Life activity of the parasite
The wide tapeworm has a fairly long lifespan, during which time more than one owner changes.
First, the parasite egg enters a freshwater body of water, where it transforms into a larva. It is called coracidium. The transformation process takes 1 month. The larva lives in a reservoir for a week, where it is swallowed by a small crustacean - daphnia.
The coracidium stays in the crustacean's body for 2 weeks and changes into a procercoid. Then the crustacean containing the parasite is swallowed by the fish. Inside it, the daphnia decomposes and the larva is released, where it transforms into a plerocercoid.
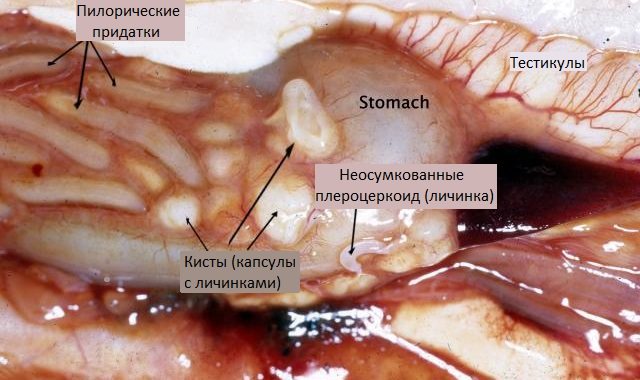
The larva is located throughout the body, the highest concentration is in muscle tissue, caviar and liver.
The tapeworm undergoes its final development in the human body, getting there by eating contaminated fish.
Development cycle of the broad tapeworm
The wide tapeworm enters the human body as a larva and turns into an adult in the intestine. Its mature eggs are released along with the feces. Then they penetrate into the water, stick tightly to aquatic plants, where they develop into ciliated larvae (coracidium). The coracidia is then consumed by an intermediate host, such as a copepod. The oncosphere is released in his body and turns into a procercoid.
A wide tape can...
Next, the crustacean with the developing flatworm is eaten by the second intermediate host - freshwater fish, for example, pike, perch. As a result, the procercoid penetrates the muscles of the fish and can remain there for up to ten years. Until the fish is eaten by the final owner - a mammal, for example, a person, where the procercoid quickly turns into an adult.
Causes of infection
It is possible to become infected with diphyllobothriasis only through intermediate hosts – fish.
Larvae living in water bodies do not pose any danger to humans.
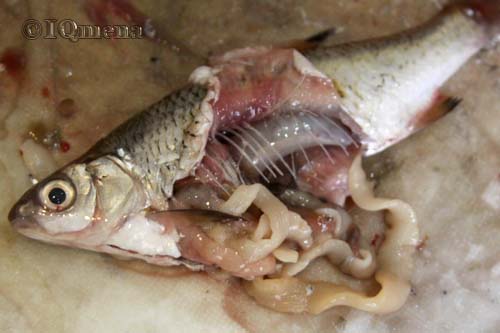
But the fish are a direct threat. A person can get a wide tapeworm even through ordinary tactile contact with it (cleaning). And also when it gets into food.
Factors contributing to infection
- undercooked fish;
- raw fish;
- lightly salted fish;
- cutting fish and tactile interaction with it;
- poorly washed hands after cutting fish.
Description
The broad tapeworm is a parasite whose location is the small intestine of the human body. These types of worms are classified as biohelminths. The helminth needs three hosts. Adult worms will develop in the body of the latter.
The wide tapeworm is capable of growing up to 9 m in length. Its structure is such that it consists of a strobile and a head part. The first was created from 4000 segments. The head size is 3-5 mm. There are hooks on it, with the help of which the worm hooks onto the walls of the intestinal mucosa.
Symptoms
After the parasite penetrates the body and actively grows, the following signs appear in a person, indicating infection:
- nausea occurs;
- there is a frequent urge to vomit;
- unpleasant and painful sensations in the gastrointestinal tract;
- bowel disorders;
- deterioration or increase in appetite;
- hypersalivation;
- slight rise in temperature;
- changes in the nervous system (numbness of the arms and legs , poor sensitivity);
- change in blood composition.
The first symptoms in a person appear after 20–60 days of the parasite remaining in the body.
If the wide tapeworm spends quite a long time inside the body (see photo above), then the following symptoms appear in a person:
- feeling of weakness and fatigue;
- blanching of the skin and mucous membranes is observed;
- blood pressure decreases;
- heart rate increases;
- headaches occur;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness.
Diagnosis and treatment

If you consider the possibility of tapeworm infestation, synchronize the memory of recently eating a piece of fresh fish, possibly causing the infestation, with changes in your health.
First of all, it should be noted whether the appetite has worsened, the weight has decreased, the stool is disrupted, or vomiting has appeared.
How often do these symptoms occur in humans?
If the results of your observations are not optimistic and the sign of infection is obvious, take blood and stool tests to an infectious disease specialist. Laboratory tests of an infected patient will show: a decrease in hemoglobin level, a decrease in the number of red blood cells, an increase in direct bilirubin, a lack of white blood cell percentage and other possible deviations of a person’s blood parameters from the norm necessary for health and active life.
