Category: Unpleasant sensations
Flatulence, especially constant, can throw anyone off balance, and today on alter-zdrav.ru we will talk about its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and recommended treatment, both with medication and folk remedies. Naturally, if there is an excess of gases, it would be useful to follow a special diet.
What is flatulence
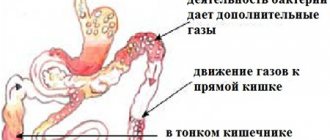
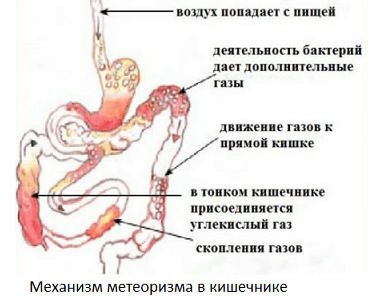
The presence of intestinal gases and their passage is a physiological process. These gases are formed during the breakdown of complex substances into easily digestible ones and consist of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and methane. Their quantity should not exceed 600 milliliters and be accompanied by extraneous symptoms - an unpleasant odor, a sharp sound. In case of foreign odors, the presence of hydrogen sulfide and ammonia was additionally detected in the emitted gas.
Approximately every third person in our country has encountered the problem of bloating and an increase in the amount of intestinal gas. If this problem occurs once, there is no need to worry. And if there is systematic bloating and is accompanied by other symptoms, treatment should be started.
This problem is called flatulence and is one of the common diseases of our time, due to the pace of life that does not leave time for a proper diet.
Intestinal flatulence causes many inconveniences, both physical and psychological. In the process of such a psychological problem, about three liters of intestinal gases are formed, which thinly line the mucous membrane in the form of mucous foam with small gas bubbles. With such a “neighborhood”, the mucous membrane cannot function at full strength and beneficial elements entering the body with food will not enter the bloodstream in the required quantities.
Due to the constant and uncontrolled release of intestinal gases, a person’s time in society is reduced, which may well lead to nervous disorders.
And if flatulence is accompanied by a fetid odor (the result of fermentation and putrefaction processes in the intestines), then the problem becomes completely aggravated.
https://youtu.be/https://youtu.be/TIShFZBbsyM
_
Medicines to treat the underlying disease
It is recommended to treat bloating in women using complex methods, targeting the main cause of discomfort. This includes not only traditional drugs, but also folk remedies, as well as a diet specially selected by the doctor.
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Sorbents | "Espumizan", "Kuplaton" | Medicines reduce gas formation. A woman is prescribed 2 tablets. up to 5 r. per day. |
| Prokinetics | "Forlax", "Motilium" | Strengthens intestinal function. The standard dosage of the drug is 1-2 sachets per day. It is recommended to take the medicine in the morning. |
| Enzymes | "Creon", "Pancreatin" | Medicines break down fats, plant fiber, and help properly absorb nutrients. Adults are prescribed 1-4 tablets. while eating. |
| Antispasmodics | "Papaverine", "No-Shpa" | The drugs reduce pain. The adult dosage is 1-2 tablets. up to 3 p.m. per day. |
| Antibiotics | "Rifaximin", "Furazolidone" | Medicines are prescribed for infectious lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. Considering the patient’s condition, he is prescribed 200 mg 3 times a day. per day. The course of therapy lasts 7 days. After 3 weeks, treatment can be repeated. |

