If the IgG type indicator is no longer present during the next examination, this is a signal that Helicobacter pylori has been destroyed. It is better to carry out the analysis 10-12 weeks after treatment. Immunoglobulin type G, when suppressing a bacterial infection, should decrease by 50% by that time.
Blood testing is undoubtedly an effective way to detect the presence of infection in the body. As a rule, one analysis is enough for an accurate result. The Helicobacter bacterium is vulnerable to antibacterial effects. And timely treatment is the key to good health.
source
Analysis and norm of Helicobacter pylori in the blood in numbers, antibodies and treatment
Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection is a complex process, since none of the available tests alone can serve as the basis for making a final diagnosis. A person can be a carrier of Helicobacter pylori throughout his life, and the manifestation of clinical symptoms is not necessary.
There is experimental data on the possibility of spontaneous elimination of infection, however, in most cases, the selection of adequate treatment methods under the supervision of a physician is required.
Helicobacter pylori: general information about the microorganism
Helicobacter pylori (Helicobacter pylori) is an opportunistic bacterium of a spiral shape, Gram-stained red (gram-negative). The predominant habitat in the human body is the stomach and duodenum.
The role of Helicobacter pylori in the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) has been denied for a long time. Only in 2005, Australian pathologist R. Warren and physician B. Marshall managed to prove the medical significance of bacteria, for which they were awarded the Nobel Prize.
Feature: in 90% of carriers, Helicobacter pylori is part of the normal microflora and does not cause the development of an infectious disease. However, there is an opinion that this particular species is the cause of many gastrointestinal pathologies (ulcers, gastritis, cancer, lymphoma).
Relation to opportunistic bacteria means their ability to provoke an infectious process in the presence of certain conditions (factors). For example, long-term use of antibiotics with subsequent dysbacteriosis, decreased immunity and the presence of concomitant pathologies. However, when infected with strains with pronounced pathogenic properties, the presence of the above factors is not necessary.
Symptoms of pathogenic microorganism activity
Sometimes a blood test for Helicobacter pylori is prescribed during a comprehensive examination, without complaints. But more often, patients come to the doctor describing symptoms:
- pain in the epigastrium and abdominal region (stomach);
- heartburn and belching;
- dyspepsia not related to diet;
- frequent nausea, vomiting;
- unpleasant (putrid) odor from the mouth;
- decreased appetite;
- weight loss;
- increased flatulence;
- frequent inflammation of the oral mucosa;
- heaviness in the stomach after eating.
Visits to the dentist become more frequent and gums become swollen. Stomatitis often develops.
The condition, after infection with a bacterium, may not change for a long time, and then worsen against the background of provoking factors - for example, due to poor diet or after stress - or the patient immediately feels a deterioration in health.
Features of infection in children
According to statistics, when deciphering a blood test for Helicobacter pylori, it was revealed that in the CIS, 35% of preschool children and 73% of primary schoolchildren are infected. Thanks to the examination, it is possible to suppress the disease at the very beginning. Symptoms in children are more pronounced; they quickly lose weight and begin to lag behind their peers in physiological development.
Indications for diagnosis

Donating blood for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori is recommended not only when characteristic symptoms appear. It may be necessary to undergo a routine examination or evaluate the effectiveness of therapy in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. Analysis for Helicobacter pylori is needed to identify patients at risk - for the diagnosis of atrophic gastritis, oncological processes of the gastrointestinal tract and esophageal cancer. If the indicator differs from the norm, specific treatment is prescribed.
Where does Helicobacter pylori come from and how is it transmitted?
The infection is not transmitted by airborne droplets, since it is a strict anaerobe (dies on contact with oxygen). You can become infected by neglecting the rules of personal hygiene (cutlery and dishes, personal cosmetics and personal hygiene products), as well as by kissing.
Primary infection can occur in childhood (from mother to child). Another route of infection is water and meat that has undergone insufficient heat treatment. Infection through an endoscope, which is used for gastroendoscopy, is possible.
