Many patients complain that they have liver colitis, but do not even know what diseases this symptom may indicate. The fact is that pain in the right side in most cases does not indicate liver pathologies, but acute obstruction of the bile ducts. In this case, the painful sensations are sharp and cramping and can radiate to different parts of the abdominal cavity. Finding out the exact reason why colitis in the right hypochondrium and determining how to relieve acute pain is possible only through a complete study.
Major diseases
Acute cholecystitis
Is an inflammation of the gallbladder.
There are two types of the disease - acute and chronic.
The first most often develops as a result of exacerbation of cholelithiasis, caused by a violation of the outflow of bile. This occurs as a result of blockage of the common bile duct or its infringement by a gallstone, which is located in the neck of the bladder or in the duct.
The second form of the disease occurs gradually, the provoking factors are poor nutrition and psycho-emotional stress, as a result of which bile ceases to flow correctly into the bile ducts, its stagnation begins to damage the bladder, and as a result, infections occur.
Among the microbes that cause this disease, E. coli, enterococci and staphylococci play a special role.
Let's pay attention to the symptoms:
In the acute form, first of all, very severe pain occurs in the right hypochondrium, usually in the front. Its intensity can change in paroxysms, irradiation occurs in the back and lower abdomen, and zones of hyperesthesia appear. If you feel under the rib, the muscles tense, and there is also acute pain when inhaling. It is difficult to immediately feel the gallbladder. In addition, vomiting appears, body temperature reaches 39 degrees. If in this critical situation you do not call an ambulance, which will take the patient to the surgical department, then the inflammation will spread to the liver, pancreas, peritonitis and other complications may occur, for example, toxic shock.
What to do if your liver “hurts”: it’s important for everyone to know!
When there is pain on the right side of the abdomen, under the ribs, they most often say: “My liver hurts.” Especially if the day before you ate fried or fatty foods or drank too much alcohol. In fact, these pains most often have completely different causes. Oksana Romanenko, a gastroenterologist of the highest category at the Boris Medical Network, told us about them. Perhaps it will be a discovery for you that the liver does not hurt. Only the edge of the liver may hurt and only in very rare cases. This occurs in diseases such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, when the liver is stretched and very dense. As a rule, people suffering from these diseases know about them.
Various pathologies of this organ occupy one of the first places in terms of prevalence, and among the most common causes of mortality - fifth place. That is why, when pain appears in the liver area, you should pay special attention to them, because this gland makes itself felt only in the most serious cases.
WATCH THE VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: Three causes of pain when inhaling. Live healthy! 04/23/2019
Do you still think that healing your stomach and intestines is difficult?
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not yet on your side...
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the stomach is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Frequent abdominal pain, heartburn, bloating, belching, nausea, bowel dysfunction... All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause? Here is the story of Galina Savina, about how she got rid of all these unpleasant symptoms... Read the article >>>
Unpleasant and painful sensations in the area where the liver is localized, aggravated by inhalation of air, usually indicate the progression of cholecystitis. They are associated with the presence of stones in the gallbladder, which completely or partially block the ducts.
But pain when inhaling in the right hypochondrium can accompany other diseases not related to the liver and nearby organs. A gastroenterologist and neurologist will help to correctly diagnose the pathological condition.
Causes of dull pain when taking a deep breath anywhere in the right hypochondrium
If the nature of the pain syndrome is aching, pulling or dull, then the following diseases can provoke it:
cirrhosis; acute or chronic hepatitis; liver cancer; cholangitis; parasitic infestations in the right lobe of the liver; calculous and non-calculous cholecystitis; intestinal diverticulosis; adrenal tumors; colitis in the early stages of development; fatty hepatosis; pyelonephritis of the right kidney; congestive heart failure; hypomotor biliary dyskinesia; bruised or broken ribs; upper acute paranephritis.
Why does a sharp pain occur in the hypochondrium on the right side when inhaling?
When the pain is very intense, it indicates the presence of a surgical emergency (“acute abdomen”), for example:
damage and ruptures of the membranes of internal organs; intestinal obstruction; acute pancreatitis; blockage of the bile duct; appendicitis; renal colic; abdominal myocardial infarction; inflammation of the gallbladder; thrombosis of internal veins and arteries.
Also, sharp or stabbing pain when inhaling in the right hypochondrium is characteristic of the following pathologies:
shingles; colon tumors; urolithiasis disease; necrosis of the renal papillae; intercostal neuralgia; colitis; lumbar osteochondrosis; thrombosis of the cava or hepatic vein; stomach ulcer.
