Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. With this disease, the insulin produced negatively affects the body and can cause significant damage to it. All internal organs suffer: kidneys, liver, entire gastrointestinal tract. The produced enzymes do not enter the duodenum, but remain at the site of their formation, causing the process of self-digestion, which is why inflammation of the gland itself occurs. The patient develops signs of intestinal disorder: diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting.
This disease is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. Therefore, you cannot ignore the doctor’s recommendations or make independent decisions without undergoing an appropriate medical examination. The consequences of not following a special diet are very serious and sometimes completely irreversible. A critical situation can even lead to hyperglycemic coma. Sugar for pancreatitis is among the foods prohibited for consumption. Moreover, over a certain period of time, its quantity is not only sharply limited, but completely excluded from the diet. Let us consider in more detail under what circumstances and how much sugar is allowed to be consumed per day for chronic pancreatitis.
Exacerbation period
This period of time is characterized by pronounced manifestations of the disease. Numerous tests show elevated blood sugar levels. This condition can be considered very dangerous for human life. The condition worsens in just a few hours and becomes irreversible.
Natural sugar can literally be considered a white poison that poisons the entire body. It should be completely eliminated from the diet to prevent the condition from getting worse. During moments of exacerbation, a person feels very bad. If vomiting occurs, then eating any food simply becomes impossible.
Remission period
This moment is characterized by a temporary attenuation of the manifestations of the disease. However, one should not assume that if general health has returned to normal, then there is no cause for concern. The absence of clear symptoms in no way means that the disease has passed and the condition has stabilized.
In fact, the period of remission should be perceived as a temporary respite, as spare weeks and months in order to gather strength and try to strengthen your body. One way or another, you still have to follow a diet. Otherwise, all this will lead to an exacerbation of the disease and a significant deterioration in the person’s condition.

During the period of remission, you are allowed to eat no more than 30-40 grams. sugar per day, but it is better to replace it with a sweetener. There is currently no shortage of these substances in stores. Doctors recommend consuming sorbitol, agave syrup, fructose, and xylitol. These substances are natural components that have a beneficial effect on overall health and are not capable of exacerbating the disease. A sugar substitute will help you not change your gastronomic habits and not harm your body.
Prohibited Products
Diet for pancreatitis should be reviewed immediately upon diagnosis. You cannot let things take their course and stoically endure paroxysmal pain. Such uncontrolled behavior will not lead to anything good, but will only cause irreparable consequences.
Sugary drinks should be completely avoided. You should not drink soda, packaged juices (they contain a very high percentage of sugar), sweet tea and coffee. You will have to learn to give up your favorite chocolates, all kinds of buns, ice cream, and cakes.
Of course, at first glance, all this seems completely impossible, because the diet will have to be followed both on holidays and on ordinary weekdays. However, with the advent of natural, high-quality sweeteners in the diet, life may seem much sweeter.
Fruits and vegetables
First of all, you need to pay attention to them. They are not only incredibly useful for humans, but are also enriched with numerous vitamins that are so necessary for full life.
You should try to consume plenty of vegetables and fruits every day. Only then will you be able to make up for the lack of vitamins and gradually improve your health. Fruits and vegetables are natural food for the human being, which is why they are so well absorbed by the body.
Anyone who eats right lives longer, without any problems with the nervous, cardiovascular and digestive systems.
Honey and berries
There is no point in suffering because you had to give up your favorite chocolate and ice cream. Instead of buying unhealthy cakes and sweets, pay attention to honey. This is a natural product that makes sense to love with all your heart. Honey can be spread on bread, or simply eaten with a spoon along with tea. Then you won't need to add extra sugar to the cup.
Dried fruits will also bring tangible benefits: they are incredibly healthy, just like berries. Especially in the summer, do not miss the opportunity to eat healthy foods. Berries are not only healthy, but also tasty. You will not have the feeling that you have given up something essential, because the food on the table will please not only the eye, but also the stomach.
It is very useful to eat freshly brewed jelly. They do not contain sugar, but contain many vitamins.
Thus, nutrition for chronic pancreatitis should, first of all, be aimed at enriching the body with all the necessary vitamins and minerals. Fresh natural juices (not packaged), fruits, and vegetables contribute to maintaining health. At the same time, you should even drink tea without sugar and, of course, not eat anything sweet.
Most people don't even know where their pancreas is because it doesn't hurt them. This is an important organ that helps the digestive process and controls blood sugar levels.
When inflammation of the pancreas occurs, or, as they say in medicine, “pancreatitis,” you can simply forget about feeling normal.
The disease is very easy to detect, because it has clear symptoms:
- acute and severe pain in the upper abdomen, mainly in the middle or left, girdling, can radiate to the back;
- systematic nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief;
- weakness, rapid heartbeat;
- food is poorly digested.
As you know, the pancreas regulates blood sugar levels; disruption of its function causes pancreatitis and diabetes. This leads to the question, is it possible to have sugar for pancreatitis?
Glucose in acute pancreatitis
A diet for pancreatic diseases usually involves serious dietary restrictions. Therefore, many gourmets have to give up their favorite dishes and products.
Sugar is also prohibited for pancreatitis, so eating confectionery is also not recommended. But is it possible to remove this restriction and what sweets are allowed during a therapeutic diet?
Sugar in acute pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. This disease seriously slows down the production of insulin, causing the organ to work almost to the point of wear and tear, making the processing of glucose almost impossible. In this regard, blood sugar increases, which causes the risk of the occurrence and development of diabetes.
If acute pancreatitis occurs, the consumption of sugar in its pure form, as well as sugar-containing products, is strictly prohibited, since they can aggravate the situation and contribute to the transition of the acute form of the disease to the chronic one. Introducing large amounts of sugar into the daily menu for pancreatitis can be downright deadly.
Pancreatitis and sugar are incompatible
The first few days after the onset of inflammation, patients should undergo a short course of fasting and a strict lean diet. But even after this period has passed and pain has ceased, glucose is potentially dangerous for the patient.
If you do not follow your doctor’s recommendations and continue to eat sweets, a serious complication may arise in the form of hyperglycemic coma.
For chronic pancreatitis
Is it possible to have sugar for chronic pancreatitis? Chronic inflammation is characterized by alternating stages of exacerbation and remission. Moreover, the first usually occurs when the patient seriously violates the treatment regimen and diet.
Just as in the acute form of inflammation, during exacerbation, eating sugar is prohibited. However, during the period of remission, a small amount of the product can be introduced into the diet - the daily dose of sugar should not exceed fifty grams.
It can be found in the following desserts and drinks:
- compotes;
- jelly;
- marshmallows, marshmallows;
- fruit drinks;
- souffle;
- marmalade;
- products from berries and fruits;
- fruit and berry purees;
- jams;
- confitures.
It is undesirable to consume overly sweet confectionery and candies. However, you can prepare homemade cakes and pastries with the addition of sweeteners.
How to replace sugar?
Currently, there are many different sweeteners of natural and chemical origin on the market, which cannot increase glucose levels. Any of those intended for diabetics will do. The most popular of them:
- fructose;
- sorbitol;
- xylitol;
- sodium cyclamate;
- sucralose;
- saccharin;
- erythritol;
- syrup, tablets and stevioside powder.
Natural sweeteners are considered the safest for the body in case of diabetes and low-calorie diets. Substitutes of chemical origin (sodium cyclamate, aspartame and others) have limited dosages due to the potential for harm to health.
