Therapeutic tactics are determined by a proctologist, based on the severity of the condition. Drug treatment includes the use of venotonics, analgesics, local anticoagulants and anti-inflammatory drugs. Surgical intervention involves removal of the affected node.
The prognosis for thrombosis of an enlarged hemorrhoidal cone is generally favorable, but only with competent and timely therapy. Read about the symptoms and causes of this unpleasant condition, as well as the basic treatment procedures, in our article.
How are hemorrhoids and hemorrhoidal thrombosis related?
You can learn about what internal hemorrhoids are, what their main features and stages of progression are, from the material of a proctologist.
Additionally, we recommend that you read the article by our expert, which discusses in detail the features of treating prolapsed hemorrhoids.
We also advise you to pay attention to such a type of disease as thrombosed hemorrhoids of external and internal localization.
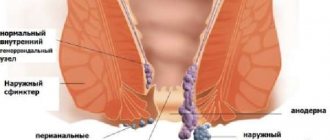
In the rectal canal and around the anus there are so-called cavernous formations. In the normal state, such bodies (together with the sphincter) perform an important task - they prevent the unauthorized exit of feces and gases from the anus.
The anal cavities are penetrated by venous vessels, which, under the influence of unfavorable factors, lose their optimal tone, as a result of which the blood stagnates, deforming the veins. The result is the formation of hemorrhoids.
In some situations, which are accompanied by a surge in pressure inside the peritoneum (for example, with a sudden lifting of weight), an exacerbation of the disease begins. The varicose vascular wall is not able to cope with the pressure and is damaged, so the body launches a kind of protective mechanism.
According to medical statistics, acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids is observed in more than a quarter of all patients with confirmed hemorrhoidal disease. In total, such thrombophlebitis accounts for about 60% of all complications.
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis: symptoms, 10 causes, 5 treatment methods
Hemorrhoids Types and stages
From the article you will learn about the causes and symptoms of thrombosis (thrombophlebitis) of hemorrhoids, methods of treatment (ointments, suppositories, tablets). An acute condition is diagnosed in more than 25% of all cases of hemorrhoidal disease, and among complications of hemorrhoids it accounts for more than 60%.
Causes of thrombosis in hemorrhoids
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node is a common complication of hemorrhoids, which is associated with impaired blood circulation in the anorectal area, the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) in the cavernous plexuses of the rectum. The patient feels severe pain in the rectum area, not associated with the process of defecation, and a constant sensation of a foreign body in the anus.
According to the ICD, hemorrhoidal thrombosis has code K.64.5
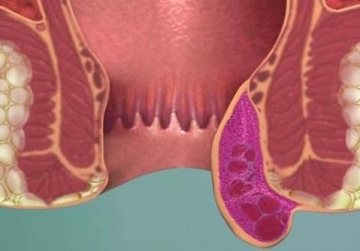
The rectum ampulla is surrounded by venous caverns, which, together with the anal sphincter, prevent the arbitrary release of gases and feces from the anus. These formations are permeated with vessels, which, under the influence of various negative factors, lose their tone. As a result, the blood begins to stagnate, the veins expand and become deformed. This is how hemorrhoidal nodules are formed.
In the process of life, work, and sports, a person’s intra-abdominal pressure changes. Deformed vessels are not able to cope with it, so the body turns on “protection”, turning stagnant blood into a blood clot. This is the main cause of thrombosis or thrombophlebitis. Contribute to the development of pathology:
- hereditary predisposition;
- bad habits;
- alcoholism, diet violations;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- constant lifting of weights;
- physical inactivity;
- "sedentary work;
- chronic inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- pregnancy;
- low temperatures.
Thrombosis of internal hemorrhoids develops due to pinching of the cones by the sphincter and occurs rarely .
What is the danger of thrombophlebitis of hemorrhoidal veins
In ordinary life, it is possible to injure the wall of the external hemorrhoid when performing hygiene procedures.
After this, with normal blood clotting, thrombosis of the blood vessels occurs, which stops the bleeding. Then, the blood clot resolves without any consequences.
But if thrombus formation occurs without injury, against the background of negative changes in the circulatory system, a condition that is dangerous to human life arises:
- acute thrombosis requiring urgent surgery;
- sepsis;
- atypia with transformation into cancer;
- detachment of a blood clot from the cavity wall with transfer through the bloodstream to the coronaries, cerebral vessels, pulmonary artery and the development of stroke, heart attack, pulmonary embolism.
Each condition can be fatal. That is why any person suffering from hemorrhoidal disease must consult a doctor.
Types and degrees of disease
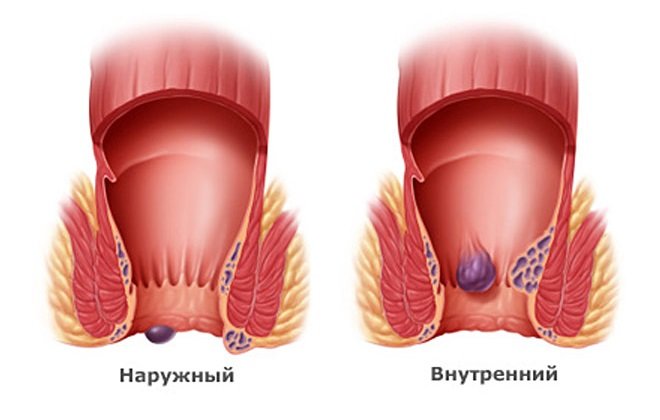
The localization of hemorrhoids with thrombosis is the basis of the classification:
- outer;
- interior;
- combined thrombophlebitis of the node.
The severity of symptoms determines the severity of the pathology:
- first - there are no signs of inflammation of the caverns;
- second - thrombosed nodes of any location give the first symptoms: pain, bruising, swelling of the anus ;
- third - inflammation affects nearby tissues, complications arise.
