Catarrhal bulbitis: what kind of pathology is it, what causes it, what symptoms signal the development of the disease and how to treat it. We will tell you about all this in more detail.
Catarrhal bulbitis of the stomach is the name given to a certain stage of the inflammatory process that affects the duodenal bulb. Although according to the international classification there is no such disease, gastroenterologists persistently try to emphasize it in the diagnosis in order to indicate the severity of the disease occurring.
General rules
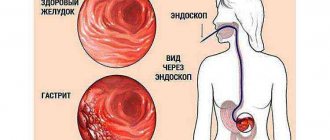
Chronic gastritis is characterized by inflammatory and dystrophic changes in the gastric mucosa, which are detected during endoscopic examination. In clinical practice, a combination of gastritis and duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum) or bulbitis (inflammation of the bulb - the initial part of the duodenum) is often encountered.
The causes of these diseases are errors in diet, nervous stress, smoking and alcohol abuse. Both diseases have much in common - this explains their combination in almost all patients. These diseases can be classified as acid-dependent conditions that develop when the protective factors of the lining of the duodenum and stomach are disrupted, and when there are aggressive factors. Helicobacter pyloric can be distinguished , but its role is more significant in the case of chronic gastritis . In chronic duodenitis, the acid-peptic factor plays a more significant role. The process in the stomach supports the process in the duodenal bulb and vice versa.
The processed stomach contents, which have an acidic environment, enter the duodenal bulb, and the main function of this section is to bring it to an alkaline environment. This is possible thanks to the Brunner's glands, which produce an alkalizing secretion. Poor nutrition and stress activate acid formation, and the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection maintains constant inflammation.
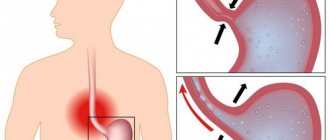
Long-term inflammation leads to damage to the Brunner's glands and loss of functional characteristics of the bulb, so the acidic contents have a constant irritating effect on its mucosa. If this is accompanied by bile reflux (bile is thrown into the stomach through the bulb), then this reduces the protective barrier of the gastric mucosa and causes chronic inflammation of the stomach. This creates a vicious circle.
Symptoms of the disease are quite varied: a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium or aching pain that occurs 2 hours after eating, loss of appetite, sometimes heartburn or belching, bloating. catarrhal or erosive gastritis and bulbitis occur .
Diet treatment for gastritis and bulbitis is of great importance, since irregular food intake, consumption of spices and spicy foods cause exacerbation. With gastritis and bulbitis, there is most often an increased acid-forming function of the stomach, so patients are recommended to follow Diet No. 1 , as with a peptic ulcer. Strict restrictions must be observed during the period of exacerbation, especially with erosive lesions of the mucous membrane, when the patient is bothered by severe pain. At this time, the gastrointestinal tract needs to create maximum peace and the doctor may recommend a version of Table No. 1 - Diet No. 1A .
It limits any effects of food (chemical, thermal and mechanical) and creates the most gentle regime. Eating only pureed food in a mushy state helps reduce inflammation. Rich broths that stimulate gastric and pancreatic secretion, any vegetables (a little later they are introduced in the form of puree, but legumes, mushrooms, radishes, radishes) and tough meat are not allowed. Frequent meals in small portions are organized.
During a period of severe exacerbation, the patient can use:
- slimy (somewhat later pureed) soups with egg-milk dressing and butter;
- boiled meat and fish dishes, thoroughly whipped in a blender and brought to the state of semi-liquid pates;
- steamed curd soufflé, milk and cream;
- steam omelette;
- pureed liquid porridges according to the patient’s preferences: buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, semolina, which are boiled in water or with milk;
- berry jelly;
- weak tea with milk, infusion of rose hips.
