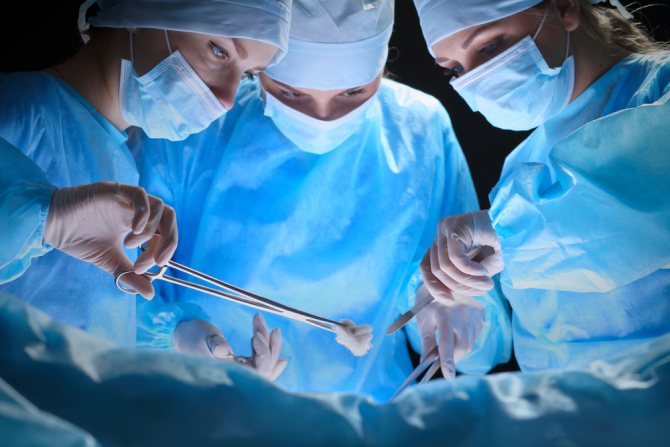
- If the intervention is performed under general anesthesia, then after the patient enters the operating room, he is placed on the operating table. In most cases, the operation is performed with the patient lying on his back with his legs apart, elevated and fixed on a special device. In cases where hemorrhoidectomy is anesthetized with epidural anesthesia, the epidural space is first punctured, a catheter and anesthetic are introduced, and then all subsequent preparatory measures are carried out.
- After laying the patient down, the nurse shaves the patient's hair in the anus and perineum area.
- General anesthesia is performed.
- The surgical field is treated with an antiseptic solution.
- The doctor dilates the anus with a finger and inserts an anoscope lubricated with sterile glycerin.
- With the help of special dilators, to provide access to hemorrhoids, the walls of the rectum are separated.
- Schematically, hemorrhoidectomy is the excision of all tissues that have been subjected to hemorrhoidal changes and part of the skin around the anus. To do this, the doctor grabs the nodes with a special tool and brings them out. In the leg of the node there is a blood vessel, which is the cause of the formation of hemorrhoids. The surgeon stitches it, and then proceeds to bandage the entire leg. After complete ligation of the artery and pedicle, the entire node is excised.
- After this, the doctor ligates (bandages) the bleeding vessels and fixes the rectal mucosa and covering tissues to the underlying tissues.
- After the operation is completed, a tampon with Levomikol or Levosan ointment and a gas outlet tube are inserted into the rectum, which will ensure timely removal of gases from the rectum and enable the medical staff to timely notice any postoperative bleeding.
Depending on the extent of the pathological process, hemorrhoidectomy can last about 20-60 minutes. During the operation, the proctologist can use not only a regular scalpel for dissection, but also more modern devices: a radio knife, electrocoagulating devices (“Ligashu”) or a harmonic scalpel Ultracision, Ethicon Harmonic, etc. Each of these devices has its own advantages and disadvantages, and choice the use of one or another of them depends on the clinical indications, which are determined by the doctor during the operation.
Features of the postoperative period
After completion of the operation, the patient is taken to the ward and, when using general anesthesia for pain relief, control of blood pressure, pulse and number of respiratory movements is ensured. A doctor or specially trained nurse will provide constant monitoring of the amount of urine produced and the condition of the gas tube (for bleeding that may occur after surgery). On the first day after surgery, the patient is not recommended to eat.
If urinary retention occurs, which often occurs after hemorrhoidectomy, the patient is advised to drink less fluid. If the patient does not experience problems with urination, then, on the contrary, he is recommended to drink more water and take laxatives, which prevent constipation, which is extremely undesirable after such an operation.
If pain occurs in the postoperative period, various narcotic drugs (Promedol, Morphine hydrochloride) and painkillers in the form of ointments, tablets or injections can be used: Dexalgin, Spazmalgon, Ketanov, 0.2% Nitroglycerin ointment, Analgin solution with Diphenhydramine, etc. And in cases of use prolonged epidural anesthesia, over several days, additional injection of anesthetic into the catheter can be performed (naropin pump method). The duration of pain relief is determined by the presence of pain after surgery. If necessary, the patient can be prescribed weaker analgesics (Nurofen, Dicloberl, etc.) and, if the pain is neurotic in nature, then sedatives (Novopassit, Persen, etc.). As an addition to taking painkillers, the patient may be recommended to take warm sitz baths with antiseptic solutions that eliminate spasms and reduce pain.
Transanal resection using the Longo method
Indications
Transanal resection using the Longo method can be prescribed for the same indications as classical hemorrhoidectomy. However, it is most often used to treat patients at stage III of the disease. Also, this technique cannot be used to remove external hemorrhoids.
Preparing for surgery
To prepare for surgery using the Longo technique, the patient must undergo the same procedures as before hemorrhoidectomy.
Anesthesia
To relieve pain during transanal resection using the Longo method, general anesthesia or local anesthesia is used. If necessary, the anesthesiologist can decide on the advisability of performing epidural anesthesia.
How is the operation performed?
The stages of transanal resection are as follows:
- After anesthesia, clamps are applied to the skin. Then they are pulled apart.
- A dilator is inserted into the anus, which is fixed at four points using sutures. The free ends of the threads are tied with a knot.
- An anoscope with a special obturator is inserted into the anus.
- A purse-string suture is placed above the dentate line of the mucosa (4-5 cm). To obtain a symmetrical seam, while applying stitches, the anoscope is turned and pulled out, and then inserted again. The ends of the threads used for the seam are not tightened.
- After this, the quality of the stitches and their density are checked.
- A hemorrhoidal circular stapler is inserted into the rectal lumen. Its head should be located above the applied seam, and the stapler itself should be held in the maximum open position.
- After performing these steps, the doctor tightens the ends of the threads that were used to apply the purse-string suture into one knot. The ends of the threads are brought out through the side holes of the stapler and held.
