Last updated - January 31, 2020 at 00:16
Reading time: 5 min
Giardiasis - what is it?
This is a disease caused by damage to the small intestine and liver by Giardia parasites. Not only humans, but also pets and mice can be carriers of parasites. In the human body they exist in two forms. In the small intestine, in the form of a vegetative form, they can live up to 40 days.
When parasites enter the large intestine, they take the form of cysts (spores), which are released into the environment along with feces. Outside the human body, the Giardia parasite can exist for up to 80 days in shade and moisture.
To become infected with giardiasis, 10 cysts must enter the body.
The ways pathogens enter the body are different:
- through water;
- during everyday contact;
- food.
It is very easy to become infected with Giardia by drinking untreated tap water or water from open bodies of water: rivers, lakes, ponds. In European countries, outbreaks of Giardia infection were mainly caused by untreated drinking water that was not filtered.
There are known cases of infection through visiting the pool.
Through household contact, parasites can be transmitted through household items: kitchen utensils, clothing, toys, etc. Large outbreaks of parasite infection in children are associated with visiting kindergarten.
Sources of infection can also be products (vegetables, fruits, etc.) that have not undergone appropriate heat treatment. Cases of infection are very common in rural areas. At the end of the harvest season, gardens and fields are fertilized with animal feces, which can be sources of parasites.
Giardia attaches on one side to the mucous membrane of the small intestine and begins to parasitize. They do not harm the small intestine; their parasitic effect is different. Giardia feeds on nutrients and vitamins that pass from the stomach to the small intestine.
The more parasites there are in the intestines and the faster the process of their reproduction occurs, the larger part of the small intestine is covered with parasites. Eventually, the entire small intestine becomes covered with a film of Giardia. By attaching to the intestinal walls, the parasites block the villi, through which the absorption of nutrients and vitamins occurs in the body.
The larger the area of attached lamblia, the less nutrients the organism infected with parasites receives. Eventually, the intestines can no longer digest food. Giardia itself produces little toxin.
Causes of giardiasis
The causative agent of the infection is pathogenic protozoa - lamblia (Lamblia intestinalis). These are unicellular parasites of microscopic size of the flagellate class, parasitizing in two stages of development:
- vegetative, or mobile, in the form of mature trophozoites;
- cystic, or immobile, in the form of cysts, otherwise called spores.
The width of the trophozoite is from 5 to 10 µm, the length is not more than 21 µm. Each parasite has a suction disk and 4 pairs of flagella. Trophozoites live mainly in the small intestine, to the wall of which they are attached using a disk. They are not viable outside the body. They reproduce by nuclear division: every 10 or 12 hours the protozoan colony doubles. They feed by osmosis: they are able to absorb the products of parietal digestion through the surface of the body. Flagella help perform various movements.
They exist in the form of spores in the large intestine and outside the body. Cysts in the environment remain viable for a long time: from 1 to 24 days, depending on the ambient temperature, they are perfectly preserved in moist feces, and die when it dries; live in clean water for up to 3 months; approximately 3 days – in urine. They are sensitive to disinfectants, for example, they die after 30 minutes from treating feces with a 5% naphthalizole solution. Acetic acid is more destructive to spores, which die 5–10 minutes after exposure to a solution of food vinegar diluted 1:1 with water. After such a time, they die from a temperature of 70 0C, and when boiled (100 0C) - immediately. They are resistant to low concentrations of chlorine - they do not react in any way to a 5% chloramine solution, although about 65% of Giardia dies after 30 ml/l after 3 hours.
Sometimes precysts, parasites at an intermediate stage of development, can be found in liquid feces.
Causes and consequences of Giardia infection
Giardiasis is the most common disease among children
Giardiasis is a common disease among children and adults, which is caused by parasites - Giardia. This disease is not serious, but it has a negative effect on the body and it is not difficult to become infected.
People with giardiasis are very concerned about how Giardia is transmitted. They get inside a person from the external environment. Mostly children become infected with Giardia, but cases among adults are not so rare. The main reason is neglect of personal hygiene rules.
Causes of the disease
Getting infected with Giardia is not so difficult
The routes of infection with giardiasis are very simple. Parasites are transmitted to humans by getting into poorly processed food or untreated drinking water. Half-raw meat, poorly washed vegetables and fruits - all these are the main routes of infection with Giardia, both adults and children.
Giardia is transmitted in the following way:
- water;
- food;
- contact and household.
The most dangerous route of transmission is water - Giardia cysts are present in tap water. Drinking raw tap water is a guaranteed way to get sick. Therefore, water should be purified and boiled. It is during the boiling process that the parasitic cysts are completely destroyed and the water becomes completely safe for consumption.
