Almost 40% of all people are carriers of Staphylococcus aureus (lat. Staphylococcus aureus).
This is an opportunistic bacterium from the genus Staphylococcus and can cause many diseases. Starting from acne and ending with meningitis.
What to do in such a situation? To get started, we recommend reading this article. This article describes in detail methods of controlling parasites. We also recommend that you consult a specialist. Read the article >>>
It often becomes the culprit of nosocomial infections and postoperative complications. Normally, the microorganism is not dangerous; suitable conditions are necessary for the development of infection.
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus in the throat, nose and intestines
The presence of bacteria on the skin and mucous membranes does not pose a threat to human health. Sustained immunity inhibits the growth of bacteria and maintains the balance between the natural microflora that every person has.
But under the influence of a number of factors, the body’s protective function decreases, and then the bacterium activates its pathogenic ability.
Compared to other infectious agents, the bacterium has two advantages:
- Antibiotic resistance. Thanks to the presence of special enzymes, the bacterium breaks down penicillin. In addition, the bacterium is widespread and indiscriminate use of antibiotics by people leads to mutation of the microorganism, thereby increasing the resistance of the pathogen.
- High resistance to antiseptics and adverse environmental factors. Even under short-term thermal exposure, the bacterium is able to survive.
In medicine, there are two types of carriage of Staphylococcus aureus:
- Temporary.
- Permanent.
With constant carriage, the bacterium transitions from the category of opportunistic to pathogenic form. In this case, the microorganism, when transmitted from a carrier to a healthy person, causes an infectious disease.
For the development of infection, special conditions are required:
- Decreased immunity, vitamin deficiency.
- Incorrect use of antibiotics and other medications.
- Nervous disorders (stress, depression).
- Various diseases. Staphylococcus aureus becomes a secondary infection.
- Surgical intervention in violation of asepsis rules.
In addition, people do not have specific immunity to the bacterium. Even if you suffer from a staphylococcal infection, a person can get sick again.
Features of staphylococcal infection
On bacterial culture, staphylococci appear in the form of clusters resembling bunches of grapes. This is where their name comes from (staphylos means “bunch” in Greek). The scope of their distribution is very wide: they are present on almost every person, on furniture, clothing, toys and other objects. But the presence of this microbe on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes of a person does not always imply the development of an infectious process.
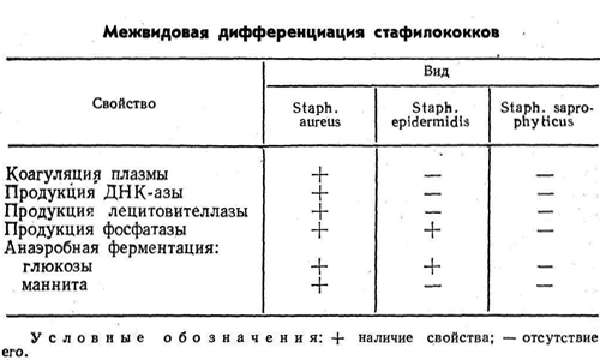
In medicine, there is such a thing as a healthy carriage, when bacteria are in balance with the body’s immune forces, and therefore are not able to subject it to aggression and cause disease. There is a wide variety of staphylococci in nature, among which only three species can be dangerous to humans:
- epidermal (S.epidemidis);
- saprophytic (S.saprophyticus);
- golden (S. aureus).
The greatest threat is posed by Staphylococcus aureus, which gets its name because of the beautiful golden yellow color in bacterial culture. This microorganism is unique in its vitality. It perfectly withstands very high and very low temperatures, drying, chemicals such as ethyl alcohol and hydrogen peroxide do not pose a danger to it, but, on the contrary, it is very sensitive to a solution of brilliant green. Therefore, all small wounds on the body must be treated with this remedy that protects against staphylococcus.
This bacterium instantly dies only when boiled, and can withstand a lower temperature of 70 degrees for an hour.

This bacterium instantly dies only when boiled, and can withstand a lower temperature of 70 degrees for an hour.