After a week, meals are expanded, and in the future a transition to Table No. 1 . The timing of its implementation is determined by the patient’s condition. The diet for gastritis and bulbitis includes:
- exclusion of irritating foods: garlic, onions, cranberries, tomatoes, citrus juices, peppers, sour fruit juices, alcohol, ginger, chocolate, turnips, radishes;
- products that increase the formation of gases: cabbage, kvass, beer, legumes, yeast baked goods;
- products that enhance secretion: rich broths, spicy, fried and pickled foods, smoked foods, mustard, coffee, tea, carbonated drinks;
- frequent meals and reducing the amount of food - 200 g per meal;
- increasing protein in the diet and decreasing animal fats (goose, duck, fatty pork, cream pies, cream, lard, fatty lamb);
- the use of stewing, as well as boiling and baking; eating food warm, excluding cold dishes and excessively hot ones that irritate the mucous membranes;
- Table No. 1 is complete and can be adhered to constantly; it can be expanded to the usual diet without the use of spices, herbs, pickles, smoked foods, spicy dishes and canned food.
Diagnostics
The appearance of symptoms of inflammation of the upper gastrointestinal tract is an indication for examination. To identify bulbitis and differentiate it from other diseases, the doctor first examines the patient, finds out complaints and history of the disease. To prescribe adequate treatment, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are recommended.
Table 2. Diagnostics
| Method | What the study shows |
| General blood test | Indicators of the inflammatory process |
| Biochemical blood test | Function of the liver, pancreas, gall bladder |
| Tests to determine the pathogenic pathogen - urease test, PCR, serological markers for Helicobacter pylori infection | Determines the presence of Helicobacter pylori |
| FGDS with mucosal biopsy | Shows the condition of the epithelium in various parts of the digestive tract, the degree of damage, and the form of pathology |
| Ultrasound | Indirect signs of changes in the tissues of parenchymal organs, functional features, developmental anomalies |
| X-ray special studies with contrast | Presence of tissue defects of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, foreign bodies |
To recognize chronic bulbitis, contact a gastroenterologist. Many tests do not always provide the result of inflammation in the bulb. Based on the general analysis of urine and blood, the manifestation of inflammation is judged. To confirm the disease, specialists use the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray examination.
- Bacteriological research.
- Ultrasound examination of the stomach and intestines.
- Gastroenterography.
Experts resort to duodenoscopy to determine gastric bulbitis. The procedure is carried out using a thin tube with a camera at the end. This device is inserted into the patient's mouth and advanced to the duodenum. Doctors conduct a monitor examination of all parts of the organ. The result of the examination is the identification of microdamages of the bulb that accompany bulbitis.
The manifestation of focal bulbitis has different symptoms. When diagnosing, pathology is detected using endoscopic examination. The specialist observes foci of inflammation, swelling and hyperemia of the gastric mucosa.
To establish the correct diagnosis, it is necessary to perform a complete examination of the patient. The gastroenterologist clarifies complaints and medical history, assesses the objective status and prescribes additional research methods. The list of auxiliary diagnostic techniques includes:
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FEGDS) with histology of mucosal biopsy from different parts of the stomach.
- pH-metry to determine the level of acidity in the upper digestive tract.
- Detection of Helicobacter pylori infection using the urease test, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, PCR (antibody detection) and other methods.
- Ultrasound to determine concomitant pathology of the biliary tract and pancreas.
Attention! In the presence of reflux with the development of esophagitis, symptoms appear that are characteristic of heart disease. To exclude cardiac pathology, ECG and Echo-CG are prescribed.
Authorized Products
Allowed to use:
- Low-fat meat and poultry, steamed and boiled. During an exacerbation, the diet includes only dishes made from minced meat (cutlets, meatballs, meatballs) or boiled meat whipped in a blender (soufflé, pates). Once the exacerbation subsides, it is recommended to switch to tender pieces of meat. Baking products is also possible.
- Cereal soups (oatmeal, rice, semolina, buckwheat) in vegetable broth with a small amount of vegetables. First, they are pureed (pureeed or pureed soups are prepared), and then you can simply boil the cereals well and chop the vegetables finely. Boiled meat minced in a meat grinder, cream, beaten egg, butter, as well as dried dill and parsley are added to soups.
- Dried wheat bread or bread croutons. During the period of remission, it is possible to eat unhealthy baked goods.
- Mild homemade sauces (milk, sour cream or cream).