Probiotics help with bloating. Medicines have a positive effect on intestinal flora, reduce the formation of gases and improve the digestive process. In some situations, the doctor prescribes antidepressants to the patient. The drugs eliminate the feeling of a full intestine, reduce fear and anxiety.
Symptoms of flatulence in an adult - associated signs
- - Bloating in the lower part of the abdomen;
- — Feeling of discomfort in the epigastric region;
- - Belching, heartburn;
- - Decreased well-being;
- — Significant increase in the passage of intestinal gases;
- - Rumbling in the stomach, audible from a distance;
- - Headache;
- - Hiccups;
- — Violation of the rhythm of heart beats;
- - A burning sensation behind the sternum;
- - Deterioration of sleep;
- - Constipation, diarrhea;
- - Decreased appetite;
- - Nausea;
- - Spastic pain radiating to the lower back or hypochondrium on the right side;
- — Violation of general or local blood circulation.
Causes of flatulence
There are many reasons that contribute to the development of flatulence in an adult. They depend on environmental conditions, the quality and quantity of food consumed and the presence of various individual diseases.
- Improper nutrition leads to dysbiosis and disruption of the functioning of intestinal enzymes. This has a beneficial effect on the development of fermentation and decay processes. Eating food on the go, while reading, watching TV or during a conversation leads to poor digestion and large pieces of food entering the stomach.
- Swallowing large amounts of air with food when talking, haste in absorbing food, frequent use of chewing gum and carbonated drinks.
- The quality of food consumed or its ability to produce increased gas (cabbage of any variety, beans, peas, beans, rutabaga, artichoke, milk, onion, ice cream, kvass, carrots, apple, mushrooms, wheat, raisins, pasta, fresh bread, fresh corn and cereals, eggs).
- The use of sugar substitutes Xylitol, Sorbitol (even found in some tablets, for example cough syrups).
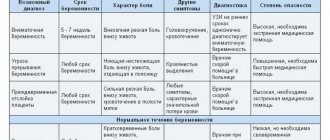
- Flatulence in women often develops during pregnancy, during which the large size of the uterus puts pressure on the intestines and other digestive organs, slowing down the passage of the bolus and provoking fermentation processes.
- The stomach may swell due to various intoxications and poisonings.
- Adhesive disease of the digestive organs.
- The occurrence of severe flatulence after surgical interventions on the abdominal organs. In some cases, there is a decrease in gastric motility, and the occurrence of bloating due to the prolonged presence of food in the stage of digestion by gastric juices.
- Systematically occurring stress and psycho-emotional stress. In this case, a spasm of the muscular walls of the intestines occurs and an increase in gas formation occurs due to the intestinal masses not being expelled. You can read about irritable bowel syndrome, of which flatulence is often a symptom, here.
- Atrophy of intestinal muscles. In most cases, this is observed in people aged 60-65 years
- Increased flatulence may occur when elevated to a significant altitude due to increased pressure in the intestinal cavity.
- Pathological processes in the abdominal organs (cholecystitis, gastritis with varying acidity, pancreatitis, duodenitis, intestinal obstruction, colitis, neoplasms of various etiologies, foreign objects entering the intestines, cirrhosis of the liver, diverticulosis, enteritis, the presence of parasites and much more).

Why does bloating occur in women?
The causes of bloating in women can be various factors: consumption of certain foods, gastrointestinal diseases, poor digestion of food, surgical operations. Flatulence can be caused by allergies, which are accompanied by high fever, runny nose, and rash. But more often, the disease in the fair sex occurs when the level of hormones changes: before menstruation, in the early stages of pregnancy, before menopause.
In early pregnancy
A pregnant woman often experiences heaviness, diarrhea or constipation, nausea and loss of appetite, and bloating. This happens during the first trimester, when serious changes occur in the body, affecting the functioning of all systems and organs. In the early stages of pregnancy, a woman’s body synthesizes a large amount of progesterone, a hormone that prevents the uterus from contracting, preventing rejection of the fetus. It affects the muscles of all internal organs, disrupting the process of emptying intestinal gases, which provokes flatulence.

Before your period
Before critical days, many women experience symptoms of increased gas formation. Each of them experiences their periods differently: one feels severe pain in the lower abdomen, while the other experiences dizziness and a general state of weakness, but the problem of bloating worries almost all women. This happens because before the onset of critical days, water retention occurs due to changes in hormonal levels, which causes flatulence. As a rule, with the onset of menstruation, all unpleasant symptoms disappear.