There are also special dietary confectionery products, however, before purchasing them, you should make sure that there is no pure sugar in the composition.
Before purchasing this or that sweetener, you must make sure that there is no individual intolerance, and also follow all the necessary rules for use. It is also important that the drug does not cause an increase in blood glucose levels.
Honey for pancreatitis
Honey is also one of the natural sugar substitutes. It contains not only glucose, but also large amounts of fructose. Due to the fact that the pancreas processes it much more easily than sugar, the product is allowed even in the second stage of diabetes.
In addition, honey contains a huge amount of vitamins and minerals, as well as components that help reduce inflammatory processes.
You should also not overuse honey. A large amount of it can cause changes in stool, flatulence, and allergic reactions. It is important to introduce the product into baby food with particular caution.
Conclusion
All patients suffering from chronic and acute inflammation of the pancreas should remember that sugar and pancreatitis are incompatible.
But it can be replaced with safer and healthier products that are not capable of causing exacerbations or complications. They do not contain glucose and can be added to drinks and a variety of dietary desserts can be prepared with them.
The mechanism of development of pancreatic diabetes mellitus
A third of patients with low-grade inflammation of the pancreas develop pancreatic diabetes.
Before becoming permanent, pancreatitis usually worries a person for quite a long time - about ten years. All this time, the patient periodically suffers from pain in the left hypochondrium, which is the main symptom of the disease. Exacerbations alternate with remissions.
Remission stage
If, after suffering the acute phase of pancreatitis, the performance of endocrine cells and iron is not changed in the ability to produce the required amount of insulin to process glucose, then the issue of consuming sugar for such patients is not so pressing. However, you still shouldn’t get carried away.
Sugar is allowed to be returned to the diet, both in pure form and in preparation, but its daily intake should not exceed 40-50g and be evenly distributed among all meals during the day.
It is healthier and best for patients with pancreatitis to consume sugar in compotes, fruit drinks, jams, jelly, souffles, confitures, fruit and berry products and jelly. In addition, if you want more sweets, then in the store you can buy special confectionery products based on sugar substitutes.
Confectionery factories produce special cookies, sweets, jams and drinks that do not contain sugar (it is replaced by saccharin, xylitol or sorbitol), so consuming such sweets does not pose any risk to diabetics or people with pancreatic problems.
Honey is also an excellent and most importantly natural sugar substitute. Even a healthy pancreas does not like sugar, let alone pancreatitis, in which consuming this product only aggravates the inflammation process. Disaccharides, which include sugar, are complex carbohydrates that are quite difficult for the pancreas to cope with.
Honey consists exclusively of monosaccharides, these are fructose and glucose, the pancreas copes with them without much difficulty. This means that this product may well become a complete sugar substitute.
Honey contains many useful substances and vitamins that the body needs during illness. Regular use of this product significantly reduces inflammation of the pancreas, increases its performance and prolongs the state of remission.
Since an important component of treatment is diet and a healthy diet, the consumption of sugar, that is, sucrose, should be minimized, or better yet, stop taking these components of the diet altogether.
Your body will only thank you if you stop consuming this product, because today there is something to replace sugar with pancreatitis without compromising taste.
Source: https://limto.ru/gljukoza-pri-ostrom-pankreatite/
How can you replace sugar with pancreatitis?

Everyone loves sweets, and if you have problems with your pancreas, you shouldn’t deny yourself, even if you’re used to consuming them in large quantities.
There are quite a lot of sweetener substitutes - there is plenty to choose from. For example, cane sugar is recommended as an alternative. Most sweeteners are sweeter than glucose.
Many of them even have beneficial properties for the body:
- reduce weight;
- improve metabolism;
- prevent caries;
- reduce the risk of diabetes;
- in case of illnesses that make it impossible to consume sugar, they allow you not to deny yourself sweets.
Sorbitol and xylitol, unlike cane sugar, are very high in calories and people who are overweight should not consume them. But for other patients it is an excellent sweetener for pancreatitis.
In many stores in the sweets department you can find products containing sugar substitutes for pancreatitis. Now manufacturers produce a huge assortment of a wide variety of sweets and desserts without the usual sugar.
So, what do our favorite sugar-free sweets consist of? Most often, these are saccharin, sorbitol, xylitol. Specifically, xylitol improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and stimulates the secretion of bile. Possessing diuretic properties, it reduces the amount of fatty acids in the body and prevents the so-called “acidification” of the body.
Xylitol is not as sweet as sugar and fructose, and does not greatly affect blood glucose levels, and it is practically non-toxic.
Saccharin tastes much sweeter and dissolves well in water, but if it is heated, it acquires a bitter taste, so it must be added to ready-made dishes and drinks to improve the taste. But still, saccharin is not so harmless - you should not consume it in large quantities. This substitute is contraindicated for kidney and liver diseases.
Fructose as a natural alternative

To absorb fructose, the body also needs to produce insulin, but unlike glucose, which is absorbed in the stomach and mouth, fructose is absorbed in the intestines. It is absorbed much more slowly and insulin is required for processing gradually and in small quantities.
Many patients are interested in whether they can take fructose for pancreatitis? Fructose is not considered a sugar substitute, but it can be safely consumed in case of pancreatitis without fear of consequences.
The disadvantage is that fructose is high in calories and overweight people should definitely not abuse it. Excessive use may cause side effects such as:
- increased blood sugar;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- violation of fat metabolism.
Fructose is found in many foods in our diet and is noticeable in cold, acidic drinks. The less distinctive taste of fructose in hot drinks and baked goods.
Fructose for pancreatitis is considered by experts to be an excellent alternative to sugar, because it is a harmless, but at the same time sweet product. Food prepared on its basis is useful, especially if you have problems with the pancreas.
The advantage is that while the energy value is the same as sugar, fructose is sweeter and therefore less can be added to food.
Brown sugar for illness

Brown sugar is not particularly different in properties and benefits from regular white sugar. Perhaps it is not as sweet as white, and contains cane juice, consisting of various trace elements, vitamins and organic substances. The presence of such components makes it somewhat healthier than its beetroot counterpart.
If you have pancreatitis, you can also use cane sugar, but it is quite difficult to get it, and in the process you can run into a fake and harm your health.
Within limits, sugar is beneficial and even necessary for the body. Scientists have come to the conclusion that moderate consumption of brown sugar helps reduce excess weight with physical activity and a balanced diet.
Sugar is also beneficial:
- for the functioning of the nervous system;
- prevention of atherosclerosis;
- regulates liver activity;
- normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Based on research by the International Sugar Organization, cane sugar for pancreatitis can be safely taken only in strictly limited quantities, and if you have diabetes, it is advisable to completely exclude it.
Natural stevia or honey herb

Stevia is another healthy plant that is many times sweeter than the usual beet and cane sugar. At the same time, it contains a maximum of useful substances and a minimum amount of calories, without having a harmful effect on the body and the diseased organ.
Stevia for pancreatitis is suitable for making desserts and baked goods, home canning, and for sweetening tea, compotes and other drinks. This is the best sweetener for patients with a diseased pancreas.
- Firstly, it is used in the form of a decoction, which is made from the dried leaves of the plant. The raw materials are thoroughly crushed in a mortar and then poured with boiling water in a proportion of 15-20 grams per 250 ml. liquids. The broth is boiled over low heat for 50 minutes and filtered. The remaining raw materials are refilled with 150 ml. boiling water, combine with the first decoction and filter again. The resulting product is ready for further use in cooking.