How does infection occur?
Rapid colonization of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is ensured due to the high degree of mobility of Helicobacter pylori (using flagella). Specific proteins and lipopolysaccharides on the surface of the membrane help bacteria attach to the surface of cells. The presence of foreign antigens provokes the development of an immune response (the release of specific antibodies to Helicobacter pylori) and initiates inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Bacteria release enzymes into the external environment that dissolve the protective mucus of the stomach. Survival in the acidic environment of the stomach is ensured by the enzyme urease, which decomposes urea with the release of ammonia (neutralizes hydrochloric acid). A side effect of ammonia is chemical irritation of cells followed by their death. Along with this, bacteria release toxins that enhance the process of cell degradation and death.
ELISA blood test for the presence of Helicobacter pylori
A study using special staining enzymes to determine the titers or concentration of IgG, antibodies to Helicobacter pylori. Enzyme immunoassay is performed using classes A, M and G.
These immunoglobulin indicators indicate the number of pathogenic microorganisms:
- IgG. They appear at an early stage of infection. In 3-4 weeks. An increased number of titres warns of a prolonged life of pylori in the body;
- IgM. The presence of bacteria on the mucous membrane. Primary penetration.
False positive and false negative results are often observed. This is due to the incubation period of the disease. More than 50% of all people who have undergone treatment and gotten rid of microorganisms can still show its presence for a long time.
The explanation when a blood test shows the normal level of immunoglobulins is as follows:
- A is less than 0.9 U/ml;
- G less than 0.9 U/ml;
- M less than 30 U/ml.
When any indicator increases, the decoding has different indicator values:
- IgG. The early period corresponds to 3-4 weeks of infection;
- IgM. If there are no other antibodies, then the result is negative;
- IgA. Active acute phase.
The norm for the presence of an inflammatory process and infection is 30 for IgG and IgA antibodies. If immunoglobulin IgA is not detected in the results, the study must be repeated. With increased levels of IgG, IgA, IgM, there is a danger of exacerbation of infection.
Symptoms of Helicobacter pylori in adults
In most cases (up to 70%), carriage does not manifest itself in the form of clinical symptoms and is discovered accidentally during a comprehensive examination of the patient. However, pathologies of the stomach and intestinal tract, accompanied by Helicobacter pylori infection, have certain signs:
- feeling of pain in the abdominal area (stomach);
- frequent heartburn and belching;
- unexplained loss of appetite and weight;
- nausea or vomiting;
- heavy coating on the tongue;
- inflammation of the gums;
- putrid odor from the mouth (with the exception of dental diseases);
- feeling of heaviness after eating food;
- increased gas formation.
It was noted that in children the severity of clinical signs is higher than in adults. This situation is especially often observed in the presence of physical or emotional stress, as well as when the diet changes for the worse (replacing soups with sandwiches or eating irregularly).
Patients ask the question: when should you get tested for Helicobacter pylori? A referral for laboratory diagnostics can be issued by a general practitioner, pediatrician, gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist. Indications for testing for Helicobacter pylori: suspicion or presence of gastrointestinal disease, as well as the manifestation of the above symptoms.
Indications for use
If Helicobacter is present in the body, timely diagnosis and treatment are important.
A helicobacter pylori test is recommended for anyone who has:
- erosive lesions of the stomach walls;
- gastritis;
- gastrointestinal ulcers;
- gastroduodenitis;
- gurgle;
- reflux esophagitis.
The test is done for the primary diagnosis of the patient and to check the effectiveness of anti-Helicobacter therapy. After completing the course of treatment, it is recommended to carry out a follow-up examination.
If one of the family members is diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori, then this test is recommended for everyone else.
Helicobacter provokes not only problems with the gastrointestinal tract, but also other unpleasant phenomena that are not related to digestion. The examination diagnoses whether this bacterium is the cause of the illness. This helps to begin adequate treatment.
