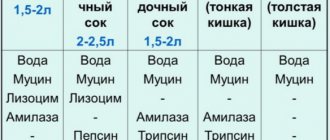
Discomfort and pain in the intestines after eating food occur for various reasons. Fermentation in the stomach is a common condition that occurs in adults and children. It is accompanied by unpleasant processes, such as increased gas formation and frequent, sometimes difficult bowel movements. This problem is dangerous to health; at the first manifestation of symptoms, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
What is dyspepsia?
Dyspepsia is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract associated with indigestion.

Pathology occurs due to nutritional disorders and can often manifest itself due to insufficient amounts of digestive enzymes in the body.
Dyspepsia is a disease that is a consequence of a disease of the gastrointestinal tract and in itself is not fatal, but significantly reduces a person’s quality of life. The consequences of dyspepsia can be such phenomena as the rotting of proteins and amino acids in the intestines, the processes of food fermentation in the intestines, etc.
Depending on what type of enzyme is missing, there are:
- cholecystogenic dyspepsia - a disease resulting from impaired bile secretion;
- hepatogenic dyspepsia – the result of liver diseases;
- gastrogenic dyspepsia – a pathology resulting from disorders of the stomach;
- pancreatogenic dyspepsia – a consequence of a lack of pancreatic enzymes;
- enterogenous dyspepsia – a pathology that occurs due to disturbances in the secretion of intestinal juice;
- mixed dyspepsia is a pathology that combines the signs of several of the above varieties of the disease.
If left untreated, the pathology becomes chronic and can provoke serious functional disorders of the body, for example, metabolic imbalance - a fatal phenomenon for patients with diabetes, etc.
The child has fermentation in the intestines
I want to see a doctor first, maybe there are special medications there. It’s just that this story has been tormenting us for half a year, I thought maybe someone has it too
Is this curable at all? We find it more difficult to go to the garden
How did you diagnose the fermentation? What was wrong in the tests?
What do you have in your analysis? How did you get it?
Well, they found klepsiella in us, we took Enterol for several days, then the bacteria Normoflorin. We ourselves went to a paid doctor and there the tests revealed this and fermentation too. The pediatrician in the nursery said that everything is fine? So listen to them
And we had Klebsiela.
Do you have a bowel disorder?
Before giving anything to your child, get tested, and it is advisable to find a smart doctor. The pediatrician at the hospital prescribed us Creon and Bifidumbacterin, they were of no use, we need to look at the tests to see what bacteria are missing and populate the intestines with them, and of course it’s better to live bacteria, Normoflorin, for example, they are more expensive, but the improvements are obvious
Fermentative dyspepsia is a complex disorder of the digestive system, accompanied by pain and discomfort in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of fermentative dyspepsia in infants directly depends on its form. But all types of this disease have similar symptoms:
bloating, frequent regurgitation, rapid satiety, rumbling in the stomach, increased gas formation, vomiting, heaviness in the stomach, loss of appetite, abnormal bowel movements, foamy stools, pain in the abdominal area.
Diagnosis of fermentative dyspepsia in newborns
If at least one of the above signs is detected, the baby must be examined by a specialist. In this case, the doctor should pay attention to the following information:
what does a nursing mother eat? how long have symptoms of dyspepsia been observed; How often do problems with stool occur?
After examining the newborn, the doctor prescribes the following clinical tests:
hematological blood test, stool analysis, scatological studies.
After receiving test results, you may need to consult a pediatric gastroenterologist. If necessary, in order to verify the presence of fermentative dyspepsia in newborns, the specialist will refer for instrumental studies. These include:
gastric juice test to determine its acidity, endoscopic examination, biopsy examination, examination of stomach contents for the presence of Helicobacter pylori, colonoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, computed tomography, electrogastroenterography.
Such a thorough diagnosis allows not only to determine the form of dyspepsia in a newborn, but also to find its root cause and create an effective treatment regimen.
Complications
If the doctor’s recommendations are not followed and proper treatment is not given, fermentative dyspepsia can cause serious changes in the newborn’s body. Ultimately, this leads to the following consequences:
underweight or loss of body weight, prolonged loss of appetite, developmental defects in an infant, dystrophy, gastric bleeding.
With timely treatment and proper treatment, a single case of fermentative dyspepsia in a newborn is unlikely to entail tangible consequences. The progression of symptoms of this disease indicates a serious pathology and is a reason for mandatory consultation with specialists.
What can you do?