Many patients complain that they have liver colitis, but do not even know what diseases this symptom may indicate. The fact is that pain in the right side in most cases does not indicate liver pathologies, but acute obstruction of the bile ducts. In this case, the painful sensations are sharp and cramping and can radiate to different parts of the abdominal cavity. Finding out the exact reason why colitis in the right hypochondrium and determining how to relieve acute pain is possible only through a complete study.
Causes of tingling in the lower abdomen in women. Why tingling in the lower abdomen - possible causes
The most common cases of complaints of tingling in the lower abdomen are observed during pregnancy. Stitching pain and tingling in the abdomen appear with a disease such as intestinal diverticulitis. Tingling in the lower abdomen may not be related to gynecology. Inflammation of the appendages may also accompany tingling in the abdomen.
Similar symptoms can be observed at different periods of life: before menstruation, in the middle of the cycle or during pregnancy. Discomfort in the lower abdomen is most often associated with gynecological problems. True, in some cases this may also be a sign of problems with the urinary system or intestines. It happens that a woman has a tingling sensation in her lower abdomen before her period.
Causes of abdominal pain
The problem may appear in the middle of the cycle. It's all about ovulation. The process is accompanied by rupture of the follicle, which becomes the main cause of tingling in the lower abdomen. Here you should remember that tingling may be its first sign. If the expectant mother has a tingling sensation in her lower abdomen, perhaps she is simply not eating properly.
Disturbance in the gastrointestinal tract
For girls who do not intend to become mothers in the near future, tingling may indicate a common cold. If the discomfort in the lower abdomen is short-term and does not recur too often, then there is no need to sound the alarm.
Tingling and discomfort in the lower abdomen is a common symptom, characteristic of both women and men. In women, tingling in the abdomen may indicate natural processes such as menstruation or pregnancy. One of the common causes of tingling in the lower abdomen is appendicitis. It can occur in both women and men.
Pathologies of pregnancy
In addition to Crohn's disease, the intestines can signal possible diverticula and tumors. In acute appendicitis, discomfort in the lower abdomen is replaced by sharp pain. The person may experience attacks of nausea and vomiting. An increase in temperature is also possible.
Unlike men, tingling in the lower abdomen for women is a characteristic symptom of the first trimester of pregnancy. However, during a normal pregnancy, a woman may feel a slight tingling sensation on the right side. Tingling in the lower abdomen, in this case accompanied by severe pain. Painful sensations come from the right and have a pulling or aching character.

Intestinal diverticulitis
Sometimes pain on the right side, as well as tingling in the lower abdomen, are signs of Crohn's disease. This disease is dangerous for both women and men. In addition to pain on the right side, this disease is characterized by an inflammatory process in the intestines. The causes of Crohn's disease are disorders of the immune system.
The danger with this disease is ulcers that form on the intestines during the development of the disease. Also, with intestinal tumors, problems such as obstruction and bleeding are possible. In many cases, these symptoms indicate malignant tumors.
However, it is characterized by frequent constipation and is located in the left abdomen. A disease such as diverticulitis is especially dangerous due to the formation of suppuration in the intestines and the development of fistulas.
Tingling in the abdomen is accompanied by paroxysmal pain. During the development of diseases of the upper urinary tract, pain and tingling in the abdomen radiate down to the groin. Sometimes the patient feels sharp pain when urinating.
Causes of acute pain in the right hypochondrium
Painful sensations in the area of the liver projection are the main manifestation of cholelithiasis. They bother 75% of patients with this pathology, mostly men. Pain occurs if sharp stones injure the walls of the gallbladder or if large stones block the bile ducts.
The causes of pain in the liver area may vary, but they are mainly associated with various disorders of the outflow of bile into the duodenum. Among them are:
- spasm of the biliary tract;
- obstruction of the ducts associated with their blockage by stones or mucus;
- the process of moving a stone through the bile ducts;
- spasm of the sphincter of Oddi or its blockage;
- eating junk food or alcohol.
Inflammatory processes in the gallbladder or biliary tract (cholecystitis, cholangitis) can also cause hepatic colic. A characteristic sign that the symptom is associated specifically with these diseases is pain in the right side that becomes constant over time. In addition to painful sensations, the patient complains of a general deterioration in health, tension in the abdominal wall, and changes in the color of urine and feces.
