What is the best position for my baby to give birth?
Labor is almost always faster and easier if your baby is in a head-down position with the back of his head facing your belly. This position of the fetus is called “cephalic presentation, anterior view.” In most cases, the baby takes exactly this position by the end of pregnancy. Being in the forward position, the baby is most comfortable in the curve of your womb. During labor, the baby tilts his head forward so that his chin touches his chest. In this position, childbirth proceeds easier and faster, because in this case:
- During contractions, the crown of the baby puts gentle and even pressure on the cervix. This promotes the dilation of the cervix and the release of hormones necessary for the successful course of labor.
- During pushing, the child passes through the pelvic bones at an angle at which the smallest circumference of his head is in front. To better visualize this, try wearing a shirt with a tight-fitting high collar, without hiding your chin, and everything will immediately become clear to you.
- When the baby reaches the pelvic floor, he turns his head slightly so that the widest part of it is in the widest part of the pelvis. In this case, the back of his head may pass under your pubic bone. When born, the baby leaves the mother's body, sliding his face along the surface located between the vagina and the anus (perineum).
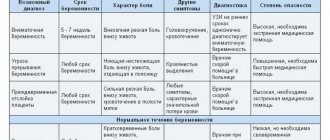
Signs and diagnosis of pain in the left side during pregnancy
Left abdominal pain during pregnancy varies in location and nature. Based on these signs, a preliminary diagnosis can be made. So, you need to listen and determine exactly how your left side hurts.
The pain may be:
- peritoneal – acute-piercing, aggravated by movement and turns of the body;
- visceral – having a “aching” character, sometimes cramping, most often occurring when the functions of the gastrointestinal tract are disrupted;
- unstable localization, “wandering”;
- radiating, manifesting itself in the area of healthy organs.
Short-term pain that is not periodic should not worry the expectant mother. Most likely they are associated with the growth and vital activity of the fetus.
But if they are constant, it hurts to sleep on your left side, the discomfort intensifies when walking, after eating, you need to undergo an examination to establish the cause of this condition.
What is back position?
The posterior position is a position in which your baby's head is down and the back of his head is facing your spine. By the time labor begins, approximately every tenth child is in this position. In most cases, these babies are born during a normal, vaginal birth, but this placement creates additional difficulties for the mother, especially if the baby's chin is raised up instead of down. As a result:
- you may experience lower back pain caused by the pressure of the baby's head on your spine,
- your water may break early,
- labor can be long and slow,
- you may begin to feel pushing before your cervix is fully dilated.
When the baby reaches the pelvic floor, he will have to turn almost 180 degrees in order to get into the position most comfortable for birth. This process may take some time, and it also happens that the child prefers not to roll over at all! In the latter case, he is born face up, as if looking at you. In addition, in this case, to help it be born, you may need forceps or a vacuum extractor.
Causes of pathological pain
Stabbing on the side can also occur for more dangerous reasons:
- Ectopic pregnancy. If the fetus is lodged on the left side in the ovary or fallopian tube, as it develops it will stretch and interrupt the area, causing acute spasm and possibly bleeding.
- Risk of miscarriage. If the pain in a certain area of the abdomen increases and resembles contractions, then you need to go to the hospital for treatment.
- Corpus luteum cyst. In the early stages, a cyst may appear in the left ovary, the torsion of the pedicle or rupture of which causes aching pain. It spreads throughout the abdomen and can radiate to the back, perineum and rectum. Frequent urge to urinate, constipation, and fever are also noted.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Digestive disorders (gastritis, ulcers, colic, diarrhea, high acidity, etc.) can be accompanied by spasms that radiate to different areas of the intestine. The cause of pain can also be other internal organs - an inflamed spleen or kidneys (pyelonephritis in pregnant women).
- Injuries. Sometimes during pregnancy, an old injury to the spine or lumbosacral region or lower extremities causes colitis in the left side.
- Diseases of the genitourinary area. Less commonly, the cause of pain on the right or left side can be an inflamed bladder (cystitis), stones in the kidneys or bile ducts, STIs and other pathologies. Renal colic most often radiates to the left lower back or abdomen. Also, a large fetus can impede the flow of bile from the ducts, which leads to their dyskinesia. Additionally, the following symptoms are noted: bitter taste in the mouth, belching, heartburn, bloating and colic.