- Secondly, a more concentrated product or syrup can be obtained by boiling the resulting decoction to a thick consistency over low heat or a water bath. The finished product can be stored in the refrigerator for several months, and a couple of drops of syrup can sweeten an entire mug of tea.
- Thirdly, you can prepare a natural herbal infusion: take 250-300 ml for 20 grams of chopped herbs. hot water. The mixture is left to infuse in a sealed container for 12 hours, after which it is filtered and the remaining leaves are re-filled with 150 ml. boiling water and leave for another 8 hours. Both decoctions are mixed together and filtered through cheesecloth.
A sweet decoction or syrup from stevia prepared at home helps lower blood glucose levels and increase the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels, improves digestion, eliminates heartburn, and has a weak diuretic, antibacterial and antifungal effect. Raw materials are produced in the form of dried leaves, powder, tea, tablets and finished syrup.
Blood test for pancreatitis - biochemical analysis indicators
Why do you need a general and biochemical blood test for pancreatitis? Today we will answer this question in more detail. Laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are prescribed in order to accurately determine the severity of the inflammatory process.
With pancreatitis, the clinical picture at the initial stage of the disease may be blurred. Therefore, doctors prescribe a blood test at the first stage.
It should immediately be noted that one blood test for pancreatitis will not help prescribe further treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis.
Blood analysis
In case of pancreatitis, a general blood test helps to more accurately identify the degree of inflammation. With this disease, when examining the blood under a microscope, you can notice a decrease in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
In this case, there is a sharp increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (in the analysis noted as ESR) and hematocrit. Before knowing how to decipher the analysis received in hand, you need to pass the standard standards.
The blood test shows the level of leukocytes, erythrocytes and ESR
It is worth drawing your attention to the fact that during the inflammatory process all indicators change.
Leukocytes have an equal rate for both women and men. The norm is from 4-9* 109 liters.
Chief gastroenterologist of the Russian Federation: “PANCREATITIS does not go away?! A simple treatment method has already healed hundreds of patients at home! To cure the pancreas forever you need...” Read more »
Biochemical blood tests for pancreatitis help to more accurately identify not only inflammation, but also determine the exact state of the entire human body.
Biochemical research has many positions, and a particular doctor can include only those points that, in his opinion, are important in diagnosing the disease
If a diagnosis of pancreatitis is made, an increased level of amylase is noted in the biochemical analysis. To make it more clear, amylase is a pancreatic enzyme.
It is this enzyme that is responsible for a very important function in the human body, namely the breakdown of starch.
Also read: Acute pancreatitis in adults: treatment drugs
Additionally, an increase in the level of not only elastase, but also lipase and trypsin is observed. Pancreatic elastase is a product of the activity of the pancreas. Based on its level, you can quickly determine the condition of the affected organ and whether there are any deformations.
This indicator is very important for making a diagnosis of “Pancreatitis,” since elastase passes through the entire digestive tract and at the same time retains its primary qualities.
Elastase in pancreatitis increases over 1.5 weeks, immediately from the onset of an exacerbation of the disease with a chronic course.
A component such as lipase is responsible for metabolic processes in the human body, as well as for the absorption of beneficial vitamins and polyunsaturated acids. The maximum concentration of lipase is observed due to the rapid elimination of the variable from the body.
Trypsin is synthesized only in the pancreas, has esterase activity and helps break down peptides and proteins.
Additionally, the biochemical analysis notes:
- There is a decrease in total protein. It is worth noting that protein starvation can occur against the background of poor nutrition, directly during the period of drug treatment of pancreatitis.
- In the acute course of the disease, transaminase levels may increase.
- Bilirubin increases.
Doctors prescribe a biochemical blood test on the first day of hospitalization. At the time of treatment, a repeat examination may be prescribed. During this period of time, doctors determine the level of amylase in the analysis; this helps to monitor the condition of the pancreas and observe the dynamics of improvement or deterioration of the condition.
Amylase in pancreatitis begins to increase in the interval from one hour to 12 hours, immediately from the onset of the disease. The highest level is reached in 20-30 hours.
It is during this period that it is necessary to determine the method of treatment and, if necessary, prescribe additional examination methods. Why? The fact is that during the first few days and up to four days, amylase disappears.
To the question: is it possible to cure a stomach or duodenal ulcer at home, a gastroenterologist, head of the gastroenterology department, Mikhail Vasilievich Arkhipov, answers.
If the patient has severe pain and an increase in pancreatic enzymes is noted in the analysis at the time of treatment, then this indicates the progression of the disease, so there is a risk of serious complications. In this case, it is necessary to urgently change treatment tactics.
What else is determined in blood tests?
In case of pancreatitis, it is very important to determine the concentration of tumor markers, especially if there is a suspicion of a chronic course.
The level of tumor marker can increase not only with pancreatitis, but also with stomach cancer. Normally, the CA19-9 value ranges from 0-34 U/ml.
If a patient has a high level of glucose in the blood, this indicates insufficient insulin secretion.
When sugar is elevated during pancreatitis, it is dangerous for human health and life. It is necessary to understand that the outcome of the chronic course of the disease may be diabetes mellitus. The patient must be given blood for glucose determination several times.
How to get tested correctly:
- Avoid physical activity.
- Do not eat until the examination.
- The day before you should not eat fried, spicy or sweet foods.
- Do not take medications.
Normal glucose levels are up to 5.5 mmol/l.
What other tests can be prescribed?
As mentioned above, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive laboratory examination.
Additionally, the tests determine immunoreactive trypsin for pancreatitis. But it should be noted that if the indicator is positive, this does not always indicate pancreatitis. A positive result additionally indicates cholecystitis or, for example, persistent renal failure.
To identify not only pancreatitis and other diseases, including disorders, it is necessary to determine trypsinogen in a urine test. The examination is expensive, but it also allows us to make an accurate diagnosis with a fairly high guarantee.
It is mandatory to undergo a stool test, which helps determine the exact functional level of the pancreas. When important enzymes decrease, the patient’s entire fat digestion process begins to suffer.
Main characteristics of feces during inflammation of the pancreas:
- Fat is clearly visible in stool analysis.
- Undigested food remains may be detected.
- Light-colored feces indicate blockage of the bile ducts.
Violation of exocrine function can be determined independently. In this case, feces are poorly washed off the walls of the toilet, have a fairly shiny surface and have a persistent, unpleasant odor. Often at the initial stage of pancreatitis there is loose and frequent stool. Such signs should alert a person and they should immediately consult a doctor.
Also read: How to treat chronic pancreatitis
Now you know why you need to take tests and what they mean for making a diagnosis. Remember, the sooner you detect the first signs of the disease, undergo laboratory testing, a variety of instrumental methods and appropriate treatment, the greater the chance of avoiding health complications.
Symptoms of pancreatitis
Not everyone can recognize pancreatitis in a timely manner, so let's briefly look at the main signs of the disease.
Thinness usually reveals the presence of the disease. Weight loss occurs due to the fact that the gland does not secrete enough enzymes to digest food passing through the small intestine, and the substances are not absorbed.
A patient at the initial stage of the disease experiences toxic syndrome. Fever appears, pulse changes, renal colic and blood pressure decreases.
