What is staphylococcus
Staphylococcus is a bacterium that belongs to positive non-motile microorganisms. In humans, such a microorganism in some situations is considered conditionally pathogenic, that is, it is constantly present on the body.
Staphylococcus aureus is found on the skin and mucous membranes of almost every person.
If the patient has good immunity, streptococcal infection usually does not develop.
Normal microflora manages to suppress the growth of the microorganism and prevent it from expressing its pathogenic essence.
If there are malfunctions in the functioning of the immune system, this results in the activation of the microbe and the possible development of dangerous conditions such as blood poisoning or sepsis.
Experts also identify pathogenic staphylococcus, the penetration of which into the human body clearly provokes pathology.
When favorable conditions for development are created, Staphylococcus aureus manifests its activity and causes the progression of the pathological process in absolutely any organ or system.
The danger of such a microbe lies in the fact that it is capable of producing toxins - harmful substances that pose a threat to cells and disrupt their normal functioning.
Staphylococcus negatively affects the epidermis, connective tissue and subcutaneous tissue.
Such a microorganism provokes the development of such dangerous pathologies as toxic shock, sepsis, pneumonia, purulent skin lesions, damage to the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system, and deterioration of the patient’s general well-being.
The insidiousness of such a pathogenic microorganism lies in its resistance to environmental influences. In addition, staphylococcus is highly resistant to antibacterial drugs, which greatly complicates the fight against it.
Classification and diagnosis
Various signs of staphylococcus depend on the location, degree of activity, and emerging diseases. Thus, intestinal inflammation initially has the symptoms of a cold. Staphylococcal poisoning is characterized by a pronounced severe course. Depending on the titer of microorganisms, there are four stages of development of the pathological process.
Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella multiply quite quickly. The incubation period for the disease is short, no more than a day. The first symptoms can be observed within a few hours. The presence of staphylococcus in infants and newborns is especially dangerous.
Treatment of staphylococcus begins after diagnosis. To do this, appropriate analyzes and studies of pathological microorganisms are carried out. The presence of Staphylococcus aureus is confirmed by detecting the coagulase enzyme. The presence of inflammatory and purulent processes can be confirmed by the leukocyte blood count.
To successfully treat intestinal staphylococcus, bacteriological examination of stool is prescribed. The analysis makes it possible to detect the type of pathogen, the number of colonies and the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics.
Diagnostic tests for staphylococcus
If a patient develops a clinical picture that suggests the presence of Staphylococcus aureus, a general blood test . During such a study, the leukocyte formula is calculated, which makes it possible to get an idea of the signs of a purulent process.
It is possible to determine the amount of a pathogenic microorganism in the body of an adult by analyzing stool for dysbacteriosis .
Such a study is carried out when there is a suspicion of infection in a person, as well as in maternity hospitals and during a medical examination by hospital workers.
Staphylococcus aureus is considered the only coagulase -positive pathogen, so the test is performed with a coagulase test .
It should be remembered that if Staphylococcus aureus is found in feces, this does not yet serve as an indication for treatment. It is important to determine the amount of such a pathogenic microorganism, as well as the presence or absence of other bacteria and viruses.
Experts say that if stage 4 Staphylococcus aureus is detected in the stool, this is considered normal.
In such a situation, it is allowed to limit oneself to only preventive measures aimed at increasing the body’s defenses and replenishing the lack of vitamins.
It is important to maintain body hygiene at all times, avoid various injuries and avoid excessive sweating.
If Staphylococcus aureus is found in stool 10 to 4 degrees , then this pathological condition requires mandatory treatment.
The fact is that this type of pathogenic microorganism is considered the most difficult to treat, that is, the strain develops resistance to a certain antibacterial drug in a short time.
It is important to complete the prescribed course of therapy and take only those medications prescribed by a specialist.
Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines: symptoms and treatment:
Staphylococci are part of the normal intestinal microflora. 25% of it consists of coccal microorganisms. The appearance of Staphylococcus aureus in humans is often associated with nosocomial infections, but there are other routes of infection.
The beginning of problems
It should be understood that all babies are born with sterile intestines. When first applied to the breast, lactobacilli begin to colonize it. But, in addition to them, other microorganisms also enter the intestines, creating opportunistic microflora.
Do not panic if Staphylococcus aureus was found in the intestines. It is part of the normal microflora, of course, provided that positive bacteria can inhibit its growth. When assessing the results of an analysis, it is important to pay attention to the concentration in which it is found. A level of 103 is considered normal. Although ideally there should not be this coccal microorganism in the intestines. But we must understand that in most cases the problem is not that there is too much Staphylococcus aureus, but that beneficial microorganisms cannot restrain its growth.
Symptoms of the disease
Most often, problems begin when immunity decreases. This condition causes Staphylococcus aureus to actively multiply in the intestines. Symptoms of the disease in most cases are pronounced.
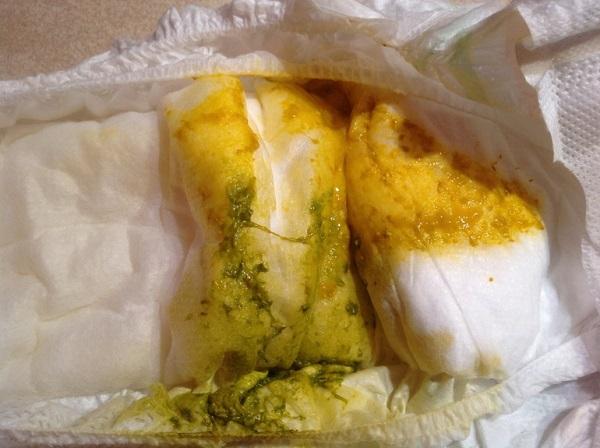
The patient begins to have loose stools (frequency - more than 8 times a day). The bowel movements are copious, watery, and may be mixed with blood and mucus. Children and adults often develop diaper rash, which is difficult to treat. Sometimes the disease begins suddenly. At a relatively low temperature, abdominal pain appears, which is accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting.
These problems begin because Staphylococcus aureus produces toxins. The symptoms of the infection are similar to severe food poisoning. The disease cannot be ignored, because in advanced cases the infection can cause death.
Necessary research
An accurate diagnosis can be made using a special analysis. In the laboratory, stool is cultured and the microflora is determined. And Staphylococcus aureus is not always the cause of problems. There are other pathogenic microorganisms in the intestines that can also lead to the development of severe intestinal infections.
For example, if as a result of the examination it was found that the concentration of Staphylococcus aureus is 105, and Klebsiella is 109, then with a high degree of probability it can be assumed that it was the latter microorganism that caused the problems. Each specific case must be assessed by an infectious disease specialist. He is the one who can choose the optimal treatment.
Problems for infants
When assessing laboratory tests, one must remember that there is nothing to worry about if Staphylococcus aureus was detected in the intestines of an adult in a concentration not exceeding 103.
The situation is a little different with young children. In the first year of life they should not have this microorganism. After a year, they look at the quantitative indicator and use it to determine the seriousness of the situation.
Naturally, one cannot ignore the situation when Staphylococcus aureus was discovered in the intestines of a baby. Symptoms of the development of the disease may be the following: watery or mucous mushy stools, repeated up to 15 times a day, regurgitation, vomiting, bloating. If such signs are present, the baby must be examined. If the pathogenic microorganism mentioned above is detected, they speak about the possibility of fecal-oral transmission of infection from the mother or from medical personnel. Infection from environmental objects is also possible. After all, Staphylococcus aureus can live on them for up to 50 days. You can get rid of it only by treating surfaces with disinfectants.
Treatment with antibacterial agents
Doctors often have different views on how to treat staphylococcus. Some talk about the need for long-term use of antibacterial agents, others demand to completely abandon this group of drugs and simply restore the microflora.