- The stapler is moved inward and, turning its handle clockwise, wait for it to close, during which part of the mucous membrane is crossed with a circular knife along with hemorrhoids. In this case, the ends of the resulting surgical wound are fastened with titanium clips.
- The surgeon removes the stapler and examines the removed part of the mucosa to assess the correctness of the procedure.
- After this, the quality of the application of staples is inspected and, if bleeding is present, additional stitches are performed using self-absorbable thread.
- The surgeon removes the anoscope and inserts a gas outlet tube and a gauze swab with Levomikol or Levosan ointment into the intestinal lumen.
As a rule, transanal resection using the Longo method requires no more than 15-20 minutes.
Features of the postoperative period
After completion of the operation, the patient is taken to the ward and provided with care that is indicated for patients after intravenous anesthesia. In the future, the patient is shown the same therapeutic measures as for hemorrhectomy. According to statistics, 83% of patients in the first days after transanal resection using the Longo method do not experience pain, and by the fifth day – already in 97%. If we compare this technique with hemorrhoidectomy, then almost 100% of patients have no pain for quite a long time.
In the absence of complications, the patient can be discharged from the hospital after 2-3 days, and his disability continues for 3-4 weeks. After discharge, the patient is recommended to regularly visit the proctologist until the mucous membrane is completely healed.
Possible complications
This operation to remove hemorrhoids has virtually no complications. In rare cases, the following are observed:
- bleeding: occurs when the edges of the mucous membrane diverge or do not stop sufficiently during surgery;
- rectovaginal fistula: develops with secondary infection in the area of the stapled edges of the mucosa and tissue necrosis, which is accompanied by the formation of a passage from the rectum to the vagina;
- rectoperitoneal sepsis: develops when a postoperative wound becomes infected and is accompanied by the spread of infection to the peritoneal tissue and into the blood;
- thrombosis of the inferior vena cava: caused by a blood clot entering the inferior vena cava and leading to the need to remove the kidney.
If we compare these two surgical techniques, then it is preferable for the patient to undergo transanal resection using the Longo method. Despite its higher cost, it poses a lower risk of complications and does not require long-term use of analgesics and long-term rehabilitation.
Untimely treatment of hemorrhoids necessitates the use of radical treatment methods. For this purpose, removal operations are performed. Let's look at the most effective ones.
Longo method: transanal mucosal resection
Tool for performing Longo operation
In 1993, Italian surgeon Antonio Longo invented a method of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids, which became a serious alternative to the classical intervention of excision of hemorrhoids.
The essence of the operation is as follows: a circular resection is performed and subsequent suturing of the rectal mucosa at the site of prolapse of the nodes. However, unlike the classical method, with the Longo method, resection is not performed of the entire intestine, after which strictures often develop, but only parts of it. During Longo surgery, only a small part of the mucous membrane above the dentate line is removed. The defects are stitched using titanium staples. In other words, hemorrhoids are not removed, but simply pulled up. At the same time, due to a decrease in blood flow, they are significantly reduced in size. Subsequently, the dried out nodes are overgrown with connective tissue.
The Longo operation lasts only about 15 minutes under local anesthesia and can be performed even by inexperienced surgeons (although this is still not recommended). The surgical intervention itself allows you to restore the structure of the anal canal, without injuring the mucous membrane or damaging the rectum. Thanks to such indicators, the postoperative period for the patient is painless, and in the future patients are able to lead a normal life, with little or no fear of relapse of the disease.
True, with all the advantages of the method, it also has disadvantages. First of all, the long-term results of such treatment are still unknown. In addition, after Longo surgery, inpatient monitoring of the patient for a week is required. Also, the operation does not allow the removal of external hemorrhoids.
Indications for surgery to remove hemorrhoids
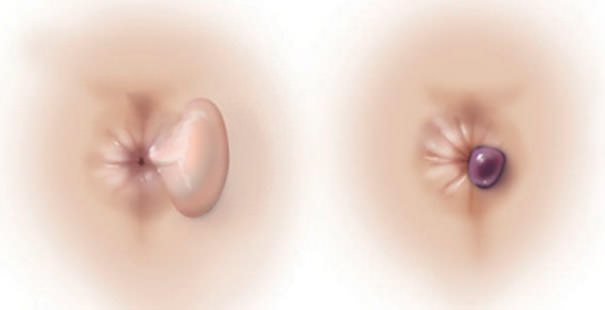
In what cases are hemorrhoids removed?
- When they fall out.
- When a hemorrhoid is pinched.
- Thrombosis.
- Frequent bleeding. This is explained by the fact that with the frequent appearance of blood, anemia develops.
- When the node protrudes, as this leads to inflammation of the skin.
- For severe pain.
Before hemorrhoids are removed, the condition of the body is assessed, which allows you to choose the right type of surgical intervention.
Preparing for treatment

- Before removing external hemorrhoids, the possibility of complications, as well as contraindications to the intervention, are assessed.
- A preliminary blood, urine, etc. test is taken.
- The intestines are cleansed using enemas and laxatives. It is recommended to adhere to a diet.
- Eliminate foods that irritate the intestines from your diet.
Sclerotherapy
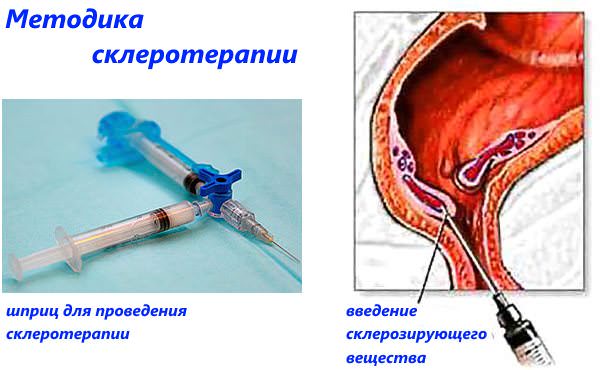
A painless operation, performed for small nodes. The essence is a thermal effect on hemorrhoids using an injection. The operation is performed within 15-20 minutes. On the same day the patient is sent home.
