Of course, not everyone scrupulously analyzes their excrement. And the design of current toilets is not conducive to such research. However, the appearance of uncharacteristic impurities and inclusions in the stool may be the first “alarm signal” indicating the emergence of serious problems in the body. Some of them are a good reason to go to the clinic and get examined.
Usually our feces are a fairly homogeneous mass. The appearance of impurities or foreign inclusions in it may be due to both the nature of the diet and the development of diseases. Any sane person should be wary of the following visible signs in fecal matter:
- blood;
- pus;
- mucus;
- food leftovers;
- foreign inclusions.
What is mucus?
Mucus is a clear or yellowish jelly-like substance that is normally mixed with stool and passed during bowel movements. It is almost impossible to notice it with the naked eye.
Normally, mucus performs a number of functions in the body in adults and children:
- envelops the intestinal walls, allowing feces to leave the body freely and painlessly;
- provides protection to the intestinal walls, because if the stool is very hard, it can lead to cracks or ruptures in the intestines, but we previously wrote how to soften the stool;
- The mucus that is in the lungs, nasopharynx or other organs in which it performs its functions comes out along with the feces.
Mucus in the stool can be of pathological or non-pathological origin. Non-pathological mucus usually has a whitish or yellowish tint, sometimes clearly white, and with pathology it can be pink, yellow, brown, black, orange, red, bloody, or simply mixed with blood in the form of clots or veins, or in the form of a thread.
This phenomenon cannot be ignored and you should immediately consult a doctor for advice and treatment. Only a specialist will determine why feces and mucus leave the intestines and how this can be corrected.
One of the main causes of constipation and diarrhea is the use of various medications.
.
To improve bowel function after taking medications, you need to drink a simple remedy
.
White mucus in stool: all possible causes
The appearance of white mucous discharge in the stool is a reason to pay close attention to your health. White mucus in stool can be caused by certain foods or an infection.
Note! If the phenomenon appears once and does not cause pain in the abdomen or discomfort, then there is no reason for special concern. But the regular presence of mucous secretions in the stool, an increase in their number, indicates problems in the digestive system.
What should a chair be like?
Feces are a waste product of the human body.
Is the presence of mucus in them normal? The human body receives various components from food, which are processed into feces in the gastrointestinal tract.
Normally it is brown in color with a characteristic odor. There is a small amount of mucus in the stool, but it is not noticeable - the discharge can only be detected in the laboratory.
A viscous consistency begins to form in parts of the large intestine. It is necessary to ensure that the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is not injured during the digestion and passage of feces.
Thick stools cause constipation.
A small amount of mucous secretions provides the necessary protection of the entire digestive system from injury to the walls of the gastrointestinal tract and the negative effects of harmful toxins.
The mucus contains glycoprotein - a kind of organic lubricant to protect the stomach and intestines. Without a small amount of mucus in the stool, a person will have difficulty bowel movements. Also, fecal mucus contains some leukocytes and epithelial cells, which prevent constipation. However, such discharge should not exceed the norm.
Important! If during bowel movements there is a white coating in the stool, you should definitely consult a doctor and undergo an examination. When white mucus appears in the stool of an adult, various pathologies and diseases can be detected.
What causes excess mucus?
The causes of the phenomenon can be very diverse - digestive problems, inflammation, damage to the gastrointestinal tract by infection. Often, increased mucus secretion is promoted by non-hazardous physiological factors, rather than pathology.
Often mucous discharge can be found in an infant. The phenomenon is due to the fact that the baby’s digestive system is not yet sufficiently developed. Viscous discharge in a child's stool appears due to a lack of certain enzymes.
The presence of white plaque on stool in this case should not cause concern.
Various physiological causes often cause increased secretion of whitish mucus in the intestines. Children are especially susceptible to the phenomenon. Non-pathogenic factors for the appearance of viscous discharge in feces include:
- With a profuse runny nose, nasal mucus flows down the back wall of the nasopharynx;
- consumption of certain foods - cottage cheese, bananas, watermelons, oatmeal;
- consumption of poor quality drinking water;
- a sharp change in the usual diet;
- prolonged fasting;
- hypothermia of organs located in the pelvis;
- swimming in ponds and pools;
- taking an antibiotic.
As can be seen from the above, the causes of stool in white mucus can also be physiological. However, stool with mucus is not always safe.
If you can see white-gray mucous streaks in the stool, then this indicates pathology in the sigmoid colon. White stools indicate pathology in the rectum.
Yellow, flaky stool indicates damage to the large intestine.
The appearance of a mucous substance in pathologies
Viscous impurities can be observed with food allergies and lactase deficiency. In such cases, it is impossible to avoid the appearance of mucous discharge along with feces.
This is facilitated by a diet containing dairy products. In such a situation, dairy products become dangerous allergens.
The same phenomenon is caused by the consumption of cereals that contain large amounts of gluten. The pathology is called celiac disease.
If mucus appears in the stool due to the above, then you should not worry too much. It is necessary to exclude dairy products and grains from the diet. You can eliminate the reasons why a viscous substance is passed through stool with the help of a strict diet. It helps to improve the digestive process in the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes of mucus in stool
A person may notice an increased amount of mucus or its color change when feeling normal or when something is bothering him. He may also note that after the enema, stool and mucus are released, which either floats on the surface or is mixed with the stool.
If a person consumes large quantities of fermented milk products, oatmeal, or, conversely, starves for a long time or does not receive protein foods, then mucus may appear in the stool. This is not a pathological process and there is nothing to worry about. It is enough to change your diet and everything will return to normal.
But if there are no problems in nutrition, then this indicates the development of a fungal, infectious or viral disease of the body, and not just the gastrointestinal tract.
Such diseases include:
- diverticulitis, when the intestinal lining bulges inward;
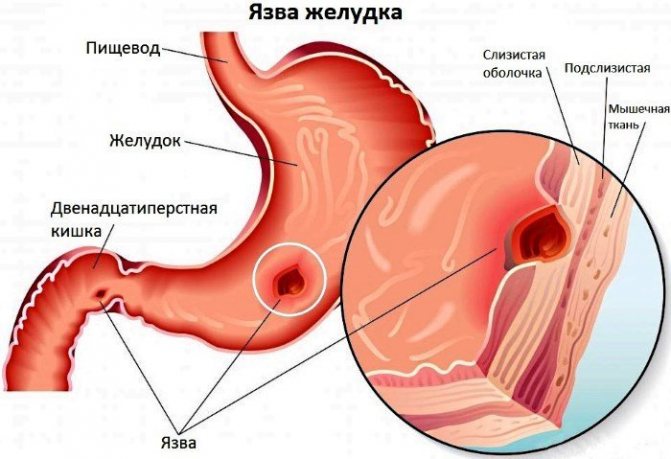
- ulcer of the stomach, duodenum or any part of the intestine (small, colon or rectum);
- tumor neoplasms of the intestine, the appearance of polyps;
- cracks in the rectum, hemorrhoids;
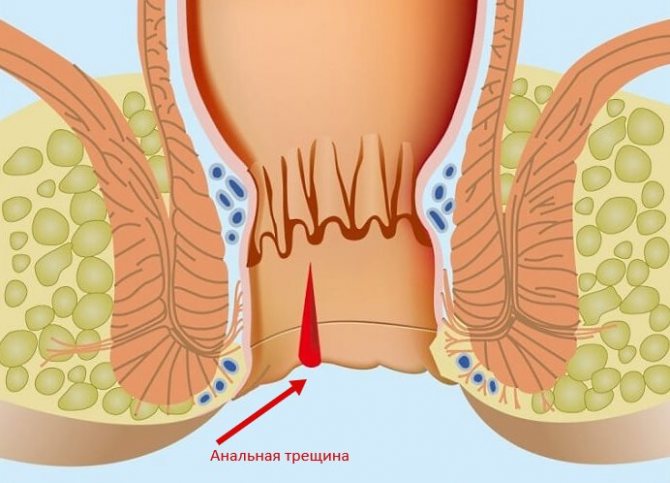
- dysbiosis, when the normal intestinal microflora is destroyed, food is not completely digested and irritates the mucous layer, causing mucus to come out along with feces;
- intestinal obstruction, which occurs for various reasons: constipation, the formation of adhesions or cracks, all this can provoke the disease;
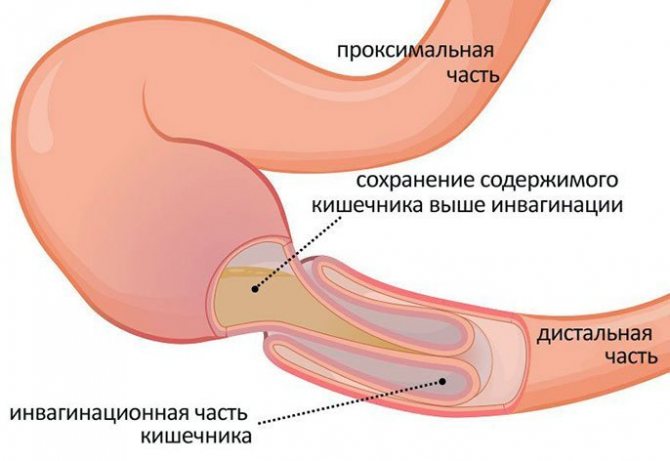
One type of intestinal obstruction - Irritable bowel syndrome is a specific condition that affects the entire intestinal tract. Frequent spasms and weak secretion of enzymes cause a violent reaction in the body, causing feces to be released with mucus or even blood;
- rectal cancer;
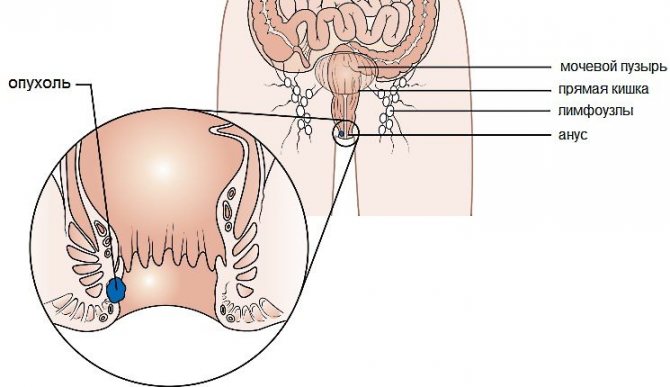
- intolerance of the body to any food products;
- acute respiratory infections, there is no pathology as such, because the mucus that comes out is the one that is swallowed by a person from the nasopharynx and, when the runny nose is cured, then the mucus from the feces will also disappear;
- infectious diseases caused by salmonella, shigella or other bacteria;
- fungal infection of the body;
- insufficient production of enzymes by the gastrointestinal tract.