After a child is diagnosed with fermentative dyspepsia, it is necessary to limit the intake of foods containing large amounts of carbohydrates. If the newborn is breastfed, then the nursing mother should also avoid the above foods. In doing so, she must comply with the following recommendations:
Source: https://kishechnik-zhivot.ru/voprosy/u-rebenka-brozhenie-v-kishechnike
Digestion process
A simplified process of digesting food looks like this. From the oral cavity, food enters the stomach, where it begins to break down under the influence of gastric juice and hydrochloric acid. Food is digested and partially enters the bloodstream through the walls of the stomach. Since the food mixture interacts with hydrochloric acid in the stomach, the balance of acid and alkali in the organ changes - acidity in the stomach increases. However, the pH level returns to normal after the digested food enters the small intestine.
The passage of processed food from the stomach to the intestines is carried out through the pyloric valve, which periodically opens and closes with constant changes in the environment in the small intestine.
Excess acidity is neutralized by intestinal juices. Due to the neutralization of intestinal contents, the pH level periodically changes from alkaline to acidic and vice versa.
The stomach and small intestines (albeit for a short time) are protected by increased acidity from putrefactive microflora, which contributes to the rotting of decay products. In these parts of the digestive tract there are no microbes, including putrefactive ones.
Due to insufficient enzymes, food is not completely digested. The decomposition products undergo pathological processes, the formation of toxic products of rotting proteins in the intestine occurs, accompanied by the release of gas.
What food does not ferment?
Nutritionists advise that in case of flatulence, increase the consumption of foods that do not cause gas formation during digestion.
Products that do not cause fermentation:
| products | kinds |
| beverages |
|
| fish | species with low fat content, for example, hake, cod; |
| meat |
|
| vegetables |
|
| cereals |
|
| bakery | bread baked without yeast; |
| spices, herbs |
|
It's not just the choice of products that is important. Nutritionists recommend adjusting your diet and choosing more gentle cooking methods.

Nutrition rules:
- eat at least 4-6 times a day, in small portions;
- do not abuse the quantity;
- take your time, chew foods well;
- any drinks are acceptable half an hour after the main meal;
- you should eat regularly;
- do not irritate the digestive system with too cold or hot food;
- choose gentle cooking methods: boiling, stewing, baking;
- drink at least 1.5 liters of water every day.
The right choice of products and adherence to nutritional standards will solve the problem of increased gas formation if these are not symptoms of pathology of the digestive system.
Types of dyspepsia
Any food consists of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The percentage of these substances in different products is different. Therefore, a person’s diet should be varied - he should receive all three components with food. However, the abuse of any products can cause disruptions in the digestive system and lead to the development of dyspepsia.

There are three forms of the disease:
- Putrefactive dyspepsia is a type of pathology that develops as a result of excessive consumption of protein, especially protein that takes a long time to digest. This could be red meat, pates, sausages. A favorable environment is created in the body for the development of putrefactive microflora, which causes rotting of proteins in the intestines. Treatment of this form of dyspepsia is aimed primarily at unloading the gastrointestinal tract and restoring the balance of normal intestinal microflora.
- Fermentative dyspepsia occurs with excessive consumption of foods containing carbohydrates. These include flour products, sweets, cabbage, legumes, honey, as well as mash, kvass, and pickled vegetables. Such products contribute to the development of fermentation microflora, which results in fermentation in the digestive chain.
- Fatty dyspepsia is a type of pathology that develops against the background of increased consumption of foods containing large amounts of fat. These include pork or lamb lard. Fat dyspepsia is sometimes called soap dyspepsia.
Fermentable foods
You can avoid discomfort in the digestive system if you eliminate the cause.
Products that cause fermentation:
| products | kinds |
| dairy and fermented milk |
|
| beverages |
|
| fruits |
|
| vegetables |
|
| cereals |
|
| sweets |
|
| bakery |
|
| dried fruits |
|
It is not always possible to completely eliminate foods that cause fermentation; you can simply reduce their quantity. There are products that relieve discomfort. It is useful to drink a glass of herbal tea and eat a tablespoon of bran. To quickly solve the problem, you should make one day a fasting day. If flatulence does not go away, then it is recommended to spend a week on a diet that relieves flatulence.
Read: Calcium content in food: eating for health benefits
We recommend watching the video:
Causes of development of putrefactive dyspepsia
Putrefactive dyspepsia develops not only as a result of excessive consumption of foods high in protein. The cause of the pathology can be stale meat products, as well as a low amount of enzymes in the body - intestinal proteases, pepsin, trypsin. Enzyme deficiency is often caused by a person's lifestyle, but can sometimes manifest itself as a congenital defect.
If there is a lack of substances that decompose proteins in the body, or there is a lot of protein food, then it does not completely decompose, but enters the large intestine in a semi-processed form. There it decomposes, but not under the influence of normal microflora, but under the influence of opportunistic microflora.