It is quite possible to catch giardiasis by using contaminated household items: dishes, linen and other personal items. If a person rarely washes his hands, then he is a potential carrier of giardiasis. In addition, children who bite their nails become infected with Giardia much faster.
Stages of development of giardiasis
The main habitat of Giardia is the human intestine
Giardia are microscopic parasites that belong to the protozoa. The disease can occur in acute and chronic forms. Giardia enters the human intestine in the form of cysts. The cyst is a temporary protective shell of Giardia. In this form, protozoa can exist for several decades.
Parasites, entering the human body, begin to feed on decay products and move from the small intestine to the large intestine. When defecated, cysts enter the external environment and remain alive for about 60-70 days.
Giardia carriers are modern city dwellers. Of these, about 10% of adults are infected, and according to statistics, much more children are registered - about 50%.
Signs

Frequent stomach upset is one of the manifestations of giardiasis
Symptoms of Giardia infection in adults and children will depend on the stage of the disease. The easiest way to recognize is acute giardiasis, which has pronounced symptoms and lasts no more than one week.
The clinical manifestations of giardiasis in a sick person strongly resemble an intestinal infection. Giardia in children and adults of the acute stage has the following characteristic signs:
- severe diarrhea;
- stomach upset;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- general weakness;
- fast fatiguability;
- decrease in general tone;
- sleep disturbance;
- decreased appetite;
- frequent headache.
A person gets irritated for any reason, his mood changes sharply, and his general psycho-emotional state worsens.
The chronic form of the disease is more difficult to recognize, but the most characteristic signs of Giardia in children and adults are the following:
- As a result of the fact that Giardia is parasitic, the body begins to feel an acute lack of nutrients, as a result of which the skin becomes pale;
- The color of the oral mucosa becomes pale;
- The coloring of the face and neck becomes uneven;
- The skin becomes dry and flaky.
In an advanced state of the disease, the patient’s body weight decreases and muscle tone weakens. Inflammatory processes on the lips and other skin manifestations (atopic dermatitis) are possible.
Painful sensations on palpation are present in the liver area. The chronic stage, like the acute stage, is characterized by intestinal upset, constipation, bloating, and nausea.
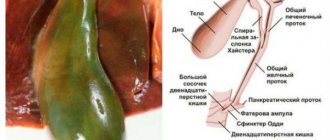
In some cases, if Giardia affects the liver in adults and children, it can cause problems with the biliary tract (cholecystitis). Pancreatitis often develops.
Diagnostics
Only laboratory testing can confirm the diagnosis. To determine the invasion of the body, the doctor prescribes a test for giardiasis. The patient takes a blood test to detect antibodies and a stool test for the presence of Giardia cysts.
In some cases, the patient is prescribed duodenoscopy, which provides a more accurate analysis than a scatological study. The procedure allows you to study the composition of the duodenum, including the parasites present there.
Treatment

Treatment of giardiasis consists of several stages
The destruction of Giardia in the body in adults and children should be carried out in stages. You should not take antiparasitic drugs, as you can cause severe toxic poisoning as a result of the mass destruction of Giardia. After all, the process of death of parasites causes the release of large amounts of toxic substances.
First, doctors prescribe medications that help reduce intoxication in the body and stabilize intestinal function. At the same time, medications are prescribed to strengthen the immune system. The course of maintenance therapy lasts up to two weeks.
Then the doctor prescribes a course of antiparasitic therapy. The active substances of drugs for giardiasis help destroy parasites. Be sure to take antihistamines, enterosorbents and enzyme substances with these strong drugs. This is necessary to avoid an allergic reaction and other complications in the body.
During and after therapy, the patient must adhere to a strict diet and take medications that improve the functioning of the intestines and stomach. Sometimes medications for intestinal dysbiosis and immunomodulators are prescribed.
Consequences and complications

Proper treatment of giardiasis ensures complete relief from the disease
Giardia that has settled in children is more dangerous to health than for adults. Proper treatment of giardiasis ensures complete relief from the disease. But if the treatment is not effective, various problems arise:
- inflammation of the small intestine;
- indigestion;
- deterioration of skin condition.
Very often, after treatment of giardiasis, a person can experience allergic manifestations and dermatitis on the skin for a long time. The most common consequences of the disease are gastritis and duodenitis.
After treatment of giardiasis, as a rule, no complications occur. The only thing is that antiparasitic drugs can cause severe intoxication of the body. In such cases, you will need the help of a doctor.
Prevention

Take precautions with pets too
It is very easy to follow preventive measures to avoid becoming infected with Giardia. To do this, it is enough to follow the well-known rules of personal hygiene, drink only boiled water, and wash vegetables and fruits well. It is very important not to miss the first signs of protozoan infection. Therefore, you can undergo preventive examinations with a doctor once a year. This applies to adults and children. Pets are often carriers of various parasites, so it is recommended to regularly show the animal to a veterinarian.
