Symptoms of esophageal dysphagia
The appearance of symptoms of dysphagia indicates a violation of the movement of the food bolus through the esophagus into the stomach cavity. The act of swallowing is complete and the patient does not experience any pain. The main complaints of patients include the lump getting stuck and bursting in the back of the sternum, which is absolutely painless. A pronounced sign of the condition is diffuse spasm of the esophagus, when the patient feels intense pain.
The main symptoms include:
- Impaired movement of food at the level of the oropharynx. The process is accompanied by the throwing of the swallowed lump into the nasal or oral cavity;
- Increased salivation (salivation);
- Feeling of suffocation;
- Cough;
- Inability to swallow food.
These symptoms develop when eating solid foods, especially in the early phases of the disease. The process of eating is simplified when the patient drinks food with plenty of water or juice. As the disease progresses, even with the help of water, the food bolus cannot be moved through the esophagus.
Depending on the cause of its occurrence, swallowing disorders are considered as a separate pathology or dysphagia syndrome for a specific disease (secondary).
The violation causes:
- Belching of food and air;
- Heartburn as a result of the return of gastric contents;
- Hoarseness of voice (dysphonia).
How to diagnose the disease
Belching and rumbling in themselves are not a disease and do not require special treatment. You can diagnose the phenomenon yourself, without turning to specialists. An exception is the situation when, in addition to sounds in the abdomen, there is a deterioration in health, pain, nausea, heartburn, headache, etc. It is necessary to visit a specialist. To determine the disease, a comprehensive examination is prescribed, where the main diagnostic method is instrumental examination.
Additionally, you need to donate blood for general and biological analysis, urine, and feces. The condition, smell, and consistency of the stool determine the presence of bacteria, the quality of the digestive system, as well as the presence or absence of helminths. A breath test for Helicobacter bacteria reveals an indicator of microorganisms. An increased amount of them causes the development of gastritis and other concomitant diseases of the stomach, esophagus, intestines, and pancreas.
Causes
There are several types of esophageal dysphagia, each of which has predisposing and directly causing factors:

- True. Associated with disruption of the areas of the nervous system that control the swallowing process;
- Functional. It appears when the central nervous system is damaged, in particular with pseudodysphonia (a condition caused by hysteria);
- Anatomical. Swallowing disorders are caused by an anatomical obstacle to the passage of a bolus of food through the organ.
The cause of dysphagia in most cases is food impaction. The condition occurs when microbes and small particles are retained on the surface of the tonsils. In a healthy person, the condition cannot cause pain, since a natural self-purification process occurs. When the tonsils are unable to cleanse themselves, food plugs form and difficulty swallowing bolus.
Often the cause of difficulties with the passage of food is an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, when disruptions in its functional activity are recorded.
The reason for food to solidify in the lumen of the esophagus may be a disruption of the lower sphincter, which is detected by the reflex reflux of food from the stomach into the esophagus (reflux esophagitis). The manifestation of a decrease in the tone of the lower sphincter is facilitated by diaphragmatic hernia, improper diet, gastric ulcers, increased acidity of gastric juice, high intra-abdominal pressure, and constant overeating.
Dysphagia can be caused by the inability of the muscles and nerve endings located in them to perform their function - to transport the bolus of food through the esophageal tube. These conditions include:
- Stroke;
- Spinal column injury;
- Spasms of the esophagus;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Achalasia;
- Muscular dystrophy;
- Scleroderma, against the background of which there is a progression of hardening of the tissues of the esophagus;
- Pathologies of the immune system that contribute to the progression of tumor and inflammatory processes (polymyositis, dermatomyositis).
Secondary causes of dysphagia include complete or partial blockage of the esophagus. The pathological condition occurs as a result of:
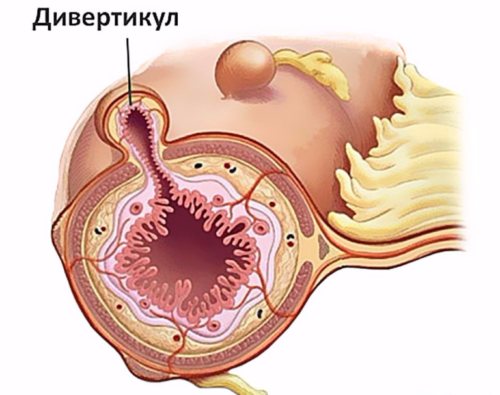
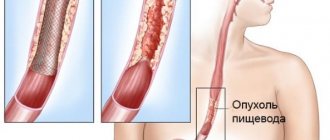
- Tumors of the esophagus (both benign and malignant);
- Esophageal tissue dissection. It is a congenital anomaly, very rarely – an acquired pathology;
- Esophageal diverticulum;
- Gastroesophageal reflux;
- Tumor pressing on the esophagus from other organs (enlarged lymph nodes);
- Age. The cause of a food bolus getting stuck in the esophageal tube can be age-related changes in the body.
Food gets stuck in the esophagus: measures to take in this condition
The upper part of the digestive system is often subject to the development of various types of pathologies, the most common of which is characterized by food getting stuck in the esophagus.
Swallowing dysfunction often occurs as a result of various functional disorders in the human body, organic failures, or the entry of foreign bodies into the esophageal tube.
The subsequent development of such conditions entails dangerous deviations in the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, so it is important to pay attention in time to the warning signals accompanying these processes.
Causes of foreign bodies getting stuck in the esophagus
Retention of foreign objects in the esophageal canal is a common phenomenon. It is not uncommon for children to swallow buttons, small parts of construction sets, coins and badges.
Let's consider a number of factors that lead to the retention of food and foreign objects inside the body:
- large size of the foreign object compared to the esophageal lumen;
- the presence of sharp edges on the foreign body, thanks to which it easily digs into the soft tissue of the esophageal tube;
- prolonged spasm of the muscles of the esophageal canal in the area of its narrowing;
- the presence of neoplasms, scars, hernias and other pathologies of the esophageal tube, which partially block its lumen and prevent the normal passage of food masses through the esophagus into the stomach.
What to do if a foreign body is stuck in the throat?
Often, swallowing disorders can be caused not only by diseases of the esophagus, but also by foreign objects that spontaneously linger in the esophageal tube when swallowed. For example, if a fish bone gets stuck in the esophagus, this can lead to the formation of an inflammatory process and suppuration in the esophageal walls.
Fish bones, for the most part, have sharp edges that easily dig into the delicate tissues of the throat. In addition, they are very thin and cannot always be noticed while eating.
Symptoms of a bone stuck in the throat:
- Pain when swallowing. Stitching sensations are localized at the site where the bone is stuck. The pain can be sharp and sharp, especially if it concerns fish bones.
- A persistent sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the pharynx, larynx or esophageal tube.
- scratching sensation when trying to swallow food.
- A feeling of swelling in the throat , due to possible swelling of the soft tissues of the neck.
- Cough caused by a sore throat.
- Vomiting , often resulting from continuous coughing.
- Labored breathing. The symptom manifests itself as a result of swelling of the tissues of the throat.
What measures should be taken in this case?
If a bone is stuck in the esophagus, you can use age-old, proven methods for removing the bone at home:
- Ingest products with a viscous consistency, such as kefir , mashed potatoes or yogurt . These products can push bone into the esophagus, but only if the bone is not stuck too deep in the tissue. You can also use products with a soft texture (marshmallows, bananas), which will envelop the bone and it will not be able to continue to harm the integrity of the mucous membrane.
- Swallowing a piece of stale rye bread is perhaps the most common method for pushing bone down the esophagus. However, the danger of this method is that a piece of bread can break the bone and plunge it even deeper into the tissue.
- Slowly drink honey, preferably liquid consistency. In this case, it is necessary to be active with the swallowing muscles. This method is very effective if food is stuck in the esophagus.
- Ingest a couple of tablespoons of vegetable or olive oil , so that the bone can slip out and travel further along the digestive tract.
- Vomiting will help dislodge the stuck bone from the tissues of the larynx. You need to induce vomiting by gently pressing on the root of the tongue.
- You can try to remove the bone using a small piece of gauze wrapped around your finger. You need to carefully run your finger and gauze over the supposed place of the jam, as a result of which the foreign body can get caught in the fabric and get out.
- You can eliminate the feeling of food stuck in the esophagus by causing a severe sneezing attack. If you smell black pepper, the effect will not take long to appear. When sneezing, dynamic muscle contraction occurs, which promotes bone rejection.