The latter, developing rapidly, suppresses the normal environment and contributes to the occurrence of dysbiosis, and opportunistic bacteria penetrate into the lower parts of the small intestine and trigger rotting processes in it.
The putrefaction is aggravated by additional proteins that are secreted by the intestinal walls during increased peristalsis. During the decay process, toxic substances are formed that are absorbed into the blood and cause intoxication of the body. The main task in the treatment of dyspepsia is to find a way to stop the rotting of proteins in the intestines. And ways to neutralize toxic products in the body also need to be determined.
It is important to remember that, within reasonable limits, eating the above foods does not lead to pathological disorders in the body. However, an excess of such food or eating it in the evening, when intestinal activity decreases, causes undesirable consequences and has a negative effect on the body.
General recommendations
To improve the functioning of the digestive organs, reduce gas formation, and flatulence, you need to be more attentive to your diet and eliminate foods that cause fermentation.
Nutritionists recommend adhering to the following rules:
- use vegetable oil for dressing salads;
- Avoid drinking sweet soda while eating;
- pre-soak legumes for 5-7 hours;
- in the evening, do not eat foods that take a long time to be processed in the body, for example, meat, mushrooms;
- You should not drink water half an hour before or after meals.
In addition, you should lead an active lifestyle. Hiking, running, swimming and other outdoor sports will be useful.
Some foods cause increased gas formation. To get rid of the problem, you need to make changes to your diet. Be responsible about what and in what quantities enters the body.
Recommended video:
It is necessary to reduce foods that cause fermentation. If this does not help, then you can stick to the diet for a week. If the proposed measures do not lead to an improvement in the condition, then you need to consult a specialist, undergo diagnostics and a course of treatment.
Read along with this article:
- Easily digestible foods and their role in the diet
- Flatulence - is it worth fighting this phenomenon?
- The reasons for the feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach...
- How to get rid of gases in the intestines? The best ways and...
- Diet for bloating: what and how to eat
- Causes of bloating and gas: intestinal bacteria and...
- Diet rules for thrush in women
- What can you eat when your stomach hurts to relieve the condition?
- A newborn has a stomach ache, what to do, how to help and how to do it...
Symptoms
As noted earlier, dyspepsia is a background for the development of diseases of the digestive tract, therefore the signs of pathology are similar to the symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders. Manifestations of functional dyspepsia depend on the type of pathology.
Fatty dyspepsia, for example, is manifested by heaviness in the stomach, belching, and flatulence. Patients report abdominal pain that worsens when eating. The stool is quite copious and often contains inclusions of undigested food.
Fermentative dyspepsia is characterized by strong rumbling in the intestines and flatulence. Patients note pain in the upper abdomen, as well as frequent trips to the toilet. In this case, the stool has a sour odor and a liquid consistency. Fermentation in the intestines also results in frequent constipation.
Symptoms of fermentation should never be ignored. Lack of proper treatment leads to gradual contamination of the intestinal walls. At the same time, the protective film of the mucous membrane ceases to be produced, which will subsequently allow pathogenic bacteria to become active. Over time, fecal stones form in the intestines.
Patients suffering from fermentation dyspepsia also note an external sign of the disease - the so-called “fecal” belly. It occurs due to the fact that the intestines sink down under the weight of unprocessed food.
Anti-bloating diet
If abdominal discomfort does not go away, it will be useful to follow a special diet for a week. Be sure to avoid foods that cause fermentation.
Menu table for 7 days:
| day | meal | dishes |
| Monday | breakfast dinner dinner | oatmeal, cottage cheese, rosehip decoction; fish soup, mashed potatoes, chicken fillet, green tea; buckwheat porridge, compote; |
| Tuesday | breakfast dinner dinner | omelette, green tea; chicken broth, baked vegetables, jelly; stewed vegetables; cocoa; |
| Wednesday | breakfast dinner dinner | boiled egg, cottage cheese, herbal tea; mashed potatoes, turkey fillet, compote; buckwheat, fish cutlets, a glass of fermented baked milk; |
| Thursday | breakfast dinner dinner | semolina porridge, boiled egg, rosehip infusion; stewed vegetables, beef meatballs, compote; 200 g of boiled chicken, a glass of kefir; |
| Friday | breakfast dinner dinner | omelette with herbs, bird cherry decoction; millet porridge with prunes, jelly; baked vegetables, chicken cutlets, blueberry juice; |
| Saturday | breakfast dinner dinner | 150 g cottage cheese, green tea, toast; stew of tomatoes, peppers, jelly; boiled potatoes, jelly; |
| Sunday | breakfast dinner dinner | oatmeal, boiled egg, compote; chicken broth, vegetables stewed with rabbit meat, green tea; casserole of cottage cheese and apple, cocoa. |
Read: Menu for a week for stomach ulcers: cooking features
Dairy and fermented milk products should be consumed with low fat content. By following this menu for a week, you can get rid of fermentation in the digestive system.