According to the severity of the process, hemorrhoidal thrombosis is distinguished between acute (complicated) and chronic (recurrent).
Clinical symptoms
The photo shows live external thrombosis of a hemorrhoid.
The very first symptom or sign of hemorrhoidal thrombosis is sudden pain that is accompanied by discomfort in the anorectal area.
The nodule formed as a result of thrombosis begins to grow, and the person feels a foreign body in the anus. The nature of the pain changes.
If with hemorrhoids of any localization the pain is caused by the act of defecation, then a blood clot in the venous plexus causes constant pain that is not associated with anything.
The clinical picture develops gradually and corresponds to the stages of pathology, which are presented in the table.
Pathology stageSymptoms and signs
| First |
|
| Second |
|
| Third |
|
Possible complications
The progression of thrombophlebitis of hemorrhoids causes a number of complications requiring medical intervention:
- bleeding;
- varicose veins of the anal veins;
- abscess of soft tissues of the perianal area;
- necrosis of thrombosed nodes with symptoms of severe intoxication;
- addition of a secondary infection;
- anal dermatitis;
- postoperative fistulas, suture dehiscence, narrowing of the anus.
Any of the complications requires prompt attention to a specialist.
Source: //sosudy.info/thromboz-gemorrhoidalnogo-uzla
Types and degrees of thrombosis
Based on the location of the formation of a blood clot, a distinction is made between thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid, if the external cavernous formations are damaged, and thrombosis of the internal hemorrhoid, if platelets accumulate in the veins of the submucosal rectum.
The pathological condition develops gradually, this allows us to distinguish three successive stages or degrees in its progression. For ease of gradation, we have presented their distinctive features in the form of an informative table.
Causes of the disease
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node can be localized inside the anus or outside. Simultaneous thrombus formation occurs very rarely. If a vessel breakthrough occurs in the area of the external nodes, this pathology is known as anorectal thrombosis. Causes of pathology:
- severe straining during bowel movements;
- intestinal disorder;
- alcohol abuse;
- constant consumption of spicy food;
- pushing during childbirth;
- lifting weights;
- frequent sitting;
- heredity;
- physical exercise.
Thrombophlebitis of the anal veins develops as a consequence of impaired blood outflow. Stagnation of fluid causes an increase in pressure in the cavity of the vessel. To avoid internal bleeding in the event of a breakthrough in the vascular wall, the human body starts the process of forming a blood clot. Often the cause of this pathology is hypothermia.
The prolapse of internal hemorrhoids is known as anal thrombosis.
Initial symptoms of hemorrhoidal thrombosis
This condition is characterized by severe clinical symptoms. In order to seek medical help in time, you need to know the initial signs of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins.
The first signs of thrombosis are pain that occurs suddenly and discomfort in the anus. The nodule begins to increase in size, so the person notices the presence of a foreign body in the rectal canal.
Another sign is bleeding of varying degrees of intensity. In the initial stages of thrombosis, it can occur due to damage to the rectal or external nodule by solid feces. In this case, the blood clot can come out through the wound, and the patient will feel serious relief.
Bleeding often occurs in the last stage of thrombophlebitis of hemorrhoidal veins. In this case, we can talk about the beginning of the necrotic process, since the surface of the nodules is covered with bleeding ulcers.
With thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node, swelling and an increase in the size of the cavernous formations are observed almost immediately and in a short time. And if before they were not very noticeable, then with the appearance of a blood clot they quickly “swell”.
If these symptoms are detected, you must immediately consult a doctor who will determine the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Although usually the pain due to a blood clot is so severe that even those people who were previously embarrassed by hemorrhoids or did not attach any importance to them seek medical help.
Classification of forms
Thrombosis is divided into internal, external, combined, depending on the location of its formation. There are also several degrees.
- At the first stage, itching, burning, and discomfort occur in the anal area. Problems arise with defecation, droplets of blood appear on stool and toilet paper. Painful symptoms may disappear on their own without special treatment. In this case, the disease becomes chronic, and repeated symptoms are more pronounced. This is how the second stage begins.
- At the next stage, the pain is constant. Going to the toilet turns into real torture. There is significant bleeding and protrusion of nodes.
- The third stage of thrombosis is especially difficult. All signs of the disease intensify several times. The pain is present in any position and intensifies with physical activity. In such a situation, the person must be urgently hospitalized.
Causes of the condition
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node and the causes of its occurrence, as already noted, are closely related to hemorrhoids. Therefore, the “provocateurs” are the same factors that play a negative role in the development of varicose anal veins. Let's take a closer look at them.
- Diet violation. Abuse of alcoholic beverages, spices, pepper or spicy foods stimulates blood circulation in the peritoneum and increases pressure in the cavernous formations. As a result, a blood clot forms.
- Problems with bowel movements. Constant constipation and problems with the gastrointestinal tract do not have the most favorable effect on blood circulation in the pelvis. When straining, the pressure in the hemorrhoidal plexuses again increases.
- High physical activity. If you have hemorrhoids, it is not recommended to lift weights, since such physical activity leads to a sharp increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity. By the way, thrombosis often occurs for this reason during pregnancy.
- Physical inactivity. It is curious, but the lack of optimal physical activity, prolonged sitting, and low mobility can also lead to thrombosis due to increased congestion in the cavernous formations.
- Hypothermia. As a result of prolonged exposure to low temperatures on varicose veins, damage to their walls occurs. The body “turns on” a protective mechanism, resulting in the formation of a blood clot.
Reasons for development
The consumption of spicy foods, bitter spices, and alcohol can provoke blockage of the vessels of the rectal plexus.