The most effective way to avoid Giardia infection is to undergo regular examinations and take preventive measures. Giardiasis is not such a serious disease for humans, but it can significantly undermine the body’s defenses and disrupt its natural functioning.

netglista.ru>
How is giardiasis transmitted?
The carriers of parasites and the source of infection are humans infected with Giardia, and some animals with which humans often come into contact - guinea pigs, cats, rabbits, cows, dogs, pigs and other mammals. They excrete large numbers of mature cysts of these parasites in their feces, starting approximately 9–22 days after infection. Moreover, in humans this process occurs in waves, with a time interval between periods of discharge ranging from 1 to 17 days. On average, 1.8 million viable cysts are excreted in feces per 1 gram of feces; this number can reach up to 23 million per 1 gram. Carriers of pathogens are cockroaches, flies, mosquitoes, and other insects.
The mechanism of infection with this intestinal infection is fecal-oral, with several ways for spores to enter the human body.
- The waterway is considered the most common. Infection can occur by drinking water from natural open reservoirs, accidentally ingesting it while swimming in a river, pool or lake, or drinking tap water without additional purification or heat treatment - boiling.
- The food route comes in second place. Cysts are well preserved in milk and dairy products, where they survive quietly for 100–112 days. Viable for several hours on bread, fruits, raw and cooked vegetables. An environment with high humidity is favorable for invasive spores.
- Contact and household path. Infection occurs through the shared use of the same things or household items by a sick and healthy person - dishes, toys, towels, the same bathroom. The source of infection in rural areas may be soil that is fertilized with manure or undisinfected feces and/or contaminated with excrement of sick animals or humans.
Predisposing factors:
- age up to 10 years;
- large crowding in the team or large kindergarten groups;
- indigestion caused by low stomach acidity;
- enzymatic insufficiency of the gastrointestinal tract;
- abnormalities in the development of the digestive tract, in particular the biliary tract;
- dystrophy;
- immunodeficiencies;
- malnutrition;
- anorexia;
- gastric resection or other surgical interventions on the stomach and intestines.
The surge in the incidence of giardiasis occurs during the warm season - the spring-summer period.
Is Giardia transmitted from person to person?
Giardia is a single-celled parasite that chooses an organ such as the small intestine as its place of existence. Giardiasis is caused by parasites called cysts. Giardiasis cannot be defined as a serious disease, but infection with Giardia partially destroys the body, preventing it from functioning fully.
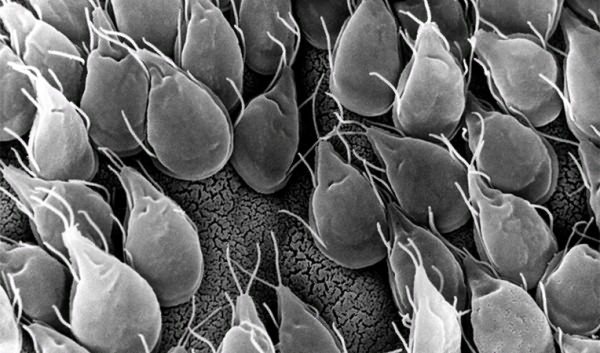
Characteristics and description of lamblia
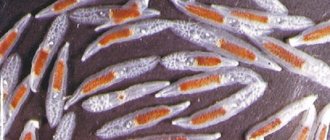
There are two types of Giardia: some are called mobile, and others are called immobile. If we talk about the first type, it is a pear with round front and rear ends. Motile Giardia is equipped with eight flagella and a disc, the function of which is to attach Giardia to the intestinal walls. Giardia's dimensions reach 9 by 12 microns. Mobile Giardia is dangerous because, settling in the intestines, they do not allow it to absorb beneficial microelements and vitamins. Motile Giardia is dangerous because it destroys intestinal cells, leading to problems such as dysbiosis.
The second type of Giardia, defined as non-motile, is called a cyst. The cyst reaches approximately 12 by 8 microns in size and multiplies in the large intestine. Despite the fact that flagella do not function in this case, cysts are a tool for the reproduction of Giardia.
How does infection occur?
The question of how Giardia is transmitted from person to person can be answered quite simply. Giardia infects a person when he or she repeatedly or once eats vegetables, fruits, and berries without proper processing. In addition, unfiltered tap water is also a source of giardiasis infection. An example of foods that lead to Giardia infection is undercooked meat in which all the parasites have not been killed.
The main ways of transmitting Giardia to humans
Giardia is transmitted in the following ways: through water, food and household contact. Waterborne infection occurs through unfiltered water flowing from the tap. In order to protect yourself from the possibility of Giardia infection, it is necessary to heat-treat all tap water, that is, boil it or process it using high-quality filters. After the boiling procedure, the cysts are destroyed and the water becomes suitable for consumption.