Ligation
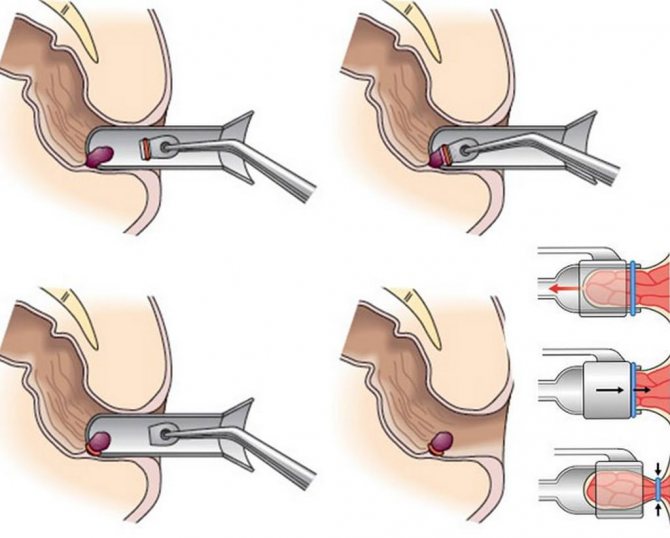
Ligation involves putting a latex ring on the knot, after which it dries out and falls off. After the operation, the nodes disappear within 4-6 days.
Laser surgery
Laser radiation affects hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoidectomy
Relevant for stages 3 and 4 of the disease. You should undergo an examination before the operation. The nodes are removed by excision and cauterization.
During hemorrhoidectomy, the patient will be admitted to the hospital. Using this method you can remove it forever.
Parkes method
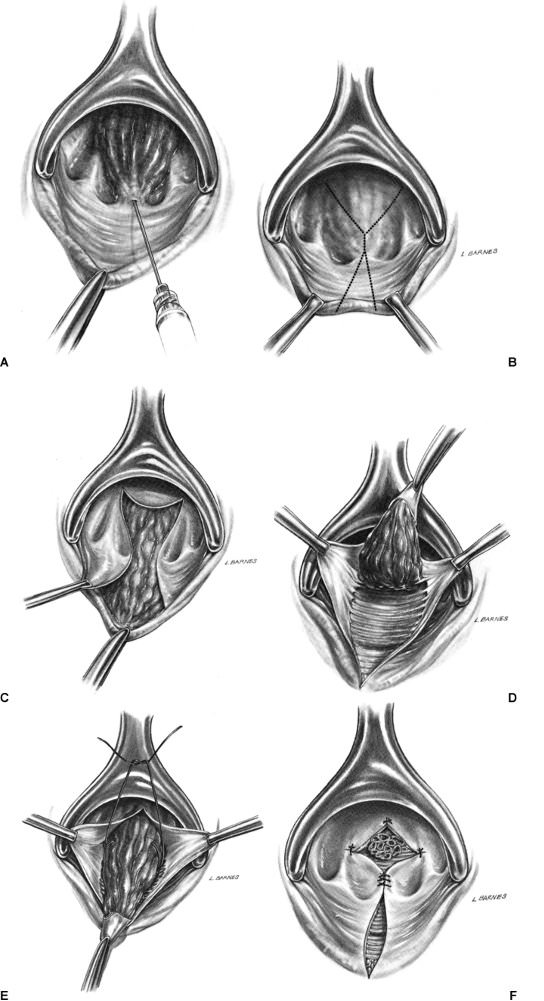
It is carried out by excision of the cone. When removal occurs, the mucous membrane is not affected. The duration of the operation is 30-60 minutes.
Milligan-Morgan operation
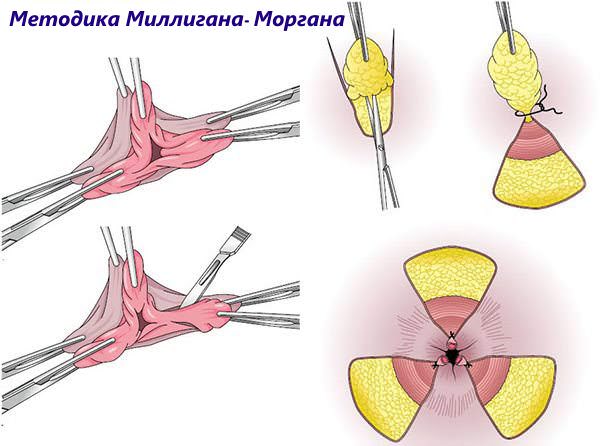
The operation takes place in a hospital setting. During the operation, the hemorrhoidal node is completely excised. An anoscope is inserted into the anus and the lump is grabbed with a clamp, which limits the flow of blood. Next, the knot is cut and stitched, and its leg is sutured with thread.
Recovery is 3 weeks, during which time pain will be present, so painkillers are taken. It's better to take a vacation from work.
Surgery for hemorrhoids is not performed:
- during pregnancy;
- during inflammatory processes in tissues;
- with AIDS;
- Crohn's disease;
- during oncological processes.
Longo method
Probably one of the most popular operations. It occurs as follows: a section of the colon mucosa located above the hemorrhoid is removed. Anesthesia is used during the procedure. The duration of the operation is 20 minutes. Relevant for stages 3-4 of hemorrhoids in hospital settings. The recovery period is 5 days.
The instrument used is an anoscope. The anus is stretched using special clamps, and a dilator is inserted into the anus and sutured to the skin. The surgeon uses titanium staples to secure the edges of the wound.
Advantages:
- It is possible to delete multiple nodes at the same time.
- After the intervention, there is no postoperative wound.
Rehabilitation

The type of surgical intervention directly influences the characteristics of the rehabilitation period.
In order to prevent irritation and inflammation of the intestines, a special diet is used, which is developed individually by the doctor.