But the final diagnosis will be given by the results of an examination of the patient’s stool, where white round eggs of the parasite may be found.
Treatment of broad tapeworm begins with the widespread use of a course of vitamins and iron supplements. It is necessary to restore the balance of microelements in the blood. Vitamin B12 is prescribed intravenously several times a week for one month. In parallel with this, antiparasitic actions are carried out.
These include:
- anthelmintic tablets and suspensions: Praziquantel, Azinox, Biltricid and others. Modern pharmaceutical companies offer a very wide selection of anthelmintic drugs. A doctor will help you choose your remedy. He will also develop the required norm individually for your condition and prescribe a remedy for children;
- treatment with folk remedies: pumpkin seeds, ground into flour, mixed with honey and water; wormwood, consumed in dry form on an empty stomach for 10 days. These folk remedies have special components that have a paralytic effect on worms and gradually kill them;
- a course of dry or water fasting: there are many authors who have compiled specialized fasting cycles, during which you can completely renew the cells of some of your organs, including the intestines, and remove any parasites. But you need to fast correctly, doing exercises to remove bile from the body, giving enemas, etc.;
- a special strict diet excluding any products of animal origin.
What remedy to get the wide tapeworm out and what treatment to apply is up to you to decide. Treatment methods vary in time and effectiveness. Remember that you need to start treatment immediately as soon as you have established the presence of this parasite in your body.
After a course of treatment, you should also be tested again after three months, since parasite eggs may remain in the folds of the intestines.
How the wide tapeworm exits the body will be visible to the naked eye. The peculiarity of this representative of worms is that it is too large, so the body will not leave it at once and will leave it in parts.
Diagnostics
If a number of symptoms characteristic of this parasitic infection occur, the first thing to consider is the possibility of infection, namely whether there was contact with fish.
The following research methods are used to diagnose diphyllobothriasis:
- PRC examination of feces is considered the most informative way to detect the disease, but has a fairly high price;
- a smear is performed to identify the presence of eggs or segments of the broad tapeworm, which have a specific appearance. Examination of feces is carried out under a microscope;
- serological methods, which are based on the detection of antibodies. These methods are of a low-informative nature.
In addition, diagnosis includes studies such as:
- a blood test aimed at detecting anemia, elevated ESR levels, eosinophilia, etc.;
- a biochemical blood test helps to identify a drop in protein and albumin levels, and an increased level of total bilirubin.
Life cycle of a worm
The life cycle of the broad tapeworm is multi-stage. With feces, worm eggs from the source of infection infect the soil. They then contaminate the water. At this stage they are still immature, but after 14-20 days at a water temperature of about 15 C, embryos emerge from them.

The life cycle of the broad tapeworm is multi-stage
That is why diphyllobothriasis often occurs in those people who eat fish from fresh water bodies.
Sea water inhibits many parasites. In order for the tapeworm to develop further, the embryos are swallowed by copepods. After just a couple of weeks, they hatch into larvae 0.7 mm long. Crayfish become the first intermediate hosts of the common tapeworm. The next reservoir is predator fish. In their body, the larvae make their way into the muscles and other tissues.
After 30 days, plerocercoids are formed. The last hosts for the tapeworm are domestic animals and people who have consumed contaminated fish.
Plerocercoid is the larval stage of development of the broad tapeworm. The larvae infect the intestines, where they continue to grow. Sexually mature parasites can live in the human body for two decades. The development cycle can be 25 weeks.
Consequences of parasite infection
- due to the fact that the parasite attaches to the intestinal mucous membranes, tissue necrosis and atrophic ulcers subsequently occur at the site of attachment of the tapeworm;
- a gastrointestinal tract disorder occurs because the parasite damages the nerve endings of the mucous membranes and intestinal functions are disrupted;
- products secreted by the broad tapeworm during its life processes lead to allergic reactions;
- Anemia occurs due to a deficiency of vitamin B12, the level of which decreases due to the effects of the parasite.
What causes the harmful effects
Attaching to the intestine, the wide tapeworm irritates its mucous membrane with its hooks. Inflicting such an injury leads to the appearance of ulcers, and the affected area undergoes atrophy. Extensive infestation by the broad tapeworm provokes the development of intestinal obstruction. Associated complications are catarrhal manifestations of the mucous membrane.
The helminth provokes the disease diphyllobothriasis. The course of the pathology often goes unnoticed, without pronounced symptoms. Toxic substances produced by the parasite cause toxic poisoning, manifested in allergic skin rashes. Provoking a lack of vitamin B12, wide tapeworm causes the development of anemia. There are known advanced cases of invasion that led to malignant anemia.
Symptoms of broad tapeworm infestation
Often the symptoms of broad tapeworm infestation are not expressed. Sometimes you may feel slight discomfort in the lower abdomen. The main signs signaling infection are the presence of segments in the stool. Characteristics of long-term helminth parasitism:
- pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes becoming spasmodic;
- increased salivation;
- fickle appetite - alternating severe hunger and reluctance to eat, accompanied by severe weight loss and decreased performance;
- development of anemia;
- irritability and depression develop;
- pain while eating;
- with extensive infection, the liver and spleen may increase in size.