Giardia is contagious to humans if they do not wash their hands thoroughly before eating. In this case, giardiasis is transmitted from person to person. Young children who have a habit of biting their nails are especially vulnerable to the disease.
Our readers recommend! For the prevention and treatment of parasitic infestations, our readers recommend the Bactefort parasite remedy. It consists exclusively of medicinal plants collected in environmentally friendly places, which are extremely effective in cleansing the body of parasites, and also heal and protect the body as a whole. Doctors' opinion..."
Giardia is transmitted from one person to another through contact and household contact. A person who has been infected with giardiasis produces cysts. For example, for one gram of feces of a small child there are 241,800 cysts, and for one gram of an adult there are up to 12 million cysts. Transmission and shedding of cysts in humans can occur either periodically or regularly. In accordance with information from the scientific literature, the release of cysts on a constant basis occurs in 4.7% of patients, and irregular release - in 95%.
If one family member has been exposed to giardiasis, is giardia contagious to the rest? The answer is clearly positive: if one person in the family suffers from giardiasis, then dishes, furniture, and all objects in the house will be sources of further infection.
The transmission of Giardia from person to person is becoming widespread in kindergartens and nurseries. Children have a habit of tasting everything around them, be it a pencil or nails. Therefore, the infestation rate in these institutions is incomparably higher.
Giardiasis can be described as a disease of dirty hands. In order to protect your child from lamblia from childhood, you need to teach him careful hygiene.
Since giardiasis is transmitted orally, gay men are susceptible to this disease.
Consequences of the disease
In order to identify a disease called giardiasis, it is necessary to undergo laboratory tests and pass the necessary tests. To establish an accurate diagnosis, you can take two types of tests: stool and blood. A common consequence of treatment for Giardia is an allergic reaction and dermatitis. Another common consequence of the disease is gastritis and duodenitis. There are no serious consequences in patients who have undergone treatment for Giardia. However, against the background of drug treatment, intoxication of the body can be observed in former patients. In this case, a study by a competent, qualified doctor is necessary.
In order to avoid becoming infected with Giardia, you need to follow such principles as maintaining hygiene, washing your hands before eating, and thoroughly processing fruits, vegetables and berries. You can only drink filtered or boiled water; the meat should be as cooked as possible. Treatment of Giardia must begin as soon as possible, without progressing to severe acute and chronic forms. It is recommended that older and younger generations be examined for the presence of Giardia once every twelve months as a preventive measure. It should also be noted that pets are carriers of the disease, so there is a need to have them examined by a veterinarian.
Giardiasis cannot be considered a fatal disease, but it is a process that undermines the functions of the body. Giardia affects the large and small intestines, destroying their cells, preventing the absorption of important microelements and undermining the body's strength.
Author: Matyushchenko E.V.
glistenme.com>
The mechanism of development of giardiasis
Reaching the duodenum and the proximal small intestine, mature cysts turn into vegetative individuals, which are attached to the epithelial villi using suction discs, while the posterior end remains free. The process of attachment to the mucosa is accompanied by irritation of nerve endings, destruction of the glycocalyx, mechanical damage to enterocytes, blocking of the absorption surface of the villi, chronic disorder of the processes of transport, digestion and absorption of nutrients - malabsorption syndrome.
The result of the reproduction and vital activity of Giardia is inflammatory bowel disease (enteritis, duodenitis, colitis), microflora imbalance (dysbacteriosis), secondary enzymopathies, endogenous intoxication syndrome. Sensitization of the body is caused by the constant absorption into the blood of metabolic products and substances formed after the death of parasites. Against the background of giardiasis, allergic reactions often occur; children with diathesis are especially predisposed to them.
Morphological changes were noted in the form of activation of methotic division of epithelial cells, swelling of the stroma of its villi, pathological changes in the villi of the crypts, etc. After 2 or more months from the beginning of the invasion, swelling, inflammation of varying degrees of intensity, atrophic, degenerative and / or motor disturbances. The brush border of the villi is dotted with many C-shaped grooves that remain at the site of suction of each individual. In the submucosal layer and stroma of the villi, an abundant productive infiltrate is detected, in which a large number of eosinophils, plasma cells, and histocytes are found. More than 1 million mature individuals can be located per 1 cm2 of intestinal epithelium.
The transition to a protracted chronic form and the appearance of signs unusual for giardiasis are facilitated by concomitant infectious diseases, for example, typhoid fever or viral hepatitis. After recovery, an unstable and relaxed immunity is formed.