In ordinary unpasteurized milk, after two hours of being outside the refrigerator, these microbes begin to multiply, so you must boil it, especially if you are going to give it to children. An antiseptic such as a 5% solution of phenol (carbolic acid), which is used to disinfect premises, is also destructive to staphylococcus.
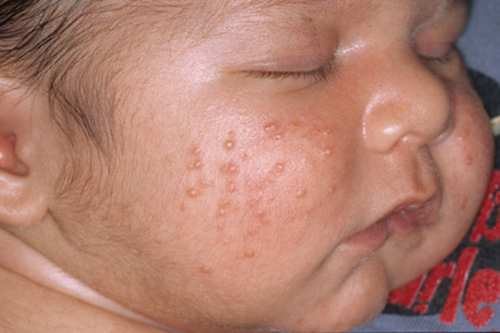
Staphylococcus aureus in children and infants
In newborn children, the infection most often occurs in the form of pharyngitis and enterocolitis (inflammation of the mucous membranes of the intestinal walls).
Mostly, children suffer from the bacterium in the first months of life and up to 1 year, especially if they were born prematurely or with congenital pathologies.
Symptoms in children
The clinical picture of the disease caused by Staphylococcus aureus depends on the state of immunity, the location of the bacteria and their pathogenicity. With weak immunity, an increase in body temperature and general intoxication of the body are characteristic.
Localization of bacteria in human systems and organs:
- Upper respiratory tract . Favorite location of the pathogen. Viruses, hypothermia and abuse of nasal drops contribute to the development of pathology.
- Gastrointestinal tract. Food poisoning occurs and is manifested by nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Infection mainly occurs through consumption of food products contaminated with the pathogen.
- Internal organs. Pathology manifests itself in the form of pneumonia and bacterial endocarditis.
Table with the most common diseases caused by staphylococcus infection.
| Name of the disease | Characteristic symptoms |
| Pneumonia | Fever, general weakness, shortness of breath, anemia, cough with sputum. |
| Pharyngitis | On the 2nd or 3rd day, a dry cough appears, the voice becomes hoarse, and a runny nose appears. |
| Enterocolitis | Nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal dysfunction. |
| Ritter's disease or scalded skin syndrome | Skin rash and foci of inflammation with clear boundaries.
|
Most often, staphylococci cause abscesses, dermatitis and boils. The main threat to children is the waste products produced by bacteria, which can cause infectious-toxic shock.
Treatment in children
Before carrying out therapy, it is necessary to study the resistance of the pathogen to antibiotics. In some cases, ointments containing mupirocin are used if it concerns local diseases: Levomekol, Baneocin and methyluracil ointment.
The main medicines used are:
- Bacteriophage. The drug contains viruses that infect staphylococci.
- Antibiotics Amoxiclav, Oxacillin, Vancomycin, Lincomycin and others.
Treatment is approached with all seriousness, without violating the dosage and timing of administration. Otherwise, you can increase the resistance of bacteria to medications.
Treatment and preventive measures for Staphylococcus aureus
Treatment of diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus
As mentioned earlier, Staphylococcus aureus can cause the development and exacerbation of many diseases . To treat each disease, complex therapy is used, which is aimed at eliminating the general symptoms of the disease and suppressing pathogenic bacteria.
An integral part of therapy is a course of penicillin antibiotics. In this case, treatment without an antibiotic is impossible, since the infection can only be removed with its help.
So, for the treatment of back and lower respiratory organs, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of tablets. However, in the acute course of the disease or its complications, antibiotics can be administered intramuscularly or intravenously using drip systems. To eliminate purulent rhinitis, mixed nasal drops are prescribed, which also contain an antibiotic and vasoconstrictor drugs. To eliminate general symptoms of bronchitis, laryngitis or pneumonia, expectorant, sedative and thinning mixtures are prescribed. To treat acute tonsillitis, in addition to antibiotics, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions are prescribed for rinsing the mouth and throat.
When treating the gastrointestinal tract, enzyme preparations and drugs to restore intestinal microflora are prescribed. Painkillers may be prescribed to relieve spasms. For kidney and urinary tract diseases, antifungal urological drugs are prescribed along with antibiotics. Urological preparations of plant origin help relieve pain and restore normal kidney function.