Such food accelerates blood circulation in the pelvic organs and increases pressure in the hemorrhoids, which leads to damage to the epithelium. To avoid bleeding, the body forms clots from fibrin and platelets. The formed thrombus blocks the lumen of the arteries, preventing the reverse outflow of blood and the delivery of oxygen. Hypoxia develops, metabolic products accumulate in tissues, and cells gradually die.
Causes of acute thrombosis:
- autoimmune diseases;
- thrombophilia;
- damage to the walls of blood vessels after mechanical trauma, surgery, childbirth;
- venous congestion in heart failure, sedentary lifestyle;
- leukemia, kidney cancer;
- chemotherapy.
Acute thrombosis of the venous nodes can occur due to severe straining during constipation, after heavy physical work, strength sports, or during childbirth in women.
With ulcerative colitis of the intestine, anal fissures, adhesions, benign or cancerous tumors of the intestine, spasm of the anal sphincter often occurs. This causes poor circulation and can cause blockage of blood vessels.
Diagnostic measures
Usually, making an accurate diagnosis does not take much time due to the pronounced and characteristic clinical picture. The doctor listens to complaints, clarifies the medical history (presence of hemorrhoids, provoking factors) and, of course, examines the anorectal area.
A visual diagnostic method at the initial stage of the pathological process reveals the presence of compacted and enlarged hemorrhoids, moderately painful when touched.
In subsequent stages, inflammation and redness of the nodes are detected. The third degree of pathology is characterized by the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate in the anorectal area. In the most unfavorable cases, partial necrosis of cavernous formations that have a bluish or even black tint cannot be excluded.
External hemorrhoidal thrombosis is localized under the so-called pectineal line. In the case of thrombosis of the rectal node, there is a groove between the emerging cavernous formation and the swollen skin of the perianal area.
Instrumental examination (rectoscopy) is prescribed if rectal thrombosis is suspected, to differentiate this condition from pathological processes with similar symptoms: rectal tumor, strangulated polyp, acute paraproctitis.
Manifestations

Local thrombosis of external nodes manifests itself in the form of swelling and inflammation directly in a limited area of the anus. The onset of the disease is characterized by compaction of small areas of blood vessels. The main symptom of this pathology is acute thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins. A sick person experiences the following symptoms:
- itching in the anus;
- pain when walking or during any physical activity;
- discomfort at rest;
- bulging dark red bumps.
Perianal venous thrombosis of internal nodes is localized directly in the lumen of the rectum. The patient may not feel any pain for some time. The pain syndrome manifests itself after the bonds fall out of the anus and a reflex spasm of the sphincter muscles occurs. The following symptoms of pathology are distinguished:
- difficulty defecating;
- increased body temperature;
- urinary retention;
- severe swelling of the anal tissue;
- bleeding.
Consequences
Pathology develops regardless of a person’s age, and can sometimes manifest itself even in a child. Hemorrhoidal thrombosis without appropriate treatment often causes serious complications. After therapy, the resulting seals remain under the skin in the form of small moving nodules. If you do not adhere to a healthy lifestyle, the disease will recur constantly. Frequent consequences of the disease:
- bleeding;
- infectious infection;
- strictures;
- tissue death;
- inflammation of the rectum;
- necrosis;
- sepsis.
Treatment options
The question of how to treat thrombosis of hemorrhoids is within the competence of a specialist. After clarifying the diagnosis, he selects the optimal therapeutic regimen, taking into account the degree and severity of the pathological process.
In general, treatment for thrombosis can be either medical or surgical. Moreover, the use of medications may precede surgery, and the surgical method does not exclude the subsequent use of medications.
Drug therapy
For the first and second degrees of hemorrhoidal thrombosis, doctors give preference to multicomponent drug therapy, which includes the use of systemic and local drugs. An integrated approach helps improve microcirculation, resolve blood clots and relieve inflammation.
Read also: Pulmonary thrombosis, what is it?
Systemic medications include venotonics - drugs that increase the tone of blood vessels, which improves the outflow of blood from hemorrhoids and reduces congestion. The drugs of choice include Detralex, Phlebodia 600, Aescin, Troxevasin. The issue of their use during pregnancy is decided by the attending doctor.
To dissolve blood clots, anticoagulants containing heparin are prescribed in the form of suppositories and ointments. Thus, for thrombosis of the external node, heparin ointment, Hepatrombin G, Proctosedyl, Heparoid Zentiva are indicated. In the case of internal hemorrhoids, Gepatrombin G and Proctosedyl suppositories are indicated.
In cases of severe pain and inflammation, ointments and suppositories with hormonal and anesthetic components are prescribed. Medicines such as Ultraproct, Procto-Glivenol, Proctosan and Proctosan Forte, Aurobin are very popular.
In case of pronounced pain syndrome, alcohol-novocaine blockades according to A.M. are often prescribed. Aminev. This procedure is carried out every 3-4 days and is usually combined with the topical use of Levomekol and Levosin ointments. After the blockade, the pain decreases or disappears altogether.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment of thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid is required in the case of the most severe, third degree. In this case, intervention can be carried out almost immediately if there is bleeding and strangulation of the node, or in a delayed manner if it is necessary to stop an acute inflammatory process.
Thrombectomy
External thrombosis of hemorrhoids, which occurs without complications, is sometimes treated with thrombectomy. In this case, the surgeon opens the affected cavernous formation, removes the blood clot from it and leaves the wound to heal on its own.
The advantage of thrombectomy is low trauma, rapid healing and the possibility of performing it during pregnancy. However, this method is not always justified, since it is only suitable for external hemorrhoids.
In addition, there is a high risk of repeated thrombosis in the same node due to damage to the venous walls at the time of surgery.
Hemorrhoidectomy
The most common method of surgical treatment of thrombosed anal veins is hemorrhoidectomy - an operation that involves excision and further complete removal of the hemorrhoid.
