The need to determine the HCV genotype
Carrying out genotyping will clarify many points:
- Selection of therapeutic regimen.
- Duration of treatment.
- Estimated productivity of therapy.
- The likelihood of complications.
The hepatitis C virus has 6 genotypes. Below we will look at each of them and give their characteristic features:
- Genotype 1. Considered the most difficult of the species. You can order a treatment drug containing both active ingredients simultaneously (Hepcinat Plus). Doctors recommend not a universal, but a specialized regimen, which includes Sofosbuvir and Ledipasvir.
- Genotype 2. Less common. No high viral load. An excellent regimen is Sofosbuvir and Daclatasvir.
- Genotype 3. Easy to treat. In 80% of cases the prognosis is positive. Lack of treatment can cause serious complications (fibrosis, cirrhosis). A universal treatment regimen (Sofosbuvir and Daclatasvir) is recommended.
- Genotypes 4, 5, 6. Rarely encountered. You can get infected in Asian countries. Recommended therapy includes two substances - Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir.
What are the genotypes of HCV?
Genetic types of a virus are pathogen categories that differ from each other in a special set of genes. In turn, they have quasi-types (subtypes), constantly mutating and changing versions of the virus with extremely unstable genetic material.
Discoveries in modern science suggest that there are more than 8 genotypes of viral hepatitis C, but the most studied and treatable are only 6. These genetic categories of HCV are called the main ones.
With regard to geographical distribution, the most typical for the European continent are gens 1, 2 and 3. In turn, genotype 4 is more common in the United States and North Africa, 5 is characteristic of Asia, and 6 is characteristic of South Africa.
The study was supported by the research institute of the Indian pharmaceutical manufacturer Zydus Heptiza. Official website in Russia Zydus.ru
If we talk about age categories, then in patients who have reached adulthood, 1 genotype of the disease predominates with quasi-type “b”. In children, infection with genotype 5 or 6 is not observed at all, while infection with gen 3 is very common.
In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of cases of infection with hepatitis C genetic type 2 with quasi-type “b”. Approximately 9-10% of the total number of infected people suffer from a mixed disease, characterized by the presence of pathogens of different genotypes. Moreover, each subspecies of the pathogen has its own distinctive features and characteristics. Let's look at them separately.
1 genotype
The first genetic type has quasi-types a, b and c. It is found in all countries of the world, but it is most widespread in continental Europe, especially in the countries of the former USSR. On the territory of the Russian Federation, Belarus and Ukraine, infection with HCV gen 1a and gen 1b is most often observed.
The main feature of the flavavirus genotype under consideration is that the infection provoked by it is quite difficult to treat. The most dangerous quasi-type is b, since it very quickly becomes chronic, which greatly complicates the diagnosis of the disease.
Unlike most other strains, gen 1 is highly resistant to drugs and resistant to mutation. Therefore, in response to the question “Which genotype of hepatitis C is the most dangerous?” most hepatologists will name the strain in question.
The success of therapy for viral hepatitis C genotype 1 depends on the following factors:
- Patient age
- Stages of the disease
- The level of viral load in the patient's blood
- Compliance with diet and healthy lifestyle standards
Detection of the disease in the early stages provides a favorable prognosis when treating the disease.
2 genotype
The second genetic type has quasi-types a, b and c. Quite common in the world, but less common than other strains of hepatovirus. The second genotype of HCV is recognized as the most benign type of flavavirus. The disease provoked by it is characterized by a low viral load and a moderate course of inflammatory processes in the damaged liver.
If the disease is not diagnosed at an advanced stage, the risk of complications is low. 90% of the total number of patients recover, even with treatment with Interferon-alpha and Ribavirin. There are practically no relapses in this form of viral hepatitis.
3 genotype
The third HCV genotype has quasi-types a and b. Like the first strain, it predominates in the countries of the former USSR and is often found in continental Europe. Cases of infection have also been recorded in South Asia and Australia.
Genetic type 3 hepatitis C is the most studied of all HCV strains. The disease is treatable at different stages. With properly selected therapy, the health of most patients returns to normal.