Gastrointestinal enzymes
What causes the appearance of white mucus in stool - features of the condition and methods of control
Humaira Almeera
Normal stool should not contain any impurities and be brown in color. But any problem with the digestive system is manifested by a change in the color and consistency of feces. There are situations when white mucus appears in the stool.
These impurities are leukocytes and epithelium. The reasons for its appearance in excrement can be very diverse. And sometimes they can be completely harmless, and sometimes they are a signal of acute alarm that pathological disorders are occurring in the body.
This unusual condition is typical for both children and adults, so everyone should know what this could mean and be able to react correctly to all these cases. Don’t be shy about looking into your baby’s potty or toilet, sometimes it can save a life.
Mucus in stool, as normal
There are cases when white mucus in the stool of an adult and a child does not have serious consequences.
These reasons are described in a small list:
- Colds, accompanied by a profuse runny nose, can provoke mucus from the upper respiratory tract into the stomach, where it cannot be completely digested, and in children it is not processed at all. In this case, the mucous impurity in the feces is a simple runny nose.
- Excessive consumption of watermelons, bananas, cottage cheese and oatmeal also often causes a similar phenomenon. The reasons for this are the high fiber content.
- Children can often poop with mucus due to the immaturity of the digestive tract; this is also considered normal.
Feces in white mucus or with its additions are considered normal in all these cases, so there is no need to worry about this. The reasons for this condition are in the specifics of processing mucus, which is produced in other parts of the body. Gastric juice cannot break down its dense structure.
What pathologies can this phenomenon indicate?
Feces with a white coating or mucus particles may also be evidence of diseases of the internal organs.
The reasons may lie in the following ailments:
- Membranous colitis, which is accompanied by mucus in the form of ribbon formations or clots.
- The presence of hemorrhoids or polyps in the intestines. In this case, the mucous mixture does not mix with feces, since it is a consequence of damage to the integrity of the intestinal walls.
- With the development of irritable bowel syndrome, the body also malfunctions during the digestion of foods, and mucus, which serves as a lubricant, comes out separately from the feces. It may even cause difficulty in bowel movements.
- Most intestinal infections also cause white mucus in the feces as the immune system is triggered.
- Dysbacteriosis can also cause a jelly-like addition to excrement.
- Diverticulitis provokes the appearance of mucous impurities, which often also contain blood.
- Cystic fibrosis is a congenital disease that often manifests itself from the first months of a baby’s life. It manifests itself in that it affects all systems that are responsible for the production of mucus, so the child develops a number of side disorders of all organs.
- Thick accumulations of mucus in or on the stool may indicate that a person is developing a tumor in the intestines. It can be benign or malignant in nature, and is often accompanied by blood in the feces. In these cases, particles similar to pieces of jelly are passed along with the feces, which indicates a malfunction of the digestive system.
These diseases require serious treatment and can seriously affect the functioning of all organs if you do not pay attention to them in time. It is especially important to pay attention to this phenomenon if you notice similar impurities in your child’s stool. Therapy can vary significantly in different cases, so you should not self-medicate.
Also, a white coating on stool or mucous impurities may indicate the following:
- Damage by parasites.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Disturbance of microflora.4
- The effect of bad habits such as alcohol or smoking in excessive quantities.
These cases also require the intervention of doctors, since they gradually disable the digestive system and cause targeted attacks on the organs.
How to behave when mucus appears
If mucus appears in or near the stool, then you immediately need to correctly assess the overall situation. If there are no additional symptoms, then you should wait a few days, and perhaps everything will pass. And if you have a cold, then you need to wait until complete recovery, since the mucus will be eliminated even longer than the illness will go away.
If there are reasons for concern in the form of additional symptoms, then you should consult a doctor. And in order to find out the essence of the problem, you need to go through a series of diagnostic procedures. Until the cause is established, you need to drink as much water as possible and reduce your diet.
Do not drink tea, coffee, sweet drinks, etc. You can take absorbents. Nothing else can be done without consulting a doctor. Many of these ailments are treatable, but you need to seek help in time and not create panic. Modern specialists can solve many problems.
You may also be interested in
Source: https://prosimptom.ru/az/belaya-sliz-v-kale.html
Symptoms of the disease
Usually people detect mucus in their stool not by chance, but in cases where something bothers them. That is, a large amount of mucus is one of the symptoms that signal the development of the disease.
In addition, patients usually feel:
Blood in stool
- severe abdominal pain, cramps;
- bloating and excessive gas formation;
- abdominal tightness, constipation or diarrhea;
- in severe cases, vomiting or other signs of intoxication;
- pain during defecation;
- blood or pus in the stool, possibly undigested food debris;
- change in the shape and consistency of feces, its nonspecific smell;
- mucus or bloody substance may remain on the patient's toilet paper or underwear;
- for respiratory diseases, characteristic symptoms of cough, nasal congestion, rhinitis and more;
- headaches and fatigue.
What it is and how to treat it can only be told by a competent specialist, and there is no need to self-medicate.
One of the main causes of constipation or diarrhea is poor diet.
.
Therefore, to improve bowel function, you need to drink a simple drink
.
Diagnostics
Mucus in the stool of an adult is sometimes the first sign of a serious disease of the human body, and most often specifically of the gastrointestinal tract. To recognize it in the early stages, you need to consult a therapist. He will study your symptoms, the presence of not only mucus, but also other signs of the disease, find out the frequency of stool and its nature, and refer you to a specialized specialist (gastroenterologist, proctologist, oncologist). The specialist doctor will definitely prescribe a number of tests and examine the patient.
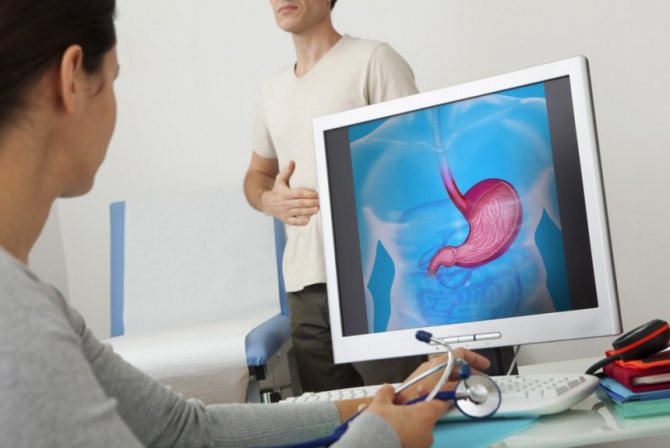
Studies to determine the causes of mucus in the stool include:
- collection of feces for coprogram;
- analysis for eggworms and protozoa;
- more specific tests for helminthic infestations (opisthorchiasis, strongyloidiasis, amebiasis, fasciliasis) as prescribed by a doctor;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (including the intestines);
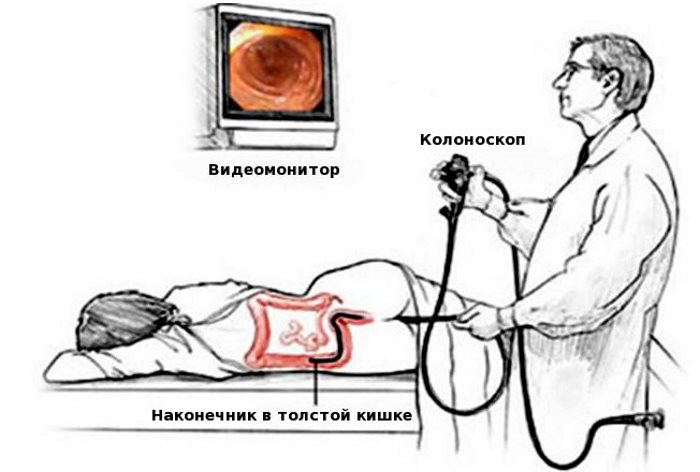
- sigmoidoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- anoscopy;
- endoscopy;
- computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
- blood test for the presence of viral diseases;
- Additionally, you can take biochemical blood tests, as well as a general clinical blood test.
After studying the results of the examinations, the doctor will diagnose the patient and prescribe appropriate treatment, which will be selected individually for the given case, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Accurate diagnosis of the disease
To draw up a detailed clinical picture, the doctor examines the patient and inquires about his diet and diet. After this, a number of events are planned:
- Analysis of stool to identify pathogenic microorganisms in it.
To choose adequate treatment with antibiotics, you need to know exactly the type of causative agent of the disease. - Studying mucus in laboratory conditions.
A clinical and biochemical study is carried out to identify the level of leukocytes, indicating a progressive inflammatory process. The presence of red blood cells is also assessed. - If damage to the stomach
or duodenum is suspected, FGDS is prescribed. An ultrasound is performed to examine the abdominal organs. The list can be supplemented with an X-ray examination using contrast - a barium mixture. - Study of the intestinal lumen through rectoscopy.
This technique is indicated for suspected polyposis, neoplasms or hemorrhoids.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on the diagnosis made by the doctor. But even if an infection, helminthic infestation or cancer is detected, treatment should be comprehensive and include:
- Drug treatment.
- Compliance with diet and proper nutrition.
- Maintaining a daily routine.
If worms are detected in a patient, tablets are prescribed to eliminate parasites; for fungal infections, it is more appropriate to use antibiotics or antifungal suppositories. When the cause of mucus in the stool is a viral infection, a complex of antiviral drugs is prescribed, as well as symptomatic treatment.
For pancreatitis, medications are prescribed to normalize the functioning of the pancreas. If a patient is diagnosed with cancer or other neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed.
An important stage of not only recovery, but prevention is maintaining proper nutrition and daily routine. Products such as rolled oats or cottage cheese cause excessive formation of white, dense mucus, but bananas or persimmons will better bind it to a normal state.
So before treating a symptom, consult a doctor. Perhaps in your case there is no reason to worry, but unjustified use of medications can only do harm.