The classic version of hemorrhoidal resection is the Milligan-Morgan method. The affected cavernous formation is simply cut off from the blood vessels along the pedicle. Such an intervention can be performed under either general or epidural anesthesia.
Today, there are several modifications of classical hemorrhoidectomy, which differ to a greater extent in the completion of the procedure:
- open intervention (without suturing the truncated area);
- closed intervention (closed suturing of the wound after resection);
- submucosal surgery.
Hemorrhoidectomy is the most effective method of treating thrombosis of hemorrhoids. This procedure allows not only to get rid of blood clots, but also to remove the cavernous formation itself, which practically reduces to zero the likelihood of re-development of blood clots.
If thrombosis is accompanied by inflammation of the perirectal tissue, additional surgical procedures will be required. For example, the surgeon may prescribe drainage of the perianal area to reduce the volume of inflammatory infiltrate.
Traditional methods
It is impossible to cure thrombophlebitis of hemorrhoidal veins using traditional treatment methods! Moreover, the use of various unconventional practices is fraught with only deterioration of the condition and the occurrence of serious complications.
Perhaps the proctologist will recommend, as an additional treatment, sitz baths with medicinal plants, such as chamomile, strawberries, kidney grass, etc. But, we repeat once again, such procedures can only take place in combination with the main method of therapy and only after consultation with a doctor.
Ointments for hemorrhoidal cones and thrombosis of nodes: the best and inexpensive drugs
At the initial stages of treatment of rectal diseases, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory ointments.
These drugs relieve inflammation, reduce severe thrombosis of the node, and reduce pain. What drugs are best to use to reduce hemorrhoidal cones and nodes? Hemorrhoids occur in almost every third person today. And not everyone is so decisive as to seek help from a specialist at the first appearance of symptoms of this disease. Thus, surgical treatment is often recommended for patients with already formed and irreducible hemorrhoids.
In order to avoid radical measures, it is necessary to undergo a course of therapy on time. It should be comprehensive and include not only oral medications, but also products for topical use. These products include rectal suppositories and ointments.
Hemorrhoidal ointments effectively fight thrombosis, relieving inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory ointments for hemorrhoids, which can simultaneously contain anti-inflammatory components and venotonic substances, have proven to be very convenient.
Various ointments can relieve pain due to the action of the anesthetics included in their composition.
Some proctological ointments have a hemostatic effect by activating the blood coagulation system when applied to the affected areas of the skin. And some are even able to dissolve a blood clot in the affected hemorrhoid.
The use of local drugs for hemorrhoids
| Pain syndrome | Gepatrombin G, Proctosedin, Posterisan, Procto-glivenol, Aurobin, Ultraproct. |
| Thrombosis of hemorrhoids | Hepatrombin G, Nigepan, Heparin ointment. |
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Aurobin, Proctosan, Relief, Fleming's ointment. |
| Antibacterial agents | Levomekol, Vishnevsky Ointment, |
Anti-inflammatory ointments and suppositories recommended for the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease are distinguished by their ease of use and the depth of penetration of active medicinal substances locally, without systemic effects. It is very convenient to use them during pregnancy and after childbirth, as well as for children.
The only negative point is that the fatty components of some products are poorly absorbed into the skin and remain on the underwear.
Ointments in the form of monotherapy are ineffective, so treatment of hemorrhoids must be comprehensive! The drugs should be considered as a source of relief of symptoms of the disease.
Popular and inexpensive ointments
Before starting treatment for hemorrhoidal disease, you must consult a proctologist. A specialist will help you choose the most effective and good ointment in each specific case.
The best hemorrhoidal ointments that dissolve cones:
- Heparin ointment.
The main active ingredient in its composition is the anticoagulant heparin. It reduces blood clotting, thereby improving blood flow through the hemorrhoidal veins. Heparin ointment for hemorrhoids reduces severe swelling. Prevents thrombosis of nodes and promotes their rapid resorption. - Relief (Ultra, Advance). The ointment includes components of shark liver tissue. It is these components that provide the anti-inflammatory effect. The product promotes rapid healing and resorption of rectal nodes, and also eliminates discomfort in the anal area.
- Proctosedyl. The composition includes a whole complex of active substances: heparin, hydrocortisone, framycetin and esculoside. This complex effectively relieves inflammation and swelling of affected tissues. Prevents the development of hemorrhoidal bleeding, relieves itching and other unpleasant sensations. It has a hemostatic effect, tones and normalizes the elasticity of blood vessels.
- Gepatrombin G. Ointment promotes the healing of damaged tissues by normalizing tissue metabolism and eliminates inflammatory processes.
Heparin, which is part of the drug, prevents the formation of thrombotic masses, eliminates swelling and itching. - Methyluracil ointment. Has a healing effect. Used to treat fissures around the anus and hemorrhoids (external). Stimulates the functioning of the body's immune system.
- Aurobin is a universal remedy against hemorrhoids in the form of a gel, which includes a hormonal component (prednisolone), lidocaine, triclosan and dexpanthenol, as well as a complex of vitamins. The drug has a rapid healing effect, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and bactericidal effect.
- An ointment called Bezornil relieves pain and inflammation. It has a pronounced astringent effect and quickly relieves swelling. This product actively stimulates regenerative processes in damaged tissues.
- Proctosan. The ointment contains lidocaine, bismuth and bufexamate. Effectively relieves inflammation, disinfects and dries damaged skin areas. Relieves itching and swelling well.
- Combined drug Posterisan. Widely used to relieve inflammation and eliminate allergic manifestations. Suitable for eliminating itching and swelling in the anal area. The composition includes microbial cells in an inactivated state, as well as cortisone.
- Troxevasin.
The cream facilitates the process of defecation by promoting vein contraction. Restores the elasticity of the vessels of the rectum, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and also effectively eliminates swelling and itching around the anus. Most often used in the presence of external hemorrhoids.