As a rule, pathological pain is not asymptomatic and may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increasing sharp spasms that do not go away after a long rest and a warm bath;
- duration of pain for several days;
- vaginal bleeding;
- temperature increase;
- eating disorders (diarrhea or constipation, nausea and vomiting, heartburn, flatulence, loss of appetite, etc.);
- pale skin;
- numbness of legs and arms;
- generalized edema;
- high blood pressure;
- visual impairment;
- general weakness and apathy, sleep disturbances;
- pathological impurities (protein, pus, blood, mucus, etc.) in urine or feces.
With such symptoms, consultation with specialists of a narrow profile is necessary: a surgeon, traumatologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, urologist, etc. To make a diagnosis, it is important to describe in detail the nature of the pain: dull or sharp, aching or sharp, bursting or burning, etc.). If your left side hurts during pregnancy, you should not self-medicate and guess what it might be connected with. Contact your gynecologist with complaints and results of standard tests (stool, urine, blood). The doctor will assess whether there is cause for concern. Perhaps, to eliminate discomfort, it will be enough for you to use a prenatal bandage and spend a little time on bed rest.
Why do some children take a back position?
If your baby is in a posterior position, it may be due to the type and shape of your pelvis. The female pelvis is sometimes not round, but rather narrow, oval-shaped (the so-called anthropoid pelvis) or wide, heart-shaped (the so-called android pelvis or male-type pelvis). If your pelvis is not round but oval or heart-shaped, then there is a relatively high chance that your baby will take a back-to-back position at the widest part of your pelvis. The fact is that in this position it is easier for him to support his head. The mother's lifestyle also plays a role. It appears that posterior fetal position is much more common among European women than among women in developing countries, who are accustomed to working in the fields all day and eating or preparing food while squatting. The reason is quite obvious. When you watch TV, sitting comfortably in a chair, or work for hours at a computer, your pelvis is tilted back. In this case, naturally, the heaviest part of the child’s body (the back of the head and spine) also tends to lean back. So, in the end, the child ends up in a back-to-back position. If you work a lot or spend time standing, your baby will most likely take an anterior position in the pelvic cavity because your pelvis is always tilted forward.
Pain in the iliac region
Pain in the iliac region is not a specific symptom indicating a specific disease. Rather, this is a sign that should prompt a person to listen carefully to his feelings, analyze them and consult a doctor in a timely manner to find out the cause of the painful symptoms.
The iliac zone regio iliaca is part of the peritoneum, more precisely its anterolateral zone. The iliac fossa is not included in the anatomical international atlas as an independent zone; it is considered the groin region - regio inguinalis. In the international medical community, the iliac fossa is referred to as the ilioinguinal fossa. In clinical practice, this concept refers to the peritoneal area and the iliac fossa.
Pain in the ileum is a typical complaint from female patients, as it most often indicates many gynecological diseases. Of course, both men and even children suffer from pain in the iliac fossa. Also, a pain symptom can develop as a temporary sign of fatigue or excessive physical activity.
Causes of pain in the iliac fossa
Chronic or acute inflammatory processes in the uterine appendages, postoperative adhesions, various types of gynecological tumors.
Pain is provoked by a static body position, causing varicose veins of the pelvic venous system. This is typical for women who work sitting or standing. Varicose veins can also be caused by prolonged sexual abstinence.
if your period is delayed, what can you do? If a woman’s hormonal system functions normally, then the menstrual cycle is relatively stable. There may be a delay of 1-2 days, but this is a normal option that does not require treatment.
Pathology of the structure of the sigmoid colon or dolichosigma is one of the reasons that provokes pain in the ileum. In addition, lengthening of the sigmoid colon, which is unstable, that is, freely moves in the peritoneum, can result in intestinal torsion and intestinal obstruction
Source
How can I help my child get into a forward position?
You may have heard about so-called methods to give the fetus an optimal position. These are techniques that can help your baby achieve a forward position by changing your posture, especially when sitting. Remember: you want your pelvis to tilt forward, not backward. Therefore, when you sit, make sure that your knees are always lower than your hips. Try the following:
- Pay attention to the design of your favorite chair. It should not be such that your knees rise above your hips when you sit down. If this happens, try turning the chair 180 degrees, kneeling on the seat and leaning forward, leaning over the back.
- Clean the floors. Our grandmothers liked to repeat that cleaning the kitchen floor is the best way to prepare for childbirth. And they were right! While you are on all fours, your baby turns the back of his head towards your stomach.