The main danger of viral liver damage gen-3 lies in its complications. If treatment for the disease is not started in time, the patient may develop:
- Liver fibrosis . According to the research activities of scientists from Switzerland, fibrotic changes most often occur in the liver affected by genotype 3 flavavirus with quasi-type a. Currently, there are no medications that can completely cure fibrosis. However, with the help of modern drugs it is possible to stop destructive processes in a vital organ for many years.
- Steatosis. Fatty replacement of liver cells is observed in 70% of the total number of patients with this form of hepatitis C.
If the disease is allowed to progress, the complications listed above can lead to death or disability.
4, 5 and 6 genotypes
Hepatitis C genotype 4 has the largest number of quasi-types - a, b, c, d, e, f, h, i and j. This strain of flavavirus is most often found in the northern part of the African continent, mainly in Egypt.
Genetic types 5 and 6 have only one subtype each – 5a and 6a. HCV strain 5a predominantly predominates in South Africa, 6a – in Asian countries.
All the genotypes listed in this paragraph are currently poorly studied. What is certain is that, like other varieties of the HCV flavavirus, infection occurs through contaminated blood. You can become infected during unprotected sexual contact only if there is mechanical damage to the genitals or during menstruation in a female carrier.
How is the viral strain determined?
The genotype is determined using a specialized laboratory test - PCR analysis with genotyping. The virus does not remain in its previous form, it continues to mutate, so human immunity is not able to resist it.
The analysis is extremely sensitive. Its accuracy is 99%. Laboratory testing is carried out provided that, as a result of other diagnostic measures, HCV was detected in the population.
Indian manufacturers have provided the opportunity to buy the drug against different HCV genotypes. After a complete diagnosis, the patient will be able to order the drug based on the formed clinical picture.
Why is genotyping needed?
Genotyping is one of the most important blood tests needed to diagnose hepatitis C virus. This diagnostic method helps:
- Determine the therapeutic regimen, select drugs suitable for treating the disease, and their daily dosage;
- Establish a prognosis for the course of the disease and the effectiveness of its therapy;
- Predict the duration of the therapeutic course.
Thanks to modern technologies, it is possible to determine the genotype of the hepatovirus with maximum accuracy. For this purpose, blood samples from a pathogen carrier are examined.
The most effective methods for identifying the hepatitis C genotype are:
- Direct sequencing
- Polymerase chain reaction
- Reverse hybridization with membrane probing
Hepatitis with genotype 1b: how long do patients live?
Life expectancy with viral hepatitis C depends on the following factors:
- Genotype of the causative agent of the infectious disease.
- Degree of liver damage.
- Stages of the disease during the period of detection of infection.
- The presence or absence of concomitant chronic pathologies.
- The age of the patient and the characteristics of his body.
- The presence or absence of timely therapy.
But in the case of hepatitis C genotype 1b, how long do patients live? In the absence of therapy, the disease develops quite slowly. With the exception of unique cases of rapid progression of the disease, the patient may not be aware of the pathology for 10 years or more. With alcohol abuse, fast food and smoking, inflammatory processes in the gland progress.
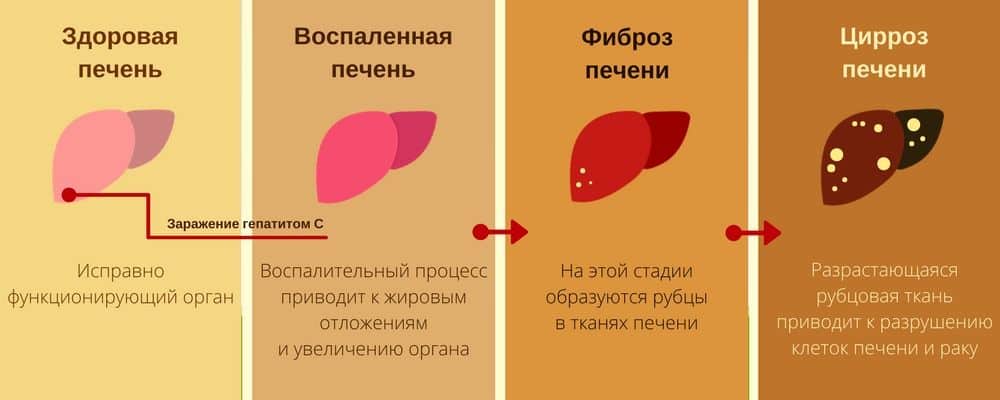
This leads to the gradual replacement of functional tissues with connective material and the formation of a life-threatening condition for the patient - liver fibrosis . The pathology develops over 4 stages.