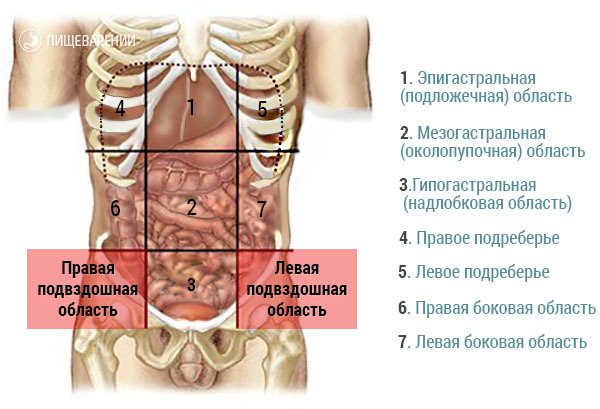
Causes of pain in the right side under the ribs
The appearance of a pain symptom in the front under the rib on the right is associated with many diseases. Not only the liver, pancreas, and stomach, which are in the projection of pain, can hurt, but also the heart, lungs, and spine. Many diseases may have a similar clinical picture, so only a medical examination will help differentiate the cause.
Liver diseases
The liver is located in the upper part of the abdominal cavity behind the ribs on the right, so pain concentrated in this area is often associated with inflammatory, viral, infectious, destructive damage to this organ.

Liver pathologies causing pain in the right side of the abdomen:
- viral hepatitis - inflammation of the liver can be acute or chronic, accompanied by pain of varying intensity and signs of jaundice (yellowing of the skin, itching);
- cirrhosis - heaviness and pain in the liver area appears in the later stages of the disease, characteristic signs are ascites, “stars” on the abdomen, swelling in the legs;
- hepatosis – intense pain syndrome that occurs simultaneously with fever, severe vomiting, and loose stools;
- liver cancer and metastases - the frequency and severity of pain increases as the cancer progresses.
Patients with serious liver pathologies practically cannot tolerate fatty foods and quickly lose weight.
Gallbladder diseases
A small hollow organ that performs an important function in the digestion process often bothers women. Unpleasant sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium are a constant companion to gallbladder diseases. Despite the latent (hidden) course of pathologies, pain will definitely appear sooner or later.
| Name of the disease | Features of the clinical picture |
| Cholecystitis | The painful focus is localized in the center of the inflammation and spreads to the subscapular region on the right. The symptom is accompanied by heaviness in the right hypochondrium, bitterness in the mouth, nausea, and less often vomiting. |
| Cholelithiasis | Metabolic pathology with the formation of gallstones may not show itself for years. Pain occurs when the mucous membrane is irritated by stones as they move along the biliary tract. |
| Empyema of the gallbladder | Severe painful sensations against the background of an increase in body temperature to high values are characterized by an inflammatory process with the accumulation of a large amount of purulent secretion in the organ cavity. |
| Perforation | An “acute abdomen” refers to a rupture (perforation) of the gallbladder wall. This dangerous condition is accompanied by severe pain and bile discharge into the abdominal cavity. |
Pancreas problems
The main cause of girdle pain in the hypochondrium is pancreatitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the pancreas, in which pain is constantly present and is not relieved by painkillers. Minor relief occurs if you sit down and lean forward a little. The disease can be recognized by additional signs: weakness, sweating, severe nausea on an empty stomach, uncontrollable vomiting with bile.
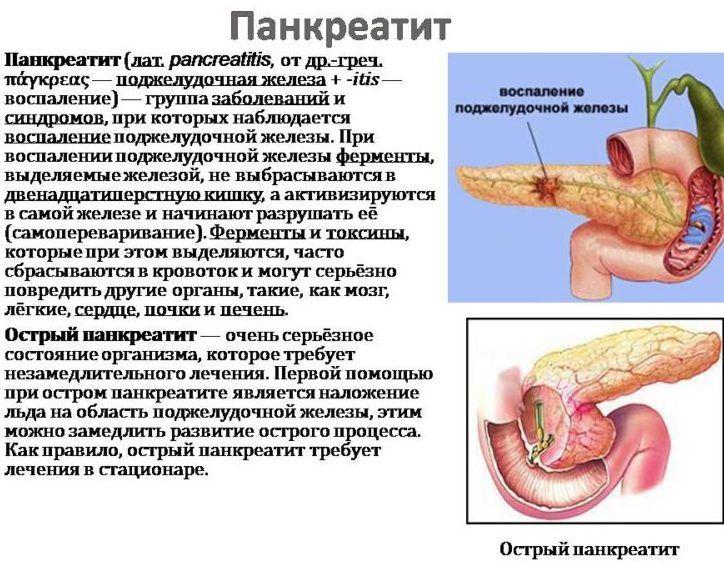
Bowel diseases
When the stomach is full, and pain periodically appears in the navel area, spreading to the right hypochondrium, groin area and lower back, an examination of the intestines is carried out. The upper part of the small intestine covers the projection of the lower edge of the right rib. Inflammatory processes in the small and large intestines are a common occurrence. They cause bloating, impaired bowel movements (constipation and diarrhea), feces may contain mucus, pus, and streaks of blood.