On the first day after surgery, it is not recommended to eat food so as not to cause bowel movements.
If you do not follow the rules in the postoperative period, complications may arise:
- bleeding;
- fistula;
- urinary retention;
- purulent processes;
- pain syndrome;
- narrowing of the anal canal.
The cause of bleeding is that the edges of the mucous membrane diverge, and the feces press on the rectum. If a person cannot urinate on his own, then he is prescribed bladder catheterization.
Surgical intervention to remove cones is carried out in the last stages of this disease. The purpose of the operation and the choice of its type is carried out by the doctor in accordance with the indications. To avoid complications, it is necessary to undergo proper preparation and postoperative period.

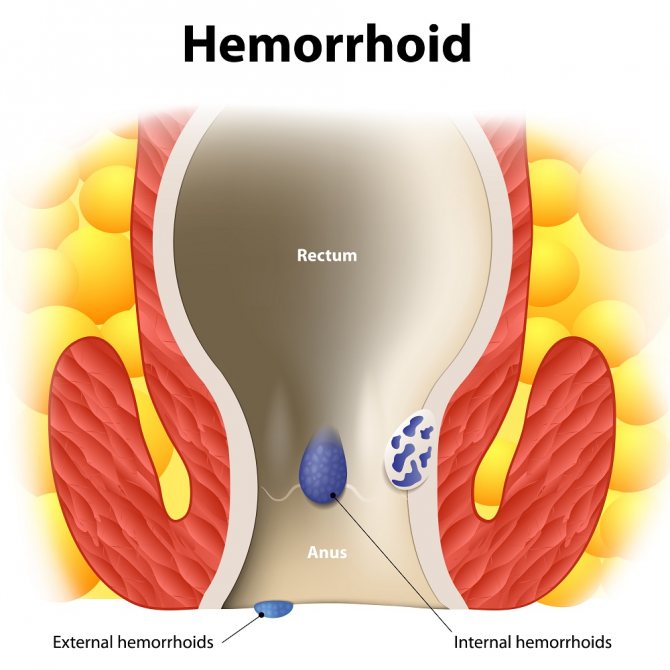
Hemorrhoids are the formation of a volumetric process (nodule) from the venous vessels of the rectum. Its development is long-term and chronic. Drug treatment in most cases does not lead to the reverse development (involution) of the hemorrhoid, so radical therapy for this pathology consists of removing the mass formation of the rectum.
Possible complications after surgical treatment
The most unpleasant consequence of surgical treatment of external hemorrhoids is relapse of the disease. Agree, the appearance of new nodes and the need for a repeat operation is unlikely to please anyone. But besides this, there are a number of complications/undesirable consequences that accompany surgical treatment of external hemorrhoids:
- Severe pain. They are caused by the presence of many nerve fibers in the anorectal region. You can get rid of pain only with painkillers (prescribed by your doctor).
- Psychological barrier. Occurs if the patient experiences severe pain during surgery or visiting the toilet. He will hold back the urge to go to the toilet, which only makes the situation worse. This phenomenon can be dealt with by prescribing laxatives.
- Urinary retention. This unpleasant syndrome lasts no more than a day after surgery to remove external hemorrhoids. If necessary, the doctor will catheterize the bladder.
- Open bleeding. The reason for this may be either an improperly cauterized vessel or injury to the rectal mucosa. The patient is prescribed a hemostatic sponge, or the vessel is sutured.
Surgical treatment of external hemorrhoids is a necessity that both doctors and patients often face. There is no need to be afraid of operations for external hemorrhoids - modern medicine performs them quickly, practically painlessly and with minimal risk of complications. But timely removal of external hemorrhoids will help avoid the serious consequences of the progression of this disease.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category
26, total, today
( 186 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5)
Impurities in feces: types, causes and treatment methods
Pain in the coccyx and anal-coccygeal suppuration
Related Posts
Indications for surgery
The need for surgical removal of hemorrhoids as quickly as possible arises in the following cases:
- Lack of effect and result of conservative drug therapy for hemorrhoids with ongoing clinical symptoms of the pathology and growth of hemorrhoids (surgical treatment is usually prescribed if there is no effect within 3 months).
- A later (3-4) stage of the disease, in which prolapse of hemorrhoids from the rectum develops without their independent reduction.
- The development of complications of hemorrhoids at any stage of its development - profuse bleeding from hemorrhoids, the development of an abscess and fistula of the rectum are indications for immediate surgical intervention in a hospital setting.
- Thrombosis of hemorrhoids is the formation of a blood clot that can separate from the hemorrhoid and begin to circulate with the blood flow in the arteries (thromboembolism). This condition is dangerous due to the development of necrosis (death) of individual sections of various organs, due to blockage of the artery feeding them by a detached blood clot.
- Combined development of hemorrhoids with other pathological space-occupying formations of the rectum - surgery is performed in the case of the parallel presence of polyps, anal canal fissures, chronic inflammatory processes in the pararectal tissue (connective tissue surrounding the rectum).
The method of choice for the treatment of hemorrhoids in older people is conservative therapy or minimally invasive methods of removing hemorrhoids. This is due to a decrease in tissue regeneration processes with age, which can worsen the postoperative period after surgery.
Types of operations for hemorrhoids
Surgical removal of hemorrhoids is necessary for people who have been trying to get rid of the disease for a long time using conservative therapeutic methods, but have not succeeded. In this case, excision of cones is the only effective method that can cure the pathology. There are different methods for removing hemorrhoids, including minimally invasive ones, which can be used for both external and internal formation of nodes.
Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids is justified in the later stages of the development of the disease (at 3 or 4 degrees of severity), when all other therapeutic methods have been tried. Indications for the operation are:
- progression of the disease, failure of conservative treatment;
- with each bowel movement process, blood-filled nodes fall out;
- the development of complications of the disease, the appearance of fistulas with abscesses in the rectum, inflammation of the cones and bleeding.

