Description of the disease
Some domestic doctors in many classifications often consider non-erosive GERD as a syndrome rather than a separate form of the disease, so treatment is carried out in accordance with the therapy of the underlying disease.
The causes of non-erosive GERD are similar to other forms of this disease. The main feature of the leading pathogenetic factor in the development of this disease is considered to be reflux of stomach or intestinal contents, as well as damage to the mucous layer of the esophagus. There are also the following reasons for the development of non-erosive reflux:
- low tone of the esophageal sphincter;
- dysfunction of the esophagus to self-cleaning by removing food particles;
- strong exposure to gastric or intestinal contents that are thrown into the esophagus;
- the inability of the esophageal mucosa to withstand the damaging factor of the action of the contents thrown from the stomach;
- impaired ability to empty the stomach;
- increased pressure inside the peritoneum.
To enlarge the picture, click on it.
In addition to the main factors that provoke the appearance of such a pathology as gastroesophageal reflux without esophagitis, there are also predisposing reasons that accelerate the formation of the disease, creating excellent conditions for its manifestation. These include disturbances in the abdominal cavity where the stomach is located as a result of:
- obesity;
- wearing tight clothes;
- pregnancy, etc.
Abuse of various foods, especially fatty and spicy foods, coffee, chocolate, alcoholic beverages that irritate the gastric mucosa, as well as poor diet, become ideal factors for the development of non-erosive GERD.
Contraindications for use
The medication should not be used if you are hypersensitive to the active ingredient. The medicine is prohibited for use by pregnant and lactating women.
The active substance is excreted primarily through the kidneys, so for pathologies of this organ, the use of tablets is also not recommended. De-Nol is not prescribed for children under 4 years of age.
Uncontrolled and long-term use of De-Nol can cause the accumulation of bismuth in the body, which creates a risk of encephalopathy. Like all medicines, the drug can provoke an allergic reaction.
If, during use, dyspeptic disorders associated with the entry of the active substance into the body occur, it is necessary to interrupt therapy and consult a doctor.
Interesting! Medicine Gastracid - composition, indications and regimen of use

Symptoms
The symptomatic picture of non-erosive reflux esophagitis is as follows:
- the presence of heartburn, which intensifies after eating and taking the body into a horizontal position, or excessive physical exertion;
- the presence in the oral cavity of a sensation of bitterness and acidity as a result of reflux of stomach contents;
- increased secretion of saliva at night;
- painful attacks;
- the appearance of a certain hoarseness in the voice;
- hiccups, cough after eating.
Non-erosive GERD may also be accompanied by:
- belching;
- regurgitation;
- narrowing of the esophagus;
- swallowing disorders;
- tension in the soft tissues and muscles of the throat;
- asthma;
- laryngitis;
- an increase in kyphosis, that is, a backward curve of the thoracic spine, causing stooping.
The above manifestations of non-erosive GERD may appear as single symptoms or in various combinations with each other. Also for non-erosive GERD, a characteristic manifestation is:
- thickening of the basal layer;
- elongation of the papillae, as well as infiltration of the esophageal mucosa by various cells.
The same manifestations can be observed in the erosive form of GERD, so diagnosing the non-erosive form is sometimes difficult.
Complications
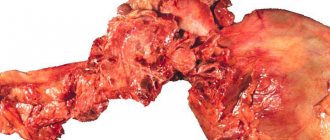
Peptic esophagitis at the initial stage of the disease responds well to treatment with medications and diet. Lack of qualified therapy, non-compliance with nutritional rules and lifestyle causes complications. Chronic inflammation of the esophagus is dangerous due to tissue deformation, resulting in erosions and ulcers. In the future, this can lead to cell mutation, the inability of the organ to perform its functions, and the development of cancer. Inflammation and constant burns from acidic masses cause swelling and narrowing of the esophagus, which subsequently requires surgical intervention to eliminate. In addition to complications in the digestive tract, problems arise with breathing, blood circulation, and the functioning of the heart muscle.
Diagnostics
Doctors cannot always immediately determine this form of GERD, so they resort to different studies. During the examination, the gastroenterologist collects anamnesis and complaints. A complete blood count from the urine may be needed. A mandatory test for patients is EGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy). Using this procedure, you can identify changes in the mucosa, as well as their severity. If necessary, an endoscopic biopsy of the mucous membrane can be taken from the patient for histological examination of biological material.