Additional symptoms:
- dry mouth;
- the patient experiences sticky sweat;
- yellowness of the skin;
- general weakness appears;
- Pancreatitis is additionally accompanied by constipation or diarrhea.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, a white coating is observed on the tongue, loss of appetite occurs, and thus the patient begins to rapidly lose weight.
Recommendations from Elena Malysheva in the special issue “Live Healthy!” on how to overcome pacreatitis using the healing effects of natural remedies.
Pain with pancreatitis in the form of spasms can radiate to the back. An attack of pain begins to appear 30 minutes after eating. In rare cases, the pain radiates to the sternum area.
At the time of manual examination, in case of pancreatitis, the gastroenterologist recognizes the Grotta or Shchetkin-Blumberg symptom.
Source: https://pankreatitos.ru/metody-lecheniya/analiz-krovi.html
Main functions of the organ
The pancreas is an organ of internal secretion and performs two main functions in the body: exocrine (secretion of enzymes) and endocrine (production of hormones). It also secretes pancreatic juice, which enters the initial part of the intestine. This fluid begins to be produced a few minutes after food enters the stomach from the esophagus. Depending on the amount of incoming food, the gland can produce from 500 ml to 2 liters. digestive juice.
Pancreatic enzymes include:
- Amylase, sucrase, maltase. They break down complex carbohydrates into simple ones: glucose and fructose. Reduce fermentation and gas formation in the intestines.
- Lactase. Promotes the absorption of dairy products.
- Trypsin is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of proteins. In the pancreas it is formed in an inactive form, otherwise the gland would digest itself. It is activated only upon entering the duodenum.
- Lipase. Breaks down fats into easily digestible fatty acids, promotes the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
The amount of enzymes produced depends on the predominance of food entering the body: protein, carbohydrate or fatty. This allows you to break down all incoming substances and improve their absorption.
The second main function of the pancreas is the production of insulin and glucagon. Insulin regulates blood glucose levels and has the following effects: increasing blood pressure, increasing the number of heart contractions.
Increased blood sugar with pancreatitis - endocrine problems of a gastroenterological nature
The concentration of glucose in peripheral blood is regulated by pancreatic hormones - insulin and glucagon. With inflammation, damage or necrosis of the organ, this indicator changes greatly towards an increase or decrease. The article examines how blood sugar and the pancreas are related.
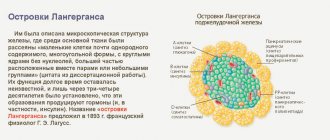
Insulin is a fairly simple hormone in its structure, produced by specialized beta cells. They are part of the islets of Langerhans and represent the endocrine apparatus of the pancreas.
Part of the secretion is produced constantly, part - in response to the influence of certain stimulants:
- high concentration of free glucose in human blood serum;
- eating food that contains not only carbohydrates, but also proteins and fats;
- intake of amino acids (valine, arginine) into the body;
- exposure to certain hormonally active substances (cholecystokinin, estrogen, somatostatin, etc.).
With elevated blood sugar, the pancreas begins to actively produce its most important hormone - insulin.
It breaks down glucose, after which it binds to receptors located on muscle cells, liver, and adipose tissue. This causes them to open their channels to glucose molecules.
Consequently, from the peripheral blood it gradually enters the cells, where it continues to accumulate.
How insulin works
The antagonist of insulin is glucagon, another gland hormone that is produced by the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans.
Under its influence, sugar previously deposited in cells begins to flow back into the systemic bloodstream.
Thus, under the influence of glucagon, a pronounced decrease in blood sugar levels, which can develop due to increased insulin secretion, is prevented.
Serum sugar concentration in pancreatitis
In any form of chronic or acute pancreatitis, the function of the pancreas is impaired to one degree or another. This is due to the fact that pathological changes occur in the structure of the organ:
- swelling of the parenchyma, increased pressure in the Wirsung duct;
- severe hemorrhage into the thickness of the gland with hemorrhagic pancreatitis;
- Some pancreatic cells die without the possibility of recovery.
Consequently, the pancreas does not fully synthesize its digestive enzymes and hormones. This is manifested by the development of protein-energy and pancreatic insufficiency, malabsorption syndrome (impaired absorption of nutrients).
During the acute course of pancreatitis, with exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease, blood glucose often increases. This is due to the fact that when the gland becomes inflamed, its functional activity decreases, and some endocrine cells die.
Pancreatic hormones affecting glucose
In most cases, elevated sugar levels in pancreatitis are a transient condition and recover on their own after the acute period of the disease subsides.
If, as a result of massive pancreatic necrosis, more than 90% of the gland tissue has died, then secondary diabetes mellitus develops.
Find out what tests are needed to identify pathologies of the pancreas in this material...
Diabetes mellitus and pancreas
Diabetes mellitus is a severe endocrinological disease characterized by an absolute or relative deficiency of insulin in the body. The result is persistent hyperglycemia, gradual damage to blood vessels, kidneys, and the nervous system.
In some cases, acute hormone deficiency is a consequence of massive death of beta cells as a result of autoimmune or infectious inflammation of the gland or injury. Primary (insulin-dependent) diabetes is a genetically determined pathology and most often manifests itself in childhood.
The nature of nutrition, excess weight, physical inactivity have a detrimental effect on the functioning of the pancreas. The above factors, especially when taken together, often lead to impaired glucose tolerance.
As a result, insulin, which normally lowers blood sugar levels, becomes difficult to utilize glucose due to a decrease in the number of receptors for it. Fat cells, liver cells, muscle cells simply do not respond to the hormone.
This condition is often called “prediabetes”.
Impaired glucose tolerance at the heart of type 2 diabetes
Read more in the article: Hyperfunction and hypofunction of the pancreas.
And yet, is sugar possible for pancreatitis?
In acute pancreatitis, in the first days of illness, therapeutic fasting is often used, after which the patient is transferred to a special diet - table No. 5. During the illness, doctors strongly recommend not eating “simple” carbohydrates, which quickly change the level of glucose in the blood (chocolate, baked goods , fruits, sugar).
This is due to the fact that in acute pancreatitis, the function of the pancreas is significantly affected, and a hormone such as insulin may be produced in insufficient quantities.
Sugar is made up of sucrose and glucose, so the body will need insulin to move these substances from the blood into the cells.
With its temporary deficiency, the level of glucose in the blood can increase sharply, which will worsen the patient’s condition.
During the period of remission of chronic pancreatitis, you should not completely give up sugar, but the amount of carbohydrates should be limited. It is recommended to consume no more than 40 g of sugar per day so as not to overload the pancreas.
How to avoid hyperglycemia
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from a persistent increase in blood glucose levels. In the acute period of pancreatitis, the patient is prescribed a strict diet (in the first 2-3 days - therapeutic fasting, and then the patient is transferred to table No. 5p). This allows you to improve your condition and reduce risks.
Dietary nutrition for inflammation of the pancreas completely excludes quickly digestible carbohydrates, which can sharply increase the concentration of sugars. After 3 days of fasting, the patient is gradually transferred to diet table No. 5, in which only porridges with water (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice) are allowed from carbohydrates.
We recommend reading:
People with impaired glucose tolerance are advised to constantly adhere to a diet, get rid of bad habits and supplement their daily routine with dosed physical activity.
Source: https://lechigastrit.ru/pankreatit/analizy/saxar-v-krovi-i-podzheludochnaya-zheleza.html
Pathological changes in diabetes
In diabetes mellitus, structural changes in the pancreas may not be observed. Basically, with this disease, the functional ability of the organ deteriorates. The size, echogenicity, contours of the gland or other changes can be determined using ultrasound or CT.