- If the stuck bone is clearly visible, you can use a mechanical extraction method - tweezers . It must first be disinfected with an antimicrobial substance, such as alcohol. The procedure should be carried out in good lighting, gently pressing down on the tongue with a spoon. Can a pill get stuck in the esophagus? Such cases are not uncommon, and this is observed in the upper, cervical part of the esophagus, where it has a physiological narrowing. If a tablet gets stuck in the esophagus, what should you do? There is no need to panic, since any medicinal pill intended for oral administration tends to dissolve within 30 minutes. If the patient has impaired swallowing function and needs to take pills constantly, it is recommended to grind them to a powder consistency and wash them down with water before taking them.
What to do if the tablet is stuck in the esophageal tube and does not want to leave its confines?
- first of all, do not panic: during times of fear and fright, a spasm of the muscles of the larynx occurs, which will aggravate the situation;
- drink a few mugs of warm water or tea - plenty of warm drink will neutralize the spasm and soften the tablet;
- perform smooth, circular movements with your neck, while constantly swallowing saliva;
- take a small piece of boiled potato and swallow it, if possible;
- A gentle cough can also push the tablet through if it is not deep.
What to do if food is stuck in the esophagus and remains there for a long time?
In this case, severe complications may develop, such as necrosis of the mucous membrane, bedsores , ulcers and inflammatory processes (esophagitis). It is important to understand that the entry of a foreign object or food stagnation inside the esophageal tube is directly related to injury to the esophagus and the development of serious pathologies.
Source: https://GastrituNet.online/bolezni-pishhevoda/glotanie/pishha-zastrevaet-v-pishhevode.html
Main manifestations
In many patients, the condition appears as a result of fears and stress. Nervous overexcitation is accompanied by increased pressure and swelling of the mucous membranes; in addition, there is a narrowing of the lumen of the throat, which in turn leads to difficulties in passing food through the digestive tube. The accumulated food begins to become covered with mucus, and the body begins to accept it as a foreign body. This causes an increase in the size of the mucus plug, consisting of mucus and food particles.

All symptoms intensify when the patient is in a horizontal position, as well as after eating before bed.
The occurrence of dysphagia in children is associated with a disorder of underdeveloped nervous regulation of swallowing. The disease can be congenital or acquired, and can often accompany cerebral palsy and developmental abnormalities. Signs of the disease in children may include refusal of nipples with a large hole, choking during slow feeding, and milk flowing into the nose. Rarely, but there is a possibility of detecting the disease against the background of frequent bronchitis and pneumonia, bronchial asthma.
Health care
If the methods described above do not help, you should go to the doctor. At the hospital, they will first induce vomiting to try to push the lump out. Next, the person is fully examined to understand why food is getting stuck in the esophagus.
Interesting! Composition, analogues and rules for using the drug Bobotik
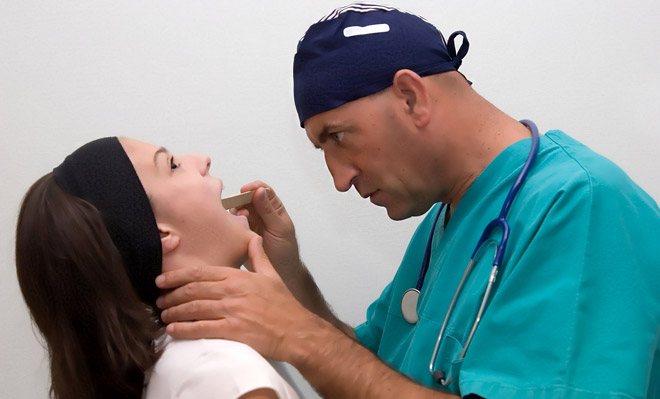
Examination methods include radiography and endoscopy. The first method is needed to determine in which part of the esophagus the foreign body is located. Endoscopy allows the doctor to assess the condition of the mucous membrane. If food does not pass due to the presence of tumors, then using this device you can take tissue for a biopsy.
Note! Quite often, if food does not pass and causes pain, this may mean the presence of a pathology called achalasia cardia. That is, when the migration of food into the stomach is impaired.
And also if food regularly gets stuck in the esophagus, then there may be other pathological reasons for this:
- tumor formations in the esophagus;
- esophageal stenosis;
- atony;
- esophagitis of an infectious nature;
- chemical burn.
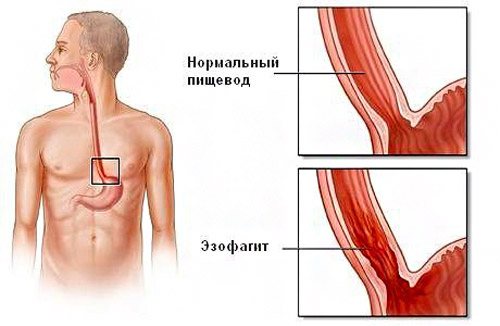
In such cases, a person needs serious treatment, since these pathologies can lead to negative consequences. In all these conditions there will be pain or discomfort behind the sternum. In some pathologies, pain spreads to the neck or arm.
Neuroses also lead to the sensation of a lump in the esophagus. When a person is stressed, blood pressure rises, and as a result, the mucous membrane swells. In this state, a person wants to eat, and food passes through a narrow hole. This is also characterized by food getting caught in loose tonsils and the walls of the esophagus. As a result, discomfort appears, which a person may mistake for a lump of food. For this reason, the person is fully examined, and it is especially important to prescribe a psychiatrist. These will be sedative medications.
What to do if food is stuck in your throat
Food stuck in the throat or a small foreign body can block the airway and lead to suffocation. The condition is quite dangerous and can be fatal.

If a person has food stuck in their throat, the first thing you need to do is monitor their breathing. An encouraging situation is when the airways are not completely blocked and the victim can cough or make sounds.
With partial blockage, coughing serves as a defensive reaction, so the body tries to get rid of the stuck foreign body on its own. In order to get rid of a piece of food in the throat, the patient must continue to cough.
If breathing is partially blocked, care must be taken to ensure that the windpipe is not completely blocked. A situation is considered dangerous when the victim cannot make sounds, but is still conscious. In this case, the use of the Heimlich maneuver is recommended. You need to clasp the patient’s arms under the chest and bend forward, thereby provoking the movement of stuck food down the throat outward. After this, you should hit the area between the patient’s shoulder blades with the outside of the wrist.
The foreign body must come out of the windpipe during the applied method; if this does not happen, the action must be repeated.
If a positive result does not occur, but breathing is preserved, you need to place your hand between the ribs and the navel, then gently press on top several times until the stuck food is completely released. If all first aid methods do not bring the desired effect, you must call an ambulance.
Causes of sore throat
Probably every person has experienced heaviness and discomfort in the throat at least once in their life. It may appear for a short time after swallowing medications (tablets, capsules) or solid foods (crackers, seeds, peels). Help in such cases consists of coughing, drinking a glass of water, or eating a piece of bread. But even after this, discomfort in the throat persists for some time, and then disappears without a trace.
The feeling of a spasm in the throat often bothers people whose profession is associated with constant tension on the vocal cords (teachers, educators, lecturers, singers, actors, etc.). This is due to fatigue of the vocal cords, it is caused by mechanical reasons (natural friction). To restore their normal functioning, it is necessary to organize speech rest and simply remain silent for 30-60 minutes (if the voice breaks down, up to several days).
Also, unpleasant painful sensations in the throat sometimes occur when consuming certain foods and drinks that “burn” the mucous membranes of the throat (spicy, smoked, too hot or cold foods, strong alcohol). In addition, many smokers experience a feeling of heaviness in the throat due to its constant irritation by nicotine. Similar sensations may also occur in people who are far from this habit, who are forced to inhale tobacco smoke, work with ethereal or volatile substances, or live in industrial and gas-polluted cities. In this case, the severity goes away when the provoking factor is eliminated.
After invasive medical examinations (gastro-, bronchoscopy), surgical interventions (tonsillectomy, removal of the thyroid gland, laryngeal tumors), patients are concerned about discomfort in the throat, a feeling of heaviness, and moderate pain. Over time, the discomfort goes away.
Classification of dysphagia
The development of the disease is distinguished into 4 stages:
- Inability to swallow only specific types of solid foods;
- Inability to swallow solid food. Semi-liquid or soft foods are easy to swallow;
- The patient can only eat liquid food;
- The act of swallowing is not performed.