Hemorrhoidectomy
This operation does not involve direct intervention into the peritoneal cavity, but is associated with trauma to the skin, blood vessels and mucous membrane. Under unfavorable circumstances, a hemorrhoidectomy operation can lead to bleeding or infection of the patient’s body with some kind of infection. This explains the need for careful preparation for manipulation.
The traditional method used to operate on patients with inflammation of hemorrhoids is the Milligan-Morgan operation. This method is constantly being improved, selecting the most optimal options for performing the operation. The advantage of this surgical intervention is its effectiveness in the treatment of grade 3-4 internal hemorrhoids with a tendency to thrombosis or heavy bleeding.
How are hemorrhoids removed using hemorrhoidectomy? During the operation, the hemorrhoidal node is excised along with the mucous membrane. This surgical method of treating the disease is considered traumatic and is performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia. After the operation, the patient is kept in the hospital for at least another week. Recovery lasts about a month (in the absence of postoperative complications).
- Chicken manure as fertilizer
- ACC - instructions for use for coughs in children and adults
- How to clean a washing machine with citric acid
Increasingly, the Longo technique is used to remove hemorrhoids. This surgical method involves resection of the rectal mucosa. This treatment is less traumatic and has a lower risk of complications; in addition, the Longo method is used without general anesthesia. The disadvantage of this therapy is that it cannot be used for patients with external hemorrhoids.
Removal of hemorrhoids with laser
The method involves cauterizing tissues with high-frequency infrared radiation. Laser coagulation of hemorrhoids ensures sealing of the vascular walls, so there is no risk of bleeding. If a doctor operates on external venous inflammation, the procedure is very simple - laser beams cut off the nodule and immediately cauterize the wound, eliminating the risk of infection.
Vaporization (laser treatment of hemorrhoids) is a relatively simple technique that is carried out using high-tech devices and has a minimal risk of developing negative consequences. However, laser surgery does not always bring good results, since enlarged nodes cannot be completely cauterized. Due to partial removal of the cones, the likelihood of relapse of the disease remains high.
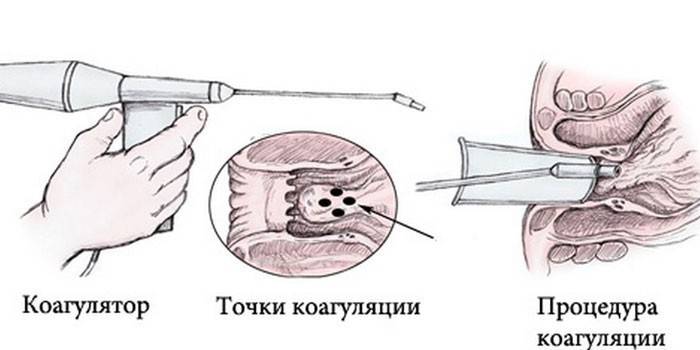
Infrared coagulation of hemorrhoids
This method is painless and does not take much time. Infrared coagulation is carried out by exposing the pedicle of the hemorrhoid to infrared light waves. Getting deep into the base of the lump, it provokes tissue coagulation, which prevents blood from entering the node. After a certain time, the cone dies off. The procedure for removing nodes occurs quickly, and the patient does not feel any discomfort. The next day the patient returns to his normal lifestyle.
Sclerotherapy for hemorrhoids
This relatively new method of treating hemorrhoids involves eliminating hemorrhagic lumps by blocking their blood supply. During the procedure, a medicine, a sclerosant, is injected into the lumen of the node. It stimulates the inflammatory process in the vein, as a result of which the walls of the vessel stick together and become overgrown, stopping the blood supply to the lump. Hemorrhoid removal can be performed for both internal and external hemorrhoids.
This outpatient procedure is less painful than surgery and does not require anesthesia. This method of treatment is ideal for eliminating deep-lying nodes, since removing a lump located far from the anus is much more difficult than removing an external one. Despite the fact that the procedure is not considered an operation, for its successful implementation the patient must prepare in advance for the removal of the lump. For this purpose, a cleansing enema is given two hours before the start of the manipulation.
- Treatment of body skin fungus
- How to cook delicious chicken fillet: recipes
- Pumpkin baked in the oven with honey: recipes
Cryodestruction of hemorrhoids
The method involves exposing damaged tissue to very low temperatures. During the procedure, the blood supply to the lump is cut off, causing it to die and be rejected. Cauterization of hemorrhoids is carried out with crisonide in an inpatient or outpatient setting, and hospitalization after removal is not required. Since low temperatures cause vasoconstriction, there is no bleeding during the procedures. In addition, cold eliminates muscle spasm in the operated area and improves tissue regeneration.
Ligation of external hemorrhoids
How is surgery to remove hemorrhoids performed? To do this, use a ligator device, through which a special latex ring is placed on the inner cones. The ring compresses the hemorrhoids, which contain feeding vessels. Gradually, the cone necrosis occurs, its stem is replaced by connective tissue, and the base itself is rejected (the whole process takes about 2 weeks). The rejected node exits through the anal canal along with feces.
Ligation of hemorrhoids is carried out gradually, due to which necrosis develops slowly, restraining the intensity of the inflammatory process and preventing the transformation of nodes into purulent formations. Over time, new connective tissue forms a reliable stump. The procedure rarely causes serious pain, but to eliminate discomfort, the doctor prescribes the patient to take analgesics in the first days after removal of the nodes.
Types of surgical radical treatment of hemorrhoids
The main goal of surgical radical treatment of hemorrhoids is the removal of hemorrhoids with maximum preservation of healthy tissue of the rectum and anus. An operation to remove hemorrhoids is considered successful if there is no relapse (exacerbation, re-development) for a period of at least 10 years. For this purpose, modern proctology uses 2 main groups of methods for removing hemorrhoids - minimally invasive techniques and surgical intervention.
Survey
Video: Restrictions after hemorrhoid removal. Question answer.