The test is indicated for people who experience the following symptoms:
- pain and discomfort in the stomach;
- recurring heartburn;
- bad breath (not associated with caries);
- belching;
- lack of appetite;
- vomiting, nausea;
- flatulence, constipation, diarrhea;
- allergies, nail fungus, hair loss.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Dream Interpretation: ladybug - why do you dream about it?
A referral for a helix test is issued by the attending physician. For consultation, you need to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist, therapist or dermatologist.
How to get tested for Helicobacter pylori?
Methods for identifying Helicobacter pylori are different:
- breath (urease) test;
- real-time PCR to detect pathogen DNA;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to determine the level of antibodies produced in response to infection;
- one-step immunochromatographic method for detecting pathogen antigens in the test material;
- biopsy during esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Depending on the diagnostic method, the biomaterial studied, the cost and timing of the study differ. It is important that the patient follows the rules for preparing for the analysis; the accuracy and reliability of the results obtained depends on this. Let's take a closer look at each method.
Video “Diagnostics of Helicobacter Pylori”
In this animated video you will learn how to detect and diagnose Helicobacter pylori in the human body.
Helicobacter pylori is a dangerous microorganism that, when it enters the human body, provokes a lot of troubles, such as ulcers, gastritis, erosion, and in some cases, cancer. To determine the correct treatment method, you must first undergo a diagnosis. Typically, blood serum is tested for the presence of bacteria.
In this case, the amount of antibodies relative to the pathogen in the patient’s biomaterial is determined. It is worth noting such a test as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent test (ELISA). Depending on the results obtained, the specialist determines the presence of pathology, the degree of its development and the effectiveness of therapy.
What is a urease test for Helicobacter pylori?
Detection of Helicobacter pylori using a breath test. The Helicobacter pylori test is increasingly used in routine diagnostic practice. Advantages of the method:
- short time to obtain results (up to several hours);
- low cost;
- painlessness;
- no contraindications;
- no need for expensive equipment.
Disadvantages include the possibility of obtaining a false negative or false positive result. Reduced reliability of the study due to internal bleeding.
In what cases can a urease breath test for Helicobacter show a false negative result? In addition to improper preparation of the patient for the test and errors at the stage of collecting biomaterial, a false negative result can be obtained when infected with strains that do not produce urease. In other words, even if bacteria colonize the patient’s gastrointestinal tract but do not release urease, the test result will be negative.
Preparing for the ureaplase test
For 3 days, alcohol and medications in which alcohol is a solvent are completely eliminated. For 6 hours, food intake is limited, clean unsweetened water is allowed to drink. The minimum interval between the last dose of antibiotics and bismuth-containing drugs is 6 weeks. It is advisable to stop taking any medications 2 weeks in advance, in consultation with your doctor.
Collection of biomaterial (exhaled air) is allowed 24 hours after FGDS (gastroscopy).
10 minutes before collecting air, you should drink juice (grapefruit or orange) in order to slow down the evacuation from the stomach. Then the patient exhales as much air as possible into a special bag.
After which you need to drink a solution of urea labeled with a carbon isotope (50 ml for adults, 25 ml for children under 12 years of age). The solution has no specific taste or smell; it must be prepared immediately before use. After 30 minutes, a control collection of exhaled air is carried out.
Both samples are analyzed on a special device and the carbon dioxide ratio is determined.
What is included in preparation for analysis?
Preparing for a blood test for Helicobacter using the enzyme immunoassay method involves avoiding fatty foods and alcohol at least 24 hours before. It is also necessary to limit physical activity during the day, including sports. It is necessary to donate blood on an empty stomach, that is, at least 8–10 hours must pass between the last meal and the collection of biomaterial.
The analysis is carried out mainly in the morning, which allows the subject to prepare with the least discomfort. After all, it is forbidden to have breakfast in the morning, you can only drink water, and this will not be so easy for a person with hunger pains. Half an hour before the procedure, you must refrain from smoking.