The disease, depending on the localization of the process, can be:
- Oropharyngeal or oropharyngeal. In this case, the bolus of food moves with difficulty from the pharynx to the esophagus;
- Esophageal or esophageal. It progresses if the lumen of the esophageal tract is blocked or as a result of disruption of its muscle structures. Experts divide this type into certain subtypes: upper, middle and lower;
- Cricopharyngeal incoordination.
Depending on the course, dysphagia can be:
- Constant;
- Intermittent (appears from time to time);
- Progressive. There is a gradual deterioration of the patient.
Other causes of gurgling sounds in the stomach
There are many reasons that cause gurgling in the stomach. One of them is the manifestation of a side effect from medications taken by a person. Look at the leaflet for the drug. If it lists: bloating, flatulence or diarrhea as side effects, then ask your doctor to replace it with another one.
Doctors also identify a number of other reasons that cause gas formation in the intestines:
- an excess of fatty, floury, spicy and sweet foods in the human diet. In order to get rid of gas formation, add vegetables, fruits, and cereal-based bread to your diet;
- intolerance to certain nutritional components. If a person is intolerant to gluten or lactose, then it is necessary to limit the consumption of foods containing them;
- excessive consumption of tobacco and alcoholic beverages causes discomfort in the stomach;
- excess of chemical additives in food. Flavor enhancers, preservatives, sweeteners and other additives cause discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract.
The occurrence of diseases that cause discomfort in the stomach should not be excluded:
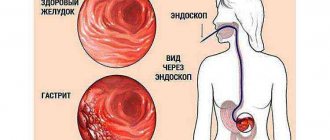
- gastritis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ;
- gastroparesis;
- increased or decreased acidity.
Poisoning also causes stomach upset. One of the reasons that causes stomach turmoil can be the smell of food. Thus, a person receives a signal about the need for the next meal. There can be many reasons that cause gurgling in the stomach. If gurgling sounds appear too often and cause you discomfort, then contact a gastroenterologist for a medical examination.
Be sure to read about it
- 8 diseases that can bankrupt you
- What substances does a cigarette actually contain?
- Why are men more susceptible to heart disease than women?
Methods for diagnosing dysphagia
Diagnostic studies of dysphagia are aimed at clarifying symptoms, identifying connections and causes, and establishing the level of damage to the swallowing act. General tests of blood, feces and urine make it possible to detect the primary disease against which the pathology arose. For an accurate diagnosis, differential diagnosis is carried out.
The doctor prescribes liver tests and an ECG; to identify the pharyngeal form, the main indicators are obtained using:
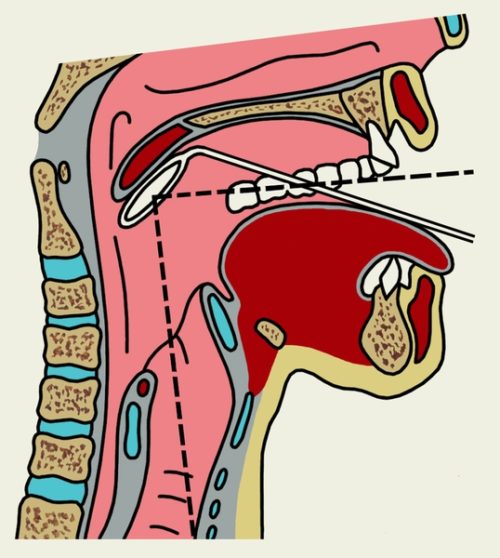
- Screening test. The patient is given 150 ml of water to drink as soon as possible and the number of sips and time are counted. The data obtained makes it possible to calculate the rate of swallowing and the volume of the sip. This method is quite reliable.
- Examination of the upper esophageal sphincter using fluoroscopy during the period of contrast diagnostics;
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Gives the opportunity to visually evaluate the internal surfaces of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, and take a tissue specimen for biopsy.
- Checking the motor activity of the esophagus. The study is carried out using a four- or eight-channel device called a water-perfusion catheter. The device allows you to determine the tone of the upper and lower esophageal sphincters, the thoracic region;
- 3d manometry. Is a more accurate way. Allows you to obtain not only indicators, but also color images of peristalsis in the form of waves;
- Method of radionuclide scintigraphy of the esophagus. The method is based on measurements of radioactivity after ingestion of a liquid containing technetium in 99 patients;
- Differential diagnosis. This involves performing an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, MRI of brain structures, and electroencephalography of the brain. Consultations with a gastroenterologist, neurologist, and otolaryngologist are provided;
- Laryngoscopy. The method allows you to examine the posterior walls of the larynx.
Esophageal dysphagia is quite difficult to identify due to the need to exclude various ailments that contribute to the formation of a mechanical obstruction. The doctor must make sure that there are no malignant neoplasms.
In the presence of a tumor, long-term dysphagia (more than 4 months), a progressive course, severe symptoms when consuming non-liquid foods, and a sharp decrease in the patient’s weight are recorded.
Contrast radiography reveals abnormalities in the contours of the esophagus, signs of ulcers or tumors, diverticulitis, achalasia and other organic pathologies.
Lack of timely treatment for dysphagia can cause:
- Asphyxia with respiratory arrest;
- Aspiration pneumonia, abscess;
- Cancer in the throat, esophagus and stomach;
- Severe inflammatory process in the esophagus;
- Alimentary cachexia, which appears as a result of prolonged fasting.
Causes of belching, rumbling in the stomach
In most cases, belching and rumbling in the stomach are a normal physiological process and do not require special treatment or special attention.
- Hunger. The digestive tract is constantly in motion. Regardless of whether food arrives or not. In the absence of food, the stomach is filled with air, the contraction of smooth muscles becomes noticeable acoustically - rumbling sounds appear. Burping is needed to get rid of excess air. Under normal circumstances, air constantly enters the stomach and comes out imperceptibly in small portions. There is nothing dangerous in this, if one day the belching becomes noticeable and it is an isolated phenomenon. To get rid of unpleasant sounds, you just need to eat.
- Binge eating. When eating a large amount of food, especially after a long fast, a lump forms in the intestines, the movement and digestion of which requires increased work of the gastrointestinal tract and peristalsis. A person feels this process by seething, rumbling in the stomach. Belching air often occurs during or after a feast and does not leave an unpleasant taste or odor in the mouth. This happens because the stomach needs to make room for the next portion of food.
- Some foods are provocative. Consumption of certain foods and drinks causes increased intestinal motility, fermentation, bloating, and flatulence. With normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, the symptoms are temporary, disappear a few hours after they are completely digested and leave the digestive tract. Provocateurs include sweets, legumes, cabbage, coffee, carbonated drinks, alcohol, kvass, beer, and whole milk.
- Jar of Hearts. The central system is not directly related to the work of the digestive tract, but leaves its mark. With severe stress, depression, exhaustion, muscle spasms, including intestines, are observed. The result is rumbling and belching of air. To eliminate the unpleasant phenomenon, it is enough to drink tincture of valerian, motherwort, glod, Nova-Passit remedy or tea from mint, chamomile, lemon balm.
- Menstruation. On the eve of menstruation, hormonal changes occur in the body, the amount of progesterone increases, which activates intestinal motility and forces muscles to work. This is necessary so that the uterus can reject the unneeded layer of endometrium. However, changes in hormones also affect bowel function. Additionally, there is a change in taste preferences, nausea, decreased or increased appetite. The rumbling disappears on its own 1-2 days after the start of menstruation.
Also, there are a number of pathologies accompanied by rumbling in the stomach and belching. In this case, there is a deterioration in general health, weakness, upset stool, pain, nausea and some other painful symptoms.
- Intestinal dysbiosis. A common phenomenon that occurs due to an imbalance of beneficial and harmful microorganisms. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, against the background of decreased immunity, the activity of opportunistic microorganisms is activated. Their waste products cause fermentation, rotting, flatulence, rumbling, and bloating. In addition, there is a violation of the stool - constipation or diarrhea, nausea, chills, general weakness, a slight increase in temperature, pain in the lower abdomen around the navel. Common provocateurs are medications, especially antibiotics, fatty, spicy, salty foods, alcohol, and hormonal drugs. This disease is characterized by unpleasant-smelling stools, the appearance of mucus, colic, and spasmodic pain.