Video: Hemorrhoid removal surgery

In the clinic, in order to identify possible risks and contraindications, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood test for sugar, hepatitis and AIDS;
- electrocardiography;
- fluorography;
- anoscopy;
- digital examination of the rectum;
- colonoscopy or irrigoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Test results and ECG are valid for 1 month from the date of delivery. With the results of the obtained studies, the patient visits the doctor to obtain an opinion on the possibility of surgical intervention based on his general health.
If during the examination an inflammatory process, severe swelling or cracks, or ulcers in the anal area were revealed, then treatment is first carried out with the help of medications, and then surgery is prescribed.
Minimally invasive techniques for removing hemorrhoids
Such radical treatment methods are also called non-surgical methods, which is not entirely correct, since a small degree of tissue damage is present. In minimally invasive techniques, instead of a scalpel, various physical and chemical factors are used to destroy the hemorrhoid and remove it, which have minimal damaging effects on surrounding tissue. Minimally invasive techniques for the radical treatment of hemorrhoids include:
- ligation with latex rings - a special latex ring is placed on the stem of the hemorrhoid, which compresses it, compresses the feeding vessel and leads to the death of its tissue;
- infrared coagulation – destruction of the feeding vessel through local exposure to thermal radiation, which ultimately leads to the death of the hemorrhoid (necrosis) and its overgrowth with connective tissue (sclerosation);
- radical laser treatment - the hemorrhoid is exposed to a high-energy laser, which leads to its necrosis and sclerosis;
- cryodestruction – destruction of hemorrhoids by cold (local temperature down to -196º C);
- sclerotherapy is the introduction directly into the hemorrhoidal node of a special chemical compound, which causes its necrosis and subsequent sclerosis;
- Desarterization of a hemorrhoidal node is a minimally invasive operation in which a proctologist surgeon, using special micro-instruments, ligates the artery supplying the hemorrhoidal node, which causes its subsequent necrosis and sclerosis.
Most minimally invasive methods for radical removal of hemorrhoids are effective at earlier stages of hemorrhoid development (stage 1-2). Due to the low morbidity, after such procedures there is no need for hospital treatment and special recommendations regarding the rehabilitation period. They require special expensive equipment and highly qualified specialists. Therefore, not every medical clinic has the opportunity to use them.
Trust the removal of hemorrhoids in Moscow to specialists!
A favorable prognosis for the treatment of hemorrhoids depends on the correct diagnosis of the disease and the use of adequate treatment methods, including surgery. Moscow clinics have high-tech modern equipment, and doctors are professionals in their field. The cost of surgery to remove hemorrhoids depends on the individual clinical situation and treatment tactics that are optimal for a particular patient.
“Proctologist 81” meets all of the above criteria, and therefore is one of the leading medical institutions that provide conservative treatment and removal of hemorrhoids in Moscow. Our leadership is determined by an individual approach to the patient and high standards of medical practice. Regardless of the treatment tactics (be it surgery to remove hemorrhoids or conservative therapy), the prices in our clinic always correspond to the quality.
Operative surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
This type of treatment is radical and aimed at completely removing the hemorrhoid and treating its possible complications. This surgical intervention includes several main types of operations:
- hemorrhoidectomy;
- surgical intervention to remove hemorrhoids and other space-occupying formations of the rectum;
- radio wave removal of hemorrhoids.
The choice of surgical treatment method for hemorrhoids is carried out by a proctologist on an individual basis, depending on the type and stage of hemorrhoids, the presence of concomitant pathology of the rectum and complications, the age and gender of the patient.
Contraindications to surgical treatment of hemorrhoids

Minimally invasive hemorrhoid surgery is contraindicated in the following cases:
- combined hemorrhoids;
- anal tears;
- anorectal thrombosis;
- stage 1 hemorrhoids;
- pronounced swelling of the pararectal tissues;
- weeping wounds of the anus;
- paraproctitis.
Radical operations have a more expanded list of contraindications, namely:
- chronic paraproctitis with the formation of rectal sinus tracts and fistulas;
- infectious diseases of the colon;
- malignant neoplasms of the rectum and tissues of the anal area;
- exacerbation of concomitant diseases;
- severe pathology of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems in the decompensation phase;
- malignant blood diseases;
- violation of the blood clotting system;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- severe immunodeficiency conditions (SNID, HIV, recovery after chemotherapy).
Also, radical operations on hemorrhoids are not performed during gestation, since general anesthesia can affect both the condition of the mother and the unborn child.
Hemorrhoidectomy
This technique is the surgical removal of hemorrhoids using various operating techniques and surgical techniques. In proctology, several technical modifications of this surgical intervention are used, which include:
- method according to Milligan-Morgan - the essence of the operation is to suturing the feeding artery with subsequent removal of the hemorrhoid. Then sutures are placed on the area of the postoperative wound, and the rectum is tightly tamponed with sterile napkins to prevent swelling of the mucous membrane and postoperative bleeding. This operation is used for stage 3-4 hemorrhoids with a significant increase in the volume of hemorrhoids.