Changes occur in the composition of the blood: the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin decreases, the color index increases. The level of leukocytes and platelets decreases. With anemia, the degree of its severity is directly proportional to the degree of invasion, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases, the strength of the immune system and the quality of the patient’s diet. There are known cases of latent disease without any symptoms.

Broad tapeworm is evident in stool and blood tests.
Treatment
To treat diphyllobothriasis, drugs are primarily used that involve the destruction of the parasite. In addition, drugs are used to treat anemia.
Folk remedies are also effective in treating the disease.
Drug treatment
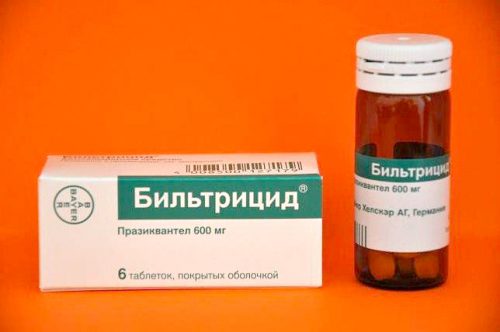
When detecting the presence of broad tapeworm in the body, a drug such as Biltricide .
The dosage must be prescribed by a doctor and, if necessary, it is adjusted.
The drug, acting on the parasite, paralyzes it, which leads to its death and exit. This drug has contraindications.
In addition, a number of other drugs directed against helminths are used, for example:
- Praziquantel - paralyzes the parasite. Can be used in children from 4 years of age;
- Niclosamide – used for children over 2 years of age and adults;
- Antihistamines are used together with antiparasitic drugs, for example, Suprastin, Tavegil .
Broad tapeworm: symptoms in humans and methods of treatment
The broad tapeworm (Diphyllobothrium latum) is a parasite from the Cestode class that causes the disease diphyllobothriasis. It is manifested by the penetration of the worm into the human intestine with the progression of characteristic clinical symptoms and B12-deficiency anemia.
wide tapeworm is a very dangerous parasite
Diphyllobothriasis: general information
The disease is classified as intestinal helminthiasis. Infected fish are the main factor in transmitting the parasite to humans. When eaten, immature forms of tapeworm enter the body. The prevalence of diphyllobothriasis is associated with the residence and life of people in areas near water bodies.
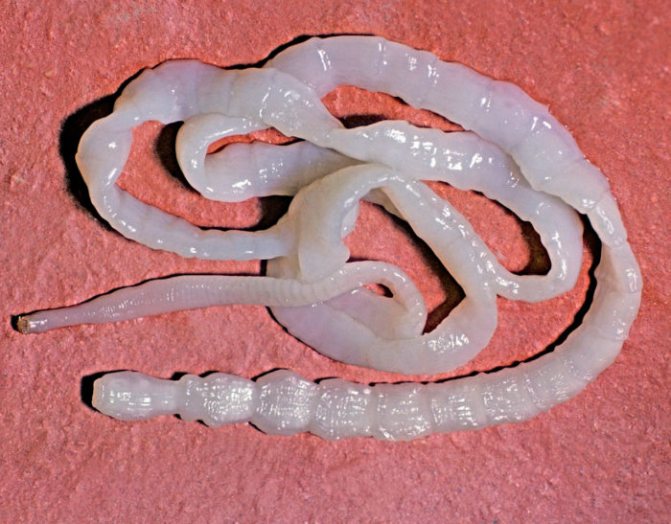
The total lifespan of the worm in the patient's intestines can be up to 20 years. The length of its body ranges from 2 to 10 meters. It consists of individual segments, the total number reaches 4000. Each of them can be separated from the body of the parasite and removed from the body.
In addition, eggs are formed in this part of the worm. They cannot mature in the human body, so they must be excreted in feces. They are oval in shape, covered with a double shell and a lid on one side. Reach sizes of 70 microns.
The worm itself changes three hosts during its development:
- The final remains are man, cattle, cats, dogs.
- Intermediate is the small crustacean Cyclops.
- Freshwater fish remain additional.
After the egg enters the environment, it is swallowed by small crustaceans in bodies of water. An intermediate form of the parasite, a procercoid, develops in their intestines. Then predatory fish (perch, pink salmon, ruffe and others) swallow the crustacean itself. In their muscles, the worm transforms into a plerocercoid, which can already infect humans.
In the process of consuming low-quality fish meat, immature forms of tapeworm enter the patient’s intestines and begin their active activity there.
Pathogenesis of disease symptoms
The main clinical signs of diphyllobothriasis are caused by its activity in the lumen of the human gastrointestinal tract.
There are several most important points that lead to the progression of symptoms:
- Mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the intestinal tube, which occurs at the sites of attachment of the parasite. These areas atrophy, and sometimes necrosis develops. As a result, the quality of digestion deteriorates significantly.
- Constant irritation of individual nerve endings of the intestine leads to disturbances in its motor activity. This is the cause of defecation disorders.
- The body's immune response to the waste products of a worm is the form of an allergy. At the site of attachment of the helminth to the mucous membrane, a focus of local inflammation is formed.