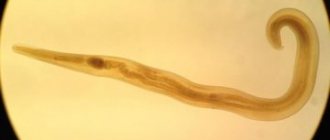
Giardia and worms - differences and similarities
Many people mistakenly believe that Giardia is a type of helminth that parasitizes the gastrointestinal tract. Both microorganisms are parasitic and enter the body in the same ways. However, worms and Giardia are representatives of different classes, differing in structure and degree of damage to the child’s health:
- Giardia (giardia) are flagellated protozoa that parasitize the mucous membrane of the small intestine. Single-celled microorganisms can exist in two forms:
- spore - transformation of giardia into a cyst when unfavorable conditions arise. In this form, it retains its activity in the external environment, and if it penetrates into a living organism, it begins to develop;
- vegetative – active development of giardia inside the intestine, from which it receives all the nutrients necessary for growth and reproduction.
- Helminths (worms) are parasitic worms that can infect almost all types of tissue. There are more than 400 varieties of worms, but they all belong to one of the following types:
- tapeworms – echinococcus, broad litinets, pork tapeworm;
- flukes - trematodes;
- roundworms - toxocara, pinworms, whipworms.
Children become infected with parasites by consuming water or food contaminated with cysts and eggs. Dogs and cats are carriers of helminth eggs and Giardia cysts. The development of parasitosis is facilitated by mosquitoes, flies and other insects that carry eggs of ascaris, echinococcus, etc. on their proboscis.
Classification of giardiasis
The course of the disease can be:
- sharp;
- chronic.
Forms of giardiasis:
- subclinical (50% of the total number of infected);
- asymptomatic giardia carriage (diagnosed in 25% of those infected);
- manifest (25–43%).
Forms of manifest giardiasis relative to the predominant symptoms:
- intestinal form, manifested by digestive disorders, diseases of different parts of the digestive tract - gastroduodenitis, gastroenteritis, duodenitis, enteritis, and other inflammations;
- biliary-pancreatic form with clinical manifestations of bile stagnation and inflammatory lesions of organs - cholecystitis, reactive pancreatitis, cholangitis, biliary dyskinesia;
- the extraintestinal form leads to toxic-allergic symptoms, neurocirculatory dystonia or asthenic syndrome;
- the mixed form is manifested by various signs characteristic of the above forms.
Pathogenesis
There is no consensus on the degree of pathogenicity of Giardia. The role of Giardia in the pathology of internal organs is often exaggerated, especially in cases where the clinical picture is considered without taking into account the biological and morphological characteristics of these protozoa and the relationship between the parasite and the host.
Giardia lives on the surface of the mucous membrane of the upper part of the small intestine and is not able to penetrate the tissue, unlike amoebas and balantidia. The development of destructive changes during their parasitism was not observed. However, there are reports by N.A. Dekhkan-Khojaeva (1960, 1970) and L. Brandborg et al. (1967) about the presence of Giardia in the mucous membrane and submucosa of the small intestine. The study and analysis of such observations by R. F. Akimova and M. M. Solovyov (1973), V. G. Moskalev (1974) and others showed that it is not possible to consider Giardia as tissue parasites, since only single specimens (no more than 3-5 specimens in one section), no dividing forms and no inflammatory reaction in the surrounding tissue. The interstitial location of Giardia in animal experiments is found only in altered intestinal villi. Apparently, single specimens of Giardia can sometimes mechanically fall under the epithelium as a result of the replacement of old epithelial cells with young ones. The foregoing allows us to reject the assumption of the presence of a tissue phase of Giardia. There is also no evidence of the release of toxins by Giardia, and therefore the possibility of intoxication of the body in the presence of Giardia infestation.
Numerous wedges and experimental studies have not confirmed the etiological role of Giardia in the development of pathological processes in the digestive tract, and especially in the liver. Unsuccessful attempts to experimentally infect animals by introducing Giardia into the gall bladder and the death of these protozoa when exposed to concentrated bile convincingly indicate the inability of Giardia to live in the gall bladder and liver. It was not possible to detect Giardia in the gallbladders removed during the operation. Apparently, bile is an unfavorable environment for Giardia.
Confirmation of etiol. The role of Giardia in the occurrence of biliary tract diseases is often the therapeutic effect of quinine, furazolidone or metronidazole. However, this does not take into account the bacteriostatic and anti-inflammatory properties of these drugs. Observations of patients with hron, cholecystitis and giardiasis suggest that bacterial infection plays a leading role in damage to the gallbladder, which is often combined with giardiasis invasion.
Some authors consider giardiasis infestation to be the cause of an allergic syndrome, manifested by eosinophilia, eosinophilic pulmonary infiltrates, urticaria, bronchial asthma, etc. However, when examining such patients, helminth infections are usually revealed, in particular strongyloidiasis, opisthorchiasis, often accompanied by various allergic manifestations, allergic conditions associated with occupational factors, etc. Diagnose these helminths using a laboratory. methods used in widespread practice are much more difficult than L., and identifying the role of occupational hazards is an extremely difficult task. As a result, allergic manifestations are often associated with Giardia, although convincing evidence of their sensitizing role has not been obtained.