Also, during the diagnosis, radiography may be necessary to identify disturbances in the motor activity of the esophagus. This procedure makes it possible to more accurately determine changes in the contours of the esophagus, swelling of the walls, accumulation of mucus, and ulcerations. Based on the results of all the data and the general condition of the patient, the doctor selects an individual treatment regimen.
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore we will be glad to hear your feedback about peptic esophagitis in the comments, it will also be useful to other users of the site.

Elena : “Relapses happen often, I undergo treatment with different pills up to 5 times a year. Relief does not come for long. I am almost constantly on a diet, I don’t drink alcohol, the main provocateurs for me are stress and pills. I had to be treated with antibiotics for inflammation 2 times in gynecology, as a result, now I’ve been treating esophagitis for a month.”
Natalya : “There are no comforting forecasts. Once it gets worse, then you just have to learn to live with it. There are a lot of pills at home. Which one to take depends on the situation. When a course of antacids saves you, and when you have to drink everything you can eat – prokinetics, inhibitors, probiotics, sedatives, antispasmodics, sorbents.”
Treatment
Therapy for the non-erosive form of GERD involves the following steps of health-improving actions:
- lifestyle changes;
- special diet;
- drug therapy.
The main goal of drug treatment is measures aimed at preventing gastroesophageal reflux, protecting the mucous membrane from the damaging effects of ejected contents, and maximizing its aggressiveness. For this purpose, patients diagnosed with non-erosive GERD are prescribed medications with an antisecretory effect.
Moreover, the best drugs in the treatment of GERD, regardless of its clinical and endoscopic type, are recognized as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which effectively suppress the secretion of juice in the stomach, maintaining the intraesophageal pH at the required level for a long time. Most often, patients are prescribed benzimidazole derivatives, which contain the active ingredient:
- Esomeprazole;
- Omeprazole;
- Rabeprazole.
However, the use of PPI monotherapy during the treatment of non-erosive reflux disease is not always able to eliminate the unpleasant manifestations of the disease. According to statistics, a positive effect is observed in only half of patients with non-erosive GERD. The rest do not have a therapeutic response that relieves the onset of symptoms, even after a monthly therapeutic course of standard doses of PPIs. Therefore, they require an expanded option for wellness activities.
The second group of drugs used in the treatment of the disease is headed by anthracids. The use of these drugs makes it possible to quickly remove heartburn by neutralizing a certain amount of hydrochloric acid. The advantage of this group:
- point action;
- there are no side effects on other organs.
This makes it possible to prescribe anthracids for the treatment of patients of any age and gender. Their main disadvantage is their short-term effect. The most common types of these funds are:
- Maalox;
- Gaviscon;
- Almagel.
During treatment, prokinetics are necessarily prescribed - agents that enhance the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, ensuring the rapid exit of elements from the stomach, ensuring the rapid elimination of the possibility of penetration of masses through the lower sphincter into the esophagus. But these medications have a number of contraindications. For GERD caused by the entry of bile acids and other duodenal contents into the esophagus, a good result can be obtained with the help of ursodeoxycholic acid. This drug is recommended to be taken in combination with certain prokinetics.
One of the latest achievements that helps to cope with the problem not only in a hospital setting, but also at home, is the use of a technique for exposing the patient to an electromagnetic field of the decimeter wave range directed to the collar area. For this purpose, the “Volna-2” device is used, with the help of which non-drug regulation of the neurohumoral function of the lower sphincter, which has various pathologies, is carried out.
The use of a device with a pulsed magnetic field on the plasma membrane of a cell changes its permeability, and autonomic regulation is also observed. The pathogenetic feature of using a low-frequency magnetic field in the treatment of this disease is explained by the activation of blood circulation processes at the point of inflammation.
How is the procedure performed? The patient takes a comfortable position on the couch. The manipulation is performed through thin clothing. An inductor-solenoid is taken and placed directly above the epigastrium and lower half of the patient’s chest. The solenoid receives alternating current. The session lasts about 12–15 minutes, the course of therapy using this device is about 12 procedures performed every day. As a result of this treatment method, the patient experiences:
- disappearance of nausea and heartburn;
- lack of regurgitation after eating;
- cessation of belching;
- cessation of tongue burning;
- improving the patient's mood.
Treatment of non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease using this technique can only be carried out in consultation with a doctor.
Surgery
In case of ineffectiveness of therapeutic intervention or serious violations of the esophageal patency, surgical treatment is recommended. It can be gentle, performed using an endoscope, or radical, when a full-fledged operation is performed.