In type 1 diabetes in the initial stage there are no changes: the echostructure is not disturbed, the contours are smooth and clear. As the disease progresses, the iron decreases in size and secondary wrinkling develops. Normal cells are replaced by connective and adipose tissue, and lipomatosis develops.
The mechanism of development of pancreatic diabetes mellitus
With a lack or low bioavailability of insulin, the pancreas undergoes significant changes.
Deformation of the islets of Langerhans is noted. Due to dystrophic damage, the size of endocrine cells decreases. Some of them die.
Subsequent pathological changes develop according to two scenarios. The first option leads to pancreatitis. The second causes organ death. Consequently, diabetes not only changes the functioning of the pancreas, but can also destroy it.
Since the organ produces biologically active substances that control metabolic processes, its functional changes in the form of a decrease or stop in insulin production are classified as diabetes. Failure of type 1 carbohydrate metabolism is considered dangerous.
The patient uses daily insulin injections.
Without a sufficient amount of the hormone, the process of converting glucose becomes impossible, and increased blood sugar is excreted through the urine.
According to statistics, up to 70% of patients suffering from hyperglycemia experience the development of chronic inflammation of the digestive organ.
Symptoms of manifestation
Diabetes mellitus is a pathology characterized by absolute or relative insulin deficiency. Complications from the blood vessels, nervous system, internal organs, and eyes are possible. Absolute – characterized by reduced production of insulin by pancreatic cells. There is not enough of it in the blood, and the penetration of glucose into the cell is impaired. Type 1 diabetes mellitus develops.
With relative deficiency, the amount of insulin produced is normal, but the sensitivity of tissue receptors to insulin is impaired. This is the so-called type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms characteristic of each type of diabetes are listed in the table:
| Sign | 1 type | Type 2 |
| Increased thirst and passing large amounts of urine. | Is one of the main signs. Due to insufficient insulin production, its amount in the blood decreases. Glucose does not penetrate the cell, but circulates freely in the plasma. Excess sugar is excreted from the body through urine, which causes excessive urination. | These symptoms are not pronounced or may be caused by other reasons |
| Appetite. | Elevated. Glucose is the main supplier of energy in the body. With a lack of insulin, sugar cannot penetrate the cell membrane and therefore is not absorbed by the cells. The tissue does not receive enough carbohydrates and energy. | Promoted. This is most dangerous for this type of diabetes. Overeating causes an increase in blood sugar levels. |
| Change in body weight. | Often there is a sharp weight loss of 10 - 15 kg in 2-3 months. Protein synthesis is disrupted, breakdown increases, and its reserves are depleted. This helps reduce body weight and muscle mass. | Uncharacteristic. The patient is overweight or obese. |
| Itchy skin. | Expressed Typically, the skin itches in the genital area, between the fingers, and on the flexor and extensor surfaces of the joints. | Appears very often. |
| Fatigue, weariness. | Glucose is the main source of energy. In diabetes, it cannot enter the tissues, since a small amount of insulin is produced. Glucose remains circulating in the blood. The body does not receive energy. Not typical. | Not typical. |
| Visual impairment. | Small blood vessels are first affected and diabetic retinopathy develops. Possible development of glaucoma, cataracts, and decreased vision. | Develops gradually. There may be age-related diseases of the organs of vision. |
| Age. | It occurs more often in children, adolescents, young men and women. | In persons over 45 years of age who are prone to obesity. |
| Onset of the disease. | Fast, impetuous. | Gradual. |
A characteristic sign of diabetes is the smell of acetone on the breath. This symptom occurs as a result of ketoacidosis (accumulation of ketone bodies in the blood), causing bad breath and urine.
If at least one of these signs appears, you should check your blood sugar level and consult a doctor.
Sometimes symptoms may appear that indicate a malfunction of the pancreas: nausea, vomiting, undigested pieces of food in the stool. In such a situation, many people think about how they can clean the pancreas at home.
Sometimes insufficient substances that promote the breakdown of fats, proteins and carbohydrates may be produced. In this case, enzyme replacement therapy is prescribed. This includes medications: Panzinorm, Festal, Creon. These methods will also prevent the development of type 2 diabetes.
Blood sugar and cholesterol: normal for women and men, tests, risk groups
- Sugar norm
- Norm for men
- Norm for women
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Analyzes
- The relationship between cholesterol and glucose in the blood
- Classification of lipoproteins
- Beneficial properties of cholesterol
- Cholesterol standards
- Taking tests
- At-risk groups
To maintain good health, every person must eat properly and variedly. For the normal functioning of the body, it is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, etc.
But due to an incorrect lifestyle, an unbalanced diet and a number of other features, the content of certain vital components may be overestimated or underestimated. This article will discuss the normal levels of blood sugar and cholesterol.
Sugar norm
Doctors call blood sugar the glucose contained in it. It is simply necessary for the normal functioning of the body, as it is one of the main sources of energy. Glucose enters the body through foods containing sugar or carbohydrates. The processing and absorption of glucose is carried out with the help of insulin, a special enzyme.
Blood sugar levels for men and women of different ages are slightly different. This is due to the characteristics of the body of men and women. In addition, over the years, sugar gradually accumulates in the body, so the level of its content in the blood only increases with age.
Norm for men
For newborns less than a month old, the normal blood sugar level is only 2.8 to 4.4 millimoles per gram.
For children aged from one month to 14 years, the normal level is from 3.3 to 5.6 millimoles per gram. The normal blood sugar level from 14 years to the end of life is 4.6 - 6.4 millimoles per gram.
Bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking), unbalanced diet, eating fatty, spicy or highly salty foods can lead to a lack or excess of glucose in the blood. In men, this problem can lead to infertility or impotence.
Norm for women
- The normal blood sugar level for female children under one month is 2.8 - 4.4 millimoles per gram.
- At the age of one month to 14 years, this figure can vary from 3.3 to 5.5 millimoles per gram.
- For girls and women from 14 to 50 years old, the norm is 3.3 - 5.6 millimoles per gram.
- After the 50th birthday, this figure drops again to 5.5 millimoles per gram.
Women's sex hormones actively participate in the metabolism and absorption of carbohydrates. That is why glucose is eliminated from a woman’s body several times faster than from a man’s body. But after menopause, the level of sugar content can jump sharply. This is due to the cessation of the production of sex hormones.
Hyperglycemia
An excess of sugar (glucose) in the blood is called hyperglycemia. It may be caused by the following factors:
- Disorders of the thyroid gland;
- Poor nutrition;
- Lack of regular physical activity;
- Wrong lifestyle;
- Diabetes;
- Insufficient synthesis of insulin, the hormone responsible for processing glucose;
- Prediabetes.
The main symptoms of hyperglycemia are:
- Frequent urination;
- Weakness, inability to work;
- Drowsiness;
- A sharp decrease in vision;
- Rapid weight loss;
- Constant dry mouth.
There are several ways to maintain glycemic levels at the proper level. This issue should be approached comprehensively. It is necessary to balance your daily diet, fill it with healthy foods and exclude those foods that contain excess glucose. These include sweets, jam, sweet baked goods, etc.
Hypoglycemia
A lack of sugar in a person's blood is called hypoglycemia. It can be caused by:
- Pancreatic cancer;
- Diseases and disorders of the adrenal glands;
- Insulinoma, etc.