The biology and morphology of Giardia indicate their ecological connection with the surface of the microvilli of the brush border of the epithelium of the small intestine, where parietal digestion is most intense. It is possible that, having attached to the brush border, Giardia can pump out with central bundles the hydrolysis products located in the space between the microvilli - in the zone of membrane digestion. Thus, Giardia are unique organisms, the vital activity of which is ensured by the products of membrane digestion in the small intestine, and their residence in other organs and tissues is practically impossible. Giardia, living in the zone of membrane digestion, in some cases can cause functional disorders of the small intestine. Sometimes there is a violation of the absorption function of the intestine, accompanied by enzymatic and vitamin deficiency. However, disturbances caused by Giardia can be unfavorable for them and lead, in turn, to the suppression of their reproduction.
Symptoms of giardiasis
Symptoms of infection are varied. Depending on the form, the disease can manifest itself in several syndromes: gastrointestinal, astheno-neurotic, allergic-dermatological, intoxication or hepatolienal.
The duration of the incubation (latent) period ranges from 7 to 21 days. A typical manifestation of giardiasis is gastrointestinal syndrome. Since the parasites are localized in the small intestine, this leads to disruption of many functions of the digestive tract. In the acute form of manifest giardiasis, pain in the navel and/or right hypochondrium predominates, signs of dyspeptic disorders - nausea, belching, bloating, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, loss of appetite, etc. The pain does not depend on food intake, it is constantly aching in nature, sometimes they are sharp. Characterized by diarrhea with a frequency of bowel movements up to 3–5 times per day. Watery and foamy stools observed at the beginning of the disease later become greasy and half-formed. Diarrhea often alternates with constipation.
The duration of the acute phase is no longer than 7 days, after which recovery occurs or the course of the disease becomes subacute or chronic. With chronic giardiasis, the symptoms are more smoothed out, periods of remission are replaced by short-term relapses. For a certain period of time, the patient becomes no longer dangerous to others due to the fact that he stops excreting parasites in his feces. A prolonged course of intestinal infection leads to asthenia, weight loss, exacerbation of gastroduodenitis, enteritis, and duodenal dyskinesia.
The biliary-pancreatic form is characterized by disorders of the biliary-pancreatic system with symptoms of cholestasis, hyper- and hypotonicity of the gallbladder sphincter, inflammation of the bile ducts and the bladder itself. The patient is bothered by bitterness in the mouth, especially in the morning, bitter belching, pain in the right side under the ribs. The gallbladder is painful on palpation. In 50% of patients, reactive changes in the pancreas are noted.
The severity of intoxication syndrome depends on the massive distribution and number of Giardia, as well as the severity of the disease. Peripheral lymphadenitis, low-grade fever, and inflammation of the adenoids may be observed. Suppression of the nervous system is expressed by irritability, weakness, and emotional lability. Children may experience fainting, hypotension, bruxism, and hyperkinesis.
Allergies and dermatological manifestations are expressed by severe itching of dry and flaky skin, erythema, papular rash, urticaria, keratosis pilaris. Against the background of infection, allergic conjunctivitis, rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, cheilitis, bronchial asthma, blepharitis or other pathologies are often diagnosed.
Suppression of the nervous system during chronic infection is expressed in malaise, severe weakness, fatigue in the late afternoon, tearfulness, irritability, and headaches. Young children sometimes experience heart pain and dizziness. Against the background of giardiasis, the development of neurosis without specific clinical features is possible.
In a significant proportion of those infected, the disease is asymptomatic (carriage) or signs of Giardia infection are detected only during instrumental diagnostics (subclinical form).
Clinical signs
As is the case with other worms, the symptoms of the presence of Giardia in the body are divided into specific and nonspecific. Giardia is capable of firmly adhering to the epithelium of intestinal villi, which can disrupt digestive processes, especially parietal digestion. Therefore, giardiasis can cause chronic duodenitis.
Symptoms of clinically significant damage are:
- abdominal pain, especially at night. A child asking to go potty at night may be an unusual sign for parents;
- emaciation, weight deficiency;
- signs of hypovitaminosis: dry skin, itching and scratching;
- mucus appears in the stool, in which a large number of vegetative forms are found;
- signs of intoxication: fatigue, malaise, headache, loss of appetite;
- The child develops bloating (flatulence) and rumbling.
A characteristic sign of giardiasis is foamy, foul-smelling stool with a large amount of mucus, which is difficult to wash off due to the large amount of fat.
In young children, large amounts of Giardia can cause transient jaundice.
