There are different ways to become infected with hepatitis C. The main route of transmission is through infected blood. As a result, donors' blood is carefully tested to prevent hepatitis C infection.
Do you think it is possible to become infected with hepatitis C through a kiss?
Cannot
The virus is also found in small concentrations in the seminal fluid of men and menstrual blood of the fairer sex. The likelihood of infection increases with a weakened immune system.
general description
Hepatitis C is a chronic anthroponotic viral disease caused by infection with the hepatitis C virus. Inflammation of liver hepatocytes and their damage occurs.
Viral hepatitis C can be chronic or acute. According to WHO, about 150-170 million people worldwide suffer from chronic hepatitis C. In approximately 10-15% of people, the disease progresses to cirrhosis of the liver and possibly cancer.
Every year, about 350-500 thousand people die from liver cirrhosis and cancer associated with hepatitis C.
Types of disease
Hepatitis is divided into:
- viral: A, B, C, D, E, F, G;
- non-viral: toxic, autoimmune, radiation (arise from exposure to alcohol, poisons, chemicals, drugs, radio radiation, when the functions of the immune system are impaired).
Infectious species include only viral forms. They arise as a result of the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. The blood carries viruses to the liver, where they attach to hepatocytes. Infectious agents multiply quickly, destroy cellular structures, which leads to degeneration of the liver tissue.
There are several ways to become infected with hepatitis. But in any case, they are transmitted from infected people to healthy ones.
Routes of transmission of hepatitis C
- Use of parenteral drugs when sharing injection devices
- When providing medical care (reuse or insufficient sterilization of medical equipment - syringes and needles)
- Transfusion of blood and/or blood products contaminated with hepatitis C virus
- Having unprotected sexual intercourse with a patient with hepatitis C
- Transmission from a mother infected with hepatitis C virus in utero to her child
- Hepatitis C is not transmitted through breastfeeding, food, water, or household contact (hugs, kisses)
Mechanisms of infection in everyday life
Infection in everyday life and beauty salons is quite real. But not all conditions and cases predispose to infection. Let's figure out whether the virus can enter the body in the following situations:
- Through a wound on the skin. Hepatitis B and C are transmitted through the bloodstream. If a healthy person is scratched by an infected person, infection will occur if the blood of the latter gets into the wound of the first. You can definitely find out whether the virus has entered the body or not by taking tests.
- When bedding and hygiene items are for the personal use of a sick and healthy person. In this situation, hepatitis A and E poses a danger to women carrying a child. When living together with an infected person, everyone must follow hygiene rules. This infection is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. The source of infection is dirty hands and common objects. Washing with the same washcloth or eating from shared dishes is dangerous. For personal use you must have individual items. With this approach, the likelihood of infection is greatly reduced.
- Using someone else's razor. Cutting and stabbing instruments are sources of infection. Hepatitis B and C pass through them - diseases that enter the body through the bloodstream. People often get injured while shaving. They have scratches and cuts on their skin. If infectious blood remains on the instrument, a healthy person will receive a dangerous virus through it and become ill. Pathogenic microorganisms can live on the surface of various objects for a long time. You must only use your own personal razor.
- Dental treatment. Is it possible to become infected with hepatitis by visiting a dentist? This is not an idle question. Types C and B enter the body if the doctor uses insufficiently sterile instruments on which droplets of infected blood remain. When treating teeth, injuries to the mucous membranes and soft tissues are inevitable. Therefore, it is not in vain that people who care about their health watch how the dentist processes the instruments that are necessary for dental treatment.
- Procedures in beauty salons. The master serves many clients, including infected ones. Sometimes during cosmetic manipulations the integrity of the skin is compromised. Hepatitis C and B can be transmitted through poorly sterilized instruments. This happens when removing a cuticle, a hangnail, or trimming nail plates.
It is possible to become infected with hepatitis in a variety of everyday situations. Basic prevention protects against infection. Everyone needs to take precautions. We must demand from those around us that they adhere to hygiene rules, and not violate them ourselves. This reduces the risk of infection.
Symptoms of hepatitis C
From the moment of infection to clinical manifestations, it takes from 2-4 weeks to 6-12 months. The clinical manifestations of the disease itself are not strictly specific:
- General weakness
- Decreased appetite
- Increased fatigue
- Dyspepsia, manifested in the form of nausea, bitterness in the mouth, alternating constipation with diarrhea, pain in the epigastrium and in the right hypochondrium
- Sometimes there is a low-grade fever
- Rarely, yellowness of the skin, sclera
Causes of liver damage
The liver performs about 200 different functions to maintain normal functioning of the body:
- formation of bile for digestion;
- purification of blood from toxic substances;
- excretion of bilirubin (a breakdown product of red blood cells), cholesterol, hormones and medications;
- metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins;
- activation of enzymes and proteins to carry out various body functions and hormonal levels;
- storage of glycogen, minerals, and vitamins (A, D, E and K);
- synthesis of blood proteins (albumin);
- synthesis of blood clotting factors.