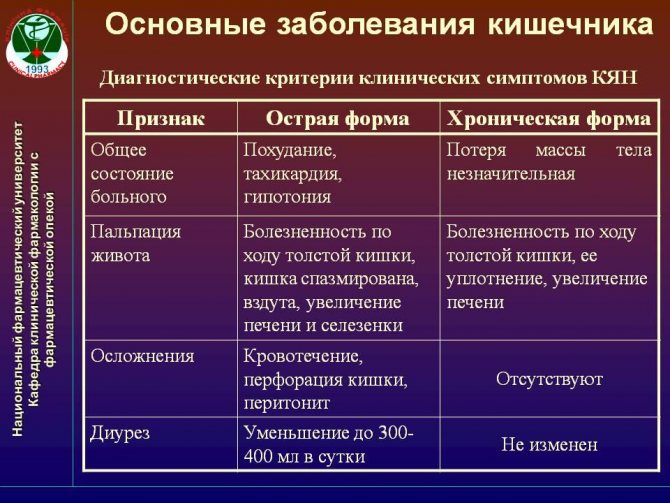
Kidney problems
Right-sided pyelonephritis - inflammation in the renal pelvis is manifested by aching pain from the back, involving the area of the right hypochondrium at the top, frequent urination, hyperthermia. If the right side suddenly becomes ill, the pain impulse is cramping, piercing, does not go away when changing body position, spreads to the area of the external genital organs and the inner surface of the thigh, pain under the rib - this is renal colic. It develops with kidney stones, when stones damage the ureteral mucosa.
This is a condition requiring emergency medical care and hospitalization.
Muscle diseases
Myositis is an inflammatory lesion of muscle tissue. A disease with severe acute pain appears after hypothermia or sudden lifting of heavy objects. Intense physical activity, prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, sudden bending, cause overstretching of muscle fibers and their micro-tears. Temporary pain may be a consequence of the accumulation of lactic acid after intense sports training. This is a manifestation of a normal physiological process that goes away without special treatment.
Intercostal neuralgia
Disease of the peripheral nervous system has a characteristic clinical picture:
- piercing, burning pain in the ribs radiating to the collarbone, lower back and lower edges of the ribs;
- the symptom persists day and night;
- pain increases with inhalation, coughing, sneezing, movement;
- the pain intensifies when pressing on trigger points in the thoracic spine, between the ribs, or when squeezing the chest;
- severe tingling along the nerves;
- muscle twitching;
- redness or paleness of the skin.
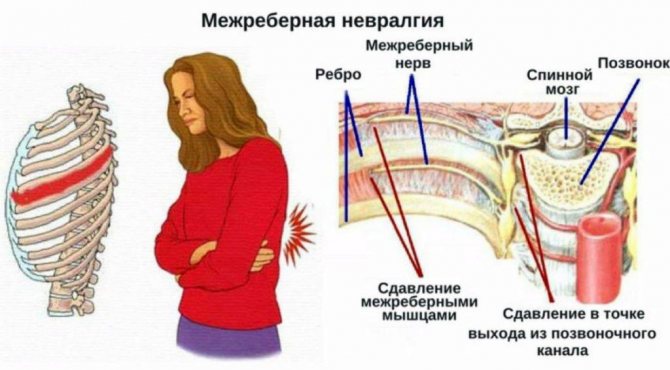
The root cause of the disease is pinching of the spinal roots in the thoracic spine. There is numbness in the area of the affected vertebrae when pressed.
Gynecological problems
In women, with unpleasant sensations in the right side, the lower abdomen may pull. This symptom is often included in the clinic of diseases of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes (adnexitis, endometriosis). Ovarian cysts cause a cutting pain reaction, and if the tumor is torsioned or ruptured, it causes nausea, vomiting, and uterine bleeding.