Lack of fluid in the diet is one of the main causes of constipation. To get rid of it in 3 days, you need to drink a simple remedy every day.
Why mucus may appear in the intestines, video:
What do muscle fibers with and without striations mean in feces?
In medical terms, stool analysis is called a coprogram.
This study is necessary and important at the same time, since it allows you to assess the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, identify parasitic diseases and detect problems not related to the functioning of the digestive system. Solid stool may contain various inclusions. Some of them are normal, others are pathological, abnormal. Sometimes you may notice the presence of muscle fibers in the stool.
Their appearance is due to various factors that must be determined by the doctor. Such inclusions can be striated or unstriated.
And it is taking into account the type of muscle fibers that a diagnosis will be made and the necessary therapy will be prescribed.
Types of muscle fibers
What are muscle fibers in adult feces? Such inclusions are detected during laboratory examination of solid feces. Muscle fibers are particles of protein products that have been incompletely digested by the intestines. Normally, such impurities should not exist. However, their appearance also does not always indicate the presence of a serious pathology.
The medical term for undigested muscle fibers in stool is creatorrhea. There are several types of such deviation:
- Unchanged fiber shape. We are talking about completely undigested particles of protein food. Under a microscope, they look like long cylinders with sharp corners and transverse, clear stripes.
- Little modified form. It is characterized by the presence of white fibers in the feces, which are partially digested. In their shape, if you look at them under a microscope, they resemble squares or rectangles. Their corners are rounded and less clear than in the previous case.
- Changed form. The muscle fibers in the coprogram are completely digested and look like a shapeless whitish lump with a smooth surface and a round shape.
Thus, creatorrhea is the presence of undigested muscle fibers in the feces. In a healthy person they are unstriated. That is, when speaking about the norm, we mean the appearance of such impurities for physiological, not pathological reasons.
Unstriated muscle fibers
The appearance of muscle fibers without striations in excrement is a relative norm. That is, the reasons for such a deviation are often physiological, not related to the presence of diseases.
Why do muscle fibers appear without striations in feces? To understand this, you need to know the basics of the digestion process.
Food that enters the gastrointestinal tract is susceptible to the action of enzymes, hydrochloric acid and bile. In healthy people, protein fibers are neutralized precisely under the influence of all of these substances.
The end products of protein breakdown are uric acid, water and ammonia. But sometimes, fibrous feces can still occur.
If we talk about the physiological reasons for this phenomenon, they often lie in:
- Poor cooking of protein foods, especially meat. Such food is difficult to digest, so after eating it, especially in large quantities, digested muscle fibers may appear in the feces.
- Insufficient chewing of food. Many people have the habit of eating at a gallop, that is, very quickly. This is a very bad addiction. First, eating at an increased pace puts greater stress on the digestive tract. Secondly, often against this background a deviation occurs, which is popularly called “gastric arrest.” Even if it works normally, it is unable to completely digest all the meat eaten. The consequence of this is the appearance of muscle fibers in the coprogram.
- Overeating. If a person systematically overeats, his stomach, as in the previous case, cannot cope with the load. This is especially noticeable when eating a variety of foods at one time.
These are the most harmless reasons for the appearance of muscle tissue in stool without signs of striation. But if we are talking about striated CF, then we will be talking about extremely serious and dangerous pathologies.
Causes of striated muscle fibers in stool
Muscle fibers with striations in the stool are an extremely alarming sign. Such a deviation indicates serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, and requires a mandatory and comprehensive examination of the patient.
The reasons for the appearance of striated muscle fibers in the feces of an adult may be as follows.
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the stomach. Develops due to impaired production of hydrochloric acid. And if a stool analysis shows the presence of muscle fibers with striations with the presence of transverse lines, then this indicates achylia.
Ahilia is the absence of hydrochloric acid or enzymes in gastric juice.
Pancreatitis
Muscle fibers with striations appear in feces and with inflammation of the pancreas - pancreatitis. The reason for the appearance of such impurities is enzymatic deficiency.
In other words, the diseased organ begins to secrete fewer enzymes necessary to maintain and organize the digestive process. As a result, the secondary processing of proteins occurs with malfunctions, and there is no talk of its usefulness at all.
As a result, amino acids are not absorbed into the blood, but leave the body with feces.
The fact that connective tissue is present in the stool of an adult is evidenced by fragments that look like longitudinal lines.
On a note. The appearance of such structures in feces may be due not only to a deficiency of pancreatic enzymes. When the intestines begin to produce reduced concentrations of enzymatic elements, undigested muscle fibers may also appear in the feces of an adult. That is why such a deviation requires a thorough and comprehensive diagnosis.
Putrid dyspepsia
Such a deviation is spoken of when proteins do not undergo the process of complete absorption in the intestine. As a result, they enter the large intestine almost in their original form, and begin to rot there. Therefore, after defecation, the patient may notice stool with white fibers.
Often, such a deviation leads to the development of an inflammatory process in the large intestine, and then to secondary infection.
Pancreatic tumors
Pancreatic cancer is the most dangerous cause of creatorrhoea. With this disease, the appearance of red fibers in the stool can be noted. This color may indicate the presence of blood, which in itself is an extremely alarming and dangerous sign.
Creatorhea – dangerous or harmless?
Physiological creatorrhea is not considered life-threatening, but it can be harmful to health. More precisely, not she herself, but those factors that provoke her.
Overeating, eating food quickly or not chewing it completely are mistakes that many make. At the same time, a person does not even think about the damage he can cause to his health.
As a result of such actions, digestive disorders occur, and against this background, a number of gastrointestinal pathologies can already develop.
As for creatorrhoea with the release of striated protein fibers, its danger is greater, and the complications can be the most severe. So, such a deviation is fraught with:
- Acute appendicitis. It develops against the background of a long-term lack of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
- Stomach ulcer. Its causes lie not only in the lack of hydrochloric acid, but also in the enzymes necessary to ensure a normal digestive process. With this disease, gastric bleeding often occurs in places where ulcerative lesions are located. It is often impossible to recognize their presence on your own, so over time they lead to other consequences - anemia, perforation of the gastric or intestinal wall, blood poisoning, etc.
- Chronic intestinal inflammation. This is also a rather serious consequence of untreated diseases accompanied by creative rheumatoid arthritis. And peritonitis developing against this background can lead to death.
- Tumors. A sluggish but stable inflammatory process in the intestinal walls can cause the formation of tumors. They can be either benign or malignant. However, the first ones (polyps, adenomas) are not so harmless and can seriously harm the patient’s health.
In some cases, the test results may be false. This occurs in a situation where the patient does not follow a protein-free diet before submitting stool for examination. In such circumstances, the test is repeated after a few days or weeks.
Finally, let’s say a few words about why muscle fibers can be found in a child’s stool. If the test was carried out with the feces of a baby, then there is nothing to worry about the appearance of such impurities.
The baby's digestive system has not yet developed properly, so a protein fragment may be present in the stool.
Over time, when the process of food digestion improves, such inclusions will disappear.
However, in older children who already eat the same food that adults eat, such a deviation should not go unnoticed. If it is not associated with excessively frequent eating of meat or cereals containing protein, a more thorough examination is required. The sooner the cause of such a disorder is discovered, the lower the risk of developing serious and dangerous complications.
Source: https://vseproanalizy.ru/myshechnye-volokna-v-kale.html
What could this mean?
During a medical diagnosis or examination, the color, texture, and appearance of stool can reveal a lot about a person's health. If you have white spots in your stool, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
The color and characteristics of the stool may change each time for various reasons. Some of them are not serious, while others are in need of mandatory treatment. What you eat undoubtedly has a big impact on the color and texture of your stool. In addition, the health of the body can influence many of its characteristics.
It is recommended that a professional help determine the underlying cause of this problem. If the inclusions appear once and then disappear, there is probably no cause for concern. However, when they continue to appear, it may be a sign of something serious that requires immediate medical attention.

In humans, most often light or white spots in the stool are particles of food undigested by the body, which can be caused by disruption of the biliary system, certain diseases, food intolerance and other reasons.
Impurities in stool: 5 signs that should alert you
Of course, not everyone scrupulously analyzes their excrement. And the design of current toilets is not conducive to such research.
However, the appearance of uncharacteristic impurities and inclusions in the stool may be the first “alarm signal” indicating the emergence of serious problems in the body.
Some of them are a good reason to go to the clinic and get examined.
Usually our feces are a fairly homogeneous mass. The appearance of impurities or foreign inclusions in it may be due to both the nature of the diet and the development of diseases. Any sane person should be wary of the following visible signs in fecal matter:
- blood;
- pus;
- mucus;
- food leftovers;
- foreign inclusions.
Blood
Finding blood in feces is always a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention. It can be a manifestation (often the first):
- colon cancer;
- inflammatory autoimmune bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease);
- large benign neoplasms (for example, polyps);
- pathologies of the rectum and anus (fissures, ulcers, hemorrhoids, proctitis, etc.)
- ischemic colitis (caused by pathology of the vessels feeding the intestines);
- intestinal angiodysplasia;
- blood coagulation pathology;
- infectious damage to the intestine (for example, dysentery, amoebiasis, intestinal tuberculosis, etc.);
- drug damage to the intestine (due to taking antipyretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.);
- helminthic diseases (ascariasis, trichocephalosis, etc.).
The amount of blood can vary: from barely noticeable streaks to several glasses. Sometimes, instead of stool, when the patient has a bowel movement, only blood or blood with mucus comes out. The color of the blood reflects the location of the source of blood loss.
Scarlet fresh blood is characteristic of a “low” location (anus, rectum, sigmoid colon or descending colon). Often it is located on top of the feces.
Dark blood (especially if mixed with fecal matter) or blood clots indicate a “high” localization, that is, the pathological process is in the right side of the colon or small intestine.
Pus
An admixture of greenish or yellowish pus in excrement is always a sign of a serious inflammatory process. It appears when:
- infectious colitis;
- proctitis;
- autoimmune inflammatory processes in the colon (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's colitis);
- diverticulitis;
- breakthrough of abscesses into the intestine;
- disintegration of a malignant tumor (this happens in advanced stages of the disease).