- Low-fat fish in the form of cutlet-based dishes. They are steamed or baked. Considering that the amount of animal protein in the diet needs to be increased, meat or fish dishes are included in the menu twice a day.
- Cereals (rice in the absence of constipation, buckwheat, oatmeal, semolina) from which first pureed porridge is prepared, and then boiled. At the request of the patient, they can be prepared with water or with the addition of some milk. A piece of butter is added to prepared dishes.
- Vegetable puree from potatoes, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin with the addition of cream or butter. These same vegetables can be added to soups and also prepared vegetable soufflés.
- Milk (if tolerated well, you can drink up to 3-4 glasses a day), milk jelly, non-sour cottage cheese diluted with milk, cottage cheese soufflé. During the period of remission, you can eat baked cheesecakes or lazy dumplings.
- Eggs (up to two daily) are prepared soft-boiled or as a steam omelet.
- Vegetable and butter.
- Berries only in processed form at first - jelly, jellies, mousses, baked apples, to which honey can be added after cooking.
- Drinks include bran decoction, rosehip infusion, weak tea (possibly with added milk), diluted juices, filtered water.
- Desserts include meringues, marshmallows, marshmallows, meringues, jam and honey - all in moderation.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
Bakery products | ||||
| white bread crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| meringues | 2,6 | 20,8 | 60,5 | 440 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| milk sauce | 2,0 | 7,1 | 5,2 | 84 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| boiled beef | 25,8 | 16,8 | 0,0 | 254 |
| boiled veal | 30,7 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken | 25,2 | 7,4 | 0,0 | 170 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| juice | 0,3 | 0,1 | 9,2 | 40 |
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| jelly | 0,2 | 0,0 | 16,7 | 68 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Treatment of the disease
Gastrobulbitis can be treated only after undergoing an examination and consulting a doctor. In such cases, doctors first prescribe drug therapy, which includes a complex of medications.
Drug therapy is initially aimed at relieving symptoms and normalizing stomach acidity. For these purposes, antacid drugs are prescribed. They give a quick effect: the patient becomes better, and the development of pathology begins to occur at a slower pace.
To cure gastrobulbitis, you need to consult a doctor no later than 3 days after the first symptoms are detected.
To eliminate pain, antispasmodics are prescribed. It is spasms - strong tension in muscle tissue - that causes discomfort in this disease.
If the disease is caused by harmful microorganisms, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. They are selected individually.
Fully or partially limited products
Excluded:
- Any broths, pickled and pickled vegetables, fried and spicy foods, fats, fatty meats, smoked meats and sausages, coarse meat with tendons.
- Vegetables, fruits and berries in raw form (during an exacerbation period). A little later they are introduced into the diet.
- Millet, pearl barley, barley, and corn cereals, which are considered difficult to digest.
- On an ongoing basis, mushrooms, onions, garlic, radishes, radishes. Legumes and white cabbage are limited if tolerated poorly.
- Fermented milk drinks with high acidity.
- Hot sauces, vinegar, pepper, spices, horseradish, mustard, ketchup, mayonnaise.
- Strong tea and coffee, any drinks containing gas, sour fruit juices, kvass.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ginger | 1,8 | 0,8 | 15,8 | 80 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| chilli | 2,0 | 0,2 | 9,5 | 40 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| ham | 22,6 | 20,9 | 0,0 | 279 |
Sausages | ||||
| dry-cured sausage | 24,1 | 38,3 | 1,0 | 455 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| dried fish | 17,5 | 4,6 | 0,0 | 139 |
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| bread kvass | 0,2 | 0,0 | 5,2 | 27 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Methods of official treatment of bulbitis
As a rule, in order to quickly get rid of this infection, it is necessary to destroy harmful bacteria, since they are the ones that cause the disease. Of course, antibiotics do the best job. In addition to these medications, the doctor additionally prescribes antacids. Products of this type are necessary in order to regulate the processes of acid secretion.
In advanced stages (for example, with the development of Crohn's disease), you will additionally have to take steroid-type drugs, salt, zinc, vitamin C. If general intoxication has occurred, then, as a rule, doctors recommend taking sorbents that help neutralize the toxic components formed in the body.