The helic test is quite simple to perform, but it requires careful preparation. This is the most important step to obtain the most accurate result.
Rules for preparing for the Helicobacter breath test:
- in the morning before the procedure, you need to brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with plain water;
- the procedure is carried out strictly on an empty stomach;
- It is permissible to drink some water (1/2 glass) 1 hour before the test;
- on the day of the analysis, smoking and chewing gum are excluded;
- the dinner menu on the eve of the test should be dietary and can be eaten no later than 22:00;
- 2 weeks before the test, cancel all antibiotics and agents that inhibit the secretion of hydrochloric acid;
- a week before the examination, you should not take painkillers, antacids, anti-inflammatory medications and bismuth preparations;
- 3 days before the test, alcohol and all legumes are excluded.
Any medications the patient is taking should be consulted with a physician. He can give additional recommendations regarding preparation for the helic test.
Antibodies to Helicobacter pylori
Infection with Helicobacter pylori infection triggers protective immune responses. Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is produced first, followed by large quantities of IgG and IgA. Blood testing for antibodies to Helicobacter pylori allows one to establish the fact of infection, since IgG is detected in 90–100%, and IgA in 80% of cases.
It should be noted that a blood test for Helicobacter pylori may be an alternative to invasive diagnostic methods (if endoscopy is not possible). This rule does not apply to elderly patients. The strength of their immune response is insufficient, so it is possible to obtain false negative results.
A high titer of IgG indicates recent infection and an active process of infection, provided that the patient has not taken antibiotics. The IgG concentration remains moderately elevated for a long time (up to 1.5 years), so this test is not used to assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment.
The IgA value allows you to determine the severity of the infectious disease. A low IgA content persists for up to several years; however, the absence of positive dynamics in reducing its value indicates the ineffectiveness of treatment.
How is blood donated for Helicobacter pylori (how is the test taken)? The biomaterial is venous blood from a peripheral vein on the elbow. No special preparation is required for the analysis. It is advisable to donate blood for Helicobacter pylori after 2-3 hours without food; smoking is prohibited for half an hour.
What does it mean if Helicobacter pylori IgG is positive?
If antibodies to Helicobacter pylori IgG are detected in the biomaterial, then a conclusion is drawn about:
- active infection - in the presence of a pronounced clinical picture;
- bacterial carriage.
A decrease in the IgG titer in a blood test for Helicobacter by 25% within six months after completion of treatment indicates the death of bacteria.
Decoding the analysis results
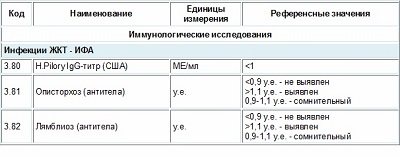
If the test was carried out in a qualitative version, that is, without determining the quantitative values of immunoglobulin titers, then the norm is the absence of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori, which will be reflected in the study form. It should be borne in mind that if there is one or more of the complaints listed above, a negative result does not provide grounds to assert that this patient does not have helicobacteriosis. It is recommended to repeat the analysis after 2 weeks and, in addition, conduct a urease breath test or any other one suggested.
Interpretation of quantitative analysis is based on comparison of the obtained titres with reference values. Each laboratory has its own sets of reagents, so the norm both in digital terms and in units of measurement differs from others. The form must indicate the norms and units accepted in this laboratory. The titer values obtained during patient examination are compared with standard ones. Indicators below the reference ones indicate a negative result, that is, that no antibodies to Helicobacter were found. Indicators above the reference ones indicate a positive result.
If the laboratory gives a “doubtful” result, the examination should be repeated after 2-3 weeks.
TABLE OF ASSESSMENT OF THE TEST FOR IMMUNOGLOBULIN IgG TITERS TO HELICOBACTER PYLORI. NORM AND DEVIATIONS
RESULT
S\CO INDICATORS UNITS\ML INDICATORS
Negative less than 0.9 less than 12.5
Doubtful 0.9 – 1.1 12.5 – 20.0
Positive more than 1.1 more than 20.0
In IFE units, the norm for immunoglobulin A and G is 30 IFE.