- Dyspepsia. It is a difficult, incomplete digestion of food due to an insufficient amount of enzymes. Most often occurs due to pathologies of the pancreas. Rumbling stomach and belching are accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, esophagus, upper abdomen, and distension. The main symptom is rapid satiety, lack of appetite, and deterioration of well-being a few minutes after eating.
- Intestinal obstruction. It is a narrowing of the intestinal lumen. It occurs as a result of prolonged inflammation, the formation of a benign or malignant tumor, and the accumulation of too hard stool. In this case, the cause of rumbling in the stomach and other sounds is increased gas formation. Traces bloating, flatulence, pressure, abdominal pain of different localization.
- Irritable stomach and intestinal syndrome. It occurs for various reasons, due to the negative impact of unfavorable factors. This can be caused by chemicals, mechanical manipulation, ingestion of a foreign object, long-term use of medications, rough food, dry food, etc. The syndrome is manifested by bloating, distension, flatulence, and rumbling. There is belching of air, sour, bitter substances.
- Poisoning. When low-quality food with the presence of bacteria and harmful microorganisms enters the digestive tract, the activity of the gastrointestinal tract increases. The body tries to free itself from the contents. It all starts with rumbling in the stomach, bloating, then pain, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting appear. There is headache and weakness. Belching is not always present. This also includes alcohol poisoning.
- Helminths. The presence of parasites in the intestines causes dysbiosis, decreased local immunity, fermentation processes, putrefaction, and toxicosis. In addition to rumbling and belching, there is constant pain in the abdomen - acute or aching in nature, nausea, itching in the anus, and abnormal bowel movements. With a large number of helminths, intestinal obstruction may occur.
Almost all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract cause rumbling and belching. Making a diagnosis yourself is problematic. A specialist consultation and a comprehensive examination will be required. You can independently determine the cause of the temporary appearance of rumbling in the stomach and belching by analyzing the events of the current day, diet, quality, and quantity of food.
Pregnancy is also a cause of unpleasant phenomena. Rumbling in the stomach is observed even before a woman finds out about conception. This symptom is considered the first sign of pregnancy. Occurs due to hormonal changes. The amount of progesterone, which is needed for the normal development of the egg after fertilization, increases. By mid-term, progesterone levels gradually decrease, and the rumbling in the stomach disappears.
In the last months of pregnancy, unpleasant symptoms appear due to a narrowing of the intestinal lumen and stomach due to an increase in the size of the uterus. Additionally, heartburn, belching of air, sour, bitter, and constipation appear.
In addition to this harmless cause of sounds in the digestive system during pregnancy, there are others that require attention. During gestation, all organs work under load and undergo some changes. In the presence of chronic diseases, exacerbation occurs. In the first months, a woman experiences signs of toxicosis, including bloating, rumbling, and belching.
Treatment methods for dysphagia
After clarifying the cause of the obstruction, therapy is prescribed aimed at eliminating the underlying disease causing dysphagia.
The main methods of treating swallowing disorders include:
- Surgical method. Used to remove a foreign body and eliminate other causes of obstruction of a food bolus in the esophagus;
- Radiation therapy. Used for tumor processes;
- Endoscopic method. The affected areas of the esophageal mucosa are treated;
- Installation of self-expanding stents, with the help of which the esophageal lumen is increased. Helps normalize patency;
- Drug treatment that alleviates the symptoms of the pathology;
- Diet therapy. Involves adjusting the diet and revising the list of dishes used.
Therapy is chosen strictly individually; in severe conditions, the patient is fed with a flexible tube inserted through the oral cavity or gastrostomy tube.
Medicinal treatments
For dysphagia caused by peptic ulcers, enveloping agents (phosphalugel, Maalox) are used, which protect the mucous membrane and neutralize hydrochloric acid, reducing the activity of the stomach contents. The treatment course includes drugs that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid (rabeprazole, omez, ranitidine), which help normalize its production and reduce its aggressive effect.

Prokinetics are prescribed, which accelerate the passage of the food bolus through the esophagus and stomach, preventing the development of reflux. Drugs that stimulate gastrointestinal motility are used.
Surgery
For certain diseases, surgical treatment is indicated for patients with dysphagia. Surgery is used to treat tumors, particularly squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus and adenocarcinoma. In such cases, only surgery can improve the prognosis of life expectancy.
Surgeries are also performed when a hiatal hernia is diagnosed, since medications can only temporarily hide the symptoms, but do not affect the causes of their manifestation. Surgical intervention is aimed at restoring the standard arrangement of the abdominal organs and strengthening the esophageal opening of the diaphragm.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment includes reducing the acidity of gastric juice, treating diseases of the pharynx and esophagus using antibacterial drugs, and using sedatives to eliminate psychogenic manifestations if the pathological condition is caused by a disorder of a psycho-emotional nature.
Food stuck in the esophagus - folk remedies
While eating, it may happen that a large piece gets stuck in the throat due to poor chewing, or swallowing foreign objects may occur accidentally. In such cases, if help is not provided, the person experiences discomfort, pain, etc. Everyone should know what to do in such a situation.
If swallowed incorrectly, the bolus gets stuck in the tracheal bifurcation area and near the lower alimentary sphincter. Most often, this situation occurs in young children, mentally ill people and during alcohol intoxication. That is, for those who, due to some circumstances, cannot fully control themselves.
A person who feels that a bone is stuck in the throat should immediately eat something with a viscous consistency. For example, mashed potatoes, bread, full-fat kefir, etc. If the lump does not go away after eating these foods, it may mean it is lodged deep in the tissue. In this case, it is better to consult a doctor so as not to worsen the situation. Doctors say that if you chew bread, it can cause harm, since the hard mass can break the bone, and the piece that has stuck into the walls of the esophagus will remain there. Next, the inflammatory process may be activated.
If a poorly chewed piece of food is stuck, it is recommended to drink liquid honey. There is no need to rush; with each swallow, it is recommended to especially actively use the swallowing muscles. You can also cause a sneezing attack, as this causes the muscles to begin to contract rhythmically, and the lump moves forward on its own.
Another effective method of extracting bones is to use vegetable oil. Sometimes 1-2 tablespoons of oil are enough for the bone to slip out and pass into the stomach.
If the methods described above do not help, you should go to the doctor. At the hospital, they will first induce vomiting to try to push the lump out. Next, the person is fully examined to understand why food is getting stuck in the esophagus.
Examination methods include radiography and endoscopy. The first method is needed to determine in which part of the esophagus the foreign body is located. Endoscopy allows the doctor to assess the condition of the mucous membrane. If food does not pass due to the presence of tumors, then using this device you can take tissue for a biopsy.
Note! Quite often, if food does not pass and causes pain, this may mean the presence of a pathology called achalasia cardia. That is, when the migration of food into the stomach is impaired.
And also if food regularly gets stuck in the esophagus, then there may be other pathological reasons for this:
- tumor formations in the esophagus;
- esophageal stenosis;
- atony;
- esophagitis of an infectious nature;
- chemical burn.
In such cases, a person needs serious treatment, since these pathologies can lead to negative consequences. In all these conditions there will be pain or discomfort behind the sternum. In some pathologies, pain spreads to the neck or arm.
Neuroses also lead to the sensation of a lump in the esophagus. When a person is stressed, blood pressure rises, and as a result, the mucous membrane swells. In this state, a person wants to eat, and food passes through a narrow hole. This is also characterized by food getting caught in loose tonsils and the walls of the esophagus. As a result, discomfort appears, which a person may mistake for a lump of food. For this reason, the person is fully examined, and it is especially important to prescribe a psychiatrist. These will be sedative medications.
Every person should know what to do if food is stuck in the esophagus, since such a situation can arise anywhere and anytime. But if food often gets stuck in the esophagus, then you should undergo an examination.
source
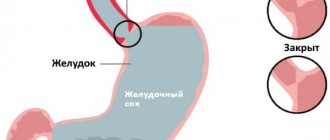
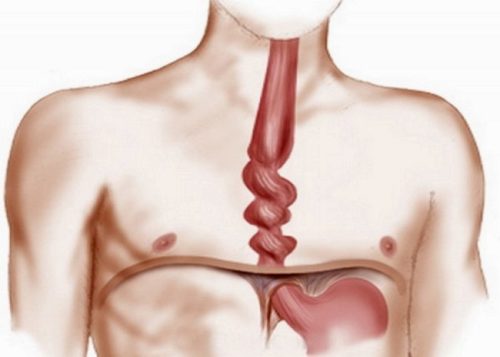
The main job of the esophagus is to carry food from the pharynx to the stomach. During normal functioning, this tubular muscular organ contracts to gradually move it. The action occurs gently, painlessly for the body, which practically does not notice the wave-like movements. If this natural process is disrupted by convulsive contractions of the esophageal muscles, causing pain and panic, the main thing is to find the cause of the spasm and eliminate it.