- Hypovitaminosis B12. The reason for this is the binding of gastric mucoprotein, which is responsible for the absorption of the corresponding biological substance. The helminth in this case absorbs most of the vitamin, causing the corresponding clinical manifestations of the disease.
In addition to the above mechanisms, there is a general decrease in immunity, which leads to the addition of concomitant infectious pathogens.
What are the symptoms of a person with this disease?
Helminthic invasion leads to the development of a number of pathological phenomena. All of them progress gradually and are associated with increased parasite activity in the intestines.
It’s worth starting with the fact that the incubation period of diphyllobothriasis is from 20 to 60 days. At this time, the patient may not note any particular complaints. The worm is just beginning its active activity, which is still invisible.
The first symptoms of broad tapeworm in humans are manifested by disturbances in the digestive system.
They are presented:
- Decreased appetite.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Painful sensations in the abdominal area.
- Changing the stool. It becomes irregular and runny.
- An increase in general body temperature.
When a large number of helminths accumulate in the intestines, they can even cause mechanical obstruction, which is a serious threat to the health and life of the patient.
It requires surgery to promptly remove the clump of worms. With a mild degree of progression, this formidable symptom can be eliminated with the help of drug treatment.
However, it is necessary to carry out therapy under the supervision of a doctor.
One of the most common signs of diphyllobothriasis remains B12-deficiency anemia.
It is caused by a malabsorption of the corresponding biologically active substance in the stomach and is manifested by a number of characteristic symptoms:
- General weakness.
- Dizziness and headache.
- Fatigue quickly.
- Disability.
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat).
- Paleness of the skin.
- Swelling on the legs and face.
One of the special signs that are characteristic of such a disorder in the blood system is the “varnished tongue.” It is represented by the phenomenon of glossitis (the formation of cracks in the tongue followed by atrophy of the papillae). A similar lesion can also occur on the mucous membrane of the entire oral cavity, gums, and esophagus.
Diphyllobothriasis often affects the human nervous system. Minor disorders of superficial and deep skin sensitivity appear. The “pins and needles” symptom often progresses.
Broad tapeworm symptoms and treatment are almost always the same in all patients. Very rarely, diphyllobothriasis can occur in a latent form without a pronounced clinical picture.
This may be due to a strong immune system, which is able to block the development of helminths for a long time.
However, in the absence of appropriate drug intervention, the problem will sooner or later enter the active stage.
Laboratory symptoms of helminthiasis
One of the important manifestations of the presence of a worm in the body is a change in the patient’s blood test. Thanks to a simple examination, a number of characteristic signs can be established that will confirm the suspected diagnosis.
The most important remain:
- A decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin with an increase in the color index.
- The appearance of Joly fragments or Cabot rings in the blood.
- Presence of megaloblasts and megalocytes.
- Decrease in the number of leukocytes and platelets.
The severity of these symptoms depends on the severity of the infestation.
How is wide tapeworm treated?
Treatment of broad tapeworm with medications involves the use of antiparasitic agents.
The most effective and in demand at the moment remain:
- Niclosamide (Fenasal) . It is used once in a dose of one to three grams orally. The amount of active substance required for use is determined by the doctor depending on the severity of the problem and the weight of the patient.
- Biltricide . A good anthelmintic drug, which is used in a dose of 25 mg per 1 kg of patient body weight. Used once. Positive reviews from almost every infectious disease specialist confirm the effectiveness of this medicine.
Adjuvant therapy involves following a diet with limited intake of fats and heavy proteins. In addition, cleansing enemas, which are performed to mechanically free the intestines from worm particles, demonstrate a good therapeutic effect.
The prognosis of the disease is favorable. The treatment is going well. Patients make a full recovery and continue normal household activities.
You might be interested
Important! All content presented on the site is for educational and informational purposes only, aimed at giving visitors to the resource a clearer understanding of various parasites and related diseases. It is strictly forbidden to use the information posted on the site for self-diagnosis and self-medication; always contact a specialist!
Source: https://parazitof.ru/borba-s-gelmintami/lentets-shirokij-simptomy-i-lechenie-u-cheloveka.html
Additional treatments at home
Some folk remedies help very well in the fight against broad tapeworm. Treatment at home should be used only as additional methods. It includes the use of some remedies that have proven themselves in the fight against the disease. The most effective are pumpkin and fern.
Herbs

Male fern extract requires some preparation before use.
2 days before taking the drug, you should follow a diet: do not eat fatty or spicy foods. Before starting treatment, you should drink a laxative at night.
In the morning, an enema must be performed on an empty stomach. Then he drinks the medicine according to the schedule prescribed for the age category.
After 30 minutes you need to take a laxative. And after 1 hour 30 minutes you can have breakfast, but the food should be light.
If there is no stool within 3 hours, then a cleansing enema is necessary.
Another very effective remedy in the fight against broad tapeworm is pumpkin seeds. They are also recommended by doctors for those who cannot take medications due to contraindications for children.