In most cases, with rapid progression of the disease and high fever, antibiotics are immediately prescribed. Moreover, most often doctors do not wait for the results of bacterial culture, so they do not know whether Staphylococcus aureus is in the intestines of the baby. The symptoms of the disease suggest that it may be caused by the uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microflora, which must be stopped.
Selection of antibacterial agents
Many strains of this microorganism are resistant to penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics. In an ideal situation, it is necessary to prescribe the drug only after receiving test results, which will indicate which drugs the detected microorganisms are sensitive to.
Statistics show that in almost 70% of cases, glycopeptides and carbapenems help if Staphylococcus aureus was detected in the child’s intestines. Treatment consists of taking drugs such as Vancomycin, Imepinem, Meronem.
If the causative agent is unknown, then, as a rule, cephalosporins of the first and second generations are prescribed. Many strains exhibit moderate sensitivity to them. Drugs such as Cefuroxime, Cefamandol, and Cefazolin are prescribed. To increase efficiency, they are used in combination with aminoglycosides. These are drugs such as “Neomycin”, “Amikacin”, “Isepamycin”, “Streptomycin”.
Different tactics
An infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus does not always occur in an acute form, requiring immediate intervention and the prescription of antibacterial agents. Quite often, treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines is aimed at restoring normal microflora.
For these purposes, special bacteriophages and antiseptics can be used (drugs “Ersefuril”, “Enterofuril”). In addition, therapy should be aimed at colonizing the intestines with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. They will suppress the growth of pathogenic microflora and restore balance naturally.
If Staphylococcus aureus was detected in the child’s intestines during the examination, then antibiotics in most cases are not needed. In the absence of fever and pronounced symptoms of infection, it will be enough to undergo a course of conservative treatment. It consists of taking a special staphylococcal bacteriophage. Also, in combination with it, sorbents are prescribed, for example, Enterosgel. Prebiotics and probiotics are used to populate beneficial microflora and accelerate their growth.
Features of using bacteriophage
Regardless of the patient’s age, Staphylococcus aureus may begin to actively multiply in the intestines. It will “kill” all beneficial microflora and release toxins, causing symptoms of poisoning. Even if Staphylococcus aureus was found in the intestines of a baby, a staphylococcal bacteriophage can be prescribed to it. In these cases, it is recommended to use a solution form. If adults can drink it anyway, then for children it is recommended to dilute the drug with boiled water. If well tolerated, you can give it in its pure form.
To alleviate the condition caused by the fact that Staphylococcus aureus has begun to actively multiply in the child’s intestines, treatment should last 3-4 days. But the full course lasts up to 15 days. The exact period should be determined by the doctor, taking into account the scale of infection and the patient’s condition. In some cases, relapses occur after completing the course of therapy. In this case, the treatment is repeated.
Carriage of the disease
It is worth knowing that about 30% of people live peacefully with Staphylococcus aureus. They do not have any manifestations of the disease; in most cases, they may not even know that they have this microorganism. Of course, with a significant weakening of the immune system, Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines can begin to multiply and release toxins.
But if this microorganism was identified as a result of the examination, do not start panicking. Treatment with antibacterial or any other agents is often not required. Of course, the doctor may recommend taking a course of bacteriophage therapy. He can also prescribe drugs belonging to the groups of prebiotics and probiotics. These can be products such as “Prelax”, “Lactofiltrum”, “Linex”, “Lactofil”, “Probifor”.
But in most cases, it’s enough just to monitor your diet and strengthen your immune system.
www.syl.ru
Symptoms of pathology
If Staphylococcus aureus is detected in the stool of an adult, symptoms may indicate the presence of the microorganism in the intestines. Based on the location of the inflammatory process in the intestine, the following are distinguished:
- Enteritis and enterocolitis. With such diseases, there is a slow increase in signs of the disease, and the occurrence of intestinal manifestations is usually preceded by an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract.