A spasm is an uncontrolled, sharp and painful compression of the esophagus tube in different parts, which stops the movement of the food bolus.
Convulsive contractions of the muscles of the esophageal tube during spasm
The main symptoms that the patient complains about:
- dysphagia (swallowing disorder);
- attacks of acute pain behind the sternum, in the throat, in the area between the shoulder blades;
- heaviness and feeling of a “lump” stuck in the throat;
- tightness in the chest or upper stomach.
Symptoms occur for a short time not only when swallowed, but also during walks, work, and while resting.
In most cases, the disease in its primary form (in the form of episodes) manifests itself when:
- severe fatigue;
- food or drug poisoning, general intoxication of the body of various origins;
- infectious diseases such as acute bronchitis, influenza, measles, scarlet fever;
- overexcitation, stressful situations; strong fear;
- lack of sleep;
- high temperature, convulsions;
- foreign body entering the esophagus (small objects, chicken, fish bone);
- microtrauma of the walls of the esophagus due to eating too hard food;
- eating very cold, spicy, dry or hot food;
- incorrectly selected dentures.
Difficulty swallowing liquid due to esophageal spasm
The chronic course of the disease is associated with a violation of the reflex mechanism of swallowing, which occurs due to:
- inflammation of the vagus nerve;
- damage to the nerve nodes surrounding the esophagus;
- intoxication of the body during infectious and allergic diseases;
- weak tone of the muscular tube of the esophagus or its paralysis caused by diseases of the connective tissue and endocrine organs;
- damage to the nervous system (neuroses, panic attacks, long-term hidden stressful situations);
- inflammation of the mucous membrane or tissues of the esophageal tube (esophagitis, gastroesophageal reflux, peptic ulcers and cholelithiasis, hiatal hernia);
- meningoencephalitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain.
The disease can manifest itself in several types, differing in symptoms and manifestations.
Manifests itself in uncoordinated prolonged muscle movements along the entire length of the esophageal tube. The x-ray shows an extended spasm of the wall.
- severe pain behind the sternum or in the area of the transition of the esophageal tube into the stomach, which spreads up to the neck, radiating to the shoulders and lower jaw. An attack of pain occurs regardless of the act of swallowing;
- paradoxical difficulty in swallowing, so-called dysphagia, manifests itself more strongly when swallowing mushy food or drinks and less when trying to swallow solid food;
- At the end of the attack, regurgitation is possible.
Duration - from ten minutes to several hours.
Frequency - from several times while eating food or outside of this process to several attacks per month.
Development of diffuse spasm of the esophagus
With this type of contraction, contractions occur in certain areas with great intensity. Deformation of the esophageal tube in the form of a “nutcracker esophagus” or in the form of a “rosary” is observed.
- difficulty swallowing pureed foods (soft cottage cheese, liquid porridge, sour cream), as well as foods rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, bread);
- frequent manifestations of dysphagia when consuming any liquids;
- the pain is moderate, manifesting itself in the lower part of the sternum; the spasm begins and ends gradually.
Duration from a few seconds to three to four hours.
Frequency - from two to four times with meals to several times a month.
Contraction of the esophageal muscles during spasm
With this form, an involuntary, convulsive contraction of the muscles of the esophagus occurs. The cause of this condition is considered to be severe nervous shock, fear, prolonged stress, and depression.
- During meals, when the food bolus is retained when it is compressed by the muscles of the esophagus, it is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- occurs suddenly, acutely;
- food does not enter the stomach, getting stuck for a while in the esophagus, pushing through in the direction of the stomach with great difficulty;
- if it is impossible to get into the stomach, the food bolus is removed through involuntary vomiting movements;
- vomiting during esophagospasm of a neurotic nature differs from ordinary gastric vomiting - it occurs almost during meals, and the vomit consists of undigested food without hydrochloric acid and pepsin.
2. With severe neurological impairment, an attack develops suddenly, regardless of food consumption. Symptoms:
- pain resembles angina attacks, affecting the chest area;
- Pain sensations range from slight pressure to sharp pain, burning, squeezing, and a feeling of a foreign body getting stuck (“lump” in the throat). The sensation of “coma” occurs during contractions of the initial sections of the esophageal tube and is observed in neuroses and hysteria;
- feeling of suffocation;
- spasm and retching can occur with strong smells, sounds, or fear.
The pain in these cases lasts from a few seconds to many hours with varying degrees of intensity.
During the initial attack, which occurred while eating, the symptom of dysphagia can take hold subconsciously and subsequently arise reflexively when trying to swallow something.
Rough, spicy food increases pain, causing a person to refuse food.
It should be remembered that the patient may simultaneously exhibit different types of esophagospasm.
- In a state of spasms, the patient is often able to drink a small amount of warm liquid (preferably milk or chamomile infusion). This usually helps the food move further and the pain subsides.
- If urgent assistance is necessary, in order to quickly relieve spasm, an injection of atropine is given intravenously or intramuscularly.
- Nitroglycerin, which is absorbed under the tongue, gives quick results. But at the same time it is necessary to monitor blood pressure, since nitroglycerin sharply lowers it.
- Medications such as diltiazem and nifedipine can help reduce spasm of the esophageal muscles when swallowing. However, before using them, you should consult your doctor to exclude possible contraindications.
It is necessary to differentiate (distinguish) the condition of spasm of the esophageal muscles from an attack of angina . Chest pain is an unreliable sign. With this symptom, the suspicion of heart disease increases if the patient is over 50 years old, and the pain subsides after the nitroglycerin is absorbed. The fact is that nitroglycerin helps well in both cases, relieving both an attack of esophagospasm and the pain of angina pectoris. To exclude the diagnosis of angina, a heart examination is performed based on electrocardiography.
With spasm of the esophagus, pain manifests itself mainly during the swallowing of water or food, and this symptom is important for making a diagnosis if other research methods are unavailable or uninformative.
Special studies are carried out to find out whether signs of spasms are a consequence of stomach cancer, achalasia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, neurological problems in which the muscles of the esophagus and its sphincter function abnormally.
Spasm of the esophageal tube is visible on radiography with a contrast suspension
To confirm the diagnosis of esophagospasm, patients undergo examination by a gastroenterologist, undergo an X-ray examination, and fiberoscopy. When diagnosing esophageal spasm, fluoroscopy using a contrast agent reveals spasm in certain areas where barium suspension is retained. It is often observed that the spasmodic or narrowed area takes on the shape of a funnel.
To cure esophageal spasm, you must:
- make the correct diagnosis;
- detect the root cause (the underlying disease) that provoked the spasm;
- liquidate it.
Complex therapy is used, aimed at simultaneously eliminating all the symptoms that arise from spasms of the esophagus.
| A drug | Goals and objectives of the reception | How to use |
| Ranitidine |
* If the pain subsides only an hour after the administration of atropine, and reappears 2 hours later, this indicates functional obstruction.
Any medications have contraindications and allergenic components in their composition. Use in doses and according to the schedule prescribed by your doctor.
To stabilize the functions of the nervous system, physiotherapy courses are successfully used:
- novocaine electrophoresis;
- galvanization procedures;
- inductotherapy;
- microwave therapy;
- warm radon, pine, carbon dioxide baths;
- wet wraps for up to 1 hour, every other day.
If treatment with medications and physical therapy does not help, surgery is recommended. It is carried out in rare, serious cases when other methods do not work.