The main signs of hypoglycemia are:
- Constant feeling of hunger;
- Weakness, fatigue;
- Constant feeling of fear;
- Cardiopalmus;
- Irritability;
- Chills;
- Headache and migraines;
- Sweating;
- A sharp decrease in vision.
The main problem with treating hypoglycemia is that it is difficult to diagnose. Failure to act in the presence of this violation can lead to the death of a person.
Analyzes
There are several features of taking tests to determine blood levels. Tests must be taken in the first half of the day, before 11 o’clock.
Blood sampling is carried out only on an empty stomach. Approximately 15-20 minutes after eating, the level of glucose in the body increases significantly. After a few hours, this indicator returns to normal. This process is called nutritional hyperglycemia. It does not affect human health in any way. Blood is taken from a finger or from a vein.
A glucometer is used to determine blood sugar levels at home.
The relationship between cholesterol and glucose in the blood
The processes of carbohydrate and fat metabolism are closely related. Excessive consumption of carbohydrates can lead to the accumulation of excess sugar in the body. This one way or another leads to rapid deposition of fat cells. Due to disturbances in the process of lipid metabolism, blood vessels lose their former elasticity, and cholesterol plaques begin to form in them.
Many medical scientists claim that all patients with type 2 diabetes suffer from hypertension. It is caused by high cholesterol levels.
In addition, elevated cholesterol and blood levels have exactly the same prerequisites:
- Lack of regular physical activity;
- Wrong lifestyle;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Overweight.
Classification of lipoproteins
At the end of the 20th century, there was a huge amount of debate about the benefits and harms of cholesterol in the body. Many argued that cholesterol is an extremely harmful substance that can cause hypertension and a number of other diseases. Others divided cholesterol into “bad” and “good.”
None of the above classifications are completely correct. Lipids play a huge role in the life of the body. They have a significant impact on the functioning of many organ systems. But some of them can also lead to bad consequences (plaque deposition, hypertension). The further fate of lipids depends not on their structure and composition, but on which protein they will be attached to. Lipoproteins are responsible for this.
They are divided into several types:
- Low density level. They transport particles from the liver to other organ systems. An increased content of such lipoproteins can lead to cardiovascular diseases.
- Increased level of density. The complete opposite of the previous variety. Such lipoproteins help avoid cardiovascular diseases. They transport lipids from all organ systems to the liver.
- Triglycerides. They are the body's energy resource. They are deposited when consuming dietary fats. In case of food shortage, the body will use triglycerides as the main source of energy.
Beneficial properties of cholesterol
Cholesterol is a very important element that is necessary for the normal functioning of the body. It performs many tasks and has a number of useful properties. The first of them is that cholesterol takes an active part in the processing and absorption of food. Without such an element it is impossible to imagine the production of the necessary salts and digestive juices.
The next property is that cholesterol is very important in such a process as the production of sex hormones in male and female bodies. These hormones include, for example, estrogen or testosterone. Without cholesterol, human reproductive function would be seriously impaired.
Cholesterol is also involved in the production of vitamin D. With a lack of lipids, weak immunity, frequent viral diseases, etc. are observed.
You can control your cholesterol levels on your own. To do this, you need to completely reconsider your diet, make it more varied and balanced.
Cholesterol standards
The cholesterol index largely depends on a person’s gender and age. It is worth considering this indicator for women and men of different age categories.
Cholesterol standards for women
Girls under the age of 30 do not suffer from high cholesterol levels. This largely depends on the fast metabolism of the young body. In some cases, even with an unhealthy diet and lifestyle, the cholesterol level in a girl under 30 years old will be normal.
But diseases such as diabetes mellitus and kidney failure can lead to a sharp increase in the content of these elements in a young body.
Below is a table of average cholesterol levels for girls under 30 years old.
| Total lipid content | High density lipids | Low density lipids |
| 5.8 | 2.2 | 4.3 |
Women between the ages of 30 and 50 experience a significant reduction in the production of estrogen, a special hormone that controls cholesterol levels in the blood. Below is a table of cholesterol norms for this age category.
| Total lipid content | High density lipids | Low density lipids |
| 6.6 | 2.5 | 4.8 |
For the age category of women over 60 years old, there is an increased level of cholesterol in the blood. This is due to the accumulation of lipids over the years. Below is a table of the norm for this parameter for this age category.
| Total lipid content | High density lipids | Low density lipids |
| 7.7 | 2.5 | 5.8 |
Cholesterol standards for men
Men's blood cholesterol levels are significantly lower than women's. The highest rates are observed at the beginning and end of life.
It is worth considering the cholesterol norm for men of different age categories in table format.
| Age | Total lipid content | High density lipids | Low density lipids |
| up to 30 years old | from 3 to 5.8 | from 1 to 1.6 | from 1.6 to 4.3 |
| from 30 to 50 years | from 3.3 to 6.8 | from 0.7 to 2.1 | from 2 to 5.3 |
| from 50 years and above | from 4 to 7.7 | from 1 to 1.9 | from 2 to 4.9 |
Taking tests
Tests to determine lipid levels must be taken in the morning, before 11 o'clock. Approximately 11 hours before going to see a specialist, you should refrain from eating and drinking drinks (except water). For the most accurate results, avoid highly spicy, salty and fried foods for several days before the test. These requirements are due to the fact that some foods can significantly change the level of lipids in the body.
Before taking tests, be sure to inform the specialist about the medications you have been taking recently. Many antibiotics and strong medications can significantly affect the test result.
Blood is taken from a vein or from the ring finger.
The patient can undergo both a biochemical and a complete blood test. Biochemical analysis is simpler. It reveals the total lipid content in the human body and establishes whether these readings correspond to the norm.
A detailed blood test gives a more accurate idea of the lipids in the patient’s body. Otherwise, this type of study is called a lipid profile. It allows not only to determine the overall level of lipid concentration, but also to identify the ratio of lipids of high and low density levels.
At-risk groups
People at any age and with any physiological characteristics can suffer from abnormalities associated with a lack or excess of cholesterol or sugar in the body. But there is a special risk group that is most susceptible to such ailments.
This group includes:
- People over 40 years old. They must undergo regular medical examination at least once a year. It will help determine the level of cholesterol or glucose in the body and prescribe treatment if necessary;
- People suffering from bad habits. These include smoking, excessive drinking, etc.;
- People who are overweight;
- Patients with disorders of the endocrine system;
- Physically inactive people.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis includes determining the form of diabetes, its severity and the presence of possible complications. If diabetes is suspected, the following types of inheritance are prescribed:
- Fasting blood glucose. Normally it is 3.3 – 5.5 mmol/l. An increase in this indicator above 11 mmol/l in the absence of errors in the diet allows a diagnosis of diabetes to be made without further examination.
- Blood sugar with load. Blood is drawn on an empty stomach and 2 hours after ingestion of a glucose solution. Normally it is 7.8 mol/l. Anything above is regarded as a prediabetic condition or impaired glucose tolerance.
- Sugar in urine. Normally it shouldn't be there. Glucose in urine is determined only when the renal barrier is exceeded (over 6 millimoles per liter).
- Glycosylated hemoglobin. Determines whether there has been an increase in sugar over the past 3 months. Blood for this test is taken only from a vein.
Ultrasound is one of the methods for diagnosing the pancreas
To diagnose possible complications of diabetes, additional research methods are performed: fundus examination, ultrasound of internal organs, electrocardiogram.