Positive values of immunoglobulin A over 30 IFE indicate:
- early period of infection, latent active process;
- chronic form of the disease.
- For immunoglobulin G, positive values over 30 IU mean:
- residual antibodies after treatment;
- phase of active inflammation, risk of developing gastritis, peptic ulcer, oncology;
- simple carriage of the bacterium in the absence of symptoms;
- indicates a fresh infection, about a week old.
Negative values of less than 30 IFU for immunoglobulin A indicate:
- recent infection;
- stage of convalescence or continuation of antibiotic therapy;
- negative Helicobacter when combined with a similar response for immunoglobulin G.
A negative value of less than 30 IU immunoglobulin G suggests:
- absence of infection, but with a small risk of development;
- early infection within 28 days.
- A negative immunoglobulin M titer means:
- early infection (first decade);
- adequate antibiotic therapy;
- convalescence stage;
- negative results similar to those for other antibodies.
An increase in all titers for all antibodies indicates an aggressive inflammatory process. ELISA can be positive in healthy people who are simply carriers of Helicobacter pylori. This conclusion can be made after a thorough laboratory and clinical examination of the patient.
Fast laboratory diagnostics allows you to immediately begin treatment and select effective treatment regimens for bacteria in order to eradicate them as quickly as possible.
During treatment monitoring, an indicator of effectiveness is a decrease in antibody titre by 20-25% within six months.
Stool analysis for Helicobacter pylori
Feces are examined using 2 methods: immunochromatography (detection of antigens) and PCR (presence of pathogen DNA). Both methods are characterized by high sensitivity and act as complementary methods.
Determination of antigens
Testing stool for Helicobacter pylori antigen is a qualitative method, the accuracy of which reaches 95%. Obtaining positive results 7 days after taking antibiotics indicates the ineffectiveness of treatment. A repeat test is carried out after 1.5 months of therapy, and the absence of antigens in the patient’s stool indicates complete destruction of the bacterium.
The method does not allow one to determine the type of bacteria: H. suis, H. Baculiformis or H. Pylori, since all their biomaterial is foreign (antigen) to humans.
Real-time PCR
The sensitivity of the stool PCR method for Helicobacter pylori infection reaches 95%. The analysis makes it possible to determine infection by unculturable forms of bacteria. Disadvantages include the possibility of obtaining false-positive results after a successful course of treatment, since destroyed bacterial cells (and their DNA) remain in the human body for a long time.
The possibility of obtaining false positive results is excluded, since the specificity of the method reaches 100%. The method is an alternative to the breath test or FGDS for young children.
No special preparation is required for collecting biomaterial for both studies. Feces are collected naturally without the use of laxatives, preferably before starting antibiotics.
Explanation of each diagnostic method
When taking a breath test, you do not need to wait for a response from the laboratory. The doctor compares the indicators of the first and second stages of testing. Normally, the indicators should not differ – zero value. If helicobacter pylori is present in the body, the result will be greater than zero.
Table. Interpretation of analysis values.
| Test indicator, ppm | Decoding |
| 0 | Absolute norm, absence of Helicobacter pylori |
| 1,5-3,5 | Trace amount, inactive phase |
| 3,5-5,5 | Low level |
| 5,5-7 | Small level |
| 7-15 | Active phase of reproduction of Helicobacter pylori |
| 15-70 | High degree of infection of the gastric mucosa by bacteria |
At low subthreshold values of 3-5 ppm, it is worth repeating the test. Such results may indicate a latent form of the disease or carriage.
The presence of pathogenic bacteria, viruses, toxins and other harmful factors in the human body causes activation of the humoral immune system. Antibodies are produced in response. These are protein compounds that are synthesized by plasma cells formed from B lymphocytes.
They are characterized by two functions:
- binding – by combining with an antigen, its negative effect on the body is stopped;
- effector – the formation of a specific response of the immune system.