In addition, bulbitis can be caused by Giardia or other parasites. In such a situation, it is necessary to take drugs that can suppress their vital functions. It all depends on the specific reasons for the development of the disease.
Regardless of the root causes of bulbitis, in a situation where the patient suffers from severe pain, he can be prescribed analgesics that quickly help cope with the discomfort. Antispasmodics and anticholinergics are also used. These include “No-shpa”, “Baralgin” and others.
If treatment of acute bulbitis is required, then in this case you need to immediately take an antacid, which helps to very quickly neutralize the acidic environment and stop the development of the pathology. In order to alleviate a person’s condition as quickly as possible, it is recommended to give him “Almagel”, “Gastal” or “Rennie”.
Menu (Power Mode)
If during an exacerbation the diet is very limited, then when the state of health improves, it expands significantly. Therefore, food can be considered quite varied and complete. Only coarse vegetables and some cereals are excluded. In the diet, preference is given to dietary products: milk, lean meat and fish, chicken eggs, cereals, low-fat cottage cheese. Alternating meat and fish dishes significantly diversifies the diet. These can be dumplings, cutlets, meat casseroles, soufflés, zrazy, and during the period of remission - beef stroganoff.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
general description
Bulbitis, although not dangerous to human life, still brings a lot of inconvenience. It is worth noting that this pathology is most often chronic. Considering gastric bulbitis, what it is and how this disease is usually dealt with, it is worth paying attention to the provoking factors of the pathology. For example, a disease can occur if a foreign object or the causative agent of a particular infection enters the human body. Improper hygiene and nutrition can also lead to complications in the form of bulbitis. If a person leads an incorrect lifestyle, then he also runs the risk of encountering this disease in the future. Very often, bulbitis appears against the background of parasite activity.
Based on the type of pathology, the doctor develops the necessary therapeutic measures that will help get rid of the disease. However, the person himself is able to alleviate his condition.
Reviews and results
Nutritional treatment is important for gastrointestinal diseases. It is not necessary to adhere to strict restrictions all the time, but during an exacerbation it is necessary. The composition of the main Table No. 1 is varied and complete, so it is suitable for constant nutrition. Feedback from patients confirms the need for therapeutic nutrition and its effectiveness.
- “... I was worried about nausea and belching, discomfort in the stomach, pain when pressing on it. Gastroscopy - superficial gastritis and bulbitis. Helicobacter was found. I took an antibiotic for a week and Ganaton for a month. I was also prescribed a diet that helps me. In general, I noticed that if I eat something rough or irritating (garlic, onions, horseradish, even radishes), pain and aggravation appear. I came to the conclusion that I need to follow the diet constantly. Porridge with milk and milk came up. I cooked soups first with water, and then with weak chicken broth. At first I ate well-cooked cereal soups, then I started making vegetable soups, but I crushed the vegetables or lightly beat them in a blender. I cooked cutlets and omelettes in a double boiler. I stuck to this diet for 2 months, and I managed to eliminate inflammation in the stomach and lose weight.”
- “... I consider this diet beneficial for the stomach and health in general. The diet is well tolerated and the lack of fried foods doesn’t bother me. I cook fish or chicken cutlets in a double boiler or in the oven (I hardly brown them), but the taste changes a little. I noticed that when an exacerbation begins, you need not to let the situation go, but immediately switch to dietary nutrition, excluding spicy foods, spices, fried and pickled vegetables. All this makes me feel worse. So for stomach diseases, the main thing is to eat right.”
Folk remedies for catarrhal bulbitis
If a patient has been diagnosed with catarrhal bulbitis, treatment with folk remedies can be very effective, but it should be carried out only after consultation with a professional doctor.
The choice of specific treatment is determined by the cause of the disease. For the parasitic form of catarrhal bulbitis, you should use medicinal plants such as:
The following will help relieve inflammation and heal tissue:
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- Oak bark;
- calendula;
- plantain;
- Icelandic moss.
For neurasthenic syndrome, treatment with sedative folk remedies is recommended: yarrow, valerian, etc.