You will need 300 g of pumpkin seeds, which must be finely chopped. Then you need to fill them with 50-60 ml of warm water. Take the resulting mixture in the morning on an empty stomach. After 3 hours you need to take a laxative. After this, after 30 minutes, perform a cleansing enema.
Pumpkin seeds with carrots
For cooking you will need 3 tbsp. spoons of grated carrots and 30 g of well-crushed pumpkin seeds. Season with 2 tbsp. spoons of vegetable oil.
The resulting remedy must be taken on an empty stomach, and 1 hour 30 minutes after administration, drink 1 tbsp. a spoonful of castor oil for a laxative effect. This way the parasite will leave the patient’s body.
Pumpkin seeds with milk
This remedy is used for children. You will need peeled and well-ground pumpkin seeds, which are poured with milk. The dose is calculated based on the child’s age.
This remedy is taken on an empty stomach. If the child does not drink milk. You can use honey instead.
You can have breakfast after treatment. After 3 hours, you should give the child 2 teaspoons of castor oil or olive oil.
Broad tapeworm in humans: symptoms and treatment
Broad tapeworm is a helminth of the class of tapeworms (Cestoda), the causative agent of diphyllobothriasis, characterized mainly by dyspeptic disorders and deficiency anemia.
The geographical distribution of the tapeworm is very wide - Central and Northern regions of America and Europe, Japan, Central Africa, Chile. In Russia, infection with the tape parasite is most common in the Volga, Irtysh, Yenisei, Ob, and Amur basins.
Development cycle
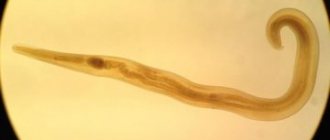
The wide tapeworm is the largest helminth of all existing ones, its length can reach 20 m. It consists of a small (3-5 mm) head, neck and long body. The head has 2 slits with the help of which the tapeworm attaches to the intestinal walls of the final host.
The body of the parasite consists of many rectangular segments (proglottids), which bud from the neck and gradually move towards the end of the body, filling with eggs - oval-shaped capsules measuring up to 75 microns. When released along with feces, the eggs contaminate the environment, exposing people to the risk of diphyllobothriasis. One helminth is able to release up to 1 million or more eggs per day.
The broad tapeworm is a hermaphrodite. The female ovaries and male testes are located in each segment. The digestive system in its usual form is absent. Nutrients (semi-digested food, vitamin B12) are absorbed by the entire surface of the worm's body.
The life cycle of the tapeworm occurs with a change of several hosts. The final ones are carnivorous domestic and wild animals (dogs, bears, arctic foxes, foxes, etc.) and humans. In their body, the tape parasite grows from a larva to an adult capable of reproducing. First, freshwater crustaceans act as intermediate hosts, and then the fish that feed on them.
The entire cycle of transformations of the wide tapeworm looks like this. The segments with mature eggs that have come off the end of the helminth leave the intestines along with the feces. In order to develop further, the egg of the broad tapeworm must fall into the water, where the larva hatches from it. To move through water, it has cilia that constantly vibrate.
The larva is swallowed by freshwater crustaceans (the first intermediate host), in whose body the parasite undergoes another molt. A fish that swallows an infected crustacean becomes a 2nd intermediate host. In it, the wide tapeworm develops into a plerocercoid - a worm-like larva 2-80 cm long, which is an invasive form for humans and animals.
Routes of infection
A person becomes infected with a broad tapeworm by eating undercooked or fried fish containing a helminth larva. Once in the human intestine, it attaches to its wall and begins to grow rapidly.
In 2 months, the larva of the broad tapeworm in the human body develops into an adult, which, under favorable conditions, can live in the host’s body for up to 20 years, producing a huge number of eggs during this time and causing great damage to health.
Living in the human intestine, the parasite has multiple pathogenic effects on the human body.
- The fixation organs (bothria) physically affect the intestinal mucosa, injuring it and causing inflammation.
- Metabolites secreted by the parasite inhibit the intestinal microflora, prevent the formation of red blood cells (reduce hemoglobin), and intoxicate the host’s body.
- By consuming nutrients and vitamin B12, the broad tapeworm deprives humans of some of the food they consume, leading to weight loss and anemia.
. The wide tapeworm is capable of regeneration. When there is a lack of glucose, tapeworms can shed their body (so-called destrobilization), and begin to grow again from the head.
Regeneration can also occur when parts of the helminth’s body are torn off during removal during surgery or during bowel movements. Therefore, to combat tapeworms, it is recommended to use drugs that have a paralyzing effect.
In this case, it is possible to bring the helminth out intact, along with the head.
Symptoms
Obvious symptoms of infection appear after about 2 months or more. Until this time, the symptoms of diphyllobothriasis are mild or erased.
After the tapeworm reaches sexual maturity, it becomes possible for its segments to appear in feces. If they are detected, we can confidently speak about infection with broad tapeworm.
The shape of the tapeworm segments has a peculiarity: their width exceeds their length, hence the name “wide”.