Therefore, pus in the stool is also considered an alarming signal. Self-medication for these diseases is ineffective and can result in dire consequences.
Slime
A healthy intestine always contains cells that produce mucus. It is necessary for the timely passage of feces through the intestines. Therefore, a small amount of clear mucus in feces can be found normally.
In addition, small specks or lumps of mucus are common in the stool of breastfed infants. They are associated with excessive fat content in mother's milk, which the still weak digestive enzymes of the child's body are not able to cope with.
However, a large amount of mucus and its yellowish or brownish color are often manifestations of:
- increased intestinal motility;
- infectious diseases (salmonellosis, typhoid fever, dysentery, etc.);
- inflammatory processes in the intestines of non-infectious origin (diverticulitis, etc.);
- helminthic diseases;
- neoplasms;
- cystic fibrosis.
In addition, mucus can be a companion to constipation and a harbinger of exacerbation of chronic autoimmune intestinal diseases (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis).
Leftover food
Some types of food cannot be completely digested, so the presence of seeds, poppy seeds, bones, fragments of dense peel, veins and cartilage of meat, and fish bones should not be a cause for concern. Digestive enzymes are not able to cope with such coarse fiber and connective tissue.
You should be wary if there are traces of meat, eggs, cottage cheese, or fat in the stool. Their presence reflects a severe deficiency in the formation of enzymes necessary for digestion. This happens when:
- widespread and severe atrophy of the gastric mucosa;
- inhibition of the production of pancreatic juice (a consequence of pancreatitis or removal of part of the pancreas);
- intestinal enzyme deficiency.
Also, food residues in feces are observed with accelerated intestinal motility (irritable bowel syndrome).
Foreign inclusions
Sometimes, when examining feces, you can see round or oblong white or light yellow dense inclusions in them. These can be fragments of worms (tapeworms) or the worms themselves (pinworms, whipworms, roundworms, etc.).
It is highly advisable to collect such stool with all foreign bodies and take it to the laboratory of an infectious disease clinic.
After all, the treatment of helminthic diseases largely depends not only on the very fact of presence, but also on the type of worms found.
Films in the stool can appear with serious damage to the intestine: pseudomembranous colitis associated with antibiotic treatment. Sometimes suspicious patients mistake dense lumps of mucus for films or worms. In addition, in some cases, excrement may contain remains of drug shells (usually granular) or the drugs themselves (for example, grains of activated carbon).
Thus, the appearance of certain impurities in fecal matter should alert patients. Most of these inclusions require a comprehensive examination and active medical action.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have impurities in your stool, contact your gastroenterologist. If this is not possible, the primary diagnosis will be carried out by a general practitioner or family doctor. After clarifying the diagnosis, the patient may be scheduled for an examination by a proctologist, oncologist, surgeon, hematologist, or infectious disease specialist. For diagnosis, the qualifications of the endoscopist and the equipment he uses are very important.
Prepared based on the article: https://myfamilydoctor.ru/primesi-v-stule/
Causes
Doctors can use stool tests to gain information about the immune system, stress levels, how hydrated the body is, and whether it is getting the nutrients it needs.
It is believed that stool is ¾ water, with the remainder being a combination of fiber, bacteria, mucus and other body cells. Doctors add that their color is no less important than their shape and texture.
The color of healthy stool varies from light brown to sometimes green, depending on what is eaten.
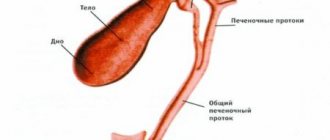
Bile deficiency
In a healthy person, the color of the stool is usually brown, this is because it contains bile juice produced in the liver, which helps in the digestion of fat. A problem with the liver that affects the efficient production of bile can cause some changes in its color.
Bile deficiency can be caused by diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatitis. In other cases, it may be caused by a problem with the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Hepatitis
This is a disease characterized by inflammation of the liver. Some people have no symptoms, while others have the following:
- Changing skin color to yellow
- Poor appetite
- Vomit
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea.
Inflammation of the liver tissue can affect the production of bile, which is important for digestion, which in turn can cause white spots in the stool as evidence of undigested food.
Cirrhosis
It is a chronic liver disease characterized by cell degeneration, inflammation and fibrous thickening. It is common in people who drink frequently and heavily and have hepatitis, as cirrhosis of the liver can also affect the production of bile, which is necessary for digestion.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder, the main function of which is to store and concentrate bile. The gallbladder also carries waste from the liver to the duodenum.
Gallstones
A gallstone is a small, hard, crystalline mass formed in the gallbladder (bile duct) from the bile pigment cholesterol or calcium salt. It causes severe pain and can block the bile duct, which affects the proper digestion of fat.
The gallbladder is associated with the removal of bile from the liver through the duct. The stone can block it, causing a lack of bile in the digestive system, which then shows up as white spots in the stool.
Pancreatitis
This is an inflammation or infection of the pancreas, which produces certain enzymes that work with others to digest and process sugar.
Inflammation or infection of this organ can prevent the digestive system from working efficiently.
Biliary atresia
Bireal atresia is a liver dysfunction that causes a deficiency of bile when digesting fat. Biliary atresia is a birth defect that causes a blockage in one of the ducts connecting the liver to the gallbladder.
Use of certain medications
It is not uncommon to notice inclusions in the stool after using certain medications. One of them is an antacid, which contains aluminum hydroxide, which affects the color of stool.
In rare cases, white specks may be particles from certain antibiotics. It is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible in such cases.
Celiac disease
Celiac disease causes the small intestine to lose its ability to digest certain nutrients, particularly gluten. It is an autoimmune systemic disorder that occurs when the immune system attacks the cells of the small intestine. If a person suffers from this condition, undigested food may appear in the stool as white specks.
Candida yeast infection
White spots can also be a sign of a yeast infection (Candida albicans). A weak immune system or a course of antibiotics can lead to thrush, which can be confirmed by the presence of grains in the stool.
A candida yeast infection can also cause increased sugar cravings, itching around the anus, in the vagina, and other symptoms.
Treatment may include strengthening the immune system by eliminating sugar, alcohol and refined carbohydrates. You should increase your consumption of organic vegetables such as carrots, spinach, asparagus, etc.
Parasitic infection
Parasitic infection is a common cause of abnormally colored stool. During reproduction, tapeworms shed several body segments each day containing eggs, which may appear as white spots in the stool. They resemble fly larvae and may move around in the stool for some time.
In cases of parasitic infection, other symptoms may be observed, such as:
- Nutrient deficiency
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Other digestive problems
- Bloating
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting and nausea.
Lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance means that the body cannot digest this type of sugar found in milk and other dairy products. If a person suffers from this problem, then one may notice white marks after consuming foods such as milk, butter, cheese.
Mucusy stool
Mucus in the stool can cause it to appear white or have white flecks. Typically, the lining of the intestines or digestive system may produce mucus due to allergies, infection, or inflammation. During bowel movements, too much of it can cause stools to appear whitish.
What are the causes of white stool?
Why is white stool in an adult?
The reasons can only be identified by a doctor after diagnostic procedures. The appearance of this shade may be associated with diseases of the abdominal organs or the consumption of certain foods.
One thing is certain, a visit to the doctor is mandatory, since white feces can be caused by serious diseases that require immediate treatment.
Causes of white stool
Before starting treatment, it is important to find out why a person’s stool became light-colored and what disease caused this symptom.
Normal, brown feces in humans are associated with the liver's production of bilirubin, which is a component of bile.
And if pathological processes have begun in the gallbladder or liver, people experience white poop. This is not the norm. Therefore, when the stool has changed color, you need to visit a doctor. Also, the causes of colorless stool can be:
- taking antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs;
- if you constantly eat only fatty foods, unlimited amounts of butter or sour cream;
- in adults, light-colored stool occurs if the required amount of bile does not enter the duodenum;
- a shade of white is associated with the presence of gastritis in a person;
- with alcohol abuse;
- after poisoning with chemicals;
- if the stool becomes light-colored, there is a high probability of hepatitis;
- The color of stool changes with cholecystitis. In this case, the patient feels pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea;
- white stool may indicate stones or sand in the gall bladder;
- with pancreatitis;
- if Crohn's disease is diagnosed;
- if there are oncological formations. Often, the development of malignant tumors can occur for a long time without symptoms. And only congestion in the organs, due to which the fecal matter becomes light yellow, indicates serious diseases.
- dysbacteriosis affects the color of stool;
- bending of the gallbladder;
- blockage of the biliary tract.
Symptoms
Having determined what may cause light-colored stools, it is important to know the accompanying symptoms that indicate certain signs of the disease.
White, beige, or discolored stool causes the following general symptoms:
- elevated temperature;
- digestive disorders;
- pain in the abdomen, which is most often observed in the right side;
- yellowing of the whites of the eyes or skin;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea or vomiting;
- general malaise;
- weakness;
- the shade of urine becomes dark;
- Liquid stool may be observed. Diarrhea may continue for a long time;
- mucus inclusions in stool or white spots;
- weight loss;
- flatulence;
- brown feces with white spots indicate the presence of parasites in the body;
- pain in the left side;
- intolerance to many foods;
- lumps or fibrous tissue in feces;
- repulsive odor of discharge;
- muscle pain;
- strong heartbeat;
- increased thirst;
- bleeding gums.
White-yellow feces
The first sign of a malfunction in the gastrointestinal tract is a symptom when the feces lighten and become white-yellow.
There is no pain or discomfort.
This pathology does not pose a health hazard. Most often this is due to the consumption of poor quality food or the abuse of fatty foods.
It is enough to switch to dietary nutrition, and the color of feces will normalize.
If there are no changes after the diet, it is recommended to visit a doctor.
Perhaps the cause of this phenomenon was the use of a certain group of medications, especially contraceptives and antibiotics.
White mucus in stool
If a person has light beige or sand-colored feces interspersed with mucus, they most often speak of dietary errors. Very often, the appearance of mucus is associated with the consumption of large amounts of fermented milk products, bananas, melon or watermelon. If there is a lot of mucus, the patient is diagnosed with an increase in pathogenic microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract.
Yellow-pale feces with mucous patches may also indicate:
- for food poisoning;
- for the presence of polyps in the intestines;
- for irritable bowel syndrome;
- if a person is allergic to certain types of food;
- for the presence of malignant formations in the gastrointestinal tract;
- The appearance of mucus may indicate diverticulitis or mucoviscytosis.