Immunoglobulins are presented in five classes:
- IgA – produced by plasma cells when the integrity of the mucous membranes is damaged. There are two types - serum and secretory. The latter protects the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract.
- IgM - are identified during the initial introduction of a foreign agent into the body.
- IgG is the main immunoglobulin that is involved in antitoxic immunity and the secondary immune response.
- IgD - the functions of the fraction are not fully understood; it is defined as an antigen receptor with a high content of carbohydrates associated with protein for B lymphocytes.
- IgE plays a decisive role in allergic inflammation, especially during parasitic infestations.
Decoding
The main options that have diagnostic significance are antibodies to Helicobacter pylori IgA, IgM, IgG. During the initial penetration of bacteria into the digestive tract, all types of antibodies are detected. IgM is determined by 5–7 days. Up to 4 weeks increase to maximum concentration. Then there is a gradual decrease in the indicator.
IgG to Helicobacter pylori appears a month after the onset of the disease against the background of a decrease in IgM.
IgA is detected within a few weeks and persists for several years. A high level is a marker of chronic gastritis. With effective therapy, the antibody titer begins to decrease after 6 weeks. Therefore, specialists prescribe a test for class A AT to monitor the quality of treatment.
Important!
IgG begins to be detected 4 weeks after the onset of the disease against the background of a decrease in IgM. An increase in antibody titer indicates the development of chronic inflammation.
In chronic inflammation - gastritis - Helicobacter pylori is constantly present in the gastrointestinal tract. A month after infection, a secondary immune response is formed. Its marker is IgG class antibodies. During the inflammatory process, the level of AT is increased. After eradication of the pathogen for some time, the tests will be positive. However, over time, the titer decreases and remains within low values until the end of life, which indicates a previous illness.
Various types of studies are interpreted according to the obtained values. At the initial stage, high-quality diagnostic methods are used that do not require complex manipulations. These include non-invasive options.
The study of serological markers of infection is a screening that allows one to determine the duration and severity of the disease. A test for total antibodies is prescribed, which detects HP from the first days of the disease.
Attention!
Additionally, an examination is prescribed for the presence of Helicobacter, which produces CagA. The presence of the antigen increases the risk of developing stomach cancer.
A stool antigen test and a urease breath test may be positive or negative. Invasive tests are used according to indications and generally also give qualitative results.
The quantitative method is histological examination with microscopy of smears. The degree of contamination is determined by counting bacteria in the field of view:
- up to 20 units – ;
- 20-50 units – ;
- More than 50 units – .
Norm Helicobacter pylori in the blood in numbers
Decoding the blood test for Helicobacter pylori, as well as other data obtained, is the work of the doctor and does not allow the patient to independently interpret the results.
The table shows normal values for each diagnostic technique. [td] Method name
| Norm | Approximate cost (for a private laboratory), rub. | Deadline for receiving results (excluding the day the biomaterial was taken) | |
| Breath test | Less than 4 ‰ | 850 | Up to 6 days |
| PCR | Not detected | 500 | Up to 2 days |
| Antigens | 750 | 1 day | |
| Biopsy | 600 | ||
| Antibodies | IgG 0-0.9 IU/ml | 550 | |
| IgA 0 – 13.5 IU/ml | 650 | Up to 8 |
Patients are concerned about the question - what does Helicobacter negative mean? Obtaining such a result indicates the absence of Helicobacter pylori infection or successful therapy with complete destruction of bacteria.
ELISA
Helicobacter pylori can be detected in the blood after a laboratory test called an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. This test uses reactions to determine the presence and amount of specific substances in a blood sample. An analysis for Helicobacter Pylori using ELISA is aimed at identifying the corresponding antibodies in the body, since Helicobacter is not contained in the blood. These specific cells are produced by the body's immune system against the infectious agent.