Ointments for node thrombosis
What ointments are used for hemorrhoidal thrombosis?
Thrombosis of hemorrhoids
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoid is an acute and rather painful complication of hemorrhoids that requires timely and correct treatment. In the absence of adequate combination drug therapy, surgery is indicated.
If hemorrhoidal thrombosis has been diagnosed, the ointment should contain substances to resolve blood clots.
In case of thrombosis, it is recommended to lubricate the external hemorrhoid with Hepatrombin G ointment. It has the most pronounced thrombolytic effect, as it improves tissue metabolism and promotes rapid regeneration of epithelial cells. Many proctologists often prescribe Proctosedyl and Proctoglivenol to patients.
Treatment should be comprehensive and long-term (about 7-14 days).
Note! Timely contact with a specialist will help prevent the development of adverse consequences and help avoid surgical interventions. Ointment for hemorrhoidal cones can be used without consulting a doctor. In case of acute symptoms of hemorrhoids, you should consult a proctologist.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS CONSULTATION WITH YOUR DOCTOR IS REQUIRED
Author of the article Alexey Alexandrovich Egorov, proctologist
Source: //gemorroj03.com/gemorroidalnye-mazi.html
Prevention of thrombosis
The main way to prevent thrombosis of hemorrhoids is to treat anal varicose veins and avoid risk factors for the development of the pathological condition, which we wrote about in detail above.
To prevent injury to hemorrhoids and further formation of blood clots, you should monitor the functioning of the digestive tract, normalize stool consistency, and avoid constipation and diarrhea if possible.
Dietary nutrition, which involves the exclusion of fatty, spicy, salty and spicy foods, and alcoholic beverages, will help cope with this. Preference should be given to products with natural dietary fiber (fruits, vegetables, cereals), which normalize intestinal motility.
Another important tip is to optimize physical activity, avoiding both physical inactivity and excessive strength exercises. It should be especially noted that thrombosis can develop during pregnancy when several risk factors are combined. Therefore, expectant mothers should especially carefully monitor their health.
Prognosis and possible complications
In the absence of adequate treatment and late consultation with a doctor, dangerous complications such as necrosis of the hemorrhoid, purulent paraproctitis and even sepsis may develop. The latter poses a direct threat to the patient’s life and can lead to death.
With timely seeking medical help and adequate therapy, the prognosis for thrombosis of the vessels of hemorrhoids is generally favorable. Medical or surgical treatment at the present stage allows one to cope with this unpleasant condition.
Thrombosis of hemorrhoids is a frequent companion to varicose anal veins. This condition is dangerous due to its consequences and requires prompt attention to a specialist. It is an experienced proctologist who will determine how and with what to treat circulatory disorders in the anorectal area. Be healthy!
Suppositories with heparin in the treatment of hemorrhoids
This pathology is often observed in patients in the later stages of the disease. In this case, for treatment it is necessary to use combination drugs that not only have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, but also resolve blood clots formed in the anal area. These include medications containing a direct-acting anticoagulant, heparin, widely used in medical practice for the prevention and treatment of various thromboembolic diseases. The most effective of local preparations are suppositories with heparin for hemorrhoids. They stop the process of thrombus formation and promote the resorption of formed blood clots, which has a positive effect on the further course of the disease.
Suppositories effective for hemorrhoids
The best suppositories for hemorrhoids with nodes - this is precisely the requirement that the patient makes at the pharmacy. It is difficult to answer the question unambiguously, since the general properties of this dosage form are only the appearance and glycerin, and the main active substances are different.
The shape and stage of hemorrhoids is also important. For example, at the initial stage, suppositories for resolving hemorrhoids are very helpful.
With significant sizes of external and internal nodes, massive bleeding, necrosis of formations, no suppositories are effective; only surgical intervention will radically solve the problem.
What kind of candles are there?
Suppositories for hemorrhoids vary in composition and mechanism of action. The following groups of drugs are most effective:
- reducing the severity of all signs of inflammation (hormonal agents);
- local anesthetics (reduce pain);
- hemostatics (stop bleeding from damaged hemorrhoids);
- venotonics, which increase the tone and strength of the walls of venous vessels;
- anticoagulants, which reduce the rate of blood clot formation.
A proctologist will determine which suppositories are more effective for hemorrhoids. The combined use of several dosage forms is possible. The effectiveness of any therapy increases with careful compliance with medical recommendations and regular use of suppositories.
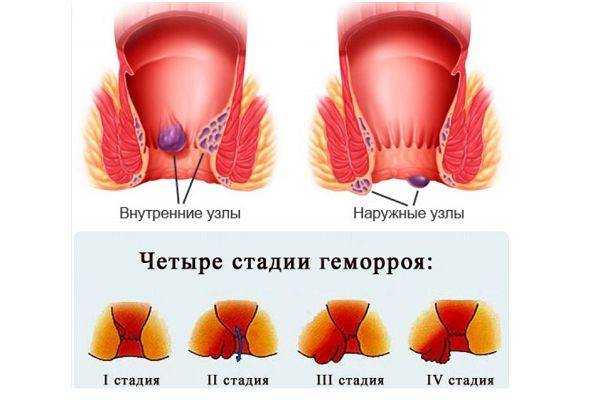
Hemorrhoids and its stages
Anti-thrombosis drugs
One of the main problems of hemorrhoids is the development of thrombotic complications. Inside the hemorrhoidal node, blood circulation is disrupted; against the background of a reduced blood flow rate, areas of thick consistency are formed; the accumulation of blood cells contributes to the formation of blood clots. If this is a parietal thrombus, then it does not cause much concern to the patient. The worst case scenario is when such a blood clot, even of a small size, breaks off and can clog a vessel in the human body, which will lead to tissue necrosis. The most severe type of such complication is pulmonary artery thrombosis.