As the helminth grows, the symptoms of infection increase. The main ones:
- decreased appetite;
- excessive salivation;
- nausea;
- stomach ache;
- weight loss (often due to a good appetite);
- physical weakness, fatigue;
- anemia (caused by a deficiency of vitamin B12 absorbed by the tapeworm, as well as a decrease in nutrients entering the body due to their consumption by the helminth);
- glossitis (inflammation of the tongue);
- possible increase in the size of the spleen and liver;
- headaches and dizziness;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- fainting.
Severe infection also manifests itself as neurological and mental disorders. It is noted:
- ataxia (impaired muscle motility);
- paresthesia (numbness, impaired skin sensitivity);
- depression, nervousness, irritability.
Complications
The most serious complication of diphyllobothriasis is intestinal obstruction, caused by helminths blocking the intestinal lumen.
Diagnostics
The most obvious sign of tapeworm infection is proglottids in the stool. But they are not always found. The main way to diagnose diphyllobothriasis is microscopy of the patient's stool to detect eggs and tapeworm fragments.
Additional methods include laboratory blood tests.
- A general blood test can reveal anemia, which is a frequent companion to diphyllobothriasis;
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) allows you to detect antibodies formed as a response of the immune system to the presence of helminth antigens;
- Using PCR diagnostics, tapeworm DNA can be detected in the blood.
Treatment
You can get rid of broad tapeworm with the help of narrow- and broad-spectrum anthelmintic drugs.
- Biltricide with the active substance Praziquantel is widely used. Its mechanism of action is based on increasing the permeability of parasite cell membranes to calcium, which leads to paralysis of helminths. The dose of Biltricid is determined at the rate of 25-40 mg of drug 1 per kg of weight. Take up to 3 times a day, course of treatment – 3 days. Depending on the patient's condition, the doctor may prescribe a different treatment regimen.
- Broad-spectrum drugs containing albendazole may be prescribed.
Symptomatic and restorative medications are taken simultaneously with deworming drugs.
- To increase hemoglobin, cyanocobalamin (B12) and preparations with iron (Hemofer, Ferroplex, Aktiferrin, Ferronal) are prescribed;
- Pain is relieved with analgesic and antispasmodic (no-spa) agents;
- To normalize the digestive system and restore intestinal microflora, enzymes, probiotics and sorbents are indicated;
- The load on the liver is relieved with the help of hepatoprotectors.
Prevention
Methods for preventing infection with broad tapeworm include avoiding the consumption of insufficiently heat-treated fish. Broad tapeworm larvae die at a temperature of + 55 °C. Frying fish for 10 minutes, even on one side, ensures their death.
Strong salting (salt must contain at least 9%), keeping it for 24 hours at a temperature of –15 °C, or –10 °C for 3 days also makes the fish safe.
Broad tapeworm is not as dangerous as pork tapeworm; with timely and adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable. However, this does not mean that it can be treated with disdain.
Long-term diphyllobothriasis can cause great harm to the body.
Therefore, when the first symptoms appear that may indicate infection with a wide tapeworm, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnostic tests.
Source: https://glisty24.ru/parazity/shirokij-lentets-u-cheloveka/
Recovery period
Since the parasite causes serious damage to human health, after treatment it is necessary to carry out comprehensive recovery.
For example, you can use a collection consisting of equal parts of rose hips, black currants and raspberries. 1 teaspoon of the collection is poured with 1 glass of boiling water and left for 1 hour. Take 100 ml of infusion 3-4 times a day.
You can also use linen. You will need 1 tbsp. spoon of flax seeds, which needs to be poured with 1 glass of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours. Take 50 ml 3 times a day. This infusion helps restore the intestinal mucous membranes.
Initial signs of infection
For some time a person may not notice changes in well-being. The incubation period for diphyllobothriasis ranges from 20 to 60 days. Then the first symptoms of broad tapeworm associated with damage to the gastrointestinal tract occur:
- pain and discomfort in the abdominal cavity;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- bloating and increased gas formation;
- loss or increase in appetite.
Most often, a person mistakes these manifestations for signs of food poisoning or gastritis. And the parasite continues to poison the host’s body with waste products.
The parasite's habitat is freshwater bodies of water.
The broad tapeworm is a tapeworm type helminth, characteristic of the human body and some animals, and lives in fresh water bodies. It is not difficult to guess how a person becomes infected with this parasite. When eating contaminated fish that has undergone insufficient heat treatment, tapeworm larvae enter the body. The broad tapeworm causes a disease in humans called diphyllobothriasis; it parasitizes the walls of the large intestine.
The distribution of the wide tapeworm is typical for areas where there are many freshwater bodies of water. The invasion is most common in northern European countries, the northern USA and Canada. Adults have a higher risk of invasion compared to children, especially adults involved in catching and processing fish.
Description
The wide tapeworm can reach up to 10 meters in length; the worm has two suckers that resemble slits, and it is with their help that it clings to the wall of the colon. There are approximately 3-4 thousand segments of the hermaphroditic type on the body of the parasite; helminth eggs are formed in them. The eggs, as a rule, are oval in shape, have a yellowish-brown shell, and have a kind of cap at one end.