Cirrhosis leads to disorders of digestion, blood clotting, fat metabolism, thyroid function, and immunity.
The condition of the liver is affected by taking medications, alcohol, exposure to chemicals from water, air, and autoimmune diseases. Viruses that cause mononucleosis and cytomegalovirus infection lead to inflammation of the liver. However, for most diseases, the liver is just one of the targets. When making a diagnosis, doctors often mean the inflammatory process caused by specific viruses, which provoke the disease in 50% of cases.
Diagnostics:
The main methods for diagnosing hepatitis C:
- Biochemical blood test (for markers of liver damage and assessment of function - levels of ALT, AST, GGTP, total protein and its fractions, bilirubin, creatinine, urea, glucose levels)
- Short coagulogram
- Complete blood count (white blood cell count, platelet count, hemoglobin level, ESR)
- Determination of HIV infection, HBsAg, Anti-HBc, anti-HBs, anti-HAV
- Quantitative determination of hepatitis C virus RNA
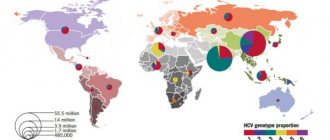
- Determination of the genotype of the hepatitis C virus
Who's at risk
There are certain categories of people whose likelihood of infection is excessively high. These include:
- drug addicts;
- patients who have received blood transfusions;
- people with a transplanted organ;
- those who have suffered liver disease;
- infants born to an infected mother;
- a person with many sexual partners;
- HIV-infected;
- medical workers, laboratory assistants, cosmetologists.
Hepatitis viruses act according to an elementary mechanism. They live where life is chaotic. It's easier to find victims in the chaos. People who follow a healthy lifestyle are less likely to contract any infectious disease.
Found an error in the text? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter
, and we will fix everything!
Source: venerbol.ru
Treatment of hepatitis C
Specific antiviral therapy is prescribed. There are many treatment regimens and depend on the genotype of the hepatitis C virus:
- HCV genotype 1a: 12 weeks - ledipasvir and sofosbuvir or 12 to 24 weeks - paritaprevir, ombitasvir, dasabuvir and ribavirin
- HCV genotype 1b: 12 weeks - ledipasvir and sofobusvir or 12 weeks - paritaprevir, ombitasvir and disabuvir
- HCV genotype 2: from 12 to 16 weeks - sofosbuvir and ribavirin. HCV genotype 3: 12 weeks - sofosbuvir, ribavirin and pegylated interferon or 12 weeks - daclatasvir isofosbuvir
Forecast
Modern progress in medicine and pharmacology makes it possible to successfully treat patients with this diagnosis. If you seek medical help in a timely manner, the probability of a complete recovery is at least 70%. The most sensitive to treatment is the second and third genotype of the pathogen. The effectiveness of the treatment directly depends on the following factors:

- Floor. Scientific research has proven that it is much easier for the female body to cope with an infiltrated infection;
- Age of the infected person. The younger the patient, the easier it will be for him to cope with the developed disease;
- Body mass. The presence of excess body weight is an obstacle to successful recovery from this disease;
- The degree of viral load on the body;
- The presence of minimal structural changes in the liver tissue, which were obtained during histological examination of biopsy specimens.
The criteria for complete recovery in this case is a negative test for the detection of RNA of the viral pathogen.
People suffering from this infectious disease, as well as carriers of the virus, are strictly prohibited from acting as donors of organs, blood, plasma and seminal fluid. Such patients are recommended to follow the rules of sexual hygiene, which include the use of barrier contraceptives (condoms). These measures will help avoid the spread of infectious pathology among a healthy population. If there is even minimal damage to the surface of the skin, it is recommended to refrain from visiting the swimming pool. It is important to remember that any damage to the skin or mucous membranes is an entry point for various infections, including viral hepatitis C.
If preventive recommendations are followed, a person is not at particular risk of contracting such a serious infectious pathology.
Main causes of serum hepatitis
Serum hepatoviruses B and C are considered the most dangerous when they become chronic. The virus is transmitted exclusively through blood, therefore the following causes of infection are distinguished:
- transfusion of infected blood;
- using a disposable syringe repeatedly (hepatitis C is a drug addiction disease);
- the use of unsterilized instruments with blood residues (in dental offices, tattoo and cosmetology salons, manicure salons);
- use of razors, toothbrushes of infected people;
- the child receives viral antibodies from the mother;
Blood transfusion stations use test systems that operate on the principle of enzyme immunoassay. However, no one checks the tests purchased from various suppliers. Therefore, situations occur when a healthy donor is told about an infection or, conversely, receives “pure” blood with hepatitis. Whole blood transfusions stopped in 2002.