Diarrhea
Light brown or yellow diarrhea may appear if a person has consumed large amounts of milk and fermented milk products.
It is enough to change your diet and take medications prescribed by your doctor so that the stool is restored and acquires a normal, brown tint.
Acholic feces in pregnant women
Women often experience acholic stool during this period. Pregnant women who encounter this phenomenon panic and do not know what to do.
First of all, you need to see a doctor.
While carrying a child, all organs begin to work with double the load. Therefore, pregnant women may often experience disruptions in the digestive system.
Also, the appearance of acholic feces can be caused by dysbiosis or abuse of multivitamin preparations.
Diagnosis of white stools
The doctor decides how to treat the patient only after conducting diagnostic procedures.
It is important to rule out serious pathological diseases of the digestive system or select a course of medications that will restore their functioning.
If the problem of light or white stool is due to the presence of stones in the gallbladder, the gallbladder is removed. This is especially true for elderly patients. To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the following procedures:
- to exclude chronic diseases and infections, the patient undergoes a general stool test;
- perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- the patient undergoes a biochemistry test.
Treatment
If a person’s stool has lightened or become discolored for the first time, and the patient does not experience pain or discomfort, we can talk about eating fatty foods.
Quite often, after strong alcoholic drinks and beer, a pale tint of feces can also be observed.
As soon as the body self-cleanses from alcohol poisoning, uncolored feces will acquire its normal shade.
If diarrhea is not associated with poisoning, the patient is prescribed such drugs
, like Stopdiar or Smectu.
The patient should also follow the following recommendations:
- follow a diet during treatment;
- maintain bed rest;
- drink plenty of liquid or mineral water;
- exclude fatty, fried or spicy foods.
If the appearance of light brown or whitish stool is associated with infection and the presence of pathogenic microflora, a course of antibacterial drugs is prescribed:
- Claforan;
- Cefotaxime;
- Doxycycline;
- Monomycin;
- Gentamicin.
When diagnosing cholecystitis
No-Shpa or Spazmolgon are prescribed for spasms. Taking choleretic drugs is also important:
- Holosas;
- Chophytol;
- Allohol;
- Holenzim.
For dysbacteriosis
The following drugs are indicated for the patient:
- Linux;
- Bifidumbacterin;
- Hilak-Forte.
Diet for white stools
Diet is of great importance in the treatment of white feces.
It is important to exclude the following foods from your diet:
- fatty, salty, spicy foods;
- preservatives and marinades;
- mushrooms;
- chocolate.
– 3 chair colors
If the stool has become light-colored, it is important to visit a doctor first.
He will prescribe effective drug therapy. It is also recommended to introduce fractional meals. The last meal should be 3 hours before bedtime. It is advisable to grind and steam the products.
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/netgastritu/kakovy-prichiny-poiavleniia-belogo-kala-5a84891648c85e611de5517f
White spots in the stool of children
Typically, children have different types of stool. Most of them are caused by food and are completely normal. But according to a Mayo Clinic gastroenterologist, white or speckled stool is something that needs to be investigated as soon as possible.
As in adults, the problem can be caused by impaired bile secretion. This may be caused by the liver not being able to produce enough of it or by blocking the pathways leading to the small intestine.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, if a baby is breastfed, taking antibiotics, antifungals, or antacids may cause the baby to have white stools.
Candidiasis
Candida fungus is a common cause of yeast infections. In humans, it is considered a natural fungus that helps the body digest food and absorb nutrients. For those with a weak immune system, white spots in the stool are quite common. This may be a sign of overgrowth of this fungus, in such cases the spots are clusters of it. This disease is known as candidiasis or thrush.
Candida often leads to symptoms such as fatigue, skin problems, and confusion among others.
The "good" bacteria in the body help keep yeast under control. High consumption of sugar, carbohydrates and antibiotics can reduce the number of these bacteria, causing the fungus to get out of control. Other causes of candida overgrowth include emotional stress, high alcohol consumption, and oral contraceptives.
This may manifest itself in the following symptoms:
- Fungal infection on the skin and nails
- Seasonal allergies
- Outbreak of autoimmune disorders
- Fatigue
- Bloating, constipation, or diarrhea
- Anxiety and mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating or brain fog.
There are some simple tests that can be used to determine the level of this fungus in the body. The main ones include a general analysis of blood, stool and urine. The doctor will then be able to prescribe the best treatment for the problem.
Treatment for candida is aimed at stopping the overgrowth of yeast and restoring friendly bacteria. In some cases, therapy will also include treatment of the intestines to stop the infection from entering the bloodstream.
What forms white streaks in stool?
Very often, adults have white streaks in their stool. This is caused by inflammation in the intestines, and in its most diverse parts. Foci of inflammation can be provoked by both infectious microflora and candidiasis, which is usually combined with intestinal dysbiosis. The most likely reason for the appearance of not only streaks and white grains in the stool, but also mucus is dysbacteriosis and candidiasis. A fungus of the genus Candida forms a cheesy coating on the surface of the intestinal mucous wall, which gradually becomes mixed with the movement of feces. Treatment must be carried out by a gastroenterologist under constant monitoring of the composition of the intestinal microflora.
Externally, black dots in feces can look like small inclusions, grains, grains or grains of sand, and even thin threads. If they have clear boundaries, then these are most likely partially or completely undigested food remains. For example, stool may contain black kiwi or poppy seeds, parts of grape seeds, and so on. In addition, inclusions may appear in response to the use of certain medications.
Paying attention to your body is the key to a healthy life.
So let's take a closer look at why a person may develop blackheads.
Constipation and white spots
Constipation occurs when a person has heavy or infrequent bowel movements. Stool or digestive waste moves too slowly through the digestive tract. The problem can also often be accompanied by dry and hard stools, which become so due to their slow movement.
Constipation can be caused by a blockage in the colon or rectum, a problem with the nerves around the anus, or other conditions that affect hormones in the body. Other causes include colon cancer, eating disorders, irritable bowel syndrome, overuse of laxatives and emotional stress.
Chronic constipation may present with the following symptoms:
- Having fewer than three bowel movements per week
- Hard, dry, and lumpy stool
- Excessive straining during bowel movements
- Painful or swollen belly
- Vomit.
If you are constipated, do the following:
- Drink plenty of water and fruit juice to keep your body hydrated
- Increase the amount of fiber you consume
- Laxatives can be used to soften stool
- Call a doctor if constipation, abdominal pain, or cramping suddenly occurs.
White grains in feces
Often, white specks in the form of grains can simply be undigested food. This is especially true after eating fruits and grains. If this occurs once or twice, then you can attribute them to undigested food, however, if they continue to appear or are accompanied by other symptoms, then you need to see a doctor for examination as soon as possible.
Parasites and worms, such as tapeworms, may also appear as white specks in the stool. A parasitic infection can lead to nutritional deficiencies and abdominal pain.
Yellow dense lumps in stool. Therefore, a visit to the doctor is mandatory – All about allergies
Changed structure and color of stool can signal disturbances and malfunctions occurring in the body. Therefore, when faced with such a problem, you should pay close attention to your health and try to understand the reason for this phenomenon. After all, balls in the stool may indicate an inflammatory process occurring in the large intestine.
White lumps in the stool of an infant and inclusions in the stool of an adult
Many diseases can be diagnosed by the color, consistency and composition of stool. Changes in the color of feces are a consequence of certain pathological processes in the body. Normally, stool can range from light yellowish to dark brown in color.
A change in shade within normal limits is a normal condition and depends on nutritional characteristics. However, a significant change in the color of stool, its white color or light grains in the stool should alert you, since they indirectly indicate some pathologies.
Causes of white stool
Light-colored stool or white streaks in the stool often indicate a cessation of bilirubin flow into the intestines. It is bilirubin that is synthesized in the intestines into stercobilin, a special pigment substance that gives feces its characteristic brown color.
White lumps in the stool of an infant or light-colored stool in an adult occur due to dietary habits or consumption of certain foods. If an adult has white grains in their stool after drinking milk, this indicates a high fat content of the milk. For the same reason, light lumps appear in the baby's stool, but in this case we are talking about breast milk.
Often, white lumps in stool appear after eating butter, kefir, sour cream or lard. In such situations, it is enough to adjust your diet so that the white coating on the stool no longer appears. Important! There is a connection between light-colored stools and alcohol, since this toxic product has a negative effect on the liver.
Light inclusions in stool may appear due to the use of certain medications:
- antifungal drugs;
- antibiotics;
- oral contraceptives;
- medicines to treat gout;
- medicinal anti-tuberculosis drugs;
- antiepileptic drugs;
- medications containing acetylsalicylic acid;
- NSAIDs – non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- some rectal suppositories;
- with an overdose of paracetamol;
- Smecta;
- Tramadol.
Usually, after you stop taking medications that cause changes in the color of your stool, the white spots in your stool should disappear. If this does not happen, you should consult a specialist.
White lumps in stool may appear due to the following conditions:
- Light particles and strings in a woman’s feces can be detected both during pregnancy and immediately after childbirth. This is usually due to dietary habits or pathologies of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
- Light-colored lumps in a baby's stool are not a cause for concern; they usually indicate immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract.
- White grains in the stool of an adult and generally light-colored stools occur after surgical removal of the gallbladder.
- This shade of feces may appear after an X-ray examination with contrast in the form of barium sulfate.
- After poisoning, white feces may also appear.
- Light-colored feces may indicate excess carbohydrate intake in the human body.
In a newborn and infant, white curdled grains and flakes in the feces do not indicate any disease. Such stools may be due to formula milk, complementary dairy products, or the characteristics of mother's milk. The stool of a baby under one year old who is exclusively breastfed can be of any color.
Something white in an adult's stool should alert you. This is a reason to contact a medical facility or review your diet. In old age, white feces are definitely a sign of a serious illness.
Associated symptoms of light stools
Often, white spots in feces do not appear independently, but accompanied by some accompanying symptoms that will help to understand the reason for this color of feces and identify pathology. So, you should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Whitish worms in the stool indicate a parasitic disease. These could be roundworms, pinworms or cat flukes. In this case, it is necessary to deworm the body, since many parasites cause dangerous complications.