Biochemistry and general clinical tests are also taken.
What tests are taken for pancreatitis and how are they interpreted?
Tests for pancreatitis are necessary in order to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. The inflammatory process leading to degenerative changes in the tissue of the pancreas and affecting its function is called pancreatitis.
The peculiarities of the structure and functions of the gland are such that even when the primary symptoms of the disease are eliminated, the changes that have occurred in the tissues of the gland do not disappear, but continue to progress.
The initial stage of the disease of chronic pancreatitis can proceed for a long period almost asymptomatically, appearing only when pathological factors of influence increase. As the changes progress, the symptoms bother the patient constantly, changing only in the strength of their manifestation.
Diagnostics
If at least one of the symptoms is present, then we can assume the presence of changes in the gland and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. Diagnostic measures include:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- stool analysis;
- saliva analysis.
The listed studies are mandatory. In some cases, to clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe additional tests:
- examination of pancreatic juice;
- Lasus sample;
- glycoamisamic test;
- proserine test;
- elastase test.
Analysis data
| Object of study | Normal indicator | Objective indicator |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Leukocytes | 4-9.0×10 9/l | exceed many times |
| ESR | 2-15 mm/h | much longer |
| Pancreatic antigen | — | acute pancreatitis - yes, chronic - no |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Blood sugar | 3.5-5.9 mmol/l | elevated |
| Cholesterol | 3.0-5.9 mmol/l | demoted |
| α 2-globulins | 7-13% | reduced |
| Amylase | 28-100 units/l | units/l |
| Lipase | 22-193 U/l | elevated |
| Trypsin | 10-60 µg/l | elevated |
| C - reactive proteins | 150 mg/l | elevated |
| Conjugated bilirubin | — | elevated |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Urine amylase | 0,48 — 0,72 | There is |
In the analysis of stool in patients with pancreatitis, undigested pieces of food are detected, the color of the stool is gray, with a shiny, oily surface.
Amylase is tested in saliva. In acute pancreatitis, the amylase content increases, in chronic pancreatitis it decreases.
The duct of the gland opens into the duodenum. From it, using a probe, the secretion of the pancreas is selected, the composition and quantity of enzymes in which indicate pathology. When assessing test results, you need to pay attention to the levels of amylase and lipase. Elevated levels of bicarbonates and enzymes also indicate pathology.
Decoding the results
When assessing the results of a blood test, you should pay attention to the following:
- Elevated levels of enzymes related to liver function and bilirubin confirm the presence of pancreatitis and gallstones.
- Elevated sugar levels indicate a change in the structure of the pancreas.
- The change in the level of α-amylase in the blood after loading the gland with glucose (glucoamylase test) shows how much the functions of the gland have changed. When amylase activity increases by 4-5 times, we can confirm the presence of pancreatitis.
- The proserine test shows the degree of structural damage to the pancreas. After administration of the cholinesterase inhibitor prozerin, α-amylase levels are monitored. If the norm is 2-3 times higher and there is no downward trend, we can say that the gland tissue has changed. In tissue sclerosis, the level of α-amylase does not change after administration of the inhibitor.
- A blood test reveals an increase in the level of leukocytes, ESR and C-reactive protein, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. Less commonly, a decrease in the number of eosinophils is observed.
- A decrease in α-amylase activity below normal indicates complete disintegration (necrosis) of the gland.
- With an exacerbation of the process in the blood serum, there is a decrease in the level of calcium below 2 mm/l, the level of magnesium and chlorides.
- An increase in the level of elastase-1 in the blood indicates an acute course of the disease and the presence of foci of necrosis. The most indicative level is neutrophil elastase, but currently such analysis is carried out only by advanced laboratories.
- The ratio of the formed elements of blood and its liquid part (hematocrit) allows us to judge the water-electrolyte imbalance.
- If the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells decreases, a hemorrhagic complication of the disease can be suspected.
Clinical analysis indicators confirm or refute the presence of tissue inflammation. The most important and informative result of a biochemical blood test is that it shows functional disorders of the organ.
Treatment options
Treatment of diabetes is aimed at increasing insulin levels in the blood, improving tissue sensitivity to glucose, normalizing metabolism and preventing complications. The main treatments for type 1 and type 2 diabetes include:
- Drug treatment. Antihyperglycemic tablets or insulin injections are used.
- Diet. Carbohydrates and fats are limited. Food should be rich in proteins, vitamins and microelements.
- Moderate physical activity. In this case, increased breakdown of glucose occurs, and therefore its content in the blood decreases. Sometimes, when active in the gym, diabetics can reduce their insulin dose.
The diet uses such a concept as a bread unit. 1 XE is approximately equal to a small piece of black bread and contains 12 g of carbohydrates or a tablespoon of sugar. To break down one unit of bread, 1 to 2 units of insulin are needed. When consuming foods, you need to pay attention to their carbohydrate content. This number must be divided by 12, the resulting quantity will be equal to the content of bread units in the product. Depending on body weight, height, and physical activity, the body needs to consume 18–25 bread units per day. They are distributed over 4 to 5 meals, and more than half of the total amount should be consumed for lunch and dinner.
Therefore, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the prescribed drug therapy.
The exocrine function of this organ is subject to correction.
It is possible to treat and restore the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis by following a strict diet and simultaneous use of medications. It is impossible to restore endocrine function in diabetes mellitus. Achieving “remission” in this disease is possible only with strict adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician.
Medication
Drug treatment includes the use of tablet forms aimed at lowering blood sugar and insulin injections.
Insulin can be:
- Ultra-short action. It starts working five to ten minutes after the injection. After this, you need to eat food. Such drugs are rarely used in complex treatment, since they have a very short insulin-lowering effect. These include: apidra, novorapid.
- Short action. Actrapid and humulin are often used in the treatment of diabetes. They are administered 15-20 minutes before meals. The dose and quantity of insulin administration is calculated individually.
- Medium duration. Medicines such as protafan, insuman are usually prescribed in the morning and evening an hour and a half before meals. Their effect lasts from 16 to 20 hours.
- Extended or prolonged. Levemir and Lantus are the basic therapy for diabetes mellitus. Injected once a day, the effect lasts for 24 hours. They do not have peaks of activity and establish a uniform concentration in the blood.
Actrapid is a drug for the treatment of pancreas in diabetes mellitus
The dose of insulin and hours of administration are determined by the doctor. It is not recommended to allow irregularities in the timing of injections. This is fraught with the development of coma or other complications.
Tablets for the treatment of diabetes are divided into two groups:
- Increasing insulin production: gliclazide, glipizide.
- Increasing tissue sensitivity to insulin: Siofor, metformin.
It is impossible to completely recover from diabetes. Treatment for this diagnosis is aimed primarily at preventing complications. In type 2 diabetes, hyperglycemia can be successfully eliminated through nutritional correction, normalization of body weight, and moderate physical activity.
Folk
It must be remembered that when using traditional methods you cannot refuse insulin. Otherwise, serious complications may develop that can lead to death.
There are many ways and methods aimed at cleaning the pancreas with folk remedies. Here are a few of them:
- Buckwheat. You need to grind a tablespoon of cereal, put it in a bowl, pour in 1 cup of kefir. Cover with a lid and leave overnight. In the morning, drink the resulting mixture 30 minutes before meals.