Blood transfusions during operations are the most common cause of the spread of hepatitis C. For example, among patients with hemophilia, approximately 85% are infected.
There are preventive methods to protect recipients from infection:
- Quarantine – storage of blood until the donor is retested in six months.
- Leukofiltration is the removal of leukocytes from the donor’s blood plasma.
It is to leukocytes that herpes viruses and cytomegalovirus are fixed, but HIV and hepatitis, being inside the cells, cannot be screened out in this way. Since 2002, patients have been transfused with red blood cells, which simply cannot be “set aside” while the donor is being tested.
Among those wishing to donate blood there are fewer and fewer verified people, and more often those who end up are drug addicts who need money. An imperfect donation system is the main cause of hepatitis C.
Sometimes the results of tests for hepatitis C are false positive, and this is due to the peculiarity of the person’s immune status at the time of diagnosis. The presence of antibodies can be caused by several reasons:
- An undiagnosed autoimmune disease that results in inflammation due to an overactive immune response to one's own cells.
- Tumor processes that exist in the liver similarly change the biochemistry of the blood.
- Gastrointestinal tract infections caused by enterovirus, influenza.
- Tuberculosis intoxication, herpes, recent vaccination.
- The human body may have a hereditary feature - increased levels of bilirubin.
The cause of infection is an asymptomatic form of viral liver inflammation in the carrier. The average asymptomatic period before jaundice is 6 months, but it is not strict.
The disease can develop into a chronic latent form and proceed without yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin. The carrier can be recognized only by liver tests, detection of DNA or RNA of the virus and antibodies in the blood. Such tests are regularly carried out by medical workers, employees of kindergartens and other educational institutions. Every adult can get vaccinated against hepatitis B to reduce the risk of infection.
Viral hepatitis A
Viral hepatitis A is the mildest form of this infectious disease. An alternative medical name is Botkin's disease. This infectious disease differs from other forms of the disease in that a person who has recovered from the disease subsequently provides himself with lasting immunity to this group of viruses.
The incubation period of viral hepatitis A lasts from 7 to 45 days. Since the clinical picture is erased in most cases, it is quite difficult to detect the disease in a timely manner.
With this form of the infectious process, the following symptoms can be observed:
- enlarged liver, which is easily diagnosed by palpation;
- a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, especially the symptom intensifies after eating;
- nausea and severe vomiting;
- clayey feces;
- brownish urine.
As the infectious process develops, the clinical picture is complemented by the syndrome of general intoxication, which manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- pain in muscle fibers;
- headache for no apparent reason;
- increased fatigue;
- increased body temperature;
- lack of appetite;
- sleep disturbance.
As a rule, the elevated temperature lasts no more than 5 days, after which the patient’s condition improves for a short time, but the skin acquires a yellow tint. In some cases, yellowness appears on the eyeballs.
In more severe clinical cases, during the development of pathology, the patient may experience itching. After about 1.5–2 weeks, the symptoms almost completely disappear. In the third week, complete recovery occurs.
If hepatitis A is suspected, instrumental and laboratory tests are performed:
- general analysis of urine and feces;
- thymol test;
- ALT test.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor can prescribe the correct treatment.
Treatment of acute viral hepatitis includes the following measures:
- strict adherence to diet No. 5;
- bed rest;
- drug therapy.
It should also be noted that during the treatment period the temperature should not be lowered. It is advisable to keep it at the same level: +38 degrees. This therapy allows you to develop strong immunity and speed up recovery.
Drug therapy includes not only taking medications, but also special decoctions to improve bile secretion.
Read more: symptoms and treatment of hepatitis A.
A vaccine will help
Vaccination is indicated as an effective prevention of hepatitis B and D. Vaccination against hepatitis B has been done in many countries for a long time. In Russia, since 2002, a child is given a vaccine against hepatitis B in the first hours of his life. Vaccination is repeated at the age of one and six months of life. Children born before 2002 receive compulsory free vaccination at age 11 at school. Vaccination against hepatitis B is advisable at any age, because the hepatitis B virus is often transmitted from one person to another through tiny cuts on the skin and mucous membrane. Therefore, sources of infection, in principle, can be someone else’s toothbrush, nail scissors, comb, dental instruments and other household items. Moreover, the owner of a comb or razor may not know about the hepatitis virus circulating in his blood. Mutant varieties of the hepatitis B virus that “evade vaccination” are very rare.
There is no special vaccine against hepatitis D, but antibodies to hepatitis B protect those who have been ill and vaccinated from infection with hepatitis D (the main condition is the absence of HBsAg and the presence of antibodies to the hepatitis B virus).
According to the World Health Organization, at least 170 million people, or 2-3% of the world's population, are infected with hepatitis C. The highest prevalence of the disease occurs between the ages of 30-50 years, regardless of gender.