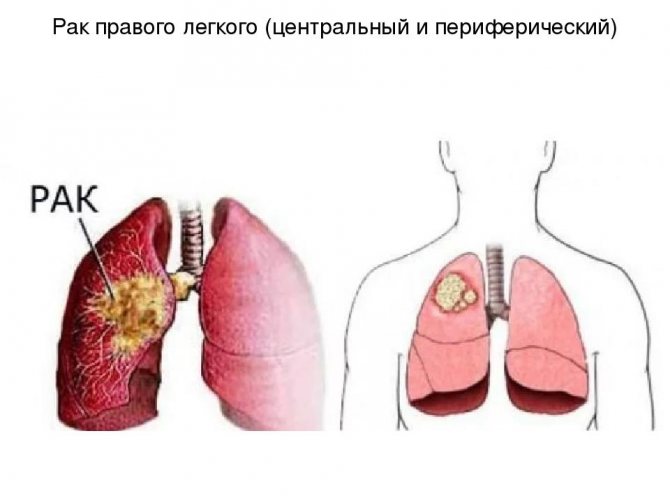
Diseases of the right lung
When pressing pain in the right side in front is accompanied by a wet cough and increased body temperature, the development of inflammation of the right lung cannot be ruled out. Intoxication and severe respiratory dysfunction appear with pleurisy, when the pathological process spreads to the pleural layers.
The person is in a difficult situation, it is difficult for him to take a breath, his veins can be seen pulsating. He takes a forced position, lying on his right side. The cause of pleurisy can be not only inflammation, infection, tumors provoke a serious illness. The side hurts due to cancer of the right lung, while the person quickly loses weight, the skin takes on a gray, waxy tint.
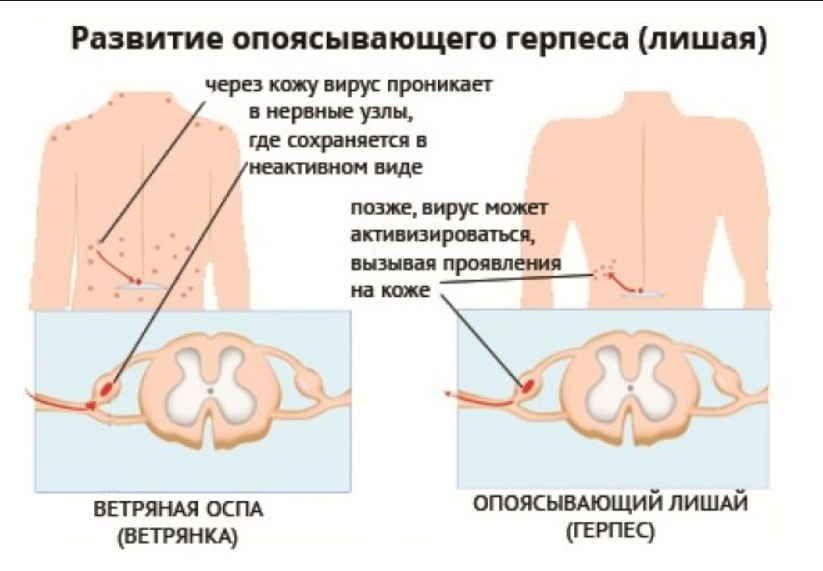
Shingles
The causative agent of the disease, the chickenpox virus, causes unpleasant sensations on the right side of a neurological nature. Rashes in the form of swollen red blisters, itchy skin, tingling at the site of the rash - a typical picture of the pathology. A herpetic infection lasts 3–4 weeks if treated promptly. In some patients, after the rash disappears, postherpetic neuralgia develops, which is difficult to treat.
Acute appendicitis
Inflammation of the appendix begins with epigastric pain, which after a couple of hours moves to the right side of the abdomen. Body temperature rises slightly (up to 38 degrees), nausea and vomiting may occur. The condition is an emergency and requires urgent surgical treatment.

Hepatic colic and its manifestations
Hepatic colic is a term that refers to acute pain in the right hypochondrium. In most cases, it is caused by a spasm of the gallbladder muscles or the passage of a sharp stone through the bile ducts. Unlike the constant sensations of hepatitis or cirrhosis, the pain is not constant and often goes away on its own.
Colic in the liver can be distinguished by the following signs:
- its localization is in the area of the right hypochondrium, less often extends to the upper part of the abdominal wall;
- in some cases, the patient has a stabbing sensation in the sternum, shoulder blade or neck, which can confuse the patient, reminiscent of an angina attack;
- pain is accompanied by nausea and vomiting with bile;
- the patient cannot find a comfortable body position in which the attack would stop;
- if vomiting does not stop for a long time, this may mean that the pancreas is involved in the process;
- acute bloating is observed.