In humans, tapeworm eggs are also excreted along with feces, which can remain viable from three to thirty days, but they continue their further development only if they fall into water. In fresh water, after about two to three weeks, coracidia emerge from the eggs, and they are swallowed by an intermediate host, which is copepods. Already in their organisms, the coracidium is transformed into a procercoid and enters the organisms of additional hosts - predatory or migratory salmon fish.
The wide tapeworm clings to the mucous membrane of the colon and pinches it with its suckers, as a result of which ulcers appear and injured areas can atrophy. With multiple infestations, broad tapeworm can cause intestinal obstruction. To this is also added eosinophilia and catarrhal phenomena in the mucous membrane, which is caused by the increased sensitivity of the human body to tapeworm antigens.
A person may develop hypovitaminosis and vitamin deficiency B12 and folic acid of internal origin. Such phenomena occur due to diphyllobothriasis megaloblastic anemia. If the broad tapeworm parasitizes the body for a long time (up to 20 years), in this case anemia may be accompanied by damage to the peripheral nervous system and spinal cord.
Symptoms
Quite often, there are simply no symptoms of the disease caused by tapeworm. Often the symptoms are mild, manifested by a slight feeling of discomfort in the abdomen. However, in any case, you can observe the release of the helminth along with the feces.
If the symptoms of prolonged parasitism of the broad tapeworm are still pronounced, it is manifested by the following signs:
- Abdominal pain that periodically takes on the character of contractions. Similar symptoms may be accompanied by nausea.
- Increased secretion of the salivary glands.
- Appetite disturbances: sometimes it is increased, but it can sharply decrease; even with increased appetite, the patient can lose weight and his performance decrease.
- Symptoms of anemia: increased fatigue, palpitations, dizziness, glossitis.
- Symptoms of neurological disorders: paresthesia, numbness, ataxia, irritability, depression.
- Pain that occurs when eating.
- In severe cases, tapeworm can cause an increase in the size of the liver and spleen.
Before starting treatment, be sure to consult your doctor
Broad tapeworm is primarily diagnosed by taking a medical history and asking about clinical manifestations. The doctor asks the patient if he has been to endemic areas or eaten raw or poorly cooked fish. Next, the diagnosis of broad tapeworm is carried out using diagnostic studies in the laboratory.
The patient undergoes a general blood test, which determines whether the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is reduced, whether Jolly bodies and Cabot rings appear in the blood. Coproovoscopy is also performed to determine the wide tapeworm.
After diagnostic measures are carried out, the patient is prescribed treatment, which is aimed at eliminating the tapeworm from the body.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Treatment of demodex on the face with sulfur ointment
Treatment
To get rid of broad tapeworm with severe anemia, first of all, the patient is prescribed vitamin B12, 200-500 mcg intramuscularly. Administer two to three times a week for one month. At the same time, treatment is carried out with iron preparations (Hemofer, Ferronate, Ferronal, Aktiferrin).
The treatment, which is carried out in order to destroy the tapeworm, uses the drug Fenasal for its purposes. Treatment with Fenasal is carried out once, the dose is prescribed by the doctor, depending on the age of the patient and the clinical picture of the disease caused by the tapeworm.
Treatment to eliminate tapeworms can also be done using male fern extract and pumpkin seeds. Treatment of fern extracts is carried out in this way: for two days before taking the drug, follow a light diet, take a saline laxative at night, and in the morning give an enema on an empty stomach.
Here's how to remove tapeworm using pumpkin seeds: take 300 grams of dried seeds, grind them in a small amount of water and add a little honey, take the product for an hour on an empty stomach. This treatment is also effective.
Prevention
Prevention of infection involves following certain rules that will help avoid illness and unpleasant consequences due to the parasite;
- carefully examine the fish for the presence of parasites;
- purchase fish products only from trusted retail outlets;
- cook the fish for 30-40 minutes;
- Pouring fish should take at least 10 days;
- fish should be stored frozen;
- Maintain personal hygiene (wash hands thoroughly, use clean utensils);
- timely medical examinations of fish processing industry workers;
- compliance with sanitary standards on ships and improvement of river reservoirs where fish are caught.
Methods of infection

In order to avoid the penetration of uninvited guests into the human body, you should clearly understand where they are most often found. Therefore, an article such as the habitat of parasites will be extremely useful for the basics of prevention.
Basically, infection of a person or animal occurs after eating fish affected by plerocircoid. Poorly prepared or insufficiently heat-treated dishes can cause diphyllobothriasis. Also, the larvae do not die in lightly salted, dried fish, in shish kebab cooked over an open fire, or in caviar. Sliced bread and sushi lovers expose themselves to particular danger. You can become infected with tapeworm larvae by cutting up an infected carcass. For these purposes, be sure to use separate dishes and cutlery, and wash with a special detergent when finished.
It is not always possible to identify a contaminated product. The larvae are practically invisible to the eye. The fish appears healthy and has no spots or other signs of infestation. Potentially dangerous species include carp, salmon, pink salmon, pike perch, trout, and perch.
Forecast
The prognosis for recovery is favorable if all doctor’s recommendations are followed. But after recovery, a rather weak immunity is developed and therefore re-infection with diphyllobothriasis is possible.
The main thing that leads to a quick recovery is a timely visit to a doctor who will conduct an examination and prescribe treatment.