In the treatment of diseases associated with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the heart and brain, cardiac drugs and drugs are prescribed to improve cerebral circulation and restore normal functions.
Each antibiotic has a detrimental effect on the intestinal flora, so to prevent unpleasant consequences, eubiotics and drugs containing lactobacilli are prescribed. Such drugs protect the mucous membrane and normalize its functioning.
Prevention of Staphylococcus aureus
In order to prevent the entry of pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus bacteria into the body or the exacerbation of chronic diseases that it causes. Some preventive measures must be followed . Namely:
- avoid general and local hypothermia;
- monitor vitamin balance and the state of the immune system;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene and sanitary measures;
- avoid contact with infected people;
- When in contact with an infected person, take precautions (use disposable medical dressings;
- raw meat products should be subject to prolonged heat treatment;
- During an outbreak of acute infectious diseases that are transmitted by airborne droplets, after visiting public places and transport, wash your hands and face with soap, and also sanitize the oral cavity.
Staphylococcus aureus is a very dangerous bacterium that causes serious disruptions in the functioning of human organs. Treatment of these diseases is quite complex and is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. Therefore, in this case, it is better to refuse self-medication and promptly seek qualified medical help. This will help avoid unwanted complications and infection entering the circulatory system.
Staphylococcus aureus in adults
Staphylococcal infections are difficult to treat. Typically, adults begin to self-medicate and put off visiting a doctor. This only increases the number in the clinical picture.
Symptoms and treatment in adults
Characteristic signs of infection depending on the location of infection:
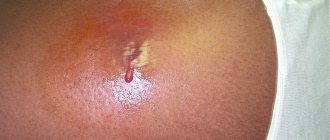
- Hyperemia (redness) . The flow of arterial blood to the site of inflammation increases and venous stagnation occurs. Thus, the body removes toxins and bacterial breakdown products.
Hyperemia
- General or local increase in body temperature . It is a bacteriostatic mechanism to combat foreign agents.
- Swelling . Formed elements of blood (leukocytes, etc.) leak through blood vessels into the inflammatory focus to destroy foreign bodies. As a result, swelling appears.
Swelling
- Organ dysfunction . As the infection progresses, healthy cells and tissues are damaged. Dystrophy, necrosis and other pathologies impair the functioning of the organ.
To achieve a therapeutic effect, tests are taken and the sensitivity of staphylococcus to antibiotics is determined.
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus infection
Infection with Staphylococcus aureus manifests itself differently in each baby.
In the early form of infection, within a few hours the child experiences:
- temperature increase;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bowel dysfunction;
- flatulence.
When the gastrointestinal tract is upset, the baby begins to groan, strain, and sometimes cry. The child's stool is liquefied, greenish in color, and contains white lumps.
Constipation, which replaces diarrhea, is accompanied by severe bloating.
If unpleasant symptoms are not alleviated, the child may quickly weaken.
Signs of a late stage of infection appear three or five days after Staphylococcus aureus has become active and has settled comfortably in the baby’s body. The bacterium reveals itself through:
- damage to internal organs and epidermis;
- blood poisoning.
It happens, although rarely, that Staphylococcus aureus does not manifest itself in any way, and the infection is almost asymptomatic. Unless minor skin pathologies occur. But a stool test will definitely reveal the bacteria if it has settled in the baby’s body and multiplied above permissible limits.
Staphylococcus aureus: degree of bacterial growth
Normally, staphylococci live in the human body and do not cause any health problems. In this connection, there are certain standards for the content of bacteria on the skin or mucous membranes.
4 degrees of bacterial growth:
- Weak growth.
- Growth of up to 10 colonies of the same species.
- Growth from 10 to 100 colonies.
- More than 100 colonies.
The first 2 degrees are considered normal. The 3rd degree indicates a decrease in immunity and the beginning of an increase in the number of bacteria. The 4th degree indicates the presence of pathology.
Treatment
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus is carried out by specialists of various profiles - surgeons, dermatologists, ENT specialists, ophthalmologists, therapists, pediatricians and infectious disease specialists.