An attack of pain can last from 15–20 minutes to several hours. Colic, which occurs when a small stone passes through the bile ducts, will be especially long-lasting. If the attack does not stop, this may indicate acute cholangitis or cholecystitis. Body temperature may also increase; it will return to normal levels only after the pain is relieved.
Blockage of the biliary tract can also be accompanied by obstructive jaundice. If bile does not exit into the duodenum, its components enter the bloodstream and are distributed throughout the body. Normally, they are excreted in feces and urine, coloring them in a characteristic shade. In case of acute blockage of the bile ducts, it accumulates in the gallbladder, causing expansion and inflammation of its walls, which is accompanied by acute pain.
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract
Disorders of the intestines and inflammatory processes in the intestinal walls are the most common causes of intestinal colic on the right side. In order for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis, the patient must accurately describe the nature of the pain and its location. Acute colic on the right side, repeated regularly, may be a sign of serious illnesses requiring urgent hospitalization: Crohn's disease and diverticulitis. No less dangerous causes of this pain syndrome are intestinal infections, colitis and duodenitis.
Diseases based on the location of pain
Foodborne illnesses and poisonings
Intestinal infections and food poisoning are usually accompanied by cramping or nagging pain in the lower abdomen, but with moderate damage, the pain syndrome can resemble intestinal colic. Bacteria (salmonella, staphylococcus, hemophilus influenzae) and viruses can cause intestinal infections. The most common viral infection is intestinal influenza caused by rotaviruses.
Infections of any type are always accompanied by pronounced symptoms, manifested by the following signs:
- severe intoxication;
- refusal to eat;
- heat;
- chills;
- frequent, profuse loose stools;
- change in the consistency of stool (they become liquid and foamy);
- vomit.
Localization of acute pain in surgical diseases
Only an experienced doctor can suspect an intestinal infection if the pain is stabbing, so you should not delay going to the hospital - this can lead to severe dehydration and deterioration of well-being.
To treat most infectious intestinal diseases, a standard treatment regimen is used, presented in the table below.
| Group of drugs | What medications are included? | Image |
| Antibiotics and antibacterial agents (for bacterial infections) | "Clarithromycin", "Enterofuril", "Amoxicillin", "Flemoxin", "Zinnat", "Hemomycin" | Hemomycin |
| Antiviral medications (for viral infections) | "Anaferon", "Interferon", "Arbidol", "Tiloron", "Ergoferon", "Amiksin" | Amiksin |
| Rehydration products | "Regidron" | Regidron |
| Digestive enzymes | "Pancreatin", "Creon" | Creon |
| Histamine blockers | "Suprastin", "Diazolin", "Zodak" | Zodak |
| Preparations with probiotics and prebiotics | "Linex", "Bifiform", "Acipol", "Normobakt", "Yogulakt" | Yogulact |
| Sorbents | "Neosmectin", "Activated carbon", "Enterosgel" | Enterosgel |
Important! In some cases, food poisoning and intestinal infections must be treated in a hospital, so you should not refuse hospitalization if the attending physician insists on it.
Granulomatous colitis
This is a severe systemic pathology of the ileum, which usually develops over a long period of time (up to several years). An exacerbation of this disease in terms of symptoms is very similar to inflammation of the appendix, but there are signs that allow it to be differentiated from acute appendicitis, so taking an anamnesis is of great importance for diagnosis.
Symptoms of granulomatous colitis
What is the difference between granulomatous colitis (enteritis) and appendicitis?
| Clinical symptom | With inflammation of the appendage of the cecum | For regional enteritis |
| Diarrheal syndrome | Appears after pain, usually of a moderate nature | Abnormal bowel movements (diarrhea) occur long before the attack and can recur periodically over several months or years |
| Localization of pain | Occurs around the navel with subsequent displacement to the right lower abdomen and possible irradiation | Has a clear localization in the right iliac region |
| Vomit | A single discharge of vomit is typical. | Vomiting is not usually observed |
Important! If the attack is not stopped in time, perforation of the ileum may occur - a deadly pathology that requires emergency surgical care. Treatment for Crohn's disease is also surgical in most cases.
Video - Why does the right side in the lower abdomen hurt?
Mesadenitis
In approximately 8-9% of cases, acute stabbing pain in the lower abdomen on the right is a sign of mesadenitis. The pathology is an inflammation of the lymphoid tissue located in the fold of the peritoneum connecting the small intestine and the posterior wall of the abdominal space (mesentery). The disease is a chronic pathology and can occur without pronounced symptoms.