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
To prevent such serious complications, suppositories are used for hemorrhoidal thrombosis. Their main basis is anticoagulants, which thin the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots. These include:
- Nigepan;
- Gepasolone;
- Hepatrombin.
All of the above drugs are contraindicated in patients with low blood clotting. Suppositories are used 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days, but no more.
Suppositories for hemorrhoidal thrombosis are effective only in the first 1-2 days from the onset of the complication.
Painkillers
Only certain suppositories for hemorrhoids eliminate pain. This effect is achieved thanks to local anesthetics (lidocaine, procaine) included in the suppositories. These substances interact with certain receptors and reduce the speed of pain impulse transmission.
Suppositories with a predominantly analgesic effect include:
- Doloproct;
- Relief.
Some patients may experience allergic reactions and skin changes. If pain does not disappear within 7 days, then the drug should be changed.
Allowed for bleeding
Only certain suppositories are effective when bleeding begins. They contain substances that strengthen the wall of damaged venous vessels and help stop bleeding.
This group of medicines includes:
- Relief Advance;
- Procto-glivenol.
These drugs cannot be used for a long time and are contraindicated in patients with a high risk of thromboembolic complications and arterial hypertension.
After stopping the bleeding, suppositories are advisable, dissolving hemorrhoids and cones, that is, having a wound-healing effect. These include suppositories:
- with sea buckthorn;
- based on methyluracil.
Wound-healing suppositories for resorption of hemorrhoidal cones can and should be combined with other dosage forms: ointments and gels.
Pharmacological action of heparin for hemorrhoids
Heparin is a direct natural anticoagulant, one of the main components of the human blood anticoagulant system. It is found in almost all organs, but mostly in the liver, lungs and heart. The mechanism of action of heparin is associated with its direct effect on blood clotting factors. It inactivates thrombin circulating in the blood, the main enzyme that causes blood clotting. This leads to inhibition of the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, the threads of which are the basis of the blood clot. Heparin reduces the ability of platelets to stick to each other, and also increases the fibrinolytic activity of the blood by reducing the concentration of antiplasmins in it.
Read also: Will there be children after varicocele?
When using topical medications containing heparin for hemorrhoids, the following is observed:
- thinning the blood and reducing thrombus formation in it;
- relieving inflammation and reducing swelling;
- accelerating the processes of regeneration and healing of affected tissues;
- decrease in the permeability of vessel walls.
Heparin suppositories for hemorrhoids can be used in the treatment of this disease at any stage. They are especially effective for acute thrombosis of inflamed hemorrhoids.
Important: Heparin suppositories should be used only as prescribed by a doctor, as they have contraindications. They cannot be used for hemorrhoidal bleeding, disorders of blood clotting processes in the body and individual intolerance to any of the components included in the composition.
Heparin suppositories used in the treatment of hemorrhoids
Modern pharmaceutical preparations with heparin in the form of suppositories, in addition to it, also contain other active ingredients, which enhances the therapeutic effect of these drugs and their effectiveness for various symptoms of hemorrhoids. For thrombosis of hemorrhoids or for the purpose of its prevention, suppositories such as Nigepan, Hepazolon and Hepatrombin G are most often prescribed.
Nigepan candles
Nigepan suppositories contain the anticoagulant heparin and the local anesthetic benzocaine, as well as vitepsol, monoglycerides and purified water as excipients. The course of treatment with this drug is usually two weeks, but noticeable improvements in the patient’s condition are observed after the first use. For hemorrhoids, Nigepan helps:
- rapid pain relief;
- eliminating burning and itching in the anal area;
- reducing the inflammatory process;
- preventing the formation and growth of blood clots;
- regeneration of damaged tissue.

Direct indications for the use of Nigepan include thrombosis of external or internal hemorrhoids. The drug is administered into the rectal cavity in the morning and evening at equal intervals.
Hepazolon suppositories
Heparin suppositories for hemorrhoids Gepazolon include three active ingredients with a different spectrum of pharmacological action, which makes this drug very effective. They contain:
Prednisolone is a synthetic analogue of glucocorticosteroid hormones of the adrenal cortex, which has a higher activity than them. In hemorrhoids, it has a pronounced local anti-inflammatory effect, inhibiting the release and activity of inflammatory mediators. This allows you to quickly eliminate pain, swelling and other unpleasant symptoms.
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic and helps to instantly relieve pain, burning and itching in hemorrhoids by blocking sodium channels, which prevents the occurrence and transmission of pain impulses along nerve fibers.
Gepasolone is used to treat thrombosis of external and internal hemorrhoids. It is also prescribed for anal fissures, itching, and preparations for operations in the anal area. However, the use of the drug has one peculiarity: when treating external hemorrhoids, it cannot be completely introduced into the rectal cavity. According to the instructions, the therapeutic course is one week.
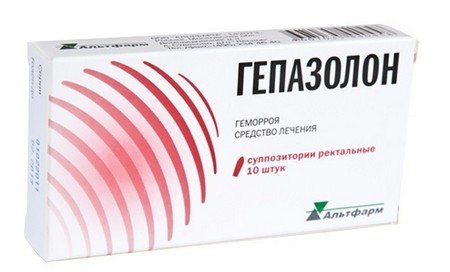
Candles Gepatrombin G
The drug is indicated for external and internal hemorrhoids, as well as for thrombophlebitis of the anal veins. It can be used once or twice a day for a week. This drug is also available in the form of an ointment. The combined use of ointment and suppositories is most effective.
Important: The therapeutic effect of all suppositories with heparin for hemorrhoids depends on the correct use of the drugs. Before administering suppositories, it is necessary to empty the intestines and perform a thorough hygienic toilet of the perianal area, and then spend at least 30 minutes in a lying position to prevent leakage of the drug.