- Various light lumps and dots in the stool indicate the removal of undigested food debris from the intestines. This is usually food of plant origin. This may also be indicated by stool with thin white streaks. By themselves, such lumps and dots are not a reason to go to the doctor, but in combination with light, loose stools they indicate cholecystitis, which requires treatment from a specialist. The same can be said about stool with white fibers.
- Liquid white feces indicate a malfunction of the liver or pancreas. This usually happens with hepatitis, chronic pancreatitis, bile duct dyskinesia.
- White feces in combination with dark urine and yellowing of the skin indicate hepatitis. Contact a medical facility immediately.
- Light-colored feces in combination with pain in the area of the right hypochondrium indicate pathologies of the liver and gall bladder. In this case, the consistency of stool may be normal.
- Liquid white stools combined with high fever appear at the beginning of the inflammatory process. These symptoms, combined with vomiting in a child, are a symptom of a viral infection.
- White-coated feces and mucus in it may indirectly indicate fistulas in the intestines (proctitis). Often with this disease, whitish balls of mucus are found in the feces. An accompanying symptom may be pain during bowel movements and fever. Often, with cracks in the anus, blood appears in the stool.
- Foul-smelling white feces occur with cancer of the pancreas, liver itself, or gall bladder. With pancreatitis, this may indicate a transition of the disease to a chronic form.
- Constipation in combination with such discharge indicates a malfunction of the gallbladder and liver.
- Light foamy stools occur with enterocolitis, ulcers and other gastrointestinal pathologies.
- This symptom, combined with bloating, can be due to dysbacteriosis. In this case, the feces may take on a slightly greenish tint.
What ailments can light-colored feces indicate?
The presence of a large number of white grains in the stool of an adult and the white color of the stool may indicate the following pathological conditions:
- Hepatitis. With this disease, such feces are combined with yellow skin and dark urine.
- Pancreatitis. Usually the patient feels pain in the left hypochondrium. Often the cause of the disease is the abuse of fatty foods and alcohol.
- Cholecystitis. In this case, in combination with white stool, other symptoms are present: nausea, vomiting, high fever, poor appetite and pain in the stomach area.
- Oncology of the gastrointestinal tract. In the initial stages, there may be no other symptoms. In the later stages, pain occurs, appetite worsens, and weight loss is often observed.
- Crohn's disease. This is a pathology of infectious, psychosomatic or allergic origin. Usually the disease is accompanied by fever, vomiting, loss of appetite, and weight loss.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. Such feces in this disease are at the stage of decompensation or subcompensation.
Who to contact?
If your stool is light-colored, you can contact different specialists depending on the accompanying symptoms. So, for helminthiasis, treatment is carried out by a parasitologist. If the illness is caused by an infectious disease, then you should consult a therapist or infectious disease specialist.
If light-colored feces appear against the background of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive organs, then you need to see a gastroenterologist.
If in addition to white specks, mucus and blood appear in the newborn’s stool, or the stool is too liquid, foamy and smelly, then first of all you should tell the pediatrician about this.
This specialist will order additional tests and, if there is cause for concern, refer the child to a specialist.
Source: https://alerguya.ru/zheltye-plotnye-komochki-v-kale-pojetomu-pohod-k-vrachu-javljaetsja-objazatelnym.html
Treatment
As stated above, white spots can be a sign of various conditions that need to be identified and treated as soon as possible.
When they appear once and then disappear, there is no need to worry about this, however, if you notice them regularly (more than 3 bowel movements), then you need to undergo a medical examination.
Treating the underlying cause is often the best way to get rid of this symptom. For example, if the cause of the problem is a lack of bile, then treatment should certainly include correcting this situation. The doctor may examine the liver and gallbladder to confirm this condition.
On the other hand, if the spots are a side effect of certain medications, the doctor may change the prescribed medications to others.
Maintaining a healthy diet with enough fiber and water can help prevent dehydration and other problems such as hard or soft stools, constipation, and more.
Feces (feces, stool) is one of the most important diagnostic indicators of human health. Feces are a formed lump containing the remains of undigested food gruel, microorganisms, toxic substances, waste products of bacteria, and salts. In a healthy person, stool has a light brown color, a smooth surface and an elongated sausage shape . The density of the masses can be medium or low - the final consistency of excrement depends on the drinking regime and the functioning of the large intestine, in which water is absorbed and intestinal mucus is formed.
Feces are one of the most important diagnostic indicators of health
The appearance of various impurities in feces may indicate disturbances in the intestines, infectious diseases, and helminthic infestation. One of the alarming symptoms that requires laboratory examination of feces and comprehensive diagnostic measures is the appearance of white spots. If in infants such a sign may be a variant of the norm and the result of immaturity of the digestive tract, then in an adult, white flakes and particles mixed with feces almost always indicate intestinal pathologies and require treatment or correction.
White spots in the stool of an adult
Diagnosis and treatment of IBS
If a patient is suspected of having IBS, the doctor will prescribe the following procedures:
Diagnostics is necessary to exclude the possibility of a deficiency of vitamins B12 and B3, as well as iron deficiency anemia.
As a rule, the following are prescribed for the treatment of the syndrome:
There are many drugs, and only a doctor can prescribe the correct course of drug therapy, taking into account all the symptoms and characteristics of the patient’s body.
Also, if you have IBS, you will need to follow a diet, go to physical therapy and massage, do physical therapy, and also change your lifestyle. After this, after a certain period of time, the white spots in the stool will go away, as will other symptoms.
Intestinal candidiasis
This is the most common cause of white spots in stool. Candidiasis refers to fungal infections that are sexually transmitted. The main causative agent of the disease is microscopic fungi of the Candida albicans family. This is a diploid fungus that inhabits the normal microflora of a healthy person. With sufficient activity of the immune system, opportunistic Candida microorganisms are in a latent state and do not manifest themselves in any way, but when the protective functions of the body are weakened, active reproduction and mating begin.
A characteristic symptom of candidiasis is a specific white coating that has the consistency of cottage cheese or thick sour cream, which is why the pathology is popularly called thrush. Candida plaque forms on the surface of the affected mucous membranes and causes characteristic local symptoms: itching, irritation, redness and burning. The main localization of infection is the oral cavity and genitals, but systemic forms of thrush, for example, intestinal candidiasis, are also common.
With this disease, one of the symptoms is the appearance of white particles and inclusions on the surface of feces (less often, milky flakes mixed with feces). Other manifestations of intestinal candidiasis include:
- burning in the anorectal/perianal area;
- irritation of the skin of the groin and area around the anus;
- lack of appetite;
- pain in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of intestinal cramps;
- “rumbling” in the stomach, not associated with periods of fasting.
The temperature with intestinal candidiasis rarely rises beyond the subfebrile level; in most patients it can remain within normal limits.
Important! Intestinal thrush in people with autoimmune disorders, as well as patients with various forms of immunodeficiency, can lead to severe blood damage and death, so possible symptoms of the disease cannot be ignored.

Intestinal thrush requires immediate treatment
What can cause balls to appear in stool?
Changed structure and color of stool can signal disturbances and malfunctions occurring in the body. Therefore, when faced with such a problem, you should pay close attention to your health and try to understand the reason for this phenomenon. After all, balls in the stool may indicate an inflammatory process occurring in the large intestine.
What do the white balls indicate?
Feces may contain white specks for the following reasons:
- inflammatory process occurring in the intestines;
- the presence of parasites that have already laid eggs;
- intestinal candidiasis;
- taking medications whose remains have not yet left the body;
- erosion of the large intestine.
The course of the inflammatory process of the intestines can be recognized by the appearance of white lumps in the stool, which appear steadily over several days. If such lumps have a heterogeneous structure, then we can talk about an open focus of inflammation. In this case, a person may feel painful cramps in the stomach area throughout the day.
If the cause of the appearance of white balls in the stool is the vital activity of parasites, then this phenomenon occurs once, or for two days, but no more. After a certain time, it may arise again, but there is no permanence in such a violation.
With helminthiasis, a person may notice a lack of appetite, pale skin, allergic rashes all over the body, frequent headaches and nausea. A laboratory analysis of stool can make an accurate diagnosis.
In this case, the type of parasite is determined and the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Another reason why white spots in the form of balls can be found in stool is candidiasis. This disease refers to fungal infections that are sexually transmitted. With this disease, the surface of the intestinal mucosa becomes covered with a white coating. Intestinal thrush can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- white particles in stool;
- itching and burning when visiting the toilet in the anorectal area;
- irritation of the skin surface near the anus;
- stomach twists;
- lack of appetite;
- unpleasant cramps in the lower abdomen;
- Rumbling in the stomach not associated with food intake.
It is important to pay attention to such signs in time and be sure to visit a doctor. Otherwise, a person may face serious complications.
Black balls in stool
Black balls in stool may be associated with a safe factor such as excessive consumption of pears, bananas or apples. All these fruits lead to dark streaks appearing in the stool.
Black inclusions can also be associated with foods such as beets, liver, and blood sausage. And if this phenomenon goes away on its own after a few days, and the person does not observe any other disturbances in his well-being and body, then there is no need to worry.
The food is completely digested, and the stool returns to its previous color.
Sometimes the cause of black balls in the stool can be taking certain medications. Most often this applies to activated carbon, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Vikalin. This reason is also considered quite safe.
Sometimes pathologies affecting the gastric and intestinal tract can cause black balls in the stool. This phenomenon is caused by bleeding, which can begin inside the body. In addition to black spots in the stool, a person may experience frequent dizziness.
He may be bothered by physical weakness, he may notice paleness of the skin. Blood pressure will also decrease, and the heartbeat, on the contrary, will increase. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Black balls in the stool may indicate diseases such as:
- Haemorrhoids.
- Gastritis, diverticulitis, gastric ulcer.
- Crohn's disease.
- Inflammation of the gastric mucosa.
- The presence of a malignant tumor in one of the upper parts of the intestinal and gastric tract.
If the cause of this phenomenon is an intestinal infection, then the feces themselves turn greenish, emitting a fetid and pungent odor. At such a moment, a person complains of attacks of nausea and vomiting, his temperature rises, and the feverish state is replaced by chills.