- Bay leaf. Rinse 10 medium leaves well under running cold water. Pour two cups of boiling water. Leave for 12 hours, take 50 ml 2 times a day.
- Grind 1 large lemon, 300 g each of garlic and parsley in a meat grinder. Place in a cool place, apply one teaspoon 3 times a day.
The pancreas can also be cleansed with herbs. To know which herbal mixture will properly cleanse the gland, you need to consult a doctor. The following herbs are often used:
- Linden. One tablespoon of linden flowers is brewed with one glass of boiling water. Infuse, strain and drink instead of tea for several weeks.
- Sea buckthorn leaves are poured with boiling water in the evening. Insist until the morning, drink one third of a glass twice a day.
- One teaspoon of mint and two tablespoons of milk thistle are poured with boiling water. The infusion is taken 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
- A tablespoon of St. John's wort, rose hips, oregano and elderberry is poured into 500 mm of boiling water. Infuse for 10-12 hours, drink 1/3 tbsp. 3 times a day.
- Chamomile is brewed and drunk instead of tea.

Linden decoction is a folk remedy for the treatment of pancreas in diabetes mellitus.
The use of such drugs must be carried out under strict control of blood sugar in order to prevent its sudden jumps.
Pancreatogenic diabetes
- 1 Causes and factors for the development of pathology
- 2 Features of the flow
- 3 Symptoms of the disease
- 4 Diagnostic measures
- 5 Treatment of pancreatogenic diabetes mellitus 5.1 Drug therapy
- 5.2 Diet for illness
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use DiabeNot to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
A constant increase in blood sugar due to deviations in the exocrine and endocrine functions of the pancreas is called pancreatogenic diabetes mellitus. Most often, such dysfunction is observed in acute and chronic forms of pancreatitis. Diabetes in this case is called secondary and is manifested by decreased muscle tone, a feeling of hunger, and increased sweating. Late detection and treatment of the disease leads to dangerous complications. Therefore, when the first signs of pathology appear, you need to urgently contact specialists at the clinic.
Causes and factors for the development of pathology
The main causes of pancreatogenic type diabetes mellitus include chronic and acute damage to the pancreas. There are also factors that provoke inflammation of the internal organ, after which pancreatic diabetes mellitus develops:
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- surgical interventions on the pancreas;
- gallstones;
- excess weight;
- eating junk food;
- drug-induced damage to the pancreas;
- cancer;
- traumatic damage to the pancreas;
- development of pancreatic necrosis;
- genetic predisposition.
Return to contents
Features of the flow
Thinness is a risk factor for the development of pancreatic dysfunction.
The appearance of abnormalities in carbohydrate metabolism in pancreatogenic diabetes is most often observed after 5 years from the onset of pancreatitis in humans. Endocrine disorders against the background of a chronic inflammatory process in the pancreas are detected in the form of a decrease in blood sugar and pancreatic diabetes mellitus. Even in the chronic form of pancreatitis, a number of features of the course of diabetes are distinguished:
- People who are prone to thinness often suffer from this pathology.
- Increased sugar levels in this condition are easily tolerated by people.
- When eating low-calorie foods, diabetes is mild and does not require insulin.
- After the first signs of pancreatic disease, signs of diabetes appear a few years later.
- Tendency to low blood sugar.
- Skin diseases and infectious pathologies often appear.
- Later than with classic diabetes, a complication such as ketoacidosis occurs. Hyperosmolar conditions and microangiopathies may also occur.
- The pathology is well treated by following dietary instructions, exercise and the use of sulfonylurea drugs.
- There is little need for additional insulin use.
Return to contents
Symptoms of the disease
Excessive sweating is an alarming symptom of the disease.
In pancreatogenic diabetes mellitus, the following symptoms are distinguished:
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- intestinal disorder;
- hunger;
- heavy sweating;
- decreased muscle tone;
- tremor;
- strong excitement;
- vascular damage;
- development of trophic ulcers.
Return to contents
Diagnostic measures
If a person has developed pancreatogenic diabetes, he needs to immediately go to the hospital to see a specialist. The doctor will listen to all complaints and conduct an objective examination. When examining the abdomen, tenderness in the pancreas area is revealed. Next, the specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis with other diseases. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe additional research methods:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- blood sugar test;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- analysis for the amount of diastase in urine and blood.
Return to contents
Treatment of pancreatogenic diabetes mellitus
It is important for the patient to consult a doctor in a timely manner.
If a person has the first signs of the disease, you should not try to cure yourself at home, as this can lead to dangerous consequences. Therefore, you need to consult a doctor. Upon admission, the specialist will collect anamnesis, examine the patient and prescribe special research methods. After making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will create a treatment plan.
As therapy, medication and dietary nutrition are prescribed.
Return to contents
Drug therapy
For the disease, the drugs presented in the table are prescribed:
| Drug groups | Titles |
| Enzyme preparations | "Panzinorm" |
| "Pangrol" | |
| "Pancreatin" | |
| Painkillers | "Duspatalin" |
| "Mebeverine" | |
| Sulfonylureas | "Daonil" |
| "Glyurenorm" | |
| "Diabeton" | |
| Biguanides | "Silubin" |
| "Diformin-retard" | |
| Thiazolidinediones | "Aktos" |
| "Avandyya" | |
| Combination drugs | "Amaril M" |
| "Glymecombe" |
Return to contents
Diet for illness
For this type of diabetes, a high-calorie diet is recommended, rich in complex carbohydrates and low in fat - no more than 25% of the total calories. The number of meals should be 5 times a day in small portions. Fatty, fried, salty and starchy foods should be excluded from the diet. It is recommended to limit the consumption of whole grain bread and sweets, as well as foods high in fiber. It is not recommended to eat cabbage, meat broths, or fresh apples. You also need to remove various sauces and mayonnaise from your diet.
Complications
Complications of this disease include:
- Vascular damage: angiopathy, retinopathy, nephropathy.
- Damage to peripheral nerves, development of polyneuropathy.
- Impaired blood circulation in the lower extremities, the formation of “diabetic” foot and trophic ulcers.
- Hyperglycemic state. Develops with a sharp increase in sugar and ketone bodies in the blood.
- Hypoglycemic coma. Occurs with a significant decrease in sugar, often associated with an overdose of insulin.
Adequate treatment and constant self-monitoring of blood sugar levels will help prevent possible complications.
Prevention
To minimize the likelihood of developing this pathology, you must follow some rules:
- Limiting carbohydrates and fats.
- Physical activity.
- Normalization of body weight.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Frequent, fractional meals in small portions.
- No stress.
- Vitamin therapy.
The development of this disease cannot be completely prevented, since it has a hereditary predisposition. However, by following the above measures, you can reduce the risk factors for developing diabetes.
Useful video about chronic pancreatitis, its treatment and diet
Timely treatment of pancreatitis in the early stages will avoid complications such as diabetes. If, however, it was not possible to prevent the latter, the fight against illnesses will take a lot of time and effort. But it must be maintained at any cost, because increased glycemia has a destructive effect on all systems and organs, provoking tissue death, which is an irreversible process.
The main goal of treatment is to inhibit the degradation of the pancreas. This is facilitated by taking hormonal medications (statins), which help the gland function normally and slow down the death of cells. Also, as a rule, specialized enzymes are prescribed to ensure the normalization of carbohydrate metabolism.
If you have type 1 diabetes, regular insulin injections are necessary. At the initial stage of type 2 disease, tablet antidiabetic therapy will help.