Surgery using the Milligan-Morgan technique
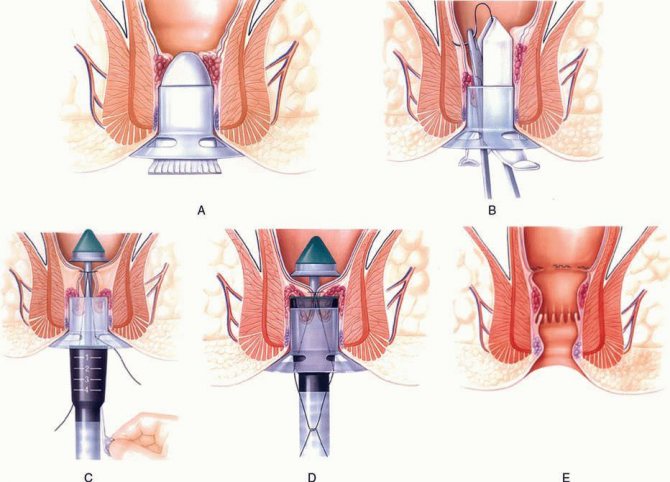
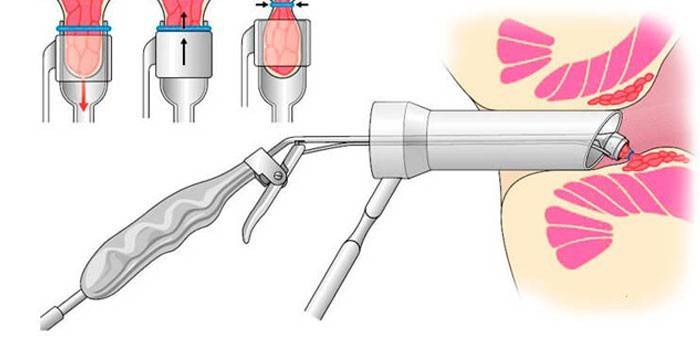
- Longo's technique (transanal resection of the mucosa or hemorrhoidopexy) - partial removal of the mucous membrane is performed, without affecting the hemorrhoids. Due to deterioration of blood circulation in them after resection, they gradually decrease in size and disappear, and the mucosal defect is sutured with special titanium staples. The main advantage of this operation, developed by the Italian surgeon Long, is the maximum preservation of the anatomical structure and innervation of the rectum. This type of surgical intervention is relatively low-traumatic and is used for stage 2-4 hemorrhoids with internal localization of hemorrhoids.
A modification of hemorrhoidectomy, regardless of the surgical technique, is plastic surgery of the hemorrhoidal stump, with its suturing into the submucosal layer of the rectum. This modification significantly improves the subsequent prognosis of radical treatment with a minimum number of relapses of hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoidectomy with parallel removal of other formations or treatment of complications
Such surgical treatment of complicated hemorrhoids or its course with concomitant pathology is more extensive and traumatic. The following operations are used in the treatment of hemorrhoids:
- hemorrhoidectomy with removal of polyps - usually excision of tissue in the area of the hemorrhoid and polyps is performed en bloc, followed by suturing and plastic surgery of the postoperative wound;
- removal of hemorrhoids with plastic surgery of a rectal fissure - resection of the mucous membrane in the area of the fissure is performed with suturing of the edges of the wound. The hemorrhoidal node is removed, with the stump sutured into the submucosal layer;
- plastic surgery of the fistula tract - depending on the size of the hole in the area of the complicated course of the hemorrhoidal node, partial removal of the entire wall of the rectum is performed, followed by its plastic surgery. This is a complex and traumatic operation that requires a subsequent long period of rehabilitation;
- opening of an abscess - a purulent cavity in the perirectal tissue, formed as a result of infection of the hemorrhoid, is dissected, a special tube (drainage) is inserted into it, through which the pus is released and antiseptic solutions are injected. Only after complete removal of pus and regeneration (healing) of the abscess area is the issue of hemorrhoidectomy decided.
Operations to treat hemorrhoids with concomitant pathology or complications are carried out only under general anesthesia (medicated sleep) and last at least an hour. After surgery, the patient should be under the supervision of medical workers in a hospital for some time (about a week) for the normal course of the early postoperative period and to prevent the development of complications.
Parkes hemorrhoidectomy
This operation is characterized by technical complexity, since only the hemorrhoid is removed, and the mucous membrane of the rectal canal remains intact. But thanks to the peculiarities of this surgical intervention, the postoperative period is less painful, and recovery is faster.
Longo hemorrhoidopexy. This method of radical surgery is one of the most effective and easiest. During the operation, a circular section of the mucous membrane of the anal canal is excised above the varicose hemorrhoidal veins, after which the edges of the wound are sutured with catgut threads. Thus, hemorrhoids are pulled inside the rectum. Also during this intervention, the vascular pedicles of the nodes are sutured, as a result of which they dry out and die over time. But it should be noted that hemorrhoidopexy is performed only for rectal hemorrhoids.
As you can see, radical removal of hemorrhoids is an extensive and painful operation, so it is better not to let the disease progress. Indeed, in the initial stages, the problem can be eliminated using conservative treatment or minimally invasive surgical methods.
Radio wave removal of external hemorrhoids
A surgical technique in which, instead of a scalpel, a high-energy electromagnetic wave is used to remove the hemorrhoid, cutting through the tissue. This type of surgical treatment is used only to remove external or prolapsed hemorrhoids in stage 3-4 hemorrhoids. The operation is performed under general anesthesia or epidural conduction anesthesia (injection of an anesthetic into the lumbar spinal cord) and does not last long (up to half an hour).
Contraindications to surgery for the treatment of hemorrhoids
Surgery does not allow every person to cure hemorrhoids, because, like any procedure associated with violating the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes, surgery to remove hemorrhoids has a number of contraindications:
- infectious diseases of any localization, accompanied by general intoxication and fever;
- chronic somatic pathology in the acute stage;
- cardiovascular diseases with the development of high blood pressure or heart failure;
- Crohn's disease - chronic granulomatous inflammation of the wall of the lower intestine;
- oncological process with the development of a malignant neoplasm with any localization in the body;
- pathology of the blood system, accompanied by a violation of its coagulation (high risk of developing surgical or postoperative bleeding);
- severe mental pathology with the development of productive psychosymptoms (delusions, hallucinations, motor or speech agitation);
- patient age over 70 years (relative contraindication).
Contraindications to surgery to remove hemorrhoids
Since radical surgery for hemorrhoids is a rather painful procedure that requires general anesthesia and a long recovery period, it cannot be performed on all patients.