Herbal remedies are prescribed to stabilize the nervous system, normalize sleep, relieve panic, anxiety, and fears. Among such folk remedies are preparations of motherwort, peony, valerian rhizomes, and hops. Herbs with antispasmodic properties are also used: sage, peppermint, chamomile flowers. Elecampane root is most often used as an anti-inflammatory herbal remedy.
| decreased gastric acidity | orally | |||
| Motilium | increased contraction of the lower esophageal sphincter and decreased gastric emptying time | orally | ||
| Cerucal | relieving cramps, nausea, vomiting | orally | ||
| Gastal | protection of the mucous membrane from ulceration, neutralization of the action of acid and enveloping effect on the cavity of the esophagus and stomach. | orally | ||
| Nitroglycerin and its derivatives | rapid antispasmodic effect (with mandatory monitoring of blood pressure) | orally | ||
| Atropine preparations* | urgent care for intense pain and spasms of the esophagus | orally in drops, parenterally (subcutaneously) | ||
| Sustak | pronounced antispasmodic effect | orally | ||
| Belladonna extract | relief of moderate symptoms | orally | ||
| Baralgin | relieving spasms | parenterally (intramuscular or subcutaneous); | calming for neurospastic form of esophagospasm, relieving neurosis | orally |
| Azafen | antidepressants | orally | ||
| Meprobamate | tranquilizers | orally; | ||
| Donormil | normalization of sleep | orally | ||
| B vitamins (B1, B6, B5, B12) | complex of vitamins to strengthen the nervous system | orally; | local anesthetics | orally |
| Title and action | How to use |
| Valerian is a sedative and mild antispasmodic. | |
| infusion of rhizomes | 20 g per 250 ml / 100 ml up to 3 times a day |
| pills | 2 pieces 3 times a day |
| pharmacy tincture | 30 drops up to 4 times a day |
| Motherwort for neurological esophagospasm, which is accompanied by insomnia, rapid pulse, and cardiac neurosis | |
| herbal infusion - 15 g per glass of water | drink 1/3 glass up to 4 times a day |
| pharmacy tincture (preferably together with valerian preparations) | 30–50 drops, 3 times a day |
| Tincture of peony evasive (maryin root) a strong sedative | up to 40 drops / 3 times a day / course 1 month |
| Infusion of hop cones soothing, anti-inflammatory agent - 20 g per 250 ml | 50 ml up to 4 times a day |
| Mint is a strong soothing and anti-spasm agent. | |
| Infusion of mint leaves - take 2 teaspoons per glass | one tablespoon every 3 hours half an hour before meals |
| Mint tablets | 1–2 tablets under the tongue / up to 4 times a day |
| Chamomile infusion in combination with mint, valerian and sage for diffuse spasm of the esophagus in equal proportions of 10 g per 2 glasses of water | 1/3 cup up to 4 times a day |
| Elecampane root against inflammation and heart weakness with neurological spasm - infusion 20 g per 250 ml | 50 ml 4 times a day |
After courses of medicinal herbs, it is recommended to drink 10 drops of sea buckthorn oil (if there are no allergic manifestations to sea buckthorn).
An unconventional method of treating spasms is professional acupuncture. 3 courses of 10 sessions are conducted. There are contraindications. Acupuncture can help not only with spasm, but also with paralysis of the esophagus.
Treatment of esophageal spasm using electroacupuncture
An effective way to relieve spasms is to independently massage three active points. They are located on the midline of the chest, one is below the pit of the neck, the second is between the chest, the third is in the middle between the first two. Massage them with your finger bones clockwise for 5 minutes. The pain at these points can become very severe, almost unbearable. It is believed that spastic pains are “pulled” to these places and gradually subside. The massage is done until the spasms in the esophagus disappear. Usually relief comes within 10–20 minutes.
A gentle diet is prescribed.
Basic principles of nutrition:
- frequent, fractional, small portions;
- eating mechanically gentle food, not coarse, not too hard;
- switching to liquid and mushy foods (ideally baby food);
- last meal 3 hours before bedtime;
- avoidance of dark chocolate and alcohol, which relax the sphincter between the esophageal tube and the stomach, causing acid to flow into the esophagus and causing spasms;
- a minimum of spicy, acid-containing dishes (canned food, marinades, pickles, citrus fruits);
- refusal of black strong coffee;
- do not consume cold or too hot foods, including liquids (ice cream, cold drinks, very hot first courses).
The following will also help reduce the frequency of symptoms:
- sleeping with the head raised on a high pillow;
- to give up smoking;
- losing excess weight;
- straight back when eating (the esophageal tube does not bend);
- absence of bends and forward bends (prevents the reflux of gastric juice into the esophageal tube).
The main treatment regimen, aimed at relieving the patient of spasms when swallowing food, is to make a correct diagnosis in a timely and correct manner and develop a treatment program. At the same time, it may be necessary to conduct detailed examinations to exclude the possibility of serious diseases such as angina pectoris and stomach cancer, the symptoms of which are similar to those of diffuse and neurological spasm.
source
Esophageal spasm is a disease that is associated with impaired motor function of the smooth muscles of the esophagus. Attacks of the disease are manifested by the inability to swallow food and pain in the sternum.
According to statistics, spasms of the esophageal sphincters most often occur in young women aged 18-35 years. After 45, the number of men and women suffering from its manifestations is the same.
There are many reasons that can cause a spasm, from spicy food and stress to infectious diseases.
The esophagus is an elastic tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach. Its length is about 25 cm. The esophagus begins in the lower part of the neck, passes behind the sternum and opens into the stomach. It is located in front of the spine and has 4 small curves.
Along its course, the esophagus is adjacent to the trachea, aorta, bronchus, bronchoesophageal muscle, nerve trunks emerging from the spine, and the diaphragm.
The width of the lumen of the esophagus is not the same. The organ has three constrictions and two expansions. The narrowings are located where the pharynx meets the esophagus, near the aorta and diaphragm.
There are also two sphincters, which are thickened muscles in the form of a ring. These areas are especially rich in nerve endings. They are located at the beginning and at the end, where the esophagus meets the stomach. Their function is to pass food first into the esophagus and then into the stomach.
In a calm state, inside the esophagus there are grooves separated by elevations. This structure helps fluid drain into the stomach. When swallowing solid food, the folds of the esophagus are smoothed out and the lumen expands
The esophagus consists of three layers:
- The mucous membrane has the appearance of smooth multilayered epithelium. Its glands secrete a secretion that facilitates the passage of food into the stomach. Below is the submucosa made of connective tissue cells.
- The muscular layer consists of an inner circular and outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle. The inner layer is responsible for the narrowing of the esophagus, and the outer layer for its expansion.
- The adventitia is composed of loose and elastic connective tissue. The outside of the tube is covered with peritoneum.
The main function of the muscle membrane is to perform propelling movements. Due to which the swallowed portion of food moves from the pharynx to the stomach. Normally, we do not realize or feel these movements; they occur automatically. But during a spasm of the esophagus, the muscles contract strongly. The lumen narrows or closes completely. This causes pain.
Involuntary muscle contraction - spasm can be caused by a variety of reasons.
- Solid or hot food
- Microtraumas caused by small bones or hard foods
- Strong alcoholic drinks that burn the mucous membranes
- Incorrectly fitted dentures, resulting in insufficient chewing of food
- Inflammation of the intercostal nerve, which is responsible for the functioning of the esophagus
- Infectious diseases: measles, scarlet fever, influenza
- Meningoencephalitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain
- A focus of inflammation in the organ near the esophagus
- Foreign body stuck in the esophagus
- Stress
Also, the cause of spasm of the esophagus can be a disease that is accompanied by inflammation of its mucous membrane: esophagitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, cholelithiasis, hiatal hernia, gastroesophageal reflux disease in which the contents of the stomach are refluxed into the esophagus.
Esophageal spasm is divided into:
- Primary, caused by disruption of nerve endings
- Secondary (reflex), caused by concomitant diseases.
Spasm can occur at the entrance or end of the esophagus, in the area of the sphincters.
These areas are rich in nerve endings and therefore are the first to respond to disturbances in the nervous system. Also, their task is not to allow inappropriate food into the digestive tract. Therefore, they can shrink from too hot tea or a tough piece of meat. In other cases, the muscles along the entire length of the esophagus may contract. In some patients, the pain may be sharp and cutting. Others experience it as a stake or lump behind the breastbone. Such sensations may be mistaken for heart pain. Unpleasant sensations can last from a few seconds to 20-30 minutes, and in some cases up to an hour.
- Chest pain behind the sternum, between the shoulder blades
- Inability to swallow solid or liquid food – dysphagia
- Pain radiates to the back, ears, lower jaw, arms
- Tightening chest pain that occurs with exertion
Difficulty swallowing can be associated with the intake of not only solid, but also liquid food. Sometimes pain and dysphagia occur separately.
Pain can occur while eating, while performing active physical activities, at rest, when swallowing saliva, or even during sleep.