Yellow balls
Yellow balls in the stool are most often associated with a pathology such as lactase deficiency. The body of an adult does not have enough enzymes that are responsible for the breakdown of milk sugar. Because of this, whole milk, cottage cheese, cheeses, and yogurt are not digested.
Pathology can be recognized by symptoms such as loose stools, pain in the lower abdomen, and increased gas production. In rare cases, vomiting occurs that has a milky color and a sour milk smell.
Source: https://ponosanet.com/shariki-v-kale.html
Lactase deficiency in adults
This is a fairly rare pathology, which is characterized by a lack of enzymes responsible for the breakdown of milk sugar molecules (hypolactasia). The main group of patients with this disease are children of the first year of life, as well as children of the younger age group (up to 3 years). In adults, the incidence of hypolactasia diagnosis is approximately 8.9%. With lactase deficiency, the human body cannot digest not only whole milk, but also any products that contain milk sugar (lactose): cheeses, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt.

It is impossible to recognize the disease in an adult without laboratory diagnostics, but you can independently identify pathological symptoms, especially if they occur after consuming milk and milk-based products. Symptoms of hypolactasia include:
- stool liquefaction and diarrhea, provoked by an increase in osmotic pressure and the influx of water into the intestinal cavity;
- pain in the lower abdomen, which becomes spasmodic when intensified;
- bloating (mostly without flatulence syndrome - involuntary passage of gases);
- appearance of milk flakes in feces.

In some patients, hypolactasia manifests itself as chronic constipation. There may be no stool for three days or more, and the feces come out in separate dense lumps mixed with white particles.
Important! In rare cases, vomiting may be a symptom of lactose intolerance. It has a white or milky color, a sharp sour milk smell and may contain undigested particles of curd consistency. This symptom always appears after eating.
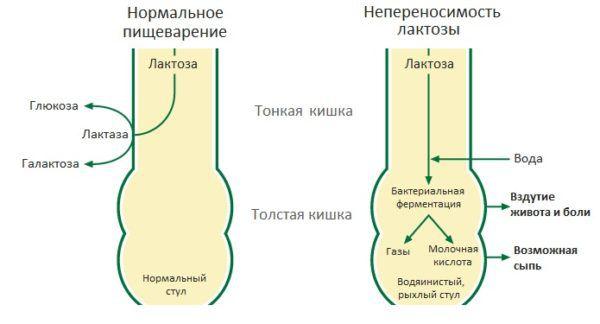
Comparison of normal digestion and lactose intolerance
Is it possible to cure lactase deficiency?
It is impossible to cure hypolactasia completely, so the main direction of treatment for such patients is dietary correction. In case of mild lactase deficiency, a person needs to exclude whole milk from the diet, but he can consume foods that have undergone heat treatment and fermentation, for example, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk, yoghurts, and some types of cheeses. In them, milk sugar is converted into lactic acid, which is more easily broken down and absorbed. To improve digestive processes, you can take artificial enzymes in the form of tablets and drops, for example, Lactazar.

In severe forms of pathology, all dairy products are excluded from the diet. They can be replaced with soy milk or lactose-free milk drinks, which were created specifically for this category of patients.
Note! For people with various forms of lactase deficiency, dairy ice cream and condensed milk are not contraindicated (if there is no allergy to these products).

Nutrition for lactase deficiency
There are white grains in the stool of an adult - no gastritis
White specks in stool are not always a sign of a problem with your body or the presence of a disease.
In order to more accurately determine the origin of foreign bodies, it is necessary to observe the feces for some time. White spots in stool are of the following types:
- In the form of lumps or grains;
- In the form of threads, veins or worms.
They can also be divided into two groups based on origin:
- Food products, in this case, white grains are harmless and are not a cause for concern;
- Parasites;
- Disturbance of microflora and inflammatory processes in the intestines.
Below we will take a closer look at all types of white inclusions and find out what they can be.
White stools can be caused by eating a lot of fatty foods, such as cream, butter, lard, and fatty sour cream. This phenomenon can also be caused by a too monotonous diet, often a plant-based diet. A large amount of dairy products in the daily diet can also give a white color to the stool of an adult. The reasons for white stool may lie in taking a number of medications:
- Drugs to combat epilepsy.
- Acetylsalicylic acid.
- Medicines to combat fungal pathogens.
- Drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis.
All of them have a great impact on the digestive system. This is why white lumps may appear in the stool, or it may even become light-colored. If the lightening of the stool is caused by food intake, then it is enough to remove fatty foods from the menu, and after a few days everything will return to normal; with the restoration of stool after taking medications, the situation is somewhat more complicated, since the body will need to recover after a shock dose of active medicinal substances.
Lightening of the stool primarily indicates a violation of the intestinal flora, and it may also indicate sand and stones in the gall bladder or liver diseases. Only a doctor can determine the exact source of the disease after a series of examinations.
When white feces appear, it is most likely that bile does not enter the intestines, which negatively affects the absorption of nutrients and the functioning of the digestive system as a whole. This can happen with the development of a group of rather complex ailments:
- Disruption of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is provoked by poor diet, alcohol abuse and infectious diseases.
- Hepatitis involves the destruction of liver cells. This disease has a fairly wide variety of subtypes, since it can be provoked by quite different reasons.
- Cholecystitis is a disease that is described as inflammation of the gallbladder, so it cannot fully perform its function. This disorder causes not only white stools, but also severe pain, changes in the consistency of stool, loss of strength and even an increase in temperature.
- Crohn's disease. This disease is considered very complex because it affects the entire digestive system. During the development of the disease, inflammation of all gastrointestinal organs is observed.
- Malignant tumors in the digestive system. In the early stages, most often there are no symptoms of this disease, and it is the clarification of feces in an adult that can help to promptly identify the disease and cure it. There is also a loss of strength, loss of weight and appetite, and the consistency of stool often changes. Indeed, in this case, the worst thing is the late detection of the disease, but in the early stages the success rate of treatment is very high.
If the feces have not yet lightened, but you see white grains or mucus of the same color in the feces, then this may indicate the development of such diseases:
- Celiac disease.
- Colitis.
- Food poisoning.
- Proctitis.
- Food allergies.
- Diverticulitis, etc.
These diseases are quite easy to treat if you start therapy at the very beginning of the development of the disease.
White spots in the stool of an adult are a deviation from the norm. In a healthy person, feces are light to dark brown in color. Typically, the symptom indicates that the body is unable to digest food normally.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JJDtfpIJ_ro{amp}amp;modestbranding=0{amp}amp;controls=1{amp}amp;rel=0{amp}amp;showinfo=1{amp} amp;enablejsapi=1{amp}amp;origin=
Sometimes the sign indicates that you are taking some kind of medication. To determine the root cause of the disorder, you should consult a doctor. The patient will be referred for a comprehensive study.
White spots in the stool of an adult are common and do not always require any treatment.
The color and structure of stool often depends on what a person eats
Often white lumps in the stool of an adult are caused by nutrition. In this case, inclusions are considered normal. The symptom does not require any special treatment. All you have to do is reconsider your daily diet.
White lumps in an adult may indicate excessive milk consumption. The product does not have time to be fully absorbed. In this case, the light grains look like sand.
If there are inclusions in the stool that look like white threads, one should suspect the presence of an excessive amount of bananas and oatmeal in the diet. A change in the structure of feces can be seen with the naked eye.
If your diet includes oatmeal and bananas, you may see whitish spots in your stool.
White balls in the stool of an adult can occur due to lactose intolerance. The body is not able to digest dairy products, and therefore light inclusions may be observed in the feces of an adult. The body excretes milk in its original form. In this case, the stool foams and has a liquid consistency. The urge to defecate is frequent.
Sometimes inclusions also indicate overeating. The digestive system does not have time to fully digest incoming foods. Leftover food leaves the body naturally, changing the structure of the stool.
White spots in the stool of adults can be in the form of:
- grains;
- veins or threads.
Taking certain medications can also cause these symptoms.
If a symptom appears while consuming any food, the inclusions should not cause concern, since they do not pose a danger to the body. Sometimes changes in stool are also associated with the presence of, for example, low-quality chicken or sausage in the diet. Bones or cartilage may get into the feces.
Often white lumps in the stool of an adult are associated with taking any medications. Therefore, the patient must remember what medications he took in the near future.
White inclusions may indicate the occurrence of some pathological process in the body. The main diseases accompanied by this symptom are described in the table.
| Irritable bowel syndrome | The condition is accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process in the intestines. The patient complains of:
In the presence of the disease, changes do not occur in the tissues of the intestinal tract. |
| Crohn's disease | The disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract. The patient complains of severe nausea and vomiting. Ulcerative lesions appear in the oral cavity. From time to time, unpleasant symptoms may disappear completely. However, the symptoms will appear again after a short period of time. |
| Ulcerative colitis | When sick, the large intestine becomes inflamed. The patient's skin color changes, there is difficulty breathing and pain in the joints. The patient's stool is disturbed. |
The listed violations most often provoke the appearance of white spots. The condition requires immediate treatment.
Also, if white spots are detected, it is worth checking for the presence of parasites.
White flakes or threads in the stool may indicate the presence of helminthiasis. There is a misconception that worms occur only in children. However, it is not. Parasites can enter the human body regardless of age and gender.
With helminthiasis, the patient may not have any symptoms for a long period of time. The main signs of pathology include:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- painful feeling in the abdomen;
- paleness of the skin;
- hair loss;
- itching in the area of the posterior opening;
- white spots in stool;
- sleep disturbance;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- refusal to eat or, conversely, increased appetite;
- causeless change in body weight;
- prostration.
Sometimes patients may experience diarrhea or constipation
White spots in feces may indicate the accumulation of Candida fungi in the body. The development of the disorder occurs when the immune system is severely weakened. If there is such a deviation, the patient complains of:
- decreased performance;
- causeless appearance of signs of an allergic reaction;
- strong cravings for sweets;
- bad breath;
- coating on the tongue;
- increased gas formation;
- painful sensation in the joints;
- infectious lesions of the genitourinary system.
With this disorder, white spots indicate that the body is fighting an increased number of fungi.
Treatment of this deviation should be carried out immediately. Otherwise, the pathology will develop into an advanced form.
Treatment methods

There is no single treatment therapy because the symptom occurs in many disorders. In the presence of fungal infections, patients are advised to take antibacterial drugs. In addition, antifungal medications are prescribed.