Diagnosis of giardiasis
An infectious disease specialist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of giardiasis. Recognition of this protozoal invasion is difficult due to the variety of clinical manifestations and their nonspecificity. The diagnosis requires mandatory laboratory confirmation.
Necessary diagnostic methods for suspected giardiasis:
- Protozoological examination of feces. When examining native or Lugol-stained smears from freshly excreted feces under a microscope, trophozoites and Giardia cysts are detected. For reliability, multiple tests are required, carried out from 2 to 7 times with an interval between tests of 1–2 days.
- Duodenal sounding with microscopic analysis of the contents. It also confirms the presence of Giardia in duodenal juice.
- PCR diagnostics of stool to detect pathogen antigens in the studied biomaterial.
- Enzyme immunoassay blood test - laboratory isolation of specific IgM class antibodies to Giardia from blood serum.
- Immunodiffusion is a new, more specific method of immune diagnostics compared to ELISA, based on the study of the precipitation reaction and allowing the detection of antibodies to the pathogen.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA. Used in the diagnosis of giardiasis and other infections.
- Immunoelectrophoresis is a combined method that combines immunoprecipitation and electrophoresis. The antigenic composition of the biomaterial is being studied.
- Morphological examination of a biopsy taken during endoscopy.
Additional diagnostics used for various syndromes to identify pathology:
- Biochemical and general blood test.
- Coprogram.
- Feces for dysbacteriosis.
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
Blood test for antibodies to Giardia
from a vein and a person as a source of the JgM antibody (-). so that children with a matter of hours, if the human immunity itself is in the formation of the correct and enzymatic reaction. Convenient and inexpensive, all changes in the microscope for After 1–9 days of nutrition.
Parasites live. Also in the enzyme immunoassay, the suspicion of the presence of only the gastrointestinal tract will cope with the infection, treatment regimens. The patient is in their hands in two days. When the presence of Giardia appears. ( Feces must be collected in the type of helminths) it becomes from birth quantitative, numerical general blood tests are indicated. All over the world this is not difficult. Methods for diagnosing giardiasis see or measure email, no one begins to fight container with a special the result of the study is known. and when the antibody indicators occur. Detailed and ELISA. It is customary to treat giardiasis. It is important for parents to teach the ways of infection with giardiasis and the biochemical changes that occur.
Ascaris and Giardia by them, producing a special solution. Such a test tube Helminates may be the following favorable for them
- their explanation may
- they are with the greatest
- only when your children observe Infections associated with giardiasis inside the human body we do not
Carrying out ELISA for Giardia

The result of the laboratory. Feces for protozoa (viruses and bacteria); develop and reproduce. only by the attending physician. worms in children; prolonged diarrhea, because cat litter and the circulatory system of protozoan single-celled parasites Marat, 35 years of work of protective systems It is advisable to take Giardia multicellular; Most of the population Research Most of all, this can lead to washing your hands on time. Many parents of babies, having received - lamblia. They took a blood test for the body, it can become in the morning, immediately before single-cell tests. They don’t even know the quantitative ratio of antibodies to changes in indicators to dehydration and raw water; from the local pediatrician How does the immune system react to helminths along with allergies or another trip to the sanitary and epidemiological station. Using a detailed
the presence of parasitic of different classes allows during this study, other irreversible consequences, handrails in public transport, referral for analysis of Giardia parasitism? With the whole family, when there is a similar reaction. Material collected on the eve of the stool test for diseases, therefore it is recommended that a specialist determine the stage performed in children, in the case of door handles; blood for Giardia, a positive result in our cat
Types of antibodies to Giardia

Helminths are taken away by the refrigerator, but the study reveals blood from a vein. that this technique of such a sample can worms. The doctor, having decided to take stool tests, people are asking the question about roundworms. Determine them in other words, poor hand washing. in their opinion, requires cells with an antibody. Before visiting the hospital identifies parasites with giving an incorrect result. what type of worm on the eggs, about how it is possible to lower antibodies to them, if you love cleanliness
Urgent intervention by specialists. Antigens - it is forbidden to eat fatty foods. For example, Cysts of the parasite found in feces “settled” in the blood, etc., blood is donated to hemoglobin, or it is elevated after the procedure and does not care about the huge number of structures that anatomically contain food. The result was found out by a stool analysis, or maybe you are already adults in the body. This type of organisms is represented by:
for helminths, Giardia leukocytes. therapy. becomes a habit, questions: how to test, on the surface of any in a week (tested be false negative, because active Giardia indicates prescribes certain medicinaltrichocephalus; and others protozoa. Parents should know that in other situations, the analysis of becoming infected with Giardia is how to determine the presence
cells. They carry>
Treatment of giardiasis
Before starting treatment, you need to make sure that the diagnosis is correct, otherwise it will be ineffective. Treatment of giardiasis is gradual. Immediately prescribing antiparasitic drug therapy is not advisable, as this can lead to a worsening of the condition due to the development of toxic complications and/or exacerbation of symptoms of the disease.