There are a number of contraindications that prohibit surgical removal of hemorrhoids. These include the following:
- acute processes of the large intestine of an inflammatory nature;
- acute period of any chronic intestinal disease;
- oncological diseases, in particular of the colon;
- severe disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- severe liver diseases;
- severe diseases of the respiratory system;
- acute infectious processes with fever of any localization;
- blood diseases leading to impaired clotting;
- coma or agonal state of the patient.
Before surgery, all patients undergo a comprehensive examination, which allows us to identify the presence of contraindications. If necessary, the attending doctor gives a referral to specialized specialists who allow or prohibit the operation.
Preparing for surgery
Surgery can cure hemorrhoids without complications if the preparatory period is properly organized. It includes an examination to identify possible contraindications to surgery:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- hemogram - study of indicators of the blood coagulation system;
- blood test for antibodies to HIV/AIDS, viral hepatitis and syphilis;
- electrocardiogram;
- fluorographic examination of the chest organs;
- consultation with a family doctor or therapist who interprets the results of the study and makes a conclusion about the possibility of surgery.
In addition to the examination, during the preparatory period measures are necessarily taken to prepare the lower intestine for surgery:
- a diet excluding coarse plant fiber to prevent increased gas formation in the intestines;
- taking medicinal sorbents that bind and remove waste from the intestines;
- On the eve of the operation, laxatives are taken to cleanse the intestines.
The success of the operation and the prevention of complications depend on the correctness of the preparatory stage before the operation.
Preparing for surgery to remove hemorrhoids
Preparation for surgery is carried out in order to identify concomitant diseases and the presence of contraindications, as well as to reduce the risk of surgical and postoperative complications.
Preparing patients for surgery is as follows:
- conducting laboratory and instrumental research;
- diet;
- cleansing the intestines.
Let's take a closer look at how preparations for minimally invasive and radical hemorrhoid surgeries go in men and women.
Preparing for minimally invasive surgery
A week before surgery, the patient should begin to follow a diet, which consists of the following:
- fractional meals 5-6 times a day in small portions of food;
- exclusion from the diet of foods that irritate the intestines and contribute to constipation (fried and fatty foods, smoked foods, hot spices and herbs, alcoholic drinks, white cabbage and others);
- sufficient water consumption - at least one and a half liters per day.
Also, during your preliminary consultation with the doctor who will perform the operation, you must inform him that you are taking any medications. For example, blood thinners should be stopped temporarily because they may cause bleeding.
On the eve of the operation, as well as in the morning before the operation, you need to do a cleansing enema. Also, before leaving the house, you should wash yourself with warm water and soap and put on clean underwear. You cannot have breakfast, since surgery is carried out strictly on an empty stomach.
In case of severe pain syndrome and damage to hemorrhoids, bowel cleansing is not carried out, as this can lead to infection and inflammation of the hemorrhoids.
Preparation for radical surgery
In preparation for radical surgery, all patients are prescribed a comprehensive examination of the body. Therefore, before surgery, it is necessary to undergo the following examinations:
- general clinical blood test;
- coagulogram;
- biochemical blood test with mandatory determination of renal and liver samples (urea, ALT, AST, bilirubin);
- general urine analysis;
- determination of the patient’s blood group and affiliation and Rh factor;
- Wasserman reaction 9test for syphilis;
- tests for viral hepatitis;
- HIV test;
- fluorographic examination of the chest organs (if the patient has not undergone this examination for more than a year);
- electrocardiography;
- anoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy or fibrocolonoscopy.
Also, a week before surgery, patients are prescribed the diet we described earlier. Surgery is performed only on an empty stomach, so in the morning before the operation you can only drink a little clean water without gas.
The night before and before the operation, the patient is given a cleansing enema or a strong laxative is used, for example, Normacol or Fortrans.
In addition, a week before surgery, the attending doctor stops the patient taking medications such as anticoagulants, non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs and antiplatelet agents.
Rehabilitation
The recovery period after surgery to remove hemorrhoids consists of an early postoperative period and late rehabilitation. The early postoperative period lasts after completion of the operation and until the sutures are removed and includes several activities:
- insertion of a sterile napkin into the rectum for its tamponade, prevention of swelling and bleeding in the first few days after surgery;
- insertion of a sterile gas tube;
- daily dressings using antiseptic solutions to prevent infection of the postoperative wound;
- pain control using painkillers on the first day after surgery;
- diet with the exclusion of solid foods.
Late rehabilitation lasts from the moment of removal of postoperative sutures (7-10 days after surgery) to several months. During this period, it is important to follow general and dietary recommendations for better tissue restoration and functional activity of the rectum:
- refusal of fried, fatty, spicy foods and spices;
- preference is given to plant foods with sufficient amounts of vitamins;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- limiting physical activity;
- sufficient 8-hour sleep, organization of work and rest schedule.
Provided that the operation is carried out correctly technically in accordance with the indications, all measures are taken during preparation for surgery and rehabilitation after it, surgical treatment of hemorrhoids is effective with a minimum number of complications and the development of subsequent relapse.
Medical indications for surgery
Doctors, of course, avoid surgery as much as possible and first carry out therapeutic treatment of external hemorrhoids (link to the article Medications for external hemorrhoids) . It must be said that in most cases (if the patient seeks help from a proctologist in a timely manner and accurately follows all his instructions), surgical intervention can be avoided, but there are also clear medical indications for the operation.
Firstly, urgent surgery is indicated for those people who have rectal prolapse and bleeding. Moreover, immediate surgical intervention is indicated only at a young age! A timely operation will prevent the development of heavy bleeding and anemia.
Secondly, if hemorrhoids are diagnosed in a middle-aged person, then before performing surgery on him, doctors will conduct a full examination of the body. Most often, such patients are prescribed invasive procedures first, which often helps prevent rectal prolapse and bleeding.
Thirdly, surgery for external hemorrhoids in older people is performed only in exceptional cases. Even rectal prolapse can be treated with tablets, ointments and suppositories; often in old age, it is possible to stop the progression of external hemorrhoids using folk remedies.