Therapy for thrombosis of external hemorrhoids
In the first stages of the disease, drug treatment is used. Preparations in the form of rectal suppositories, ointments, and tablets for oral administration relieve painful symptoms, normalize blood circulation, and eliminate inflammation.
They are used several times a day - in the morning, in the evening, after each bowel movement, with preliminary washing. The duration of therapy is at least 4 weeks. The active components act locally, practically do not penetrate into the general bloodstream, and therefore do not cause side effects. The ointment is quickly absorbed by the mucous membrane, the therapeutic effect occurs after a week of regular use.
The most effective ointments are:
- Hepatrombin G;
- Levomekol;
- Proctosedyl;
- Troxevasin;
- Heparin ointment;
- Detralex;
- Venarus;
- Aurobin;
- Venozol;
- Inovazin.
A contraindication to the use of any product in the form of an ointment is individual intolerance to the components. Before active use, it is worth conducting a sensitivity test.
Preparations in the form of suppositories have a complex effect. They relieve inflammation, protect the intestinal mucosa from irritating factors, normalize blood circulation, prevent the formation of blood clots, and promote the resorption of existing ones. Suppositories are used 1-2 times a day. The course of therapy is determined by the attending physician, on average 20 days.
The most effective drugs:
Suppositories act locally, the active components do not penetrate into the general bloodstream.

To increase the effectiveness of suppositories, ointments, and also to prevent relapse, take tablets orally. The course of therapy lasts from 1 month to a year with a short break. The tablets normalize blood circulation, eliminate congestion, strengthen blood vessels, and eliminate capillary fragility. Venotonics in tablets:
Take the tablets according to the instructions during meals or an hour before meals.
To get rid of pain, Analgin, Combispasm, Nurofen, Diclofenac, Ketalong, Ketanov are used. Mild laxatives can be used to relieve constipation.
External hemorrhoidal thrombosis and its treatment
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
During acute or chronic hemorrhoids, a complication such as thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid may develop. This diagnosis is made to many patients who consult a proctologist. If the underlying disease is treated quite simply in the initial stages, then advanced thrombosis requires more serious therapy.
Reasons for the development of blood clots
The cause of thrombosis is a strong rush of blood to the hemorrhoidal node in the absence of complete outflow. As a result, inflammation and swelling appear.
Our readers successfully use ReCardio to treat hypertension. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
This condition is promoted by constipation, pregnancy and childbirth, heavy physical activity, abuse of spicy, salty foods and alcohol. An acute problem of our time - a sedentary lifestyle and long periods of sitting also contribute to the development of hemorrhoids and its complications.
There are 3 degrees of thrombosis severity:
1. Venous blood collects in the nodes, no outflow occurs, as a result, microcirculation is disrupted there and blood clots form. After this, the bumps become sharply painful, but inflammatory reactions do not yet occur at this stage. Unpleasant sensations intensify during bowel movements. In the perianal area the following may appear:
- small bumps;
- burning sensation, discomfort and itching;
- moderate pain;
- hyperemia around the anus.
2. If treatment for the disease is not started on time, the pain is accompanied by an inflammatory process. The nodes become more sensitive and painful, especially when walking and sitting. Hyperthermia may occur. The area of swelling and redness increases, thrombosed lumps grow, and a spasm of the anal sphincter appears.
3. Acute thrombosis with inflammation spreads to adjacent tissues (groin area and subcutaneous tissue). Necrosis of the nodes themselves may develop. It is impossible to carry out a digital examination, since palpation is extremely painful. Upon examination, bluish and purple hemorrhoidal bumps that have fallen out of the anus are visible.
Clinical manifestations
A complication of hemorrhoids, such as external hemorrhoidal thrombosis, usually appears after straining. Blood clots form in a few nodes, not all nodes. A person begins to feel constant pain in the anus, which does not depend on the act of defecation. Patients are also disturbed by the feeling of a foreign body, causing constant discomfort. If the hemorrhoids were reduced before thrombosis, now it is impossible to return them inside. When straining, the pain becomes stronger.
Read also: First stage of varicocele
In a sitting position, to reduce pain, patients try to sit on one buttock so as not to affect the affected node.
Over time, the swelling of the perianal area increases, the node turns purple and then turns blue. Pain is expressed differently in all people; in some, even in advanced cases, it does not manifest itself; in others, it is so strong that the person cannot even move normally; a “duck” gait is observed.
If treatment is improper or completely absent, infection may develop and paraproctitis may appear.
Diagnostics – clarifying the diagnosis
- interview and examination of a specialist - coloproctologist;
- rectal examination;
- anoscopy.
It is usually not possible to palpate (feel) the rectum, since this manipulation will be quite painful for a person.
Effective treatment
Treatment of thrombosed nodes is carried out using conservative or surgical therapy. Drug treatment mainly consists of the use of phlebotropic, thrombolytic and analgesic agents for local and general use.
Phlebotonics for this disease provide excellent results and guarantee safety, because they are made from anti-inflammatory plants that help strengthen the vascular wall. Medicines in this group include:
- Detralex - increases the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels, improves microcirculation, relieves swelling and normalizes the rheological properties of blood.
- Phlebodia 600 – has a decongestant, angioprotective, antioxidant effect. Eliminates venous congestion.
- Angistax – improves microcirculation, provides venotonic, angioprotective effects.
- Venoruton (rutin) – increases the tone of the venous wall, has a powerful anti-inflammatory and angioprotective effect.
Also used in the treatment of external hemorrhoids are ointments and tablets of escin, troxerutin, aescusan, venitan and reparil. They are phlebotonics and angioprotectors, have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
To resolve blood clots, anticoagulants are used: troxevasin and heparin ointments, hepatrombin G. For bleeding, local hemostatics are used: spongostan, beriplast and tachycomb, adroxon.
In some cases, the doctor recommends performing sitz baths with medications.