Treatment methods for hepatic colic
Tingling in the liver area is an alarming symptom that should be a reason for more thorough diagnosis and treatment. Since it can manifest itself in various diseases, you should consult a doctor at the first attack. It is especially dangerous if the patient’s history includes gallstones, cholecystitis, cholangitis, hepatitis and other chronic pathologies.
Treatment will depend on the diagnostic results. This may include:
- conservative methods (taking medications);
- surgery - surgery to remove the gallbladder.
If it cuts in the side, you should not self-medicate. Symptomatic medications can temporarily relieve pain, but it is important to determine its cause. Perhaps it was caused by an isolated case of impaired bile flow, which may be associated with overeating or taking certain groups of medications. In this case, symptomatic treatment will be sufficient, and from now on the patient will have to be more attentive to diet and physical activity. However, additional diagnostics will help to find out what causes colic and what to do to get rid of the pain.
Should I call emergency services?
Acute pain in the liver area is a reason to call an emergency team. You should not wait for the pain to disappear on its own or take specific medications without a doctor’s prescription. A typical symptom complex, for which you should definitely call a doctor, will look like this:
- stabbing pain in the right hypochondrium, which can spread to the abdomen, neck, and shoulder blades;
- increased body temperature;
- sudden appearance of yellowness of the skin or mucous membranes;
- sudden decrease in blood pressure;
- disturbances of perception, confusion, dizziness.
Emergency physicians will assess the severity of your symptoms and may administer necessary pain medications, including intravenously or intramuscularly. In the future, hospitalization and proper treatment are necessary. There are two ways to solve this problem. If the disease can be cured with medication, it is enough to take a course of medications and normalize your diet. If the pathology is serious, surgery may be necessary. There is no need to be afraid of it - after removal of the gallbladder, the patient will fully recover and be able to live a normal life.
Gynecological pain
In the case when a woman experiences pain in the lower right part of the abdomen, most often this condition can signal the presence of pathology in the uterine appendages. There are several factors by which one can suspect the development of a gynecological disease:
- The presence of acute or chronic inflammatory process in the uterine appendages;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- The occurrence of pathological vaginal discharge;
- Unfavorable medical history.
The nature of pain in acute gynecological pathology
In the case when pain in the lower right part of the abdomen develops suddenly and is characterized by the greatest degree of intensity, the patient requires urgent medical attention.
Symptoms of an acute abdomen can be provoked by ectopic pregnancy, acute inflammation of the appendages (adnexitis), hemorrhage into the ovary, torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst. In this case, the pain is cramping, cutting or stabbing in nature.
When the fallopian tube ruptures, which is a consequence of tubal pregnancy, the so-called “dagger” pain occurs;
With an ovarian abscess or accumulation of gnosis in the fallopian tube, patients complain of sharp throbbing pain;
Algorithm of action for hepatic colic
Painful sensations in most cases are associated with spasm of the muscle layer of the gallbladder wall. Your home medicine cabinet should contain antispasmodics that relax muscles and thereby relieve pain. Conventional painkillers (No-shpa, Spazmalgon), which can be purchased at any pharmacy without a doctor's prescription, have a good effect. Nitroglycerin in the amount of 1 tablet under the tongue will be no less effective. For more severe pain, medications are administered intravenously or intramuscularly (Papaverine).
If you don’t have medications on hand, there are several ways to relieve pain before the doctor arrives. One of them is a gallbladder massage, which relaxes the walls of the organ and stimulates the outflow of bile. It is not recommended to perform it at elevated body temperature, since this symptom may indicate acute cholecystitis or enlargement of the organ. If you massage a full gallbladder in a state where bile is not able to exit into the duodenum, a rupture of the organ wall may occur.
The massage is performed in the following order:
- First of all, the sphincter of Oddi, which is located at the entrance to the duodenum, is massaged. It is located on the abdominal wall a few centimeters below the chest in the center.
- Next, you need to stimulate the gallbladder, which is located in the left hypochondrium.
- Lastly, you can start acting directly on the gallbladder. It is located under the ribs on the right side.
Massage can be performed in addition to drug treatment for hepatic colic. Some medicinal herbs also have a good antispasmodic effect. Tea with the addition of mint or lemon balm is a safe and effective remedy that can relieve spasm of the smooth muscles of internal organs, including the gallbladder.
Why does it sting in the lower abdomen on the right?
In this area of the abdomen there is the ascending part of the large intestine, loops of the small intestine, appendix, peritoneum, and partially the ureters. If stabbing pain suddenly appears in the right side and increases, most likely there is an acute pathological process:
- appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix);
- renal colic (is a painful attack that develops due to the passage of stones through the ureters during urolithiasis);
- intestinal obstruction;
- death of part of the intestine due to thrombosis of mesenteric vessels;
- pinching of internal organs in an inguinal hernia.