Patients are prescribed etiotropic antimicrobial therapy.
- If the CFU exceeds 10 3 degrees, it is believed that bacteria from the nasopharynx are actively entering the environment. Sanitation of foci of infection is indicated for such bacteria carriers.
- If the CFU value is lower and there is no obvious clinical manifestation, antibiotics should not be taken.
- If CFU exceeds grade 104, standard antibiotic treatment is performed.
- The number of microbes of 10 5 degrees and 10 6 degrees is an indicator of massive infection with staphylococcus. The disease is accompanied by a pronounced clinical picture and requires mandatory treatment with antimicrobial agents.

Antibacterial drugs are prescribed based on pathogen sensitivity tests. Typically, semi-synthetic penicillins Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, macrolides Erythromycin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, fluoroquinolones Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, cephalosporins Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime, and Vancomycin are used.
In severe cases, when antibacterial treatment is ineffective, alternative and safe agents are used - antistaphylococcal bacteriophage, antistaphylococcal plasma and immunoglobulin.
Local treatment of skin diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus: treating wounds with antiseptic solutions, using antibacterial ointments. Abscesses and phlegmons are opened surgically to drain the pus.
Staphylococcal food poisoning is treated with antistaphylococcal toxoid. Patients have their stomach washed, undergo infusion detoxification therapy - saline solutions are administered intravenously.
All patients are prescribed symptomatic therapy, in which the choice of drugs is determined by the localization of the lesion and clinical manifestations. Immunomodulatory treatment speeds up the healing process. Patients are prescribed "Polyoxidonium", "Licopid", "Bronchomunal". Antihistamines are used to relieve swelling from the mucous membrane and eliminate other irritation reactions - Suprastin, Diazolin, Tavegil.
Folk remedies used to treat pathologies caused by Staphylococcus aureus: herbal immunomodulators - extract of eleutherococcus, lemongrass, ginseng; immunostimulants - echinacea, rose hips, St. John's wort, hawthorn. Infusions and decoctions are prepared from the listed plants for oral administration.
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment of infection caused by S. aureus, severe complications develop:
- Sepsis,
- Meningitis,
- Endocarditis,
- Infectious-toxic shock,
- Coma,
- Death.
The prognosis of the disease is ambiguous. It is determined by the severity of the pathology. Mild forms involving the skin and mucous membranes in the pathological process are completely cured without negative consequences. Sepsis, brain damage and other severe complications often result in death.
Video: how to kill Staphylococcus aureus easier? – Doctor Komarovsky
Staphylococcus aureus in dogs
Many people have these animals in their home. People are constantly in contact with them, especially children, and can easily become infected. Especially in the autumn-spring period, when the immune system of animals and people weakens.
In dogs, Staphylococcus aureus disease mainly manifests itself as skin problems or food poisoning.
Externally, pathologies of the dermis resemble ringworm with pustules.
Hair falls out profusely, and extensive areas of baldness form. It is necessary to urgently contact a veterinarian.
Prevention is the most important step in preventing bacterial infection. A balanced diet, consumption of vitamin and mineral complexes, and physical exercise help maintain a strong immune system. And this will be the key to preventing all infections.
Staphylococcus aureus: normal
Staphylococcus is localized in different places of the body. Its golden appearance likes to settle in the intestines, mucous membranes of the nose and throat.
To detect the presence of Staphylococcus aureus in the baby’s body, it is necessary to examine the stool for dysbacteriosis. Such a test is carried out already in the maternity hospital, when there is the slightest suspicion that bacteria have entered the baby’s intestines.
You need to examine stool at least twice with a one- or two-day break. It is advisable to promptly deliver the test material (stool) to the laboratory (no later than three hours after bowel movement). This will allow you to get correct results.
The established norm for Staphylococcus aureus is 104. This is the maximum content of bacteria in the stool of a child who is one year old. For infants, this figure is considered high.
It is important to monitor the level of Staphylococcus aureus over time. If accelerated bacterial growth occurs, this means the development of an infection, and it’s time to start treatment.