Surgery
If conservative therapy is ineffective or in advanced cases, blood clots must be removed surgically. It is possible to perform the operation using radio wave and electrocoagulation methods. Sometimes the external hemorrhoidal node itself is removed, in which case the fimbriae (skin from the stretched node) do not remain.
The treatment method is chosen by a proctologist or surgeon, considering each individual case separately.
Hemorrhoidal thrombectomy - surgical intervention is performed under local anesthesia. During surgery, the hemorrhoid is opened and the clot is removed.
Prevention or how to avoid complications?
Advice from doctors on the prevention of hemorrhoids and its complications:
- Avoid constipation;
- Watch your weight;
- Avoid spicy, spicy, salty, smoked foods, animal proteins and alcohol;
- Drink more fluids;
- Include fiber-rich foods in your menu;
- Lead an active lifestyle;
- Do not use hard toilet paper (it is better to use wet wipes);
- Avoid hypothermia;
- If itching, do not scratch the skin, be patient;
- Don't lift heavy things.
You can also read about the symptoms of deep vein thrombophlebitis
Symptoms and severity
The pathology is characterized by severe pain in the anus and perineum. Discomfort is constantly present and intensifies during bowel movements. Depending on the location of the thrombus, internal and external thrombosis are distinguished; in 75%, a combined type of embolism occurs. One or several cones may be affected.
With thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid, its enlargement and thickening are noted; patients complain of a sensation of the constant presence of a foreign object in the anus. If an inflammatory process occurs, the surrounding tissues turn red and swell greatly. There is general weakness, malaise, fever, chills, and symptoms of intoxication of the body.
Thrombosis is classified into 3 degrees of severity:
- At the initial stage, there is a disturbance in blood circulation, the nodes are compacted, painful, but they can be set if they fall out, there are no signs of inflammation. A person is bothered by moderate pain, burning, itching in the perianal area.
- The second stage of thrombosis is characterized by the development of the inflammatory process, hyperemia, and deterioration in general well-being. The nodes increase in size, and spasm of the anal sphincter is often observed. The pain intensifies and is constantly present.
- At stage 3 of thrombosis, infiltration spreads to the surrounding tissues and subcutaneous tissue of the perineum. Thrombosed nodes change color, acquire a bright red or bluish tint, fall out of the intestine, and cannot be reduced. The pain becomes unbearable, especially when palpating the problem area; necrosis, bleeding, purulent, chronic paraproctitis with the formation of fistulous tracts may occur.
Rectal vein thrombosis can be partial or complete. While maintaining a small lumen in the arteries, a fragment of the hemorrhoidal node dies. With a complete embolism, the entire cone undergoes necrosis. Its surface becomes covered with multiple ulcers, which results in massive bleeding, infection, development of purulent paraproctitis and blood poisoning.
Symptoms of necrosis include blackening of the venous lump, a putrid odor, difficulty during bowel movements, discharge of ichor or purulent masses, and severe pain.
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node, its diagnosis, symptoms, photos and treatment methods
Description of the disease
As the name of the disease suggests, thrombosis of the hemorrhoid does not arise out of thin air: it requires a hemorrhoidal lump and a blood clot in it. In 8 out of 10 cases, the disease is preceded by existing chronic hemorrhoids. Relatively rarely, thrombosis occurs acutely - almost simultaneously with the appearance of the hemorrhoidal lump itself.
The mechanism of development of the disease is as follows:
- In the vein of the perianal region affected by hemorrhoids, as a result of various damaging factors, the integrity of the inner wall of the vessel is disrupted.
- This leads to the risk of bleeding - to prevent it, a blood clot or thrombus is formed in the lumen of the vein, which clogs the gap in the vessel wall.
- The resulting blood clot interferes with normal blood flow in the vein, leading to stagnation of blood in it.
- Swelling and local inflammation occur around the thrombosed area of the vein.
- Severe pain and discomfort occurs in the anal area, which is not directly related to the size of the blood clot. Even with a small blood clot, the pain will be severe and constant.
- For obvious reasons, a person begins to experience fear of defecation - this leads to constipation, which further increases congestion in the rectal area and aggravates the course of the disease.
- Emptying the bowel after prolonged constipation leads to damage to enlarged and thrombosed hemorrhoids - the pain intensifies.
Causes and risk factors
The immediate cause of hemorrhoidal thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot. Its appearance can be triggered by:

- Pushing during bowel movements, during childbirth, or when lifting heavy objects. As a result of pushing, intra-abdominal pressure increases significantly, which the walls of the vessels may not be able to withstand - they are damaged. As a result of straining during bowel movements, internal hemorrhoids may fall out, which are subsequently pinched by the rectal sphincter and thromboses - this is how internal thrombosis occurs.
- Injuries to the tissues of the anus and rectum during anal sex or the use of sex toys can lead to damage to the walls of blood vessels.
The risk of developing the disease increases many times under the influence of the following factors:
- Hypothermia of the pelvic area, as a result of which the vessels narrow and the outflow of blood from them becomes difficult. As a result of congestion, deformation of the vascular wall can occur.
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure as a result of a hacking cough or in late pregnancy.
- Increased blood clotting, which itself provokes thrombus formation.
- Chronic hemorrhoids.
- Poor nutrition, alcohol abuse.
- Inflammatory and tumor diseases of the pelvic organs.
- Physical inactivity.
First signs of thrombosis
The formation of thrombosis causes the sensation of a foreign body in the anal area. The patient feels that the intestines have not emptied completely. Trying to do this only causes pain. If thrombosis occurs for the first time, it contributes to the development of hemorrhoids. Along with the sensation of a foreign object inside, there is a burning sensation in the anus, itching, and problems with defecation begin. Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node at stages 3 and 4 of hemorrhoids is accompanied by severe pain, bleeding, and discharge of purulent mucus.