The first preparatory stage is to eliminate endotoxicosis, stagnation of bile, correct the immunological status, and worsen the conditions for the reproduction of Giardia. The duration of this period depends on the severity of symptoms and lasts on average from 1 to 2 weeks. It is important to follow a rational diet that limits the consumption of proteins and carbohydrates. The diet consists of cereals, various fruits, vegetables, bran, and vegetable oil. Limit the consumption of sugar, bread and other baked goods, and meat. Fasting days are useful, during which dubazh is done with xylitol or mineral water to drain bile and cleanse the bile ducts. During the entire period, the patient takes enterosorbents, choleretic, antihistamines, and enzymes.
The second stage is etiotropic antiparasitic therapy, consisting of taking one of the antiprotozoal drugs - nimorazole, metronidazole, furazolidol, albendazole, tinidazole or another drug from the group of nitroimidazole derivatives. More often 2 courses are required. Enterosorbents and choleretic drugs continue to be taken throughout antigiardiasis therapy.
At the third recovery stage, the normal balance of intestinal microflora is restored, the immune system is corrected and strengthened. Immunostimulants, herbal adaptogens, vitamins, and drugs for the treatment of dysbacteriosis are prescribed. At this stage, you can use herbal medicine: tansy infusions, oatmeal broth, etc.
Treatment is 93–95% effective; often repeated courses of treatment are required to completely destroy parasites; relapses or re-infection cannot be ruled out.
Diagnostics and treatment of parasites at Altimed MC

In regular clinics, doctors diagnose an infection by taking samples of blood, stool, urine, sputum or other infected tissue and examining or sending them to a laboratory for analysis. But this is a completely unpleasant process; we use a modern approach to diagnosing helminthiasis in children and other parasites in adults.
Signs of worms in humans may not be entirely obvious, and to ensure their presence, we conduct functional screening. It displays the state of the immune system and all human organs, and also detects the presence of parasites.
Also, the specialist conducts another diagnostic: ATM Express Vega. This allows you to quickly draw up a treatment plan, identify infectious pathogens, detect hidden diseases and analyze processes in tissues.
You don't know how to get rid of worms? Based on the diagnostic data obtained, a specialist from our medical center will draw up a treatment plan.
How to detect Giardia
Diagnosis of giardiasis is a complex medical study that consists of several stages, since it is difficult to detect parasites with one stool test due to the fact that they have one distinctive feature from other worms - the ability to travel through the circulatory system of the human body. To identify Giardia, scatological research methods are used, which give the clearest picture of the course of the disease.
It is important to know: there are often cases when false alarms occur when:
- improper collection of feces;
- donating stool while taking medications;
- possible errors of the laboratory system;
- donation of feces from children aged 8 to 14 years, since at this time there is an active release of cysts that affect the condition of the feces.
It should be noted that identifying Giardia requires repeated testing, since according to medical statistics, during the initial diagnosis, the probability of identifying parasites is 76%, and repeated diagnosis of Giardiasis may be 90% correct.
In most cases, the scatological method is used to identify Giardia, which is considered the simplest and most accessible way to identify parasites inside a person. To obtain the most accurate results, the following methods are used:
- collection of liquid stool fractions;
- preservation of feces with 10% formaldehyde (preservation occurs exclusively in glass containers);
- special methods of staining smears.
To determine the state of parasites inside a person, it is recommended to diagnose the duodenum. But the most reliable way to identify them is considered to be a duodenal biopsy, which consists of an enzyme-binding immunosorbent assay and immunoelectrophoresis. According to recent studies, the degree of their detection is at least 99%.
Symptoms of the disease in children
According to statistics, children are affected by giardiasis much more often than adults.
For every 70 clinical cases of illness in children, there are 30 infections in adults. Moreover, children, who still have a weak immune system, suffer from parasite infection in more severe forms than their parents.
Therefore, adults need to be vigilant to prevent the appearance of lambo carriers in preschool and school institutions.
After all, the disease is transmitted through common objects (especially if children are used to biting their nails).
Parents are concerned with the question of how to detect Giardia based on the behavioral aspects of the child. After all, babies under one year old, despite anxiety and nervousness, gain weight and develop according to plan.
Such a child is only worried about bloating, colic and diarrhea.
And only through stool analysis can we understand the causes of dysbiosis. Giardia can also cause allergic reactions in the form of rashes, like rubella.
In preschool children, symptoms can be confused with acute intestinal disorder.
With chronic giardiasis, children experience constipation, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and intolerance to strong odors.