It is for this reason that many patients confuse the symptoms of a streptococcal infection with a common cold. The patient's body temperature does not rise above 37.5 degrees and there is slight malaise.
Frequent, loose stools can signal that a patient has an intestinal infection.

- Poisoning . Staphylococcal infection is severe and no specific symptoms appear. It is for this reason that the course of such a disease often resembles food poisoning.
If Staphylococcus aureus is detected, symptoms of the disease may appear after 4-5 hours.
Infection with a pathogenic microorganism causes the following symptoms:
- the occurrence of digestive problems and one of the first symptoms is considered frequent loose stools. The urge to go to the toilet occurs 10-12 times, and stool with Staphylococcus aureus contains mucus and blood streaks;
- A severe pain syndrome develops, a cutting pain that does not have a clear localization. Patients note the appearance of pain in the lower abdomen or epigastric region;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting occur that do not depend on food intake;
- possible appearance of rashes on the skin, which many perceive as an allergic reaction;
- subfebrile body temperature persists, which does not exceed 37.5 degrees;
- There is general fatigue and a feeling of weakness.
In fact, the proliferation of such bacteria in the intestines occurs quite rapidly. Food poisoning can occur when food is stored at room temperature for long periods of time.
CAUSES
The first reasons for the appearance of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines is the consumption of food products that have been kept for a long time in rooms with a temperature regime that does not correspond to their storage conditions.
Causes of infection:
- The nutritional mechanism of entry is neglect of personal hygiene rules after contact with the feces and vomit of an infected person.
- The official mechanism of infection is incomplete sterilization of medical equipment.
- Insufficient qualifications of medical personnel when performing surgical operations.
- Failure to comply with the rules of the sanitary and epidemiological regime in medical institutions.
- Immunity weakened by acute viral infections.
- Using antibiotics without consulting a specialist.
In rare cases, infection with Staphylococcus aureus can occur while swimming in bodies of water with stagnant water.
Methods for eliminating pathology
In a situation where a patient is diagnosed with Staphylococcus aureus in the stool, treatment is carried out using antibacterial therapy.
If a patient is diagnosed with a mild form of streptococcal infection, no special treatment is performed. If moderate and severe forms are detected in a patient, the following medications :
- Amoxicillin - has a suppressive effect on the growth and active reproduction of microbes, and also causes their destruction.
- Vancomycin blocks a component present in the cell membrane of staphylococcus. In addition, such a drug causes a change in the degree of permeability of the bacterial wall and causes its death.
- Cloxacillin helps block the membrane, which is at the stage of bacterial division.
- Claritomycin prevents pathogenic microorganisms from producing their own proteins.
- Cefotaxime - inhibits the growth of staphylococci and prevents their reproduction.
- Cefazolin disrupts the ability of the microbe to fully divide, and also has a destructive effect on the membrane of the microorganism.
Before starting any drug for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus, an antibiogram should be performed.

Thanks to this study, it is possible to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to the selected antibacterial drug. Carrying out such an analysis is relevant because bacteria fail to develop resistance.
It is important to remember that treating Staphylococcus aureus in feces should only be done under the supervision of a doctor . The prescription of certain antibacterial drugs is carried out only after a thorough diagnosis.
To eliminate the pathology, it is necessary to observe the frequency of taking the medicine, its dosage and time of use. It is necessary to continue taking the antibiotic even when the first signs of pathology have disappeared.
Typically, the course of antibiotic therapy is 5 days, but if indicated, the specialist will extend the course.
PROGNOSIS FOR RECOVERY
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the intestines in adults takes up to 10 days, subject to strict adherence to all recommendations of the attending physician. Performance returns completely within the first 5 days after the start of treatment, when all symptoms of the disease disappear.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Staphylococcus aureus is a common causative agent of human purulent-inflammatory diseases. Almost every one of us knows what Staphylococcus aureus is.