The choice of surgical intervention or conservative therapy is decided depending on the person’s preferences, his health, the cost of treatment, the equipment of the clinic, and the likelihood of complications. Non-drug therapy still remains strictly mandatory, whatever the treatment tactics. In case of moderate heartburn, as well as the absence of complications, expensive and rather complex methods are unjustified; therapy with the use of H2 blockers is quite sufficient. Doctors often recommend first radically changing your lifestyle, then using PPIs to relieve all endoscopic symptoms, and only then using H2-blockers with the patient’s consent.
The guaranteed success of treatment depends entirely on the patient: only strict adherence to medical recommendations, adherence to diet and changes in life habits provide the opportunity to forget about the symptoms of reflux esophagitis forever. This is important, since the disease is considered one of those whose development is influenced by “lifestyle,” therefore, forgetting about the recommendations, a person quickly achieves the development of relapses of esophagitis, after which the pathology begins to progress.
Classification of the disease
The first way to classify peptic esophagitis is to divide the pathology into two forms:
- acute , developing unexpectedly and quickly. The patient feels unwell, swallowing is difficult, heartburn is almost invisible. If the disease is detected in time, it can be eliminated with therapy within a month;
- chronic , occurring over a long period of time with periodic exacerbations and improvements in health. Usually accompanied by gastritis, hiccups, burning in the epigastric region, shortness of breath and vomiting. Left untreated can lead to serious complications.
The disease is divided into two stages:
- during the catarrhal stage , there are no destructive processes, but the patient suffers from pain and a sensation of a lump in the throat;
- at the erosive stage, multiple erosions appear on the walls of the esophagus. The clinical picture worsens, and the patient experiences a persistent feeling of discomfort, including after eating and taking certain medications.
According to severity, reflux is divided into 4 degrees (or even 5, if we consider zero):
- 0 or initial, the manifestation of which is heartburn and belching. At this stage, visible changes in the walls of the esophagus, as a rule, do not occur;
- 1st, the signs of which are bright red foci of inflammation, thickening of the mucous membrane and increased mucus production. This degree approximately corresponds to the catarrhal stage of the disease;
- 2nd, in which there is a fusion of focal inflammation and the appearance of erosions. The mucous membrane begins to collapse;
- 3rd, characterized by destruction of the walls of the esophagus and erosions located in a circle;
- 4th, accompanied by a transition to a chronic process and complications such as bleeding, ulcers and contractions. The area of damage to the esophagus reaches 75 percent.
The last degree of peptic esophagitis is often accompanied by low-quality formations. Sometimes it even develops into esophageal cancer (the probability of cancer increases to almost 40%). Once the disease has progressed to this stage, it is virtually impossible to recover.
Approximate price tags for treatment in major centers
| Gastroenterologist appointment | Average cost of the procedure |
| Moscow | 1700 rub. |
| St. Petersburg | 1250 rub. |
| Omsk | 800 rub. |
| Novosibirsk | 700 rub. |
| Samara | 750 rub. |
| Chelyabinsk | 900 rub. |
| Volgograd | 850 rub. |
| Ekaterinburg | 1100 rub. |
| Kyiv | 350 UAH |
| Dnepropetrovsk | 200 UAH |
| Minsk | 25 bel. rub |
| Almaty | 5000 tenge |
Prevention
Individuals diagnosed with any form of GERD should follow a healthy lifestyle. First of all, you need to give up bad habits. Prevention of esophagitis is also aimed at eliminating the causes of its development. To do this you need to avoid:
- burns of the esophagus with chemicals;
- hot food,
- damage to the organ by foreign bodies, etc.
It is recommended to maintain a favorable psychological climate at home and in the workplace, and to acquire relaxation skills. This will be facilitated by breathing exercises, which will help get rid of skeletal muscle spasms. Particular attention must be paid to diet. For non-erosive GERD, it is not allowed to consume the following types of foods:
- salty;
- fat;
- spicy;
- smoked;
- sour.
If you are ill, it is necessary to limit the consumption of foods that cause fermentation processes:
- beer;
- kvass;
- yeast products;
- carbonated drinks.
It is also undesirable to drink coffee and strong tea. It is advisable to prepare dishes by stewing or boiling. The daily food intake must be divided into five servings. You need to eat at set hours. Be sure to chew food thoroughly before swallowing. Eating in a hurry is also prohibited. The last meal before bedtime should be two hours or more from it.