The terminal stage of the disease is cirrhosis. Survival for this disease directly depends on the stage:
- Compensated cirrhosis - 50% of the total number of patients live more than 10 years, the remaining 50% live from 7 to 10 years.
- Subcompensated - 40% of patients live 5 years or more.
- Decompensated - 5-year survival rate less than 10%. The patient can die at any moment.
Another deadly complication of hepatitis C genotype 1 b and a is hepatocellular carcinoma , an aggressive form of liver cancer. Patient survival depends on the progression of the tumor process and the number of pathological foci. In some cases, the patient can only be saved by transplanting the damaged organ.
If the threat of death of the donor tissue is excluded, the survival rate of patients with a transplanted liver is 60% and is more than 20 years. When donor tissue is rejected, complications can occur, including death.
Is it possible to cure hepatitis C genotype 1?
So, viral hepatitis C is a deadly disease. Without treatment, death is only a matter of time. But in the case of hepatitis C genotype 1, is it possible to cure the disease without serious consequences for the patient’s body?
Yes, you can.
Previously (2-3 years ago), when treating genotype 1, big problems arose: Peginterferon therapy did not cope well with the virus. 1b mutated faster than the drugs could suppress it. The therapy helped achieve remission in only 70% of the total number of patients under the age of 40 years. Other age groups had virtually no chance of recovery. To this day, hepatitis C type 1 has a reputation for being difficult to treat.
Now modern therapy with antiviral drugs will cure 1 genotype of hepatitis C ( 1a or 1b ) in 3-6 months without much difficulty or obstacles. Moreover, in addition to the standard course of treatment Sofosbuvir + Daclatasvir for genotype 1, there is a separate course of treatment - Ledipasvir + Sofosbuvir. This is a combination drug that fights the virus as effectively as possible.
How to determine the genotype?
The first genotype of hepatitis C, like other forms of this disease, is transmitted through blood. Therefore, the leading way to determine the disease is a blood test.
To determine which type of hepatitis you are infected with, take a test called HCV Genotyping .
Attention! The genotype cannot be determined by tests for Antibodies, Qualitative PCR or Quantitative PCR.
Use only Genotyping .
You can undergo complex diagnostics to determine the genetic type of hepatovirus in the following clinics:
| Clinic name, region | Telephone | Cost of examination in rubles |
| Helix Laboratory Service Saint Petersburg | +7 (800) 700 03 03 | 1 355 |
| Medical laboratory Gemotest Moscow | 8 | From 1500 rubles |
| Invitro Network of laboratories in the Russian Federation, Kazakhstan and Belarus | 8 (800) 200-363-0 | 1,110 for genotyping and 3,680 for a comprehensive study |
| Diagnostic Center of Altai Territory Barnaul | +79050845400 | 800 |
| Lab 4U Network of laboratories in the Russian Federation | 8 800 555-35-90 | Cost depends on region |
| CityLab Moscow | 8-800-100-363-0 | 1 110 |
How to prepare for the upcoming test to determine genotype 1c? Below are recommendations from specialists at the International Clinic Freiburg:
- Refuse to eat 8 hours before reporting to the laboratory.
- Do not drink alcohol for 48 hours before donating blood.
- Avoid stress and eating fatty foods in large quantities.
Based on the test results, treatment methods for hepatitis C are determined that are suitable for a specific genetic type of the virus.