- When driving a car, place a pillow on the seat so that your pelvis is elevated in relation to your legs.
- While sitting in front of the TV, lean forward, leaning over the fitball.
When you go to bed, you don't have to worry about your baby's position. However, the optimal sleeping position in late pregnancy is lying on your side, not on your back.
Causes and nature of painful discomfort in the left side
Can my left side hurt due to pregnancy itself? Of course, there are enough reasons for discomfort without pathologies of internal organs.
In the first trimester
Quite often in the first trimester of pregnancy, the left side feels tight, which is explained by endocrine changes. The pregnancy hormone, progesterone, has a relaxing effect on the muscles of the pelvic and digestive organs. The uterus begins to stretch, and a nagging pain occurs that is short-term in nature.
However, if it is accompanied by bloody discharge, then this is a dangerous symptom that may indicate a lack of progesterone and the threat of miscarriage!
In the early stages, you must warn your doctor about any abdominal pain!
In the second trimester
The second trimester is a time of intensive development of the baby, and this affects the condition of the expectant mother. The growth of the uterus causes increased pressure on the bladder and intestines, which fully explains the pain in the lower left abdomen. Due to the increase in circulating blood, the spleen also experiences stress. It increases in size and may from time to time remind itself of pain.
Will I actually be able to get my baby into the correct prenatal position?
Trying to bring a baby into the correct prenatal position is a long-known practice; there is nothing particularly new here. The first reports of “giving the fetus an optimal position” appeared in the 19th century. Today this method is known thanks to a description proposed by obstetrician Jean Sutton and published in the 1990s. Jean Sutton suggested that women in late pregnancy adopt an upright or forward-leaning position as often as possible. One often hears the question: does this really help, or does it simply create additional difficulties for a pregnant woman? So far, research on this method only confirms that in late pregnancy, staying in the knee-elbow position twice a day for 10 minutes really helps the baby take a forward position. Unfortunately, this does not seem to affect the position of the baby during birth. As for getting into an upright or forward-leaning position, Sutton recommends doing this regularly. If you practice the described technique during pregnancy, but despite this, the baby ends up in a posterior position when labor begins, this may be explained more by the shape of your pelvis than by your posture.
Diseases with pain in the right hypochondrium
Pain in the right hypochondrium is most often associated with liver disease
(viral hepatitis) and
with gallbladder pathology
(cholecystitis, cholelithiasis).
Viral hepatitis
is an infectious disease that primarily affects the liver.
There are three types of viral hepatitis
: A, B and C. Hepatitis A is transmitted through foodborne illness by consuming contaminated food and water. Hepatitis types B and C are transmitted parenterally: through blood, saliva, or through sexual contact with a carrier of this disease.
.
Symptoms
Main symptoms
developing hepatitis:
- Weakness;
- Increased fatigue;
- Nausea;
- Pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Jaundice discoloration of the skin;
- Darkening of urine and lightening of stool.
Danger If viral hepatitis is detected, the pregnant woman is urgently hospitalized in the infectious diseases department. The woman is prescribed bed rest, a strict diet, and medications to maintain liver function.
(Essentiale, Hofitol, Karsil). Taking antiviral drugs during pregnancy is strictly prohibited.
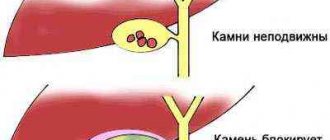
Cholecystitis
is an inflammation of the gallbladder.
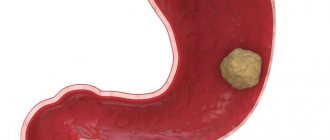
Gallstone disease
is a disease accompanied by the formation of stones in the gall bladder, or less commonly, in the bile ducts.
These diseases often complement each other and have similar symptoms
:
- Aching or sharp pain in the right hypochondrium, radiating to the right shoulder and shoulder blade;
- Belching with bitterness;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Bloating;
- Abnormal stool;
- Temperature increase.
Treatment
It is carried out only in a hospital in the surgical department.
At the first stage, conservative therapy
:
- Frequent split meals, dieting;
- Antispasmodics and painkillers to relieve pain;
- Antibacterial drugs;
- Drugs to improve the flow of bile (Allohol, Festal);
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs that have a choleretic effect (dill seeds, peppermint leaves, corn silk).
If conservative treatment is ineffective, the issue of performing surgery is decided.