A blood test for Helicobacter pylori is taken from a vein. Before submitting a biological sample, you should prepare for analysis. A blood sample is taken on an empty stomach; food intake is stopped 8-12 hours before blood collection. Also, within 2 days, alcohol and foods that irritate the stomach are completely eliminated. These factors can distort the final result of the analysis and provide the doctor with unreliable information.
A qualitative test for antibodies is normally negative, which means that the desired bacteria is not in the body. The Helicobacter pylori norm for the number of antibodies in quantitative analysis depends on the laboratory and the reagents used. Quantitative analysis determines the numerical value of antibodies per unit volume of blood. This indicator allows us to judge the development of the inflammatory process and the severity of the disease. Based on the data obtained, treatment is prescribed.
- Blood tests for IgG Helicobacter Pylori are normally a negative result, and it means that the patient does not have the microorganism. Obtaining the same result is possible with a recent infection. Antibody production may not occur for 3-4 weeks after infection.
- A weak positive result for IgG antibodies will persist for several months after successful treatment of the disease. This result implies the presence of antibodies in the patient’s blood, but in small quantities.
- A positive ELISA test for IgM Helicobacter is characteristic of the early period of development of the disease. If blood tests for antibodies to another type of Helicobacter are negative, and the IgM level is normal, there is no infection.
- Helicobacter IgA ELISA can show a high content of IgA type antibodies, which is characteristic of an actively ongoing inflammatory process that requires immediate treatment.
Treatment of Helicobacter pylori without antibiotics
Methods aimed at the complete destruction of Helicobacter pylori are called eradication. In 1987, a European group was formed whose goal is to develop the most effective, affordable and safe eradication methods. Their recommendations, formalized in the form of works, are called the Maastricht Consensus.
The main method of treatment is antibiotics. However, it is not always possible to achieve positive dynamics due to the high level of resistance of Helicobacter pylori to most known antibiotics. In addition, in certain areas of the gastrointestinal tract, pathogenic bacteria are inaccessible to antibacterial substances due to the large amount of mucus.
Independent use of alternative medicine methods does not allow achieving complete destruction of the infection. However, the technique can be used as an adjunct to drug treatment.
Treatment with flax seed, the tincture of which is taken before eating, helps reduce acidity. The consistency of the decoction in the form of mucus helps to further protect the stomach from the destructive effects of enzymes and bacterial toxins.
Treatment with potato juice involves drinking it daily before meals. It has been noted that potato juice, like other vegetables, helps relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
It is acceptable to use tinctures from various herbs, for example, St. John's wort, chamomile and yarrow. Herbs are mixed in equal quantities, poured with boiling water and infused. Before meals, you should take no more than 2 tablespoons of tincture.
Treatment with calamus root helps increase acidity levels. The tincture is taken before meals, 50-70 ml up to three times.
Reviews on the treatment of Helicobacter pylori with folk remedies are different. Many people attribute their recovery exclusively to tinctures and decoctions, with the complete exclusion of antibiotics. However, we should not forget about the known cases of spontaneous elimination of bacteria from the human body. Despite the lack of evidence for the phenomenon, its exclusion is impossible.
The maximum therapeutic effect is achieved with strict adherence to the diet, the use of antibiotics and methods of informal medicine. Treatment is considered successful if the clinical symptoms become less pronounced or disappear completely.
Certified specialist, in 2014 she graduated with honors from the Orenburg State University with a degree in microbiologist. Graduate of the graduate school of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Orenburg State Agrarian University.
In 2020 At the Institute of Cellular and Intracellular Symbiosis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, she completed advanced training in the additional professional program “Bacteriology”.
Laureate of the All-Russian competition for the best scientific work in the “Biological Sciences” category 2020.
source
Add a comment Cancel reply
- Copyright holders
- Privacy Policy
Infectious diseases and tests © 2020 All rights reserved © 2020. Attention!
The information published on the site is for informational purposes only and does not constitute a recommendation for use. Be sure to consult with your doctor! The Materials may contain information intended for users over 18 years of age. 18+ [/td]