Experts do not recommend self-medication, since it is ineffective in the fight against parasites and can only worsen the situation.
Routes of infection
Fish is included in the diet of many people. Infection occurs if a person eats infected fish that has been poorly cooked. Stroganina and lightly salted fish are another common source of helminthiasis.
The routes of infection with diphyllobothriasis are fecal-oral and food. You can become infected by using a cutting board on which fish and then vegetables are cut.
There is a risk of infection when preparing fish kebabs, since such processing does not always cope with the larvae, so they can maintain their integrity.

Most often, infection occurs when a person eats infected fish.
In many cases, only one individual develops in the human intestine. When cutting large fish, the larvae are often visible to the naked eye. As a rule, they are located in the liver and muscle tissue. The carrier of the parasite (infected person) is not able to infect others.
The risk of developing diphyllobothriasis increases if:
- One of the family members is engaged in fishing.
- A person lives near fresh water bodies, the inhabitants of which are crustaceans.
- Raw fish or poorly thermally processed fish is consumed as food.
Late symptoms of invasion
In later stages of the disease, a person experiences signs of anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency. The following unpleasant symptoms are noted:
- weakness;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- dizziness;
- darkening of the eyes;
- drowsiness;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- fainting.

In humans, hemoglobin in the blood is greatly reduced, and most of the manifestations of invasion are associated with this. In addition, the patient is bothered by discomfort in the abdomen. It seems to him that someone is moving in his intestines. However, this is not due to the movement of the worm. The helminth releases special toxins that cause intestinal contractions. Because of this, patients experience a sensation of movement in the abdominal cavity.
Sick children's behavior changes dramatically. Psycho-emotional disorders arise due to poisoning of the body with neurotoxins secreted by the helminth. A sick child becomes irritable and cries often. His performance at school is declining due to memory deterioration. Children with diphyllobothriasis sleep poorly and often have headaches.
How to prevent infection
What to do to avoid becoming infected with broad tapeworm? Since the parasite is transmitted exclusively through fish, it is necessary to subject this product to thorough heat treatment. The tapeworm dies at temperatures above +55 degrees. Therefore, freshwater fish needs to be boiled for about 20-30 minutes, after cutting it into pieces. If the product is consumed salted, then during preparation you need to use a strong saline solution. This helminth can only live in freshwater conditions. The salty water environment destroys it. When frying, you need to flatten the fish in a frying pan so that it bakes better.
It is also useful to know about the types of fish that are most susceptible to infection by tapeworms. These are ruffe, burbot, perch, pike, roach, carp, pike perch, and carp. Such fish must be processed especially carefully. It is important to remember that an individual infected with helminths does not have any alarming external signs. It is impossible to determine helminthic infestation by type of product. It is useful to periodically undergo examination for worm eggs and consult a doctor at the first signs of anemia or problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
Methods for preventing infection
The main preventive rule is to consume river and lake fish only after sufficient heat treatment. Features of the death of plerocercoids: they die at temperatures above 60 degrees Celsius, or when deep frozen for more than a day at temperatures below -15 degrees. Fish should be fried for at least 25 minutes, large fish - at least 45 minutes. After cutting raw fish, wash your hands thoroughly with antiseptic agents. Invite all family members to do the same. To prevent helminthic infestation, it is strongly recommended to constantly adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
Parasite eggs
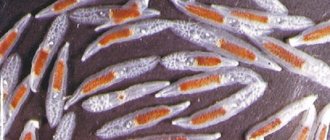
The eggs of the broad tapeworm are oval in shape and yellowish in color. On one side there is a lid through which the larva emerges. Every day, an infected person sheds about a million eggs in their feces. But these are immature forms. Their final development occurs in fresh water bodies. A photo of an egg under a microscope is shown below.
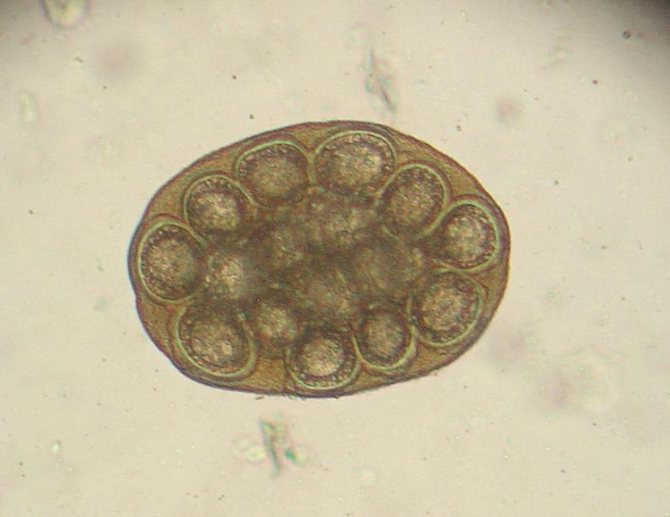
Patients often ask: is it possible to independently detect worm eggs in stool? It is impossible to see them with the naked eye, as they are microscopic in size. Only protruding segments can be found in feces; they look like a white ribbon.