Depending on the cause, the doctor must select a medicine
If there are white spots in the stool of an adult due to helminthiasis, the patient is recommended to take anthelmintic medications. It is also important to wash the back hole with warm water after each bowel movement. After completion of therapy, it is necessary to re-submit stool for examination. Sometimes secondary treatment is required.
If you have lactose intolerance, if you have a symptom, you need to reconsider your diet. All dairy products must be excluded. Only after this will it be possible to cope with the violation.
Regardless of the underlying diagnosis, the patient is always recommended to follow a diet.
The diet should include as many fresh fruits and vegetables as possible. Plant fiber has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Non-pathological
- Eating foods rich in ballast substances: nuts, seeds, mushrooms, stringy meat, raw vegetables.
- Changes in diet: overeating, abuse of fatty and meat dishes. There are not enough pancreatic enzymes to fully digest large amounts of heavy food.
- Missing several teeth. Insufficient grinding of food in the mouth disrupts digestion in the stomach and intestines.
- Overdose of laxatives. Intestinal motility increases, its contents become liquefied, and food does not have time to be digested.
Irritable bowel syndrome
The pathology is considered not to be fully studied, so experts cannot say exactly what exactly causes the appearance of a typical symptom complex. Stress and psychological instability are considered one of the main factors, so in most cases, IBS is detected in patients suffering from various psychosomatic and psychoemotional disorders. The main manifestations of irritable bowel syndrome are pain in the abdominal area (lower and central abdomen), increased gas formation, and bowel disorders, which can take the form of chronic constipation or diarrhea.

Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Other possible symptoms include:
- mucus, white streaks and lumps in feces;
- lack of relief after bowel movements;
- false urge to have a bowel movement;
- asthenia (chronic fatigue syndrome);
- chronic headache.
Of great importance in the treatment of IBS is the correction of the patient’s mental state, the elimination of increased anxiety and depressive tendencies. To eliminate abdominal pain and dyspeptic symptoms, the patient is prescribed a diet that limits the consumption of foods that increase the formation of gas bubbles (cabbage, beans, peas, carbonated drinks). In some cases, limiting fresh fruit and dairy products may be indicated.
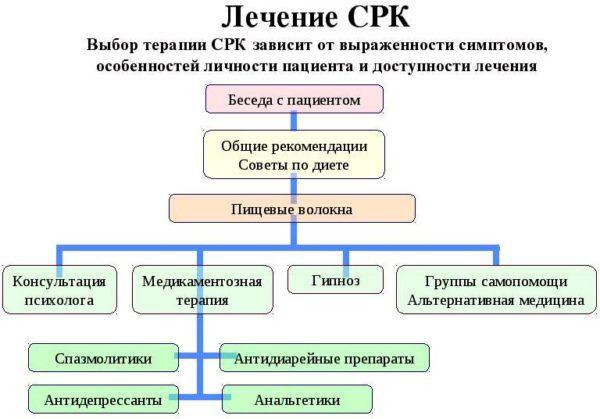
Table. Drug treatment regimen for IBS in adults.
| Group of drugs | What medications to take |
| Sedatives and antidepressants | “Tincture of Valerian” “Persen” “Afobazol” “Novopassit” “Tincture of Motherwort” “Tenoten” |
| Antidiarrheal drugs | "Loperamide" "Diara" "Stopdiar" "Enterofuril" |
| Products for liquefying stool and facilitating bowel movements | "Magnesium sulfate" "Microlax" "Goodluck" |
| Drugs to relieve intestinal spasms and pain | "Spazmonet" "Spazmol" "Drotaverine" |
| Prebiotic cultures | "Linex" "Bifiform" "Normobakt" |
Note! In some cases, antibiotics may be used for complex treatment of IBS. They are necessary to suppress gas-forming flora, however, some doctors believe that increased bacterial growth does not always lead to the appearance of IBS, so prescribing antibacterial therapy for this pathology is inappropriate.
If you have IBS, you need to eat more fiber.
Possible diseases
Intestinal diseases constitute a fairly large group of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and are almost always characterized by changes in the color, consistency and appearance of feces. Pathologies in which one of the clinical signs may be the appearance of white spots or a white film in the stool are listed below.
Enterobiasis
White spots in the stool may be the eggs of pinworms - nematodes that parasitize the intestinal lumen after entering the gastrointestinal tract. Enterobiasis is characterized by intense anal itching, burning, and redness of the skin around the anus. The stool may retain its usual consistency, but white lumps may be found on its surface, which are helminth eggs.
It is not always possible to detect signs of pathology visually, so adults are recommended to be examined for enterobiasis at least once a year.
Crohn's disease
A severe systemic disease manifested by inflammation of all parts of the digestive tract, including the esophageal tube and oral cavity. It may have various symptoms, including various pains in the epigastric and abdominal areas, vomiting, and lack of appetite (against this background, patients experience significant weight loss). Almost 65% of patients experience fecal incontinence, and the excrement itself looks like a poorly formed mush with various streaks and inclusions.
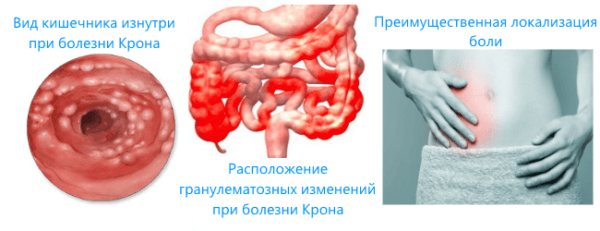
Treatment of the pathology is surgical, followed by supportive drug therapy. The risk of mortality during an exacerbation is about 35%. Patients with Crohn's disease receive lifelong disability after surgical treatment.
Stool consistency and shape scale
The appearance of any impurities in the stool is an alarming symptom, even if the person feels normal and does not have any complaints. Some intestinal pathologies may be asymptomatic for a long time , so any changes in the appearance of stool should be a reason to consult a doctor.
White stool in an adult
White plaque on stool is provoked by the development of infectious diseases, or gastrointestinal pathologies. It is necessary to consult a doctor if whitish impurities are constantly present.
What should a chair be like?
The main criteria for normal stool look like this:
- consistency – dense;
- stool color is brown. This shade is due to the presence of stercobilin. If a person eats dairy products, then the color of the stool becomes less intense and yellow tints are present. When eating meat products, stool takes on a dark brown tint.
The optimal number of bowel movements is 1-2/24 hours.
It would be a good idea to find out: Is it possible to become infected with fungus in the pool?
Probable pathologies
The main reasons for the appearance of stool with a white coating are presented in the table:
CauseDescriptionAssociated symptoms
| Lactose intolerance | A pathological condition caused by a decrease in the level of lactase, an enzyme involved in the digestion of lactose. | Loose stools, increased osmotic pressure. White plaque is combined with pain in the abdomen, which resembles cramps. Flatulence appears. Occasionally, vomiting occurs, containing pieces of undigested food. These signs appear while eating. |
| Worm infestation | A parasitic disease caused by helminths. | White plaque is accompanied by itching in the anus. The skin around the anus is irritated. Sleep is disturbed and sweating increases. In 20% of cases, sporadic pain syndrome appears in the abdominal area. Sometimes there is a urge to vomit. |
| Candidiasis | A type of fungal infection caused by microscopic yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. | White plaque forms on the intestinal wall. When feces are passed, it mixes with them. |
| Dysbacteriosis | An imbalance between beneficial and opportunistic bacteria in the body. | White plaque is accompanied by upset stool and a change in the color of stool. Weight decreases, severe abdominal cramps are present. Dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite) may occur. |
| Against the background of dietary features | The most harmless reason for the appearance of white plaque on stool is the inclusion of certain foods in the diet. | This symptom occurs due to ingestion of cartilage. Sometimes whitish impurities appear due to eggshells accidentally entering the stomach. |
| Inflammation of the large intestine | The appearance of white lumps or balls in the stool. | This symptom is constantly present for several days. If the structure of the lumps is heterogeneous, then we can talk about leukocytes gathered into a single mass. |
It is recommended to carefully review your diet and try to exclude provoking foods from it.
If the character of the stool has changed, then there is nothing more to worry about.
Diagnostics
When white plaque appears in the stool, a comprehensive diagnosis is required.
Main events:
- coprogram. The study shows the presence of occult blood in the stool, as well as the presence of leukocytes;
- test for worm eggs. This helps to detect helminthic infestations;
- general blood analysis. Helps identify hepatitis.
To clarify the information received, an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is prescribed.
Features of drug therapy for white plaque on stool
Treatment depends on the root cause of the formation of white plaque:
- mucous colitis - antiseptic drugs;
- mycosis - antifungal and antimicrobial drugs, as well as agents that reduce the risk of developing intestinal dysbiosis;
- helminthic infestation - anthelmintic drugs.
To restore intestinal functionality, you need to take anti-inflammatory drugs.
The drugs prescribed to normalize the enzyme environment are indicated in the tablet:
DrugDescriptionPrice (RUB)
| Festal | Digestive enzyme agent. Effects: choleretic, lipolytic, amylolytic, proteolytic, normalizing pancreatic functions. | 120 |
| Mezim | The drug compensates for the deficiency of pancreatic enzymes. | 260 |
| Ermental | The drug is recommended for diseases of the stomach and pancreas. | 376 |
Dietary recommendations
The diet is followed against the background of drug therapy. It involves giving up everything smoked, spicy and fatty, as well as including fiber in the diet.
In case of lactose deficiency, the patient is advised to stop consuming dairy products.
Allowed to use:
- pasta;
- cereals (except pearl barley);
- lean fish;
- boiled vegetables;
- vegetable and fruit juices;
- lean meat;
- jelly;
- berries (any).
Conclusion
Sometimes a white coating indicates abuse of antacids or drugs that contain aluminum hydroxide.
The symptom disappears on its own after stopping the medications. No special treatment is required.
Did you find useful information for yourself? Want to read more about this topic? Like ♥, subscribe to our channel and you will be one of the first to know about new publications!
And if you have something to share, leave your comments!
Your opinion is very important to us! ( 7 average 5 out of 5 )
Source: https://Netnaleta.ru/nalet/kal-s-belym-naletom-u-vzroslogo/