In addition, the following rules must be observed:
- include fruits and vegetables in the diet only in stewed, baked, boiled dishes;
- give up smoked meats;
- Do not eat fresh baked goods, give preference to dried bread.
If problems do not go away even after the diet, you should consult a doctor.
Manifestations of putrefactive dyspepsia
Dyspepsia of putrefaction leads to the release of toxic substances in the body, such as cresol, skatole, phenol. As a result of the reactions, gases are formed that cause flatulence. The gas tends to expand and put pressure on the intestinal walls, resulting in disturbances in the abdomen. The reason for this is the rotting of proteins in the intestines. Symptoms of the pathological condition are complemented by unpleasant colic and painful sensations. An inflammatory process develops in the intestines. The organ narrows, and “plugs” form in narrow places, which stretch the non-inflamed areas.
With putrefactive dyspepsia, intoxication of the body occurs, so the patient feels a loss of strength, weakness, and decreased performance. He may be bothered by dizziness and headaches, and sometimes during illness there is a slight increase in body temperature.
The pathology is also characterized by nausea and vomiting, bloating and pain in the abdomen, frequent mushy dark stools with a fetid, putrid odor.

Putrefaction dyspepsia takes two forms:
- chronic,
- spicy.
The acute form occurs after excessive single consumption of protein, for example after overeating kebab at a picnic. Such ailment is temporary and quickly goes away on its own or with the help of medications that contain enzymes.
Chronic dyspepsia indicates serious disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and requires diet, changes in habitual lifestyle, and drug intervention.
Useful video
Watch this video about the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of dyspepsia:
A simple but quite effective water diet for weight loss will not only help you lose weight even for the lazy, but will also instill proper eating habits. In this case, the menu is almost the same as the daily one, and the result can be 5-7 kg.
Sparkling water works quite interestingly for weight loss. For example, the benefit for the body lies in the removal of toxins and mineralization. But this applies to natural sparkling water. The harm of store-bought milk is increased appetite and destruction of intestinal walls. Why else can you not drink sparkling water? Is it possible to drink kefir with carbonated water?
Eating watermelon is very beneficial for weight loss. Its benefit in general lies in the removal of toxins and cleansing. You can even eat it at night, since the calorie content is very low.
Diagnostics
Screening for dyspepsia is quite varied and includes many components. In addition to a doctor’s examination, there are laboratory diagnostic methods that reveal the decay of proteins in the large intestine - biochemistry, OAC, as well as instrumental research techniques.
During the examination and conversation, the doctor determines symptoms that may indicate the patient has diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, draws up a general picture of the patient’s health status, and decides which diagnostic methods to resort to.
In almost all cases, the patient is sent for a general urine and blood test. Often, a patient is given a detailed blood test if there is a suspicion of protein decay in the large intestine (biochemistry).
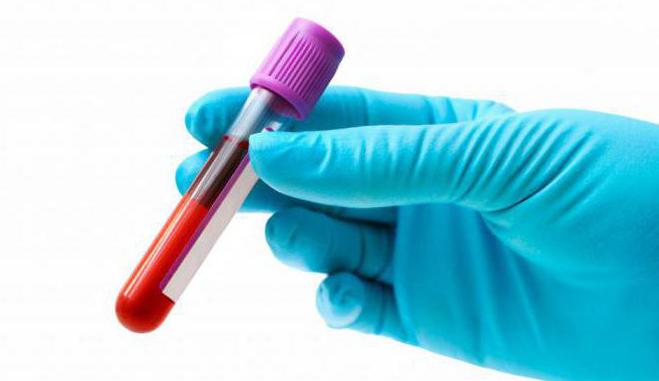
To determine the type of dyspepsia, an analysis of the patient's stool is performed. Sometimes a breath test or stool antigen test is required. A breath test allows you to determine the type of microorganisms that lead to disturbances in the digestive tract.
The occurrence of dyspepsia is evidenced by a large number of unprocessed muscle fibers in the feces; feces contain ammonia and have an alkaline reaction. In a healthy state, the environment should be acidic.
Stool analysis helps to distinguish dyspepsia from an inflammatory process in the intestines - in the case of the pathology in question, there are no red blood cells, white blood cells and mucus in the biological material being studied.