Esophageal spasm can be acute or chronic. The chronic form develops if, for some reason, chewing is impaired and in people with increased anxiety. In this case, there is an unpleasant feeling of constriction in the upper part of the esophagus and the need to drink even liquid meals.
There are two types of esophageal spasm
- Diffuse spasm of the esophagus. It occurs when the smooth muscles throughout the esophagus are uncoordinated.
- Segmental spasm of the esophagus. A strong muscle contraction occurred in a certain area. In this case, food cannot pass further.
To effectively treat esophageal spasm, it is necessary to establish the cause that causes it and eliminate it. This requires a thorough examination by a gastroenterologist, fiberoscopy and an x-ray of the esophagus with contrast agents.
To relieve the symptoms of spasm, you can use the following drugs: Papaverine hydrochloride or No-shpa, Cerucal, Atropine sulfate. They must be taken half an hour before meals.
It also helps to avoid manifestations of the disease by taking sedatives (valerian extract, Novo-Passit) and antidepressants (Trazodone), which relieve anxiety and fear. Treatment with hypnosis also has a good effect. Taking nitroglycerin under the tongue has a fairly quick effect.
Calcium antagonists help relieve symptoms and reduce muscle contractions: Nifedipine, Diltiazem. For severe pain, local anesthetic drugs Novocain and Anestezin are prescribed before meals. It is also recommended to take enveloping agents that protect the mucous membrane from irritation and trauma: Simethicone, Almagel.
Antacids are used when hydrochloric acid comes up from the stomach and burns the esophageal mucosa. These drugs (aluminum hydrate, magnesium trisilicate) help neutralize its effect. Atropine is used as an ambulance. It is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. If the pain disappeared only an hour after the injection, and then reappeared two hours later, this indicates that the obstruction of the esophagus is functional.
To normalize the functioning of the nervous system, a course of physiotherapeutic procedures is prescribed - electrophoresis of novocaine, calcium chloride or magnesium sulfate on the area of the cervical sympathetic nerve nodes, as well as a
galvanic collar according to Shcherbak .
In some cases, when acute spasm of the esophagus cannot be relieved with medication, bougienage is performed. This is a procedure to widen the opening of the esophagus using a steel probe. It is carried out under the control of x-ray equipment. Full recovery may require 2-3 sessions. In parallel, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. Such measures help to avoid the transition of an acute process to a chronic one.
In order to get rid of spasms, it is recommended to regularly drink this decoction:
- one tablespoon toasted flaxseed
- one teaspoon of anise fruit
- one tablespoon of bee honey
- 600 ml water
Bring to a boil, cool to 40 degrees. Drink the decoction warm throughout the day.
Another effective recipe. Boil 5 tablespoons of plantain and 1 liter of water over low heat for half an hour. Add 300 g of honey, 1 teaspoon of celery seeds and boil for another 10 minutes. Drink the resulting syrup one tablespoon at a time on an empty stomach.
Belladonna tincture has a good antispasmodic effect. Dilute 10 drops of tincture in a small amount of water. Drink 3 times a day before meals.
Pine baths have a powerful calming effect. The water temperature should be comfortable. Take a bath for 10-15 minutes, 10 days in a row.
Spa therapy will help you get rid of spasms of the esophagus for a long time. Sea air and bathing in salt water are a powerful means of combating this disease. Walks on the beach must last at least 3 hours, 14 days in a row.
Proper nutrition plays an important role in preventing attacks. Food should be dietary and not irritate the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach. The basis of the diet consists of boiled, stewed and steamed dishes, preferably semi-liquid. It is recommended to eat 4-5 times a day in small portions. It is necessary to eat slowly so as not to swallow air and chew food thoroughly.
Alcoholic and carbonated drinks, fatty, spicy and fried foods, sour foods and coarse fiber (apples, cabbage, radishes) are excluded. Avoid extremely cold and hot foods and drinks.
Also, people suffering from esophageal spasm need to adhere to a daily routine. It is necessary to eat at the same time. Normal physical activity is also very important. A sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise can worsen the situation. Moderate exercise and general massage are an excellent way to combat this disease.
A gastroenterologist treats spasms of the esophagus. He conducts an examination, makes a diagnosis, and prescribes a medication regimen. If the occurrence of spasm is caused by other chronic diseases, then the main attention will be aimed at eliminating them.
In the case where the cause is a dysfunction of the nervous system, then prevention will be focused on normalizing its functioning. Then a neurologist can get involved in the treatment. He prescribes vitamins and sedatives.
Spa therapy is a powerful preventative measure. Sometimes 2-3 courses of treatment are required for complete recovery. For such patients, a vacation on the sea coast or treatment with sodium bicarbonate mineral waters (Borjomi, Polyana-Kvasova) is recommended. There are such sources in the Primorsky Territory, Georgia, Ukraine and the Caucasus.
Since one of the causes of spasm is a disruption in the functioning of the nervous system, suspicious and emotional individuals are more susceptible to this disease. Often the disease develops in people suffering from neurosis, depression or under stress. Strong emotional experiences negatively affect human health.
The X pair of cranial nerves, which causes its narrowing, and the sympathetic nerve, which causes muscle relaxation, are responsible for the innervation of the esophagus. Usually they work smoothly and there is no failure. But under strong emotional stress, this balance is disrupted, and narrowing processes predominate. As a result, spasm of the esophagus occurs. The spasm is sometimes caused by self-hypnosis. In this case, we talk about a psychosomatic illness, when a mental state disrupts the functioning of various organs and causes serious illness.
If you feel a sudden attack of pain behind the sternum, first of all, you need to calm down. Most often, esophageal spasm goes away within a few minutes.
- If esophageal spasm occurs while eating, try drinking a non-carbonated drink at room temperature.
- Do a breathing exercise. Mentally count from 1 to 4 and inhale at this time. Hold your breath for a second and exhale the same slowly.
- Place nitroglycerin under your tongue or take a sedative (Persen). Drink chamomile, mint or lemon balm tea.
- If you don't have any medicine on hand, try sucking on a mint candy; chewing gum with an intense menthol flavor will also work.
- If the above measures do not help, then it is recommended to give an atropine injection.
Esophageal spasm is a rather unpleasant and painful phenomenon. However, in most cases it is not life-threatening. Therefore, if you experience signs of this disease, do not panic. After all, fear and anxiety are factors that can cause a second attack. Entrust the treatment of this disease to your doctor and follow his recommendations.
Secondary spasm of the esophagus during osteochondrosis is also called
vertebrogenic esophagospasm .
It occurs in thoracic and cervical osteochondrosis reflexively, due to pinching of the nerve root. All internal organs, including the esophagus and stomach, receive innervation from the spinal cord. Autonomic nerves regulate the functioning of organs, their secretion, and contractions. Symptoms of the esophagus and stomach caused by osteochondrosis are often difficult to distinguish from symptoms of other diseases. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment after examination and examination.
Moderate exercise can help reduce the symptoms of esophageal spasm. For example, it is useful to do yoga, jogging, and race walking. The main thing is not to overdo it. For more detailed recommendations, consult your doctor.
Esophageal spasms are more likely to occur in people with certain risk factors:
- Age from 60 to 80 years.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease ( GERD ).
- High blood pressure.
- Tendency to depression and increased anxiety.
- Frequent consumption of very hot or cold drinks and alcohol.
source
Changes in diet and lifestyle
If you have problems with swallowing, it is necessary to adjust the menu and add soft, easily digestible foods to the diet. It is recommended to use boiled vegetables, lean poultry or fish, and low-fat dairy products. It is necessary to exclude from the diet fatty, salty and hot dishes, fast foods that can cause irritation of the mucous membranes.

It is necessary to exclude carbonated and alcoholic drinks from the diet of patients. You should eat in small portions, several times a day in small portions. You need to swallow food after chewing thoroughly, wash down the food with one or two glasses of clean water.
After eating, it is advised to take a vertical position and ensure complete rest for the body.
Food getting stuck in the throat or dysphagia is a serious disease that can be caused by various factors. Timely treatment of chronic illnesses, proper nutrition and stability of the nervous system will help prevent the occurrence of a pathological condition.
Diagnosis and treatment
Only a comprehensive examination using an objective examination, instrumental techniques and laboratory tests will help determine which pathology symptom may be a heaviness in the throat. After making a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes appropriate therapy.
- Infections are treated with a course of antibacterial, antiviral or antifungal drugs.