Diagnostic methods for flatulence in adults
Sometimes patients don’t even know which doctor to contact for flatulence, let’s say right away, in most cases, it’s a gastroenterologist, sometimes a local therapist, if the hospital doesn’t have a gastroenterologist, but this happens.
And what does the specialist pay attention to...
- Collecting an anamnesis, which includes questions about diet, food consumed, complaints, and associated symptoms.
- Visual inspection. Palpation, percussion, and assessment of the skin occur. With such an examination, you can find out in which part of the intestine the bloating was localized. It will give itself away with its characteristic sounds.
- General and biochemical blood test. With this laboratory diagnosis, the level of leukocytes, red blood cells and hemoglobin can be detected.
- A coprogram is a study of stool to determine the state of the intestinal microflora and the functionality of the digestive organs. And also inflammatory processes and the presence of parasites will not go unnoticed.
- X-ray examination is performed either with or without a contrast agent. Using this method, muscle tone, peristalsis and the structure of the gastrointestinal tract are checked.
- Ultrasound is a diagnostic method that allows you to detect tumors and cysts in the intestines.
- Endoscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach, and various parts of the intestine (duodenum, sigmoid, rectum and colon). During endoscopy, a biopsy of pieces of tissue or organs of the digestive system can be performed, as well as pronounced flatulence can be noted.
And now the most important thing - how to get rid of flatulence at home?
Diagnostics
To understand the degree of bloating, as well as to identify the cause of its development, doctors carry out the following manipulations.
- Palpation - special pressure, a kind of palpation of the abdominal cavity for any seals, pain points, and other changes that are not normal.
- Prescribes a coprogram - a stool examination that allows you to find out: how food is digested;
- what organs function with impairments;
- why did the consistency, color, smell of stool, etc. change?
Without tests, it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis, determining the cause of bloating
Only after the patient has passed all the necessary tests and undergone research will it be possible to determine the specific disease that has affected his body. You should also understand that the required medical measures will require a considerable amount of your free time and effort, however, they are really necessary.
Treatment of flatulence
Treatment of flatulence in an adult is in most cases medicinal and aimed at curing the primary disease.
Anti-flatulence medications used by doctors are aimed at:
- — prevention of dysbacteriosis;
- — improvement of intestinal motility;
- - increased proliferation of beneficial bacteria;
- — destruction of pathogenic microflora;
- — reduction of fermentation and decay processes;
- - acceleration of the passage of accumulated intestinal gases;
- - removal of toxins and waste from the body.
Groups of drugs used for flatulence
- Pancreatic enzymes. They help cope with low-quality and poorly chewed food, in case of eating disorders or intestinal diseases (Mezim, Pepsin, Creon).
- Antispasmodics help get rid of increased muscle tone and soreness (Papaverine, Drotaverine, No-shpa, Dicetel).
- Prokinetics work to increase intestinal motility. These drugs eliminate dyspeptic disorders (nausea, diarrhea, discomfort in the abdomen and others), facilitate the release of bile and accelerate the passage of food through the intestines (Metoclopramide, Peristil, Tegaserod).
- Adsorbents remove toxins and excess gases during flatulence (Activated carbon, Polysorb, Simethicone, Smecta).
- Carminatives. Their principle of operation is to divide large gas bubbles into smaller ones, which either exit or are absorbed by the intestinal walls (Espumizan, Pepsan - p).
- Probiotics are preparations containing acid-resistant live bacteria (Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Enterozermina).
- Prebiotics create a favorable environment for the proliferation of existing beneficial intestinal bacteria (Inulin, Hilak Forte).
Tablets (medicines) for flatulence - list and effect of popular and effective drugs
- Mezim. Improves the functioning of the pancreas and promotes complete absorption of fats, proteins and carbohydrates in the intestines. It is prescribed for chronic pancreatitis, inflammatory processes of the digestive organs and in case of a violation of the diet in a healthy person.
- Drotaverine. Reduces smooth muscle tone and improves motor activity. It is used for muscle spasms of the digestive system, genitourinary system and blood vessels.
- Metoclopramide. It is an antiemetic drug. Strengthens intestinal motility, eliminates dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting, hiccups. Accelerates the movement of food through the intestines and normalizes the functioning of the gallbladder.
- Polysorb. Removes toxic substances of various origins, pathogenic bacteria and allergens, poisons and alcohol from the body.
- Espumisan. Removes intestinal gases by improving intestinal perilstatics. It is used for increased gas formation, before diagnostic tests, and poisoning with certain drugs.
- Linux. Normalizes the composition of intestinal lactic acid bacteria. Treatment is prescribed for dysbacteriosis, constipation, and complex therapy for the treatment of gastritis.
- Inulin. It is a dietary supplement prescribed for conditions such as dysbiosis, colitis, cholecystitis, hepatitis and metabolic disorders.
Medicines for gas formation
Abdominal bloating (causes in women are provoked by physiological or pathological factors) is often treated by a person with medications that quickly eliminate discomfort and associated symptoms. There are medications for flatulence in every medicine cabinet, but it is recommended to take them strictly according to the instructions or following the doctor’s prescription.
Motilium
The medicine not only affects intestinal motility, but also breaks up large gas bubbles.
| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Domperidone |
|
| The adult dosage is 1 tablet. 3-4 r. per day. |