The diagnosis is also confirmed by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - intestines, stomach, pancreas - identified during instrumental examination methods.
Instrumental research techniques
In order to correctly prescribe a treatment regimen to a patient, it is necessary to establish which organ of the gastrointestinal tract has malfunctioned. After laboratory tests are carried out, if protein decay in the intestines is suspected (biochemistry, OAM, OAC), instrumental research methods are started. At this stage, it is necessary to exclude from consideration organic diseases with symptoms similar to dyspepsia.
The range of research conducted today is diverse. The most common examination technique is endoscopy, during which the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines is examined. During the procedure, a small piece of mucous tissue is often removed for histological analysis. The study allows us to judge the presence or absence of the spiral-shaped bacterium Helicobacter pylori in the body.
In addition to endoscopic examination, the following are carried out:
- Ultrasound diagnostics, which helps to identify diseases such as chronic pancreatitis, cholelithiasis, etc.
- Electrogastrography and electrogastroenterography are procedures that help identify disruptions of gastroduodenal motility. The technique is based on studying the ability of the muscles of the walls of the stomach and intestines to contract under the influence of electrical impulses. Electrogastrography examines gastric motility, electrogastroenterography is a fairly young technique that examines intestinal motility.
- Stomach scintigraphy helps identify indigestion caused by low activity of the stomach muscles (gastroparesis).
- Esophagomanometry is a procedure that evaluates the ability of the esophagus to contract.
- Antroduodenal manometry allows you to evaluate the motility of the duodenum, as well as the stomach. The method is based on recording pressure in the stomach, duodenum and jejunum, which is performed simultaneously.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a manipulation that can be used to identify ulcers, stomach tumors, and reflux esophagitis in a patient.
- Radiography.
Treatment of putrefactive dyspepsia
Treatment of patients diagnosed with putrefactive dyspepsia begins with a strict diet. This measure is necessary in order to relieve the gastrointestinal tract and stop the rotting of proteins in the intestines. And the neutralization of toxic putrefaction products released during putrefactive dyspepsia can be avoided through dietary restrictions. Initially, the patient is prescribed a fast for 1-1.5 days, and is allowed to eat only weak unsweetened tea and water. The following is a diet that excludes from the diet for several days:
- carbohydrates – bread and baked goods;
- dairy products;
- marinades and pickles;
- fried foods;
- semi-finished products.
If there has been severe intoxication of the body, the patient is prescribed intravenous drips with nutrient solutions (5% glucose solution, etc.). Carbohydrates are gradually introduced into the patient’s diet, but at the same time the consumption of plant fiber with coarse fibers is limited. As a rule, after a few weeks the patient’s condition returns to normal; protein can be gradually introduced into his diet. Fermented milk products help stop rotting processes.
Taking astringents helps normalize stool, and adsorbents, such as activated carbon, help get rid of flatulence.
Antispasmodics (“No-Shpa”) relieve the patient of pain by relieving spasms of the intestinal muscles.
In case of enzyme deficiency, the patient is prescribed replacement therapy, along with which it is recommended to take B vitamins.
In some cases, antibiotic therapy may be required, which is relevant when there is a threat of infectious or inflammatory bowel diseases.
Fermentation in the intestines: causes and treatment, what foods cause it, how to remove it
Among all the signs, fermentation in the intestines is the most common manifestation of impaired digestion. In most clinical cases, the symptom is associated with the consumption of irritating foods or due to overeating.
Then a change in diet leads to an improvement in well-being: pain, bloating, and a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen are eliminated. If even after correcting the diet the patient’s condition does not improve, you should consult a gastroenterologist.
The reason is the development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which require drug correction and the development of a dietary nutrition program.
Alternative medicine against fermentation
When traditional medicine was at the beginning of its development, it was possible to get rid of the disease only with the help of folk remedies. Ancient healers knew exactly how to remove fermentation in the intestines, so some recipes are still used today:
- The most common remedy designed to stop fermentation is dill water. It’s easy to prepare: pour a tablespoon of dill seeds into 350 ml of boiling water and leave for 3 hours. After this, strain and drink before meals, throughout the day, dividing the entire volume into 4 doses. The good thing about this recipe is that it is suitable for use by infants. The dosage in this case will be less.
- A decoction based on chamomile has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and carminative properties. To prepare it, boil a tablespoon of pharmaceutical raw materials in a glass of water for 5 minutes, and filter after 3 hours of infusion. Take 20 ml 4 times a day. Continue therapy until symptoms disappear completely.
Source: https://polic-5.ru/simptomy/brozhenie-v-zhivote.html