- Metabolic and endocrine pathologies can be stabilized with hormonal replacement agents.
- Injuries are treated with symptomatic medications and agents that restore the functions of the mucous and muscular membranes of the throat.
- Tumors are removed or attempts are made to stop their growth using conservative methods (taking cytostatics, courses of chemotherapy).
- Nervous disorders require individual conversations and consultations with a psychologist, psychotherapist or psychiatrist and attendance at group classes and trainings.
Prevention
To get rid of unpleasant sounds in the stomach, belching, you need to normalize the regime, create the right diet, and get rid of a sedentary lifestyle.
- The most common, harmless reason is missed meal times. The body gets used to working according to the clock. If food does not arrive, the stomach begins to make characteristic sounds. To get rid of them, you need to eat something immediately.
- Large amount of water. Experts recommend drinking at least 2 liters of water daily for adults. However, with a large amount of liquid in the stomach and intestines, gurgling, squelching, and rumbling appears.
- The cause of unpleasant symptoms is carbonated drinks, alcohol, whole milk, coffee, chocolate, cakes, pastries, as well as cabbage and legumes. To get rid of rumbling, you should take activated carbon or another sorbent. In the future, try to avoid such products or minimize their consumption.
- Avoid overeating, especially before bed. The body needs a certain time to digest each product; poorly broken down food causes rumbling in the stomach and belching.
- Rushing during meals and talking contribute to the entry of air into the stomach, which must then be released. To prevent this phenomenon, you need to eat slowly, chew thoroughly, and not talk.
- Complete meals instead of snacks. Eating dry food is one of the causes of rumbling, belching, and the development of gastritis.
- Limit consumption of raw vegetables. Often the cause of rumbling in the stomach and belching is cucumber or zucchini.
The frequent occurrence of unpleasant symptoms is the basis for seeking help from specialists.
How to get rid of a lump in the throat: the best advice from doctors
In stressful situations, when suffering from a sore throat, as well as in other cases, each of us may experience a feeling of a lump in the throat. It happens that from time to time there is a feeling of “something extra” in the throat, and it becomes difficult to breathe. If this condition turns into an annoying one, then you will inevitably think about the reasons for this phenomenon, and how to effectively get rid of it.
The feeling of a lump in the throat was first documented by Hippocrates about two and a half thousand years ago.
For some time, a lump in the throat was called “globus hystericus” (hysterical globe) - the name hinted at the hysterical nature of this symptom, mostly in women.
In later years, namely in 1968, the name globus pharyngeus (literally - ball of the pharynx) was proposed due to the fact that, according to statistics, the majority of patients with this symptom do not have a hysterical personality type.
Symptoms of a lump in the throat
Patients may describe unpleasant symptoms as follows:
- a feeling of “something extra” in the throat;
- difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- fear for one’s life (fear of choking or suffocation, particularly in sleep);
- throat discomfort, soreness, soreness;
- hoarseness of voice;
- dry throat, thirst;
- desire to “swallow” a lump, cough;
- “pressing” sensation, feeling of suffocation.
Discomfort can occur under certain circumstances (severe distress, anxiety and fear, after eating, along with the appearance of heaviness in the stomach and belching, in a lying position or when tilting the head incorrectly).
The sensation of a lump in the throat can be periodic, temporary, and also an annoying reminder of itself, which can seriously disturb a person’s well-being and complicate life.
Possible reasons for the appearance
There are several causes of a lump in the throat.
The phenomenon of the so-called “hysterical lump” is quite common - a false sensation of a foreign body in the throat, intensifying in anxious and conflict situations, at the beginning of a hysterical attack.
Nervous overload and stress can provoke the development of psychosomatic diseases; a feeling of coma can be a manifestation of some kind of neurosis.
Other objective reasons for the sensation of a lump in the throat may be:
- inflammatory diseases of the throat and larynx (pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, as well as granuloma and cyst);
- pathologies of the thyroid gland (for example, nodular goiter);
- pathologies of the esophagus (impaired functions, motility);
- hypofunction of the salivary glands;
- diseases of the nasopharynx, accompanied by mucus flowing down the back wall of the pharynx (adenoiditis, chronic rhinitis, rhinosinusitis);
- consequences of a hysterical cough;
- inflammation of the cervical or submandibular lymph nodes;
- osteochondrosis, neck injuries;
- tumor formations;
- neurological pathologies (myasthenia gravis, post-stroke conditions, vagus nerve injury);
- atypical manifestation of an allergic reaction;
- adverse reactions due to long-term use of certain medications.
Diagnosis of coma in the throat
Without torturing yourself with guesses about where the lump in your throat came from, make an appointment with a doctor to determine the causes of this disorder. First of all, MirSovetov recommends seeing a therapist.
To clarify the diagnosis, various diagnostic studies may be needed:
- general urine and blood test, as well as biochemical blood test;
- ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland, if large nodes are detected - fine-needle biopsy;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- computed resonance and magnetic resonance imaging, x-ray of the cervical spine.
After examining a therapist, you may need to consult the following specialists:
Otolaryngologist (ENT): quite often the feeling of a lump in the throat is caused by chronic inflammatory diseases of the throat and nasopharynx.
In the presence of an infectious pathogen on the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, tonsils, the spread of pathological microflora to the back wall of the pharynx - in addition to traditional patient complaints of irritation, sore throat, sore throat, complaints arise about the sensation of a so-called lump.
Otolaryngologists in their practice resort to physiotherapeutic treatment to eliminate this symptom, in particular, mineral irrigation of the throat mucosa followed by restorative therapy is effective.
Sometimes a feeling of a lump in the throat, provoked by inflammatory processes in the throat and larynx, can indicate serious illness.
For example, an abscess of the epiglottis is a dangerous condition that can block breathing when allergic or inflammatory edema develops. Therefore, when diagnosing it, urgent measures are necessary.
The pathology of “curved epiglottis” is also known - due to its contact with the base of the tongue or the back wall of the pharynx, a sensation of “lump in the throat” may occur.
Endocrinologist: will examine for pathological changes in the thyroid gland, accompanied by growth or changes in its structure with squeezing in the throat. It is important to know that with a coma in the throat associated with pathological changes in the thyroid gland, swallowing disorders are usually not observed.
Gastroenterologist: if the appearance of a lump in the throat can be correlated with food intake, then it is possible that the cause lies in problems with the digestive system, impaired motility of the esophagus.
For example, with a disease such as gastroesophageal reflux, intestinal contents reflux into the esophagus, a feeling of discomfort in the stomach appears, a sour taste in the mouth, and an unpleasant lump rolls up in the throat.
Irritation of the esophagus (spicy foods, alcohol, swallowing a probe during endoscopic examination), as well as hiatal hernia, can also manifest themselves in a similar way.
Vertebrologist: if the feeling of a lump in the throat is accompanied by painful sensations when turning, moving the neck and back, or headaches, there is a need to visit this specialist. A spine specialist specializes in the treatment of diseases of the spine and will examine for disorders in the cervical region.
Neurologist: if a lump in the throat is combined with dizziness, nausea and apathy, a painful reaction to weather changes, then we may be talking about disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system. Perhaps these are manifestations of autonomic dysfunction.
Oncologist: the cause of the sensation of a lump in the throat in rare cases may be neoplasms of the pharynx, larynx, or cervical esophagus. In the early stages of detection of the disease, the prognosis is favorable.
Psychotherapist: if a symptom suddenly appears during mood swings, disappears after taking sedatives, or when getting rid of a traumatic situation, then the nature of the disorder is of an emotional nature. Sedatives and antidepressants are prescribed, and short-term therapy for neuroses and panic attacks is carried out.
Relaxation methods will be effective, including sets of exercises for the neck and shoulder girdle, phonopedic exercises to relieve vocal discomfort and relieve tension. The doctor will prescribe complex treatment with medications and (or) psychotherapeutic methods.
Thus, a lump in the throat may be due to the presence of diseases and serious pathologies in the body, as well as disorders of the psycho-emotional state.
To prevent a lump in the throat, we recommend maintaining a healthy lifestyle, timely consultation with a doctor in the presence of painful symptoms, regular health examinations and treatment of chronic diseases.
Press! Subscribe! Read only the best!
Source: https://www.obozrevatel.com/health/digest/15623-chuvstvuete-komok-v-gorle-eto-mozhet-byit-ne-ot-obidyi-a-priznakom-etih-zabolevanij.htm