If the right lower abdomen stings periodically, then the following diseases should be suspected:
- colitis (inflammation of the ascending colon);
- enteritis (acute or chronic inflammation of the small intestine);
- disorders of the intestines, accompanied by fermentation processes, accumulation of gases, constipation;
- pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis (inflammatory processes in different structures of the kidney);
- intestinal and kidney tumors.
In addition, periodic tingling in the lower abdomen can be caused by the presence of adhesions, which usually form where there was inflammation or surgery. To prevent the development of adhesions, patients are given drainage; they are advised not to linger after surgery so that inflammatory fluid does not stagnate in the abdomen; special medications and physiotherapy are prescribed.
What absolutely should not be done in case of acute pain in the liver?
When acute pain occurs, it is very important not to provoke further development of the disease. There are several things that are strictly prohibited if hepatic colic is suspected. These include:
- taking water and food;
- warm heating pads;
- massage directly in the area of pain;
- active movements.
Eating food is prohibited, since its entry into the stomach stimulates the formation of a new portion of bile. It is better to prefer tablets or injections to medicines in the form of tea. It is better not to take medications with water, since it also provokes the synthesis of bile by liver cells. The fact is that hepatic colic is often caused by an overflow of the gallbladder and the impossibility of fluid outflow. If it continues to be produced, it can cause acute stretching of the walls of the organ until it ruptures. Until food enters the stomach and affects its receptors, this secretion will not be synthesized.
Active movements can also aggravate the situation. If the pain is caused by the passage of a stone through the bile ducts or blockage of the bile ducts by stones, it will intensify with physical activity. It is better to take a lying position and try to move as little as possible. Warm and hot heating pads during periods of acute pain are contraindicated in any case. Heat stimulates blood circulation in the inflamed area, which takes the process to an even more acute stage. In addition, if the pain is caused by an infection in the gallbladder and bile ducts, under the influence of a heating pad, microorganisms can spread through the bloodstream throughout the body.
Pathologies of the bile ducts
With hepatic colic, pain first occurs in the right hypochondrium, gradually descending to the lower abdomen. The pathology is characteristic of cholelithiasis and appears when stones pass through the bile ducts. In some cases, this symptom indicates biliary atresia - a severe pathology in which the outflow of bile is disrupted due to obstruction of the ducts, and concentrated bile accumulates in the liver. Signs of biliary atresia are:
- constantly high temperature;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- yellowness of the skin;
- periodic vomiting;
- yellowing of the eye sclera;
- hardening and tenderness of the liver;
- lack of appetite.
Diseases associated with abdominal pain
Important! Obstruction of the bile ducts and cholelithiasis are diseases in which the patient requires surgical treatment followed by supportive therapy and observation in a hospital setting.
Stitching pain on the right side of the lower abdomen is a symptom that always requires seeking medical help. Only in 2-3% of cases such symptoms are associated with physiological factors: an abundance of fatty and fried foods in the diet, smoking, and increased stress. In other situations, such a clinical picture requires careful diagnosis and timely treatment. If a person has a stitch in the abdomen on the right, it is important to understand that most of the causes that cause such a symptom require surgical treatment, and delay can lead to serious complications and death of the patient.
Diagnosis of hepatic colic
The doctor who diagnoses and treats hepatic colic is a gastroenterologist. At the initial examination, it is important to collect medical history and determine which diseases should be suspected as the cause of hepatic colic. With cholelithiasis, attacks occur rarely at first, and then begin to appear more often. Their duration and intensity also increases.
There are several ways to determine hepatic colic in a patient. To do this, it is necessary to palpate certain points, and if the reaction is positive, the patient will feel increased pain. Your doctor may check the following reflexes:
- muscle protection syndrome - tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall when pressing on it;
- Ker's symptom - pain when pressing on the point, which is the projection of the gallbladder, while inhaling;
- Grekov-Ortner symptom - pain when lightly tapping the ribs on the right side;
- Murphy's symptom - when pressing deeply on the area located in the area of the gallbladder projection, the patient reflexively holds his breath.
For more accurate diagnosis, instrumental research methods are used. An ultrasound can show expansion of the gallbladder and inflammation of its walls. In its cavity you can see sediment, as well as stones of different sizes and origins. Hepatic colic must be distinguished from other pathologies that manifest with similar symptoms: appendicitis, pancreatitis, renal colic, spasms or intussusception.