Moderate fluctuations in the amount of Staphylococcus aureus indicate that the child’s condition is normal.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Interesting to know:
Staphylococcus aureus in stool - how to help your baby at home
In babies, from the second week of life to six months, functional gastrointestinal disorders are a common occurrence. The intestines are inhabited by many different types of bacteria. It is never sterile.
It is advisable to treat with medications only when the amount of Staphylococcus aureus in the baby’s stool is several times higher than the permissible content.
First of all, it is necessary to normalize the functioning of the children's intestines without resorting to pharmacology. After all, we often treat one thing, but at the same time we harm another part of the body.
When your baby starts to suffer from constipation, you can help him like this:
Such procedures should be used rarely so that the gastrointestinal tract does not get used to working independently.
If the baby is breastfed, then the mother needs to temporarily stop consuming rice, legumes, cabbage, grapes and blueberries. These products hold the intestinal contents together and promote flatulence.
After several months, the child’s stool improves.
Bibliography
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Brucellosis. Parasites. Link
- Corbel MJ Parasitic diseases // World Health Organization. Link
- Young EJ Best matches for intestinal parasites // Clinical Infectious Diseases. — 1995. Vol. 21. - P. 283-290. Link
- Yushchuk N.D., Vengerov Yu.A. Infectious diseases: textbook. — 2nd edition. - M.: Medicine, 2003. - 544 p.
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases among the population, 2009 / Kokolova L. M., Reshetnikov A. D., Platonov T. A., Verkhovtseva L. A.
- Helminths of domestic carnivores of the Voronezh region, 2011 / Nikulin P. I., Romashov B. V.
An article for patients with a doctor-diagnosed disease. Does not replace a doctor's appointment and cannot be used for self-diagnosis.

The best stories from our readers
Topic: Parasites are to blame for all troubles!
From: Lyudmila S. ( [email protected] )
To: Administration Noparasites.ru
Not long ago my health condition worsened. I began to feel constant fatigue, headaches, laziness and some kind of endless apathy appeared. Problems also appeared with the gastrointestinal tract: bloating, diarrhea, pain and bad breath.
I thought it was because of the hard work and hoped that it would go away on its own. But every day I felt worse. The doctors couldn’t really say anything either. Everything seems to be normal, but I feel like my body is not healthy.
I decided to go to a private clinic. Here I was advised, in addition to general tests, to get tested for parasites. So in one of the tests they found parasites in me. According to doctors, these were worms, which 90% of people have and almost everyone is infected, to a greater or lesser extent.
I was prescribed a course of antiparasitic medications. But it didn’t give me any results. A week later, a friend sent me a link to an article where some parasitologist shared real tips on fighting parasites. This article literally saved my life. I followed all the advice that was there and after a couple of days I felt much better!
Digestion improved, headaches went away and the vital energy that I so lacked appeared. To be sure, I took the tests again and no parasites were found!
Anyone who wants to cleanse their body of parasites, no matter what types of these creatures live in you, read this article, I’m 100% sure it will help you! Go to article>>>
Still have questions? Ask them in our Anonymous group on VK
How to get rid of parasites in a week. The answer is here!
A reliable and effective remedy for combating worms. Removes all parasites in 21 days.
Go to website
Reviews
Read online
Symptoms that 100% indicate parasites! Take the Test.
How to rid your body of life-threatening parasites before it’s too late!
Read more
Website
To get a consultation
The doctor tells how to quickly get rid of parasites for adults and children!
A parasitologist explains what effective methods exist to combat helminths.
More details
Read completely
Comments
Search for cures for parasites
Other tests
We recommend reading

Smear for chlamydia mycoplasma: where and how to take it, preparation features
02.07.202002.07.2020ecoliv94
Chlamydia trachomatis: what is it in women, igg analysis, treatment methods
01.07.202001.07.2020ecoliv94
Leishmania braziliensis: description, life cycle, routes of infection and treatment
18.06.202018.06.2020ecoliv94
Isospora belli: description, life cycle, routes of infection and treatment methods
18.06.202018.06.2020ecoliv94