The discomfort caused by bloating and other associated symptoms (nausea, belching, heaviness) are reduced.
White coal
The medicine acts faster compared to activated carbon. Due to its powerful absorption capabilities, it easily eliminates increased gas formation and bloating. White charcoal also restores intestinal motility.
| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Silica Microcrystalline cellulose |
|
| It is recommended to take the medicine in 3-4 tablets. 3-4 r. a day before meals 1 hour. |
The medicine reduces the physiological load on the liver and kidneys, restores metabolism, and increases the body's defenses.
Espumisan
The drug is prescribed not only to patients with flatulence, but also before undergoing a special examination of the gastrointestinal tract.

| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Simethicone |
|
| The drug is taken 2 drops. 5 rub. per day. |
Espumisan reduces the number of bubbles that form in the intestinal tract. It also eliminates heaviness in the abdomen, bloating and pain.
Bobotik
The medicine destroys the bubbles that form and prevents the re-accumulation of gas. Reduces bloating, flatulence and pain.
| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Simethicone |
|
| The children's dosage is 8 drops. up to 4 p.m. per day. Adults are prescribed 16 drops. |
It is recommended to stop treatment with the drug as soon as all symptoms of flatulence have disappeared.
Phosphalugel
The drug has an enveloping effect, reduces stomach acidity, and protects the mucous membrane from the negative effects of pathogenic microflora.

| Compound | Indications | Contraindications | Application |
| Aluminum phosphate |
|
| The medicine is pre-diluted in 0.5 tbsp. water. The standard dosage is 1-2 packets of 2-3 rubles. per day 30 minutes before meals. |
Phosphalugel helps eliminate discomfort and pain in the epigastric area, also with heartburn and sour belching. The medicine allows you to cope with flatulence, which occurs as a result of non-compliance with the diet, after drinking large amounts of coffee. The same thing happens with nicotine or alcohol addiction.
Diet for flatulence
Nutrition for intestinal flatulence plays an important role in reducing the discomfort caused by the problem.
It is necessary to eat fractionally, in small portions, slowly and without talking, in order to prevent swallowing air with food; it is better not to drink food right away; it, mixing with the bolus of food, stimulates the manifestations of flatulence.
It is recommended to predominate in the diet of food with heat treatment; fresh fiber is more conducive to gas formation.
It is worth giving up:
- Fresh wheat and rye bread, baked goods;
- whole milk, sometimes with fermented milk, depending on tolerance;
- rich broths, fatty meats, smoked products;
- fast food and semi-finished products in any form;
- canned food, marinades and pickles;
- sausages, mushrooms;
- kvass, kumiss, beer (contain yeast);
- carbonated water, sweet store drinks;
- legumes, cabbage of any variety, onions, radishes, radishes, corn;
- boiled and fried eggs;
- sweet fruits (grapes, cherries, sweet apples, peaches, melons);
- sauces;
- coffee, cocoa.
What can you eat if you have flatulence?
- Rusks;
- lean meat, fish;
- soft-boiled eggs or omelet;
- with normal tolerance, low-fat varieties of cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt;
- greens, caraway seeds, zucchini, potatoes, carrots, beets, pumpkin;
- green tea, dill infusion, rosehip infusions;
- from cereals - rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, all cooked in water.
Flatulence - treatment with folk remedies
The most common recipe for increased gas formation is to take an infusion of dill, fennel, and carrot seeds.
One spoon of dill seeds (or other carminative plants listed above) is poured into a glass of boiling water in a thermos, let stand for at least 3 hours, strain, and drink throughout the day in equal portions for an adult.
Cumin is often used in folk recipes, brew 2 tablespoons of caraway seeds with a glass of boiling water, let it brew for 30-40 minutes, strain, consume 50 ml 4-5 times a day or 80 ml 3 times a day.
Teas with lemon balm and mint are used. They relieve spasms, have a calming effect, stimulate peristalsis and the secretion of digestive juices.
Infusions of chamomile, coriander, and ginger are useful.